Pollution Characteristics and Risk Evaluation of PAHs in Subsidence Water Bodies in Huainan Coal Mining Area, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
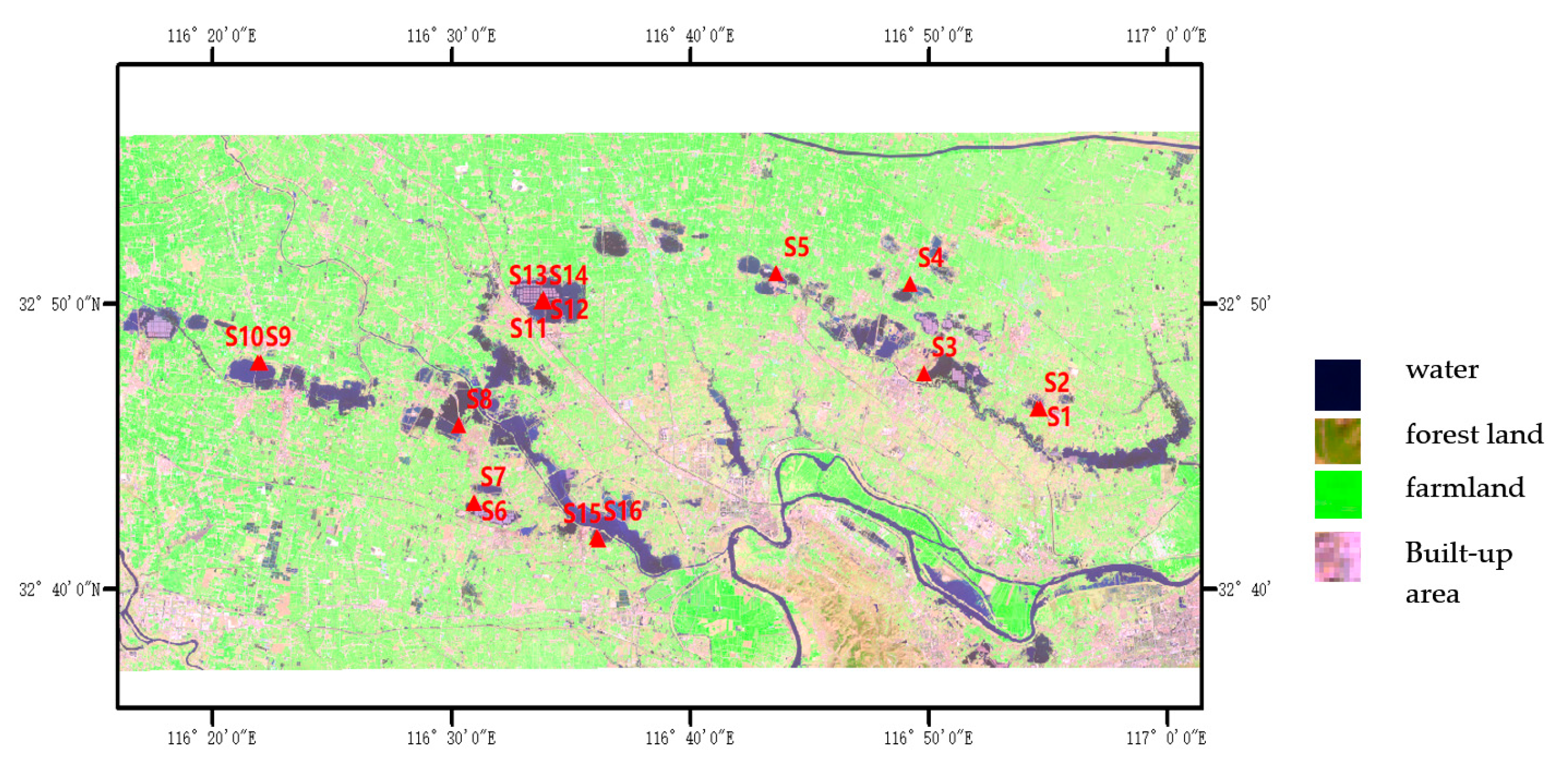
2.1. Study Area and Sampling Locations
2.2. Collection of Water Samples and Test
2.3. Risk Quotient Method
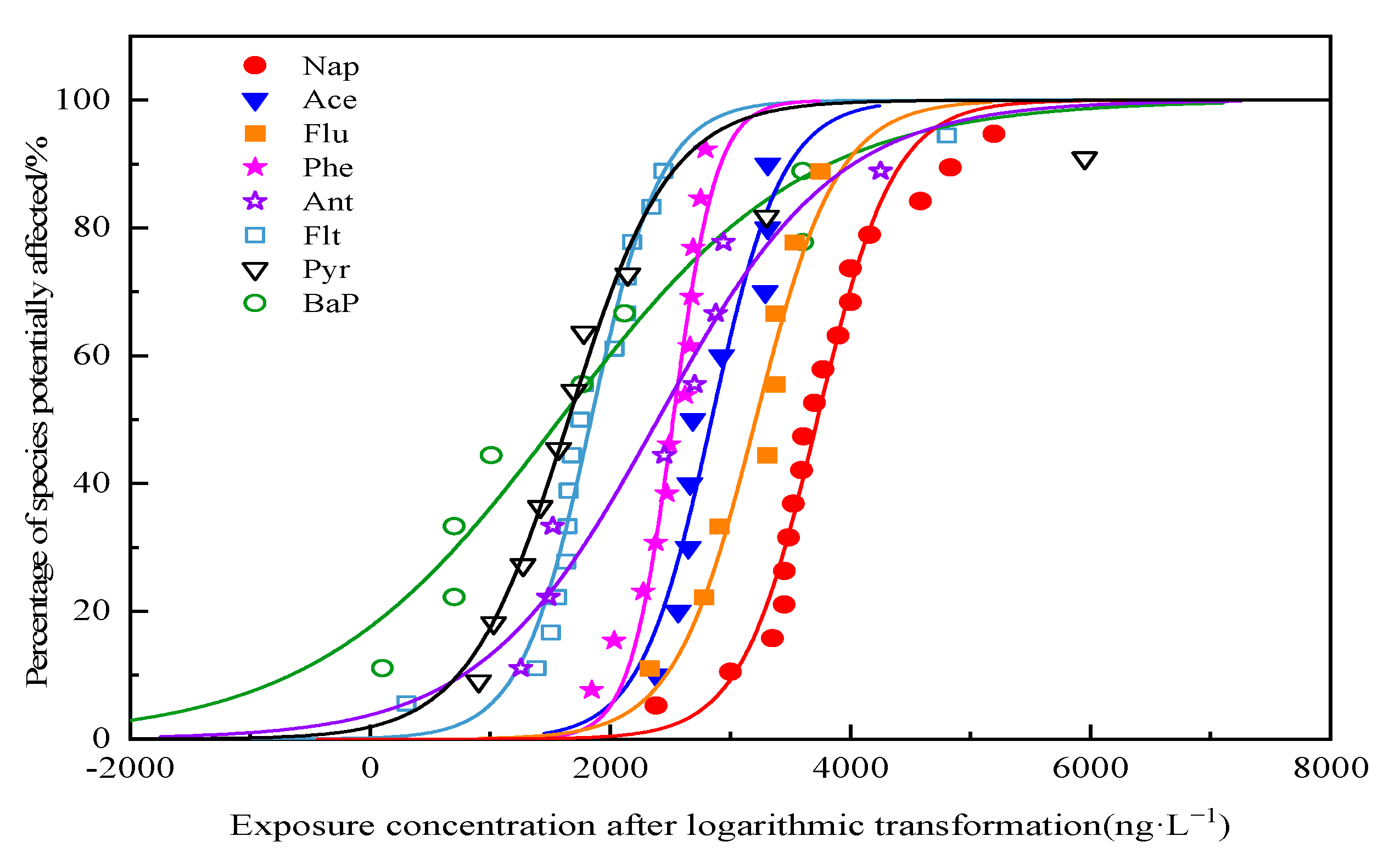
2.4. Species Sensitivity Distribution Method
2.4.1. Toxicity Data Acquisition and Processing
2.4.2. Species Sensitivity Curve Fitting
2.4.3. Ecological Risks
2.5. Method of Health RISK Assessment
2.5.1. Toxic Equivalent
2.5.2. Average Daily Exposure Dose of Pollutants
2.5.3. Incremental Lifetime Cancer Risk
2.5.4. Non-Carcinogenic Health Risk
2.6. Statistical Analysis Methods
3. Results and Discussion
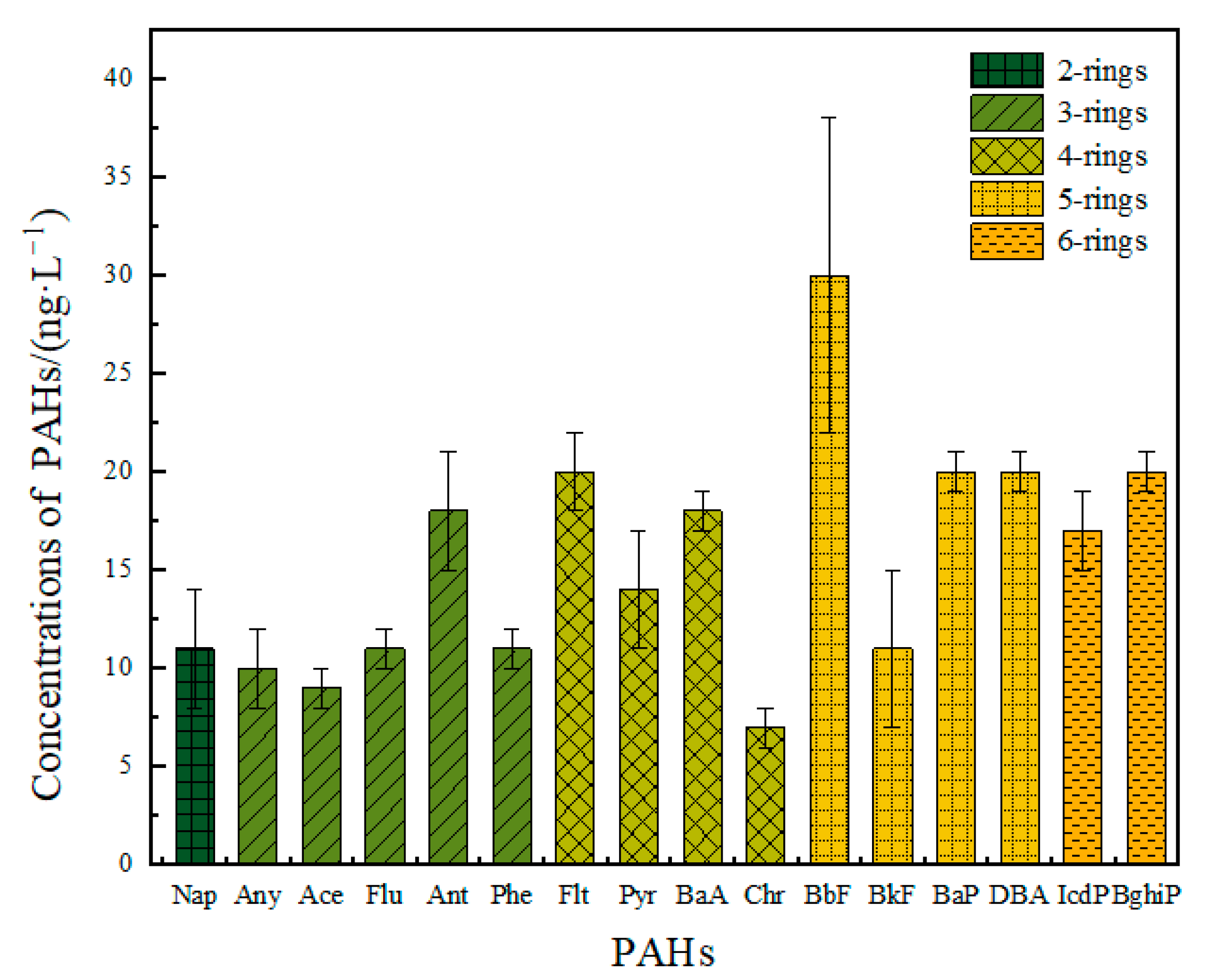
3.1. PAHs Concentration and Comparison with Other Aquatic Systems
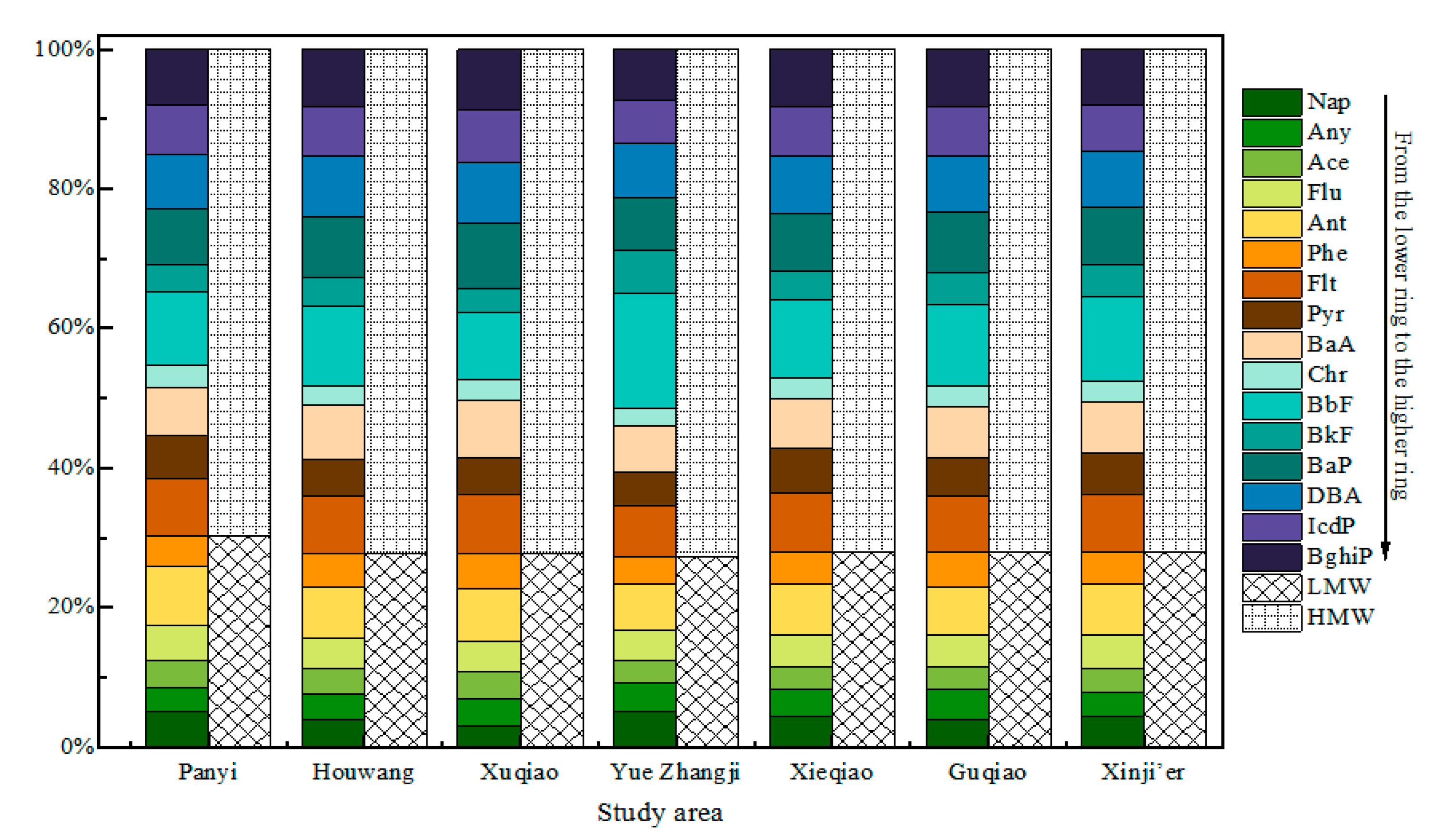
3.2. Composition Characteristics and Source Distribution
3.2.1. Composition Characteristics
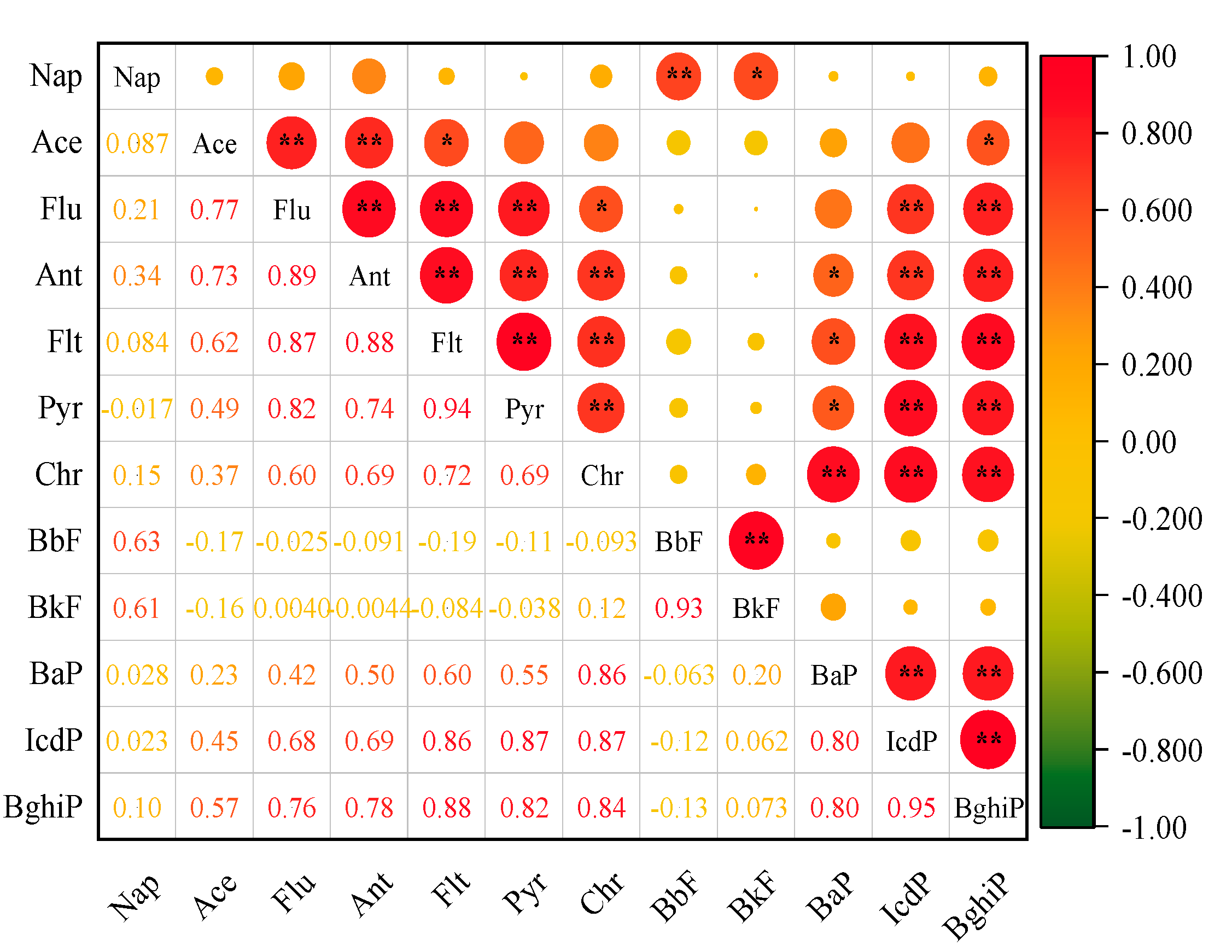
3.2.2. Source Distribution
3.3. Ecological Risk Assessment
3.3.1. Risk Quotient (RQ)
3.3.2. Ecological Risk of Single PAH
3.3.3. Joint Ecological Risk Assessment of Multiple PAHs
3.4. Human Health Risk Assessment
3.4.1. Incremental Lifetime Cancer Risk
3.4.2. Non-Carcinogenic Health Risk
3.5. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.G.; Chang, J.; Zhang, Z.X.; Lu, T.M.; He, M.H. Distribution Characteristics of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Raw Coal of Tengxian Coalfield, Shandong Province. Coal. Technol. 2019, 38, 91–93. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Q. Analysis and prevention of mined-out collapse in coal mine: An example from Changguang Coal Mine in Guangde County, China. West-China Explor. Eng. 2020, 32, 4–6. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.X.; Hu, Z.Q.; Yuan, D.Z.; Liang, Y.S.; Li, P.Y.; Yang, K.; Fu, Y.K. Dynamic evolution of cultivated land fragmentation in coal mining subsidence area of the Lower Yellow River Basin: A case study of Jining city, Shandong Province. J. China Coal Soc. 2021, 46, 3039–3055. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Gui, H.R. Characteristics and Source Identification of Heavy Metals in Subsidence Lake in Zhuxianzhuang Coal Mine in the North of Anhui Province, China. Earth Environ. 2017, 45, 277–282. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.S.; Yan, J.P.; Xu, L.J.; Gu, B.; Zhang, L. Water Environment in Different Subsidence Pools of Huainan Coal-mining Area: Investigation and Evaluation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 32, 140–143. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.Z.; Wang, X.M.; Wang, R.W.; Liu, G.J. Health risk assessment of potentially harmful elements in subsidence water bodies using a Monte Carlo approach: An example from the Huainan coal mining area, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 171, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, J. The Analysis and Evaluation of PanXie Collapse Water Environment Pollution Based on GIS. Ph.D. Thesis, Anhui University of Science and Technology, Huainan, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, Y.L.; Wang, H.C.; Xia, B.; Jiang, C.C.; Wu, W.Y.; Li, Z.L.; Li, S.M.; Su, H.; Bai, Z.H.; Xu, S.J.; et al. Pollution characterization and comprehensive water quality assessment of rain-source river: A case study of the Longgang River in Shenzhen. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 782–794. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Liu, X.H.; Lu, S.Y.; Zhang, T.T.; Jin, B.C.; Qiao, W.; Tang, Z.R.; Liu, Y.; Guo, X.C.; Zhou, J.L.; et al. A review on occurrence and risk of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in lakes of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651 Pt 2, 2497–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Xia, Z.H.; Liu, D.; Qiu, W.X.; Duan, X.L.; Wang, R.; Liu, W.J.; Zhang, Y.H.; Wang, D.; Tao, S.; et al. Multimedia fate and source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in a coking industry city in Northern China. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 181, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, S.A.; Sander, L.C.; Schantz, M.M. Analytical methods for determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs)—A historical perspective on the 16 U.S. EPA priority pollutant PAHs. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 2015, 35, 187–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.M.; Fu, D.Q.; Sun, Z.G. Blacklist of priority control pollutants in water. Environ. Monit. China 1990, 4, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, B.; Wang, X.N.; Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Gao, Y.X.; Li, W.W.; Liu, Z.T. Distribution and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water bodies in seven basins of China. Environ. Sci. 2019, 40, 2101–2114. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudka, S.; Miller, W.P. Accumulation of potentially toxic elements in plants and their transfer to human food chain. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 1999, 34, 681–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menzie, C.A.; Potocki, B.B.; Santodonato, J. Exposure to carcinogenic PAHs in the environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1992, 26, 1278–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.Y.; Xu, H.; Xu, Y.; You, S.H.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; Huang, S.E.; Bian, R.; Qi, W.X.; Lan, H.C.; et al. Distribution and health risk of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and their derivatives in surface water of the Yangtze River. Acta Sci. Circum. 2021, 41, 4932–4941. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudak, J.P.; McDaniel, J.; Lee, S.H.; Fuhrman, J.A. Mineralization potentials of aromatic hydrocarbons by estuarine microorganisms: Variations with season, location, and bacterioplankton production. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1988, 47, 97–102. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/24831561 (accessed on 12 September 2023). [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shen, J.M.; Chen, Z.L.; Ren, N.Q.; Li, Y.F. Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface water and sediment near a drinking water reservoir in Northeastern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 2535–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.F.; Xing, X.L.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Qi, S.H.; Yang, D.; Yuen, D.A.; Sandy, E.H.; Zhou, A.G.; Li, X.Q. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in multimedia environment of Heshan coal district, Guangxi: Distribution, source diagnosis and health risk assessment. Environ. Geochem. Health 2016, 38, 1169–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, H.B.; Meng, X.Z.; Zhang, S.L.; Wang, Y.Z.; Xu, W.; Xu, M.X. Pollution characteristic and source identification of PAHs in typical surface water sources in Haihe Basin. Adm. Techn. Environ. Monit. 2020, 32, 61–64. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J. Distribution, Occurrence and Environmental Impact of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Huainan Mining Area. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, Y.M. Distribution Characteristics of POPs in Coal Mining Subsidence Area. Ph.D. Thesis, AnHui University of Science and Technology, Huainan, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.J. Study on the Influence of DOM on the Environmental Behavior of PAHs in Coal Mining Subsidence Area. Ph.D. Thesis, AnHui University of Science and Technology, Huainan, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.L.; Dong, S.C.; Yao, S.P. Spatial distribution characteristics of heavy metals in Huainan subsidence pond. Coal Geol. Explor. 2018, 46, 125–134. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.L. Discussion on Characteristics and treatment measures of coal mining ground collapse in Huainan Mining area. West-China Explor. Eng. 2019, 31, 15–17. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gdara, I.; Zrafi, I.; Balducci, C.; Cecinato, A.; Ghrabi, A. Seasonal occurrence, source evaluation and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in industrial and agricultural effluents discharged in Wadi El Bey (Tunisia). Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 1609–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.N.T.; Park, M.K.; Son, J.M.; Choi, S.D. Spatial distribution and temporal variation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in runoff and surface water. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 793, 148339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, S.H.; Zhou, F.; Fan, S.Q.; Wu, T. Investigation and ecological risk assessment of PAHs in subsidence water surrounding coal gangue Hillock. Environ. Monit. 2013, 5, 45–49. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, Y.; Yan, Z.F.; Feng, C.L.; Liu, N.; Liao, W.; Hong, Y.J.; Liu, D.Q.; Bai, Y.C. Applications and differences analysis of several typical models in species sensitivity distribution. Environ. Eng. 2021, 39, 85–92+109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, J.R.; Grist, E.P.M.; Leung, K.M.Y.; Morritt, D.; Crane, M. Species sensitivity distributions: Data and model choice. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2002, 45, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.Z.; Duan, X.L.; Ma, Y.Q.; Zhao, X.G.; Qin, Y.W.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Zheng, B.H.; Wei, F.S. Health benefit from decreasing exposure to heavy metals and metalloid after strict pollution control measures near a typical river basin area in China. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 866–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Chen, W.P.; Liao, X.L.; Wang, M.E.; Ouyang, Z.Y.; Jiao, W.T.; Bai, Y. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban soils of Beijing: Status, sources, distribution and potential risk. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, J.L.; Nicewander, W.A. Thirteen Ways to Look at the Correlation Coefficient. Am. Stat. 1988, 42, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.X.; Shang, J.T.; Qian, H.; Wang, H.K.; Gao, Y.Y. Groundwater chemical characteristics and water quality evaluation in the main urban area of Xi’an. Environ. Chem. 2022, 41, 1976–1987. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Chen, H.G.; Cai, W.G.; Qing, J.F.; Jia, X.P. Oxidative stress and damage of Perna viridis by exposure to phenanthrene and benzo(b)fluoranthene. South. China Fish. Sci. 2011, 7, 24–29. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Chen, H.G.; Cai, W.G.; Qin, J.F.; Jia, X.P. Response of Antioxidant Enzymes Activities and Lipid Peroxidation Levels in Visceral Mass of Green-Lipped Mussel (Pernaviridis) to Benzo [b]fluoranthene Stress. Asian J. Ecotoxicol. 2011, 6, 539–545. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Du, H.J.; Gao, S.; Zhang, P.; Yang, Q.; Ning, J.Y.; Li, G.J. Research progress on toxic effects of benzo[b]fluoranthene and its effects on human health. J. Health Toxicol. 2020, 34, 214–219. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yao, W.X.; Cao, X.L.; Xun, X.B. Evaluation of Benzo (a) pyrene emission from industrial briquette combustion flue gas. Environ. Pollut. Control. 1992, 14, 27–30. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, P.; Peter, S.; Christian, S. The use of toxic equivalency factors in assessing occupational and environmental health risk associated with exposure to airborne mixtures of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Chemosphere 1996, 32, 639–648. [Google Scholar]
- GB5749-2006; Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China. Standardization Administration of China. Standards for Drinking Water Quality. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2006.
- GB3838-2002; State Environmental Protection Administration; General Administration of Quality Supervision; Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China. Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water. China Environmental Press: Beijing, China, 2002.
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality, 4th ed.; Shanghai Water Supply Dispatching and Monitoring Center, Shanghai Jiao Tong University: Shanghai, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. National Recommended Water Quality Criteria; Office of Water & Office of Science and Technology: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.F.; Chang, S.; Fu, Q.; Fan, Y.T.; Wang, E.R.; Sun, X.B.; Wang, S.J. Pollution characteristics and risks of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in underground and surface drinking water sources in northeast inner Mongolia. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 3005–3015. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Bu, Q.W.; Cao, H.M.; Zhang, H.D.; Liu, C.S.; He, X.F.; Yun, M.Q. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Surface Water from Wuhai and Lingwu Sections of the Yellow River: Concentrations, Sources, and Ecological Risk. J. Chem. 2020, 2020, 8458257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.L.; Gao, L.; Liang, Z.B.; Chen, J.Y.; Li, S.H.; Zhu, A.P.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Z.G.; Li, R.; Wang, Z.W. Characteristics, sources, and risks of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in topsoil and surface water from the Liuxi River Basin, South China. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 78, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, C.Y.; Rong, L.G.; Sun, L.N.; Wang, Y.G.; Luo, Q.; Wu, H.; Wang, X.X. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the surface water of the Taizi River in Northeast China. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 2020, 40, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.J.; Dai, Y.X.; Han, M.S.; He, H.; Hu, J.P.; Zhang, J.Y.; Shi, J.Z.; Xian, Q.M.; Yang, S.G.; Sun, C. Nitrated and parent PAHs in the surface water of Lake Taihu, China: Occurrence, distribution, source, and human health risk assessment. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 102, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluska, M. Dynamics of changes in the concentration of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in selected Polish surface water. Environ. Prot. Nat. Resour. 2020, 31, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grmasha, R.A.; Abdulameer, M.H.; Stenger-Kovács, C.; Al-sareji, O.J.; Al-Gazali, Z.; Al-Juboori, R.A.; Meiczinger, M.; Hashim, K.S. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the surface water and sediment along Euphrates River system: Occurrence, sources, ecological and health risk assessment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 187, 114568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambade, B.; Sethi, S.S.; Kurwadkar, S.; Kumar, A.; Sankar, T.K. Toxicity and health risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface water, sediments and groundwater vulnerability in Damodar River Basin. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 13, 100553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmine, J.; Laaly, A.; Millet, M. Environmental occurrence, spatial distribution, and source identification of PAHs in surface and groundwater samples of Abou Ali River-North Lebanon. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.H.; Zhou, L.X. Environmental behavior of PAHs in soil-plant system. Ecol. Environ. 2003, 12, 487–492. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Environmental Protection. National Pollutant Environmental Health Risk List: Chemical Volume 1; China Environmental Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bihari, N.; Fafandel, M.; Hamer, B.; Kralj-Bilen, B. PAH content, toxicity an genotoxicity of coastal marine sediments from the Rovinj area, Northern Adriatic, Croatia. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 366, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Huang, Q.H.; Li, W.Y.; Tang, Y.J.; Zhao, J.F. Source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in surface sediments of the Huangpu River, Shanghai, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 407, 2931–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.F.; Lang, Y.H.; Cao, Z.M.; Ma, Q.M. Source Apportionment of PAHs in Estuarine Sediments from the Yellow River. Res. Environ. Sci. 2008, 21, 79–84. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.F.; Hu, X.F.; Yves, U.J.; Zhan, H.Y.; Wu, Y.Q. Status, source and health risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in street dust of an industrial city, NW China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2004, 106, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.H.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.H.; Wang, D.Z.; Liu, H.D.; Wang, W.X. Characteristic of concentration distribution and source analysis of PAHs in cloud/fog water at Taishan Mount. China Environ. Sci. 2010, 30, 742–746. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Lu, L.; Pei, J.G. Source analysis and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments from suburban type underground river. Environ. Chem. 2020, 39, 2733–2741. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili, N.R.; Scheff, P.A.; Holsen, T.M. PAH source fingerprints for coke ovens, diesel and, gasoline engines, highway tunnels, and wood combustion emissions. Atmos. Environ. 1995, 29, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavouras, I.G.; Koutrakis, P.; Tsapakis, M.; Lagoudaki, E.; Stephanou, E.G.; Baer, D.V.; Oyola, P. Source Apportionment of Urban Particulate Aliphatic and Polynuclear Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) Using Multivariate Methods. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 2288–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogge, W.F.; Hildemann, L.M.; Mazurek, M.A.; Glen, R.C. Sources of fine organic aerosol. 2. Noncatalyst and catalyst -equipped automobiles and heavy-duty diesel trucks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1993, 27, 636–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.G.; Liu, J.L.; Wang, X.M.; Xue, J. Pollution characteristics, ecological risk assessment and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs)in surface water from the Zhangweinan River. Acta Sci. Circum. 2010, 30, 254–260. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerman, A.J. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Obanya, H.E.; Omoarukhe, A.; Amaeze, N.H.; Okoroafor, C.U. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in ologe lagoon and effects of benzo[b]fluoranthene in African catfish. J. Health Pollut. 2019, 9, 190605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traas, T.P.; Meent, D.V.D.; Posthuma, L.; Hamers, T.; Kater, B.J.; Zwart, D.D.; Aldenberg, T. The Potentially Affected Fraction as a Measure of Ecological Risk. In Species Sensitivity Distributions in Ecotoxicology; Posthuma, L., Suter, G.W., Eds.; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; pp. 315–343. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, N.; He, W.; Kong, X.Z.; Liu, W.X.; He, Q.S.; Yang, B.; Ouyang, H.L.; Wang, Q.M.; Xu, F.L. Ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the water from a large Chinese lake based on multiple indicators. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 24, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, C.M.; Liu, H.W.; Huang, L.; He, P.Y. Distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in different types of water in Fengfeng mining field. China Min. Mag. 2018, 27, 93–98. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
| Location | Content of ∑16PAHs (ng·L−1) | Sampling Time | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| Northeastern Inner Mongolia, China | 66.39–164.5 | August 2020 | [45] |
| The Wuhai section of the Yellow River, China | 27.5–234 | July 2019 | [46] |
| The Lingwu section of the Yellow River, China | 135–265 | July 2019 | [46] |
| The Haihe River, China | 83.7–278 | the summer of 2017 | [22] |
| The Liuxi River Basin, South China | 156.73–422.03 | April 2018 | [47] |
| The Taizi River, Northeast China | 498.09–3218.27 | May 2011 | [48] |
| The Lake Taihu, China | 255–7298 | January, May, and August 2018 | [49] |
| The Bug River, Poland | 184.4 (the average value) | January 2019 | [50] |
| the Euphrates River, Iraq | 464–992 | March to July 2022 | [51] |
| The Damodar River Basin, India | 10,110 (the average value) | February to April 2019 | [52] |
| The Abou Ali River Basin, Lebanon | ND-15162 | August 2015 to March 2017 | [53] |
| Item | Nap | Ace | Flu | Phe | Ant | Flt | Pyr | Bap |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HC5 | 612,920 | 93,880 | 161,300 | 98,110 | 1640 | 9460 | 2610 | 40 |
| Subsidence Area | PAFs/% | msPAF/% | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nap (×10−6) | Ace (×10−6) | Flu (×10−5) | Phe (×10−9) | Ant (×10−1) | Flt (×10−4) | Pyr (×10−2) | Bap (×100) | msPAFCA (×10−2) | msPAFRA (×100) | |
| Panyi | 2.28 | 7.96 | 3.22 | 1.73 | 4.17 | 6.55 | 2.63 | 3.94 | 2.25 | 4.37 |
| Houwang | 1.27 | 5.81 | 2.21 | 1.55 | 3.51 | 4.96 | 1.94 | 3.87 | 1.65 | 4.23 |
| Xuqiao | 0.83 | 5.69 | 2.16 | 1.46 | 3.47 | 4.89 | 1.84 | 3.87 | 1.60 | 4.22 |
| Yue Zhangji | 2.25 | 6.24 | 2.65 | 1.49 | 3.57 | 5.22 | 2.14 | 3.87 | 1.75 | 4.24 |
| Xieqiao | 1.71 | 5.61 | 2.64 | 1.54 | 3.73 | 6.28 | 2.65 | 3.91 | 2.07 | 4.29 |
| Guqiao | 1.46 | 5.59 | 2.53 | 2.03 | 3.50 | 5.46 | 2.18 | 3.93 | 1.86 | 4.28 |
| Xinji’er | 1.57 | 5.30 | 2.74 | 1.50 | 3.65 | 5.49 | 2.36 | 3.87 | 1.83 | 4.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, X.; Chen, G.; Wang, H.; Sun, H. Pollution Characteristics and Risk Evaluation of PAHs in Subsidence Water Bodies in Huainan Coal Mining Area, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14003. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151814003
Deng X, Chen G, Wang H, Sun H. Pollution Characteristics and Risk Evaluation of PAHs in Subsidence Water Bodies in Huainan Coal Mining Area, China. Sustainability. 2023; 15(18):14003. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151814003
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Xinyue, Guangzhou Chen, Hua Wang, and Hui Sun. 2023. "Pollution Characteristics and Risk Evaluation of PAHs in Subsidence Water Bodies in Huainan Coal Mining Area, China" Sustainability 15, no. 18: 14003. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151814003
APA StyleDeng, X., Chen, G., Wang, H., & Sun, H. (2023). Pollution Characteristics and Risk Evaluation of PAHs in Subsidence Water Bodies in Huainan Coal Mining Area, China. Sustainability, 15(18), 14003. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151814003





