Assessing Impacts of Mining-Induced Land Use Changes on Groundwater and Surface Water Quality Using Isotopic and Hydrogeochemical Signatures
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Assess the drinking water suitability of different sources of water in the mining province by using the water quality index method;
- Map the spatial distribution of the WQI for the pre- and post-monsoon seasons;
- Determine recharge sources, flow patterns, and pathways of both mine water and groundwater dynamics using stable isotopes (δ18O and δD) in the Mahan River catchment area.
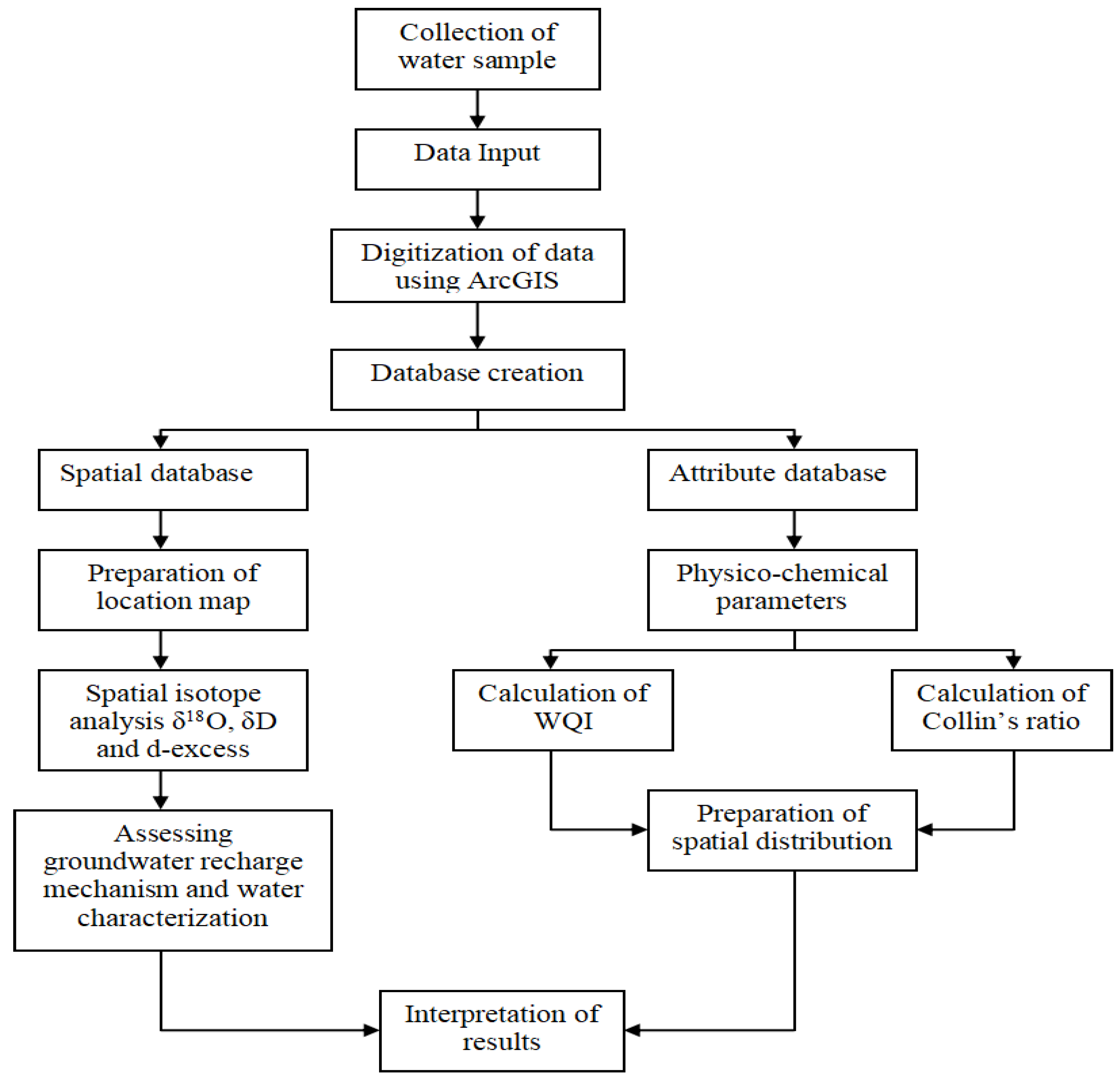
2. Materials and Methods
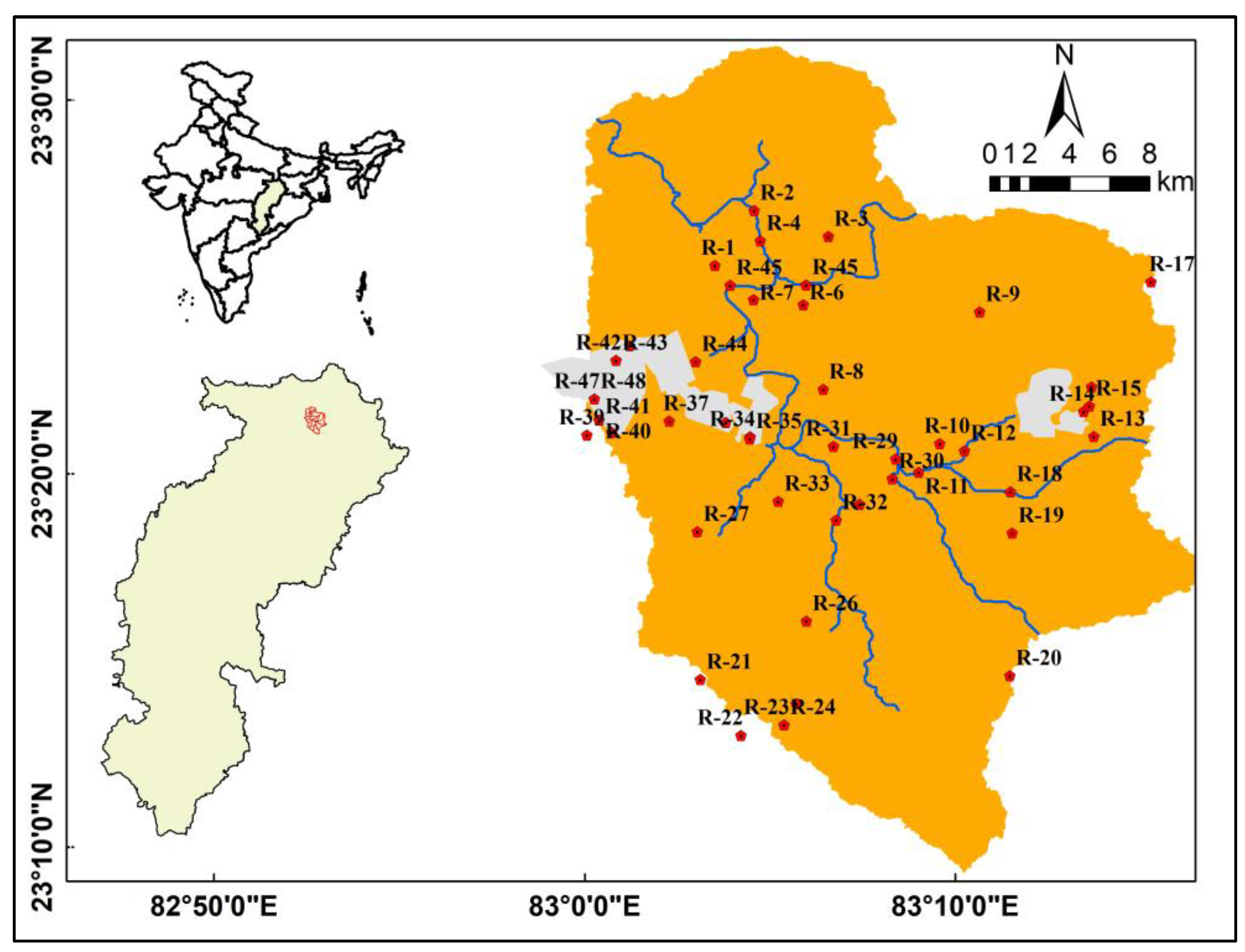
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Water Sampling and Analysis
2.3. Drinking Water Quality Index (WQI)
3. Results
3.1. Drinking Water Quality Index (WQI)
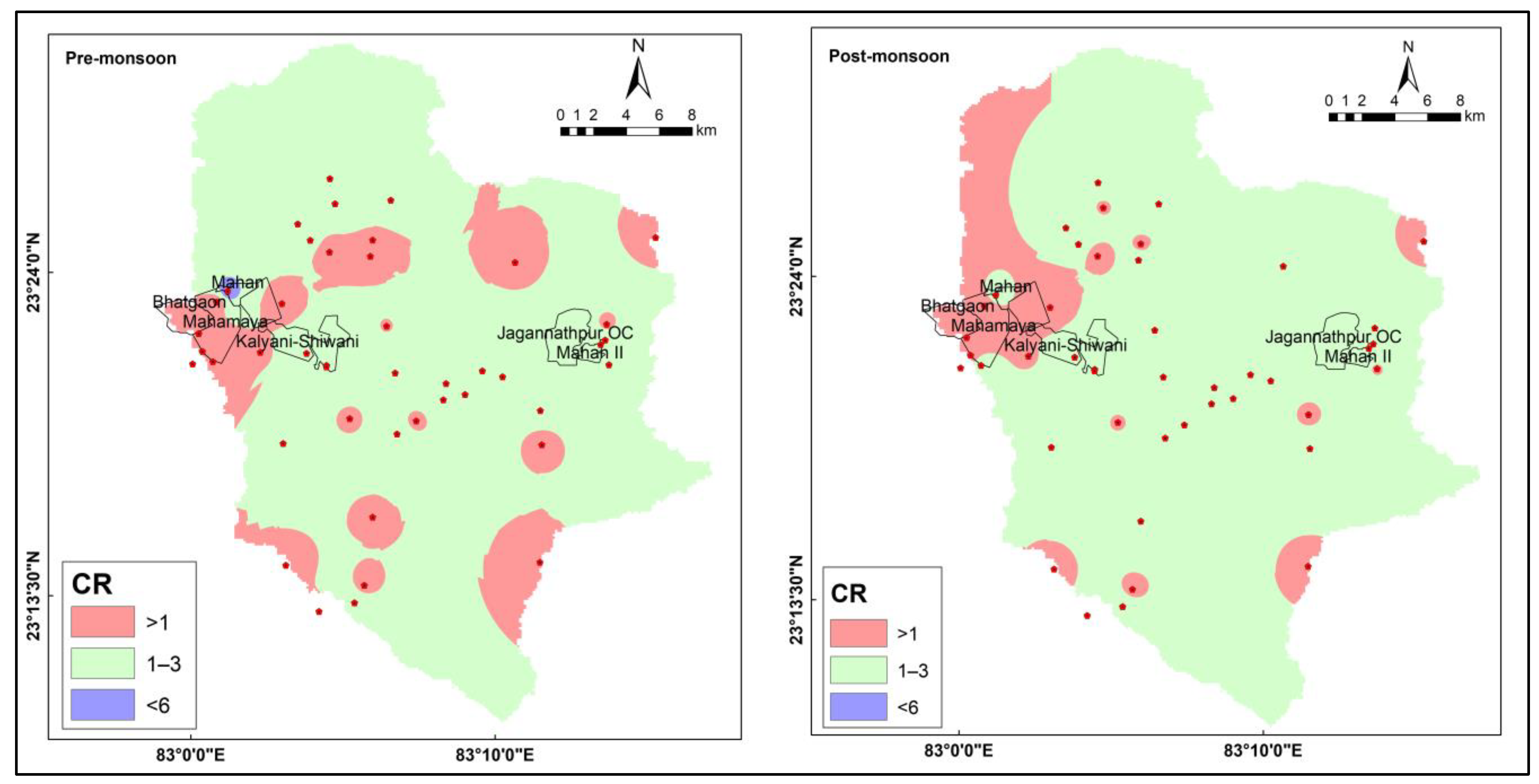
3.2. Collin’s Ratio
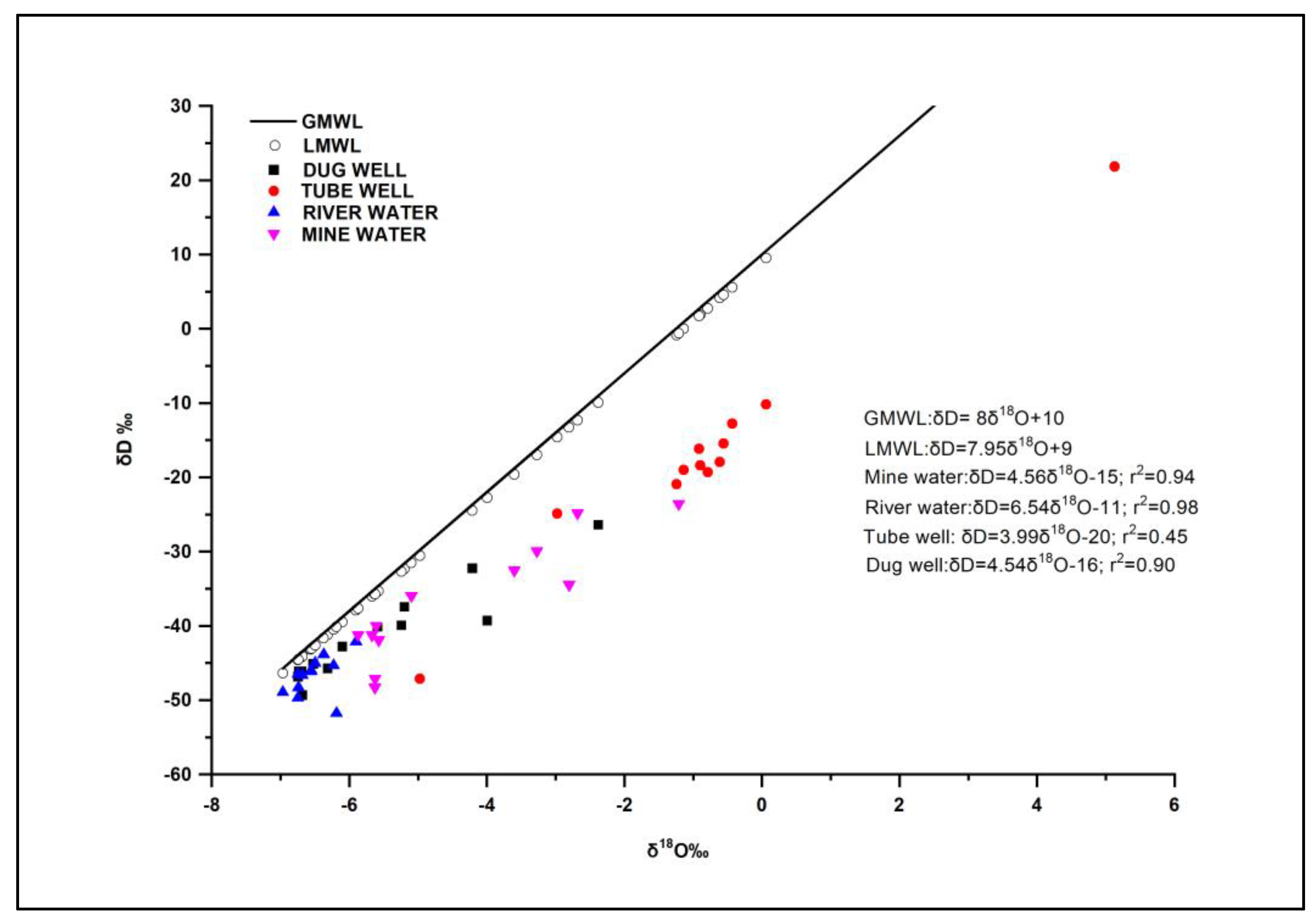
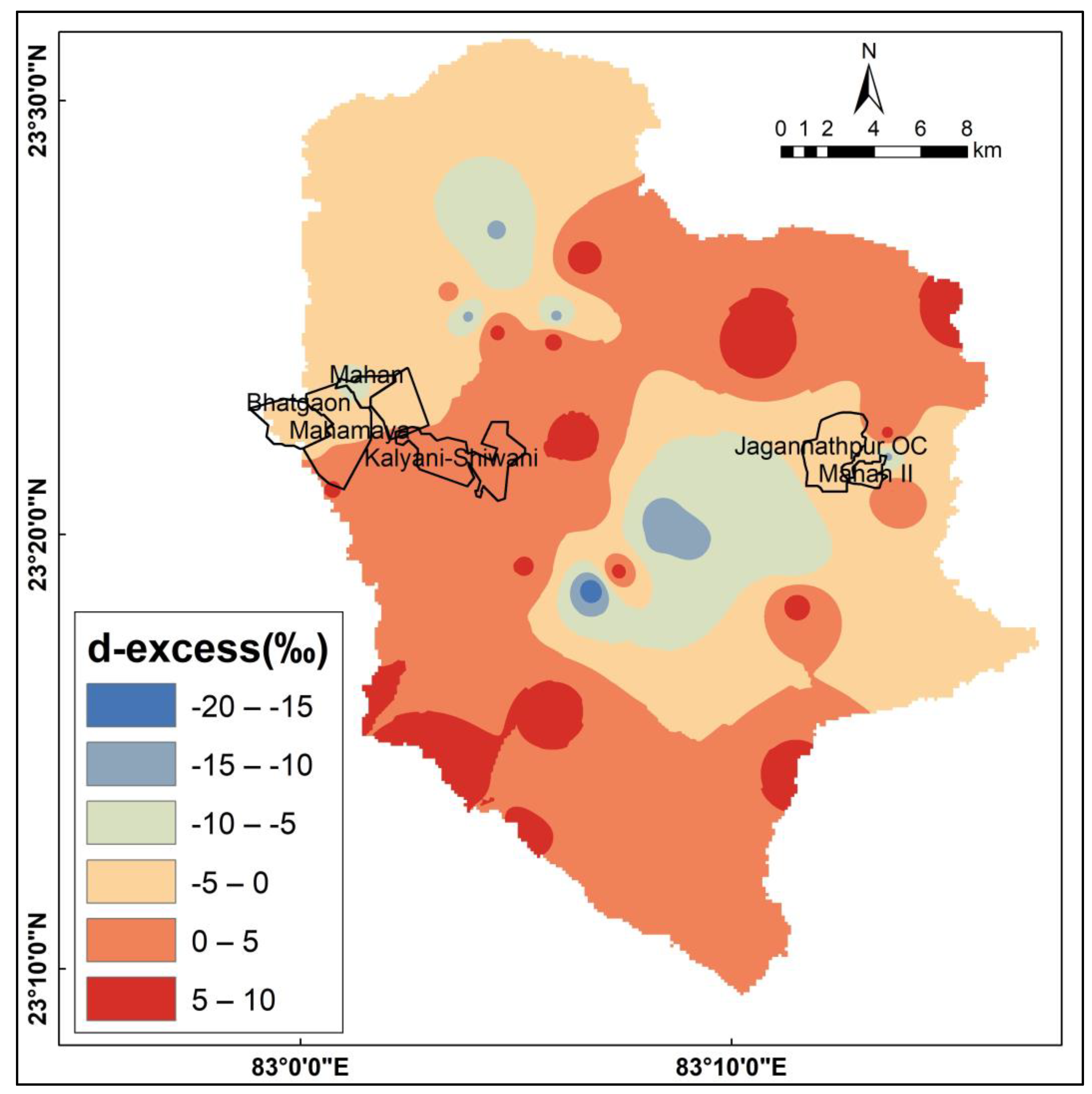
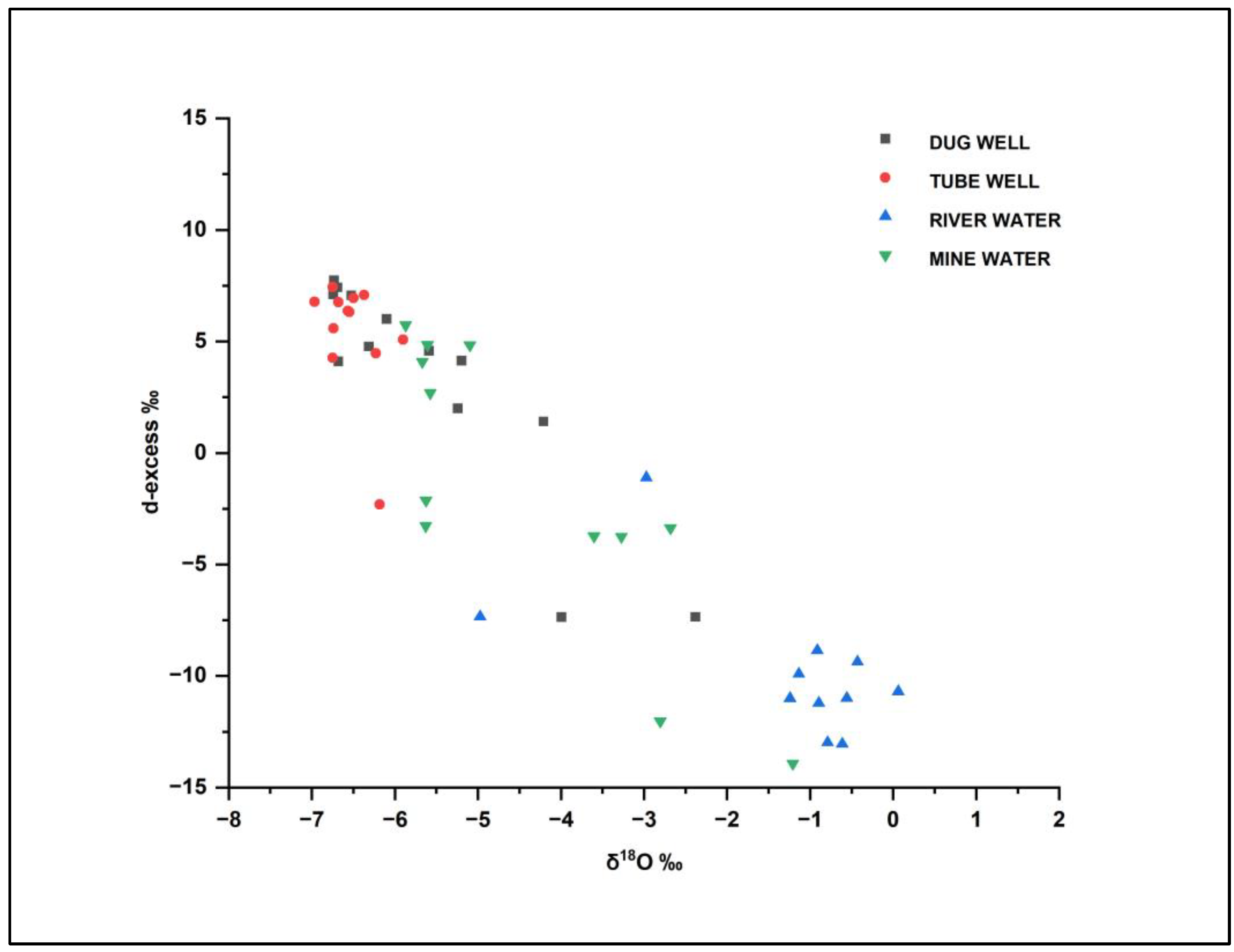
3.3. Stable Isotope Systematics
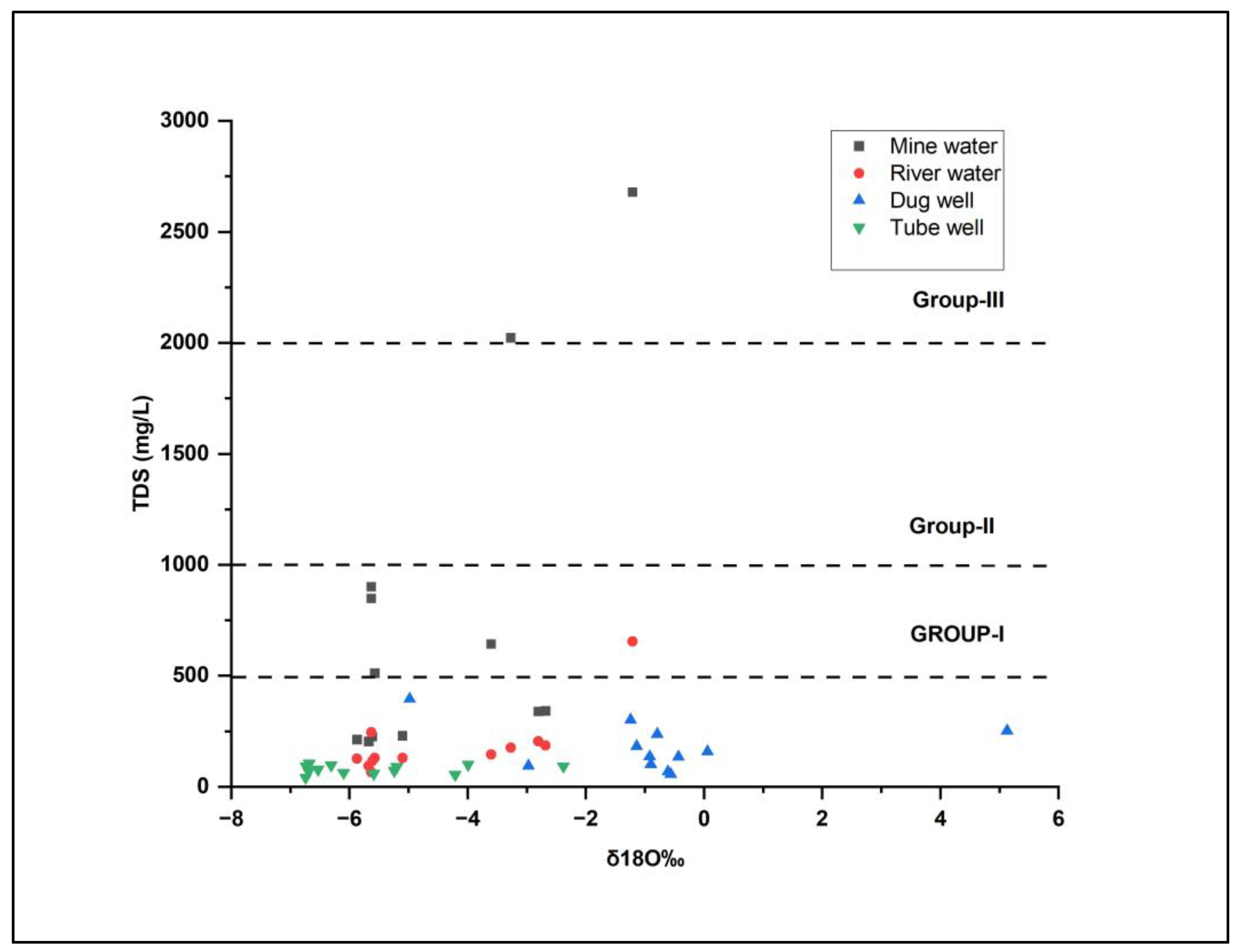
3.4. Relationship between TDS and Stable Isotopes (δ18O)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dvořáček, J.; Slivka, V. A note on the last stages of an underground coal mine life cycle in the Czech Republic. Miner. Energy -Raw Mater. Rep. 2004, 19, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choubey, V.D.; Rawat, R.K. Hydrogeologic and environmental impact of amjhore pyrite mines, India. Environ. Geol. 1991, 17, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwary, R.K.; Dhakate, R.; Rao, V.A.; Singh, V.S. Assessment and prediction of contaminant migration in ground water from chromite waste dump. Environ. Geol. 2005, 48, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surinaidu, L.; Rao, V.G.; Rao, N.S.; Srinu, S. Hydrogeological and groundwater modeling studies to estimate the groundwater inflows into the coal Mines at different mine development stages using MODFLOW, Andhra Pradesh, India. Water Resour. Ind. 2014, 7–8, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.C.; Ning, Z.G.; Li, Y.K.; Song, P.; Wu, N.; Yang, P. Dynamic biofilm component in reclaimed water during rapid growth period. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 4325–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Fourth Edition Incorporating the First Addendum; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Egbueri, J.C.; Enyigwe, M.T. Pollution and Ecological Risk Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Natural Waters from the Ameka Metallogenic District in Southeastern Nigeria. Anal. Lett. 2020, 53, 2812–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Fan, S.; Zhou, W.; Liu, S. Application of the Analytic Hierarchy Process to Assessment of Water Inrush: A Case Study for the No. 17 Coal Seam in the Sanhejian Coal Mine, China. Mine Water Environ. 2013, 32, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awaleh, M.O.; Boschetti, T.; Adaneh, A.E.; Chirdon, M.A.; Ahmed, M.M.; Dabar, O.A.; Soubaneh, Y.D.; Egueh, N.M.; Kawalieh, A.D.; Kadieh, I.H.; et al. Origin of nitrate and sulfate sources in volcano-sedimentary aquifers of the East Africa Rift System: An example of the Ali-Sabieh groundwater (Republic of Djibouti). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 804, 150072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parizi, H.S.; Samani, N. Environmental Isotope Investigation of Groundwater in the Sarcheshmeh Copper Mine Area, Iran. Mine Water Environ. 2014, 33, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Tiwari, M.K.; Singh, R.; Singh, A.K. Chemometrics in Ascertaining Hydrogeochemical Characteristics of Coal Mine Discharge vis-à-vis Behaviour of Surface and Groundwater Resources of the Mahan River Catchment Area, Central India. Mine Water Environ. 2022, 41, 518–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akudinobi, B.E.B. Qualitative Characterization of Groundwater Sources around Nigeria National Petroleum Cooperation Oil Depot Aba, Using Multiple Linear Regressions Modelling. 2018. Available online: https://sciencepubco.com/index.php/IJAG/article/view/8789 (accessed on 16 January 2018).
- Singh, R.; Venkatesh, A.S.; Syed, T.H.; Surinaidu, L.; Pasupuleti, S.; Rai, S.P.; Kumar, M. Stable isotope systematics and geochemical signatures constraining groundwater hydraulics in the mining environment of the Korba Coalfield, Central India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drever, J.I.; Stillings, L.L. The role of organic acids in mineral weathering. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1997, 120, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, J.H.; Hawkins, R.H. Flow path of rain from the soil surface to the water table. Soil Sci. 1965, 100, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.M.; McClelland, N.I.; Deininger, R.A.; Tozer, R.G. A Water Quality Index—Do We Dare. Water Sew. Work. 1970, 117, 339–343. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, L.; Huang, D.; Wang, T. Isotopic signatures of precipitation, surface water, and groundwater interactions, Poyang Lake Basin, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Venkatesh, A.S.; Singh, R.; Udayabhanu, G.; Saha, D. Geochemical signatures and isotopic systematics constraining dynamics of fluoride contamination in groundwater across Jamui district, Indo-Gangetic alluvial plains, India. Chemosphere 2018, 205, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassen, I.; Hamzaoui-Azaza, F.; Bouhlila, R. Application of multivariate statistical analysis and hydro-chemical and isotopic investigations for evaluation of groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and agriculture purposes: Case of Oum Ali-Thelepte aquifer, central Tunisia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prada, S.; Figueira, C.; Aguiar, N.; Cruz, J.V. Stable isotopes in rain and cloud water in Madeira: Contribution for the hydrogeologic framework of a volcanic island. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 2733–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K.; Deshpande, R.D.; Bhattacharya, S.K.; Jani, R.A. Groundwater δ18O and δD from central Indian Peninsula: Influence of the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal branches of the summer monsoon. J. Hydrol. 2005, 303, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenico, P.A.; Schwartz, F.W. Physical and Chemical Hydrogeology, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Epstein, S.A.; Mayeda, T.K. Variation of O18 content of waters from natural sources. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1953, 4, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbueri, J.C.; Mgbenu, C.N.; Chukwu, C.N. Investigating the hydrogeochemical processes and quality of water resources in Ojoto and environs using integrated classical methods. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2019, 5, 1443–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Khan, I.A. Groundwater quality assessment of Dhankawadi ward of Pune by using GIS. Int. J. Geomat. Geosci. 2011, 2, 688–703. [Google Scholar]
- Joji, V.S. Hydrochemistry of Ground Water; Archers and Elevators Publishing House: Karnataka, India, 2018; ISBN 978-93-86501-745. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, R.K.; Syed, T.H.; Saha, D.; Sarkar, B.C.; Reddy, D.V. Recharge mechanism and processes controlling groundwater chemistry in a Precambrian sedimentary terrain: A case study from Central India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, H. Isotopic Variations in Meteoric Waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, I.D.; Fritz, P. Environmental Isotopes; Hydrology Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Asmael, N.M.; Huneau, F.; Garel, E.; Celle-Jeanton, H.; Le Coustumer, P.; Dupuy, A.; Hamid, S. Origin and Recharge Mechanisms of Groundwater in the Upper Part of the Awaj River (Syria) Based on Hydrochemistry and Environmental Isotope Techniques. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 10521–10542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattacceca, J.C.; Vallet-Coulomb, C.; Mayer, A.; Claude, C.; Radakovitch, O.; Conchetto, E.; Hamelin, B. Isotopic and geochemical characterization of salinization in the shallow aquifers of a reclaimed subsiding zone: The southern Venice Lagoon coastland. J. Hydrol. 2009, 378, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, D.; Liu, Y.; Tian, F.; Li, D.; Huang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, H.; Liu, B.; Tian, W.; Cui, T. Pressure-induced metallization of dense (H2S)2H2 with high-Tc superconductivity. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakate, R.; Singh, V.; Hodlur, G. Impact assessment of chromite mining on groundwater through simulation modeling study in Sukinda chromite mining area, Orissa, India. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 160, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeniger, P.; Margane, A.; Abi-Rizk, J.; Himmelsbach, T. Stable isotope-based mean catchment altitudes of springs in the Lebanon Mountains. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 3708–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yuan, D.; Shen, Z. Effect of coal mine waters of variable pH on springwater quality: A case study. Environ. Geol. 1991, 17, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, H.-F.; Lee, C.-H.; Hsu, K.-C. Oxygen and hydrogen isotopes for the characteristics of groundwater recharge: A case study from the Chih-Pen Creek basin, Taiwan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 62, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansgaard, W. Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus 1964, 16, 436–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Months | Rainfall (mm) | Average Temperature (°C) | Relative Humidity |
|---|---|---|---|
| January | 23.36 | 18.60 | 51.77 |
| February | 8.22 | 20.36 | 50.72 |
| March | 7.42 | 24.68 | 33.52 |
| April | 1.60 | 29.17 | 28.73 |
| May | 2.03 | 32.92 | 23.78 |
| June | 188.69 | 31.51 | 55.20 |
| July | 455.51 | 27.42 | 73.48 |
| August | 449.48 | 27.24 | 81.34 |
| September | 208.75 | 26.55 | 71.94 |
| October | 64.84 | 24.89 | 82.31 |
| November | 13.24 | 21.36 | 65.04 |
| December | 6.01 | 18.75 | 63.17 |
| S. No. | Parameters | Desirable Limit | Assigned Weight (wi) | Relative Weight (Wi) | Impact | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BIS | WHO | |||||
| 1. | pH | 6.5–8.5 | 6.5–9.2 | 4 | 0.083 | Health/taste concern |
| 2. | EC | 1400 | 2000 | 5 | 0.104 | Health concern |
| 3. | TDS | 500 | 600 | 5 | 0.104 | Health/taste concern |
| 4. | Ca2+ | 75 | 100 | 3 | 0.0625 | Health concern |
| 5. | Mg2+ | 30 | 50 | 3 | 0.0625 | Health concern |
| 6. | Na+ | 200 | 200 | 5 | 0.104 | Health/taste concern |
| 7. | K+ | 10 | - | 2 | 0.0417 | Health concern |
| 8. | HCO3− | 200 | 200 | 1 | 0.0208 | Health concern |
| 9. | F− | 1.2 | 1.5 | 5 | 0.104 | Health concern |
| 10. | Cl− | 250 | 250 | 5 | 0.104 | Health/taste concern |
| 11. | NO3− | 45 | 50 | 5 | 0.104 | Health concern |
| 12. | SO42− | 400 | 500 | 5 | 0.104 | Health/taste concern |
| Dug Well | Tube Well | River Water | Mine Water | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δ18O (‰) | δD (‰) | d-Excess | δ18O (‰) | δD (‰) | d-Excess (‰) | δ18O (‰) | δD (‰) | d-Excess (‰) | δ18O (‰) | δD (‰) | d-Excess (‰) | |
| Min. | −6.73 | −49.34 | −7.36 | −6.97 | −51.79 | −2.32 | −4.98 | −47.15 | −19.20 | −5.87 | −47.13 | −13.93 |
| Max. | −2.38 | −32.27 | 7.74 | −5.90 | −43.89 | 7.08 | 0.06 | −10.21 | −1.11 | −1.21 | −23.60 | 5.73 |
| Average | −5.57 | −41.35 | 3.21 | −6.51 | −46.72 | 5.40 | −0.81 | −16.88 | −10.44 | −4.39 | −36.76 | −1.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kausher, R.; Singh, R.; Sinha, A.K.; Sethy, S.N.; Kumar, S.; Pandey, S.; Ragab, A.E.; Mohamed, A. Assessing Impacts of Mining-Induced Land Use Changes on Groundwater and Surface Water Quality Using Isotopic and Hydrogeochemical Signatures. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11041. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151411041
Kausher R, Singh R, Sinha AK, Sethy SN, Kumar S, Pandey S, Ragab AE, Mohamed A. Assessing Impacts of Mining-Induced Land Use Changes on Groundwater and Surface Water Quality Using Isotopic and Hydrogeochemical Signatures. Sustainability. 2023; 15(14):11041. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151411041
Chicago/Turabian StyleKausher, Rukaiya, Rambabu Singh, Anand Kumar Sinha, Satya Narayan Sethy, Sudhir Kumar, Shatrudhan Pandey, Adham E. Ragab, and Ahmed Mohamed. 2023. "Assessing Impacts of Mining-Induced Land Use Changes on Groundwater and Surface Water Quality Using Isotopic and Hydrogeochemical Signatures" Sustainability 15, no. 14: 11041. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151411041
APA StyleKausher, R., Singh, R., Sinha, A. K., Sethy, S. N., Kumar, S., Pandey, S., Ragab, A. E., & Mohamed, A. (2023). Assessing Impacts of Mining-Induced Land Use Changes on Groundwater and Surface Water Quality Using Isotopic and Hydrogeochemical Signatures. Sustainability, 15(14), 11041. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151411041










