Research on the Trade-Offs and Synergies of Ecosystem Services and Their Impact Factors in the Taohe River Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Processing
2.3. Quantifying ESs
2.4. Trade-Offs and Synergy Analysis
2.4.1. Analysis of ESs Trade-Offs and Synergies
2.4.2. ESs Trade-Offs and Synergistic Impact Factor Detection
2.4.3. Analysis of ES Trade-Offs and Synergistic Impact Factors
3. Results
3.1. Spatiotemporal Pattern of ESs
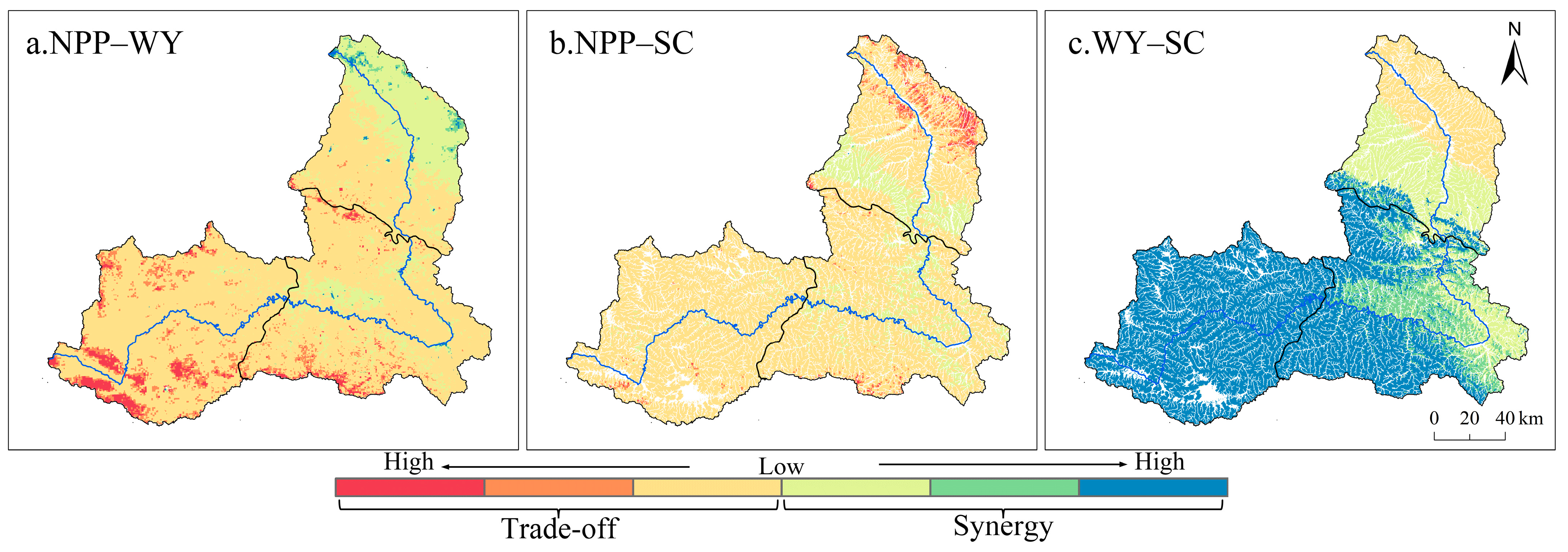
3.2. ESs Trade-Offs and Synergies
3.3. Identification of Dominant Factors for Relationships between ESs
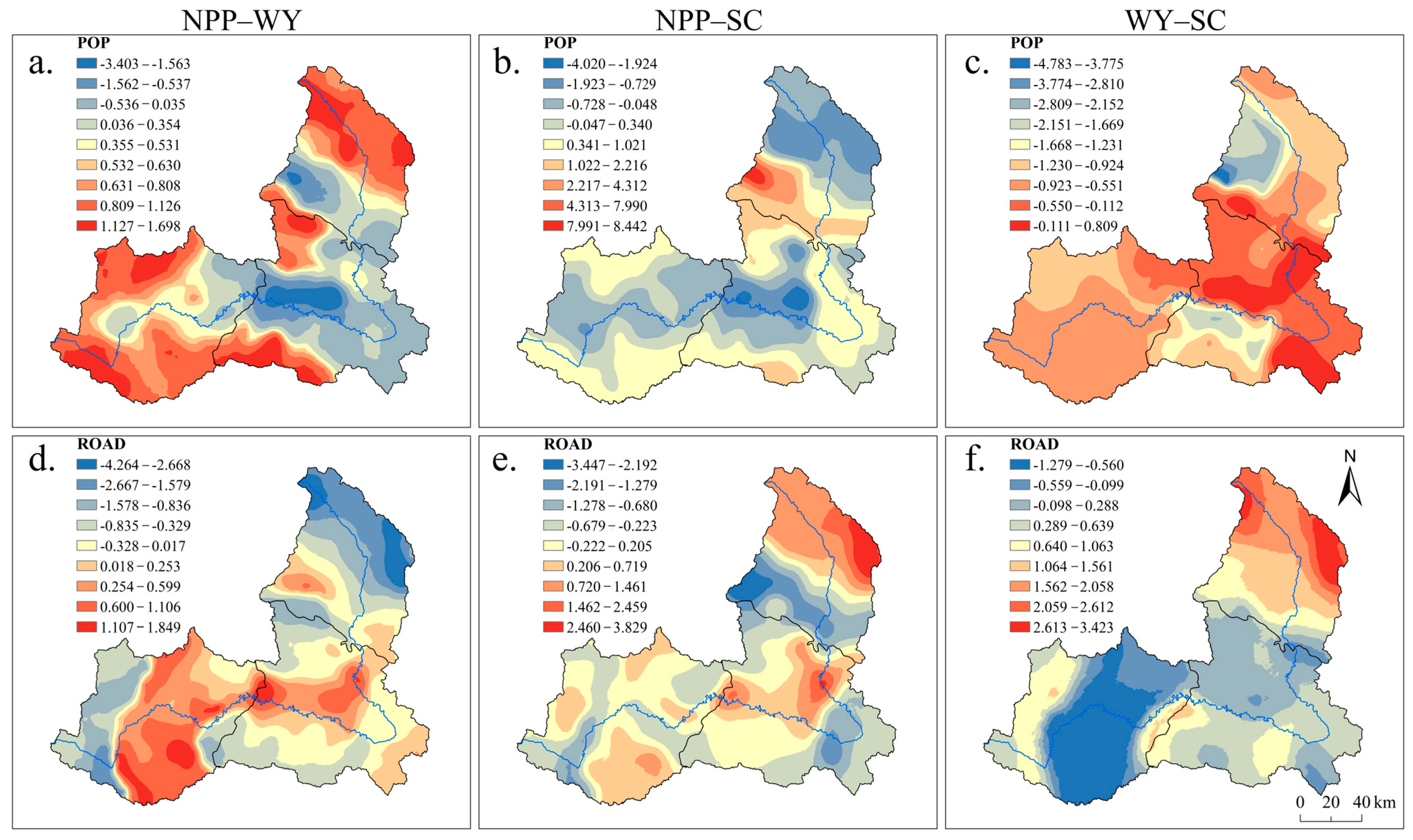
3.4. Analysis of ESs Trade-Offs and Synergistic Impact Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of ESs Trade-Offs and Synergistic Features
4.2. Management Based on Trade-Offs and Synergies
4.3. Limitations and Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lévêque, C. Ecology: From Ecosystem to Biosphere; Science Publishers: Rawalpindi, Pakistan, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Zhang, B.; Xie, G. Research on ecosystem services in China: Progress and perspectives. J. Nat. Resour. 2009, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Assessment, M.E. Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Wetlands and Water; World Resources Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, E.; Queiroz, C.; Pereira, H.M.; Vicente, L. Ecosystem services and human well-being: A participatory study in a mountain community in Portugal. Ecol. Soc. 2005, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; De Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, M.; La Notte, A.; Laporte, V.; Erhard, M. Potentials of quantitative and qualitative approaches to assessing ecosystem services. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 21, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, C.; Suich, H.; Vira, B.; Mace, G.M. Creating win-wins from trade-offs? Ecosystem services for human well-being: A meta-analysis of ecosystem service trade-offs and synergies in the real world. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2014, 28, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J.; Zhu, W.; Ma, C.; Wang, J. The tradeoffs and synergies of ecosystem services: Research progress, development trend, and themes of geography. Geogr. Res. 2013, 32, 1379–1390. [Google Scholar]
- Pedrono, M.; Locatelli, B.; Ezzine-de-Blas, D.; Pesche, D.; Morand, S.; Binot, A. Impact of climate change on ecosystem services. In Climate Change and Agriculture Worldwide; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 251–261. [Google Scholar]
- Mooney, H.; Larigauderie, A.; Cesario, M.; Elmquist, T.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Lavorel, S.; Mace, G.M.; Palmer, M.; Scholes, R.; Yahara, T. Biodiversity, climate change, and ecosystem services. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2009, 1, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhao, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhai, R. Influence of land use change on the ecosystem service trade-offs in the ecological restoration area: Dynamics and scenarios in the Yanhe watershed, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Jin, X.; Chen, T.; Wu, J. Understanding trade-offs and synergies of ecosystem services to support the decision-making in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region. Land Use Policy 2021, 106, 105446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cord, A.F.; Bartkowski, B.; Beckmann, M.; Dittrich, A.; Hermans-Neumann, K.; Kaim, A.; Lienhoop, N.; Locher-Krause, K.; Priess, J.; Schröter-Schlaack, C. Towards systematic analyses of ecosystem service trade-offs and synergies: Main concepts, methods and the road ahead. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 28, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, E.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, D. Methods, tools and research framework of ecosystem service trade-offs. Geogr. Res. 2016, 35, 1005–1016. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Li, S.; Liang, Z.; Liu, L.; Li, D.; Wu, S. Exploring the heterogeneity and nonlinearity of trade-offs and synergies among ecosystem services bundles in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration. Ecosyst. Serv. 2020, 43, 101103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, C.; Wang, S.; Bai, X.; Tan, Q.; Zhao, C.; Luo, X.; Chen, H.; Xi, H. Trade-offs and synergies of ecosystem services in southwestern China. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2020, 37, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Sang, W. Land use trade-offs and synergies based on temporal and spatial patterns of ecosystem services in South China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 143, 109335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhard, B.; Kroll, F.; Nedkov, S.; Müller, F. Mapping ecosystem service supply, demand and budgets. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 21, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Li, J.; Fu, X.; Mu, X.; Li, T. Trade-offs between carbon sequestration, soil retention and water yield in the Guanzhong-Tianshui Economic Region of China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 1449–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Huang, Q.; Wang, Q. Differentiation characteristics and driving factors of ecosystem services relationships in karst mountainous area based on geographic detector modeling: A case study of Guizhou Province. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 6959–6972. [Google Scholar]
- Nazeer, M.; Bilal, M. Evaluation of ordinary least square (OLS) and geographically weighted regression (GWR) for water quality monitoring: A case study for the estimation of salinity. J. Ocean Univ. China 2018, 17, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, M.; He, S.; Gan, M.; Yang, L.; Wang, K. Impacts of urbanization and landscape pattern on habitat quality using OLS and GWR models in Hangzhou, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahara, D.O.; Fauzan, A. Impacts of Human Development Index and Percentage of Total Population on Poverty using OLS and GWR models in Central Java, Indonesia. EKSAKTA J. Sci. Data Anal. 2021, 2, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. What factors affect the synergy and tradeoff between ecosystem services, and how, from a geospatial perspective? J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 257, 120454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Liang, E.; Shen, M.; Yang, B.; Jia, X.; Zhang, J. Precipitation dominants synergies and trade-offs among ecosystem services across the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 32, e01886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshan, T.M.; Li, Z.; Kang, W.; Wolf, L.J.; Fotheringham, A.S. mgwr: A Python implementation of multiscale geographically weighted regression for investigating process spatial heterogeneity and scale. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathurahman, M.; Ratnasari, V. Geographically weighted multivariate logistic regression model and its application. Abstr. Appl. Anal. 2020, 2020, 8353481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Feng, Q.; Li, C.; Si, J.; Wen, X.; Yin, Z. Detecting climate variability impacts on reference and actual evapotranspiration in the Taohe River Basin, NW China. Hydrol. Res. 2017, 48, 596–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Guan, X.; Shu, Z.; Yang, X.; Wang, G. Attribution of runoff change in the Taohe River Basin under a changing environment. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 27, 87–92+100. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Yang, L.; Yang, W.; Wang, S. Land use and land cover change in Taohe River Basin and its driving forces. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2014, 34, 848–855. [Google Scholar]
- Jianbing, W. Trend analysis for the variety of arid index in Taohe River basin in recent 40 years. Agric. Res. Arid Areas 2014, 32, 246–250. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, H. Dynamic changes of soil erosion in the taohe river basin using the RUSLE model and google earth engine. Water 2020, 12, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, L.; Wanrui, W.; Qi, J.; Linshan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lei, W.; Cui, X.; Wang, P. An analytical approach to separate climate and human contributions to basin streamflow variability. J. Hydrol. 2018, 559, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Wan, G.; Yang, M.; Wang, X.; Li, Y. The Runoff in the Upper Taohe River Basin and Its Responses to Climate Change. Water 2022, 14, 2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Liu, R.; Wen, J.; Zhao, M.; Wang, C. Climate change and drought evolution in the Tao River Basin in the past 50 years. J. Arid Meteorol. 2018, 36, 234–242. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Wang, S.; Yang, L.; Yang, W.; Li, W. Spatial and temporal variation of meteorologica elementsin the Taohe River Basin from 1951 to 2010. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2013, 35, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.-S.; Kang, E.-S.; Lan, Y.-C.; Chen, R.-S.; Yao, J.-Z.; Pu, R.-F.; Chen, M.-X. Trend Analysis of the Precipitation and Runoff in the Taohe River Watershed during the Past 50 Years. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2003, 25, 72–82. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Li, C.; Yang, L. Drought trend analysis based on standardized precipitation index and the Z index in the Tao River Basin. Arid Zone Res. 2015, 32, 565–572. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, F.-C.; Han, X.; Tang, S.; Song, X.; Wang, H. An improved model for evaluating ecosystem service values using land use/cover and vegetation parameters. J. Meteorol. Res. 2021, 35, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotheringham, A.S.; Yang, W.; Kang, W. Multiscale geographically weighted regression (MGWR). Ann. Am. Assoc. Geogr. 2017, 107, 1247–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quanqin, S.; Jiangwen, F.; Jiyuan, L.; Fan, Y.; Hua, L.; Xiuchun, Y.; Mingxiang, X.; Peng, H.; Xingjian, G.; Lin, H. Approaches for monitoring and assessment of ecological benefits of national key ecological projects. Adv. Earth Sci. 2017, 32, 1174. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Jin, T.; Yan, L.; Gong, J. Ecosystem services trade-off and synergy change in the Ziwuling Region, Northwest China and their influencing factors. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2022, 33, 3087–3096. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Feng, X.; Zhang, X.; Luo, G. Ecosystem service trade-off and synergy on Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Geogr. Res. 2021, 40, 18–34. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, L.; Shao, Q.; Ning, J.; Huang, H. Ecological changes and the tradeoff and synergy of ecosystem services in western China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 1059–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyssels, G.; Poesen, J.; Bochet, E.; Li, Y. Impact of plant roots on the resistance of soils to erosion by water: A review. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2005, 29, 189–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, X.; McNulty, S.G.; Vose, J.M. Potential water yield reduction due to forestation across China. J. Hydrol. 2006, 328, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Li, B.; Hou, Y.; Bi, X.; Zhang, X. Effects of land use and climate change on ecosystem services in Central Asia’s arid regions: A case study in Altay Prefecture, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607, 633–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Liu, D.; Zhang, J.; Xie, Y.; Cao, E.; Li, H. Tradeoffs/synergies of multiple ecosystem services based on land use simulation in a mountain-basin area, western China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 99, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Song, W.; Deng, X.; Xu, X. Trade-offs and synergies in ecosystem service within the three-rivers headwater region, China. Water 2017, 9, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Li, M.; An, Y.; Shi, F.; Beazley, R. Effects of the interaction among climate, terrain and human activities on biodiversity on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 794, 148497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Shi, X.; Fu, Y. Identifying vegetation restoration effectiveness and driving factors on different micro-topographic types of hilly Loess Plateau: From the perspective of ecological resilience. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 289, 112562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, S.H.; Gan, T.Y. Impact of anthropogenic climate change and human activities on environment and ecosystem services in arid regions. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1329–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desta, H.; Lemma, B.; Fetene, A. Aspects of climate change and its associated impacts on wetland ecosystem functions: A review. J. Am. Sci. 2012, 8, 582–596. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Gao, X.; Zhao, X.; Wu, P. Scale effect and spatially explicit drivers of interactions between ecosystem services—A case study from the Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.; Qin, D.; Li, S. Trade-off analyses of multiple mountain ecosystem services along elevation, vegetation cover and precipitation gradients: A case study in the Taihang Mountains. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 103, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuazo, V.H.D.; Pleguezuelo, C.R.R. Soil-erosion and runoff prevention by plant covers: A review. Sustain. Agric. 2009, 28, 785–811. [Google Scholar]
- Fatichi, S.; Ivanov, V.Y. Interannual variability of evapotranspiration and vegetation productivity. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 3275–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, P.G.; Wilby, R.L.; Battarbee, R.W.; Kernan, M.; Wade, A.J. A review of the potential impacts of climate change on surface water quality. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2009, 54, 101–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Wang, L.-J.; Jiang, J.; Chu, L.; Zhang, J.-C. Threshold effect of ecosystem services in response to climate change and vegetation coverage change in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau ecological shelter. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 318, 128592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Pan, J.; Bi, F. Can human activities enhance the trade-off intensity of ecosystem services in arid inland river basins? Taking the Taolai River asin as an example. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 861, 160662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Gong, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, D.; Ma, X. Change and tradeoffs-synergies analysis on watershed ecosystem services: A case study of Bailongjiang Watershed, Gansu. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2018, 73, 868–879. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Dai, E. Spatial-temporal changes in ecosystem services and the trade-off relationship in mountain regions: A case study of Hengduan Mountain region in Southwest China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 264, 121573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, Z.; Ma, X.; Zhang, X. Response of multiple mountain ecosystem services on environmental gradients: How to respond, and where should be priority conservation? J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhao, X.; Du, Y.; Ma, P. Spatio-temporal changes of the coupling relationship between ecosystem services and residents’ well-being in Qinba. J. Nat. Resour. 2021, 36, 2522–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Zhao, W.; Fu, B.; Ding, J.; Wang, S. Ecosystem service trade-offs and their influencing factors: A case study in the Loess Plateau of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607, 1250–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| ESs | Models | Mathematical Algorithms |
|---|---|---|
| NPP | CASA | |
| : net primary productivity of vegetation at a time for pixels (gC/m2); : photosynthetically active radiation absorbed by pixels at a time (MJ/m2); : actual light energy utilization at a time for pixels (gC/MJ). | ||
| WY | Water yield module of InVEST | |
| : annual water yield of the pixels (mm); : actual annual evapotranspiration of the pixels (mm); : annual precipitation of the pixels (mm). | ||
| SC | Sediment retention module of InVEST | |
| : soil conservation amount (t/hm2); : potential soil erosion amount (t/hm2); : actual soil erosion amount under ecological management measures (t/hm2); , , , and indicate rainfall erosion factor, soil erosion factor, slope length slope factor, vegetation cover and management factor, and measure factor of soil and water conservation, respectively. |
| Cropland | Forest | Grassland | Shrubs | Water | Bare | Constructed Land | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NPP–WY | Trade-off | 3791.52 | 2596.86 | 13,888.49 | 371.52 | 5.85 | 1.08 | 7.29 | 20,662.61 |
| Synergy | 1698.75 | 370.62 | 2410.74 | 48.06 | 42.3 | 0.09 | 4.77 | 4575.33 | |
| NPP–SC | Trade-off | 2812.14 | 2062.71 | 11,699.79 | 287.46 | 3.51 | 1.08 | 1.44 | 16,868.13 |
| Synergy | 1217.7 | 315.27 | 875.52 | 59.49 | 7.92 | 0 | 0 | 2475.9 | |
| WY–SC | Trade-off | 843.75 | 0.18 | 1387.62 | 0.27 | 1.35 | 0.09 | 0 | 2233.26 |
| Synergy | 3185.55 | 2377.8 | 11,187.36 | 346.68 | 10.08 | 0.99 | 0.72 | 17,109.18 |
| Natural Factors | Social Factors | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TEM | PRE | DEM | NDVI | SOIL | GDP | POP | ROAD | CROP | LU | |
| NPP–WY | 0.48 | 0.45 | 0.50 | 0.37 | 0.16 | 0.18 | 0.32 | 0.04 | 0.38 | 0.06 |
| NPP–SC | 0.16 | 0.21 | 0.16 | 0.23 | 0.12 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.07 |
| WY–SC | 0.59 | 0.71 | 0.67 | 0.64 | 0.11 | 0.31 | 0.56 | 0.17 | 0.33 | 0.31 |
| OLS | GWR | MGWR | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSS | R2 | AICc | RSS | R2 | AICc | RSS | R2 | AICc | |
| NPP–WY | 512.595 | 0.655 | 2662.534 | 253.196 | 0.809 | 1975.825 | 256.351 | 0.813 | 1882.806 |
| NPP–SC | 845.908 | 0.431 | 3411.415 | 379.230 | 0.704 | 2697.604 | 423.176 | 0.717 | 2632.314 |
| WY–SC | 241.130 | 0.838 | 1535.078 | 82.787 | 0.935 | 457.184 | 96.143 | 0.929 | 457.845 |
| NPP–WY | NPP–SC | WY–SC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GWR | MGWR | GWR | MGWR | GWR | MGWR | |
| TEM | 157 | 43 | 123 | 43 | 116 | 119 |
| PRE | 157 | 54 | 123 | 48 | 116 | 43 |
| DEM | 157 | 43 | 123 | 43 | 116 | 43 |
| NDVI | 157 | 66 | 123 | 118 | 116 | 244 |
| SOIL | 157 | 284 | 123 | 154 | 116 | 661 |
| GDP | 157 | 66 | 123 | 71 | 116 | 324 |
| POP | 157 | 43 | 123 | 43 | 116 | 43 |
| ROAD | 157 | 58 | 123 | 43 | 116 | 43 |
| CROP | 157 | 115 | 123 | 357 | 116 | 70 |
| LU | 157 | 354 | 123 | 899 | 116 | 59 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Su, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X. Research on the Trade-Offs and Synergies of Ecosystem Services and Their Impact Factors in the Taohe River Basin. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9689. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129689
Zhou J, Zhang B, Zhang Y, Su Y, Chen J, Zhang X. Research on the Trade-Offs and Synergies of Ecosystem Services and Their Impact Factors in the Taohe River Basin. Sustainability. 2023; 15(12):9689. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129689
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Jing, Bo Zhang, Yaowen Zhang, Yuhan Su, Jie Chen, and Xiaofang Zhang. 2023. "Research on the Trade-Offs and Synergies of Ecosystem Services and Their Impact Factors in the Taohe River Basin" Sustainability 15, no. 12: 9689. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129689
APA StyleZhou, J., Zhang, B., Zhang, Y., Su, Y., Chen, J., & Zhang, X. (2023). Research on the Trade-Offs and Synergies of Ecosystem Services and Their Impact Factors in the Taohe River Basin. Sustainability, 15(12), 9689. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129689





