An Analysis of Runoff Variation in a Small Basin in the Loess Plateau: Identifying the Variation Causes and Implications for Sustainable Water Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
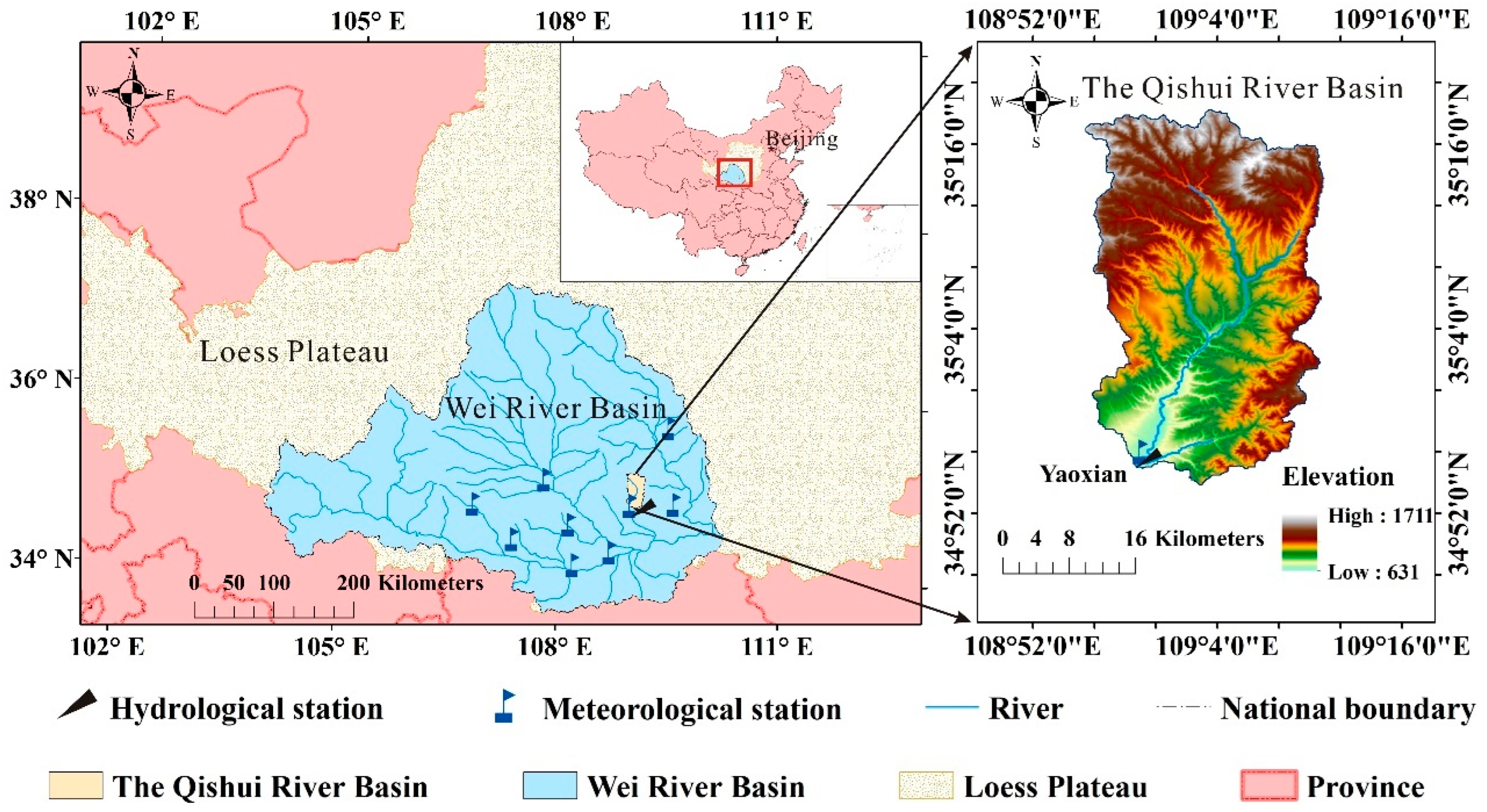
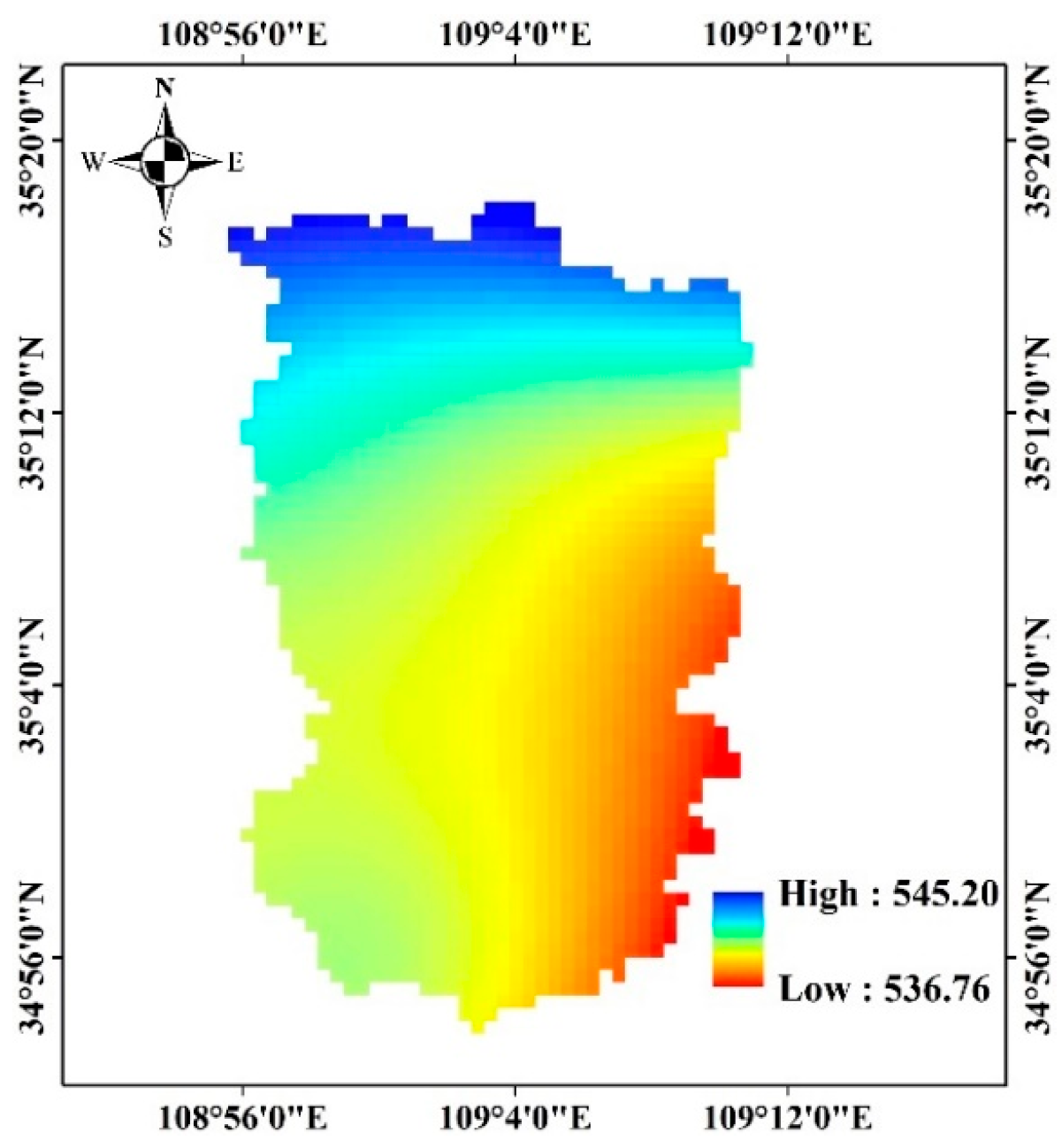
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Available Data
2.2.1. Meteorological Data and Digital Elevation Model (DEM) Data
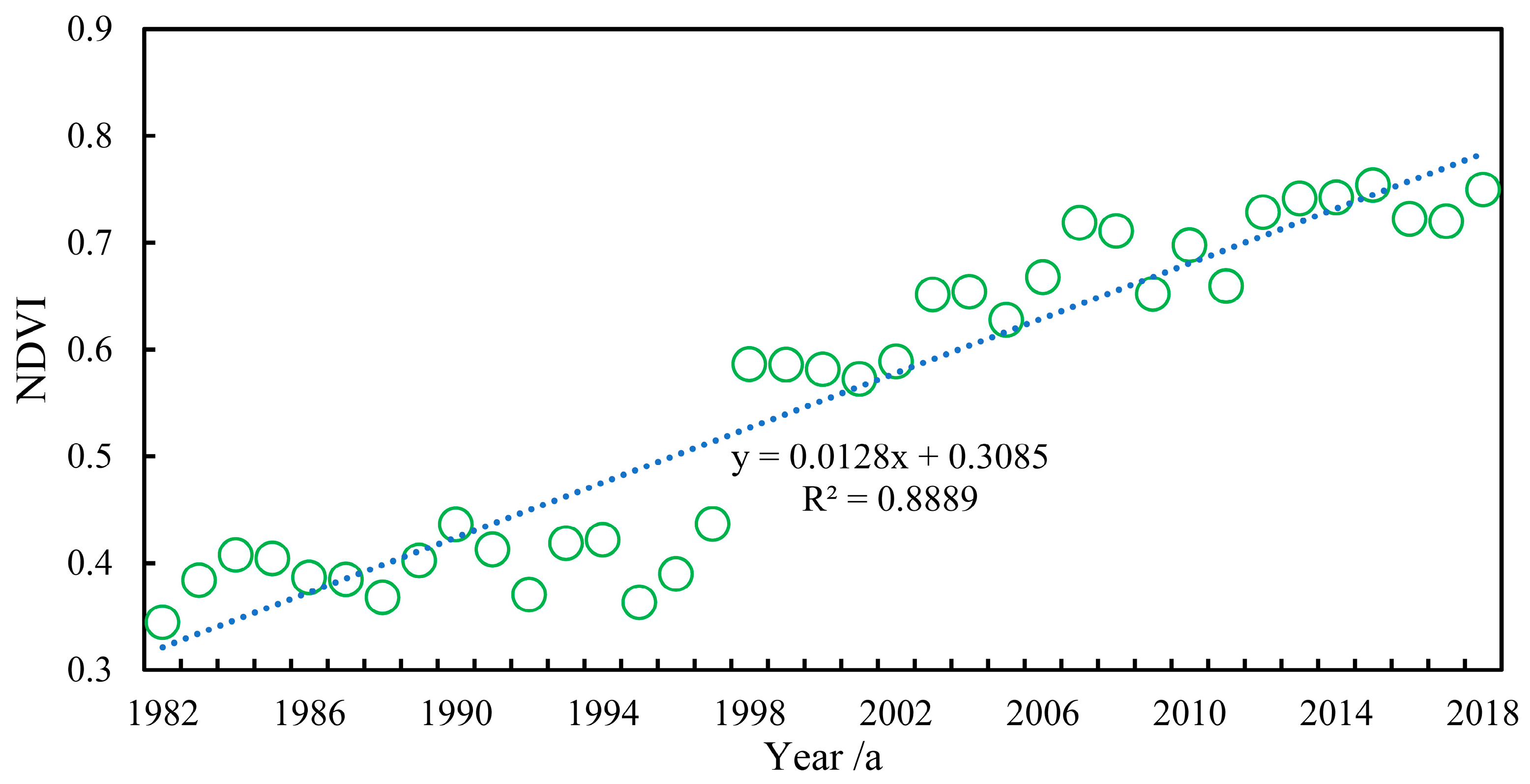
2.2.2. Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) Data
2.2.3. Observed Runoff Data
2.2.4. Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6) Data
2.2.5. Land Use Data and Harmonized World Soil Database (HWSD)
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Trend and Change Point Analysis
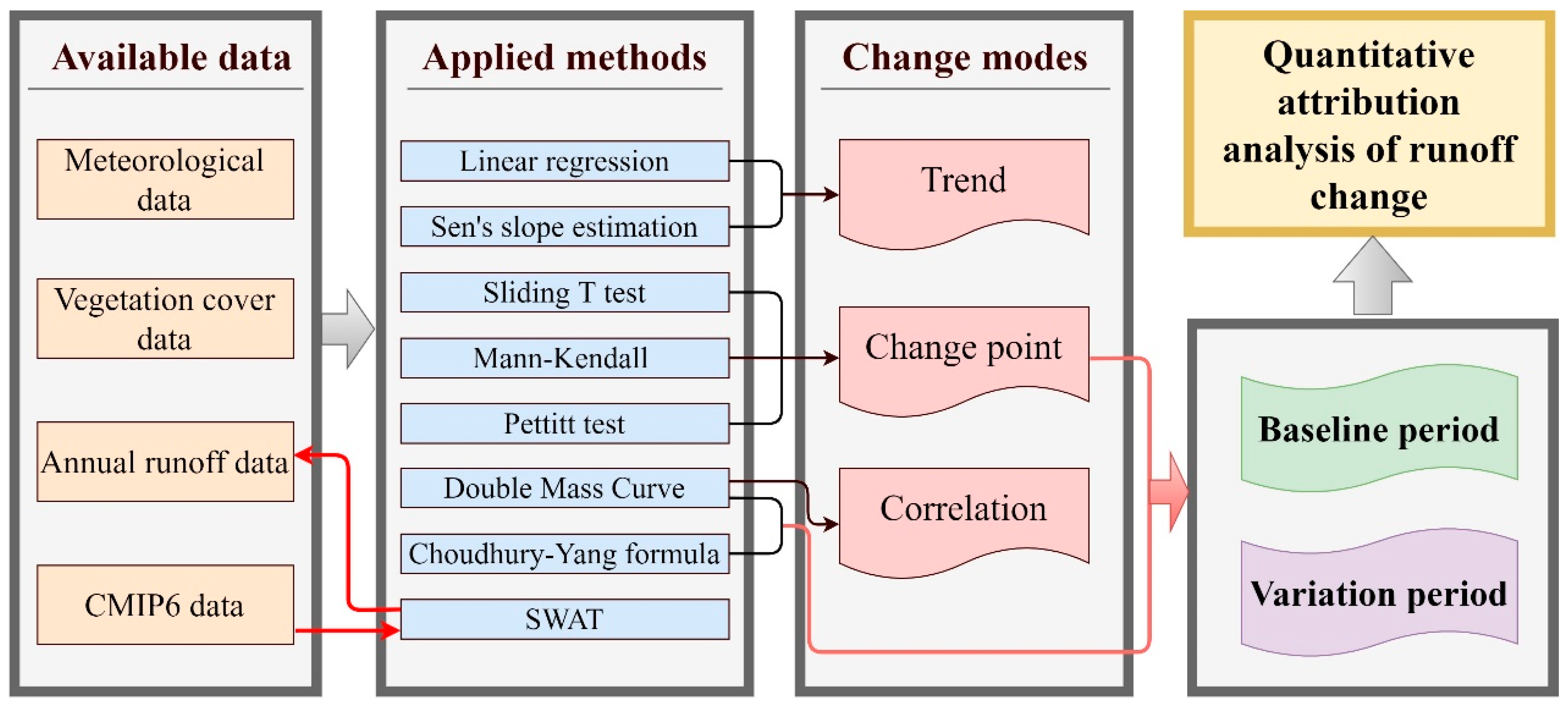
2.3.2. Runoff Variation and Attribution Analysis Methods
2.3.3. Simulation and Attribution Analysis Methods for Future Runoff under Different SSP Scenarios
3. Results
3.1. Variation Law of Hydrological Regime and Underlying Surface
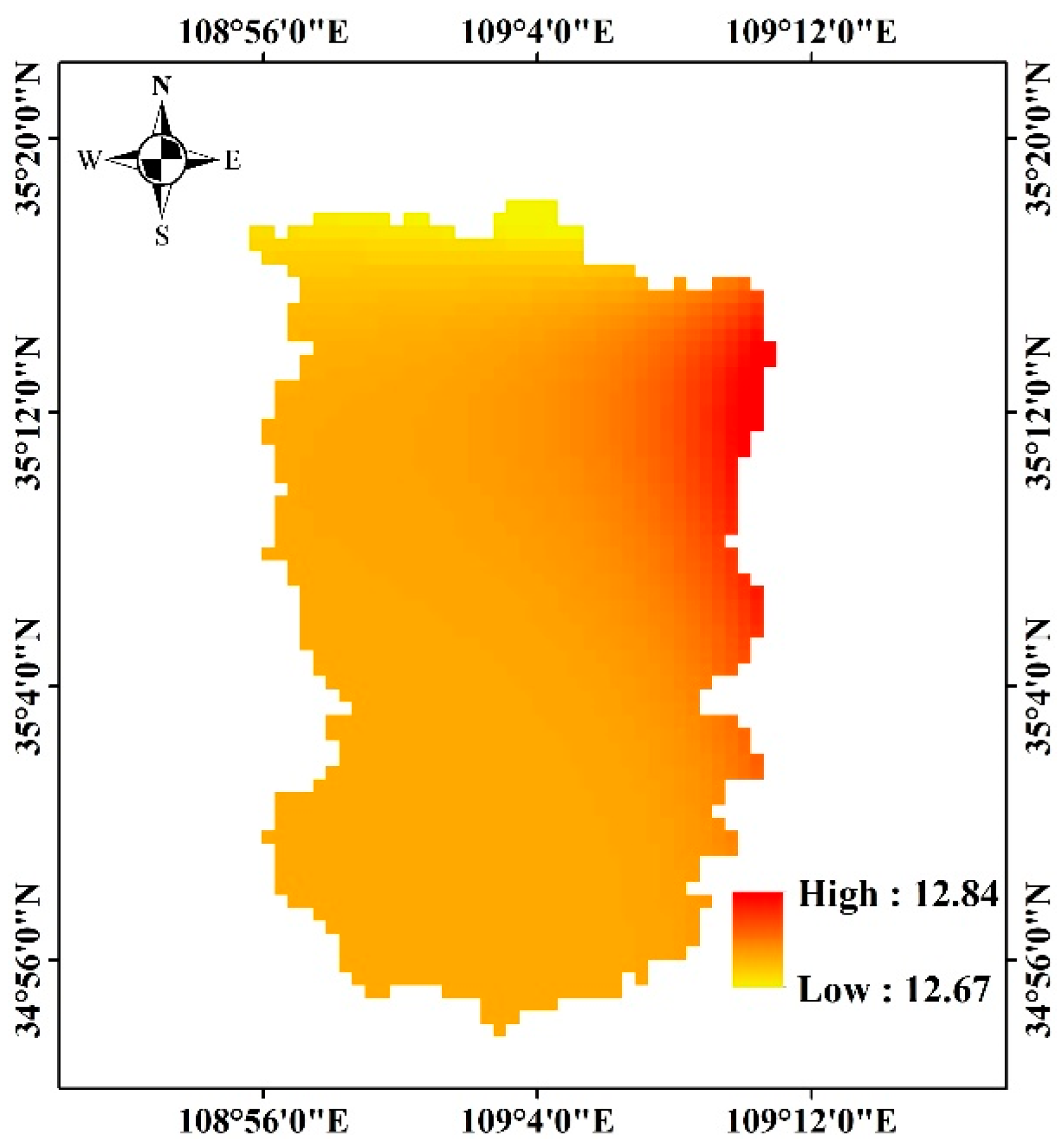
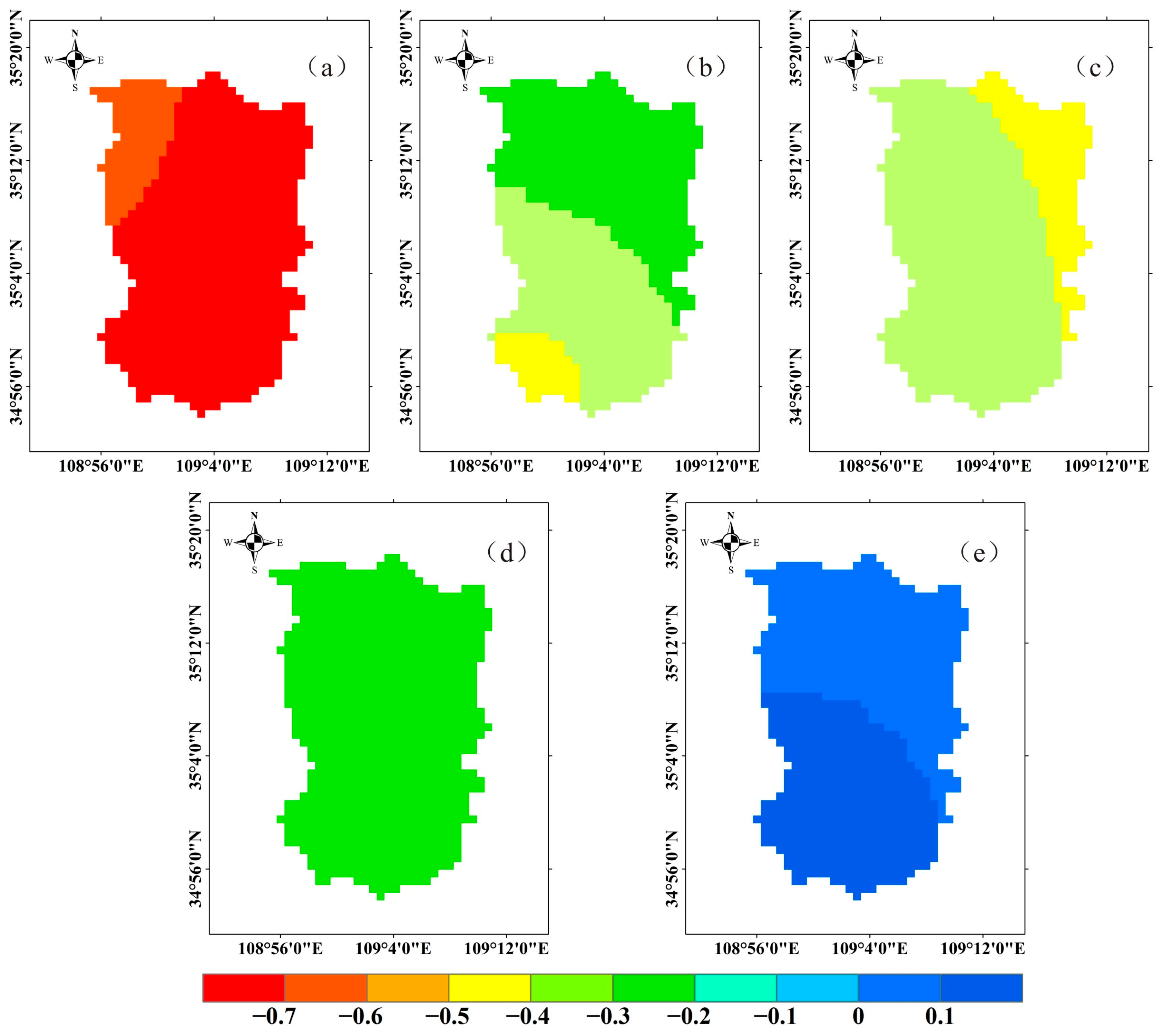
3.1.1. Temperature Trend
3.1.2. Precipitation Trend
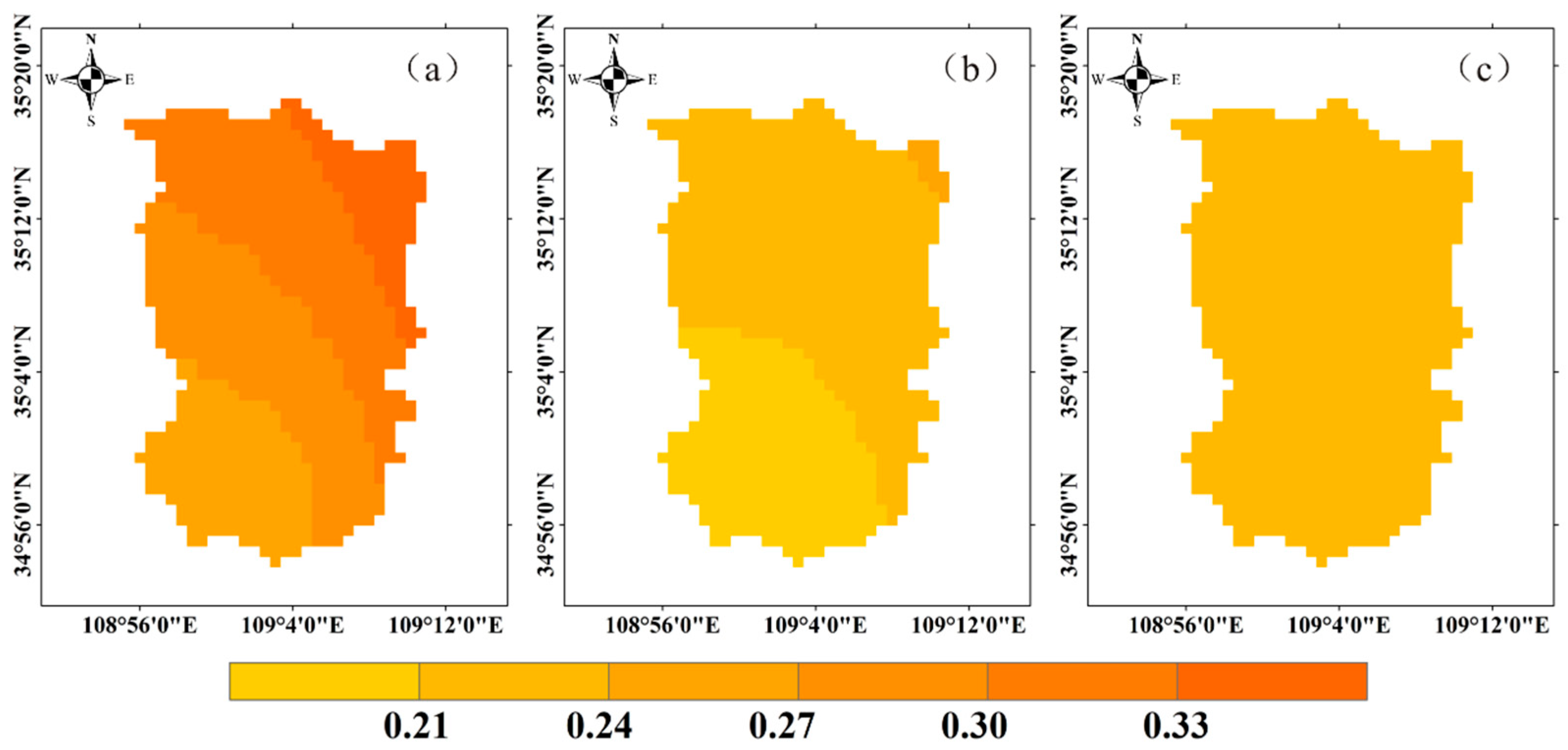
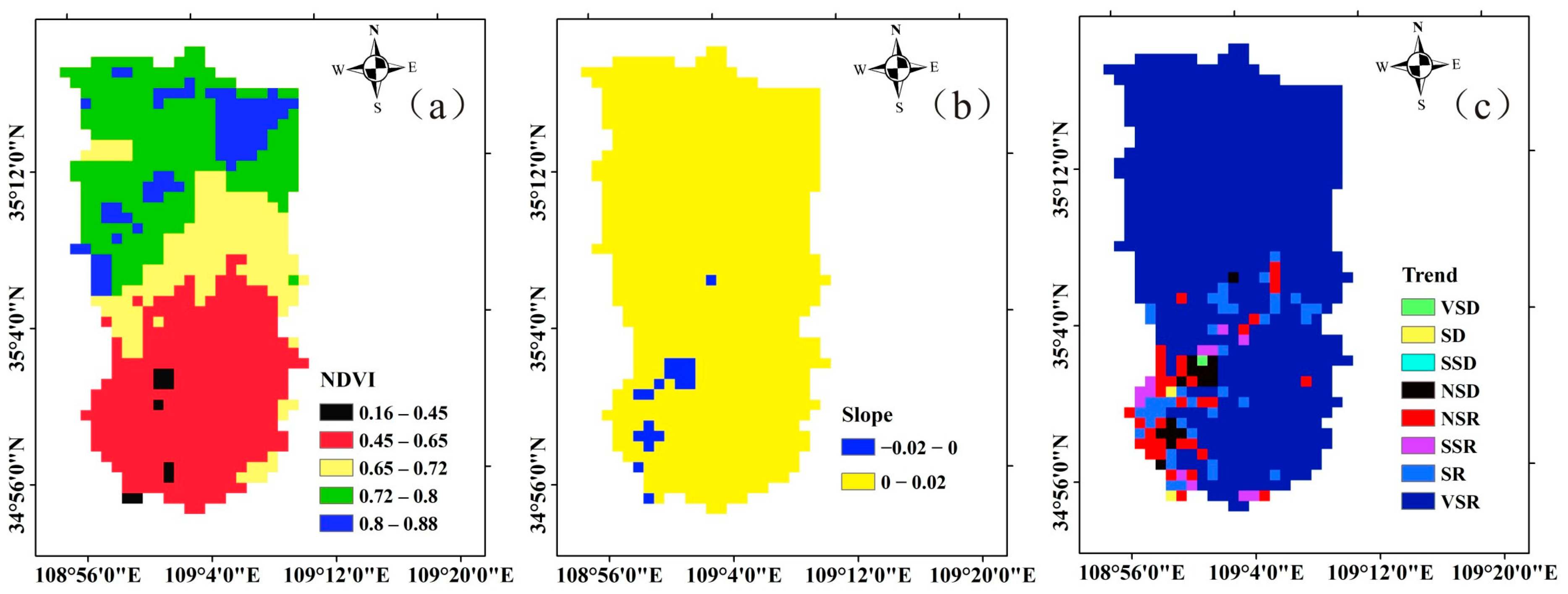
3.1.3. Variation Law of Underlying Surface
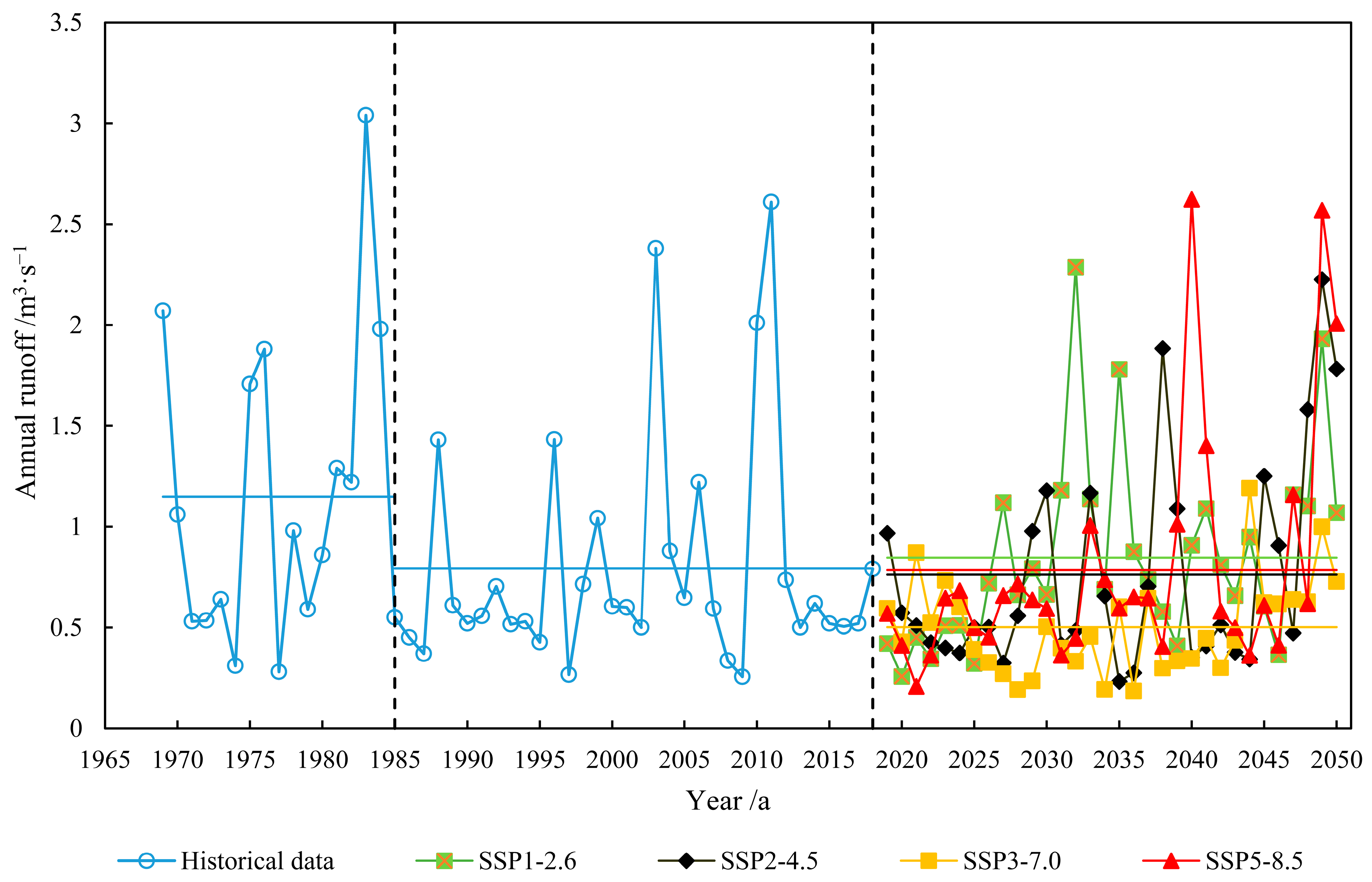
3.2. Characteristics of Historical and Future Runoff Variation in the QRB
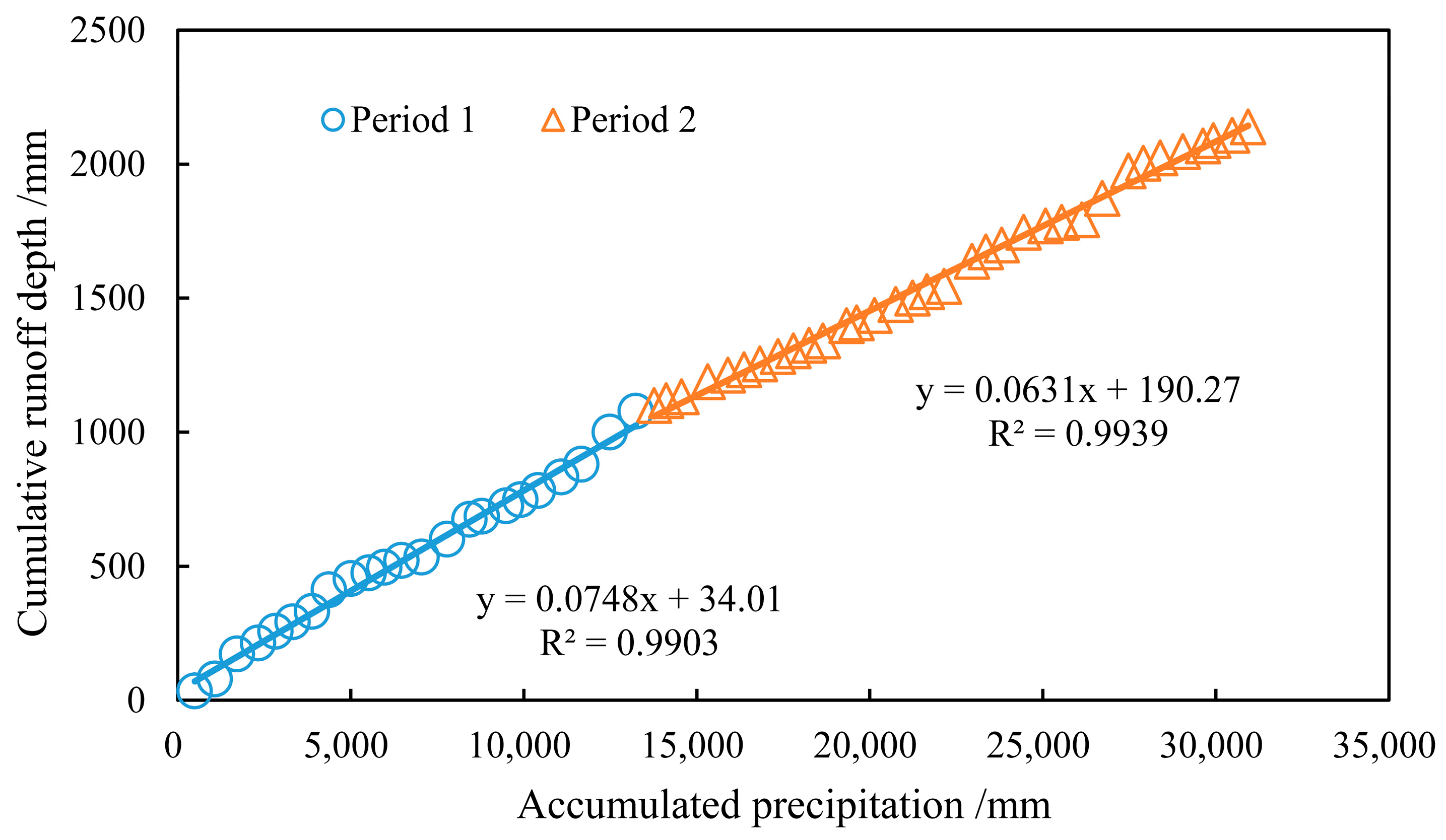
3.3. Relative Impact of Climate Change and Human Activity on Historical Runoff Change in the QRB
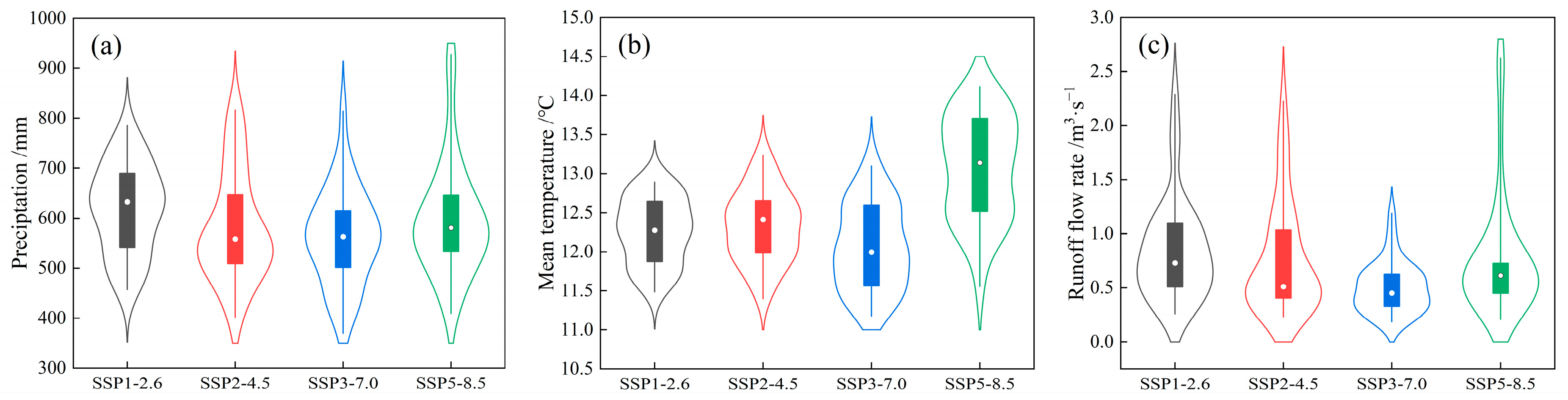
3.4. Relative Impact of Climate Change and Human Activity on Future Runoff Change in the QRB
4. Discussion
4.1. Challenges to Ensuring Water Security in the Watershed
4.2. Countermeasures to Ensure Water Resources Sustainability
4.3. Uncertainties and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, J.; Fu, B.; Gao, G.; Lü, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lü, N.; Wang, S. Effects of precipitation and restoration vegetation on soil erosion in a semi-arid environment in the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2016, 137, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, P.; Zhang, W.; Ji, J.; Liu, G.; Xu, M. Deep soil moisture limits the sustainable vegetation restoration in arid and semi-arid Loess Plateau. Geoderma 2021, 399, 115122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Jia, X.; Shao, M. Loess Thickness Variations across the Loess Plateau of China. Surv. Geophys. 2018, 39, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portenga, E.; Bierman, P. Understanding Earth’s eroding surface with 10Be. GSA Today 2011, 21, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Bi, R.; Song, X.; Hu, W.; Lyu, C.; Xi, X.; Li, H. Soil moisture response to land use and topography across a semi-arid watershed: Implications for vegetation restoration on the Chinese Loess Plateau. J. Mt. Sci. 2022, 19, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Z.; Guo, M.; Li, P.; Cheng, S.; Yuan, B. Effects of vegetation restoration on soil physical properties of abandoned farmland on the Loess Plateau, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Shao, M. Soil and water loss from the Loess Plateau in China. J. Arid. Environ. 2000, 45, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Xiong, L.; Wang, D.; Liu, P.; Guo, S.; Xu, C.-Y. Separating the impacts of climate change and human activities on runoff using the Budyko-type equations with time-varying parameters. J. Hydrol. 2015, 522, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Fu, B.; Wang, S.; Liang, W.; Jiang, X. Determining the hydrological responses to climate variability and land use/cover change in the Loess Plateau with the Budyko framework. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 557–558, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, Z.; Liu, G.; Xue, S.; Sun, C. Soil organic carbon and total nitrogen storage as affected by land use in a small watershed of the Loess Plateau, China. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2013, 54, 16–24. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Gao, P.; Tian, P.; Sun, W.; Hu, J.; Mu, X. Assessing sediment connectivity and soil erosion by water in a representative catchment on the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2020, 185, 104284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 3-North Shelter Forest Program. Available online: http://www.forestry.gov.cn/main/586/20211008/172030780867223.html (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- Shi, P.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Sun, J.; Wang, D.; Min, Z. Effects of grass vegetation coverage and position on runoff and sediment yields on the slope of Loess Plateau, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 259, 107231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Meng, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Wang, X. The contribution of human activities to runoff and sediment changes in the Mang River basin of the Loess Plateau, China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Miao, C.; Zhang, G.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Wu, J.; Gou, J. Is the runoff coefficient increasing or decreasing after ecological restoration on China’s Loess Plateau? Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2021, 9, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhu, R.; Ma, D.; Liu, D.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Z.; Yin, M.; Bandala, E.R.; Rodrigo-Comino, J. Multiple surface runoff and soil loss responses by sandstone morphologies to land-use and precipitation regimes changes in the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2022, 217, 106477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, M.; Liu, X.; Singh, D.K.; Fu, X. Quantifying the impact of climate change and anthropogenic activities on runoff and sediment load reduction in a typical Loess Plateau watershed. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 39, 100992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, X.; Wu, F.; Chen, B.; Liu, Y.; Yang, S.; Weng, Z. Quantitative analysis of climate change impact on Zhangye City’s economy based on the perspective of surface runoff. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 105, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; He, K.; Dong, Z. Effects of climate change and human activities on runoff in the Beichuan River Basin in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau, China. Catena 2019, 176, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Meng, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, M. Comprehensive evaluation of the effects of climate change and land use and land cover change variables on runoff and sediment discharge. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 702, 134401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, X.; Liu, C.; Wei, W.; Yang, X.; Li, Q.; Zhao, Y. Impacts of climate change and human activities on runoff change in a typical arid watershed, NW China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yu, X.; Jia, G.; Wang, H. Sensitivity analysis of runoff to climate variability and land-use changes in the Haihe Basin mountainous area of north China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 269, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eigentler, L.; Sherratt, J.A. Effects of precipitation intermittency on vegetation patterns in semi-arid landscapes. Phys. D 2020, 405, 132396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; McVicar, T.R. Assessing climate change induced modification of Penman potential evaporation and runoff sensitivity in a large water-limited basin. J. Hydrol. 2012, 464, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lan, T.; Wei, X.; Shao, S.; Zhang, J.; Ding, H. Attribution of runoff variation to climate and human-driven changes in the transition zone between the Qinling Mountains and the Loess Plateau under vegetation greening. Hydrol. Res. 2022, 53, 733–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Yan, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, M.; Peng, S. Attribution analysis of climatic and multiple anthropogenic causes of runoff change in the Loess Plateau—A case-study of the Jing River Basin. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 1622–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cheng, D.; Lei, Y.; Song, J.; Xia, J. Spatiotemporal distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments of a typical river located in the Loess Plateau, China: Influence of human activities and land-use changes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Lei, H.; Yang, D.; Huang, M.; Liu, D.; Yuan, X. Impact of vegetation dynamics on hydrological processes in a semi-arid basin by using a land surface-hydrology coupled model. J. Hydrol. 2017, 551, 116–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merz, R.; Blöschl, G.; Parajka, J. Spatio-temporal variability of event runoff coefficients. J. Hydrol. 2006, 331, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Yue, P.; Shi, J. Responses of the land-surface process and its parameters over the natural vegetation underlying surface of the middle of Gansu in loess plateau to precipitation fluctuation. Acta Phys. Sin. 2013, 62, 19201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, Z.; Ji, T.; Di, Q.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Wei, M.; Shi, Q.; Li, Y.; Gong, B.; et al. Genome-wide identification and characterization of the R2R3MYB transcription factor superfamily in eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). Agri Gene 2016, 2, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, Z.; Yu, Y.; Li, P.; Gong, J. Land-use changes and check dams reducing runoff and sediment yield on the Loess Plateau of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 984–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, C.; Mao, J.; Li, Z.; Jia, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B. Effects of driving factors at multi-spatial scales on seasonal runoff and sediment changes. Catena 2023, 222, 106867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Mao, D.; Feng, A.; Schillerberg, T. Will human-induced vegetation regreening continually decrease runoff in the loess plateau of China? Forests 2019, 10, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Mu, X.; Jiao, J.; Gao, P.; Sun, W.; Li, E.; Wei, Y.; Huang, J. Assessing response of sediment load variation to climate change and human activities with six different approaches. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 773–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, J.; Mo, S.; Luo, P.; Zhou, M.; Shen, B.; Nover, D. A quantitative assessment of hydrological responses to climate change and human activities at spatiotemporal within a typical catchment on the Loess Plateau, China. Quat. Int. 2019, 527, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, B. Evaluation of an empirical equation for annual evaporation using field observations and results from a biophysical model. J. Hydrol. 1999, 216, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Shao, W.; Yeh, P.J.F.; Yang, H.; Kanae, S.; Oki, T. Impact of vegetation coverage on regional water balance in the nonhumid regions of China. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Walker, G.R.; Dawes, W. Predicting the Effect of Vegetation Changes on Catchment Average Water Balance; Technical Report. 1999. Available online: https://www.ewater.org.au/archive/crcch/archive/pubs/pdfs/technical199912.pdf (accessed on 24 December 2022).
- Yang, H.; Yang, D.; Lei, Z.; Sun, F. New analytical derivation of the mean annual water-energy balance equation. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B. On the calculation of the evaporation from land surface. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 1981, 5, 23–31. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Duan, K.; Fu, S.; Gou, F.; Liang, W.; Yan, J.; Zhang, W. Partitioning climate and human contributions to changes in mean annual streamflow based on the Budyko complementary relationship in the Loess Plateau, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 665, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryal, Y.; Zhu, J. Effect of watershed disturbance on seasonal hydrological drought: An improved double mass curve (IDMC) technique. J. Hydrol. 2020, 585, 124746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budyko, M.I. Climate and Life; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Shi, C.; Sun, P.; Zhang, Y.; Collins, A.L. Attribution of runoff changes in the main tributaries of the middle Yellow River, China, based on the Budyko model with a time-varying parameter. Catena 2021, 206, 105557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Mu, X.-M.; Wang, F.; Li, R. Changes in streamflow and sediment discharge and the response to human activities in the middle reaches of the Yellow River. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xia, J.; Zou, L.; Zhan, C.; Liang, W. Estimation of time-varying parameter in Budyko framework using long short-term memory network over the Loess Plateau, China. J. Hydrol. 2022, 607, 127571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, T.; Li, Z.; Liu, W. Separating the impacts of climate change and land surface alteration on runoff reduction in the Jing River catchment of China. Catena 2016, 147, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhao, G.; Tian, P.; Mu, X.; Tian, X.; Feng, J.; Bai, Y. Runoff changes in the major river basins of China and their responses to potential driving forces. J. Hydrol. 2022, 607, 127536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Yu, Z.; Lv, X.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J. Response of runoff to vegetation change in typical basin of the Loess Plateau. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 182, 106704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Zhang, X.; Xu, B.; Li, P.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Y. Evaluating the impact of ecological construction measures on water balance in the Loess Plateau region of China within the Budyko framework. J. Hydrol. 2021, 601, 126596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; He, Y.; Jiang, X.; Nie, T.; Lei, Y. Attribution analysis of runoff variation in Kuye River Basin based on three Budyko methods. Land 2021, 10, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X. Spatial distribution of annual Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) in China. In Resource and Environmental Science and Data Registration and Publication System; Chinese Academy of Sciences: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, S.; Yang, C. Analyzing ecological environment change and associated driving factors in China based on NDVI time series data. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Gu, B.; Lindley, S.; Zhu, T.; Fan, J. Regulation factors driving vegetation changes in China during the past 20 years. J. Geogr. Sci. 2023, 33, 508–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Fu, J.; Wu, Z.; Pang, Z. Spatiotemporal Variation of NDVI in the Vegetation Growing Season in the Source Region of the Yellow River, China. ISPRS Int. J. Geoinf. 2020, 9, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Yellow River Basin Hydrological Yearbook of China; Yellow River Water Conservancy Committee: Zhengzhou, China, 2021.
- Hoeting, J.A.; Madigan, D.; Raftery, A.E.; Volinsky, C.T. Bayesian Model Averaging: A Tutorial. Stat. Sci. 1999, 14, 382–401. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, C.; Su, L.; Sun, Q.; Duan, Q. A nonstationary bias-correction technique to remove bias in GCM simulations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 5718–5735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyring, V.; Bony, S.; Meehl, G.A.; Senior, C.A.; Stevens, B.; Stouffer, R.J.; Taylor, K.E. Overview of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6) experimental design and organization. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 1937–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, B.I.; Mankin, J.S.; Marvel, K.; Williams, A.P.; Smerdon, J.E.; Anchukaitis, K.J. Twenty-First Century Drought Projections in the CMIP6 Forcing Scenarios. Earths Future 2020, 8, e2019EF001461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.; Cai, W.; Wang, C. The application and future directions of the Shared Socioeconomic Pathways (SSPs). Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2020, 16, 215. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Wang, H.; Huang, W.; Li, N.; Shi, J. Shared social-economic pathways (SSPs) modeling: Application of global multi-region energy system model. Energy Procedia 2017, 142, 2467–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, R.; Yan, C.; Wu, S. Remote sensing data set of multi-period land use monitoring in China (CNLUCC). In Resource and Environmental Science Data Registration and Publication System; Resource and Environment Science and Data Center: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, G.; Nachtergaele, F.; Prieler, S.; van Velthuizen, H.T.; Verelst, L.; Wiberg, D. Global Agro-Ecological Zones Assessment for Agriculture (GAEZ 2008); IIASA: Laxenburg, Austria; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric Tests against Trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods; Griffin: Oxford, UK, 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Panda, A.; Sahu, N. Trend analysis of seasonal rainfall and temperature pattern in Kalahandi, Bolangir and Koraput districts of Odisha, India. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2019, 20, e932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Xu, C.-Y.; Zhang, Z. Comprehensive analysis on the evolution characteristics and causes of river runoff and sediment load in a mountainous basin of China’s subtropical plateau. J. Hydrol. 2020, 591, 125597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rougé, C.; Ge, Y.; Cai, X. Detecting gradual and abrupt changes in hydrological records. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 53, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallakpour, I.; Villarini, G. A simulation study to examine the sensitivity of the Pettitt test to detect abrupt changes in mean. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2016, 61, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; Shang, F.; Ma, N. Automatic mutation feature identification from well logging curves based on sliding t test algorithm. Cluster. Comput. 2019, 22, 14193–14200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stannard, D.I. Comparison of Penman-Monteith, Shuttleworth-Wallace, and Modified Priestley-Taylor Evapotranspiration Models for wildland vegetation in semiarid rangeland. Water Resour. Res. 1993, 29, 1379–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roderick, M.L.; Farquhar, G.D. A simple framework for relating variations in runoff to variations in climatic conditions and catchment properties. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirnia, A.; Golshan, M.; Darabi, H.; Adamowski, J.; Rozbeh, S. Using the Mann–Kendall test and double mass curve method to explore stream flow changes in response to climate and human activities. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2018, 10, 725–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Sun, W.; Mu, X.; Gao, P.; Zhao, G. Run-off affected by climate and anthropogenic changes in a large semi-arid river basin. Hydrol. Process. 2020, 34, 1906–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Zheng, Z.; Ning, L. Separating variance in the runoff in Beijing’s river system under climate change and human activities. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2021, 123, 103044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Choi, H.T.; Lim, H. Effects of Forest Thinning on the Long-Term Runoff Changes of Coniferous Forest Plantation. Water 2019, 11, 2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausfather, Z. Explainer: How ‘Shared Socioeconomic Pathways’ Explore Future Climate Change. Available online: https://www.carbonbrief.org/explainer-how-shared-socioeconomic-pathways-explore-future-climate-change/ (accessed on 29 March 2023).
- Guo, M.; Zhang, Q.; Qian, H.; Xu, P.; Chen, Y. Analysis on the drought temporal-spatial distribution characteristics of Shaanxi Province based on SPEI. J. Water Resour. Water Eng. 2019, 30, 127–132+138. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Fu, B.; Wang, L.; Lu, N.; Li, J. Water use characteristics of the common tree species in different plantation types in the Loess Plateau of China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 288–289, 108020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Shao, M.; Zhu, Y.; Luo, Y. Soil moisture decline due to afforestation across the Loess Plateau, China. J. Hydrol. 2017, 546, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Zhen, L. Soil erosion control practices in the Chinese Loess Plateau: A systematic review. Environ. Dev. 2020, 34, 100493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurui, L.; Yi, L.; Pengcan, F.; Hualou, L. Impacts of land consolidation on rural human–environment system in typical watershed of the Loess Plateau and implications for rural development policy. Land Use Policy 2019, 86, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, N.; Poongothai, S.; Arutchelvan, V. Impact of land use/land cover changes on surface runoff from a rural watershed, Tamilnadu, India. Int. J. Water 2013, 7, 122–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles, M.D.; Marshall, R.M.; O’Donnell, F.; Smith, E.B.; Haney, J.A.; Gori, D.F. Effects of Climate Variability and Accelerated Forest Thinning on Watershed-Scale Runoff in Southwestern USA Ponderosa Pine Forests. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho-Santos, C.; Nunes, J.P.; Monteiro, A.T.; Hein, L.; Honrado, J.P. Assessing the effects of land cover and future climate conditions on the provision of hydrological services in a medium-sized watershed of Portugal. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 720–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, N.; Harper, R.; Li, Q.; Liu, K.; Wei, X.; Ning, D.; Hou, Y.; Liu, S. A global review on hydrological responses to forest change across multiple spatial scales: Importance of scale, climate, forest type and hydrological regime. J. Hydrol. 2017, 546, 44–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Song, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, H.; Li, Q. Threshold effects of vegetation coverage on runoff and soil loss in the Loess Plateau of China: A meta-analysis. Geoderma 2022, 412, 115720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Lu, C. Evaluation of land-use change effects on runoff and soil erosion of a hilly basin—The Yanhe River in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, L.; Yao, X.; Chen, M.; Yan, C. Effect of Ecological Construction Engineering on Vegetation Restoration: A Case Study of the Loess Plateau. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Yu, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, C.; Chen, X. Determination of ecological flow thresholds for rainfall-recharging rivers based on multiple hydrological methods. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, X.; Ren, Z.; Li, S. Spatiotemporal variations of multi-scale drought and its influencing factors across the Loess Plateau from 1960 to 2016. Geogr. Res. 2019, 38, 1820–1832. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, Z.; Yu, Y.; You, F.; Yang, Z. Spatial and Temporal Evolution Characteristics of the Drought in Weibei Loess Tableland Area Based on SPEI. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 28, 109–117. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Li, J.; Shen, X. Quantitative analysis for the response of streamflow variation to driving factors in seven major basins across China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 110081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Hong, F.; Ma, Y.; Huang, L.; Yang, H.; Hu, J.; Zhou, H.; Wang, H. Comprehensive evaluation of the ecohydrological response of watersheds under changing environments. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 74, 101985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Gao, X.; He, F.; Li, H.; Zhai, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, Y. Attribution analysis based on Budyko hypothesis for land evapotranspiration change in the Loess Plateau, China. J. Arid Land 2019, 11, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Model Name | Country | Organization | Spatial Resolution Lat. × Long. |
|---|---|---|---|
| BCC-CSM2-MR | China | BCC | 1.125° × 1.1° |
| CNRM-CM6-1 | France | CNRM | 1.4° × 1.4° |
| CanESM5 | Canada | CCCMA | 2.8125° × 2.8° |
| INM-CM4-8 | Russia | INM | 2° × 1.5° |
| MRI-ESM2-0 | Japan | MRI | 1.125° × 1.1° |
| IPSL-CM6A-LR | France | IPSL | 2.5° × 1.3° |
| UKESM1-0-LL | UK | UKESM | 1.875° × 1.25° |
| Time Scale | Slope (M-K) | Z (M-K) | b (Sen’s) | b/mm/a (LR) | Significance | Trend |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual | −0.72 | −0.57 | −0.72 | −0.91 | × | ↓ |
| Spring | −0.46 | −1.17 | −0.46 | −0.37 | × | ↓ |
| Summer | −0.32 | −0.36 | −0.34 | −0.31 | × | ↓ |
| Fall | −0.28 | −0.50 | −0.29 | −0.34 | × | ↓ |
| Winer | 0.11 | 0.84 | 0.11 | 0.10 | × | ↑ |
| n | P (mm) | E0 (mm) | R (mm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1969–2018 | 2.85 | 542.70 | 914.52 | 37.52 | 3.48 | −2.48 * | −2.26 * |
| P1 1 | 2.71 | 575.58 | 947.92 | 46.84 | 3.32 | −2.32 * | −2.12 * |
| P2 2 | 2.97 | 520.45 | 891.93 | 31.21 | 3.63 | −2.63 * | −2.39 * |
| Δ 3 | 0.26 | −55.12 | −55.99 | −15.63 | / | / | / |
| Climate Change | Human Activity | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔRP (mm) | (mm) | ΔRl (mm) | Total | |
| Variation of runoff | −13.28 * | 5.71 | −7.79 * | −15.36 ** |
| Contribution rate | 86.46% | −37.16% | 50.70% | 100% |
| Rate | 49.30% | 50.70% | 100% | |
| Time | Average Annual Precipitation (mm) | Runoff Depth and Its Variation (mm) | Climate Change | Human Activity | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obs1 3 | Obs2 4 | Calculated Value 5 | Total Change | Contribution (mm) | Rate | Contribution (mm) | Rate | ||
| P1 1 | 561.43 | 46 | 31.21 | 38.93 | −15 | −7.28 | 48.54% | −7.72 | 51.46% |
| P2 2 | 526.6 | ||||||||
| Scenario | Time | Mutation Point | Precipitation (mm) | Mean Temperature (°C) | Runoff Depth and Its Variation (mm) | Climate Change | Human Activity | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obs1 3 | Obs2 4 | Calculated Value 5 | Total Change | Contribution (mm) | Rate | Contribution (mm) | Rate | |||||
| SSP1-2.6 | P2-126 1 | 2026 | 535.70 | 12.66 | 28.87 | 40.02 | 36.90 | 11.15 | 8.03 | 72.00% | 3.12 | 28.01% |
| P3-126 2 | 641.66 | 12.48 | ||||||||||
| SSP2-4.5 | P2-245 | 2020 | 522.39 | 12.89 | 32.31 | 29.25 | 35.68 | −3.06 | 3.38 | −110.32% | −6.44 | 210.32% |
| P3-245 | 570.69 | 12.42 | ||||||||||
| SSP3-7.0 | P2-370 | 2024 | 532.48 | 12.74 | 30.39 | 18.83 | 33.88 | −11.56 | 3.49 | −30.20% | −15.05 | 130.20% |
| P3-370 | 551.78 | 12.17 | ||||||||||
| SSP5-8.5 | P2-585 | 2018 | 523.65 | 12.84 | 33.04 | 29.63 | 36.19 | −3.41 | 3.15 | −92.54% | −6.56 | 192.54% |
| P3-585 | 582.81 | 13.13 | ||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; He, G.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Z.; He, F.; Wang, H. An Analysis of Runoff Variation in a Small Basin in the Loess Plateau: Identifying the Variation Causes and Implications for Sustainable Water Management. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9651. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129651
Li W, He G, Zhao Y, Liu Z, He F, Wang H. An Analysis of Runoff Variation in a Small Basin in the Loess Plateau: Identifying the Variation Causes and Implications for Sustainable Water Management. Sustainability. 2023; 15(12):9651. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129651
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Wenqing, Guohua He, Yong Zhao, Zhao Liu, Fan He, and Haibin Wang. 2023. "An Analysis of Runoff Variation in a Small Basin in the Loess Plateau: Identifying the Variation Causes and Implications for Sustainable Water Management" Sustainability 15, no. 12: 9651. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129651
APA StyleLi, W., He, G., Zhao, Y., Liu, Z., He, F., & Wang, H. (2023). An Analysis of Runoff Variation in a Small Basin in the Loess Plateau: Identifying the Variation Causes and Implications for Sustainable Water Management. Sustainability, 15(12), 9651. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129651







