Baseline Soil Dioxin Levels from Sites Where Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Construction Is Planned throughout China: Characteristics, Sources and Risk Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- This study will develop a Chinese baseline soil dioxins database, presenting and analyzing the actual measurements of dioxin concentrations in soils determined before the construction of 292 Chinese MSW incineration plants nationwide during 2016–2020.
- (2)
- Using the database, this study will be the first attempt to comprehensively explore the baseline contamination characteristics and health risks from dioxins in soils surrounding pre-construction MSW incineration plants in China.
2. Materials and Methods
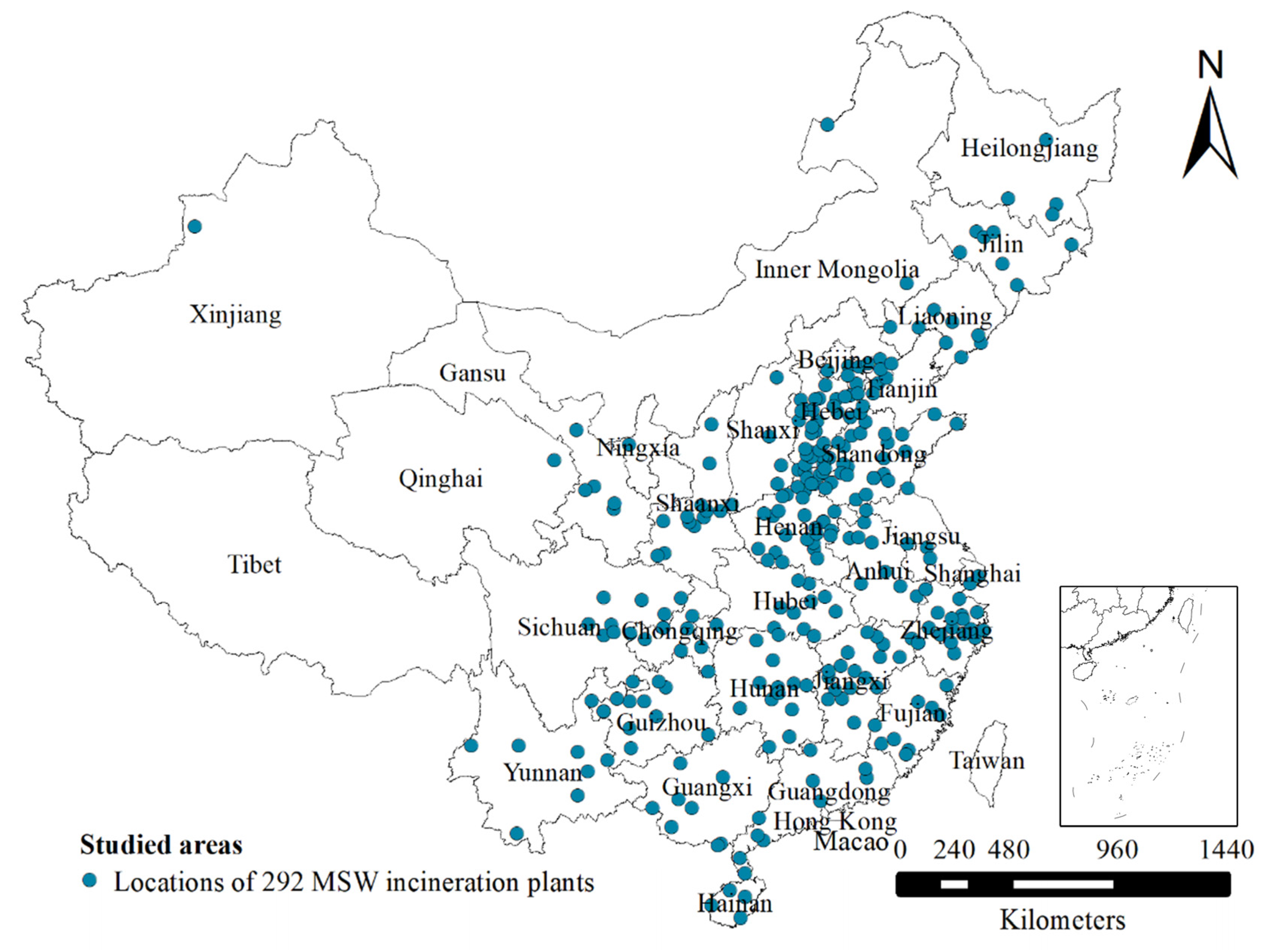
2.1. Data Preparation
2.2. Health Risk Assessment
2.3. Statistical Analysis
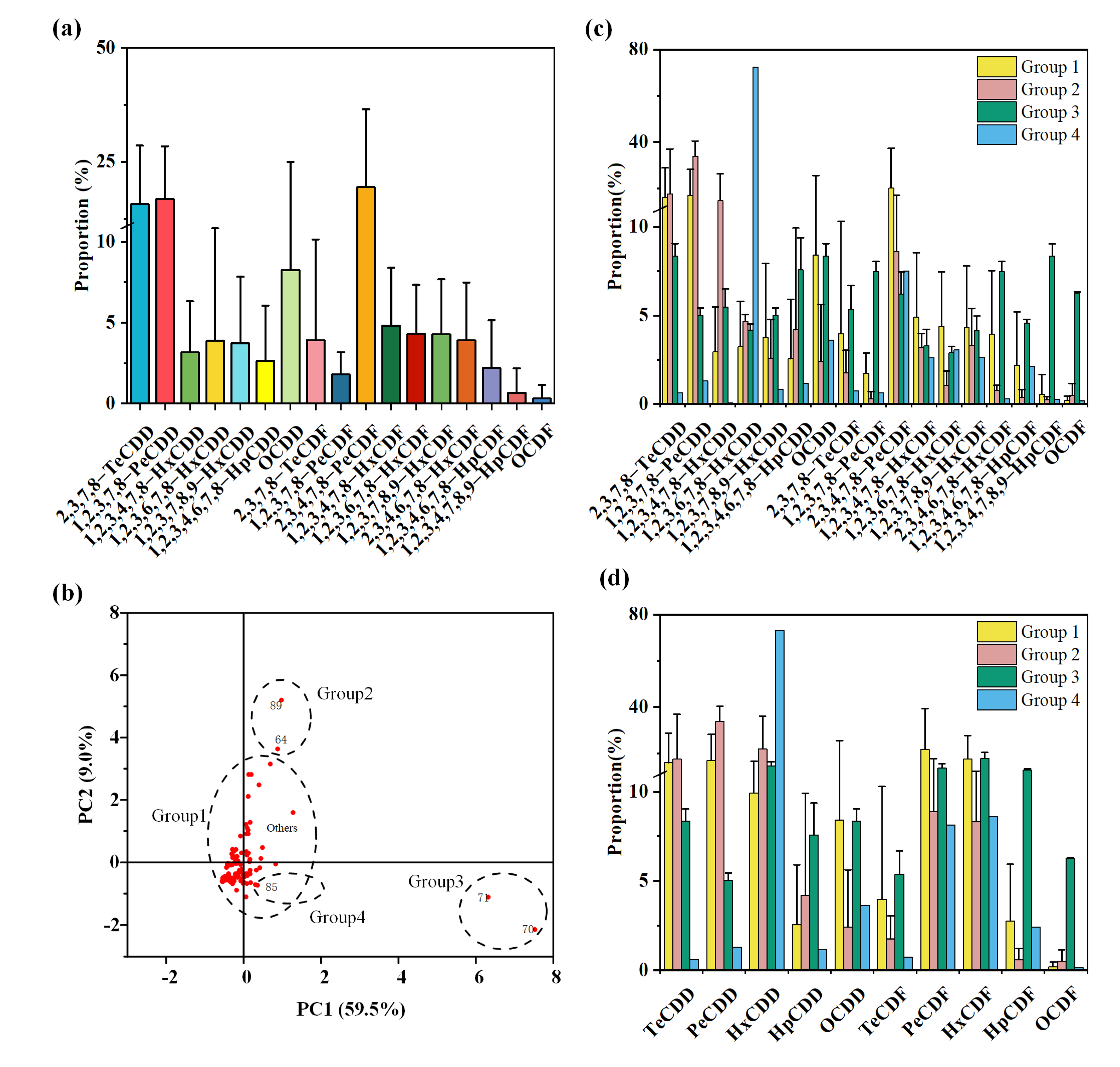
3. Results and Discussion
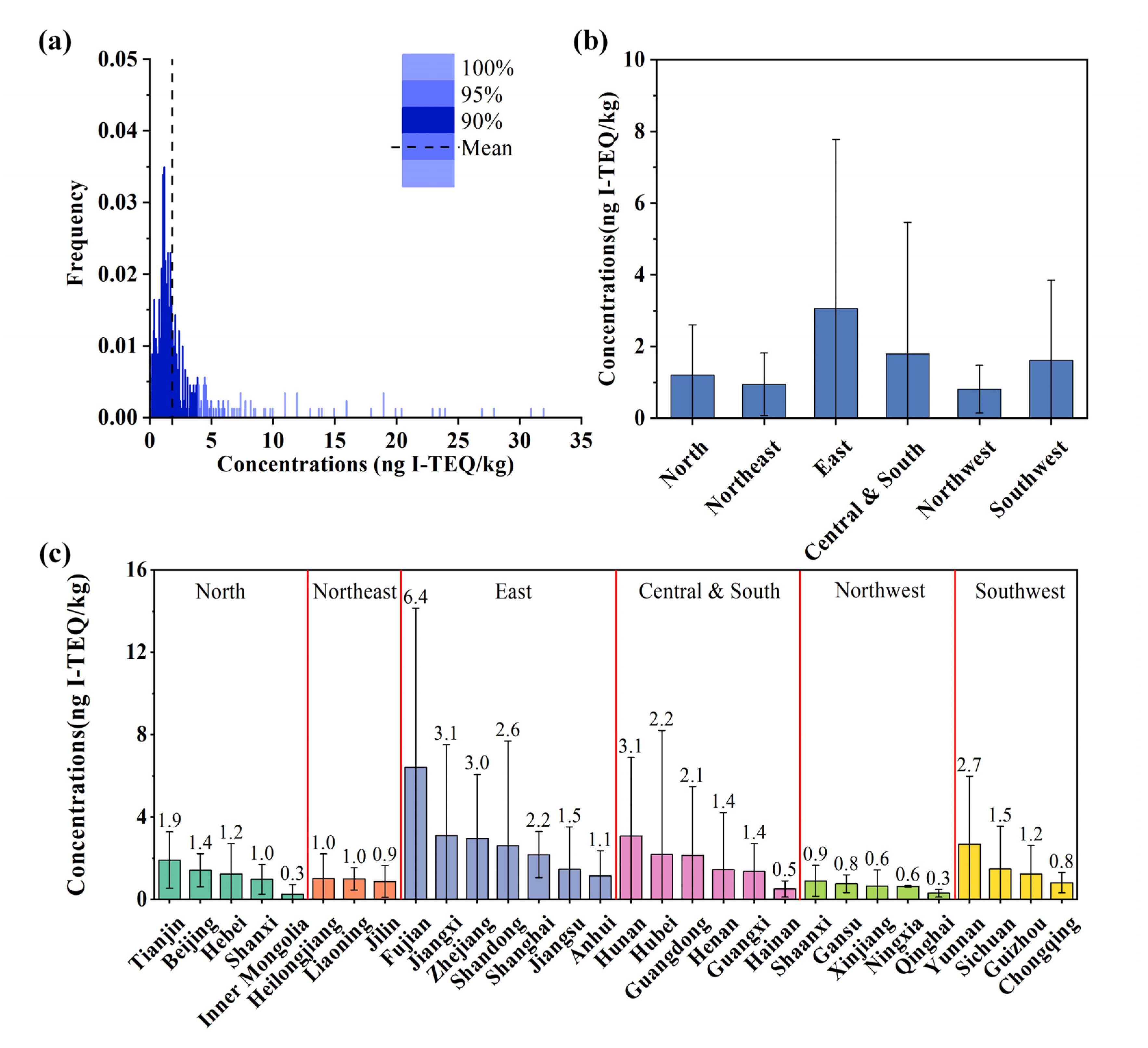
3.1. Baseline Concentration Level of Dioxins
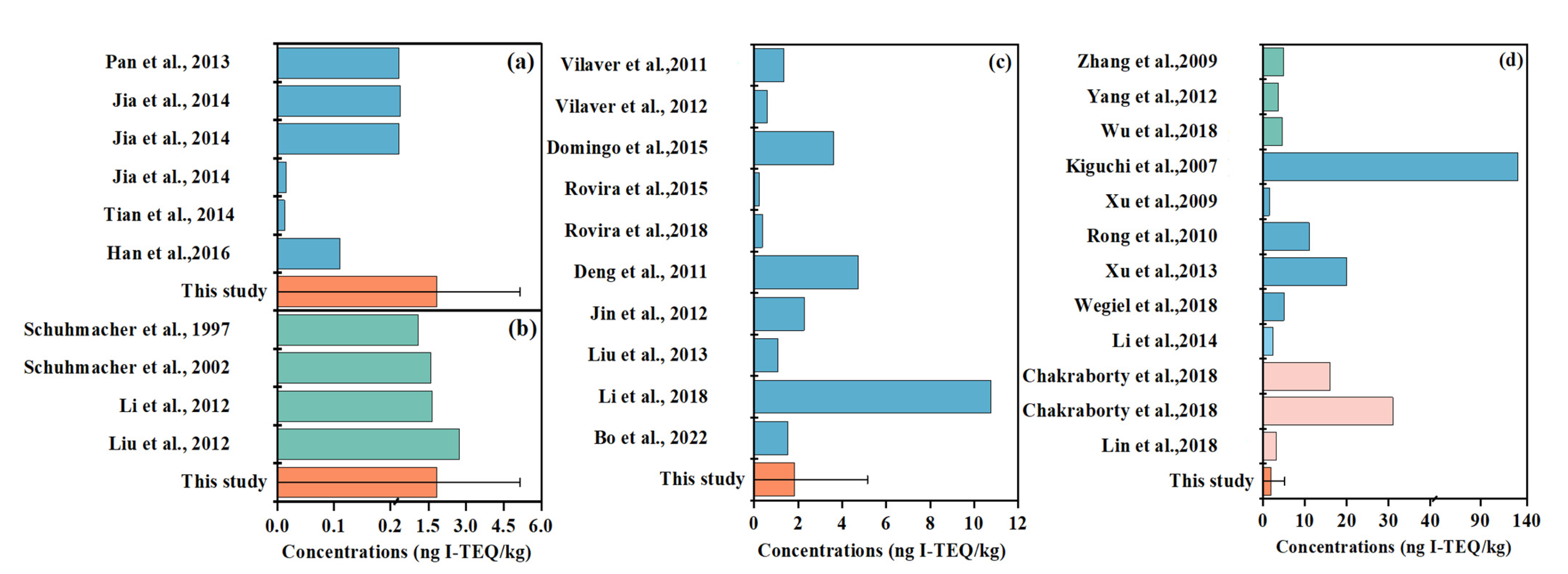
3.2. Comparative Analysis of Dioxin Concentrations
3.3. Multivariate Analysis
3.4. Multivariate Analysis
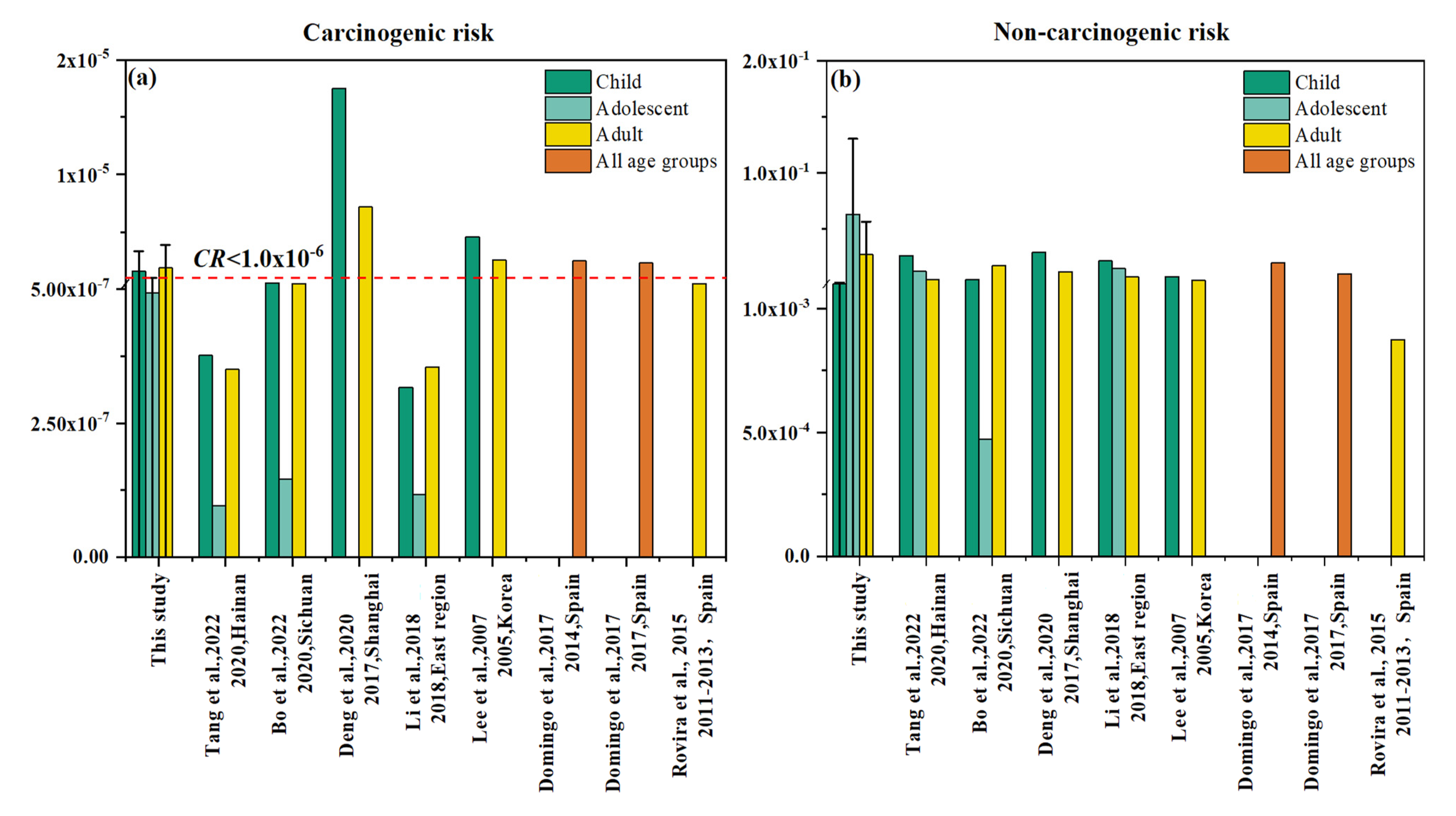
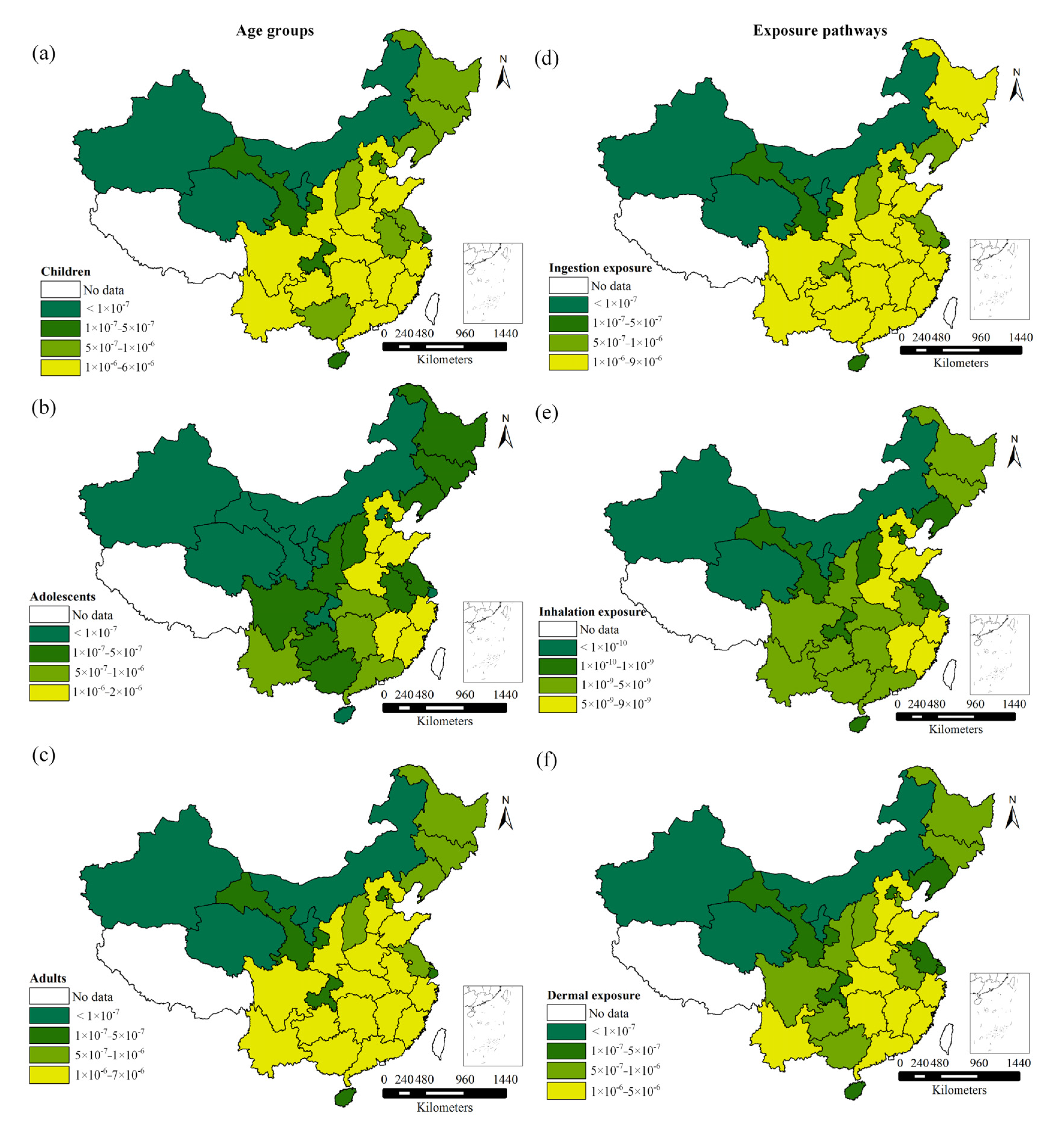
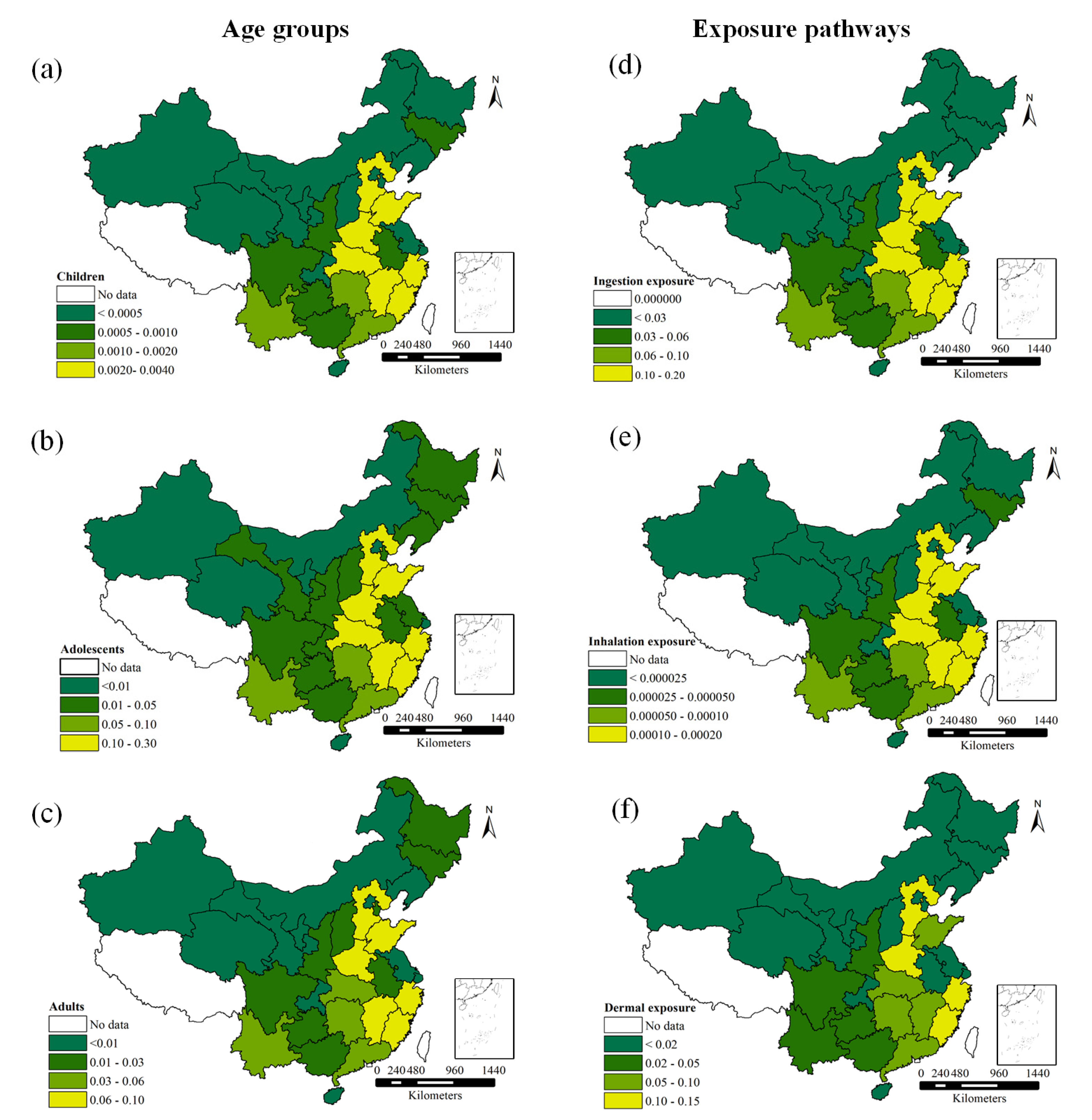
3.4.1. Carcinogenic Risk
3.4.2. Non-Carcinogenic Risk
3.4.3. Comparative Analysis of Health Risks
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, J.; Shi, F.; Yi, J.; Fu, H. Analysis of the factors that affect the production of municipal solid waste in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 259, 120808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Geng, Y.; Fujita, T. An overview of municipal solid waste management in China. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MHURD (Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development). China Urban Construction Statistical Yearbook (2020); Chinese Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2021. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Song, J.; Li, C.; Gao, Y.; Geng, P.; Qu, B.; Lin, L. Preferential policies promote municipal solid waste (MSW) to energy in China: Current status and prospects. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 36, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MHURD (Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development). China Urban Construction Statistical Yearbook (2018); Chinese Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2019. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- World Bank. What a Waste Global Database. 2019. Available online: https://datacatalog.worldbank.org/search/dataset/0039597/What-a-Waste-Global-Database (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- CQMDRC (Chongqing Municipal Development and Reform Commission). Medium and Long-Term Special Plan for Power Generation by Domestic Waste Incineration Power in Chongqing (2021–2035). 2021. Available online: http://fzggw.cq.gov.cn/zwxx/tzgg/202108/t20210810_9564871_wap.html (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- NDRC (National Development and Reform Commission). “14th Five-Year Plan” for the Development of Urban Domestic Waste Classification and Treatment Facilities. 2021. Available online: https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/xxgk/zcfb/tz/202105/t20210513_1279763_ext.html (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- FJPDRC (Fujian Provincial Development and Reform Commission). Medium and Long-Term Special Plan for Power Generation by Domestic Waste Incineration Power in Fujian Province (2019-2030). 2020. Available online: http://fgw.fujian.gov.cn/zfxxgkzl/zfxxgkml/ghjh/202009/t20200917_5387747.htm (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- ZJPDRC (Zhejiang Provincial Development and Reform Commission). Medium and Long-Term Special Plan for Power Generation by Domestic Waste Incineration Power in Zhejiang Province (2019–2030). 2020. Available online: https://fzggw.zj.gov.cn/art/2020/1/6/art_1229629046_4906231.html (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Bo, X.; Guo, J.; Wan, R.; Jia, Y.; Yang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Wei, M. Characteristics, correlations and health risks of PCDD/Fs and heavy metals in surface soil near municipal solid waste incineration plants in Southwest China. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 298, 118816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Li, H.; Liu, J. Curbing dioxin emissions from municipal solid waste incineration: China’s action and global share. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 435, 129076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Meng, X.; Peng, S. Effects of waste-to-energy plants on China’s urbanization: Evidence from a hedonic price analysis in Shenzhen. Sustainability 2017, 9, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.K.Y.; Wong, M.H. A review of environmental fate, body burdens, and human health risk assessment of PCDD/Fs at two typical electronic waste recycling sites in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463, 1111–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, T.; Hao, H.; Wu, H.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Xing, L.; Niu, Z. The health risk levels of different age groups of residents living in the vicinity of municipal solid waste incinerator posed by PCDD/Fs in atmosphere and soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Shin, S.K.; Kim, K.S.; Song, B.J.; Kim, J.G. National monitoring of PCDD/Fs in environmental media around incinerators in Korea. Environ. Int. 2008, 34, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Li, M.; Chen, Z.; Chen, T.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Lu, S.; Yan, J. Long-term monitoring of PCDD/Fs in soils in the vicinity of a hazardous waste incinerator in China: Temporal variations and environmental impacts. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovira, J.; Nadal, M.; Schuhmacher, M.; Domingo, J.L. Concentrations of trace elements and PCDD/Fs around a municipal solid waste incinerator in Girona (Catalonia, Spain). Human health risks for the population living in the neighborhood. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 630, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, T.; Zhang, J.; Meng, W.; Yan, M.; Wang, H.; Li, X. Mass balance of dioxins over a cement kiln in China. Waste Manag. 2015, 36, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Lu, S.; Buekens, A.G.; Chen, T.; Li, X.; Yan, J.; Ma, X.; Cen, K. Baseline soil levels of PCDD/Fs established prior to the construction of municipal solid waste incinerators in China. Chemosphere 2012, 86, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Die, Q.; Lu, A.; Li, C.; Li, H.; Kong, H.; Li, B. Occurrence of dioxin-like POPs in soils from urban green space in a metropolis, North China: Implication to human exposure. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 5587–5597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llobet, J.M.; Domingo, J.L.; Bocio, A.; Casas, C.; Teixidó, A.; Müller, L. Human exposure to dioxins through the diet in Catalonia, Spain: Carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic risk. Chemosphere 2003, 50, 1193–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingo, J.L.; Schuhmacher, M.; Llobet, J.M.; Müller, L.; Rivera, J. PCDD/F concentrations in soil and vegetation in the vicinity of a municipal waste incinerator after a pronounced decrease in the emissions of PCDD/Fs from the facility. Chemosphere 2001, 43, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilavert, L.; Nadal, M.; Schuhmacher, M.; Domingo, J.L. Two decades of environmental surveillance in the vicinity of a waste incinerator: Human health risks associated with metals and PCDD/Fs. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 69, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilavert, L.; Nadal, M.; Schuhmacher, M.; Domingo, J.L. Long-term monitoring of dioxins and furans near a municipal solid waste incinerator: Human health risks. Waste Manag. Res. 2012, 30, 908–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneses, M.; Schuhmacher, M.; Domingo, J.L. A design of two simple models to predict PCDD/F concentrations in vegetation and soils. Chemosphere 2002, 46, 1393–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuhmacher, M.; Agramunt, M.C.; Rodriguez-Larena, M.C.; Dıaz-Ferrero, J.; Domingo, J.L. Baseline levels of PCDD/Fs in soil and herbage samples collected in the vicinity of a new hazardous waste incinerator in Catalonia, Spain. Chemosphere 2002, 46, 1343–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuhmacher, M.; Granero, S.; Llobet, J.M.; De Kok, H.A.M.; Domingo, J.L. Assessment of baseline levels of PCDD/F in soils in the neighbourhood of a new hazardous waste incinerator in Catalonia, Spain. Chemosphere 1997, 35, 1947–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yan, M.; Yang, J.; Chen, T.; Lu, S.; Yan, J. PCDD/Fs in soil around a hospital waste incinerator: Comparison after three years of operation. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yan, M.; Chen, T.; Lu, S.; Yan, J.; Cen, K. Levels of PCDD/Fs in soil in the vicinity of a medical waste incinerator in China: The temporal variation during 2007 2009. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Yan, J.; Lu, S.; Li, X.; Chen, T.; Ni, M.; Dai, H.; Wang, F.; Cen, K. Agricultural soil monitoring of PCDD/Fs in the vicinity of a municipal solid waste incinerator in Eastern China: Temporal variations and possible sources. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquès, M.; Nadal, M.; Díaz-Ferrero, J.; Schuhmacher, M.; Domingo, J.L. Concentrations of PCDD/Fs in the neighborhood of a hazardous waste incinerator: Human health risks. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 26470–26481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mari, M.; Nadal, M.; Ferré-Huguet, N.; Schuhmacher, M.; Borrajo, M.A.; Domingo, J.L. Monitoring PCDD/Fs in soil and herbage samples collected near a hazardous waste incinerator: Health risks for the population living nearby. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2007, 13, 1255–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferré-Huguet, N.; Nadal, M.; Schuhmacher, M.; Domingo, J.L. Environmental impact and human health risks of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in the vicinity of a new hazardous waste incinerator: A case study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ/T 166-2004; The Technical Specification for Soil Environmental Monitoring. MEPC (Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China): Beijing, China, 2004. (In Chinese)
- HJ77.4-2008; Soil and Sediment Determination of Polychlorinated Dibenzo-P-Dioxin (PCDDs) and Polychlorinated Dibenzofurans (PCDFs) Isotope Dilution HRGCHRMS. MEPC (Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China): Beijing, China, 2008. (In Chinese)
- NBS (National Bureau of Statistics of China). China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2021. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- EPA/600/P-00/001Bb; USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). Exposure and Human Health Reassessment of 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-P-Dioxins and Related Compounds. Part I: Estimating Exposure to Dioxin-like Compounds. Volume 2: Sources of Dioxin-like Compounds in the United States. Draft Final Report. National Center for Environmental Assessment: Washington, DC, USA, 2000.
- EPA/540/R/99/005; USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund. Volume 1: Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part E, Supplemental Guidance for Dermal Risk Assessment). Office of Emergency and Remedial Response: Washington, DC, USA, 2001.
- OSWER 9355.4-24USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). Supplemental Guidance for Developing Soil Screening Levels for Superfund Sites; Office of Emergency and Remedial Response: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). Example Exposure Scenarios; National Center for Environmental Assessment: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Dong, H.; Sun, J.; Nie, J.; Zhang, S.; Tang, J.; Chen, Z. Composition profiles and health risk of PCDD/F in outdoor air and fly ash from municipal solid waste incineration and adjacent villages in East China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 876–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). Mid Atlantic Risk Assessment; Regional Screening Level (RSL) Summary Table; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Dong, H.; Xu, X.; Han, B.; Li, X.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, D. Prediction of the bioaccumulation of PAHs in surface sediments of Bohai sea, China and quantitative assessment of the related toxicity and health risk to humans. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 104, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ma, Z.; Van der Kuijp, T.J.; Yuan, Z.; Huang, L. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: Pollution and health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Du, W.; Yang, J.; Chen, L.; Meng, W.; et al. Atmospheric emissions of PCDDs and PCDFs in China from 1960 to 2014. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, Y.; Que, D.; Gou, Y.; Tsou, T.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Hou, W.; Lin, Y.; Chao, H.; Lee, W. National surveillance of 2,3,7,8-substituted polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins/furans in soil in Taiwan. Chemosphere 2018, 203, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, K.; Kao, S.; Liu, K.; Lee, T. Evaluation of atmospheric PCDD/F depositions via automated and traditional water surface samplers in Taiwan. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 2839–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Chen, Y. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons contamination in surface soil of China: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 605, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Bao, L.; Wu, C.; He, Z.; Zeng, E. Association of soil polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon levels and anthropogenic impacts in a rapidly urbanizing region: Spatial distribution, soil-air exchange and ecological risk. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanneau, E.J.; Saby, N.P.; Marchant, B.P.; Jolivet, C.C.; Boulonne, L.; Caria, G.; Barriuso, E.; Bispoe, A.; Briand, O.; Arrouays, D. Which persistent organic pollutants can we map in soil using a large spacing systematic soil monitoring design? A case study in Northern France. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 3719–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Wang, Q.; Li, L.; Fang, X.; Shi, Y.; Xu, W.; Hu, J. Comparative study on PCDD/F pollution in soil from the Antarctic, Arctic and Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 497, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Li, H.; Xie, H.; Tang, C.; Han, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, W. Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans and polychlorinated biphenyls in surface soil from the Tibetan Plateau. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 2041–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Yeung, L.W.Y.; Taniyasu, S.; Miyake, Y.; Falandysz, J.; Yamashita, N. Altitudinal distributions of PCDD/Fs, dioxin-like PCBs and PCNs in soil and yak samples from Wolong high mountain area, eastern Tibet-Qinghai Plateau, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 444, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Liu, W.; Hansen, H.C.B.; Chen, X.; Liao, X.; Li, H.; Wang, M.; Yan, N. Influence of long-range atmospheric transportation (LRAT) on mono-to octa-chlorinated PCDD/Fs levels and distributions in soil around Qinghai Lake, China. Chemosphere 2016, 156, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Jia, L.; Li, K.; Rong, Z.; Yin, H. Levels of PCDD/Fs in agricultural soils near two municipal waste incinerators in Shanghai, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2011, 86, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; Ma, X.; Lu, S.; Chen, T.; Yan, J. Health risk assessment of PCDD/F emissions from municipal solid waste incinerators (MSWIs) in China. Environ. Technol. 2012, 33, 2539–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingo, J.L.; Rovira, J.; Vilavert, L.; Nadal, M.; Figueras, M.J.; Schuhmacher, M. Health risks for the population living in the vicinity of an Integrated Waste Management Facility: Screening environmental pollutants. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 518, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassura, I.; Passarini, F.; Ferroni, L.; Bernardi, E.; Morselli, L. PCDD/Fs atmospheric deposition fluxes and soil contamination close to a municipal solid waste incinerator. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 1366–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Li, H.; Tian, Z.; Xie, H.; Li, C. Spatial distribution of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans in soil around a municipal solid waste incinerator. Environ. Geochem. Health 2013, 35, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovira, J.; Vilavert, L.; Nadal, M.; Schuhmacher, M.; Domingo, J.L. Temporal trends in the levels of metals, PCDD/Fs and PCBs in the vicinity of a municipal solid waste incinerator. Preliminary assessment of human health risks. Waste Manag. 2015, 43, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, P.; Selvaraj, S.; Nakamura, M.; Prithiviraj, B.; Cincinelli, A.; Bang, J.J. PCBs and PCDD/Fs in soil from informal e-waste recycling sites and open dumpsites in India: Levels, congener profiles and health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 930–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, C.; Chen, Z.; Ding, N.; Cai, Z. Levels of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in mountainous and park soils in Beijing, China. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2014, 94, 691–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Węgiel, M.; Chrząszcz, R.; Maślanka, A.; Grochowalski, A. Seasonal variations of PCDD/Fs congeners in air, soil and eggs from a Polish small-scale farm. Chemosphere 2018, 199, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Tao, B.; Li, N.; Qi, L.; Ren, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liu, A.; Huang, Y. Levels, profiles and source identification of PCDD/Fs in farmland soils of Guiyu, China. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 824–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Z.; Li, K.; Yin, H. Pilot study of the polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans level in agricultural soil in Shanghai, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 171, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiguchi, O.; Kobayashi, T.; Wada, Y.; Saitoh, K.; Ogawa, N. Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in paddy soils and river sediments in Akita, Japan. Chemosphere 2007, 67, 557–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Hu, J.; Wang, S.; Jin, J.; Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Jin, J. Levels, sources, and potential human health risks of PCNs, PCDD/Fs, and PCBs in an industrial area of Shandong Province, China. Chemosphere 2018, 199, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, C.; Dong, J.; Peng, X. Distribution patterns and major sources of dioxins in soils of the Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan urban agglomeration, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 84, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Huang, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, G. PCDD/PCDF pollution in soils and sediments from the Pearl River Delta of China. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 1186–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, A.O.; Luksemburg, W.J.; Wong, A.S.; Wong, M.H. Spatial distribution of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in soil and combusted residue at Guiyu, an electronic waste recycling site in southeast China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 2730–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB36600-2018; Soil Environmental Quality Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Development Land. MEEC (Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China): Beijing, China, 2018. (In Chinese)
- CCME (Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment). Canadian Environmental Quality Guidelines; Summary Table; CCME: Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- BMU (Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservations and Nuclear Safety). Federal Soil Protection and Contaminated Sites Ordinance (BvodSchV); BMU: Bonn, Germany, 1999; Volume 12, p. 6. [Google Scholar]
- UNEP (United Nations Environmental Programme). Standardized Toolkit for Identification and Quantification of Dioxin and Furan Releases; UNEP Chemicals: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- MfE/MoH (New Zealand Ministry for the Environmental and the Ministry of Health). Health and Environmental Guidelines for Selected Timber Treatment Chemicals; MfE/MoH: Wellington, New Zealand, 1997; Volume 9. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Liu, W. Distribution of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans (PCDDs/Fs) and dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls (dioxin-like PCBs) in the soil in a typical area of eastern China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Xu, M.; Lu, S.; Li, X.; Chen, T.; Ni, M.; Dai, H.; Cen, K. PCDD/F concentrations of agricultural soil in the vicinity of fluidized bed incinerators of co-firing MSW with coal in Hangzhou, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 151, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Choi, S.; Lee, S.; Chang, Y. Influence of a municipal solid waste incinerator on ambient air and soil PCDD/Fs levels. Chemosphere 2006, 64, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Fan, W.; Dai, W.; Hsi, H.; Wu, C.; Chen, C. Characteristics of PCDD/F content in fly ash discharged from municipal solid waste incinerators. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, N.H.; Minh, T.B.; Watanabe, M.; Kunisue, T.; Monirith, I.; Tanabe, S.; Sakai, S.; Subramanian, A.; Sasikumar, K.; Viet, P.H.; et al. Open dumping site in Asian developing countries: A potential source of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 1493–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, T.; Tsou, H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chi, K. Sources identification of PCDD/Fs in soil and atmospheric deposition in Taiwan. Chemosphere 2018, 208, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assefa, A.T.; Tysklind, M.; Sobek, A.; Sundqvist, K.L.; Geladi, P.; Wiberg, K. Assessment of PCDD/F source contributions in Baltic Sea sediment core records. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 9531–9539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). Technical Support Document EPA’s 2014 National Air Toxics Assessment; Office of Air Quality Planning and Standards, Research Triangle Park: Durham, NC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Peng, P.; Jia, L.; Mao, W.; Hu, J.; Yin, H. Environmental exposure-associated human health risk of dioxin compounds in the vicinity of a municipal solid waste incinerator in Shanghai, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 105, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, J.L.; Rovira, J.; Nadal, M.; Schuhmacher, M. High cancer risks by exposure to PCDD/Fs in the neighborhood of an Integrated Waste Management Facility. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Choi, S.; Jin, G.; Oh, J.; Chang, Y.; Shin, S.K. Assessment of PCDD/F risk after implementation of emission reduction at a MSWI. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Guo, J.; Li, L.; Wan, R.; Cui, L.; Liu, A.; Lu, Y. Contamination characteristics, coexistence relationships and health risk assessment of dioxins and metals in topsoil around municipal solid waste incinerator in Hainan, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 898934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, S.; Hsieh, D.P.H.; Yang, H.H.; Lee, H.L. Carcinogenic potencies of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons for back-door neighbors of restaurants with cooking emissions. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 417, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, Y.; Kang, Y.; Wang, H.; Lau, W.; Li, H.; Sun, X.; Giesy, J.P.; Chow, K.L.; Wong, M.H. Cancer risk assessments of Hong Kong soils contaminated by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 261, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Lang, Y.; Li, G. Cancer risk of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the soils from Jiaozhou Bay wetland. Chemosphere 2014, 112, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wan, R.; Wu, J.; Guo, J.; Qu, J.; Li, L.; Tang, L. Baseline Soil Dioxin Levels from Sites Where Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Construction Is Planned throughout China: Characteristics, Sources and Risk Assessment. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9310. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129310
Wan R, Wu J, Guo J, Qu J, Li L, Tang L. Baseline Soil Dioxin Levels from Sites Where Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Construction Is Planned throughout China: Characteristics, Sources and Risk Assessment. Sustainability. 2023; 15(12):9310. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129310
Chicago/Turabian StyleWan, Ruxing, Jun Wu, Jing Guo, Jiabao Qu, Ling Li, and Ling Tang. 2023. "Baseline Soil Dioxin Levels from Sites Where Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Construction Is Planned throughout China: Characteristics, Sources and Risk Assessment" Sustainability 15, no. 12: 9310. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129310
APA StyleWan, R., Wu, J., Guo, J., Qu, J., Li, L., & Tang, L. (2023). Baseline Soil Dioxin Levels from Sites Where Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Construction Is Planned throughout China: Characteristics, Sources and Risk Assessment. Sustainability, 15(12), 9310. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129310