Exploring Plastic-Management Policy in China: Status, Challenges and Policy Insights
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Policy Review
- (1)
- Policy documents with legal effect issued by government departments or party and government organizations;
- (2)
- Policy documents directly related to the theme of this study;
- (3)
- Procedural policy documents such as personnel appointments, meeting notices, etc. were excluded.
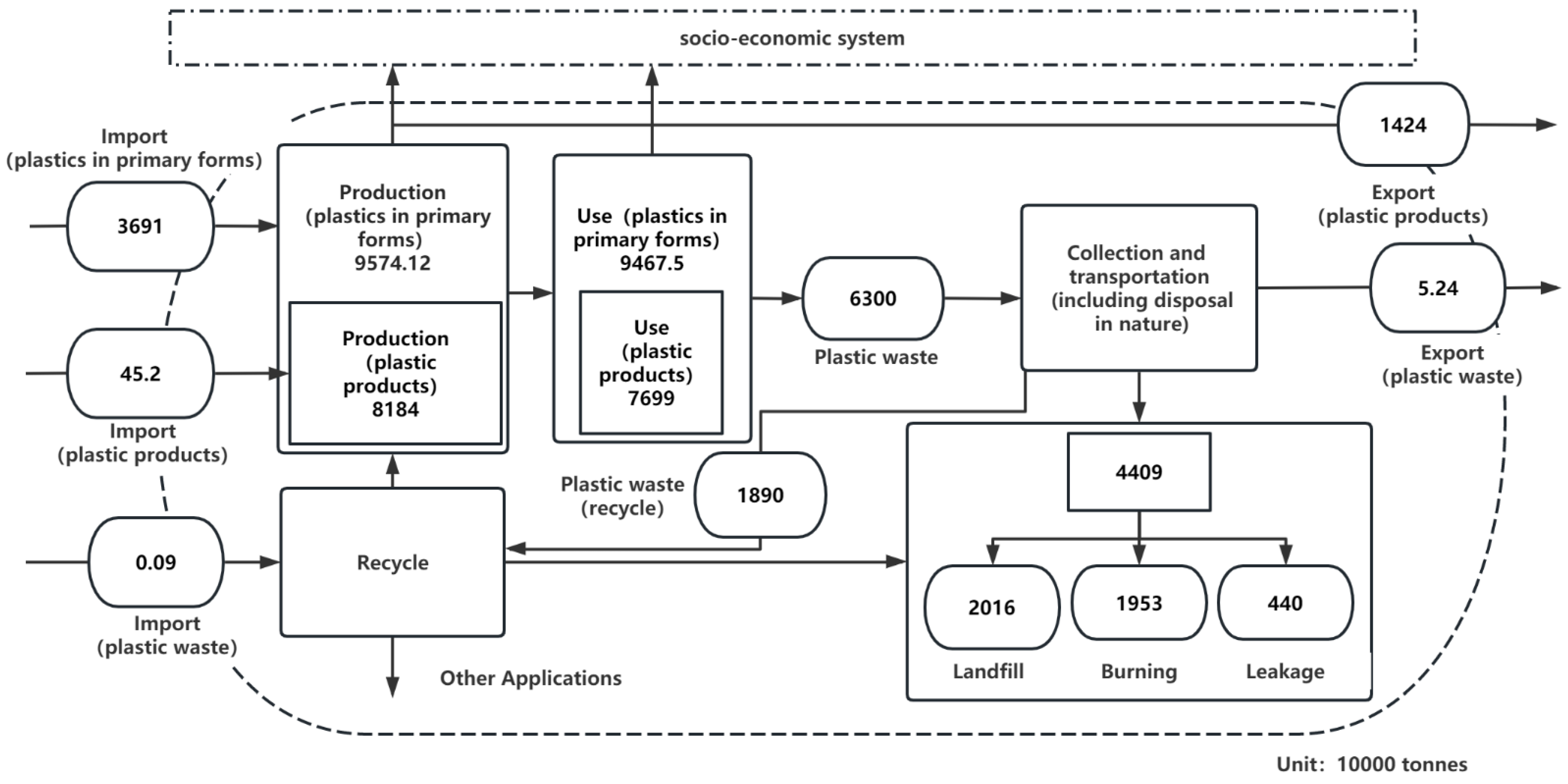
2.2. Plastic-Material-Flow Analysis
3. Results
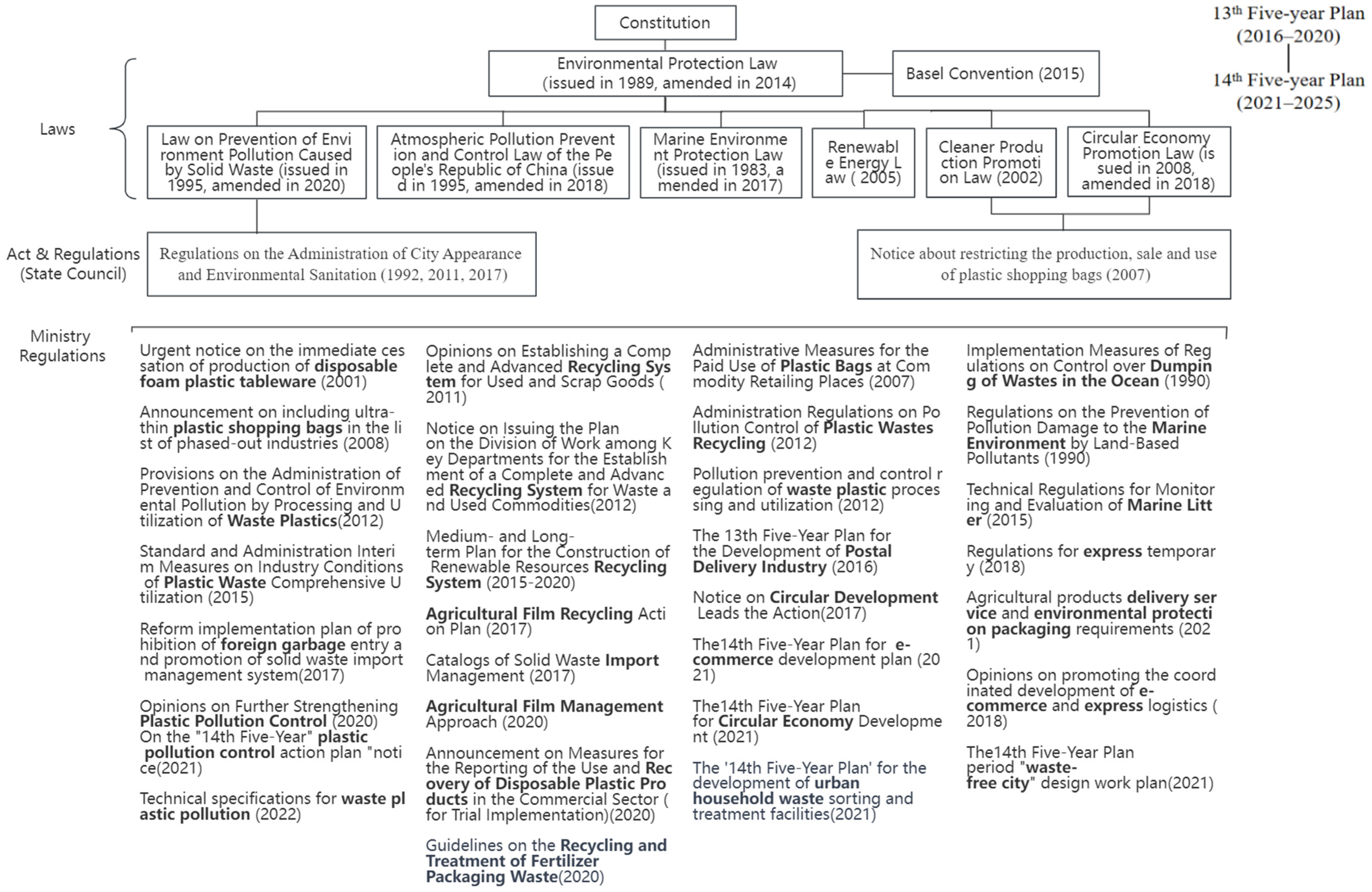
3.1. National Legislation, Regulations and Other Policies Concerning Plastics
3.1.1. Legal Framework of Plastic-Related Policies and Strategies
3.1.2. Main Direction and Key Objectives of Plastic Pollution Control
The Five-Year Plan Related to Plastics
Ban on Foreign Waste Importation
Plastic Recycling System and Related Policies
- (1)
- In January 2020, the National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) and the Ministry of Ecology and Environment (MEE) announced the Opinions on Further Strengthening the Control of Plastic Pollution (关于进一步加强塑料污染治理的意见; hereinafter referred to as the New Restrictions on Plastic), specifying that by 2025 China expects to control plastic pollution effectively, substantially reduce the amount of plastic waste in landfills of key cities, establish a complete plastics-management system along the whole supply chain and achieve progress in developing alternative products.
- (2)
- In May 2021, the National Development and Reform Commission and the Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development issued the 14th Five-Year Plan for the Development of Urban Domestic Waste Separation and Disposal Facilities (十四五”城镇生活垃圾分类和处理设施发展规划) aimed at accelerated establishment of a domestic-waste-treatment system with sorting, collection, transportation, and treatment. Specific targets were set, such as the improvement of domestic-waste classification and treatment capacity in 46 key cities, the construction of domestic-waste classification and treatment systems in prefecture-level cities and other regions, and encouragement of other regions to improve their waste-separation coverage and treatment facilities. Its goals are a national resource-utilization rate of about 60% by the end of 2025 for urban domestic waste, a national waste separation and transportation capacity of about 700,000 tonnes/day by the end of 2025, and a national urban waste-incineration treatment capacity of about 800,000 tonnes per day by the end of 2025, with the urban domestic-waste-incineration treatment capacity accounting for about 65%.
Other Related Policies to Deal with Emerging Plastic Issues
- (1)
- Agricultural plastic film
- (2)
- E-commerce express delivery industry plastic control
- (3)
- Policies on marine litter and microplastics
3.1.3. Types of Plastics Targeted and the Path to Achieving Plastic Reduction and Ban
3.2. Plastic Flow and Its Change during 2000–2019
3.2.1. Trends in Production of Plastic Raw Materials
3.2.2. Trends in Production, Consumption and Trade of Plastic Products
3.2.3. Trend of Production, Consumption and Trade of Plastic Products
4. Discussion and Policy Recommendations
- Enhance coherence and integration between policies toward multi-tasks
- 2.
- Establish a comprehensive management system that combines both vertical and horizontal approaches/governance
- 3.
- Establish a tracking system for plastics along the supply chain
- 4.
- Establish a quality certification system for recycled products to improve the quality of recycled products as well as raise public awareness
- 5.
- Develop behaviour-based solutions targeting consumers’ daily lives and social practices to prevent or reduce plastic waste generation
- 6.
- Promote a platform for stakeholder collaboration and community-based interventions
- 7.
- Create appropriate policies for the post-COVID-19 era
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Geyer, R.; Jambeck, J.R.; Law, K.L. Production, Use, and Fate of All Plastics Ever Mad. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development. Global Plastics Outlook: Policy Scenarios to 2060; OECD: Paris, France, 2022; Available online: https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/environment/data/global-plastic-outlook_c0821f81-en (accessed on 21 March 2023).
- Bläsing, M.; Amelung, W. Plastics in soil: Analytical methods and possible sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 422–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodson, M.E.; Duffus-Hodson, C.A.; Clark, A.; Prendergast-Miller, M.T.; Thorpe, K.L.; Lewis, C. Microplastics—An emerging contaminant of potential concern? Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2017, 13, 460–471. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, C.J. Synthetic polymers in the marine environment: A rapidly increasing, long-term threat. Environ. Res. 2008, 108, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joint Group of Experts on the Scientific Aspects of Marine Environmental Protection. Sources, Fate and Effects of Microplastics in the Marine Environment (Part 2); GESAMP: London, UK, 2016; Available online: http://www.gesamp.org/publications/microplastics-in-the-marine-environment-part-2 (accessed on 21 March 2023).
- Li, J.N.; Yang, D.Q.; Li, L.; Jabeen, K.; Shi, H.H. Microplastics in commercial bivalves from China. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 207, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royer, S.J.; Ferrón, S.; Wilson, S.T.; Karl, D.M. Production of methane and ethylene from plastic in the environment. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Environment Programme. Single-Use Plastics: A Roadmap for Sustainability; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 2018; Available online: https://wedocs.unep.org/20.500.11822/25496 (accessed on 11 April 2023).
- United Nations Environment Programme. Nairobi Declaration; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 2022; Available online: https://www.unep.org/environmentassembly/ (accessed on 14 April 2023).
- European Commission. Circular Economy Action Plan. Available online: https://environment.ec.europa.eu/strategy/circular-economy-action-plan_en (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- European Commission. A European Green Deal. Available online: https://commission.europa.eu/strategy-and-policy/priorities-2019-2024/european-green-deal_en (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- ERP. Draft of National Strategy to Prevent Plastic Pollution. Available online: https://www.jdsupra.com/legalnews/epa-releases-draft-of-national-strategy-3730288/ (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Ellen MacArthur Foundation. France’s Antiwaste and Circular Economy Law: Eliminating Waste and Promoting Social Inclusion. Available online: https://ellenmacarthurfoundation.org/circular-examples/frances-anti-waste-and-circular-economy-law (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- The Plastic Resource Circulation Act. Available online: https://www.env.go.jp/en/focus/jeq/issue/vol29/The%20Plastic%20Resource%20Circulation%20Act_0128%20final.pdf (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- National Action Plan on Plastic Waste Management in Thailand. Available online: https://www.iges.or.jp/sites/default/files/inline-files/S1-5_PPT_Thailand%20Plastic%20Action%20Plan.pdf (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- People’s Daily Online. New Plastic Restrictions: Plastic Waste Increases as Limits Tighten, Becoming an Intractable ‘Deadlock’; PDO: Muscat, Oman, 2020; Available online: https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1663822404558520960&wfr=spider&for=pc (accessed on 13 April 2023).
- Fürst, K.; Feng, Y.D. China’s regulatory respond to plastic pollution: Trends and trajectories. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 56, 883–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Dou, W.; Qang, Y. The implementation of the “plastic restriction” policy Effectiveness and Suggestions for Countermeasures. Ecol. Econ. 2008, 12, 70–72, 87. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhu, L.; Shen, Q.; He, Y.; Deng, Y.; An, L.H. China’s plastic pollution prevention policy analysis and recommendations. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 5326–5332. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Lang, Z.; Tang, Y. Research report on the impact of replacing plastic straws with paper straws in the context of “Plastic restriction” policy. Clean. World 2021, 37, 77–78+81. [Google Scholar]
- O’Loughlin, M. BYOB (Bring your own bag): A comprehensive assessment of china’s plastic bag policy. Buffalo Environ. Law J. 2010, 18, 295. [Google Scholar]
- He, H. Effects of environmental policy on consumption: Lessons from the Chinese plastic bag regulation. Environ. Dev. Econ. 2012, 17, 407–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Yang, T. Considerations on the construction of classification, collection and management system of plastic packaging waste. China Plast. 2021, 35, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.X.; Deng, Y.X.; Zhang, C.L.; Hao, C.L. Study on the public single-use plastics reduction policies based on the theory of environmental behaviors. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2021, 11, 888–897. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.; Xiang, J.; Ko, J.H. Municipal plastic recycling at two areas in China and heavy metal leachability of plastic in municipal solid waste. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.B.; Liang, R.L.; An, S.J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, T.; Yang, D.S.; Zeng, Y.; Yan, Y. Tax policy research to promote plastic pollution control. Guangdong Econ. 2021, 12, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y. Global Marine Plastics Governmance: Progress, Predicament and Chian’s Participation. Pac. J. 2020, 28, 79–90. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.Z.; Du, M.D. Why is the implementation of the “Plastic Restriction Order” stalled?—An analysis based on the revised “ambiguity-conflict” framework. Exec. Forum 2020, 27, 69–80. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, X.F.; Wang, Q.; Tao, G.D. Analysis and Extended Thinking on the Effectiveness of the “Plastic Restriction Order” Policy. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 3, 184–187, 190. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, Y. Policies and regulations related to plastics in 2018. Green Package 2018, 32, 87–88. [Google Scholar]
- Du, C. The improvement of China’s “plastic limit” thinking—Based on the perspective of the tax system. Price Theory Pract. 2012, 11, 76–77. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.L.; Liu, J.; Tao, Y.J. Marine plastic waste policies of the European Union and its member states and the inspiration for China. Mar. Bull. 2019, 38, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Shi, W.Z.; Wang, F.F.; Shen, X.; He, Y.N.; Deng, Y.X.; Lei, K.; Li, D.J.; An, L.H. Reflections and suggestions on “plastic ban/restriction” to help solve the problem of marine plastic waste. Environ. Prot. 2020, 48, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.F.; Jiang, W.J.; Yang, S. China Plastics Processing Industry (2019). China Plast. 2020, 34, 102–106. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.H.; Fu, K.M. Status and Thinking of Plastic Wastes Recycling Industry in China under the New Situation. China Plast. Ind. 2022, 50, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Backer, L.C. Party, people, government and state: On constitutional values and the legitimacy of the Chinese state-party rule of law system. Boston Univ. Int. Law J. 2012, 30, 331. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X. Rule of law within the Chinese party-state and its recent tendencies. Hague J. Rule Law 2017, 9, 373–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.C.; Patrick, W. The challenges of governing: The state council in China. China J. 2016, 76, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, D.H. On the Constitutional Basis for the Formulation of Departmental Regulations by Ministries and Commissions of the State Council. J. Yanbian Univ. (Soc. Sci.) 2005, 38, 74–78. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y. Local Government and Politics in China: Challenges from below. China J. 2004, 52, 118. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, W.J. Judgment and Selection of Application of Hierarchical Conflict of Laws in Administrative Trial. Shandong Trial 2007, 96–98. [Google Scholar]
- Greenpeace Southeast Asia. Greenpeace: ‘Recycling’ from Developed World Dumped in Malaysia and Left to Rot; GPSEA: Paris, France, 2018; Available online: https://www.greenpeace.org/southeastasia/press/661/greenpeace-recycling-from-developed-world-dumped-in-malaysia-and-left-to-rot/ (accessed on 16 March 2023).
- National Development and Reform Commission. The Implementation of the “Plastic Restriction” Has Achieved Significant Results. Available online: https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/fzggw/jgsj/hzs/sjdt/200908/t20090826_1131861.html (accessed on 16 March 2023).
- Observation and Research Report Network. China’s Synthetic Resin Production and Demand, Self-Sufficiency Rate Is on the Rise Import Dependence Continues to Decline. Available online: https://market.chinabaogao.com/huagong/042553b322021.html (accessed on 21 February 2023).
- People’s Political Consultative Conference Network. Where Is the Low Recycling Rate of Waste Plastics Stuck? Available online: http://www.rmzxb.com.cn/c/2020-08-06/2637446.shtml (accessed on 22 February 2023).
- National Post Office. China Express Field Green Packaging Development Status and Trends Report; NPO: Hilversum, The Netherlands, 2018; Available online: https://www.163.com/dy/article/GM7K9U110552D035.html (accessed on 18 March 2023).
- United Nations. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainale Development; United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Available online: http://refhub.elsevier.com/S0956-053X(20)30729-7/h0090 (accessed on 17 May 2023).



| English | Chinese |
|---|---|
| plastic, microplastics, shopping bags, foam plastics, recyclable, agricultural film, marine litter, marine solid waste, municipal solid waste, single use plastics, tires | 塑料,微塑料,购物袋,泡沫塑料,可回收,农膜,海洋垃圾,海洋固体废弃物,生活垃圾,固体废弃物,一次性塑料,轮胎 |
| Data | Source |
|---|---|
| Import (plastic products) | General Administration of Customs of the People’s Republic of China: Import of plastic products, 2005–2021. |
| Import (plastic waste) | China Recycling Industry Report: Import of plastic wastes, 2005–2021. |
| Export (plastic products) | General Administration of Customs of the People’s Republic of China: Export of plastic wastes, 2005–2021. |
| Export (plastic waste) | China Recycling Industry Report: Export of plastic waste, 2005–2021. |
| Import (plastics in primary forms) | General Administration of Customs of the People’s Republic of China: Import of plastics in primary forms, 2019. |
| Import (plastic products) | General Administration of Customs of the People’s Republic of China: Import of plastic products, 2005–2021. |
| Production (plastics in primary forms) | National Bureau of Statistics: production of plastics in primary form, 2020. |
| Production (plastic products) | National Bureau of Statistics: production of plastic products, 2005–2021. |
| Use (plastics in primary forms) | China Plastics Processing Industry Association. China plastics industry yearbook. China Light Industry Press, 2019. |
| Consumption (plastic products) | Huajing Intelligence Network, Huajing Industry Research Institute. China plastic products industry production and consumption analysis. Accessed online: https://www.huaon.com/channel/trend/670690.html (accessed on 18 March 2023) |
| Plastic waste | China Plastics Processing Industry (2019) [35] |
| Plastic waste (recycling) | China Recycling Industry Report: Amount of waste plastic recycling, 2005–2021. |
| Recycling rate | China Circular Economy Association. China Circular Economy Development Report. Beijing: China Circular Economy Association.Status and Thinking of Plastic Wastes Recycling Industry in China under the New Situation [36] |
| Land filled, Burning, Abandonment | China Materials Recycling Association Recycled Plastics Branch. China recycled plastics industry development report (2019–2020). Beijing: China Materials Recycling Association Recycled Plastics Branch, 2020. Accessed online: www.hnyhgf.com/news/20200407155356431.html (accessed on 18 March 2023) |
| No. | Representative Policies | Issuing Date | Issuing Division | Main Content |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Administrative Measures for the Recovery of Renewable Resources | 27 March 2007 | Ministry of Commerce, National Development, Reform Commission and other six departments | Regulating the development of the recycling industry, saving resources, and protecting the environment |
| 2 | Opinions on Establishing a Complete and Advanced Recycling System for Used and Scrap Goods | 31 October 2021 | State Council of the People’s Republic of China | By 2015, the initial establishment of a sound network, advanced technology, sorting and processing of good, standardized management of modern waste commodity recycling system |
| 3 | Pollution prevention and control regulation of waste plastic processing and utilization | 24 Agaust 2012 | Ministry of Environmental Protection, Development and Reform Commission, Ministry of Commerce | Strengthen the pollution prevention of waste plastics processing and utilization, protect the health of the people, protect environmental safety, and promote the healthy development of the circular economy |
| 4 | Medium- and Long-term Plan for the Construction of Renewable Resources Recycling System (2015–2020) | 4 February 2015 | Ministry of Commerce, Ministry of Land and Resources and other five departments | Encourage all types of domestic and foreign capital to enter the recycling, sorting and processing of renewable resources |
| 5 | Notice of the General Office of the State Council on Printing and Distributing the Implementation Plan of the Extended Producer Responsibility System | 25 December 2016 | General Office of the State Council | Producers bear more responsibility in product design, production, sales, recycling, and other stages. |
| 6 | Circular Economy Promotion Law | 12 December 2017 | State Oceanic Administration | Promote the development of circular economy, improve the efficiency of resource utilization, protect and improve the environment, and achieve sustainable development |
| 7 | Circular Development Leading Actions | 5 May 2017 | National Development and Reform Commission and other 14 departments | Promote circular production methods, establish a circular development system in towns and cities, and make an effective connection between domestic waste classification and recycling of renewable resources. |
| 8 | Agricultural Film Recycling Action Plan | 6 May 2017 | Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs | Strengthen the treatment of agricultural film pollution and improve the resource utilization of used agricultural film |
| 9 | Agricultural Film Management Approach | 3 July 2020 | Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs and four other departments | Encourage support for units and individuals to recycle agricultural films and encourage research and development of agricultural film recycling technology |
| 10 | 14th Five-Year Plan for the Development of Circular Economy | 9 November 2021 | National Development and Reform Commission | With the main line of improving the overall efficiency of resource use, focusing on three major areas: industry, social life, and agriculture. |
| No. | Representative Policies | Issuing Date | Issuing Division | Main Content |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Regulations on the Administration of City Appearance and Environmental Sanitation | 20 May 1992 | State Council of the People’s Republic of China | Strengthen the city’s urban and environmental health management, to create a clean, beautiful urban working and living environment |
| 2 | The Law of the People’s Republic of China on Solid Waste Pollution Prevention | 30 October 1995 | Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress | Protect and improve the ecological environment, prevent and control solid-waste pollution of the environment, protect public health, maintain ecological safety, promote ecological civilization, and promote sustainable economic and social development |
| 3 | Policy on urban household waste treatment and pollution prevention and control technologies. | 29 May 2000 | Ministry of Construction, State Environmental Protection Administration, Ministry of Science and Technology | Strengthen the management of the entire process of garbage generation to reduce the generation of garbage at the source. |
| 4 | Notice on Further Strengthening Urban Domestic Waste Management | 19 April 2001 | State Council | By 2030, China will basically achieve harmless treatment of urban household garbage and fully implement the collection and disposal of household garbage classification. |
| 5 | Reform implementation plan of prohibition of foreign garbage entry and promotion of solid waste import management system | 27 July 2017 | State Council of the People’s Republic of China | Comprehensive ban on the entry of foreign garbage, strengthen the management of solid waste recycling |
| 6 | Notice by the General Office of the State Council of Issuing the Work Plan for the Pilot Program of “Zero-Waste City” Building | 29 December 2018 | State Council of the People’s Republic of China | Promote the source reduction and resource utilization of MSW, reduce the amount of landfill and the environmental impact of MSW |
| 7 | Notice on Promoting the Development of Industrial Clusters for Comprehensive Utilization of Bulk Solid Waste | 9 January 2019 | General Office of the National Development and Reform Commission, General Office of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology | Accelerate the promotion of resource utilization, harmlessness, reduction and recycling of solid waste;Encourage the construction of large-scale solid waste comprehensive utilization bases in key cities and industrial parks. |
| 8 | Notice on the Comprehensive Implementation of Domestic Waste Classification Work in National Cities at and Above the Prefecture Level | 26 April 2019 | Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development, etc. | Accelerate the establishment of a household waste management system that includes classification of waste disposal, collection, transportation, and processing. |
| 9 | Plan for the Construction of Waste-Free Cities during the 14th Five-Year Plan Period | 20 December 2021 | Ministry of Ecology and Environment | During the “14th Five-Year Plan” period, about 100 prefecture-level and above cities will be promoted to carry out “zero waste city” construction. |
| No. | Representative Policies | Issuing Date | Issuing Division | Main Content |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | The 13th Five-Year Plan for the Development of Express Delivery Industry | 13 February 2017 | National Post Office | Reduce environmental pollution in the process of receiving, sorting, sealing, transporting and delivery. |
| 2 | Opinions on promoting the coordinated development of e-commerce and express logistics | 2 January 2018 | State Council of the People’s Republic of China | Develop and implement green and reduced packaging standards for e-commerce and establish and improve the extended producer responsibility system for express packaging. |
| 3 | Regulations for express temporary | 2 March 2018 | State Council of the People’s Republic of China | Encourage express enterprises and senders to use environmentally friendly packaging; encourage express enterprises to recycle express mail packaging. |
| 4 | Green packaging standards for mail and express delivery | 12 June 2020 | National Post Office | Adhere to the standardization, reduction, and recyclability of green packaging for mail and express mail. |
| 5 | Notice on Accelerating the Green Transformation of Express Delivery Packaging | 20 November 2020 | State Council | Strengthen the governance of express delivery packaging and promote the green transformation of express delivery packaging. |
| 6 | Notice by the General Office of the Ministry of Commerce of Promoting the Green Development of E-commerce Enterprises | 7 January 2021 | Ministry of Commerce | Green transformation of express packaging; promote express packaging reduction; promote the application of recyclable packaging. |
| 7 | Measures for the management of express mail packages | 8 February 2021 | Ministry of Transport | Prohibit or restrict the use of disposable plastic products such as non-biodegradable plastic bags; Encourage the use of alternative products that are recyclable, easy to recycle, and biodegradable. |
| 8 | The 14th Five-Year Plan for e-commerce development plan | 9 October 2021 | Ministry of Commerce, Central Internet Information Office, Development and Reform Commission | Establishment of green packaging standards for each link and certification of green products for express packaging. |
| No. | Representative Policies | Issuing Date | Issuing Division | Main Content |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Marine Environmental Protection Law | 23 August 1982 | Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress | Protect and improve the marine environment, protect marine resources, prevent and control pollution damage, maintain ecological balance, protect human health, and promote sustainable economic and social development |
| 2 | Prevention and control of marine engineering construction projects pollution damage to the marine environment management regulations | 19 September 2006 | State Council of the People’s Republic of China | Control over the number of marine engineering pollutants discharged into the sea in key waters |
| 3 | Technical Regulations for Monitoring and Evaluation of Marine Litter | 18 December 2015 | State Oceanic Administration | Clarified the content and methods of monitoring marine floating and seabed litter |
| 4 | Notice on Marine Standardization Management Approach | 23 June 2016 | State Oceanic Administration | Identified marine norms, including marine ecology and environmental protection, integrated management of marine areas, etc. |
| 5 | Notice on the preparation of provincial coastal zone comprehensive protection and utilization master plan pilot work guidance | 12 December 2017 | State Oceanic Administration | Adhere to the integration of land and sea, and pay more attention to land development based on the sea; Research and demonstration of marine microplastics monitoring, assessment, and prevention technologies. |
| 6 | Opinions on further strengthening the management of plastic pollution | 16 January 2020 | National Development and Reform Commission, Ministry of Ecology and Environment | Strengthening research on plastic waste and microplastic pollution mechanisms, monitoring, prevention and control technologies and policies for rivers, lakes and seas. |
| 7 | Notice on the strengthened promotion of plastic pollution control | 10 July 2020 | National Development and Reform Commission, Ministry of Ecology and Environment, Ministry of Industry and Information Technology | Regulate the collection and disposal of plastic waste Strengthen the supervision and inspection related to the ban on the production and sale of daily chemical products containing plastic microbeads. |
| 8 | Notice on establishing a sound marine ecological early warning and monitoring system | 26 July 2021 | Ministry of Natural Resources | Coastal provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government to implement early warning monitoring of marine litter and microplastics |
| 9 | Notice on the issuance of the “14th Five-Year” plastic pollution control action plan | 8 September 2021 | National Development and Reform Commission, the Ministry of Ecology and Environment | Conduct marine plastic litter and microplastic monitoring surveys. Increase the placement of garbage collection facilities at beaches and other activity sites and improve the frequency of garbage removal. Instigate microplastics pollution mechanisms, monitoring, and prevention technology in rivers, lakes, and seas. |
| 10 | Guidance on deepening the administration by the law in the field of ecology and environment and continuously strengthening the governance of pollution based on law | 9 November 2021 | Ministry of Ecology and Environment | Strengthen the Bohai Sea outfall traceability, marine microplastic pollution control, mariculture pollution ecological environment supervision, and marine engineering supervision. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Liu, C. Exploring Plastic-Management Policy in China: Status, Challenges and Policy Insights. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9087. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15119087
Liu C, Liu C. Exploring Plastic-Management Policy in China: Status, Challenges and Policy Insights. Sustainability. 2023; 15(11):9087. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15119087
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Chen, and Chang Liu. 2023. "Exploring Plastic-Management Policy in China: Status, Challenges and Policy Insights" Sustainability 15, no. 11: 9087. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15119087
APA StyleLiu, C., & Liu, C. (2023). Exploring Plastic-Management Policy in China: Status, Challenges and Policy Insights. Sustainability, 15(11), 9087. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15119087







