Study on Rock and Surface Subsidence Laws of Super-High Water Material Backfilling and Mining Technology: A Case Study in Hengjian Coal Mine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
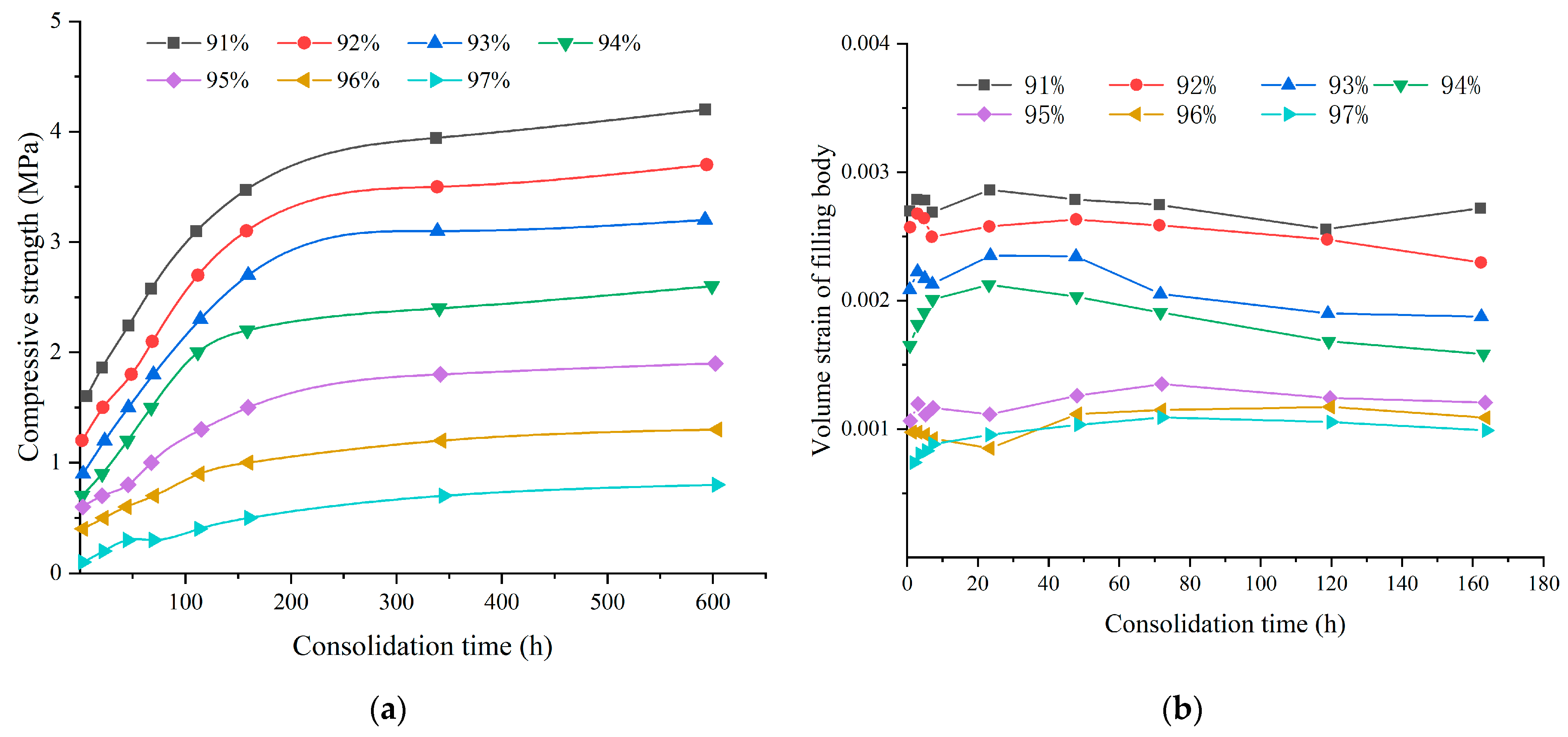
2.1. Super-High Water Backfilling Material
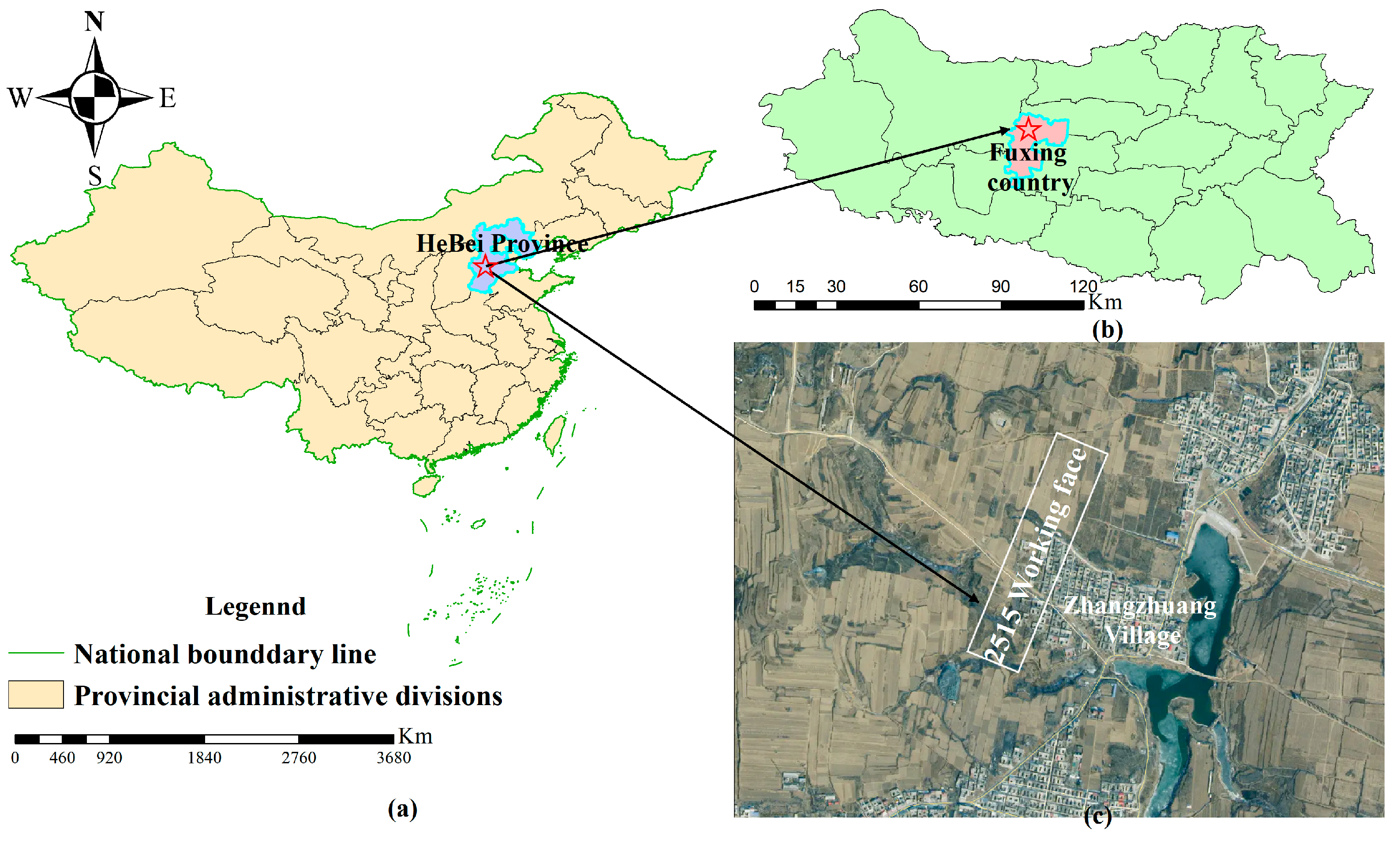
2.2. Overview of the Study Area
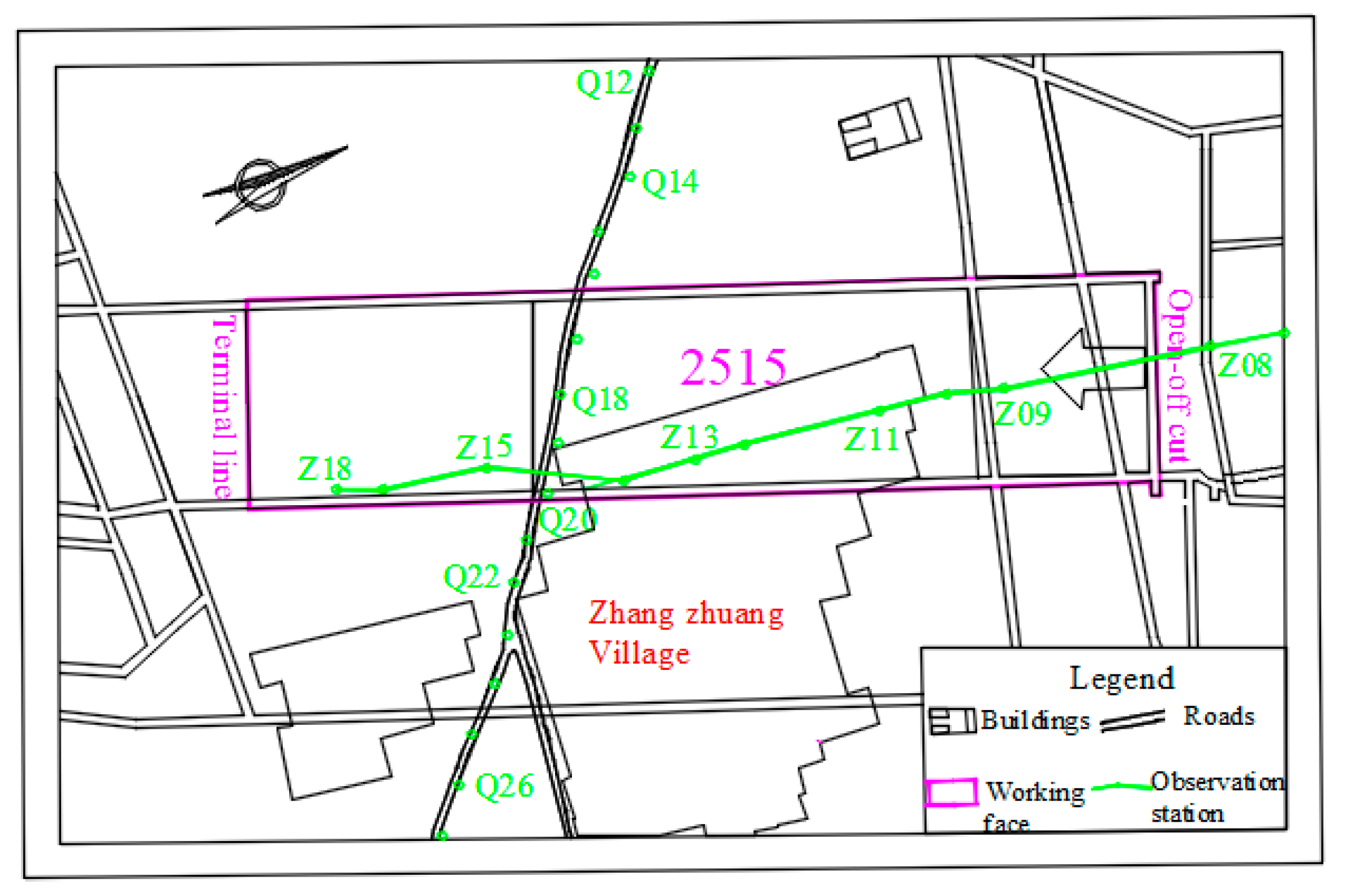
2.3. Monitoring Method
2.4. Numerical Simulation
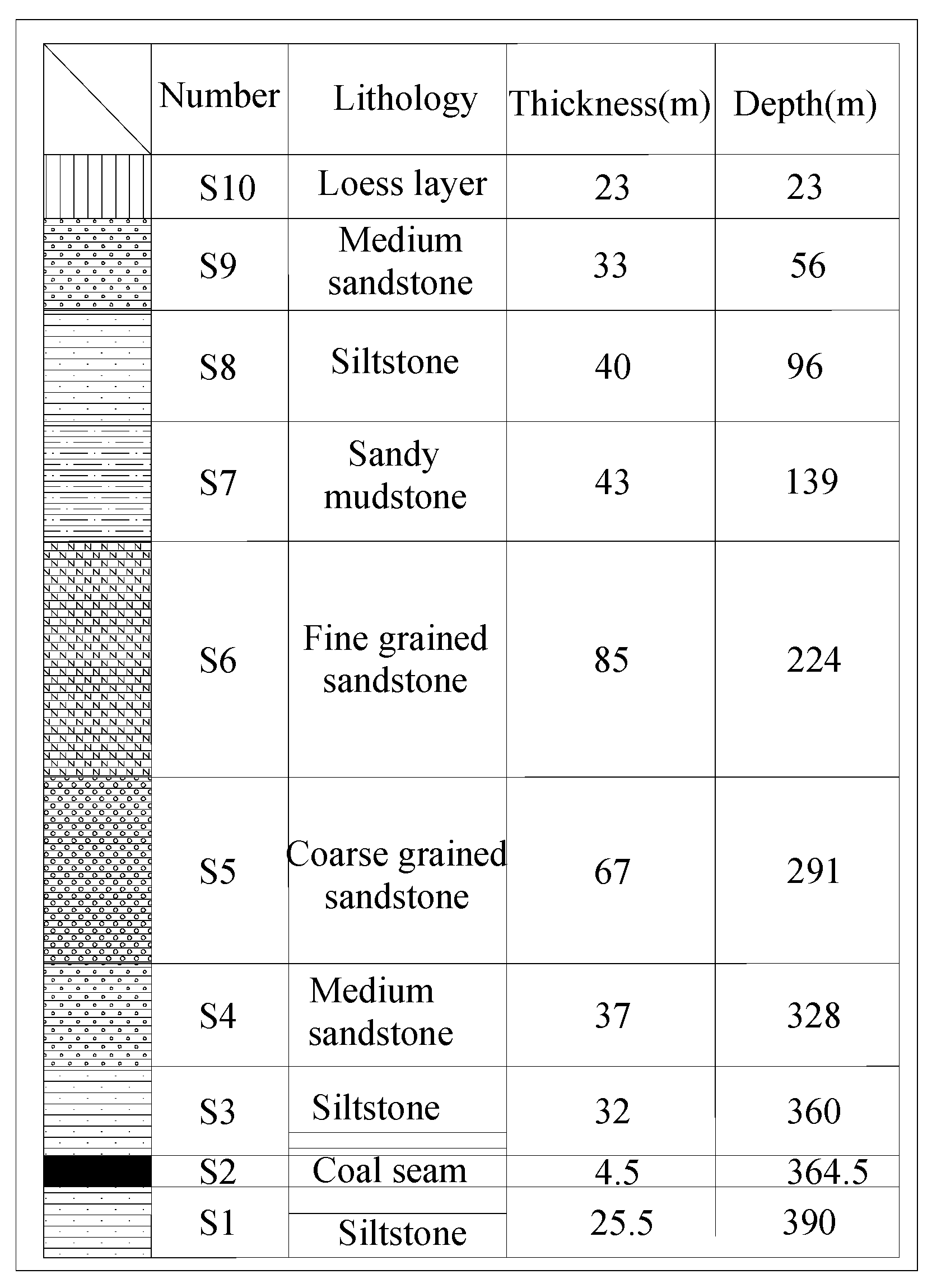
2.4.1. Model Establishment
2.4.2. Parameter Selection
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Measurement Results
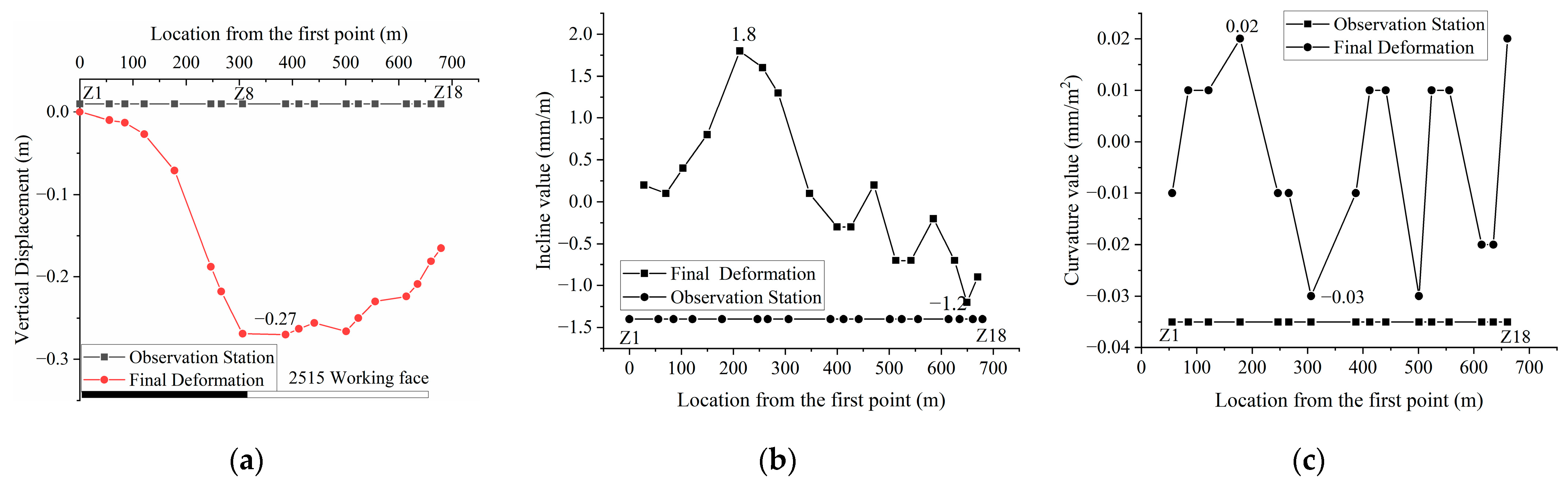
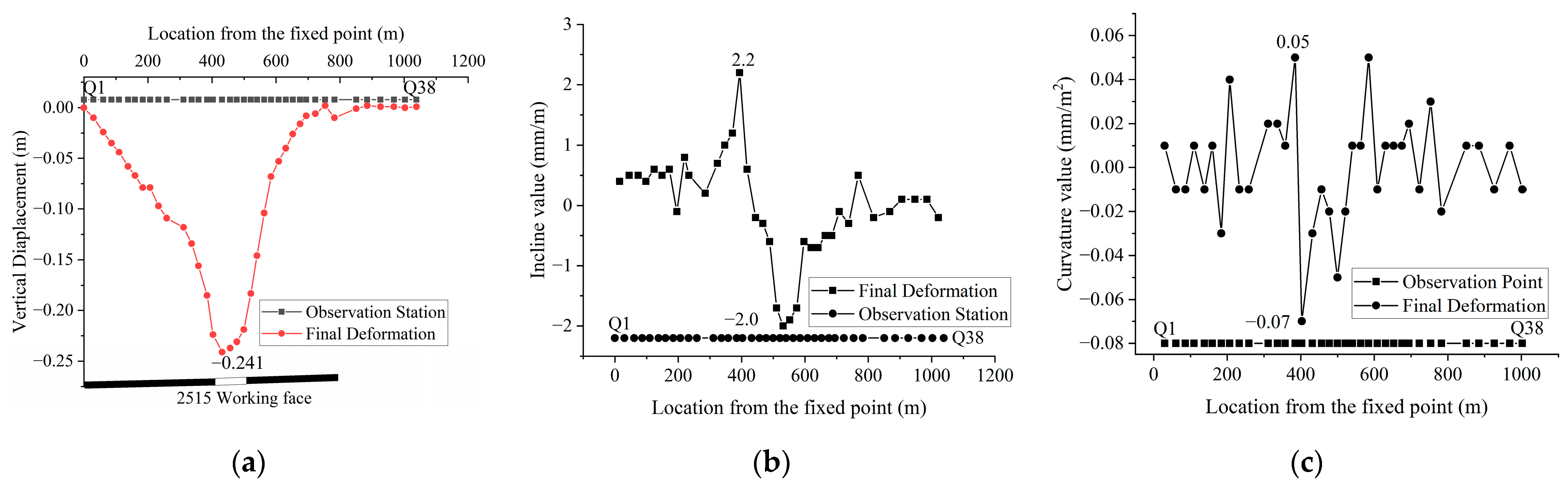
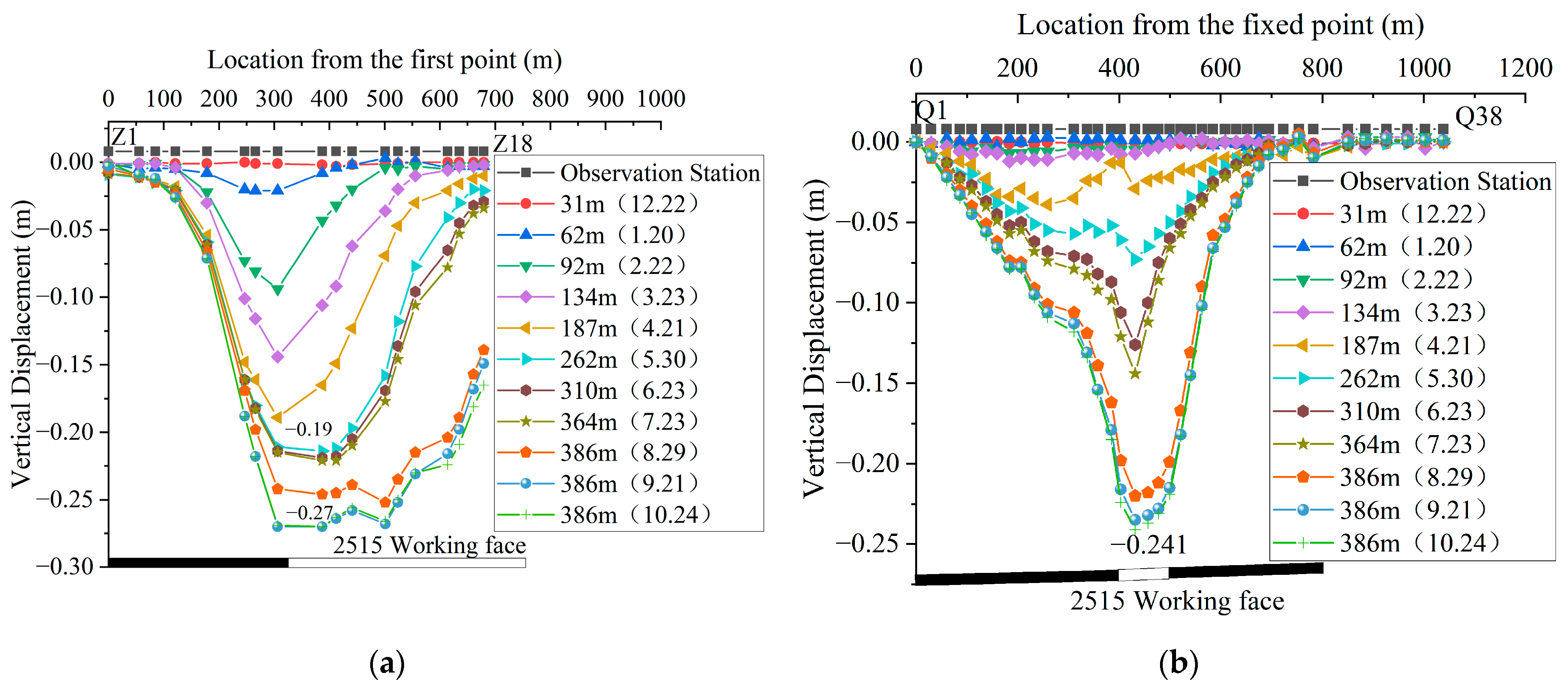
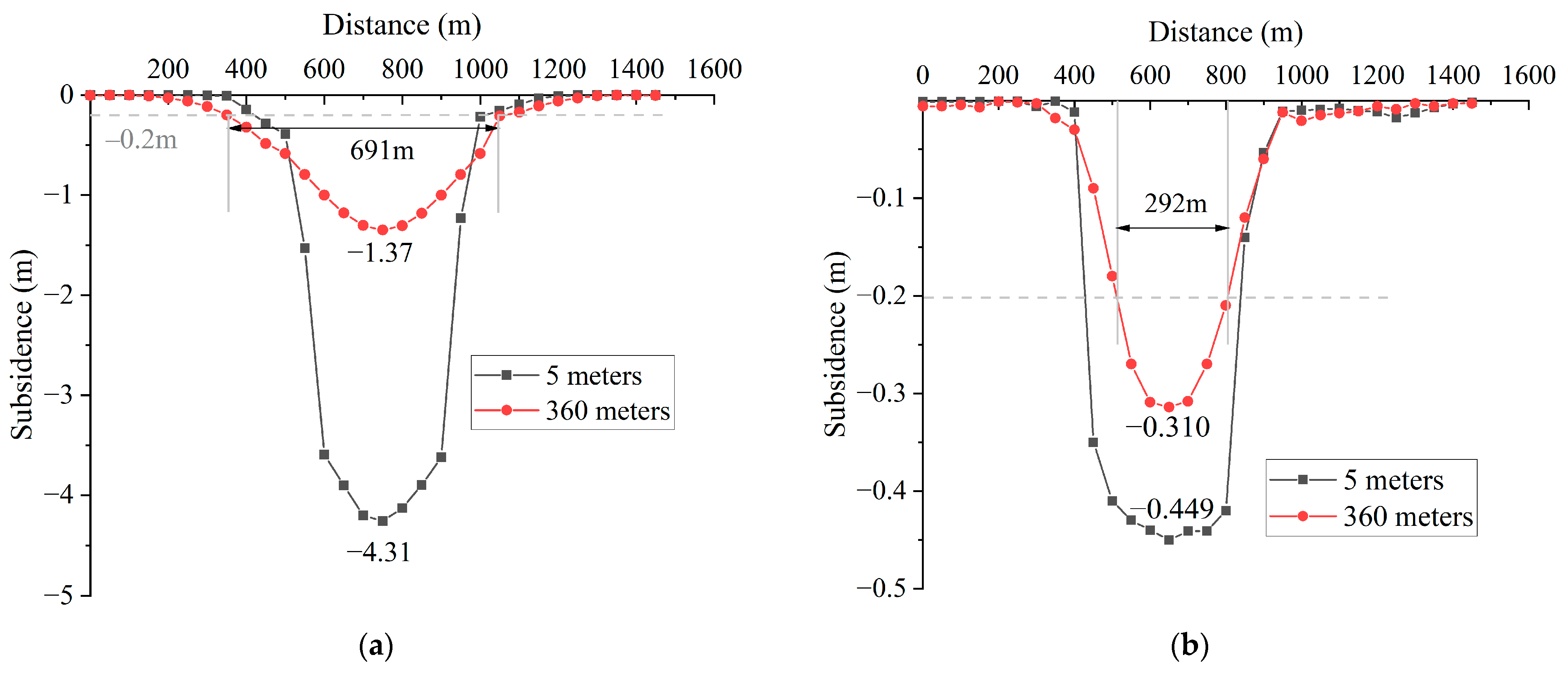
3.1.1. Characteristics of Ground Subsidence after Mining
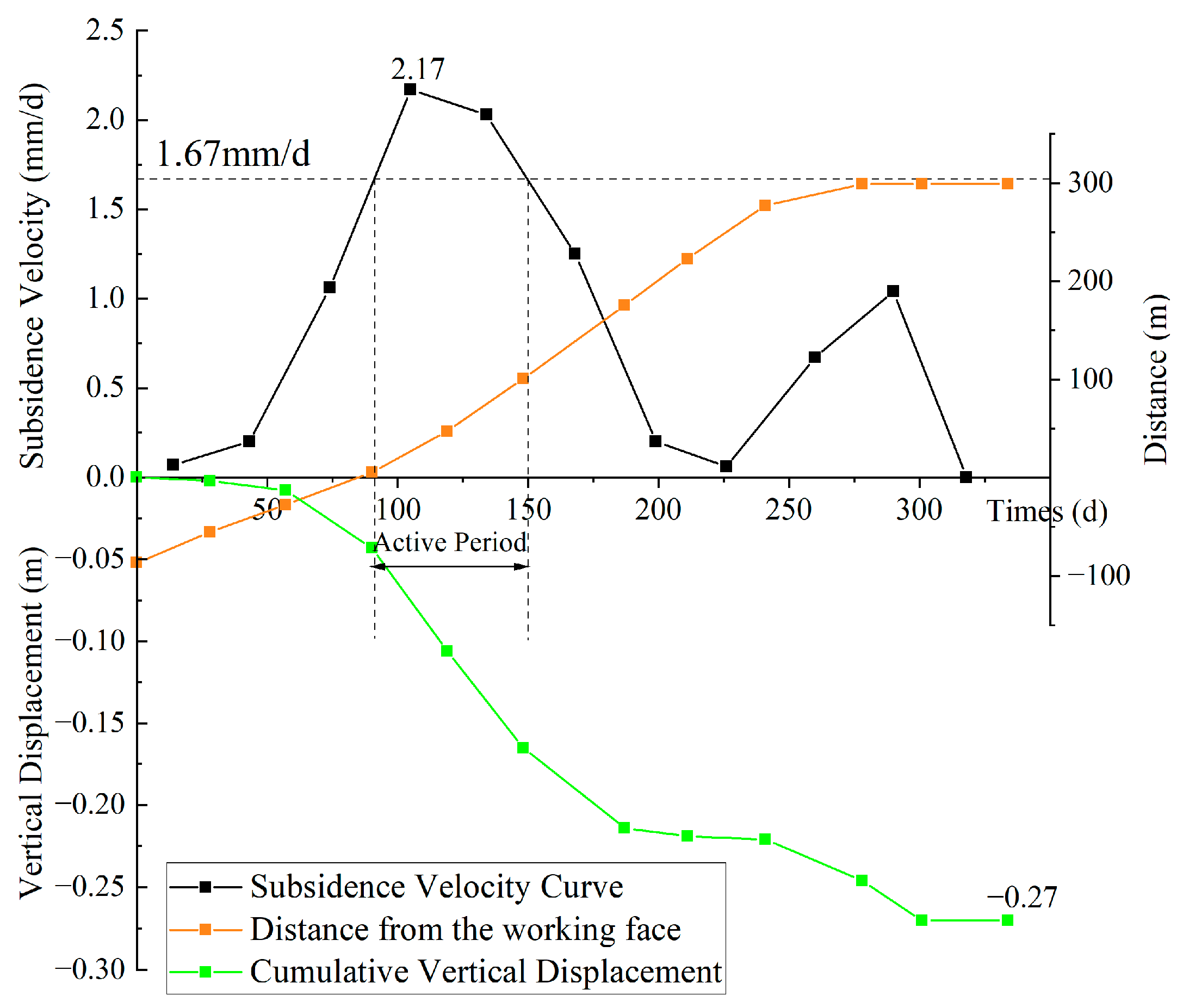
3.1.2. Dynamic Variation in Ground Subsidence
3.1.3. Related Parameters of Surface Movement
- (1)
- Factor of full extraction
- (2)
- Starting distance of surface subsidence
- (3)
- Surface subsidence factor based on measured data
3.2. Analysis of Numerical Simulation Results
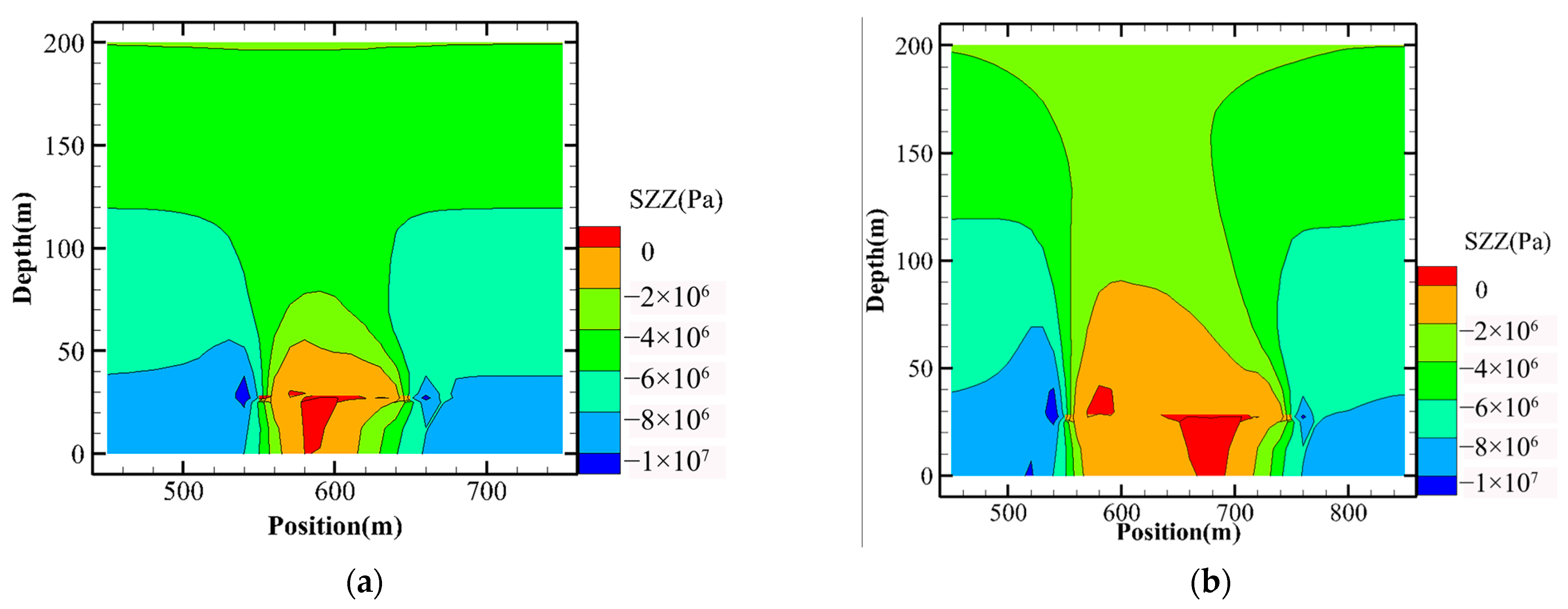
3.2.1. Rock Strata Movement Processes
- (1)
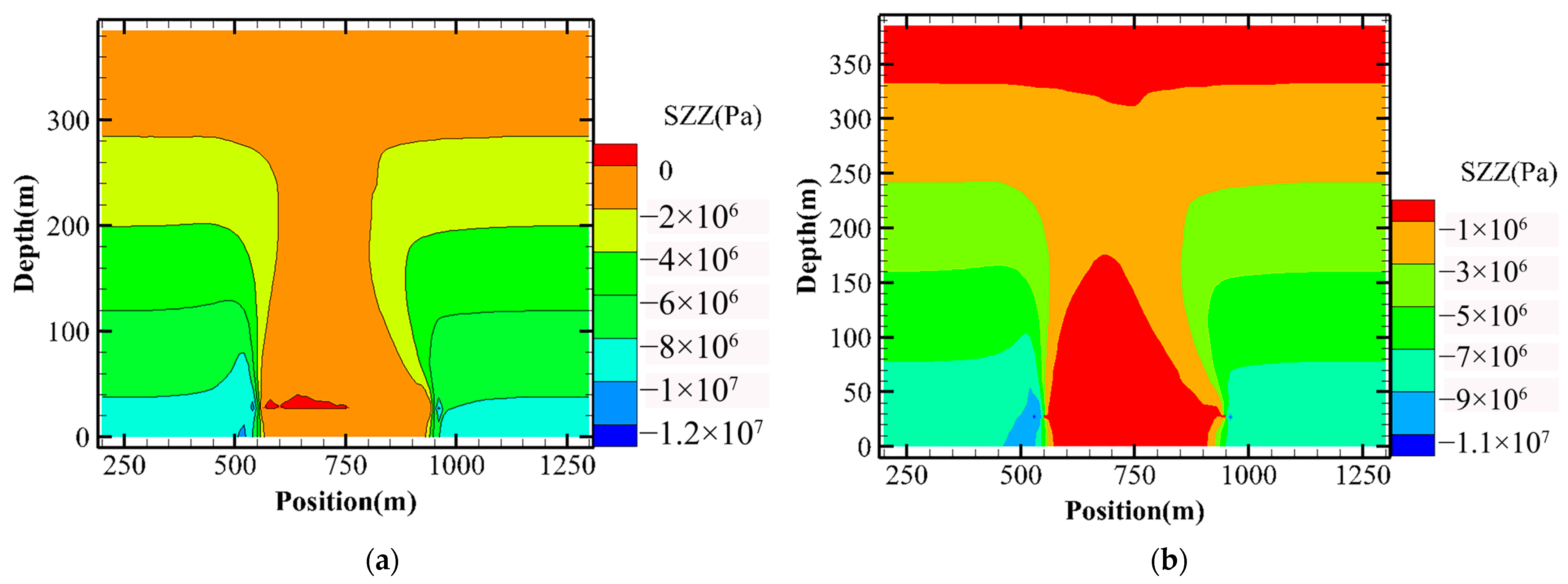
- Stress distribution variation laws
- (2)
- Vertical displacement variation in overlying strata
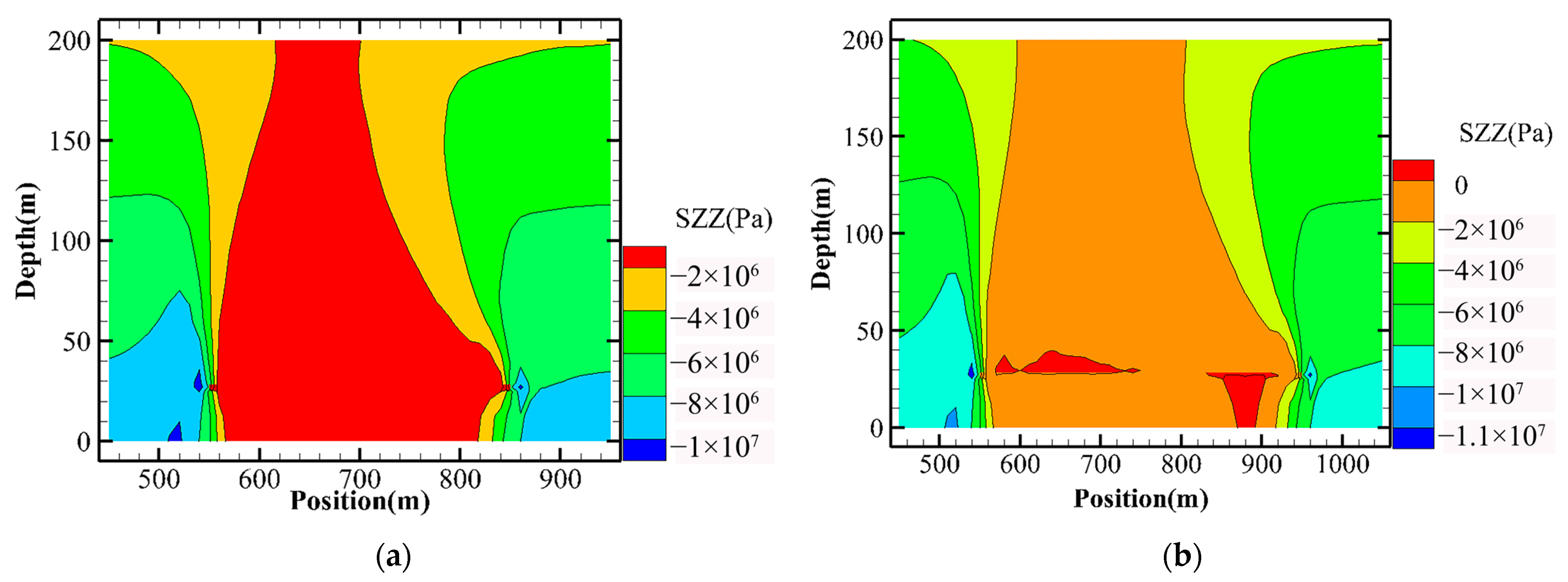
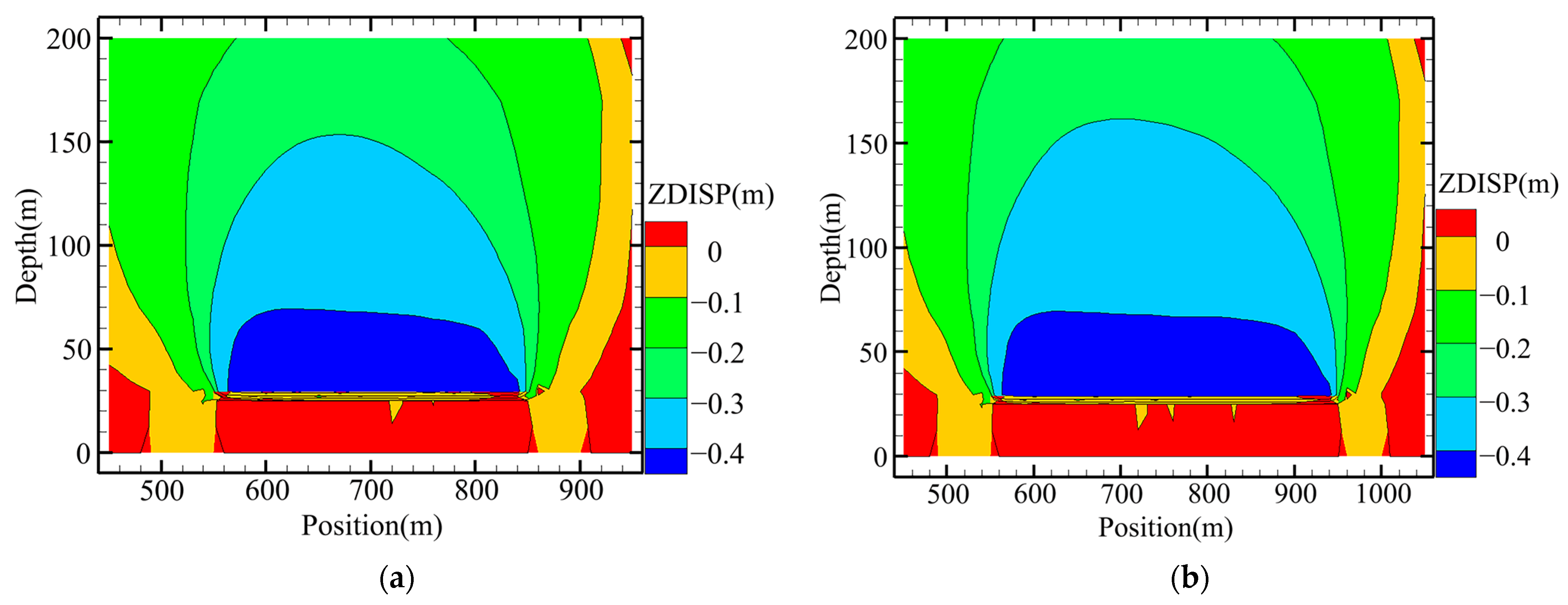
3.2.2. Comparison of Mining Methods
- (1)
- Stress distribution comparison results
- (2)
- Comparison results of overlying rock movement
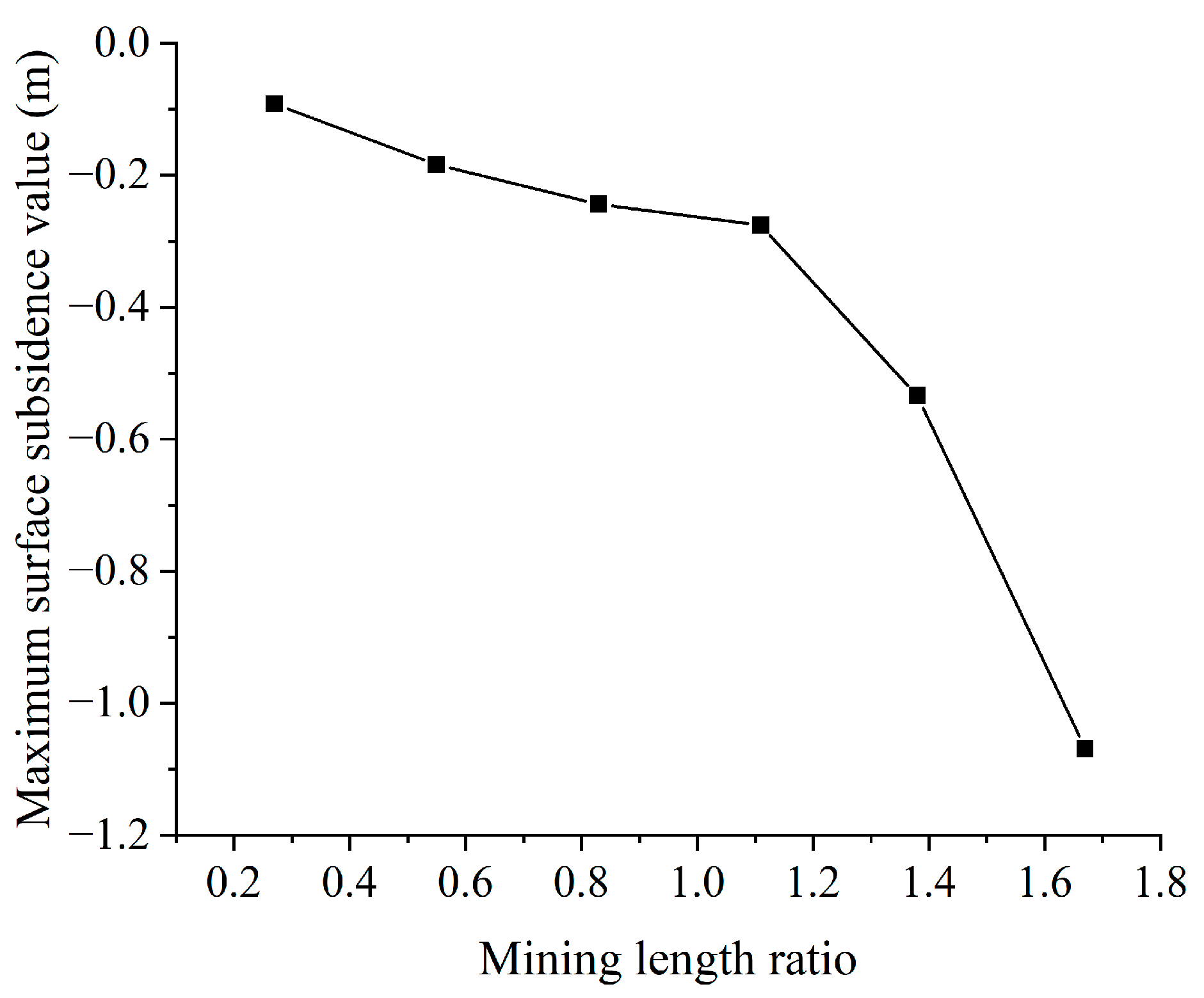
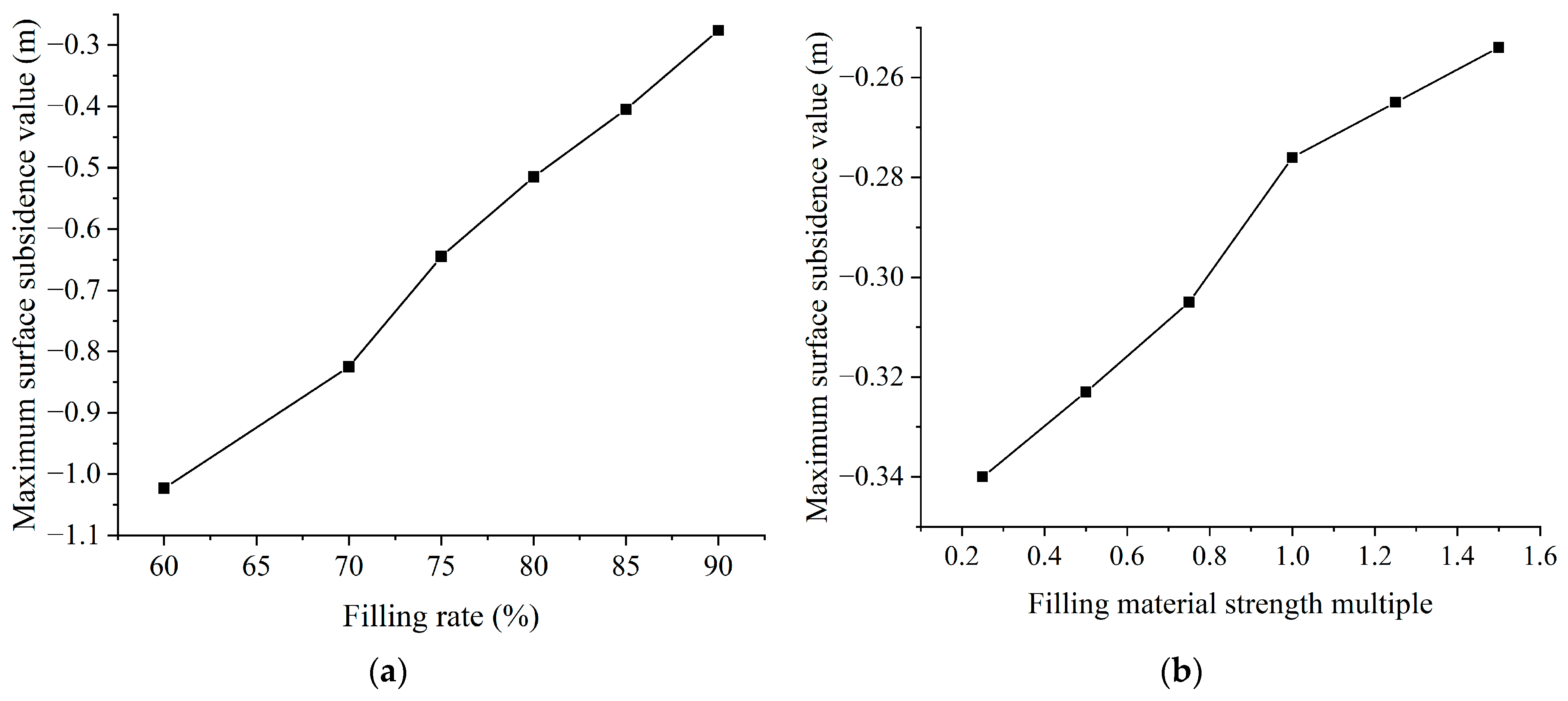
3.2.3. Analysis of Influencing Factors
- (1)
- Analysis of working condition factors
- (2)
- Analysis of backfilling material factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Subsidence Reduction Mechanism
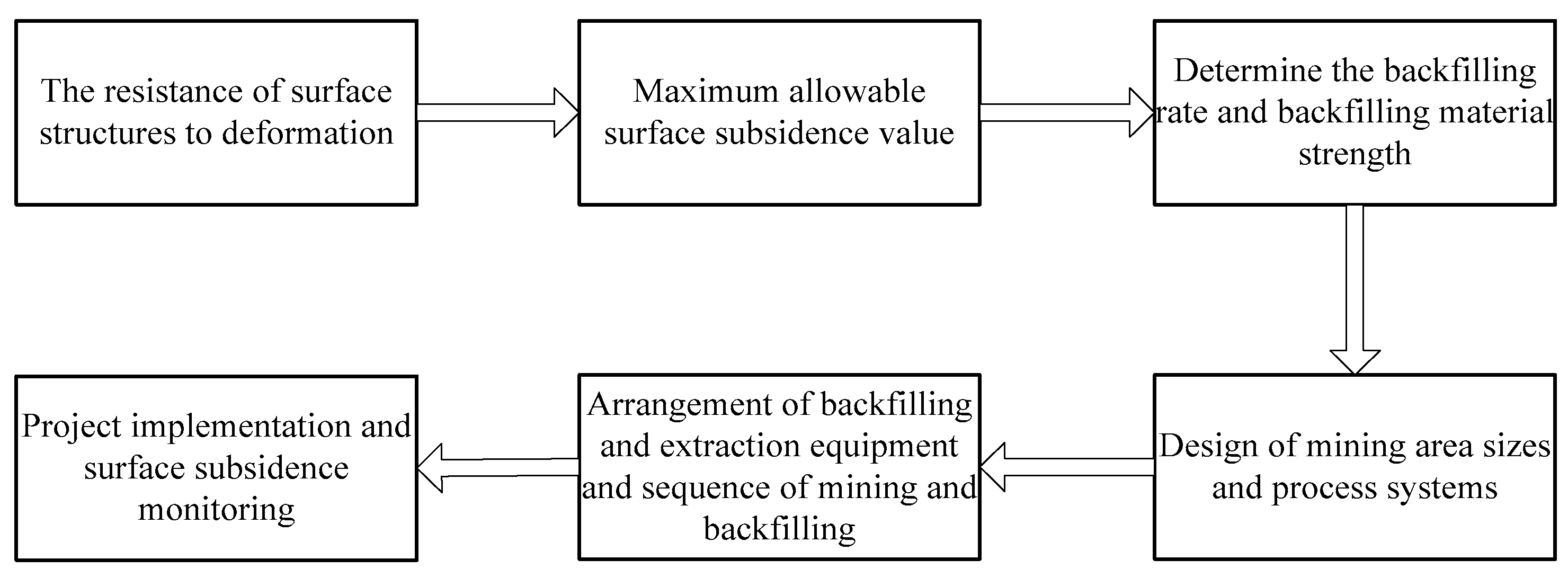
4.2. Analysis of the Process Flow
4.3. Analysis of Research Results and Future Works
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ajayi, S.A.; Ma, L.; Spearing, A.J.S. Ground Stress Analysis and Automation of Workface in Continuous Mining Continuous Backfill Operation. Minerals 2022, 12, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, D.J. Review of coal and gas outburst in Australian underground coal mines. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2019, 29, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magidi, M.; Hlungwani, P.M. Development or destruction? Impacts of mining on the environment and rural livelihoods at Connemara Mine, Zimbabwe. S. Afr. Geogr. J. 2023, 105, 157–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Wang, C.; Pan, H.; Yin, D.; Ma, J. Modeling study on the influence of the strip filling mining sequence on mining-induced failure. Energy Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 2239–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacey, J.; Malakar, Y.; McCrea, R.; Moffat, K. Public perceptions of established and emerging mining technologies in Australia. Resour. Policy 2019, 62, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marian, D.P.; Onica, I.; Marian, R.; Floarea, D. Finite Element Analysis of the State of Stresses on the Structures of Buildings Influenced by Underground Mining of Hard Coal Seams in the Jiu Valley Basin (Romania). Sustainability 2020, 12, 1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, M.; Verdel, T. Behavior of a masonry wall subjected to mining subsidence, as analyzed by experimental designs and response surfaces. Int. J. Rock. Mech. Min. 2017, 100, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapusta, A.; Szojda, L. The role of expansion joints for traditional buildings affected by the curvature of the mining area. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2021, 128, 105598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, A.; Kumar, A.; Verma, A.; Mandal, S.K.; Singh, P.K. Trait of subsidence under high rate of coal extraction by longwall mining: Some inferences. Sādhanā 2021, 46, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archundia, D.; Prado-Pano, B.; González-Méndez, B.; Loredo-Portales, R.; Molina-Freaner, F. Water resources affected by potentially toxic elements in an area under current and historical mining in northwestern Mexico. Env. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopeć, A.; Trybała, P.; Głąbicki, D.; Buczyńska, A.; Owczarz, K.; Bugajska, N.; Kozińska, P.; Chojwa, M.; Gattner, A. Application of Remote Sensing, GIS and Machine Learning with Geographically Weighted Regression in Assessing the Impact of Hard Coal Mining on the Natural Environment. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtavar, E.; Mahmoudi, H. Development of a scenario-based robust model for the optimal truck-shovel allocation in open-pit mining. Comput. Oper. Res. 2020, 115, 104539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozhanova, V.; Korenyuk, P.; Lozovskyi, O.; Belous-Sergeeva, S.; Bielienkova, O.; Koval, V. Green Enterprise Logistics Management System in Circular Economy. Int. J. J. Math. Eng. Manag. Sci. 2022, 7, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yin, D.; Cao, F.; Liu, Y.; Ren, K. An overview of integrated surface subsidence-reducing technology in mining areas of China. Nat. Hazards 2016, 81, 1129–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sroka, A.; Knothe, S.; Tajdus, K.; Misa, R. Underground exploitations inside safety pillar shafts when considering the effective use of a coal deposit. Gospod. Surowcami Miner. 2015, 31, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, A.; Shrivastva, B.K. Stability analysis of the proposed hybrid method of partial extraction for underground coal mining. Int. J. Rock. Mech. Min. 2012, 52, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrzypkowski, K. Decreasing Mining Losses for the Room and Pillar Method by Replacing the Inter-Room Pillars by the Construction of Wooden Cribs Filled with Waste Rocks. Energies 2020, 13, 3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingano, A.; Weiss, A. Subsidence over room and pillar retreat mining in a low coal seam. Int. J. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2019, 29, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, E.; Yilmaz, E. Sustainability and Tailings Management in The Mining Industy: Paste Technology. Mugla J. Sci. Technol. 2018, 4, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefni, M.; Ahmed, H.A.M.; Omar, E.S.; Ali, M.A. The Potential Re-Use of Saudi Mine Tailings in Mine Backfill: A Path towards Sustainable Mining in Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashifana, T.; Sithole, T. Clean production of sustainable backfill material from waste gold tailings and slag. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 308, 127357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefni, M.A. The potential use of pumice in mine backfill. Exp. Results 2020, 1, e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Liu, P.; Jia, Y.; Chen, Z.; Gao, F.; Huang, X. Study on overlying strata migration law of strip interval filling mining. Sci. Prog. -Uk 2023, 106, 39628441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smoliński, A.; Malashkevych, D.; Petlovanyi, M.; Rysbekov, K.; Lozynskyi, V.; Sai, K. Research into Impact of Leaving Waste Rocks in the Mined-Out Space on the Geomechanical State of the Rock Mass Surrounding the Longwall Face. Energies 2022, 15, 9522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghirian, A.; Fall, M. Coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical-chemical behaviour of cemented paste backfill in column experiments. Eng. Geol. 2014, 170, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Wang, H.; Chen, S. Coal pillar safety and surface deformation characteristics of wide strip pillar mining in deep mine. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Guo, J.; Yan, Y.; Li, P.; Liu, Y. Principle and application of subsidence control technology of mining coordinately mixed with backfilling and keeping. J. China Coal Soc. 2014, 8, 1602–1610. [Google Scholar]
- Rankine, R.; Pacheco, M.; Sivakugan, N. Underground Mining with Backfills. Soils Rocks 2007, 30, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, S.; Canbulat, I.; Zhang, C.; Oh, J.; Shen, B.; Hagan, P. Numerical investigation into the effect of backfilling on coal pillar strength in highwall mining. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2018, 28, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohenoja, K.; Pesonen, J.; Yliniemi, J.; Illikainen, M. Utilization of Fly Ashes from Fluidized Bed Combustion: A Review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Moselly, Z.; Fall, M.; Haruna, S. Further insight into the strength development of cemented paste backfill materials containing polycarboxylate ether-based superplasticizer. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 47, 103859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saedi, A.; Jamshidi-Zanjani, A.; Darban, A.K. A review of additives used in the cemented paste tailings: Environmental aspects and application. J. Env. Environ. Manag. 2021, 289, 112501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, S.K.; Mishra, D.P.; Singh, P.; Mishra, K.; Mandal, S.K.; Ghosh, C.N.; Kumar, R.; Mandal, P.K. Utilization of mill tailings, fly ash and slag as mine paste backfill material: Review and future perspective. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 309, 125120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, K.; Tomiyama, S.; Igarashi, T.; Yamagata, S.; Ebato, M.; Sakoda, M. Improvement in pH and Total Iron Concentration of Acid Mine Drainage after Backfilling: A Case Study of an Underground Abandoned Mine in Japan. Minerals 2021, 11, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, S.K.; Ghosh, C.N.; Mishra, K.; Mishra, D.P.; Singh, P.; Mandal, P.K.; Buragohain, J.; Sethi, M.K. Utilisation of lead-zinc mill tailings and slag as paste backfill materials. Env. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, B.; Gupta, A.K. Comparative analysis of different materials to be used for backfilling in underground mine voids with a particular reference to hydraulic stowing. Int. J. Oil Gas Coal Technol. 2017, 15, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheskidov, V.I.; Reznik, A.V. Features of Hydraulic Fill Formation in Mining Water-Bearing Lignite Deposit. J. Min. Sci. 2019, 55, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xie, S.; Wu, C.; Cui, J.; Chen, D.; Guo, F.; Jiang, Z.; Ren, Y.; Lu, W. Influence of the ultra-fine fly ash dosages on the mechanical properties of the sulfoaluminate cement-based high water backfilling material. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Feng, G.; Wang, C. Experimental research on basic properties of superhigh-water packing material. J. China Coal Soc. 2011, 36, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C. Backfilling Mining Technology with Super High-Water Material; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2017; pp. 9–41. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Sun, C.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; Xu, M.; Guan, K. Experimental study on engineering characteristics of super-high water filling body. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 2014, 31, 852–856. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, D.; Sun, C.; Wang, Y. Surface subsidence control during bag filling mining of super high-water content material in the Handan mining area. Int. J. Oil Gas. Coal T 2016, 1, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G. Research on the Super High-Water Packing Material and Filling Ming Technology and Their Application. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Vu, T.T.; Do, S.A. Determination of the rock mass displacement zone by numerical modeling method when exploiting the longwall at the Nui Beo Coal Mine, Vietnam. Min. Miner. Depos. 2023, 17, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncay, D.; Tulu, I.B.; Klemetti, T. Verification of 3D Numerical Modeling Approach for Longwall Mines with a Case Study Mine from the Northern Appalachian Coal Fields. Min. Metall. Explor. 2021, 38, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, H.; Yarahmadi Bafghi, A.; Najafi, M. Impact of ground surface subsidence due to underground mining on surface infrastructure: The case of the Anomaly No. 12 Sechahun, Iran. Env. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emad, M.Z.; Mitri, H.; Kelly, C. Dynamic model validation using blast vibration monitoring in mine backfill. Int. J. Rock. Mech. Min. 2018, 107, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z. Research on the Application of Super-High Water Material Backfilling and Mining Technology under Long-Walled Working Face Conditions. Masters’s Thesis, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, B.; Zhang, H.; Shen, B. Code for Coal Pillar Preservation and Press Coal Mining of Buildings, Water Bodies, and Main Tunnels; China Coal Industry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2017; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- He, G.; Yang, L.; Ling, G.; Jia, F.; Hong, D. Ming Subsidence; China University of Mining and Technology Press: Xuzhou, China, 1991; pp. 29–31. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, H. Classification Method of Balanced arch Structure of Mining Rock Mass. CN Patent Application No. 201710262816.5, 29 January 2019. [Google Scholar]


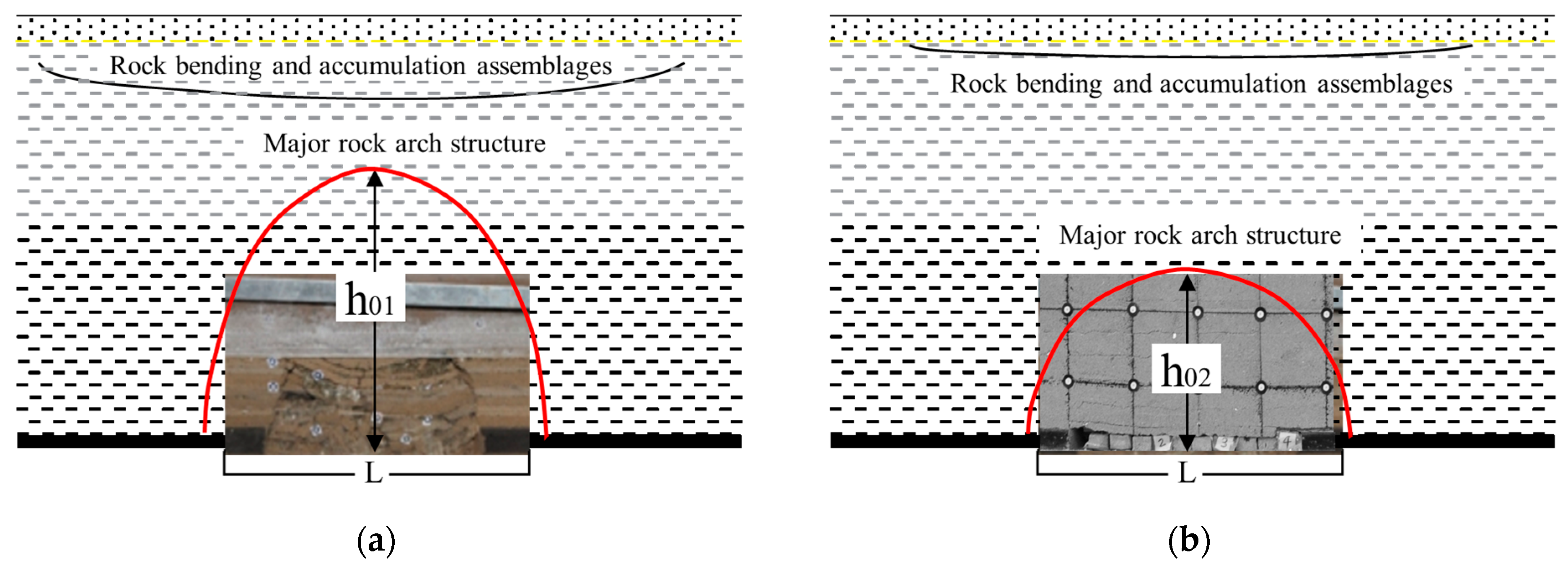
| Lithology | Density (kg/m3) | Bulk Modulus (MPa) | Shear Modulus (MPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Cohesion (MPa) | Friction Angle (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loess layer | 1650 | 166 | 27 | 0.026 | 0.03 | 24 |
| Medium sandstone | 2028 | 695 | 636 | 1.4 | 1.33 | 32 |
| Siltstone | 2280 | 1188 | 513 | 2.1 | 2.8 | 31 |
| Sandy mudstone | 2347 | 916 | 344 | 1.8 | 2.0 | 30 |
| Fine grained sand | 2300 | 833 | 486 | 3.1 | 4.2 | 30 |
| Coarse grained sand | 2136 | 857 | 692 | 4.7 | 5.7 | 36 |
| Medium sandstone | 2286 | 781 | 551 | 2.7 | 2.3 | 33 |
| Siltstone | 2480 | 1212 | 512 | 2.0 | 2.6 | 32 |
| Coal seam | 1450 | 777 | 205 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 27 |
| Siltstone | 2612 | 1223 | 525 | 2.1 | 2.8 | 32 |
| Filling material | 1350 | 833 | 535 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.; Yan, Y.; Dai, H.; Zhang, Z. Study on Rock and Surface Subsidence Laws of Super-High Water Material Backfilling and Mining Technology: A Case Study in Hengjian Coal Mine. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8713. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118713
Li M, Yan Y, Dai H, Zhang Z. Study on Rock and Surface Subsidence Laws of Super-High Water Material Backfilling and Mining Technology: A Case Study in Hengjian Coal Mine. Sustainability. 2023; 15(11):8713. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118713
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ming, Yueguan Yan, Huayang Dai, and Zhaojiang Zhang. 2023. "Study on Rock and Surface Subsidence Laws of Super-High Water Material Backfilling and Mining Technology: A Case Study in Hengjian Coal Mine" Sustainability 15, no. 11: 8713. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118713
APA StyleLi, M., Yan, Y., Dai, H., & Zhang, Z. (2023). Study on Rock and Surface Subsidence Laws of Super-High Water Material Backfilling and Mining Technology: A Case Study in Hengjian Coal Mine. Sustainability, 15(11), 8713. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15118713







