Abstract
Soil erosion poses a significant threat to land conservation, freshwater security, and ocean ecology. Climate change, with rainfall as one of its primary drivers, exacerbates this problem. Therefore, reliably predicting future soil erosion rates and taking into account anthropogenic influences are crucial for policymakers and researchers in the earth-system field. To address this challenge, we have developed a novel framework that combines the Bayesian Model Averaging (BMA) method with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) model to estimate erosion rates on a national scale. We used BMA to merge five Regional Climate Models (RCMs), reducing uncertainty in ensemble simulations and improving the plausibility of projected changes in climatic regimes over China under two Representative Concentration Pathway (RCP) scenarios (RCP4.5 and RCP8.5). The RUSLE model was applied to forecast the effects of climate change and land-use change on water erosion in China, using high-resolution climate simulation and prediction inputs. Our findings revealed that under the RCP4.5 and RCP8.5 scenarios, average annual soil loss will increase by 21.20% and 33.06%, respectively, compared to the baseline period. Our analysis also demonstrated a clear distinction between the effects of climate change and land-use change on water erosion. Climate change leads to an increase in precipitation, which exacerbates water erosion rates, with contributions ranging from 59.99% to 78.21%. Furthermore, an increase in radiative forcing will further amplify the effects of climate change. The transformation of land from one that has not been disturbed by humans to one that has been exposed to some soil and water conservation measures will have a mitigating effect on water erosion, with a contribution of −6.96% to −4.68%. Therefore, implementing effective soil and water conservation measures can somewhat mitigate the severity of ongoing soil loss. Our findings have significant implications for policymakers seeking to develop national strategies for soil conservation and model developers working to reduce uncertainty in erosion predictions.
1. Introduction
The survival of all living species on Earth is dependent on the health of the land, which is critical for protecting biodiversity and promoting the thriving of organisms within the ecosystem. However, global land degradation is a major environmental issue that is endangering sustainability [1,2]. Currently, up to 30% of land areas are degraded globally, exposing over 3.2 billion people to a decline in ecosystem services, with an annual decline of over 10% [3,4]. Soil erosion, which is the primary factor contributing to land degradation, involves the complex process of soil and its parent material, stripping, migration, and accumulation driven by external forces such as hydraulic power, wind, and freeze–thaw [5]. Climate change exacerbates soil erosion by intensifying some of the primary driving forces [6]. For instance, increasing temperatures can enhance the atmosphere’s ability to hold moisture, which will lead to intensified extreme precipitation globally in the coming decades [7]. This increased precipitation will directly separate soil particles through raindrops and indirectly enhance runoff scouring. Additionally, the increased frequency and intensity of droughts caused by climate change will exacerbate the process of dryland land degradation and desertification [8,9], which is difficult to reverse. Anthropogenic land-use change is another major factor contributing to human-induced soil erosion. The parameters of microtopography and surface vegetation cover are significantly altered by land-use change. Dramatic land-use changes can result in a decrease in soil organic matter content, destruction of soil structure, and other cascading consequences, including reduced grain yield, increased flood risk, river siltation, and water eutrophication [10,11,12,13]. To develop effective adaptation strategies and build local resilience, there is a need to understand the existing and future soil erosion hazards. Therefore, it is crucial to estimate soil erosion rates accurately and develop appropriate mitigation measures.
In light of the potential impact of soil erosion and its cascading effects on ecosystems, it is essential to utilize effective erosion models that can incorporate climate change scenarios [14]. The Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE) and the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) models, due to their simplicity, robustness, and ability to simulate erosion, have been extensively used across various spatial scales [15]. In China, the RUSLE model has been particularly successful in predicting erosion rates in the Loess and Tibetan Plateaus [16,17,18]. Given the potential of soil erosion and associated cascading effects being aggravated by climate change, it is crucial to incorporate climate modeling outputs under different climate scenarios into erosion models to examine the prospective changes in soil erosion [19,20,21]. Uncertainties inevitably reside in climate models because of parameterizations, coarse resolution, and driving conditions. Using a multiple-model ensemble can potentially reduce the uncertainty and increase the robustness of the experimental study [22]. Although previous studies have provided valuable insights into soil erosion projections for different Chinese regions, they have been limited to local scales, and the relative performance of climate simulations in an ensemble has been neglected. These limitations could lead to biased conclusions, emphasizing the importance of conducting national-scale studies that incorporate a range of climate models to better inform future decision-making processes. To achieve these goals, the study will gather and analyze spatial data on soil erosion, climate changes, and land-use changes. Soil erosion maps will be developed for the entire country, projecting the possible changes in erosion amounts compared to the historical period. The relationship between the scale and spatial distribution of soil erosion, climate changes, and land-use changes will be evaluated to determine the relative importance of these factors in contributing to erosion. To improve the accuracy of climate simulation and projection, the study will merge five Regional Climate Models (RCMs) using Bayesian Model Averaging (BMA). This approach will enhance the dependability of projection under representative emission scenarios. The RUSLE model will then be used at the national scale to predict the impact of climate and land-use changes on soil erosion in China, using the enhanced climate simulation and predictions as inputs. The findings of the study will provide valuable insights into the potential impacts of climate change and land-use change on soil erosion in China. The soil erosion maps and the assessment of erosion factors will be useful in developing effective soil conservation strategies and land-use policies to mitigate erosion risks and preserve soil productivity. The improved climate simulation and projection approach can also contribute to enhancing the accuracy of climate projections and supporting climate change adaptation and mitigation efforts.
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The study area is divided into eight soil and water conservation areas based on the Soil Erosion Classification Standard of China developed by the Ministry of Water Resources to identify hotspots vulnerable to changes in rainfall erosivity and uncover regional variations in erosion characteristics, as shown in Figure 1. Regional differences in soil erosion control measures are taken into account as well as the type, intensity, related risks, and socioeconomic factors while drawing the line of soil and water conservation regionalization.
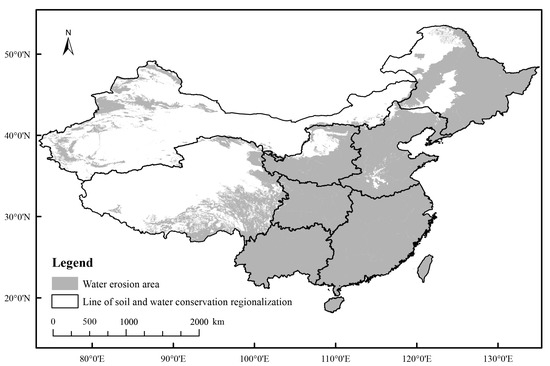
Figure 1.
The eight soil and water conservation areas in mainland China: Northeast China black soil region (I), North China mountainous region (II), Northwest China Loess Plateau region (III), North China sandstorm region (IV), South China red soil region (V), Southwest China purple soil region (VI), Southwest China karst region (VII), and Qinghai-Tibet Plateau region (VIII).
2.2. Data Used
To develop soil erosion maps and project the possible amount of soil erosion in the future, this study used two sets of precipitation data: (1) daily precipitation from APHRODITE (Asian Precipitation–Highly Resolved Observational Data Integration Towards Evaluation) dataset based on interpolation from more than 5000 valid stations across Asia and covering more than 50 years; (2) historical precipitation records (1986–2005) and the future climate simulations (2071–2090) of five RCMs, which were selected for experiments in the Coordinated Regional Climate Downscaling Experiment (CORDEX). Future climate scenarios used to drive the projection of rainfall erosivity are a medium-emission scenario (RCP4.5) and a high-emission scenario (RCP8.5). In addition to precipitation data, two sets of land use-type data were used: observed data from four periods (1990, 1995, 2000, and 2005) generated through manual visual interpretation of Landsat TM/ETM remote sensing images, and simulation data from Land Use Harmonization (LUH1) for historical and future periods. Other data such as soil, terrain, vegetation, and land use were also considered and described in Table 1. To improve the accuracy of the climate simulation and the dependability of projections under representative emission scenarios, five RCMs are merged using Bayesian Model Averaging (BMA), and the RUSLE model is used at the national scale to predict the impact of climate and land-use changes on soil erosion in China using enhanced climate simulation and predictions as inputs.

Table 1.
Data used in the study.
2.3. RUSLE Model
The RUSLE model is a modified version of the original USLE system that includes sub-elements in addition to the six factors linked with climate, soil, terrain, vegetation, and management [23]. The research goal of studying the effects of climate change and land-use change on soil erosion can be achieved by entering the data of projected rainfall and land-use type in the future. The model is given by
A is the annual soil erosion (t·hm−2·a−1); R is the rainfall erosivity factor (MJ·mm·hm−2·h−1·a−1); K is the soil erodibility factor (t·hm2·h·MJ−1·hm−2·mm−1); C is the cover management factor; LS is the slope length–steepness factor; P is the conservation support practice factor. The estimated results of RUSLE factors in the study area based on the observed data are shown in Figure 2.
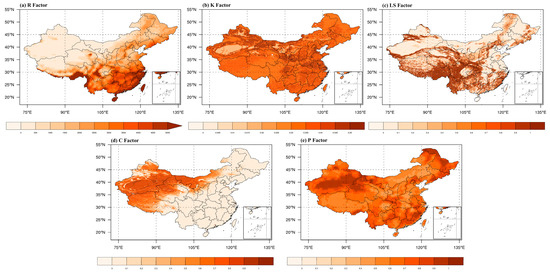
Figure 2.
The RUSLE factor estimation of the study area: (a) the rainfall erosivity (units: MJ·mm·hm−2·h−1·a−1); (b) the soil erodibility factor (units: t·hm2·h·MJ−1·hm−2·mm−1); (c) the slope length–steepness factor; (d) the cover management factor; and (e) the conservation support practice factor.
- (1)
- Rainfall erosivity (R factor)
A universal rainfall erosivity calculation method based on daily rainfall data from 71 representative meteorological stations across China is applied in this study [24]. This method has been widely used to calculate the R-factor in different regions of China [25,26,27]. The R-factor combines the rainfall characteristics of duration, frequency, and intensity in rainfall events to represent the erosive power of rainfall. Rainfall erosivity for a single rainfall event is the product of the kinetic energy of a rainfall event and its maximum 30-min intensity [28]. Due to the difficulty of data collection and the complicated calculation process, daily and even monthly rainfall data are mostly used as basic data in the practical application to establish the R-factor for a selected region [29,30,31]. The calculation process of the R-factor is as follows:
where RL is the rainfall erosivity of a half-month, MJ·mm·hm−2·h−1; L is the day in the half-month; Pj is the effective rainfall for day j in the half-month, by which Pj is set to the actual value of a rainfall event when its value is over 12 mm/day, otherwise, Pj is set to zero; α and β are parameters; Pd12 and Py12 represent the average daily and annual rainfall for erosive rainfall days, respectively. The first half and the second half of one month are divided by the 15th day in each calendar month, which results in a total of 24 half months in one year.
- (2)
- Soil erodibility (K factor)
The K-factor, defined as the interaction of soil permeability, texture, and organic content, indicates the soil particles’ role in transporting and erosion of soil by rainfall and runoff kinetic energy. In order to estimate the soil erodibility, the following equation was used [32]:
where ms, msilt, mc, orgC are percentage content of sand, silt, clay, and organic matter, respectively. The calculated K value needs to be multiplied by 0.1317 to convert to the International System of Units.
- (3)
- Slope length–steepness factor (LS factor)
The topographic factor (LS) represents the effect of topography on soil erosion by the calculation of the constituents of the slope length factor (L) and slope steepness factor (S) [23]. It was found that increases in slope length and steepness could cause a faster overland flow velocity and a higher erosion rate before reaching a certain threshold and that the effect of slope steepness on the increase in soil erosion was greater than that of slope length [33]. The LS factor was calculated for each cell as [28]:
where λ is the horizontal slope length; the exponent m is related to the ratio of rill to inter-rill erosion (n); θ is the slope angle in degree also being used to estimate slope steepness factor S [28,34]:
- (4)
- Cover management factor (C factor)
Cover management factor C refers to the ratio of soil loss from land cultivated under specified conditions to the corresponding clean-tilled continuous fallow, and it is non-dimensional. NDVI is mostly used to estimate C. This study used the equation from van der Knijff et al. [35] to calculate C.
where α = 2 and β = 1.
- (5)
- Conservation support practice factor (P factor)
Conservation support practice factor refers to the ratio of soil loss with a specific support practice to the corresponding loss with up and downslope tillage [36]. The P values range from 0 to 1, with 1 for no soil conservation and smaller vales for more significant effects of conservation measures [37]. According to previous studies, the p values can be well defined based on land use types [38,39,40]. The spatial distribution of P factor changes with the land use type.
In LUH1 dataset (Harmonized Global Land Use for Years 1500–2100, V1), land-use categories of cropland, pasture, primary land, secondary (recovering) land, and urban land, and underlying annual land-use transitions, are included. They define primary land as natural vegetation (either forest or non-forest) that has never been impacted by human activities (e.g., agriculture or wood harvesting) since the beginning of our simulation (the initial year of the simulation depends on the dataset being used). Secondary land is also natural vegetation (either forest or non-forest) that is recovering from previous human disturbance (either wood harvesting or agricultural abandonment). Secondary land can range from very young vegetation recovering from a recent human disturbance to vegetation that is very mature, recovering from a human disturbance many years ago, and which could be similar in biomass density to primary vegetation of the same type. In our model, there are no transitions in primary land; secondary land can never return to a “primary” state, even if it is very mature. Based on the definition in the literature, this study defined the P values of cropland, primary land, pasture, secondary land, and urban land as 0.4, 1, 0.5, 1, and 0.3, respectively.
2.4. Bayesian Model Averaging Method
Bayesian Model Averaging (BMA) is a multi-factor model uncertainty analysis method. In recent years, BMA has been widely used in various research fields [41,42]. The advantage of BMA over other model combing techniques is that it creates a forecast distribution, which captures the uncertainty surrounding the deterministic prediction in addition to the deterministic model weighted average prediction of the desired variable. Most studies have shown that BMA performs better than an individual model and is more accurate than other ensemble models [43,44,45]. BMA is used to calculate the aggregate average of the soil erosion results obtained from five RCM simulations. Suppose that y is the projected variable, D = [y1, y2, …, yT] is the calibration period’s observations, and f = [f1, f2, …, fK] are the models that are being examined (ensemble members). The BMA forecast’s posterior distribution, y can be expressed as
where p(fk|D) is the likelihood of model fk under the assumption that observed data D; pk(y|fk,D) is the posterior distribution of y given the prediction of fk and observed data D. This likelihood, which reflects how well this specific ensemble member matches the observations, is expressed as the weight of model f being the best model [46]. If wi is used to represent pk(fk|D), then . The ensemble output of the BMA probability density function (PDF) is essentially a weighted average of the posterior under each of the models taken into consideration [47]. The variance of y and its mean value are given as
The weights (wi) and variances (σi2) of each model forecast must be accurately estimated for the BMA approach to be applied. In this study, the probability distribution parameters wi and σi2 of the BMA simulation variables are computed using the EM algorithm.
2.5. Contribution of Climate and Land-Use Change to Soil Erosion
It is worth noting that the contribution rate is calculated by controlling precipitation and land-use factors in the simulation process. The specific scenarios include only precipitation change (ΔP) or only land-use change (ΔL), and then the contribution rate of precipitation (CP) or land use (CL) is calculated by the following formula. If the contribution rate is positive, it means aggravating soil erosion, and if it is negative, it means alleviating soil erosion.
2.6. Classification of Soil Erosion Intensity
According to the standards for classification and gradation of soil erosion (SL190-2007) issued by the Ministry of Water Resources of China in 2008, the soil erosion calculated in this paper was divided into six levels, and the higher the level, the greater the soil loss (Table 2).

Table 2.
Classification of soil erosion intensity.
3. Results
3.1. Historical Simulation of Soil Erosion
The areal mean annual rate of soil loss by water (Figure 3) calculated using RUSLE based on the observational data is 40 t·km−2·a−1 in China for the historical period (1986–2005). The high soil-loss rates are found in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau region, Northwest China Loess Plateau region, Southwest China karst region, and South China red soil region. The Qinghai-Tibet Plateau has a steep slope in its eastern part and low vegetation coverage in the western part. In addition, melting ice and snow produce large amounts of runoff, which can seriously erode waterways in the summer. The Northwest China Loess Plateau region is well known for its fragile ecological environment, loose soil, vertical and horizontal surface gullies, and sparse vegetation. The Southwest China karst region not only has a unique karst landform, high elevation, and steep slope but is also mostly cultivated land with a dense population and low soil retention. As for the South China red soil region, it is prone to intense precipitation and land-use change. Therefore, in the former two regions, natural reasons are mostly to blame for the high erosion rates, whereas in the latter two, both anthropogenic and natural factors are involved. RCMs capture the spatial distribution of soil erosion over China compared to observation, but they overstate the magnitudes over the majority of China, particularly over the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. This is mainly because the observation data are obtained by inverse distance weighted interpolation of the measured rainfall data of the rainfall stations. The reliability of gridded data is limited by the density of station data. Since there are few rainfall stations in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, this may lead to the uncertainty of the results. The results of MCLM model are closer to the observed values than those of other RCMS, except that the simulation results of soil erosion in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau are relatively high. The CCLM and IDMI models overestimate the soil erosion in the Northwest China Loess Plateau and South China red soil region, while the PRECIS model underestimates the results in the South China red soil region.
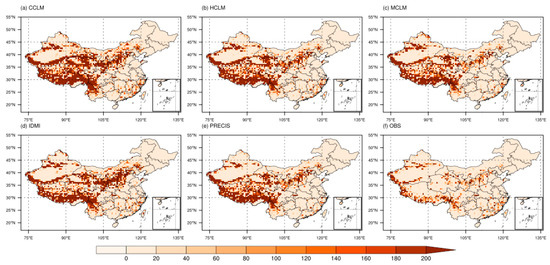
Figure 3.
Soil erosion spatial patterns over China from 1986 to 2005, as determined by (a) CCLM, (b) HCLM, (c) MCLM, (d) IDMI, (e) PRECIS, and (f) observation mean (units: t·km−2·a−1).
3.2. Future Projections of Soil Erosion
The results suggest that both climate change and land-use change will significantly increase soil erosion rates in China in the future. However, the magnitude and spatial pattern of the increase will vary depending on the region and the scenario considered. The BMA ensemble approach provides a more reliable estimate of soil erosion under future climate and land-use scenarios, considering the uncertainty associated with different RCMs [48]. A higher weight is given to the RCM, which is more adept at reconstructing historical climate in the BMA technique, which is shown to be a more reasonable process for enhancing reliability [49]. The BMA approach yields single RCM weights ranging from 0.01 to 0.46. MCLM, with a maximum weight of 0.46, and makes the largest contribution to the ensemble mean, followed by HCLM, PREC, IDMI, and CCLM with a weight of 0.31, 0.20, 0.02, and 0.01, respectively. Figure 4 illustrates the percentage of annual soil erosion change generated from the BMA ensemble under RCP4.5 and RCP8.5 in 2071–2090 relative to 1986–2005, as well as the distinction between the two scenarios. This figure takes into account the effects of both climate change and land-use change on erosion. The multi-model ensemble mean indicates that soil erosion increases under both scenarios (with a 21.20% increase under RCP4.5 and 33.06% under RCP8.5) all over the nation. The most prominent increase in soil erosion is found over the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, while the least change is located in the Northwest because of its aridity and hence low soil loss by water. In contrast, precipitation intensity is projected to be amplified over the South China red soil region which is dominated by hydraulic erosion. With the region’s gradual economic development, plenty of comprehensive and scientific soil and water conservation measures have been adopted in this region [50]. Benefiting from human interference, soil erosion over South China is found with no remarkable changes. As radiative forcing increases, not all regions are experiencing a concomitant increase in soil loss. For example, the percentage change in soil loss in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau region under the climate scenario of RCP8.5 is not as high as that under RCP4.5. This may be related to future precipitation and land-use changes in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau (Figures S1 and S2).
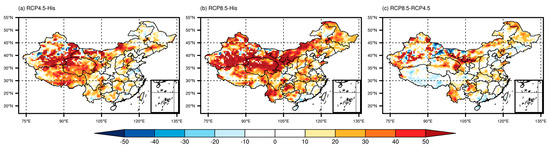
Figure 4.
Percentage of annual soil erosion change (unit: %) derived from the BMA ensemble under RCP4.5 and RCP8.5 in 2071–2090 relative to 1986–2005.
The specific variation of soil erosion in each subregion is shown in Table 3. The Northwest China Loess Plateau region’s erosion area accounts for the biggest percentage of the entire area, reaching 94.98%, while the South China red soil region’s erosion areas are the largest. The Northwest China Loess Plateau region shows the most evident increase in erosion intensity. Due to the poor spatial resolution, the erosion intensity simulated in most areas is dominated by mild erosion, and more than 90% of the area presents tolerable erosion. Moreover, the Northeast China black soil region has the least amount of gently degraded land in China, whereas the North China mountainous region has the biggest share. Impacted by climate and land-use changes, the erosion area is expanding in Northeast China’s black soil region, the Northwest China Loess Plateau region, and the Southwest China karst region.

Table 3.
Variation of soil erosion intensity in each subregion.
3.3. Impacts of Climate and Land-Use Changes on Soil Erosion
How soil erosion responds to climate and land-use changes serves as the foundation for our assessment of anthropogenic and natural factors in erosion. In this research, we consider changes in erosion induced by land-use changes to be human contributions, and changes in rainfall erosivity caused by rainfall changes to be climate-influenced. Primary land, secondary land, arable land, pasture, and urban land are the different land-use classifications identified in the land-use dataset utilized in this study. Primary land and secondary land are considered to be the lands that are not disturbed by human activities, so the P factor is 1. Increased rainfall and rainfall intensity due to climate change will increase the risk of hydraulic erosion. At the same time, the land-use type will change from primary and secondary land to cultivated land, pasture, and urban land as a result of ongoing human activity. Measures for preserving soil and water are continuously being improved thanks to human activity, and changes in land use caused by people will lessen the intensity of soil and water loss.
In Figure 5, there is a distinct difference between climate change and land-use change impacts on soil erosion. In the research area, the contribution rates of land-use changes and climate change to soil erosion range from −6.96% to −4.68%, and 59.99% to 78.21%, respectively. In addition, with the increase in radiation force, the contribution rate of climate change increases, while the contribution rate of land use change decreases. This shows that climate change will be the dominant driving factor in soil erosion change in China in the future. The increase in rainfall caused by climate warming will aggravate soil erosion. Land-use changes caused by human activities, on the contrary, mitigate soil erosion to some extent, especially in rapidly developing South China. It is believed that the conversion of the land area into farmland, pasture, and urban land will alleviate soil erosion in the future mainly due to the active transformation of land use by human beings. It is incontrovertible that soil and water conservation measures considerably contribute to the mitigation of soil erosion. Therefore, protective measures should be taken to keep the future soil erosion rate at the current level or even below it within an ideal range.
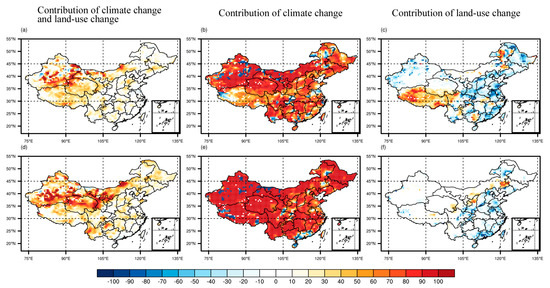
Figure 5.
The contribution of climate change and land-use change to soil erosion under two RCPs relative to the historical period. (a–c) RCP4.5 relative to the historical period; (d–f) RCP8.5 relative to the historical period.
4. Discussion
4.1. The Main Driving Forces Affecting Soil Erosion
As we know, the two major factors affecting the occurrence and development of soil erosion are natural factors and human factors. Natural factors include rainfall, vegetation, topography, and soil. From the macro point of view, the terrain and soil factors are relatively stable. They will not change much for years, decades, or even centuries [51]. Rainfall factors and vegetation factors closely related to rainfall are factors of change, but vegetation factors will not change qualitatively in the short term macroscopically. Generally speaking, the change in soil erosion in a particular area is most likely due to the change in rainfall factor among the dynamic factors. Global climate change, characterized by global warming, affects the regional soil loss process by changing rainfall, rainfall intensity and rainfall spatial distribution. As the temperature rises, the energy contained in the atmosphere increases, the airflow becomes more active and the evaporation becomes more vigorous, which then affects the atmospheric circulation and the spatial pattern of precipitation, and finally leads to the change in rainfall, rainfall intensity, and other factors affecting rainfall erosivity, so that the erosive external force is readjusted on a global scale. Rainfall erosivity is the most active factor in soil erosion. The contribution rate of climate change to soil erosion is 59.99–78.21% in China. The key factor contributing to increased erosion in most parts of China is the increased erosivity in rainfall caused by climate change. Human activities not only aggravate soil erosion but also mitigate it [52]. The modern rate of erosion is four times higher than in geological times, and soil erosion caused by human activity is 10 times higher than soil erosion caused by all natural processes combined [53,54]. However, human activities play a substantial role in effectively controlling soil erosion, mainly through water and soil conservation projects. The conservation support practice factor (P factor) used in this study serves as a reflection of how changing land use has affected soil erosion. Land use is regarded as a concentrated reflection of human activities, affecting the dynamics and resistance mechanisms of soil erosion by changing the micro-topography, vegetation types, and cover of the surface. Land-use information can indirectly reflect soil and water conservation measures in the RUSLE model. In the land-use type with more frequent human activities, the human protection of land will be considered more positive, and vice versa. The smaller the p value, the greater the mitigation effect of human activities on soil erosion through soil and water conservation action. We found that increasing human disturbance activities reduces soil erosion’s subsequent intensification, which is important for future soil erosion control. Many studies also believe that optimized land-use structures (as a result of human activities) might reduce the erosion risk [55,56]. An appropriate agricultural management system and practices also help to achieve Sustainable Development Goals by reducing soil erosion [57].
In China, rainfall erosivity is a crucial driver of soil erosion, and soil and water conservation measures can significantly reduce erosion rates. However, despite these efforts, erosion rates remain higher than the rate of soil formation needed for sustainable agriculture [58]. To address this issue, it is important to increase efforts to combat the ongoing and intensifying effects of climate change and land-use changes on soil erosion. Improving technical expertise is also essential for effective soil erosion mitigation.
4.2. Limitations
The calculation and analysis of large-scale soil erosion is a complex and challenging task, as it requires spatial accuracy and authenticity. To address this issue, we employed the BMA method to reduce inherent uncertainties in the climate model and achieve the ensemble average of five RCMs. Our results indicate that the intensity of soil erosion is reduced in the calculation results of 0.5° × 0.5° resolution, even though the RCMs were selected to reproduce the impact of rainfall on soil erosion. However, future studies conducted at a finer spatial resolution can explore responses of soil erosion to climate change at different slope lengths and slope patterns, in addition to the gradient. Moreover, given that extreme rainfall events can lead to high rates of soil erosion, it is essential to conduct further research at a finer temporal resolution to understand their effects on erosion.
In summary, our study highlights the importance of understanding the impact of climate change and human activities on soil erosion. Although soil and water conservation measures have been effective in mitigating soil erosion, the ongoing and intensifying effects of climate change necessitate continued efforts to combat soil erosion. Future studies should focus on exploring the responses of soil erosion to climate change at different spatial and temporal resolutions, taking into account the complex interactions between natural factors and human activities. This will help to inform the development of effective soil conservation strategies and support sustainable land management practices. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the impact of climate and land-use change on soil loss, assuming constant soil erodibility, slope, and vegetation cover parameters for the whole period due to data and computational limitations. Nevertheless, our projections showed different rates of soil erosion in areas with loess, purple soil, and black soil, indicating the significant effect of soil texture on erosion in addition to climate and land-use changes. Tetzlaff and Wendland [59] also highlighted the importance of the K factor, which has a strong influence on soil erosion potential along with the LS factor, especially in risk-prone areas where loess soils are prevalent. Although this study mainly focused on hydraulic erosion, it is crucial to consider all types of erosion to achieve a comprehensive assessment of soil loss in China’s various soil loss categories. Hence, future research should aim to improve the accuracy of data and methods to provide more reliable regional information for estimating large-scale soil erosion accurately. The findings will help to develop customized soil and water conservation measures tailored to different regions of China, mitigating the impacts of soil erosion and enhancing sustainable land-use practices.
5. Conclusions
In this study, a unique framework was developed to combine multiple RCMs using the BMA approach, and the RUSLE model was applied on a national scale to improve the precision of climate simulation and the dependability of soil erosion assessments under future climate and land-use change scenarios. The contributions of natural and anthropo-genic forces to soil erosion across China were quantified, and the study could provide valuable guidance for decision makers from a whole-country perspective. The study found that greater rainfall erosivity had a more significant impact on minimizing soil erosion than water and soil conservation efforts. Although the application of soil and water conservation measures greatly help to decrease erosion in China, the erosion rates still appear to be higher than the rate of soil formation needed for soil-neutral agriculture. Soil erosion will be on the rise at the end of the 21st century, which could lead to more land degradation, particularly in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau region and the Northwest China Loess Plateau region. The increase in precipitation intensity caused by climate change has an amplification effect, but reasonable and effective soil and water conservation measures could restrain the severity of soil loss to a certain extent. The results also indicated that different types of soils, such as loess, purple soil, and black soil, experience different rates of soil erosion, and the effect of soil texture is readily apparent in addition to the effects of climate change and land-use change. Future work should be carried out to comprehensively assess all erosion types and improve the data accuracy, which will provide more accurate regional information for the large-scale estimation of soil erosion and a theoretical basis for formulating customized soil and water conservation measures for different regions in China.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/su15107865/s1, Figure S1. Spatial distributions of rainfall erosivity (unit: MJ·mm·hm−2·h−1) over China for historical and future periods; Figure S2. Spatial distributions of conservation support practice factor over China for historical and future periods.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.Z.; Methodology, X.W. and B.Z.; Software, J.Z.; Validation, X.W. and J.Z.; Formal analysis, D.W.; Investigation, B.Z.; Resources, J.Q.; Data curation, J.Q.; Writing—original draft, X.W.; Writing—review & editing, J.Z.; Supervision, D.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Guangzhou Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (Grant No. 202201011403), Guangdong Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 2023A1515012046), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities-Sun Yat-Sen University (Grant No. 22qntd2001).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data used in this paper is freely available at https://esg-dn1.nsc.liu.se/search/cordex/ (accessed on 1 March 2022).
Conflicts of Interest
All authors declare no competing financial interest.
References
- Gibbs, H.K.; Salmon, J.M. Mapping the world’s degraded lands. Appl. Geogr. 2015, 57, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, C.; Wang, M.; Xiao, L.; Qi, Y. Analysis of critical land degradation and development processes and their driving mechanism in the Heihe River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 137082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nkonya, E.; Mirzabaev, A.; Braun, J.V. Economics of Land Degradation and Improvement—A Global Assessment for Sustainable Development; Economics and Finance; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Montanarella, P.; Scholes, R.; Brainich, A. The IPBES Assessment Report on Land Degradation and Restoration; Secretariat of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services: Bonn, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Amundson, R.; Berhe, A.A.; Hopmans, J.W.; Olson, C.; Sztein, A.E.; Sparks, D.L. Soil and human security in the 21st century. Science 2015, 348, 1261071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azari, M.; Oliaye, A.; Nearing, M.A. Expected climate change impacts on rainfall erosivity over Iran based on CMIP5 climate models. J. Hydrol. 2021, 593, 125826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, J.; Crow, W.T.; Wang, S.; Dong, J.; Li, Y.; Garcia, M.; Shangguan, W. Microwave-based soil moisture improves estimates of vegetation response to drought in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 849, 157535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Qiu, J.; Crow, W.T.; Mo, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, S.; Gao, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, S. Improved estimation of vegetation water content and its impact on L-band soil moisture retrieval over cropland. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 129015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Fang, H. Impacts of climate change on water erosion: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 163, 94–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David Raj, A.; Kumar, S.; Sooryamol, K.R. Modelling climate change impact on soil loss and erosion vulnerability in a watershed of Shiwalik Himalayas. Catena 2022, 214, 106279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinkowski, P.; Szporak-Wasilewska, S.; Kardel, I. Assessment of soil erosion under long-term projections of climate change in Poland. J. Hydrol. 2022, 607, 127468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullan, D.; Favis-Mortlock, D.; Fealy, R. Addressing key limitations associated with modelling soil erosion under the impacts of future climate change. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2012, 156, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Himanshu, S.K.; Mishra, S.K.; Singh, V.P. Physically based soil erosion and sediment yield models revisited. Catena 2016, 147, 595–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schürz, C.; Mehdi, B.; Kiesel, J.; Schulz, K.; Herrnegger, M. A systematic assessment of uncertainties in large-scale soil loss estimation from different representations of USLE input factors—A case study for Kenya and Uganda. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 4463–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Yang, W.; Fu, J.; Li, Z. Effects of vegetation and climate on the changes of soil erosion in the Loess Plateau of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Lu, P.; Valente, D.; Petrosillo, I.; Babu, S.; Xu, S.; Li, C.; Huang, D.; Liu, M. Analysis of soil erosion characteristics in small watershed of the loess tableland Plateau of China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.; Liang, Z.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Chappell, A.; Yu, W.; Shi, Z. Current and future assessments of soil erosion by water on the Tibetan Plateau based on RUSLE and CMIP5 climate models. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Peng, C.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, M.; Wang, H.; Peng, S.; He, H. Modelling the impacts of climate and land use changes on soil water erosion: Model applications, limitations and future challenges. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 250, 109403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruffi, L.; Stucchi, L.; Casale, F.; Bocchiola, D. Soil erosion and sediment transport under climate change for Mera River, in Italian Alps of Valchiavenna. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.G.; Nearing, M.A.; Zhang, X.C.; Xie, Y.; Wei, H. Projected rainfall erosivity changes under climate change from multimodel and multiscenario projections in Northeast China. J. Hydrol. 2010, 384, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doulabian, S.; Shadmehri Toosi, A.; Humberto Calbimonte, G.; Ghasemi Tousi, E.; Alaghmand, S. Projected climate change impacts on soil erosion over Iran. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 126432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, K.G. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); United States Government Printing: Washington, DC, USA, 1997.
- Zhang, W.; Xie, Y.; Liu, B. Rainfall erosivity estimation using daily rainfall amounts. Sci. Geol. Sin. 2002, 6, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Yu, K.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Zhang, J.; Wang, A.; Ma, L.; Xu, G.; Zhang, X. Temporal and spatial variation of rainfall erosivity in the Loess Plateau of China and its impact on sediment load. Catena 2022, 210, 105931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Qi, Y.; Zhou, T. Changes in rainfall erosivity over mainland China under stabilized 1.5 C and 2 C warming futures. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Jiang, G.; Peng, X.; Jin, H.; Jiang, N. Relationship between the periodicity of soil and water loss and erosion-sensitive periods based on temporal distributions of rainfall erosivity in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region, China. Catena 2021, 202, 105268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.; Smith, D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses—A Guide to Conservation Planning; Agriculture Handbook: Washington, DC, USA, 1978.
- Angulo-Martínez, M.; López-Vicente, M.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Beguería, S. Mapping rainfall erosivity at a regional scale: A comparison of interpolation methods in the Ebro Basin (NE Spain). Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 1907–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo-Martínez, M.; Beguería, S. Trends in rainfall erosivity in NE Spain at annual, seasonal and daily scales, 1955–2006. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 3551–3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyos, N.; Waylen, P.R.; Jaramillo, Á. Seasonal and spatial patterns of erosivity in a tropical watershed of the Colombian Andes. J. Hydrol. 2005, 314, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.R. EPIC-Erosion/Productivity Impact Calculator: 1. Model Documentation; Technical Bulletin; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1990; Volume 4, pp. 206–207. [CrossRef]
- Mccool, D.K.; Brown, L.C.; Foster, G.R.; Mutchler, C.K.; Meyer, L.D. Revised Slope Steepness Factor for the Universal Soil Loss Equation. Trans. ASAE 1987, 30, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Nearing, M.A.; Risse, L.M. Slope Gradient Effects on Soil Loss for Steep Slopes. Trans. ASAE 1994, 37, 1835–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knijff, J.; Jones, R.; Montanarella, L. Soil Erosion Risk Assessment in Europe; Report EUR 19044 EN; European Soil Bureau, European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Angima, S.D.; Stott, D.E.; O’neill, M.K.; Ong, C.K.; Weesies, G.A. Soil erosion prediction using RUSLE for central Kenyan highland conditions. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2003, 97, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K.; van der Zanden, E.H.; Poesen, J.; Alewell, C. Modelling the effect of support practices (P-factor) on the reduction of soil erosion by water at European scale. Environ. Sci. Policy. 2015, 51, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, K.; Das Bhattacharya, S. A Review of RUSLE Model. J. Indian Soc. Remote 2020, 48, 689–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Bennett, S.J.; Li, Y. Assessment of soil erosion using RUSLE and GIS: A case study of the Yangou watershed in the Loess Plateau, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 1715–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Lyu, D.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Yin, D.; Zhao, Z.; Mu, Z. Assessment of Soil Erosion Dynamics Using the GIS-Based RUSLE Model: A Case Study of Wangjiagou Watershed from the Three Gorges Reservoir Region, Southwestern China. Water 2018, 10, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Huang, G.; Yu, C.; Ni, S.; Yu, L. A multiple crop model ensemble for improving broad-scale yield prediction using Bayesian model averaging. Field Crops Res. 2017, 211, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Band, S.S.; Jun, C.; Bateni, S.M.; Chuang, H.; Turabieh, H.; Mafarja, M.; Mosavi, A.; Moslehpour, M. Solar radiation estimation in different climates with meteorological variables using Bayesian model averaging and new soft computing models. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 8973–8996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbandsari, P.; Coulibaly, P. Inter-Comparison of Different Bayesian Model Averaging Modifications in Streamflow Simulation. Water 2019, 11, 1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lu, K.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hua, J.; Lin, X. Multi-model ensemble simulated non-point source pollution based on Bayesian model averaging method and model uncertainty analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 44482–44493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zhang, S. Improving rice phenology simulations based on the Bayesian model averaging method. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 142, 126646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Ajami, N.K.; Gao, X.; Sorooshian, S. Multi-model ensemble hydrologic prediction using Bayesian model averaging. Adv. Water Resour. 2007, 30, 1371–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennifer, A.H.; David, M.; Adrian, E.R.; Chris, T.V. Bayesian model averaging: A tutorial (with comments by M. Clyde, David Draper and E. I. George, and a rejoinder by the authors. Stat. Sci. 1999, 14, 382–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, D.W.; Barnett, T.P.; Santer, B.D.; Gleckler, P.J. Selecting global climate models for regional climate change studies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 8441–8446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chu, P.; He, L.; Unger, D. Improving the CPC’s ENSO Forecasts using Bayesian model averaging. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 3373–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Luo, M. Have anthropogenic factors mitigated or intensified soil erosion over the past three decades in South China? J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 302, 114093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bou Kheir, R.; Abdallah, C.; Khawlie, M. Assessing soil erosion in Mediterranean karst landscapes of Lebanon using remote sensing and GIS. Eng. Geol. 2008, 99, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, Y.; Yang, X.; Cai, H. Quantifying anthropogenic soil erosion at a regional scale—The case of Jiangxi Province, China. Catena 2023, 226, 107081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Tang, K. Soil erosion response to climatic change and human activity during the Quaternary on the Loess Plateau, China. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2006, 6, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Sun, W.; Li, P.; Mu, X.; Gao, P.; Zhao, G. Reduced sediment transport in the Chinese Loess Plateau due to climate change and human activities. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Yu, X.; Lü, G.; Liu, Q. The changing relationship between spatial pattern of soil erosion risk and its influencing factors in Yimeng mountainous area, China 1986–2005. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 66, 1535–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, P.; Robinson, D.A.; Panagos, P.; Lugato, E.; Yang, J.E.; Alewell, C.; Wuepper, D.; Montanarella, L.; Ballabio, C. Land use and climate change impacts on global soil erosion by water (2015–2070). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 21994–22001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.C.; Chakrabortty, R.; Roy, P.; Chowdhuri, I.; Das, B.; Saha, A.; Shit, M. Changing climate and land use of 21st century influences soil erosion in India. Gondwana Res. 2021, 94, 164–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, Z.; Govers, G. Soil and water conservation measures reduce soil and water losses in China but not down to background levels: Evidence from erosion plot data. Geoderma 2019, 337, 729–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetzlaff, B.; Wendland, F. Modelling Sediment Input to Surface Waters for German States with MEPhos: Methodology, Sensitivity and Uncertainty. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 165–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).