Risk Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Agricultural Soils of Al-Ahsa Oasis, Saudi Arabia
Abstract
1. Introduction
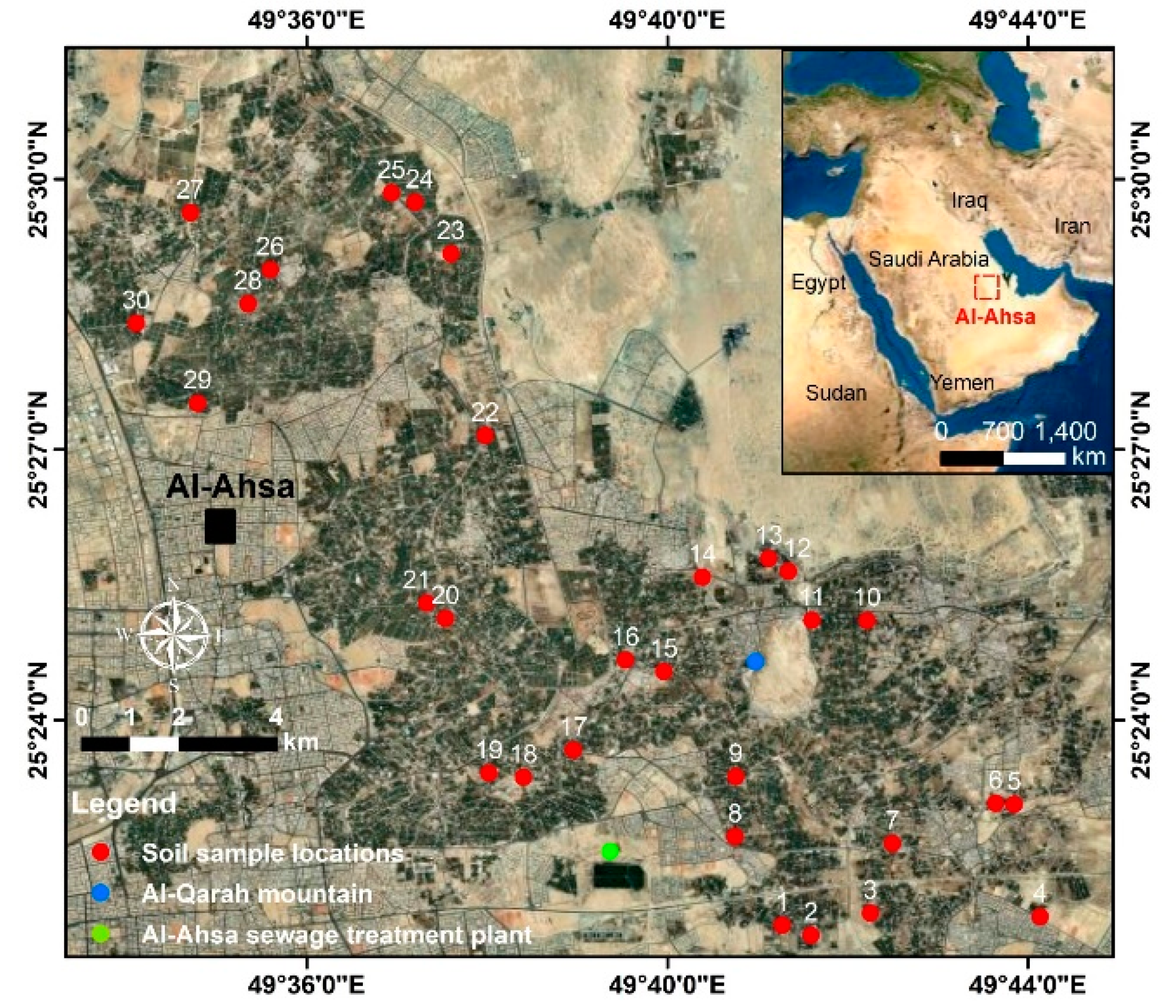
2. Materials and Methods
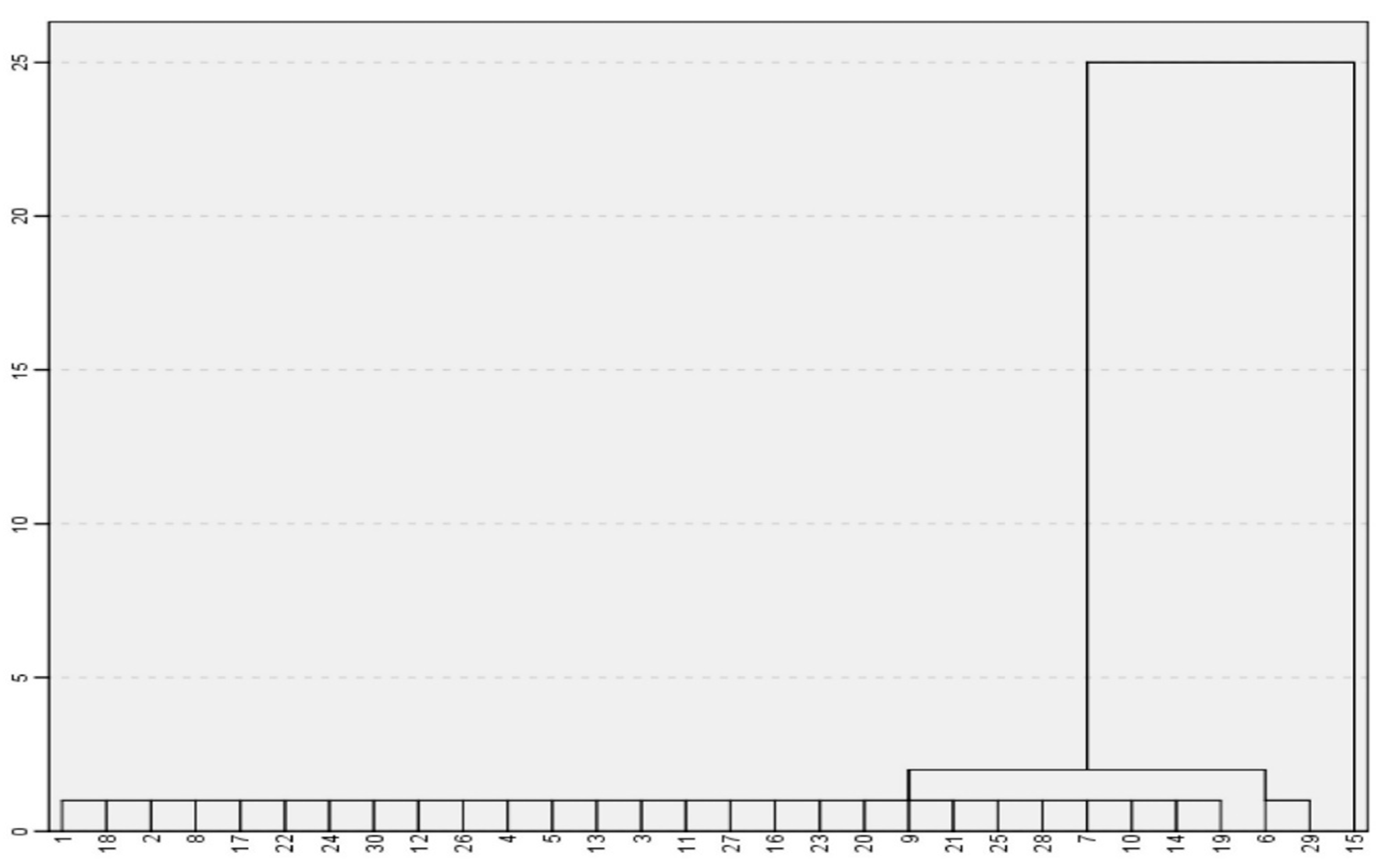
3. Results and Discussion
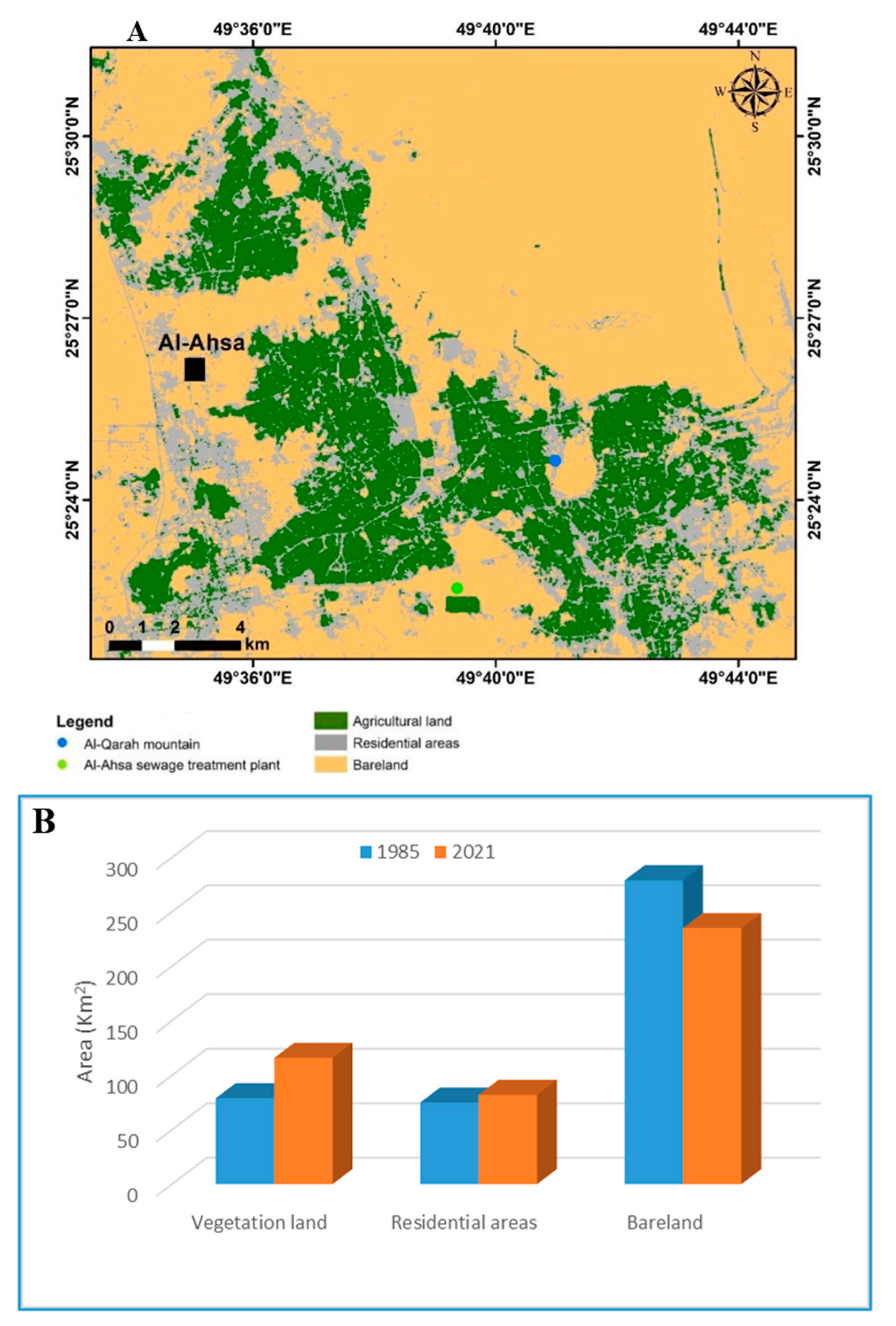
3.1. Land Use Pattern
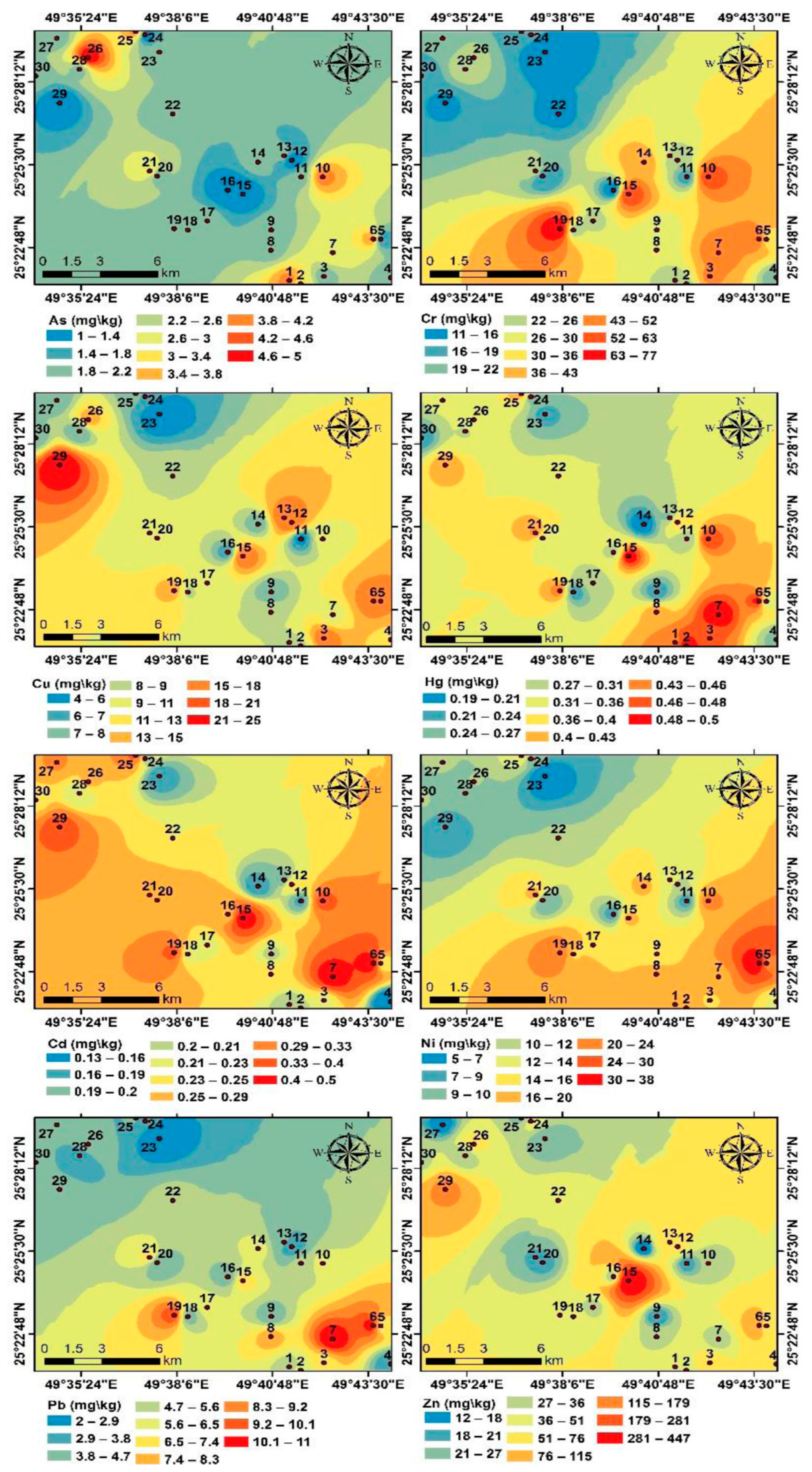
3.2. Distribution and Contamination of Potentially Toxic Elements
3.3. Risk Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Su, C.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, W.J. A review on heavy metal contamination in the soil worldwide: Situation, impact and remediation techniques. Environ. Skept. Crit. 2014, 3, 24–38. [Google Scholar]
- Nour, H.E.; El-Sorogy, A.S. Heavy metals contamination in seawater, sediments and seashells of the Gulf of Suez, Egypt. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.J.; Jiang, F.B.; Ou, J.F. Global pesticide consumption and pollution: With China as a focus. Proc. Int. Acad. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2011, 1, 125–144. [Google Scholar]
- Alfaifi, H.J.; El-Sorogy, A.S.; Qaysi, S.; Kahal, A.; Almadani, S.; Alshehri, F.; Zaidi, F.K. Evaluation of heavy metal contamination and groundwater quality along the Red Sea coast, southern Saudi Arabia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 163, 111975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Arsenic, Metals, Fibers and Dusts. A Review of Human Carcinogens; World Health Organization: Lyon, France, 2012; Volume 100C.
- Shahid, M.; Niazi, N.K.; Dumat, C.; Naidu, R.; Khalid, S.; Rahman, M.M.; Bibi, I. A metal analysis of the distribution, sources and health risks of arsenic contaminated groundwater in Pakistan. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.A.; Faruquee, M.H.; Khan, M.H. Twenty years of arsenic contamination and Arsenicosis patients in a village of Bangladesh. Am. J. Public Health Res. 2020, 8, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyothi, N.R. Heavy Metal Sources and Their Effects on Human Health. In Heavy Metals—Their Environmental Impacts and Mitigation; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyothi, N.R.; Mohamed Farook, N.A. Heavy Metal Toxicity in Public Health; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzzi, C.V.; Kruse, D.; Harrington, J.; Levin, K.; Meliker, J.R. Is urinary cadmium a biomarker of long-term exposure in humans? A review. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2016, 3, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakulski, K.M.; Hu, H.; Park, S.K. Chapter 51: Lead, cadmium and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Dement. 2020, 2, 813–830. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, I.; Hasan, M.A.; Alharbi, O.M.L. Toxic metal ions contamination in the groundwater, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2020, 14, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, A.M. The National Soil Survey and Land Classification Projects; PAO/Ministry of Agriculture and Water: Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 1991.
- Shadfan, H.; Mashhady, A.; Eter, A.; Hussen, A.A. Mineral Composition of Selected Soils in Saudi Arabia. J. Soil Nutr. Soil Sci. 1984, 147, 649–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assubaie, F.N. Assessment of the levels of some heavy metals in water in Alahsa Oasis farms, Saudi Arabia, with analysis by atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Arab. J. Chem. 2015, 8, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Barrak, S.A.; Al-Badawi, M. Properties of some salt affected soil in Al-Hassa. Saudi Arabia. Arid. Soil Res. Rehabil. 1988, 2, 85–95. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Saeedi, A.H. Characterizing physical and hydraulic properties of soils in Al-Ahsa, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 3390–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Tokhais, A.S.; Rausch, R. The hydrogeology of Al Hassa Springs. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Water Resources and Arid Environments and the 1st Arab Water Forum, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 16–19 November 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Turki, T.A.; Basahi, M.A. Assessment of ISSR Based Molecular Genetic Diversity of Hassawi Rice in Saudi Arabia. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 22, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, D.M.; Gregorio, G.B.; Oliveira, M.M.; Saibo, N.J.M. Five Novel Transcription Factors as Potential Regulators of OsNHX1 Gene Expression in a Salt Tolerant Rice Genotype. Plant Mol. Biol. 2017, 93, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, M.S.; Sallam, A.A.M.; Aleid, S.M. Assessment of soil heavy metal hazards of cultivated soil irrigated with different irrigation water qualities in Al-Hassa Oasis, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. World Rural Observ. 2014, 6, 12–22. [Google Scholar]
- AlMulla, A.A.; Dahlawi, S.; Randhawa, M.A.; Zaman Qu Chen, Y.; Faraj, T.K. Toxic Metals and Metalloids in Hassawi Brown Rice: Fate during Cooking and Associated Health Risks. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, J.B.; Mazurek, R.; Gąsiorek, M.; Zaleski, T. Pollution indices as useful tools for the comprehensive evaluation of the degree of soil contamination–A review. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 2395–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sorogy, A.S.; Youssef, M.; Al-Kahtany, K. Integrated assessment of the Tarut Island coast, Arabian Gulf, Saudi Arabia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sorogy, A.S.; Youssef, M.; Al-Kahtany, K.; Al-Otaibi, N. Distribution of intertidal molluscs along Tarut Island coast, Arabian Gulf, Saudi Arabia. Pakistan J. Zool. 2016, 48, 611–623. [Google Scholar]
- Harikrishnan, N.; Ravisankar, R.; Chandrasekaran, A.; Suresh Gandhi, M.; Kanagasabapathy, K.V.; Prasad, M.V.R.; Satapathy, K.K. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in marine sediments of East Coast of Tamil nadu affected by different pollution sources. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 121, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karrar, G.; Batanouny, K.H.; Mian, M. A Rapid Assessment of the Impacts of the Iraq-Kuwait Conflict on Terrestrial Ecosystems; Part Three: Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, a Report Prepared for the United Nations Environment Programme; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 1991; p. 67. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, M.C.; Potapov, P.V.; Pickens, A.H.; Tyukavina, A.; Hernandez-Serna, A.; Zalles, V.; Kommareddy, A. Global land use extent and dispersion within natural land cover using Landsat data. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 034050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussin, N.H.; Yusoff, I.; Wan Muhd Tahir, W.Z.; Mohamed, I.; Ibrahim, A.I.N.; Rambli, A. Multivariate statistical analysis for identifying water quality and hydrogeochemical evolution of shallow groundwater in Quaternary deposits in the Lower Kelantan River Basin, Malaysian Peninsula. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabata-Pendias, A. Trace Elements of Soils and Plants, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Taylor & Francis Group, LLC: Abingdon, UK, 2011; p. 505. [Google Scholar]
- Alharbi, T.; El-Sorogy, A.S. Spatial distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals pollution in soils of marine origin in central Saudi Arabia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 170, 112605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Boghdady, A.A.; Hassanein, K.M.A. Chemical analysis and environmental impact of heavy metals in soil of wadi Jazan area, southwest of Saudi Arabia. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17, 7067–7084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarifi, S.S.; El-Sorogy, A.S.; Al-kahtany, K.; Alotaibi, M. Contamination and environmental risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in soils of palm farms in Northwest Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caeiro, S.; Costa, M.H.; Ramos, T.B.; Fernandes, F.; Silveira, N.; Coimbra, A.; Medeiros, G.; Painho, M. Assessing heavy metal contamination in Sado estuary sediment: An index analysis approach. Ecol. Indic. 2005, 5, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, J.; Mazurek, R.; Gasiorek, M.; Setlak, M.; Zaleski, T.; Waroszewski, J. Soil pollution indices conditioned by medieval metallurgical activity: A case study from Krakow (Poland). Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 1023–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissmannová, H.D.; Pavlovský, J. Indices of soil contamination by heavy metals –methodology of calculation for pollution assessment (minireview). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitagishi, K.; Yamane, I. Heavy Metal Pollution in Soils of Japan; Japan Science Society Press: Tokyo, Japan, 1981; p. 302. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Kahtany, K.; El-Sorogy, A.S.; Al-Kahtany, F.; Youssef, M. Heavy metals in mangrove sediments of the central Arabian Gulf shoreline, Saudi Arabia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabee, A.M.; Al-Fatlawy, Y.F.; Nameer, M. Using Pollution Load Index (PLI) and geoaccumulation index (I-Geo) for the assessment of heavy metals pollution in Tigris River sediment in Baghdad Region. Al-Nahrain. J. Sci. 2011, 14, 108–114. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.S.; Ahmed, M.K.; Liyana, E.; Hossain, M.S.; Jolly, Y.N.; Kabir, M.J.; Akter, S.; Rahman, M.S. A case study on metal contamination in water and sediment near a coal thermal power plant on the eastern coast of Bangladesh. Environments 2021, 8, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nour, H.N.; Alshehri, F.; Sahour, H.; El-Sorogy, A.S.; Tawfik, M. Assessment of heavy metal contamination and health risk in the coastal sediments of Suez Bay, Gulf of Suez, Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2022, 195, 104663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sorogy, A.S.; Attiah, A. Assessment of metal contamination in coastal sediments, seawaters and bivalves of the Mediterranean Sea coast, Egypt. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Tang, W.; Chen, G.; Lu, Y.; Feng, C.; Tu, X.M. Correlation and agreement: Overview and clarification of competing concepts and measures. Shanghai Arch. Psychiatry 2016, 28, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, T.; Al-Kahtany Kh Nour Hamdy, H.E.; Giacobbe, S.; El-Sorogy, A.S. Contamination and health risk assessment of arsenic and chromium in coastal sediments of Al-Khobar area, Arabian Gulf, Saudi Arabia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 185, 114255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sorogy, A.S.; Youssef, M.; Al-Kahtany, K.; Saleh, M.M. Distribution, source, contamination, and ecological risk status of heavy metals in the Red Sea-Gulf of Aqaba coastal sediments, Saudi Arabia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 158, 111411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, T.; Alfaifi, H.; Almadani, S.; El-Sorogy, A. Spatial distribution and metal contamination in the coastal sediments of Al-Khafji area, Arabian Gulf, Saudi Arabia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolliffe, I.T.; Cadima, J. Principal component analysis: A review and recent developments. Philos. Trans. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2016, 374, 20150202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alharbi, T.; El-Sorogy, A. Assessment of metal contamination in coastal sediments of Al-Khobar area, Arabian Gulf, Saudi Arabia. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2017, 129, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, T.; Ahmad, N.; Mashiatullah, A. Heavy metals contamination and ecological risk assessment in surface sediments of Namal Lake, Pakistan. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2018, 27, 675–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahal, A.; El-Sorogy, A.S.; Qaysi, S.; Almadani, S.; Kassem, O.M.; Al-Dossari, A. Contamination and ecological risk assessment of the Red Sea coastal sediments, southwest Saudi Arabia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 154, 111125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| EF | EF < 1 | No enrichment | CF | Cf < 1 | Low contamination |
| EF < 3 | Minor enrichment | 1 ≤ Cf <3 | Moderate contamination | ||
| EF = 3–5 | Moderate enrichment | 3 ≤ Cf < 6 | Considerable contamination | ||
| EF = 5–10 | Moderately severe enrichment | Cf ≥ 6 | Very high contamination | ||
| EF = 10–25 | Severe enrichment | PLI | PLI < 1 | Unpolluted | |
| EF = 25–50 | Very severe enrichment | PLI > 1 | Polluted | ||
| EF > 50 | Extremely severe enrichment | Eri and RI | Eri < 40 and Ri < 150 | low ecological risk | |
| Igeo | I-geo < 0 | Unpolluted | 40 ≤ Eri < 80 and 150 ≤ RI < 300 | Moderate ecological risk | |
| 0 < Igeo < 1 | Unpolluted to moderately polluted | 80 ≤ Eri < 160 and 300 ≤ Ri < 600 | Considerable ecological risk | ||
| 1 < Igeo < 2 | Moderately polluted | 160 ≤ Eri < 320 | High ecological risk | ||
| 2 < Igeo < 3 | Moderately to strongly polluted | Eri > 320 and RI ≥ 600 | Very high ecological risk | ||
| 3 < Igeo > 4 | Strongly polluted | ||||
| 4 < Igeo < 5 | Strongly to very strongly polluted | ||||
| Igeo > 5 | Very strongly polluted conditions |
| Location and References | Ni | Zn | Cu | As | Cd | Hg | Pb | Cr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al-Ahsa, Eastern Saudi Arabia (present study) | 14.53 | 54.43 | 10.83 | 2.27 | 0.26 | 0.35 | 5.23 | 28.67 |
| Maximum allowable concentrations [32] | 60 | 300 | 150 | 20 | 5 | 5 | 300 | 200 |
| Al Uyaynah soil, Saudi Arabia [33] | 19.25 | 64.33 | 10.56 | 13.8 | 0.38 | 0.11 | 28.48 | 30.18 |
| Wadi Jazan, Saudi Arabia [34] | 48.66 | 75.80 | 72.85 | 14.13 | 20.97 | 19.41 | 77.22 | |
| Al-Ammariah area, northwest Riyadh [35] | 26.94 | 52.16 | 11.36 | 3.78 | 0.25 | 0.50 | 5.08 | 19.97 |
| EF | Igeo | CF | Eri | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min. | Max. | Avg. | Min. | Max. | Aver. | Min. | Max. | Aver. | Min. | Max. | Aver. | |
| Pb | 0.45 | 2.24 | 1.05 | −2.01 | −0.31 | −1.16 | 0.10 | 0.55 | 0.26 | 0.50 | 2.75 | 1.33 |
| Cd | 1.89 | 6.38 | 3.56 | -0.55 | 0.80 | 0.10 | 0.43 | 1.67 | 0.88 | 13.00 | 50.00 | 26.38 |
| Zn | 0.63 | 20.01 | 2.19 | −1.78 | 1.84 | −0.69 | 0.13 | 4.71 | 0.55 | 0.13 | 4.71 | 0.69 |
| Ni | 0.39 | 1.71 | 1.00 | −2.16 | −0.14 | −1.21 | 0.09 | 0.66 | 0.25 | 0.52 | 3.93 | 1.55 |
| Cu | 0.40 | 1.70 | 0.93 | −4.08 | −1.43 | −2.84 | 0.09 | 0.56 | 0.23 | 0.44 | 2.78 | 1.23 |
| As | 1.78 | 12.29 | 5.41 | −1.35 | 0.97 | −0.33 | 0.59 | 2.94 | 1.32 | 5.88 | 29.41 | 13.60 |
| Hg | 8.41 | 26.50 | 17.27 | 1.12 | 2.08 | 1.68 | 2.29 | 6.02 | 4.24 | 91.57 | 240.96 | 169.58 |
| Cr | 0.55 | 3.77 | 1.37 | −1.73 | 0.21 | −0.95 | 0.13 | 0.93 | 0.33 | 0.27 | 1.86 | 0.71 |
| As | Cr | Cu | Hg | Cd | Ni | Pb | Zn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | 1 | |||||||
| Cr | 0.182 | 1 | ||||||
| Cu | −0.105 | 0.344 | 1 | |||||
| Hg | 0.383 * | 0.550 ** | 0.463 * | 1 | ||||
| Cd | 0.275 | 0.594 ** | 0.410 * | 0.704 ** | 1 | |||
| Ni | 0.396 * | 0.718 ** | 0.293 | 0.556 ** | 0.514 ** | 1 | ||
| Pb | 0.302 | 0.768 ** | 0.272 | 0.634 ** | 0.650 ** | 0.813 ** | 1 | |
| Zn | −0.221 | 0.403 * | 0.531 ** | 0.359 | 0.467 ** | 0.160 | 0.188 | 1 |
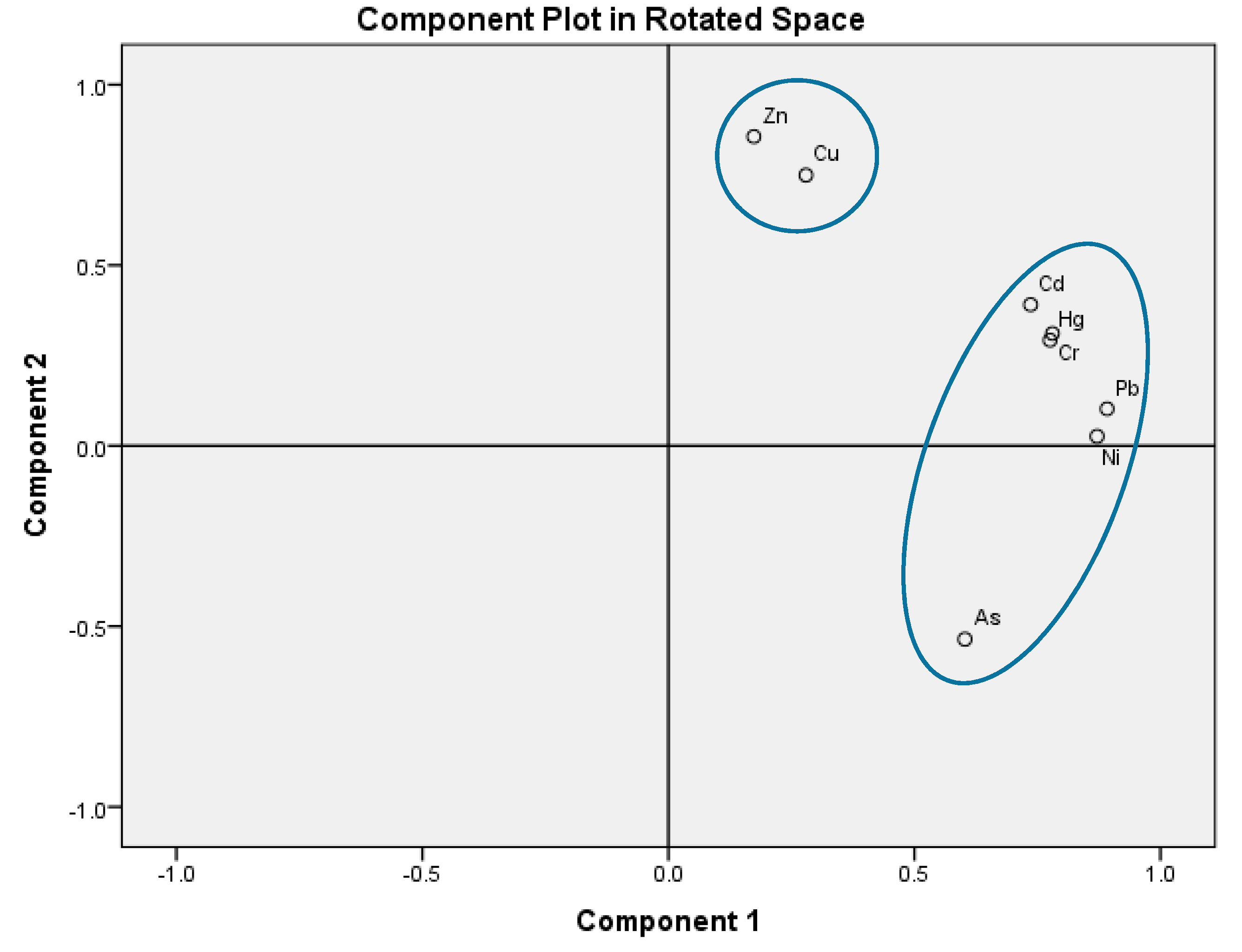
| Component | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | |
| As | 0.355 | −0.724 |
| Cr | 0.840 | −0.007 |
| Cu | 0.542 | 0.588 |
| Hg | 0.829 | −0.023 |
| Cd | 0.829 | 0.084 |
| Ni | 0.816 | −0.305 |
| Pb | 0.864 | −0.242 |
| Zn | 0.484 | 0.727 |
| % of Variance | 51.846 | 19.475 |
| Cumulative % | 51.846 | 71.321 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alharbi, T.; El-Sorogy, A.S. Risk Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Agricultural Soils of Al-Ahsa Oasis, Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2023, 15, 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010659
Alharbi T, El-Sorogy AS. Risk Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Agricultural Soils of Al-Ahsa Oasis, Saudi Arabia. Sustainability. 2023; 15(1):659. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010659
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlharbi, Talal, and Abdelbaset S. El-Sorogy. 2023. "Risk Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Agricultural Soils of Al-Ahsa Oasis, Saudi Arabia" Sustainability 15, no. 1: 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010659
APA StyleAlharbi, T., & El-Sorogy, A. S. (2023). Risk Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Agricultural Soils of Al-Ahsa Oasis, Saudi Arabia. Sustainability, 15(1), 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010659






