Digital Economy Development and Green Economic Efficiency: Evidence from Province-Level Empirical Data in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Digital Economy Development
2.2. Green Economic Efficiency
2.3. Digital Economy Development and Green Economic Efficiency
3. Theoretical Analysis and Hypothesis Development
3.1. Direct Impact of the Digital Economy Development on the Green Economic Efficiency
3.2. Indirect Effects of the Digital Economy Development on Green Economic Efficiency
3.2.1. Mediating Effect of Human Capital
3.2.2. Mediating Effect of Industrial Structure Upgrading
3.2.3. Mediating Effect of Technological Innovation
3.3. Spatial Impact of the Digital Economy Development on the Green Economic Efficiency
4. Methods and Data
4.1. Models
4.1.1. Baseline Model
4.1.2. Mechanism Test
4.1.3. Spatial Durbin Model
4.2. Explanatory Variables
4.2.1. Construction of the Digital Economy Development Index System
4.2.2. Spatial and Temporal Evolutionary Characteristics of the Digital Economy Development
4.3. Explained Variables
4.3.1. Measurement of the Green Economic Efficiency
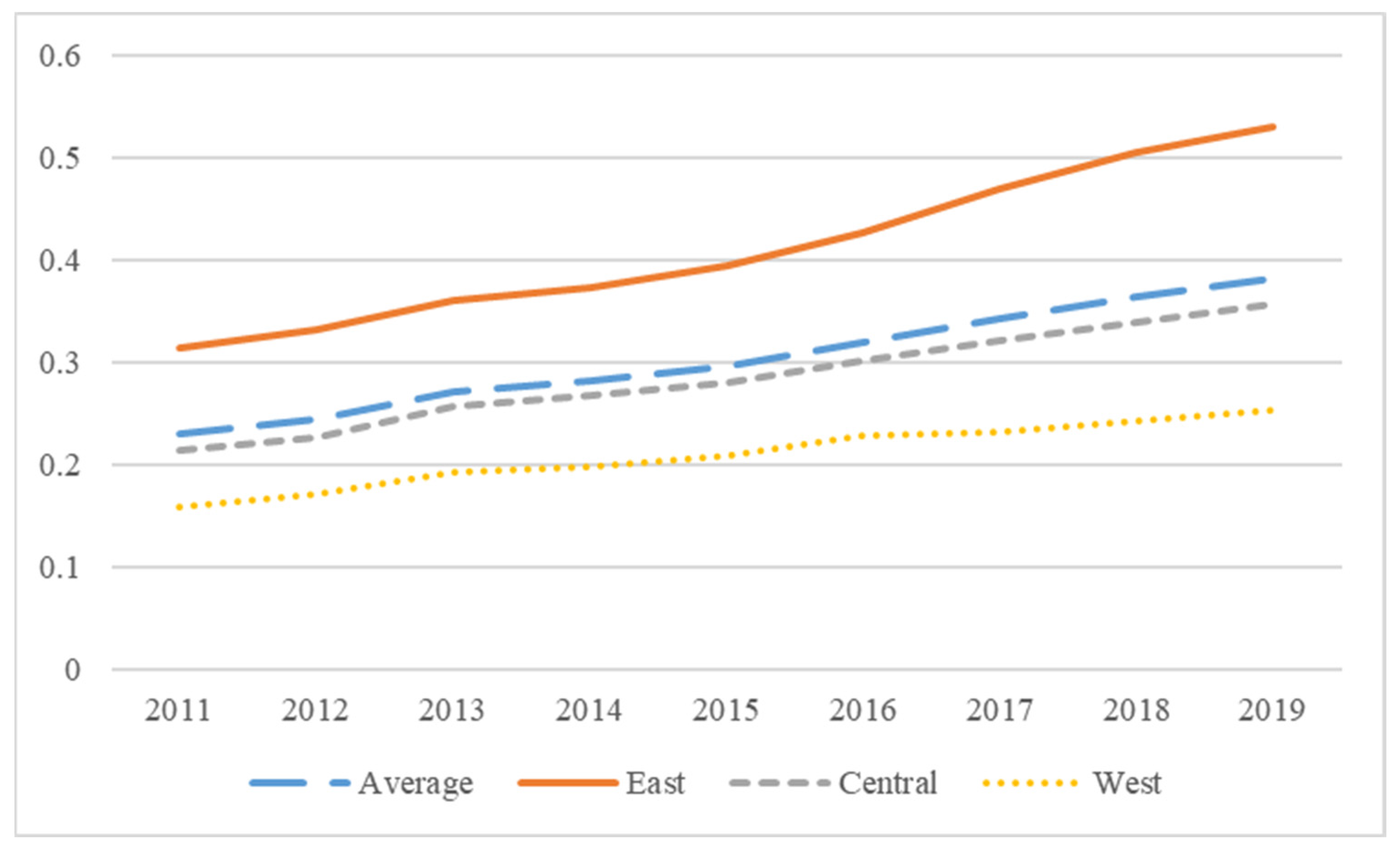
4.3.2. Spatial and Temporal Evolutionary Characteristics of the Green Economic Efficiency
4.4. Mechanism and Control Variables
4.4.1. Mechanism Variables
4.4.2. Control Variables
4.5. Data
5. Empirical Analysis
5.1. Baseline Regression
5.2. Robustness Tests
5.2.1. Replacement of the Explanatory Variable Measurement Indicators
5.2.2. Lagged Effects Test
5.3. Endogeneity Discussion
5.4. Heterogeneity Analysis
5.4.1. Analysis of the Regional Heterogeneity
5.4.2. Heterogeneity Analysis of the Digital Economy Development Levels
5.4.3. Dimensional Heterogeneity Analysis
5.4.4. Policy Intensity Heterogeneity Analysis
5.5. Mechanism Analysis
5.5.1. Digital Economy Development, Human Capital, and Green Economic Efficiency
5.5.2. Digital Economy Development, Industrial Structure Upgrading, and Green Economic Efficiency
5.5.3. Digital Economy Development, Technological Innovation, and Green Economic Efficiency
5.6. Analysis of the Spatial Spillover Effects
6. Conclusions and Policy Recommendations
6.1. Conclusions
6.2. Policy Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bukht, R.; Heeks, R. Defining, conceptualising and measuring the digital economy. Dev. Inform. Work. Pap. 2017, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardonakulovich, B.M.; Bulturbayevich, M.B. Economic growth: Quality and the digital economy. Acad. Globe Inderscience Res. 2020, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.Y.; Whinston, A.B. The future of the digital economy. In Handbook on Electronic Commerce; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 25–52. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, W.J.; Sun, B. W Digital Economy Promotes High-quality Economic Development: A Theoretical Analysis Framework. Economist 2019, 02, 66–73. [Google Scholar]
- Niyazbekova, S.U.; Moldashbayeva, L.P.; Zhumatayeva, B.A.; Mezentseva, T.M.; Shirshova, L.V. Digital economy development as an important factor for the country’s economic growth. In Socio-Economic Systems: Paradigms for the Future; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 361–366. [Google Scholar]
- Chakpitak, N.; Maneejuk, P.; Chanaim, S.; Sriboonchitta, S. Thailand in the era of digital economy: How does digital technology promote economic growth? In Proceedings of the International Conference of the Thailand Econometrics Society, International Conference of the Thailand Econometrics Society, Chiang Mai, Thailand, 10–12 January 2018; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 350–362. [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson, B. The Digital Economy: What is new and what is not? Struct. Chang. Econ. Dyn. 2004, 15, 245–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Peng, D.; Wen, H.; Song, H. Does the Digital Economy Promote Upgrading the Industrial Structure of Chinese Cities? Sustainability 2022, 14, 10235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, D.; Lyu, L.; Huang, W.; Yao, W. Digital Economy and the Upgrading of the Global Value Chain of China’s Service Industry. J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2022, 17, 1279–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogli, N.S.F.; Ogli, R.B.O. In The Context of Developing the Digital Economy Modern Forms of Employment. Eurasian Sci. Her. 2021, 1, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Valenduc, G. New forms of work and employment in the digital economy. In The Deconstruction of Employment as a Political Question; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 63–80. [Google Scholar]
- Sovbetov, Y. Impact of digital economy on female employment: Evidence from Turkey. Int. Econ. J. 2018, 32, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, R.; Li, J.Y.; Ge, T. How do price distortions of fossil energy sources affect China’s green economic efficiency? Energy 2021, 232, 121017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, S.; Fan, Z. Modeling the role of environmental regulations in regional green economic efficiency of China: Empirical evidence from super efficiency DEA-Tobit model. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 261, 110227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, H. Analysis on regional difference and convergence of the efficiency of China’s green economy based on DEA. Economist 2010, 02, 46–54. [Google Scholar]
- Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of super-efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2002, 143, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.-j.; Zeng, L.-e.; Lu, H.-y.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, H.-y.; Wei, X.-Y. Green economic efficiency and its influencing factors in China from 2008 to 2017: Based on the super-SBM model with undesirable outputs and spatial Dubin model. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Liang, L. Green economic efficiency in the Yangtze River Delta: Spatiotemporal evolution and influencing factors. Ecosyst. Health Sustain. 2019, 5, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Wang, P.; Zhu, B. Provincial green economic efficiency of China: A non-separable input–output SBM approach. Appl. Energy 2016, 171, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S. Fuzzy-based multi-criteria decision analysis of environmental regulation and green economic efficiency in a post-COVID-19 scenario: The case of China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 30675–30701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, N.; He, J.Y.; Li, B.Y. A Study on the Impact of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Digital Service Economy on the Efficiency of Green Economy. Macroeconomics 2022, 7, 105–119. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Q.Y.; Xu, W.J. Analysis of the spatial and temporal effects of new urbanization construction on green economic efficiency. Inq. Into Econ. Issues 2017, 10, 64–72. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.; Feng, Y.; Lee, C.C.; Cen, Y. How does manufacturing agglomeration affect green economic efficiency? Energy Econ. 2020, 92, 104944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.J.; Guo, A.J.; Zhong, F.L.; Wang, X.B. Can the high-tech industrial agglomeration improve the green economic efficiency of the region? China Population. Resour. Environ. 2018, 09, 93–101. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, D.; Zhu, Q. Innovation in emerging economies: Research on the digital economy driving high-quality green development. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 145, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S. Can Environmental Information Disclosure Improve Urban Green Economic Efficiency? New Evidence from the Mediating Effects Model. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 747, 920879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, S.; Wan, X.; Yao, Y. Study on the effect of digital economy on high-quality economic development in China. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, F.; Hu, M.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Pan, Y. How does digital economy affect carbon emissions? Evidence from global 60 countries. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 852, 158401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Ran, Q.; Wu, H.; Irfan, M.; Ahmad, M. Energy structure, digital economy, and carbon emissions: Evidence from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 64606–64629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; He, J. Digital economy, technological innovation, and green economic efficiency—Empirical evidence from 277 cities in China. Manag. Decis. Econ. 2022, 43, 616–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhriddinovna, A.N. The Impact of The Digital Economy on Resource Consumption. Eurasian J. Learn. Acad. Teach. 2021, 1, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P. Relationship between the digital economy, resource allocation and corporate carbon emission intensity: New evidence from listed Chinese companies. Environ. Res. Commun. 2022, 4, 075005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner-Kozlova, E.O.; Guman, O.M. Digitalization of environmental monitoring as an enabler of circular economy transition. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Scientific and Practical Conference “Modern Management Trends and the Digital Economy: From Regional Development to Global Economic Growth” (MTDE 2020), Yekaterinburg, Russia, 16–17 April 2020; Atlantis Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 1282–1286. [Google Scholar]
- Hampton, S.E.; Strasser, C.A.; Tewksbury, J.J.; Gram, W.K.; Budden, A.E.; Batcheller, A.L.; Duke, C.S.; Porter, J.H. Big data and the future of ecology. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2013, 11, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.H.; Choi, M.J. Ecological views of big data: Perspectives and issues. Telemat. Inform. 2015, 32, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, N.; Wen, H. Digital economy and environmental quality: Evidence from 217 cities in China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, I.; Goloshchapova, L.; Ivashina, N.; Shichiyakh, R.; Petrova, L.; Tkachev, B. The paradigm of human capital development capable of adapting innovations in the transition to a digital economy. Int. J. Civ. Eng. Technol. 2019, 10, 1408–1417. [Google Scholar]
- Grigorescu, A.; Pelinescu, E.; Ion, A.E.; Dutcas, M.F. Human capital in digital economy: An empirical analysis of Central and Eastern European Countries from the European Union. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdurakhmanova, G.; Shayusupova, N.; Irmatova, A.; Rustamov, D. The role of the digital economy in the development of the human capital market. Int. J. Psychol. Rehabilit. 2020, 7, 8043–8051. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.B.; Xu, Q.R. Research on Cultivation Mode and Countermeasures of Innovative Talents under Background of Digital Economy. Sci. Technol. Manag. Res. 2019, 8, 116–121. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, H.; You, J. The Heterogeneous Impacts of Human Capital on Green Total Factor Productivity: Regional Diversity Perspective. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 713562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Xu, M.; Ma, S. The effect of the spatial heterogeneity of human capital structure on regional green total factor productivity. Struct. Chang. Econ. Dyn. 2021, 59, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Guo, S.F. Formal Environmental Regulation, Human Capital, and Green Total Factor Productivity. Macroeconomics 2021, 5, 155–169. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, W.; Liu, H.; Pan, F. Digital economy, industry heterogeneity, and service industry resource allocation. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhong, K. Digital economy development, industrial structure upgrading and green total factor productivity: Empirical evidence from China’s cities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ye, W.; Huo, C.; James, K. Environmental regulations, the industrial structure, and high-quality regional economic development: Evidence from China. Land Use Policy 2020, 9, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teece, D.J. Next-generation competition: New concepts for understanding how innovation shapes competition and policy in the digital economy. JL Econ. Pol’y 2012, 9, 97. [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb, A.; Tucker, C. Digital economics. J. Econ. Lit. 2019, 57, 3–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.; Fang, D.; Sun, L.; Luo, Q. Natural resources utilization efficiency under the influence of green technological innovation. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 126, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brousseau, E.; Curien, N. Internet and Digital Economics: Principles, Methods and Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.C. Targeting Path and Policy Supply for the High Quality Development of China’s Digital Economy. Economist 2019, 6, 52–61. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, D.; Zhou, J. Digital economy and carbon emission performance: Evidence at China’s city level. Energy Policy 2022, 165, 112927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Nie, L.; Sun, H.; Sun, W.; Taghizadeh-Hesary, F. Digital finance, green technological innovation and energy-environmental performance: Evidence from China’s regional economies. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 327, 129458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Chen, W. Environmental regulation, green innovation, and industrial green development: An empirical analysis based on the Spatial Durbin model. Sustainability 2018, 10, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Ma, Y.R. Has the development of digital economy improved the efficiency of China’s green economy? China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2022, 3, 72–85. [Google Scholar]
- Nunn, N.; Qian, N. US food aid and civil conflict. Am. Econ. Rev. 2014, 104, 1630–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeSage, J.; Pace, R.K. Introduction to Spatial Econometrics; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.X.; Zhou, J.P.; Liu, C.J. The impact of digital economy on urban carbon emissions: Based on the analysis of spatial effects. Geogr. Res. 2022, 41, 111–129. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.Y.; Xin, L.; Li, J.Y.; Sun, H. The Impact of Renewable Energy Technology Innovation on Industrial Green Transformation and Upgrading: Beggar Thy Neighbor or Benefiting Thy Neighbor. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Main Index | Primary Index | Secondary Index | Variable Selection |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Economy Development | Digital Industrialization | Internet and Telecommunications | Internet broadband access ports/million |
| Ratio of the total telecom business to value added of a tertiary industry | |||
| Fixed telephone penetration rate | |||
| Electronic Information Manufacturing | Computer, communication and other electronic equipment manufacturing employment | ||
| Ratio of the main revenue of computer, communication, and other electronic equipment manufacturing industries to the main business revenue of industrial enterprises above the scale | |||
| Software and Information Technology Services | Ratio of the software business income to value added of a tertiary industry | ||
| Number of employees in the information transmission, software, and information technology services | |||
| Number of software companies | |||
| Industry Digitization | Digital Talent | Number of degrees awarded per 10,000 people | |
| Number of full-time college teachers per 10,000 people | |||
| Digital Infrastructure Investment | Information transmission, computer services, and software industry fixed asset investment (CNY billion) | ||
| Length of long-distance fiber optic cable lines (km) | |||
| Digital Trading | Ratio of new product sales revenue to main business revenue of industrial enterprises above the scale | ||
| Express delivery business volume (million pieces) | |||
| Ratio of the subtotal original insurance premium income to the value added of a tertiary industry |
| Type | Index | Specific Content |
|---|---|---|
| Input elements | Energy input | Total energy consumption (million tons of standard coal) |
| Labor input | Number of employees in units, private and self-employed, at the end of the year | |
| Capita input | Capital stock (CNY billions) | |
| Expected outputs | Economic development | Gross domestic product (CNY billion ) |
| Benefit fairness | Average wage of urban residents (CNY) | |
| Environment optimization | Park green space area (hectares) | |
| Non-expected outputs | Sulfur dioxide | Sulfur dioxide emissions (million tons) |
| Industrial wastewater | Industrial wastewater discharge (million tons) | |
| Industrial fume and dust | Industrial fume emissions (m3) |
| Variables | Observations | Mean | Standard | Minimum | Maximum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Explained variables | Green economic efficiency (GEE) | 270 | 0.2941 | 0.1358 | 0.0649 | 1.0000 |
| Explanatory variables | Digital economy development (Dig) | 270 | 0.2543 | 0.1670 | 0.0135 | 0.9843 |
| Mechanism variables | Human capital (hc) | 270 | 0.0086 | 0.0050 | 0.0006 | 0.0214 |
| Industrial structure upgrading (isu) | 270 | 1.2561 | 0.6925 | 0.5271 | 5.0221 | |
| Technology innovation (ti) | 270 | 0.0053 | 0.0071 | 0.0001 | 0.0473 | |
| Control variables | Population size (pop) | 270 | 3.5618 | 0.3194 | 2.7545 | 4.0548 |
| Economic development level (agdp) | 270 | 0.6985 | 0.3102 | 0.2304 | 4.6733 | |
| Government behavior (gov) | 270 | 0.2467 | 0.1019 | 0.1103 | 0.6269 | |
| Degree of external openness (open) | 270 | 0.0597 | 0.1150 | 0.0025 | 0.8965 | |
| Urbanization (urban) | 270 | 1.7485 | 0.0883 | 1.5441 | 1.9523 | |
| Baseline Regression | Robustness Tests | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Substitution of Explanatory Variables | Lag 1 Period | Lag 2 Periods | |||
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | |
| Dig | 0.3920 *** | 0.4703 *** | 0.1076 *** | 0.4987 *** | 0.5033 *** |
| (0.0642) | (0.1462) | (0.0273) | (0.1144) | (0.0931) | |
| pop | −0.0120 | −0.0225 | 0.2420 | 0.738 | |
| (0.0082) | (0.0541) | (0.5458) | (0.5713) | ||
| agdp | 0.0023 | 0.0091 * | 0.0181 ** | 0.0088 ** | |
| (0.0042) | (0.0049) | (0.0065) | (0.0037) | ||
| gov | −0.5091 ** | −0.1026 | 0.2276 | 0.0847 | |
| (0.1963) | (0.1047) | (0.2004) | (0.1616) | ||
| open | 0.2835 *** | 0.6011 *** | 0.2995 *** | 0.2710 *** | |
| (0.0927) | (0.0675) | (0.0678) | (0.0494) | ||
| urban | 0.5932 *** | 0.4207 *** | −0.3482 | 0.4847 *** | |
| (0.1734) | (0.1404) | (0.3558) | (0.1435) | ||
| Individual fixed effects | NO | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Time fixed effects | NO | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| N | 270 | 270 | 270 | 270 | 270 |
| R2 | 0.5387 | 0.6650 | 0.7501 | 0.6962 | 0.7014 |
| Stage 1 | Stage 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | |
| IV | 0.0784 *** | 0.0619 *** | ||
| (0.0101) | (0.0126) | |||
| Dig | 0.3703 *** | 0.5092 *** | ||
| (0.1000) | (0.1202) | |||
| pop | 0.7730 *** | 0.0196 | ||
| (0.1218) | (0.0384) | |||
| agdp | 0.1064 *** | 0.0018 | ||
| (0.0179) | (0.0062) | |||
| gov | −0.0156 *** | −0.2140 ** | ||
| (0.0019) | (0.1004) | |||
| open | 0.0702 | 0.5393 *** | ||
| (0.0805) | (0.0580 | |||
| urban | −0.2330 | 0.2374 * | ||
| (0.5472) | (0.1303) | |||
| Control | NO | YES | NO | YES |
| Individual fixed effects | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Time fixed effects | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Gragg–Donald Wald F | 36.78 | 36.78 | — | — |
| N | 270 | 270 | 270 | 270 |
| R² | 0.5291 | 0.6923 | 0.7725 | 0.8034 |
| Regional Heterogeneity | Heterogeneity in the Digital Economy Development Levels | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| East | Central | West | High Level | Low Level | |
| (10) | (11) | (12) | (13) | (14) | |
| Dig | 0.3894 *** | 0.2108 ** | 0.1229 | 0.4876 ** | 0.0211 |
| (0.0951) | (0.0762) | (0.1925) | (0.1960) | (0.0432) | |
| Pop | −1.9059 ** | 0.0039 | −1.0985 | 0.0908 | −0.0006 |
| (0.6599) | (0.0045) | (1.6914) | (0.8133) | (0.0055) | |
| Agdp | −0.0011 | 0.0000 | 0.8894 * | 0.0110 | 0.0094 *** |
| (0.0009) | (0.0017) | (0.4765) | (0.0108) | (0.0019) | |
| Gov | −0.2729 | −0.2276 ** | 1.0587 | 0.0633 | 0.0064 |
| (0.1613) | (0.1028) | (0.6479) | (0.1738) | (0.0812) | |
| Open | 0.3803*** | 0.2010 | −0.3840 | 0.2724 ** | 0.3309 * |
| (0.1161) | (0.1436) | (0.6307) | (0.0998) | (0.1896) | |
| Urban | 0.4491 | 0.2758 | −2.2379 | −0.7998 | 0.2539 |
| (0.2979) | (0.2343) | (1.4666) | (0.8690) | (0.1418) | |
| Individual fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Time fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 99 | 72 | 99 | 162 | 108 |
| R2 | 0.7030 | 0.9316 | 0.8546 | 0.6536 | 0.8484 |
| Dimensional Heterogeneity | Policy Heterogeneity | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Industry Digitization | Digital Industrialization | Experimental Group | Control Group | |
| (15) | (16) | (17) | (18) | |
| Dig | 0.1865 *** | 0.3699 *** | 0.4735 *** | 0.1235 |
| (0.0426) | (0.0662) | (0.1410) | (0.1332) | |
| pop | 1.0214 * | −0.2099 | −0.1299 | −0.0167 ** |
| (0.5637) | (0.8531) | (1.8531) | (0.0059) | |
| agdp | 0.0171 | 0.0110 | 0.0119 | −0.0027 |
| (0.0126) | (0.0124) | (0.0114) | (0.0035) | |
| gov | 0.2498 | −0.4276 *** | 0.0948 | −0.1633 |
| (0.2795) | (0.1212) | (0.2645) | (0.1089) | |
| open | 0.3291 *** | 0.2648 *** | 0.3565 *** | 0.1762 *** |
| (0.0908) | (0.0910) | (0.1024) | (0.0239) | |
| urban | −0.6078 | −0.6213 | −0.8048 | −0.5850 |
| (0.4359) | (0.4995) | (0.9271) | (0.4045) | |
| Individual fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Time fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 270 | 270 | 90 | 190 |
| R2 | 0.5810 | 0.6632 | 0.6406 | 0.7012 |
| GEE | hc | GEE | isu | GEE | ti | GEE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (19) | (20) | (21) | (22) | (23) | (24) | (25) | |
| Dig | 0.4703 *** | 0.1056 *** | 0.2073 ** | 1.1298 *** | 0.2868 *** | 0.5302 *** | 0.3034 *** |
| (0.1462) | (0.0011) | (0.1005) | (0.3117) | (0.0746) | (0.0808) | (0.0789) | |
| hc | 0.1071 *** | ||||||
| (0.0166) | |||||||
| isu | 0.1624 ** | ||||||
| (0.0778) | |||||||
| ti | 0.1618 * | ||||||
| (0.0906) | |||||||
| pop | −0.0120 | 0.0021 *** | 0.0048 | 1.1430 *** | 0.1736 * | 2.9146 *** | −0.3925 |
| (0.0082) | (0.0003) | (0.0258) | (0.0604) | (0.0868) | (0.9190) | (0.8416) | |
| agdp | 0.0023 | 0.0000 | 0.0025 | −0.0132 | 0.0044 | 0.0088 | 0.0082 * |
| (0.0042) | (0.0001) | (0.0044) | (0.0185) | (0.0036) | (0.0093) | (0.0042) | |
| gov | −0.0591 | −0.0055 ** | −0.1031 | 2.8925 *** | −0.5288 * | −0.6141 ** | 0.3613 |
| (0.0963) | (0.0020) | (0.1166) | (0.7550) | (0.2624) | (0.2584) | (0.2473) | |
| open | 0.2835 *** | −0.0011 * | 0.2746 *** | 0.5257 ** | 0.1982 ** | −0.0373 | 0.3071 *** |
| (0.0927) | (0.0006) | (0.0933) | (0.2356) | (0.0853) | (0.0589) | (0.0548) | |
| urban | −0.5932 | 0.0113 ** | −0.5024 | 0.7343 | −0.7124 | 1.7253 *** | −0.9238 |
| (0.5734) | (0.0055) | (0.4899) | (1.2376) | (0.4518) | (0.3839) | (0.6392) | |
| Individual fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Time fixed effects | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 270 | 270 | 270 | 270 | 270 | 270 | 270 |
| R2 | 0.6650 | 0.6884 | 0.6680 | 0.7436 | 0.7429 | 0.8743 | 0.7188 |
| (26) | (27) | (28) | |
| Dig | 0.4895 *** | 0.5033 *** | 0.4732 *** |
| (0.0623) | (0.0564) | (0.0603) | |
| W × Dig | 0.1875 *** | 0.1006 *** | 0.1611 *** |
| (0.0568) | (0.0212) | (0.0500) | |
| Direct effect | 0.6823 *** | 0.6000 *** | 0.5913 *** |
| (0.1072) | (0.1069) | (0.1034) | |
| Indirect effect | 0.1398 ** | 0.2053 *** | 0.1399 *** |
| (0.0551) | (0.0550) | (0.0534) | |
| Control | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 270 | 270 | 270 |
| Log-lik | 30.6794 | 39.6977 | 36.5495 |
| R2 | 0.6046 | 0.7330 | 0.5154 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, L.; Li, J. Digital Economy Development and Green Economic Efficiency: Evidence from Province-Level Empirical Data in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010003
Kong L, Li J. Digital Economy Development and Green Economic Efficiency: Evidence from Province-Level Empirical Data in China. Sustainability. 2023; 15(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Lingzhang, and Jinye Li. 2023. "Digital Economy Development and Green Economic Efficiency: Evidence from Province-Level Empirical Data in China" Sustainability 15, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010003
APA StyleKong, L., & Li, J. (2023). Digital Economy Development and Green Economic Efficiency: Evidence from Province-Level Empirical Data in China. Sustainability, 15(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010003






