Synergistic Patterns of Urban Economic Efficiency and the Economic Resilience of the Harbin–Changchun Urban Agglomeration in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials, Methods, and Data
2.1. The Relationship between Economic Efficiency and Economic Resilience
2.2. Methods and Data
2.2.1. Super-Efficient SBM Model
2.2.2. Entropy-TOPSIS Integrated Evaluation Model
2.2.3. Improved Haken Model
2.2.4. Data Sources
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Analysis of Economic Efficiency and Economic Resilience
3.1.1. Urban Economic Efficiency
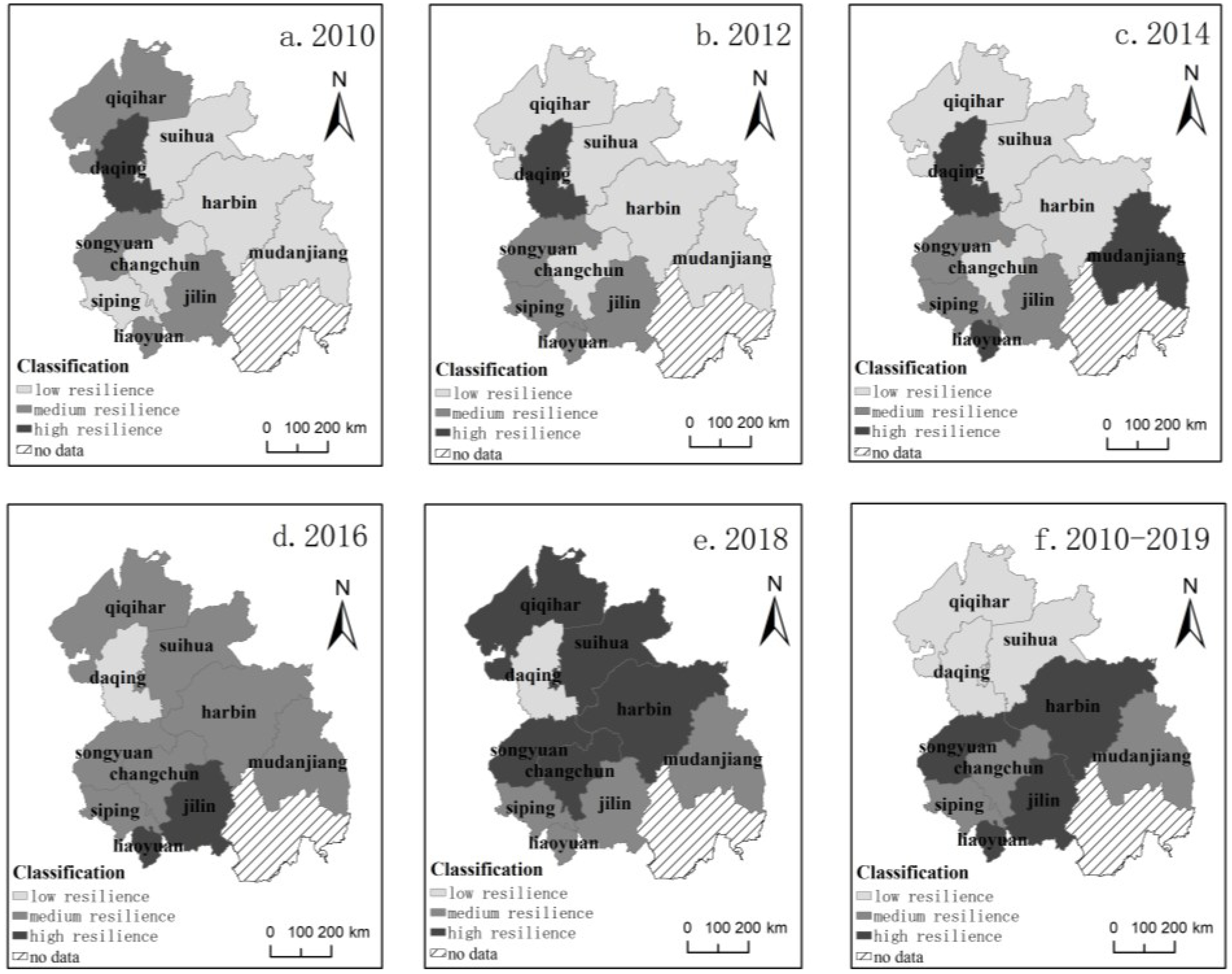
3.1.2. Urban Economic Resilience
3.2. Synergistic Evolution of Economic Efficiency and Economic Resilience in Urban Agglomerations
3.2.1. Model Construction and Identification of Order Parameter
3.2.2. Analysis of Spatial and Temporal Differences in the Synergistic Evolution of Economic Efficiency and Economic Resilience
3.2.3. Stage Division of the Synergistic Evolution of Economic Efficiency and Economic Resilience
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, J.W.; Wang, J.H.; Szmedra, P. Economic Efficiency and Its Influencing Factors on Urban Agglomeration—An Analysis Based on China’s Top 10 Urban Agglomerations. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.Q.; Ma, X.J. Measurement and difference analysis on economic efficiency of Chinese wide regional economy. Stat. Decis. 2019, 35, 116–120. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deilmann, C. Data Envelopment Analysis of Cities—Investigation of the Ecological and Economic Efficiency of Cities Using a Benchmarking Concept from Production Management. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 67, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Zhang, X.P.; Zhao, Y.Y. Spatiotemporal evolution of urban eco-efficiency in China and its influencing factors based on super-efficiency SBM model. J. Univ. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2021, 38, 486–493. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.; Sunley, P. On the notion of regional economic resilience: Conceptualization and explanation. J. Econ. Geogr. 2015, 15, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, P.; Graziano, P.; Dallara, A. A capacity approach to territorial resilience: The case of European regions. Ann. Reg. Sci. 2018, 60, 285–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, J.R.; Østergaard, C.R. Regional employment growth, shocks and regional industrial resilience: A quantitative analysis of the Danish ICT sector. Reg. Stud. 2015, 49, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breathnach, P.; Van Egeraat, C.; Curran, D. Regional economic resilience in Ireland: The roles of industrial structure and foreign inward investment. Reg. Stud. Reg. Sci. 2015, 2, 497–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowell, M.M. Bounce back or move on: Regional resilience and economic development planning. Cities 2013, 30, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.M.; Xiu, C.L.; Song, W. Urban spatial resilience: A review. Urban. Archit. 2018, 2018, 16–18. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xiu, C.; Song, W. Landscape-Based Assessment of Urban Resilience and Its Evolution: A Case Study of the Central City of Shenyang. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.G.; Zhang, P.Y.; Tan, J.T.; Guan, H.M. Review on the evolution of resilience concept and research progress on regional economic resilience. Hum. Geogr. 2019, 34, 1–7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziano, P.; Rizzi, P. Vulnerability and resilience in the local systems: The case of Italian provinces. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 553, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R. Regional economic resilience, hysteresis and recessionary shocks. J. Econ. Geogr. 2012, 12, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.; Sunley, P.; Gardiner, B.; Tyler, P. How regions react to recessions: Resilience and the role of economic structure. Reg. Stud. 2016, 50, 561–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.W.; Sun, X.Y. Research progress of regional economic resilience and exploration of its application in China. Econ. Geogr. 2017, 37, 1–9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brakman, S.; Garretsen, H.; Van Marrewijk, C. Regional resilience across Europe: On urbanisation and the initial impact of the Great Recession. Camb. J. Reg. Econ. Soc. 2015, 8, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, A.M.; Mur, J.; Trívez, F.J. Measuring resilience to economic shocks: An application to Spain. Ann. Reg. Sci. 2018, 60, 349–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakis, E.; Bruggeman, A. Determinants of regional resilience to economic crisis: A European perspective. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2017, 25, 1394–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahiluoto, H.; Kaseva, J. No Evidence of Trade-Off between Farm Efficiency and Resilience: Dependence of Resource-Use Efficiency on Land-Use Diversity. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, J.; Snakin, J.P. Quantifying the relationship of resilience and eco-efficiency in complex adaptive energy systems. Ecol. Econ. 2015, 120, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Arquer, M.; Ponte, B.; Pino, R. Examining the balance between efficiency and resilience in closed-loop supply chains. Cent. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2021, 30, 1307–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.; Song, W.; Xiu, C.; Liang, Z. Non-coordination in China’s urbanization: Assessment and affecting factors. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 23, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Sun, P.; Liu, H.; He, J. Spatial-temporal Evolution of the Urban-rural Coordination Relationship in Northeast China in 1990–2018. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 31, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Fang, C.; Lin, X.; Sun, S.; Li, G.; Fan, B. Evaluation of the eco-efficiency of four major urban agglomerations in coastal eastern China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 1315–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Song, Z.Y. Research framework and empirical study of input-output efficiency of resources and environment in China. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2020, 40, 1868–1877. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.L.; Zhu, W.C.; Li, B. Synergistic analysis of economic resilience and efficiency of Marine fishery in China. Geogr. Res. 2022, 41, 406–419. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.G.; Zhang, P.Y.; Li, X. Regional economic resilience of the old industrial bases in China—A case study of Liaoning province. Sustainability 2019, 11, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solow, R.M. A contribution to the theory of economic growth. Q. J. Econ. 1956, 70, 65–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Li, T.; Fang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, W. Spatiotemporal Pattern Evolution of Economic Efficiency in County Area of Jilin Province Based on Malmquist and ESDA. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2019, 39, 1293–1301. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickolaos, T.G. The effect of human capital on countries’ economic efficiency. Econ. Lett. 2014, 124, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramovitz, M. Resource and output trends in the United States since 1870. Am. Econ. Rev. 1956, 46, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of super-efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2002, 143, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Song, Z.Y. Input-Output Efficiency of Economic Growth: A Multielement System Perspective. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K.; Tsutsui, M. Applying all efficiency measure of desirable and undesirable outputs in DEA to US electric utilities. J. CENTRUM Cathedra Bus. Econ. Res. J. 2011, 4, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yu, F. Measurement of economic resilience of contiguous poverty-stricken areas in China and influencing factor analysis. Prog. Geogr. 2020, 39, 924–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briguglio, L.; Cordina, G.; Farrugia, N.; Vella, S. Economic vulnerability and resilience: Concepts and measurements. Oxf. Dev. Stud. 2009, 37, 229–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briguglio, L.P. Exposure to external shocks and economic resilience of countries: Evidence from global indicators. J. Econ. Stud. 2016, 43, 1057–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Zhang, J.S.; Xu, W.X. A study on the evaluation of the development of county economic resilience in Zhejiang Province. Zhejiang Soc. Sci. 2019, 2019, 40–46. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayor, M.; Ramos, R. Regions and Economic Resilience: New Perspectives. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.D.; Fang, C.L.; Liu, H.M. Progress and prospect of urban resilience research. Prog. Geogr. 2020, 39, 1717–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haken, H. Self-organization and information. Phys. Scr. 2006, 35, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, Y. The driving forces of regional economic synergistic development in China: Empirical study by stages based on Haken model. Geogr. Res. 2014, 33, 1603–1616. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, H.; Yang, G.L. Measurement Method of Regional Synergetic Development Based on Haken Model. Stat. Decis. 2019, 35, 9–13. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.Z.; Meng, C.C. Evaluation of the development coordination relationship between resilience and efficiency of regional water resources system in China. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2020, 40, 2094–2104. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Qian, Y.; Zhu, L.; Guang, X.; Zhang, Y. Coordinated development and evolution of multidimensional rail transit and new urbanization in western China. Econ. Geogr. 2021, 41, 77–86. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.H. Revealing the Synergetic Development Evolution Mechanism of Economic Growth, Energy Consumption, and Environment: An Empirical Analysis Based on Haken Model and Panel Data. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2022, 2022, 6324351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Category | Item | Indicator |
|---|---|---|
| Input | Capital | Fix assets investment |
| Financial expenditure budget | ||
| Labor | Employees | |
| Natural resources | Construction land area | |
| Administrative area | ||
| Technology | Technology, education expenditure | |
| Output | Desirable output | GDP |
| Undesirable output | Industrial wastewater emissions |
| Target Level | Guideline Level | Index Level | Action Direction | Indicator Explanation | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Economic resilience | Resistance and recovery (0.2991) | GDP | + | Level of regional economic development | 0.0542 |
| Urban and rural savings balance | + | Residents’ ability to resist risk | 0.0576 | ||
| Rural per capital disposable income | + | Rural residents’ ability to resist risk | 0.0731 | ||
| Industrial diversification | − | Level of industrial diversification | 0.0604 | ||
| Ratio of foreign trade dependence | − | Total export-import volume/GDP | 0.0537 | ||
| Adaptability and adjustability (0.2743) | Level of financial self-sufficiency | + | Local fiscal revenue/local fiscal expenditure | 0.0826 | |
| Local fiscal expenditure | + | Regional government’s resource allocation | 0.0635 | ||
| Gross fixed asset formation | + | Size of regional investment | 0.0667 | ||
| Total retail sales of social consumer goods | + | Size of regional market scale | 0.0614 | ||
| Innovation and transformation (0.4267) | Urbanization rate | + | Regional urban population/regional total population | 0.0997 | |
| The support efforts of education | + | Level of regional education | 0.0424 | ||
| Advanced stage of industrial structure | + | Production value of primary industry ×1 + production value of secondary industry ×2 + production value of tertiary industry ×3 | 0.1102 | ||
| Scientific research outputs | + | Number of patents/GDP | 0.0998 | ||
| Proportion of R&D investment | + | R&D expenditure/GDP | 0.0747 |
| Parameter | Influence Level of Parameters on System | Directions for the Synergistic Evolution of the System | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive effects | The higher the degree of synergy | The order parameter
plays a leading role. Parameter is dominated by . | |
| Negative effects | The lower the degree of synergy | ||
| Positive effects | Enhanced synergy | ||
| Negative effects | Weakened synergy |
| Parameter | Interaction between Subsystems | Relationship between Subsystems | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| > 0 | has a negative effect on | the larger the interaction, the more significant the interaction. | |
| < 0 | has a positive effect on | ||
| > 0 | has a positive effect on | ||
| < 0 | has a negative effect on |
| Model Hypotheses | Motion Equation | Significance | Model Conclusion | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| t-Statistic | Prob. | |||
| Economic efficiency (EF) Economic resilience (RES) | 13.30477 −3.92890 | 0.0000 0.0002 | The equation of motion is established. is satisfied; The model hypothesis is established. EF is the order parameter. | |
| −21.37516 6.816243 | 0.0000 0.0000 | |||
| City | Order Parameter | Model Hypotheses | Motion Equation | Model Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Harbin | EF | < 0, has a positive effect on system evolution. > 0, has a negative effect on system evolution. | ||
| a > 0, hinders . b > 0, promotes . | ||||
| Qiqihar | RES | > 0, has a negative effect on system evolution. < 0, has a positive effect on system evolution. | ||
| a < 0, promotes, . b > 0, promotes . | ||||
| Daqing | EF | < 0, has a positive effect on system evolution. > 0, has a negative effect on system evolution. | ||
| a < 0, promotes . b < 0, hinders . | ||||
| Mudanjiang | EF | < 0, has a positive effect on system evolution. > 0, has a negative effect on system evolu tion. | ||
| a > 0, hinders . b > 0, promotes . | ||||
| Suihua | RES | > 0, has a negative effect on system evolution. < 0, has a positive effect on system evolution. | ||
| a > 0, hinders . b > 0, promotes . | ||||
| Changchun | RES | > 0, has a negative effect on system evolution. < 0, has a negative effect on system evolution. | ||
| a < 0, promotes . b < 0, hinders . | ||||
| Jilin | RES | > 0, has a negative effect on system evolution. < 0, has a positive effect on system evolution. | ||
| a < 0, promotes, . b > 0, promotes . | ||||
| Siping | EF | < 0, has a positive effect on system evolution. > 0, has a negative effect on system evolution. | ||
| a > 0, hinders . b > 0, promotes . | ||||
| Liaoyuan | EF | < 0, has a positive effect on system evolution. > 0, has a negative effect on system evolution. | ||
| a > 0, hinders . b > 0, promotes . | ||||
| Songyuan | EF | < 0, has a positive effect on system evolution. > 0, has a negative effect on system evolution. | ||
| a < 0, promotes . b < 0, hinders . |
| Stage of Synergistic Evolution | Evolutionary Characteristics | Stage of Synergistic Evolution | Evolutionary Characteristics | Stage of Synergistic Evolution | Evolutionary Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low efficiency -low synergy | Primary disorderly development | Low efficiency -medium synergy | Primary transition development | Low efficiency -high synergy | Primary synergistic development |
| Medium efficiency -low synergy | Middle disorderly development | Medium efficiency -medium synergy | Middle transition development | Medium efficiency -high synergy | Middle synergistic development |
| High efficiency -low synergy | Senior disorderly development | High efficiency -medium synergy | Senior transition development | High efficiency -high synergy | Senior synergistic development |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ban, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wei, L. Synergistic Patterns of Urban Economic Efficiency and the Economic Resilience of the Harbin–Changchun Urban Agglomeration in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010102
Ban Y, Wang Y, Chen X, Wei L. Synergistic Patterns of Urban Economic Efficiency and the Economic Resilience of the Harbin–Changchun Urban Agglomeration in China. Sustainability. 2023; 15(1):102. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010102
Chicago/Turabian StyleBan, Yang, Ying Wang, Xiaohong Chen, and Liuqing Wei. 2023. "Synergistic Patterns of Urban Economic Efficiency and the Economic Resilience of the Harbin–Changchun Urban Agglomeration in China" Sustainability 15, no. 1: 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010102
APA StyleBan, Y., Wang, Y., Chen, X., & Wei, L. (2023). Synergistic Patterns of Urban Economic Efficiency and the Economic Resilience of the Harbin–Changchun Urban Agglomeration in China. Sustainability, 15(1), 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010102




