1. Introduction
In 2015, the United Nations General Assembly approved the seventeen Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), which were defined to guide the progress of societies, organizations, and individuals until 2030. Its focus is on sustainable development based on three pillars most known as the Triple Bottom Line (TBL), which are: economic sustainability, focused on liquidity and profit; social sustainability, orientated to people and society with an ethical concern; and environmental sustainability, related to our planet and its resources [
1]. Addressing sustainable development at these three levels will promote a shared vision for humanity, eradicating poverty, protecting the environment, and promoting the prosperity and well-being of all [
2].
Since 2011 the European Commission has defined corporate social responsibility as the responsibility to impact society by integrating the TBL perspective in their activities and corporate practices.
Thus, organizations are more aware of the sustainable development challenges bringing it to their business models, which will consequently bring benefits to the planet, society, organizations, and employees. To answer these challenges, the focus on sustainable development is increasing not only on the different business sectors [
3,
4] but also at business department levels. For instance, Csikósová [
3] studied the TBL in tourism organizations, Kahn and colleagues [
4] studied the manufacturing industry, and Piwowar-Sulej [
5] focused her work on industrial engineers.
Within organizations, we also see this sustainable movement across many areas of the organizational setting [
6,
7], such as accounting, marketing, retailing, management, and lately, human resource management.
Based on sustainable development some research has mainly focused on the green movement, most related to the environmental pillar of TBL. Kainzbauer and colleagues [
8] (p. 16) performed a bibliometric review regarding sustainable human resources management. Their results suggested that “of the 20 top cited documents and 20 top co-cited documents revealed a dominance of Green HRM topics”.
Therefore, we will frame our work on the Green Human Resources Management (GHRM), defined as activities developed by HR to increase employees’ environmentally friendly behaviors [
8].
Due to its importance, previous studies have shown that organizations whose corporate social responsibility policies are perceived as positive are considered more attractive to potential employees and generate a more significant number of applications [
9,
10].
For any organization, becoming “a nice place to work” implies creating the image that the organization is the ideal place to work in the perception of current and future employees. To fulfill this goal, they aim to adopt good management practices for their employees through recruitment and selection. Thus, organizations benefit from the external and internal communication of factors that make them desirable, attractive, and different from other organizations, prevailing at the decision-making time by candidates [
11]. Based on these assumptions, among the existing green human resources practices, this study will focus on the component of recruitment practices, that is, the practices used by organizations to attract and increase the number of qualified candidates [
12]. Thus, our study aims to understand to what extent organizations that transmit an environmentally friendly corporate image through their job advertisements are considered more attractive and reflected in a greater intention to apply.
We investigated the importance of pro-environmental messages in job advertisements, their influence on organizational attractiveness, and participants’ intentions to apply. Additionally, we seek to understand whether individual environmental responsibility and individual pro-environmental behavior influence the intention to apply in an organization that presents itself as environmentally friendly.
2. Theoretical Framework and Research Hypotheses
Environmental sustainability has been highlighted in debates regarding economic activity and development [
13]. As environmental concerns increase globally, organizations have become more aware of the importance of their efforts to manage and preserve the environment. An amplification of pressure on the business world to assume a more significant commitment to social and environmental issues is notorious since this impacts the corporate image and reputation [
14].
Therefore, human resources management oriented towards environmental sustainability is recently referred to the literature as “Green Human Resources Management” (GHRM), which emerged from the need of organizations to integrate environmental sustainability in their policies, practices, and business models [
15]. Thus, the GHRM concept comprises a set of human resource management practices, such as recruitment, selection, training and development, reward, and performance management, all aimed at improving the organization’s environmental performance [
16].
Among the existing green human resources practices, we will focus on recruitment practices-. The organizations’ ability to recruit and retain qualified employees is a key factor for their competitiveness in the labor market [
17]. Although several domains have been studied that impact organizational attractiveness, more recently, the sustainability factor has started to gain greater attention and interest from researchers [
18].
Several empirical studies [
9,
17,
18,
19] have shown how the pro-environmental messages present in job advertisements can influence organizational attractiveness. They consider that introducing information and indicators related to environmental practices adopted by organizations and an organizational culture that aims to conserve the environment increases the probability of attracting more and better talents.
According to Roth [
20], environmental literacy, being common to different cultural contexts, comprises individuals’ knowledge and attitudes towards environmental issues, particularly their motivations and activities that actively contribute to solving problems that compromise sustainability. Therefore, the perception of environmental responsibility is related to the trait of the individuals’ personality that influences individuals’ behavioral intentions [
21]. Based on this assumption, if people have a greater environmental culture and awareness, they will be more likely to feel responsible for contributing to a more environmentally sustainable life and, as a result, will be more willing to adopt behaviors that favor this same conservation [
22].
Therefore, it is essential to consider the mechanisms underlying the effect of pro-environmental messages on candidates regarding organizational attractiveness and the intentions to apply, since the intention to apply, according to the theory of planned behavior, will lead to individual formalizing their application, which will be beneficial to the organization as behavioral intentions are causal antecedents of behavior [
23].
The theoretical framework of the signaling theory, initially proposed in the 70s by Michael Spence, has been frequently used in human resources management. Specifically, research has been done regarding organizational attractiveness and individuals’ behavior related to job search and, as such, are at the stage of evaluating possible offers [
24]. Based on this theory, through job advertisements, organizations send signals—such as culture, climate, practices, policies, values, activities, and working conditions—that are assessed as positive or negative by candidates as predictive clues of possible future employment relationships between the individual and the organization [
19]. In addition, Jones and colleagues [
25] used this signaling theory to study how an organization’s pro-environmental practices impacted its attractiveness to potential employees, finding that corporate social performance can effectively affect an organization’s image and attractiveness.
From another point of view, Tajfel social identity theory [
26] also intervenes in this explanatory system. It suggests that in the job search process, the individual choice for an organization can be stimulated by its self-concept and its tendency to adhere to certain social groups that guarantee a positive social identity [
27]. In this sense, when the individual and the organization’s identity, goals, and values are aligned, for instance, ecological awareness and attitude towards the environment of both parties, the individual will value the possibility of becoming part of the collective. Thus, the organizational attractiveness and the candidate-organization fit should be promoted [
28].
Based on these assumptions, we proposed the following hypotheses and research model (
Figure 1):
Hypotheses 1 (H1). Organizational attractiveness mediates the relationship between the type of job advertisement (green vs. non-green) and the intentions to apply;
Hypotheses 2 (H2). The presence of pro-environmental messages in the job advertisements will increase the organizational attractiveness when compared to job advertisements without pro-environmental messages;
Hypotheses 3 (H3). In the presence of job advertisements with environmental messages, individual environmental responsibility and intentions of pro-environmental behavior have a positive and significant relationship to intentions to apply.
3. Method
3.1. Design
This quantitative and descriptive study presents a quasi-experimental design. It is characterized by two conditions, in which the information was made available to the participants. We created two fictitious job advertisements. One job advertisement contained pro-environmental messages (referred to as “green advertisement”), and the other did not contain any reference to the environment (referred to as “non-green advertisement”).
Both job advertisements contained information related to work, such as a competitive salary package, flexible working hours, and career development opportunities. The pro-environmental messages highlighted the fictitious organization’s concern with environmental protection, transmitting a sustainable culture and the assumption of a commitment to the planet’s health. These messages were only present in one of the job advertisements (green job advertisement) and absent in the other (non-green job advertisement), the only variable to change between the two advertisements.
We used PosterMyWall to create job advertisements and Qualtrics XM software to create the online survey. The link was shared on several social networks, such as Facebook, Whatsapp, and Linkedin, between November 2020 and February 2021.
We started the survey with a brief general instruction about the study. Participants were required to respond sincerely, leaving the caveat that there were no right or wrong answers, and their confidentiality was guaranteed. In the first part, sociodemographic questions were included. In the second, we randomized each job advertisement thus, participants only had access to one job advertisement (“green” and “non-green”), responding to the organizational attractiveness and intentions to apply scales. Later, they would find a final section with both scales of individual environmental responsibility and pro-environmental behavior intentions to evaluate each participant’s sustainable attitudes and behavior.
3.2. Participants
We randomized each job advertisement, resulting in 49.4% (219) of participants who viewed the “non-green” advertisement, contrasting with the remaining 50.6% (224) who viewed the “green” advertisement.
Of the total respondents, 443 valid responses were obtained to the questionnaire, of which 71.8% are female, 28% male, and 0.2% of the unspecified gender (“other”). Concerning academic qualifications, 4.3% of the sample has up to the 9th grade of schooling; 25.1% have completed the 12th year; 45.4% have a bachelor’s degree; and 24.8% have a master’s degree or a higher academic degree.
About the birth interval of the participants, it is stated that 20.5% were born between 1946 and 1964; 39.5% belong to the interval between 1965 and 1980; 27.3% birth between 1997 and 2012. 70.4% of the participants were currently employed, instead of 29.6% without any type of employment relationship.
3.3. Data Analysis Procedure
The scales adaptation included a faithful translation into the Portuguese language, which was carried out by two researchers who possessed experience in recruitment and selection and a proficient English language level. Then, 10 organizational psychology students evaluate the comprehension level of each item.
Afterward, to test the instrument’s validity, exploratory factor analysis was performed using the SPSS Statistics 27 software (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY., USA). Then, confirmatory factor analyses were performed using the AMOS 27 for Windows software to confirm the factor structure. The procedure followed a logic of “model generation”, considering the results obtained interactively in the analysis of its adjustment: for the chi-square (χ2) ≤ 5; for the Tucker Lewis index (TLI) > 0.90; for the goodness-of-fit index (GFI) > 0.90; for the comparative fit index (CFI) > 0.90; for root mean square error the approximation (RMSEA) ≤ 0.08. The construct reliability and convergent validity (VEM) values were also obtained. Finally, the internal consistency of each instrument was tested by calculating Cronbach’s alpha, and its value should vary between “0” and “1”, not assuming negative values and being superior to 0.70, advisable value in organizational studies.
The next step was to test the association between variables using Pearson’s correlations. As for hypothesis 1, as it presupposed a mediating effect, the assumptions recommended by Baron and Kenny [
29] were followed. We used the PROCESS 3.5 macro for SPSS (Hayes, NY., USA) to test the mediation model developed by Hayes, 2013 [
30]. Hypothesis 2 was tested through t-student tests for independent samples and hypothesis 3 through multiple linear regressions.
3.4. Instruments
The organizational attractiveness was measured through a set of five items adapted from [
10] Highhouse et al., 2003, such as “For me this organization would be a good place to work” and “This organization is attractive to me as a place of work”.
To assess intentions to apply, we used five items proposed by Highhouse et al., 2003 [
10], such as “This organization would be one of my first choices as an employer” and “I would make an effort to get to work in this organization”. For both scales, we used a five-point Likert-type response scale (1—Totally disagree; 2—Disagree; 3—Neither agree nor disagree; 4—Agree; 5—Totally agree).
After performing the exploratory factor analysis, a KMO of 0.86 was obtained with a total explained variance of 59% for the organizational attractiveness and a KMO of 0.84 with a total explained variance of 51% for intentions to apply.
Regarding the confirmatory factor analysis, the goodness of fit indices are acceptable (ꭓ2/df = 5.02; GFI = 0.94; CFI = 0.96; TLI = 0.93; RMSEA = 0.095). Organizational attractiveness has a construct reliability of 0.80 and a convergent validity of 0.48. As for the intentions to aplly, its construct reliability presents a value of 0.76 and the convergent validity a value of 0.49.
As for internal consistency, organizational attractiveness presents a Cronbach’s alpha of 0.87, and the intention to apply the value is 0.83.
We used two subscales from the environmentally responsible behavior scale proposed by Hsu and Roth, 1998 [
31] to assess the individual environmental responsibility and intentions for pro-environmental behavior. In the first subscale, referring to individual environmental responsibility, we used four items, such as “I feel that I have a responsibility to intervene in solving environmental problems” and “I feel that I have a responsibility to change my consumption habits in favor of environmental protection (e.g., reducing the number of purchases and/or purchasing energy-saving products)”. The second subscale measures the intentions of pro-environmental behavior, comprising four items, such as “I am willing to adopt behaviors that favor environmental protection (e.g., saving water, electricity, use of transport with reduced carbon emissions)” and “I am willing to contribute to the prevention of environmental problems, through, for example, donations, signing petitions, changing consumption habits”. We used a five-point Likert response scale to determine the frequency of behaviors: 0—Never; 1—Rarely, 2—Sometimes, 3—Quite often, 4—Always.
In the exploratory factor analysis, a KMO of 0.76 with a total explained variance of 55% for individual environmental responsibility and a KMO of 0.79 with a total explained variance of 55% for pro-environmental behavior intentions was obtained.
Regarding the confirmatory factor analysis, the goodness of fit indices obtained are acceptable (ꭓ2/df = 3.45; GFI = 0.97; CFI = 0.98; TLI = 0.95; RMSEA = 0.075). Individual environmental responsibility has a construct reliability of 0.85 and a convergent validity of 0.59. As for pro-environmental behavior intentions, their construct reliability has a value of 0.78 and convergent validity a value of 0.48.
4. Results
Concerning the association between the variables, the correlations for both job advertisements (green and non-green), revealed that all four variables are significantly correlated and positive. However, the strongest relationship was identified between the variables “organizational attractiveness” and “intentions to apply”, both for the green advertisement (r = 0.80;
p < 0.001) and for the non-green advertisement (r = 0.84;
p < 0.001). Thus, the more attractive the participants find the organization, the higher is their intention to apply (
Table 1).
Regarding the descriptive statistics of the variables of individual environmental responsibility and the intentions of pro-environmental behavior for the green job advertisement, they show an average above the central point, suggesting that participants positively perceive their environmental attitudes and behaviors. However, it is important to highlight that the individual environmental responsibility scale has a higher average (M = 4.31; SD = 0.54) contrasting with the intentions of pro-environmental behavior (M = 3.79; SD = 0.65) (
Table 1).
Our results suggested that individual environmental responsibility, when compared to pro-environmental behavior intentions, proved to be more decisive on intentions to apply and the correlations are higher for the group of participants who viewed the green job advertisement (ResAmbInd: r = 0.39,
p < 0.01; ICPAmb: r = 0.28,
p < 0.01) (
Table 1).
Hypothesis Test
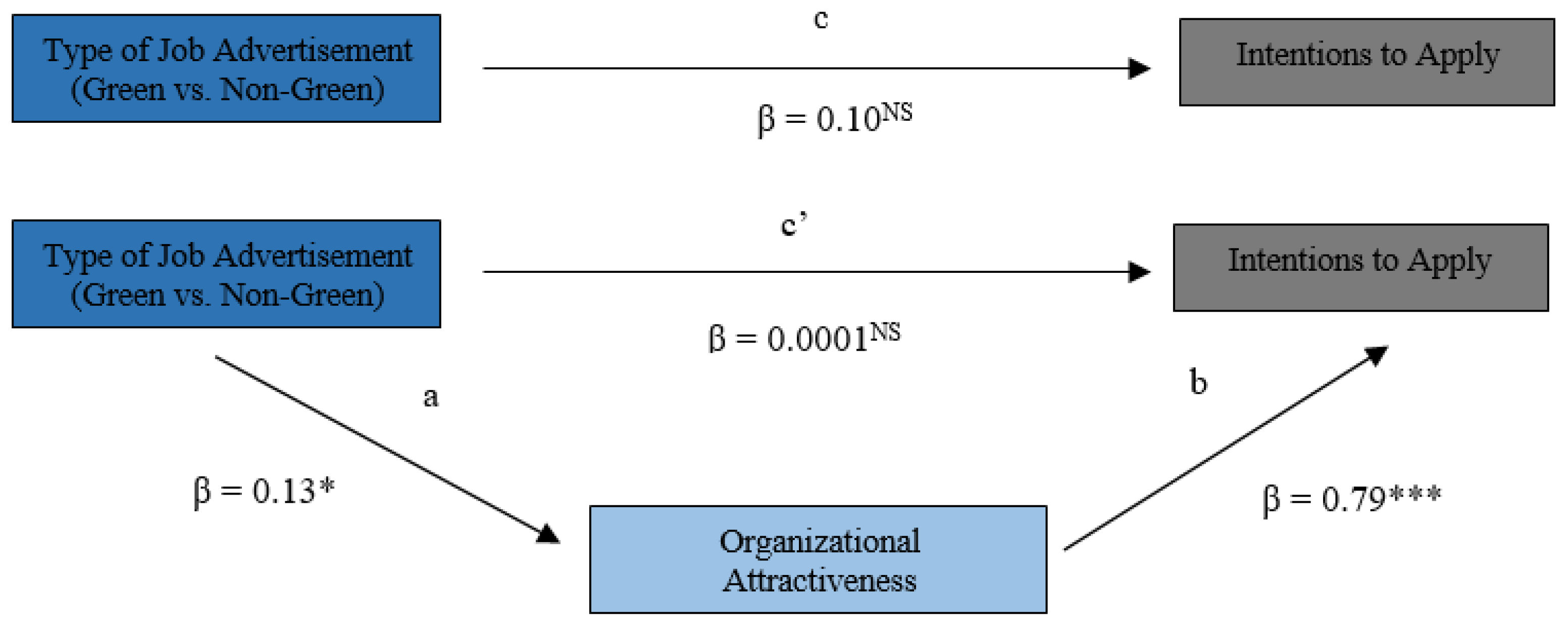
Hypotheses 1 (H1). Organizational attractiveness mediates the relationship between the type of job advertisement (green vs. non-green) and the intentions to apply;
The results obtained in the final model allowed us to observe, firstly, that the total effect (c), that is, the impact of the type of job advertisement (green vs. non-green) on the intentions to apply, was not significant (β = 0.10;
p > 0.05) (
Figure 2). Additionally, about the direct effects of the model, it was found that: (1) the effect of the type of job advertisement on intentions to apply, with control for organizational attractiveness (c’), was not statistically significant (β = 0.0001;
p > 0.1); (2) the impact of the type of job advertisement on the organizational attractiveness (a) was significant (β = 0.13;
p < 0.05), explaining 1% of its variation; (3) the effect of the mediating variable (organizational attractiveness) on intentions to apply (b) was statistically significant (β = 0.79;
p < 0.001), with this model being responsible for 68% of its variability (
Figure 2). Thus, since there is no statistical significance of all direct effects, as recommended by the authors mentioned above, it was impossible to proceed with the mediation test, so Hypothesis 1 was not confirmed.
Hypotheses 2 (H2). The presence of pro-environmental messages in the job advertisements will increase the organizational attractiveness when compared to job advertisements without pro-environmental messages;
As the assumption of homogeneity of variances was not verified, the t-student test with Welch correction was used.
The results obtained suggested that there are significant differences in the variable “organizational attractiveness” (t (426.474) − 2.1362; p = 0.034), with higher values for the green job advertisement (M = 3.88; SD = 0.59), compared to the non-green job advertisement (M = 3.75; SD = 0.69). In contrast, the results did not confirm the differences between both jobs advertisements on the intentions to apply. This result supports Hypothesis 2.
Hypotheses 3 (H3). In the presence of job advertisements with environmental messages, individual environmental responsibility and intentions of pro-environmental behavior have a positive and significant relationship to intentions to apply.
To test this hypothesis, we used a multiple linear regressions analysis and divided data by type of advertisement. For the non-green job advertisement, without pro-environmental messages, only the individual environmental responsibility is significant as a predictor of intentions to apply (β = 0.16, p < 0.05, R2 = 0.05). In contrast, for the green job advertisement, containing pro-environmental messages, both individual environmental responsibility (β = 0.32, p < 0.001) and intentions of pro-environmental behavior (β = 0.14, p < 0.05) are significant predictors of intentions to apply. The adjusted R2 is 0.15, which indicates that 15% of the intentions to apply are explained by individual environmental responsibility and intentions of pro-environmental behavior. We then confirm Hypothesis 3.
These results also allow us to understand that when individual environmental responsibility is high, and there are intentions to act in its favor, those variables have a positive and stronger effect on intentions to apply when participants face an advertisement containing ecological messages.
5. Discussion
Our main goal was to understand if organizations that transmit an environmentally friendly image can be considered more attractive and, as a result, generate higher intentions to apply. In addition, we also aim to analyze how individual environmental responsibility and intentions of pro-environmental behavior influence the intentions to apply in an organization that transmits a sustainable culture and a commitment to the environment through its jobs advertisements.
Firstly, hypothesis 1, contrary to what was expected, was not confirmed. Highhouse et al., 2003 [
11] defined organizational attractiveness as being three-dimensional (attraction, prestige, and intentions to apply), correlated dimensions. Maybe if organizations do not have any notoriety or reputation associated with them, this could have influenced the non-verification of the mediating effect of organizational attractiveness. Because we presented a controlled/fictional situation, the information presented in both job advertisements may not have been sufficiently attractive and captivating to create a favorable attitude towards the organization, nor perception of the benefits that the participant could achieve by submitting his/her application.
Secondly, in line with previous studies, the results suggested that participants who viewed the green job advertisement considered the organization more attractive than the group of participants who viewed the non-green job advertisement, confirming hypothesis 2. This information is in line with what is reported in the literature, as, previously, authors such as Bauer and Aiman-Smith [
32] and Behrend et al. [
18] carried out studies that showed similar results, by identifying that candidates for a job vacancy, when facing a company that conveyed a pro-environmental message, perceived it as more positive, generating, as a result, greater intentions to apply.
Finally, individual environmental responsibility and intentions of pro-environmental behavior also proved to be predictors of the participants’ intentions to apply, an effect that was higher for those who saw the green job advertisement, confirming hypothesis 3. This result aligns with Bauer and Aiman-Smith [
32] conclusions. Participants with a favorable individual position related to the environment may be more likely to seek employment in an organization that communicates its activities, initiatives, and pro-environmental culture through the job advertisements. In contrast, organizations whose job advertisements do not integrate pro-environmental statements are less attractive to these individuals.
In conclusion, our results suggested that, although organizational attractiveness does not mediate the relationship between the type of advertisement (green vs. non-green) and the intentions to apply, job advertisements with pro-environmental messages generated a perception of higher organizational attractiveness. Additionally, and according to social identity theory, participants who have a greater sense of responsibility towards the environment and greater intentions to act to protect it, when viewing a green job advertisement, are more likely to apply.
Regardless of the type of job advertisement, when the organization is perceived as more attractive, this reflects greater intentions to apply. Individual environmental responsibility is the most determining variable for intentions to apply, and this effect seems higher in the presence of a green job advertisement. This leads to a reflection that people who feel they have a responsibility to protect the environment and contribute to its sustainability may, in practice, not be so willing to adopt active behaviors congruent with this greener awareness and responsibility.
6. Conclusions
6.1. Theoreticaland Practical Implications
Our study contributes to an adaptation of organizational attractiveness, individual environmental responsibility, and intentions for pro-environmental behavior scales into the Portuguese population, which may allow future research to investigate this phenomenon in-depth.
In addition, Our results strengthen the theory about a significant and positive relationship between ecological messages in job advertisements and organizational attractiveness.
Second, introducing variables such as individual environmental responsibility and intentions of pro-environmental behavior allowed us to elucidate possible explanatory mechanisms for the influence of this type of message to formalize a job application. This result is more present in organizations whose culture and values are consistent with individual ecological awareness.
Since recruitment is a task that aims to achieve the right fit of the person to the organization, at a reduced cost and effort, the proper preparation of a job advertisement benefits not only the candidate in acquiring information about employment opportunities but also the organization in the projection of a positive image. For this reason, this study makes it possible to highlight the importance of pro-environmental messages on intentions to apply. Thus, highlighting sustainable practices and policies can constitute a low-cost recruitment mechanism, attracting more candidates and enabling the screening of those who have attitudes and behaviors similar to the organization, resulting in a higher candidate-organization fit.
In short, for Human Resource Management practitioners, this research adds credibility to the need to consider sustainability issues when creating job advertisements to present a more favorable image of corporate social responsibility and, consequently, gain an advantage in recruiting new employees.
6.2. Limitations and Future Research
Although this research has important strengths, certain limitations should be considered when interpreting the results of this study. First, the quasi-experimental design was based on a fictional advertisement, not an actual advertisement. Furthermore, although this was an advertisement referring to a fictitious organization, it lacked a website associated with the respective brand, making it impossible for the participant to interact and search for more information about the organization. Thus, although the study design allowed for standardizing and controlling the information viewed by the participants, this may have limited the results.
Also, regarding the quasi-experimental design, this study could be replicated by introducing more advertisements and manipulating other indicators related to the organization. For instance, comparing two advertisements, to find out to what extent the presence of pro-environmental messages, facing two job advertisements whose compensation difference is subtle, can play a decisive role in the individual’s intentions to apply.
Concerning sample limitations, approximately 72% of the total sample comprises women. It is also more prevalent in the intermediate age groups (born between 1965 and 1996), with a lower weight in the older age groups. (Generation Baby Boomers, 21%) and younger (Generation Z, 13%).
It could be interesting to carry out a study focusing on the possible generational effects on the studied variables. Considering previous studies, it could be interesting to study if younger generations, which lifes’ and works’ horizons are predictably longer, when faced with a green job advertisement, would value more strongly the perspective of working for an organization with an eco-friendly culture and values, contrasting to older generations, who might prefer other types of organizational characteristics. [
18,
33,
34,
35].
Finally, the cultural setting could also be an exciting variable to consider. Some of the results found may be due to a lack of total entrenchment of sustainable behavior in the code of conduct of Portuguese citizens, which makes them feel that they have a responsibility to act, the involvement in concrete actions is still limited. It is suggested that further studies might be carried out to explore this theme, comparing Portugal with other cultures different from ours in other fields.