A Review of Sustainable Maintenance Strategies for Single Component and Multicomponent Equipment
Abstract
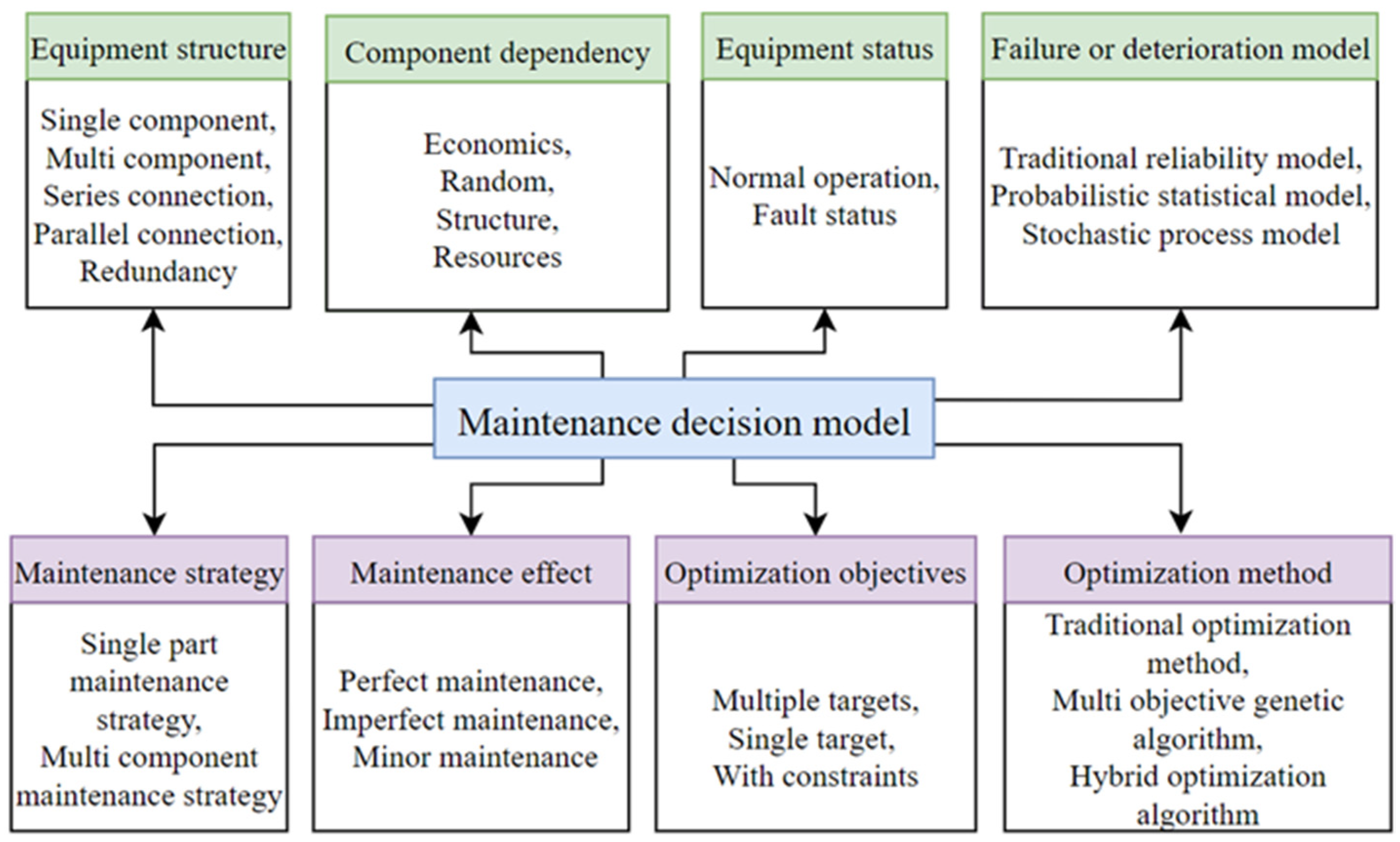
1. Introduction
2. The Maintenance Effect
3. Influence of Equipment Dependency on Maintenance
3.1. Economic Dependence
3.2. Random Dependence
3.3. Structural Dependence
3.4. Resource Dependence
4. Maintenance Strategy
4.1. Overview Single Component Maintenance Strategies
4.1.1. Corrective Maintenance Strategies
4.1.2. Preventive Maintenance Strategies
- Age dependent maintenance strategies
- 2.
- Periodic maintenance strategy
- 3.
- Sequential maintenance strategy
- 4.
- Failure limit strategy
4.1.3. Predictive Maintenance Strategies
4.2. Overview of Multicomponent Maintenance Strategies
4.2.1. Batch Maintenance Strategies
4.2.2. Opportunistic Maintenance Strategies
4.2.3. Group Maintenance Strategies
- Static group maintenance strategy
- Corrective group maintenance strategy
- Preventive group maintenance strategy
- 2.
- Dynamic group maintenance
- The finite time axis method
- The rolling time axis method
5. Application of Maintenance Strategies in Some Industries
5.1. Aviation Industries
5.2. Rail Transit Industries
5.3. Energy Industries
6. Conclusions and Future Challenges
- Maintenance Strategies for Key Equipment with Limited Condition Monitoring
- Multicomponent Maintenance Strategy Considering Maintenance Constraints
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, X.; Moere, A.; Eades, P. Evaluation of a maintenance strategy by the analysis of the rate of repair. Int. J. Ambient. Comput. Intell. 2010, 2, 59–69. [Google Scholar]
- Richard, C.; Cassady, W. Selective maintenance for support equipment involving multiple maintenance actions. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2001, 129, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohril, R.S.; Solanki, B.S.; Lad, B.K. Blockchain Enabled Maintenance Management Framework for Military Equipment. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2021, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardo, M.D.; Madonna, M. A mapping analysis of maintenance in industry 4.0. J. Appl. Res. Technol. 2021, 19, 653–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ron, S.; Amanda, P. Costliest Disaster in US History; Financial Toll Passes $60 Billion, Reaching from Wreckage and Airport Downtime to Lower Productivity and Lost Taxes. In Tribology, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2002; Volume 5, pp. 16–24. [Google Scholar]
- Mehmeti, X.; Mehmeti, B.; Sejdiu, R. The equipment maintenance management in manufacturing enterprises. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 800–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christer, A. A Review of Delay Time Analysis for Modelling Plant Maintenance; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Polese, F.; Gallucci, C.; Carrubbo, L. Predictive Maintenance-as a driver for corporate sustainability: Evidence from a public-private co-financed R&D project. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5884. [Google Scholar]
- Kihira, H. Systematic approaches toward minimum maintenance risk management methods for weathering steel infrastructures. Corros. Sci. 2007, 49, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mungani, D.S.; Visser, T. Maintenance approaches for different production methods. S. Afr. J. Ind. Eng. 2013, 24, 2224–7890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiee, M.; Chukova, S. Maintenance models in warranty: A literature review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2013, 229, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkoyuncu, J.A.; Khan, S.; Eiroa, A.L. Perspectives on trading cost and availability for corrective maintenance at the equipment type level. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2017, 168, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Halmai, Z.; Dome, P.; Dobos, J. Realization of corrective maintenance activities by application of different information systems. J. Affect. Disord. 2012, 144, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J. Research on Generator Maintenance Plan under the Environment of Power Market; China Agricultural University: Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, C.J.; Chen, W. Single-machine scheduling with periodic maintenance and nonresumable jobs. Comput. Oper. Res. 2003, 9, 1335–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yam, R.; Tse, P.W.; Li, L. Intelligent predictive decision support system for condition-based maintenance. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2001, 17, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mur, E.; Kopf, U.; Fluckinger, G. Adaptive signal analysis and interpretation for real-time intelligent patient monitoring. Methods Inf. Med. 1994, 33, 60–63. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, G.; Jiang, L.; Xu, G. A Model of Intelligent Fault Diagnosis of Power Equipment Based on CBR. Math. Probl. Eng. 2015, 3, 203083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, T.R. Depression in the Caregiving Mothers of Adult Schizophrenics: A Test of the Resource Deterioration Model. Community Ment. Health J. 1997, 33, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, L.; Lin, B.; Wang, Z. A Pragmatic Optimization Method for Motor Train Set Assignment and Maintenance Scheduling Problem. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2016, 6, 4540503. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, L.; Kwong, S.; Cao, J. Achieving balance between proximity and diversity in multi-objective evolutionary algorithm. Inf. Sci. 2012, 182, 220–242. [Google Scholar]
- Coria, V.H.; Maximov, S.; Rivas, D. Analytical method for optimization of maintenance policy based on available system failure data. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2015, 135, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, Y.C. A piecewise nonlinear optimization for a production-inventory model under maintenance, variable setup costs, and trade credits. Ann. Oper. Res. 2013, 23, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 3187-94; State Bureau of Technical Supervision GB/T3187-94 Reliability and Maintainability Terms. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 1986.
- Nardo, M.D.; Converso, G.; Castagna, F. Development and implementation of an algorithm for preventive machine maintenance. Eng. Solid Mech. 2021, 4, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelia, B.; Marc, R.; Doru, N. Approaching the Processes in the Generator Circuit Breaker at Disconnection through Sustainability Concepts. Sustainability 2013, 5, 1161–1176. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, T.; Xi, L.; Zhou, X. Modeling and optimizing maintenance schedule for energy systems subject to degradation. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2012, 63, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.H.; Chan, F.; Chan, H.K. A modified genetic algorithm approach for scheduling of perfect maintenance in distributed production scheduling. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2009, 22, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, K.T.; Barros, A.; Berenguer, C. A periodic inspection and replacement policy for systems subject to competing failure modes due to degradation and traumatic events. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2011, 96, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noroozi, A.; Khakzad, N.; Khan, F. The role of human error in risk analysis: Application to pre- and post-maintenance procedures of process facilities. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2013, 119, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkenne, C.; Jost, D.; Haruel, P.A. Insufficient quality of public automated external defibrillator recordings in the greater Paris area, a descriptive study. Emerg. Med. J. 2020, 37, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Liu, S.; Bae, S.J.; Liu, Y. A multi-stage imperfect maintenance strategy for multi-state systems with variable user demands. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 14, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, P.; Zhang, C. Fleet-Level Selective Dispatch and Imperfect Maintenance Strategy Optimization Based on Evolutionary Co-Petition Game Theory. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajjej, Z.; Dellagi, S.; Rezg, N. An optimal production/maintenance planning under stochastic random demand, service level and failure rate. IEEE Int. Conf. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2009, 18, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, M. A new framework of complex system reliability with imperfect maintenance policy. Ann. Oper. Res. 2021, 13, 7913–7927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Chen, S.; Jin, H. Optimum opportunistic maintenance schedule incorporating delay time theory with imperfect maintenance. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2021, 213, 107–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ran, Y.; Wan, F. Condition-based maintenance strategy optimization of meta-action unit considering imperfect preventive maintenance based on Wiener process. Flex. Serv. Manuf. J. 2021, 1, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Zhang, X.; Yang, X. Optimal Selective Maintenance Decision-Making for Consecutive-Mission Systems with Variable Durations and Limited Maintenance Time. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 21, 5534659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Trivedi, K.S. Optimization for condition-based maintenance with semi-Markov decision process. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2017, 90, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanasi, T. Interval Censored Data Analysis with Weibull and Exponential Distribution. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 693, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Elsayed, E.A.; Chan, L.Y. Maintenance of continuously monitored degrading systems. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2006, 175, 821–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Cheng, Z.; Luo, B. An Auxiliary Industrial Equipment Maintenance System Using Mixed Reality. In Proceedings of the IEEE 8th International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Applications, Chengdu, China, 23–26 April 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Purnachand, K.; Shabbeer, M.; Nvsrm, P. Predictive Maintenance of Machines and Industrial Equipment. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communication Systems and Network Technologies, Bhopal, India, 18–19 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ostadi, B.; Hamedankhah, R. A two-stage reliability optimization approach for solving series–parallel redundancy allocation problem considering the sale of worn-out parts. Ann. Oper. Res. 2021, 304, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Zeng, Z. Redundancy optimization for multi-state series-parallel systems using ordinal optimization-based-genetic algorithm. J. Risk Reliab. 2021, 236, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.D.; Cha, H.S.; Im, C.H. Removing the Interdependency between Horizontal and Vertical Eye-Movement Components in Electrooculograms. Sensors 2016, 16, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, L. A survey of maintenance and replacement models for maintainability and reliability of multi-item systems. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 1986, 16, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.N.; Simes, J.M. The Political and Economic Dependence of the Press in Macao under Portuguese and Chinese Rule: Continuity and Change. Commun. Soc. 2021, 34, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, B. Impact of state of economic dependence and employment status on the self-perceived health of Indian elderly people across expenditure quintiles of households. Ageing Soc. 2021, 5, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamana, P.; Ochuodho, T.O. Forest Sector Dependence and Economic Well-Being in Kentucky: An Econometric Analysis. For. Sci. 2021, 67, 659–669. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolai, R.; Dekker, R. Optimal maintenance of multi-component systems: A review. Complex Syst. Maint. Handb. 2006, 116, 263–286. [Google Scholar]
- Arijit, C.; Rajat, S.H.; Deepayan, S. From random matrices to long range dependence. Random Matrices Theory Appl. 2016, 5, 1650008. [Google Scholar]
- Murthy, D.; Nguyen, D. Study of two-component system with failure interaction. Nav. Res. Logist. Q. 1985, 32, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarf, P.A.; Deara, M. On the development and application of maintenance policies for a two component system with failure dependence. IMA J. Manag. Math. 1998, 9, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarf, P.A.; Deara, M. Block replacement policies for a two-component system with failure dependence. Nav. Res. Logist. 2003, 50, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Su, W.; Li, B. Opportunistic maintenance policy for a two-unit system with failure interactions. J. Tsinghua Univ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 52, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, M.T.; Chen, Y.C. Optimal periodic replacement policy for a two-unit system with failure rate interaction. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2006, 29, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S.; Stephens, L.I.; Mauzeroll, J. Structural dependence of effective mass transport properties in lithium battery electrodes. J. Power Sources 2021, 504, 230069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlmann, E.; Otto, F. Processes for the Introduction of the Maintenance Service Support System. Procedia CIRP 2014, 16, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, G.F.; Cobb, J.A. Resource Dependence Theory: Past and Future. Res. Sociol. Organ. 2010, 28, 21–42. [Google Scholar]
- Drees, J.M.; Heugens, P. Synthesizing and Extending Resource Dependence Theory: A Meta-Analysis. J. Manag. 2012, 39, 1666–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klauer, K.C.; Teige, M.S. Controllability and resource dependence in automatic evaluation. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 2007, 43, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zuo, D. Current status of machine prognostics in condition-based maintenance: A review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2006, 50, 297–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, Y.I.; Berry, D.C.; Perreira, K.M. A multi-component, community-engaged intervention to reduce cardiovascular disease risk in perimenopausal Latinas: Pilot study protocol. Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2021, 7, 107092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucia, A.D.; Pompella, E.; Stefanucci, S. Assessing effort estimation models for corrective maintenance through empirical studies. Inf. Softw. Technol. 2005, 47, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhat, H. Maintenance: Availability and reliability. In Operation, Maintenance, and Repair of Land-Based Gas Turbines; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 14, pp. 89–106. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.H.; Deng, C.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.C.; Xiong, Y. A corrective maintenance scheme for engineering equipment. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2014, 36, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, W. An asset residual life prediction model based on expert judgments. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2008, 188, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, A.S.; Floru, I.R.; Azzaro, P.C. Optimization of preventive maintenance strategies in a multipurpose batch plant: Application to semiconductor manufacturing. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2003, 27, 449–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Wang, H.; Men, F. Customized Preventive Maintenance Strategies for Products Sold with Two-Dimensional Warranty. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 5576455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, A.; Zhang, S.; Tan, A. Rotating machinery prognostics: State of the art, challenges and opportunities. Mech. Syst. Signal Processing 2009, 23, 724–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MD, R.; Laseinde, O. Optimization of condition-based maintenance strategy prediction for aging automotive industrial equipment using FMEA. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 16, 229–238. [Google Scholar]
- Torres-González, M.; Prieto, A.J.; Alejandre, F.J. Digital management focused on the preventive maintenance of World Heritage Sites. Autom. Constr. 2021, 129, 103813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenné, P.; Gharbi, A.; Beit, M. Age-dependent production planning and maintenance strategies in unreliable manufacturing systems with lost sale. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2007, 178, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M. Replacement model under warranty with age-dependent minimal repair. Int. J. Reliab. Appl. 2017, 18, 9–20. [Google Scholar]
- Scarf, P.A.; Cavalcante, C.; Dwight, R.A. An age-based inspection and replacement policy for heterogeneous components. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2009, 58, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artiba, A.; Jamali, M.A.; Ait-Kadi, D. Joint optimal periodic and conditional maintenance strategy. J. Qual. Maint. Eng. 2005, 11, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, T. Periodic inspection policy with preventive maintenance. Nav. Res. Logist. Q. 2010, 31, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Tsai, Y.C.; Huang, S. Single-Machine Scheduling with Fixed Periodic Preventive Maintenance to Minimise the Total Weighted Completion Times. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 8891322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, T. Optimum policies when preventive maintenance is imperfect. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 1979, 28, 331–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.I.; Cao, J.P.; Chen, G.M.; Change, L. Research on a phased periodic preventive maintenance model based on reliability constraint. Acta Armamentarii 2017, 38, 2251–2258. [Google Scholar]
- Park, M.; Jung, K.M.; Dong, H.P. Optimal maintenance and warranty strategy for second-hand roduct with periodic preventive maintenance action. J. Korean Stat. Soc. 2021, 50, 773–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xie, H. Determination of Optimal MR&R Strategy and Inspection Intervals to Support Infrastructure Maintenance Decision Making. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2664. [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa, T. Periodic and sequential preventive maintenance policies. J. Appl. Probab. 1986, 23, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedopoulos, I.T.; Smeers, Y. An age reduction approach for finite horizon optimization of preventive maintenance for single units subject to random failures. Comput. Ind. Eng. 1998, 34, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Zuo, M.J.; Yam, R. Sequential imperfect preventive maintenance models with two categories of failure modes. Nav. Res. Logist. 2001, 48, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Xi, L.; Lee, J.; Zhou, X. Optimal CBPM policy considering maintenance effects and environmental condition. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2011, 56, 1181–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, R.; Hunter, L. Optimum preventive maintenance policies. Oper. Res. 1960, 8, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Chang, Q.; Zou, J. A real-time maintenance policy for multi-stage manufacturing systems considering imperfect maintenance effects. IEEE Access 1960, 8, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, B. Optimal replacement under a general failure model. Adv. Appl. Probab. 1978, 10, 431–451. [Google Scholar]
- Lie, C.; Chun, Y. An algorithm for preventive maintenance policy. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 1986, 35, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillart, L.M.; Pollock, S.M. Cost-optimal condition-monitoring for predictive maintenance of 2-phase systems. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2002, 51, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, H.; Wang, H. Imperfect maintenance. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1996, 94, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M. Reliable Preventive Maintenance Scheduling. AIIE Trans. 1979, 11, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, T. Sequential imperfect preventive maintenance policies. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 1988, 37, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, E.; Liao, W.; Xi, L. A single machine-based scheduling optimization model integrated with preventive maintenance policy for maximising the availability. Int. J. Ind. Syst. Eng. 2017, 10, 451–469. [Google Scholar]
- Labib, A. A decision analysis model for maintenance policy selection using a CMMS. J. Qual. Maint. Eng. 2004, 10, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Gao, R.X. An integrated fault diagnosis and prognosis approach for predictive maintenance of wind turbine bearing with limited samples. Renew. Energy 2020, 14, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, K.A.; Gebraeel, N.Z. Predictive maintenance management using sensor-based degradation models. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern.—Part A Syst. Hum. 2009, 39, 840–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwany, A.H.; Gebraeel, N.Z. Sensor-driven prognostic models for equipment replacement and spare parts inventory. Iie Trans. 2008, 40, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Lin, L.; Xi, L. Modified two-stage degradation model for dynamic maintenance threshold calculation considering uncertainty. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2011, 9, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.; Do, P.; Vu, H.C. An efficient evolutionary algorithm for joint optimization of maintenance grouping and routing. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Green Technology and Sustainable Development, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 27–28 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Xi, L.; Lee, J. Reliability-centered predictive maintenance scheduling for a continuously monitored system subject to degradation. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2007, 92, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, M.Y.; Li, L.; Meng, G. Cost effective updated sequential predictive maintenance policy for continuously monitored degrading systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2010, 7, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjoul, O.; Benfriha, K.; Zant, C.E. Algorithmic strategy for simultaneous optimization of design and maintenance of multi-component industrial systems. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2020, 5, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakiru, J.; Pintelon, L.; Muchiri, P.N. Integrated remanufacturing, maintenance and spares policies towards life extension of a multi-component system. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2021, 215, 107872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, B.C.; Dohi, T. Quantifying the risk in age and block replacement policies. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2010, 61, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moakedi, H.; Seyedhosseini, M.S.; Shahanaghi, K. A block-based inspection policy for a multi-component system subject to two failure modes with stochastic dependence. J. Qual. Maint. Eng. 2019, 25, 314–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zequeira, R.; Berenguer, C. Periodic imperfect preventive maintenance with two categories of competing failure modes. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2006, 91, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Pham, H. A generalized block replacement policy for a k-out-of-n system with respect to threshold number of failed components and risk costs. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part A Syst. Hum. 2017, 42, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, S.H.; Chen, Y.L.; Chang, C.C.; Zhe, G.Z. A block replacement policy for systems subject to non-homogeneous pure birth shocks. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2012, 61, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Jiang, X.; Negenborn, R.R. Opportunistic maintenance for offshore wind farms with multiple-component age-based preventive dispatch. Ocean. Eng. 2021, 215, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Sun, B.; Chen, Z. Opportunistic maintenance policy integrating leasing profit and capacity balancing for serial-parallel leased systems. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2021, 205, 107233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakowski, T.; Werbinka, S. On problems of multicomponent system maintenance modelling. Int. J. Autom. Comput. 2009, 6, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.M. Research on Development Platform of Aircraft Maintenance System. Autom. Instrum. 2019, 83, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, F.; Tian, Z. Opportunistic maintenance for wind farms considering multi-level imperfect maintenance thresholds. Renew. Energy 2012, 45, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koochaki, J.; Bokhorst, J.; Wortmann, H. Condition based maintenance in the context of opportunistic maintenance. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2012, 50, 6918–6929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, L.; Liang, W. Opportunistic predictive maintenance for complex multi-component systems based on DBN HAZOP model. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2012, 90, 376–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Jiang, Z. An opportunistic maintenance policy of multi-unit series production system with consideration of imperfect maintenance. Appl. Math. Inf. Sci. 2013, 7, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Parlikad, A.K. Predictive group maintenance for multi-system multi-component networks. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2020, 13, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.H.; Kamaruddin, S. Assessment of distance-based multi-attribute group decision-making methods from a maintenance strategy perspective. J. Ind. Eng. Int. 2015, 11, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjidemetriou, G.M.; Herrera, M.; Parlikad, A.K. Predictive group maintenance for networks of bridges, based on condition and criticality analysi. In Proceedings of the 23rd Euro Working Group on Transportation, Paphos, Cyprus, 18–20 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, D.; Zhang, A.; Feng, Q. Group maintenance optimization of subsea Xmas trees with stochastic dependency. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2021, 209, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, J.K.; Jordaan, J. A maintenance strategy model for static equipment using inspection methodologies and risk management. S. Afr. J. Ind. Eng. 2009, 20, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.H.; Yang, C.H.; Chang, J.C. An activity-based costing decision model for life cycle assessment in green building projects. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2014, 238, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Feng, H. Maintenance strategy of multicomponent system based on structure updating and group importance measure. Commun. Stat.-Theory Methods 2020, 42, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, A.; Esameili, S. Optimal condition-based maintenance replacement based on logical analysis of data. Lect. Notes Eng. Comput. Sci. 2013, 1, 830–833. [Google Scholar]
- Hai, V.; Do, P.; Barros, A. Maintenance grouping strategy for multi-component systems with dynamic contexts. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2014, 132, 233–249. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Li, F.; Hou, C.Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, F.; Hou, C.Y. Correlation based multi-component system opportunity group maintenance optimization. Comput. Integr. Manuf. Syst. 2012, 18, 827–832. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.M.; Li, S.B.; Jin, B. Determination of cycle of mitering lock overhaul based on preventive group maintenance strategy. J. Southeast Univ. 2014, 44, 436–440. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.; Li, X.; Xiao, L.C. Optimization model of group maintenance scheme for civil aircraft. Nanjing Univ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 39, 306–311. [Google Scholar]
- Aizpurua, J.I.; Catterson, V.M.; Papadopoulos, Y. Supporting group maintenance through prognostics-enhanced dynamic dependability prediction. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2017, 16, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horenbeek, A.V.; Pintelon, L. A dynamic predictive maintenance policy for complex multi-component systems. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2013, 120, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvard, K.; Artus, S.; Berenguer, C. Condition-based dynamic maintenance operations planning and grouping. Application to commercial heavy vehicles. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2011, 96, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadi, A.; Gharbi, A.; Dhouib, K. Integrated production, maintenance and quality control policy for unreliable manufacturing systems under dynamic inspection. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2021, 236, 108–120. [Google Scholar]
- Kristjanpoller, F. Opportunistic Strategy for Maintenance Interventions Planning: A Case Study in a Wastewater Treatment Plant. Appl. Sci. 2021, 23, 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- Marutani, J.; Ohtsuka, T. A Real-Time Algorithm for Nonlinear Infinite Horizon Optimal Control by Time Axis Transformation Method. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control. 2013, 23, 1955–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, P.; Hai, C.V.; Barros, A. Maintenance grouping for multi-component systems with availability constraints and limited maintenance teams. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2015, 14, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildeman, R.E.; Dekker, R.; Smit, A.C.J.M. A dynamic policy for grouping maintenance activities. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1997, 99, 530–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chal, N.; Dahane, M.; Beldjilali, B. Optimisation of preventive maintenance grouping strategy for multi-component series systems: Particle swarm based approach. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2016, 10, 440–451. [Google Scholar]
- Vijaya, N.V.; Chaturvedi, S.K. Multi-component maintenance grouping optimization based on stochastic dependency. J. Risk Reliab. 2021, 235, 56–62. [Google Scholar]
- Doostparast, M.; Kolahan, F.; Doostparast, M. Optimisation of PM scheduling for multi-component systems—A simulated annealing approach. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2015, 7, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, Y. Group maintenance policies for an R-out-of-N system with phase-type distribution. Ann. Oper. Res. 2018, 261, 79–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Liao, H. Condition based maintenance optimization for multi-component systems using proportional hazards model. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2011, 96, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. A survey of maintenance policies of deteriorating systems. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2002, 139, 469–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, W.; Enrico, Z. The evolution of system reliability optimization. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2019, 192, 106259. [Google Scholar]
- Albakkoush, S.; Pagone, E.; Salonitis, K. Scheduling Challenges within Maintenance Repair and Overhaul Operations in the Civil Aviation Sector. In Proceedings of the TESConf 2020—9th International Conference on Through-life Engineering Services, Cranfield, UK, 3–4 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ritter, O.; Wende, G.; Gentile, R. Intelligent Diagnostics for Aircraft Hydraulic Equipment. In Proceedings of the European Conference of the Prognostics and Health Management Society, Utrecht, The Netherlands, 3–6 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Goebel, K.; Hai, Q.; Eklund, N. Modeling Propagation of Gas Path Damage. In Proceedings of the Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 3–10 March 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Saxena, A.; Kai, G.; Simon, D. Damage propagation modeling for aircraft engine run-to-failure simulation. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Conference on Prognostics and Health Management, Denver, CO, USA, 6–9 October 2008; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chiachio, J.; Chiachio, M.; Saxena, A. An Energy-Based Prognostic Framework to Predict Fatigue Damage Evolution in Composites. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the Prognostics and Health Management Society, New Orleans, LA, USA, 25–27 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Corbetta, M.; Sbarufatti, C.; Manes, A. Real-Time Prognosis of Crack Growth Evolution Using Sequential Monte Carlo Methods and Statistical Model Parameters. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2015, 64, 736–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, R.; Rahn, A.; Kai, W. Developing prescriptive maintenance strategies in the aviation industry based on a discrete-event simulation framework for post-prognostics decision making. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2021, 214, 107812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, C.K.; Kar, H. Expected Power Bound for Two-Dimensional Digital Filters in the Fornasini-Marchesini Local State-Space Model. IEEE Signal Processing Lett. 2015, 22, 1065–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Lin, Y.; Han, M. Stability and Hopf bifurcation for an epidemic disease model with delay. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2006, 30, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerineau, L.; Gouno, E. Inference for a Failure Counting Process Partially Observed. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2015, 64, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, M.; Ramirez, L.; Navarrina, F. A Mathematical Model to Evaluate the Impact of the Maintenance Strategy on the Service Life of Flexible Pavements. Math. Probl. Eng. 2019, 3, 9480675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.Q.; Lu, J.M.; Batalden, B.M. The investigation of physical explanation for proportional hazard model (PHM) for typical failure mechanisms. Reliab. Maintainab. Symp. 2017, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Prakash, G.; Narasimhan, S.; Pandey, M. Condition Based Maintenance of Low Speed Rolling Element Bearings using Hidden Markov Model. Int. J. Progn. Health Manag. 2020, 8, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalouli, S.; Benmansour, R.; Hanafi, S. An ant colony algorithm based on opportunities for scheduling the preventive railway maintenance. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Control, Saint Julian’s, Malta, 6–8 April 2016; pp. 594–599. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, H. Maintenance Modelling, Simulation and Performance Assessment for Railway Asset Management. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Technologie de Troyes, Troyes, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ricketts, N. Railway Bridge Maintenance|Preventive Maintenance; ICE Publishing: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, S.M.; Stidsen, T.; Rasmussen, K.M. The Preventive Signaling Maintenance Crew Scheduling Problem for European Railway Traffic Management System (ERTMS); DTU Management Engineering: Roskilde, Denmark, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.; Cao, Y.; Wang, J. A preventive, opportunistic maintenance strategy for the catenary system of high-speed railways based on reliability. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part F J. Rail Rapid Transit 2019, 234, 095440971988421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, Y.; Nagatomo, T. Maintenance technologies with sensors for bogies of railway vehicles. J. Jpn. Soc. Tribol. 2017, 52, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Duan, Y.; Depot, B.E. Research on Maintenance Standard for CRH3C EMU Faiveley Pantograph of Beijing-Tianjin Inter-city Railway. High Speed Railw. Technol. 2016, 7, 58–60. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.Y.; Hong, S.S. Optimization of maintenance strategy for high-speed railway catenary system based on multistate model. J. Meas. Sci. Instrum. 2019, 10, 348–360. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, R.H.; Lai, Y.C.; Huang, K.L. Decision support models for annual catenary maintenance task identification and assignment. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2021, 152, 102402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G. Research on Maintenance Strategy Optimization Model of Pumped-Storage Power Unit Based on Devices Failure Probability Distribution. Water Power 2016, 42, 83–86. [Google Scholar]
- Pargar, F. A New Mathematical Model for Scheduling Preventive Maintenance and Renewal Projects of Multi-Unit Systems; Application to Railway Track; University of Twente: Enschede, Netherlands, 2015; Volume 13, pp. 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, B.; Wu, J.; Lin, R. Optimization of high-level preventive maintenance scheduling for high-speed trains. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2019, 183, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucukoglu, I.; Ozturk, N. An advanced hybrid meta-heuristic algorithm for the vehicle routing problem with backhauls and time windows. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2015, 86, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Machemehl, R.B. Optimal Transit Route Network Design Problem with Variable Transit Demand: Genetic Algorithm Approach. J. Transp. Eng. 2015, 132, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Gupta, G. An efficient parallel dynamic programming algorithm. Comput. Math. Appl. 2015, 30, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.M.; Xiao, H. An Approach to Track Maintenance Prioritization for Urban Rail Transit. Public Work. Manag. Policy Res. Pract. Transp. Infrastruct. Environ. 2015, 20, 159–175. [Google Scholar]
- Ming, Z. Decision approach of maintenance for urban rail transit based on equipment supervision data mining. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Data Acquisition & Advanced Computing Systems: Technology & Applications, Warsaw, Poland, 24–26 September 2015; pp. 376–380. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W. Reflections on the Urban Rail Transit Vehicle Maintenance Resource Sharing. Sci. Technol. Inf. 2014, 12, 194–195. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, E.H.; Gao, M.Z.; Zhu, C.R. Study of Fault Diagnosis and Pre-alarm Method for ZDJ-9 Switch Equipment in Urban Rail Transit. Railw. Signal. Commun. 2016, 52, 71–73. [Google Scholar]
- Jie, G.; Cong, L.; Wu, Y. Design and Implementation of Equipment Operation and Maintenance Management System for Urban Rail Transit. Urban Rapid Rail Transit 2015, 28, 78–80. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, X.; Hong, C.; Lai, H. Classification and Coding for Urban Rail Transit Facility Equipment Based on BIM. Urban Mass Transit 2016, 19, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Rauwolf, G.A.; Coverstone, C.V.L. Near-optimal low-thrust orbit transfers generated by a genetic algorithm. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 2015, 33, 859–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Yin, T.; Sun, C. An adaptive model selection strategy for surrogate-assisted particle swarm optimization algorithm. In Proceedings of the Computational Intelligence, Wuxi, China, 16–19 December 2016; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Byon, E.; Lewis, N.; Yu, D. Optimal maintenance strategies for wind turbine systems under stochastic weather conditions. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2010, 59, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y. On the promotion strategy of power equipment maintenance. Priv. Technol. 2018, 11, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Aseel, A.; Mezhera, A. Determining the Efficiency of Maintenance Programs Using Performance Indicators: Case Study in Electric Cables and Wires Factory. Int. J. Innov. Creat. Change 2020, 11, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Sitinor, A. Forensic of Solar PV: A Review of Potential Faults and Maintenance Strategies. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Engineering and Emerging Technologies, Istanbul, Turkey, 27–28 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, J. A deep belief network based fault diagnosis model for complex chemical processes. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2017, 107, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghaee, A.; Aghaee, M.; Fathi, M.R. A novel fuzzy hybrid multi-criteria decision-making approach for evaluating maintenance strategies in petrochemical industry. J. Qual. Maint. Eng. 2020, 27, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakir, I.; Yildirim, M.; Ursavas, E. An Integrated Optimization Framework for Multi-Component Predictive Analytics in Wind Farm Operations & Maintenance. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 138, 110639. [Google Scholar]
- Yildirim, M.; Xu, A.S.; Nagi, Z.G. Sensor-driven condition-based generator maintenance scheduling—Part I: Maintenance problem. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2016, 31, 4253–4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayesteh, E.; Yu, J.; Hilber, P. Maintenance optimization of power systems with renewable energy sources integrated. Energy 2018, 149, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, M.D.; Leonardi, F.; Messina, F. Anomaly Detection and Predictive Maintenance for photovoltaic Systems. Neurocomputing 2018, 310, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, S. Analysis on operation and maintenance strategy of power transmission line. Decis. Explor. 2018, 11, 60. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R. Analysis on management and maintenance strategy of high voltage line. China’s New Technol. Prod. 2018, 20, 134–135. [Google Scholar]
- Zcan, E.; Yumuak, R.; Eren, T. A novel approach to optimize the maintenance strategies: A case in the hydroelectric power plant. Eksploat. I Niezawodn.—Maint. Reliab. 2021, 23, 324–337. [Google Scholar]





| Name | Characteristic | Examples of Maintenance Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Perfect maintenance | Equipment status is restored as new | Replace component |
| Imperfect maintenance | Equipment status is restored to between new equipment and failed equipment | Repair failure location |
| Minor maintenance | Equipment status returns to before the failure | Fastening component |
| Dependency | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Economic dependence | The cost of the joint maintenance of several components is not equal to that of maintenance of these components separately |
| Random dependence | The failure of one component in a piece of multicomponent equipment will affect the performance of the other components |
| Structural dependence | For a multicomponent system with a cooperative relationship between components, if one component is repaired, the other components also need to be removed or replaced |
| Resource dependence | Maintenance operations can only be carried out when all required resources are available |
| Maintenance Strategy | Characteristics and Applicability | Limitations | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corrective maintenance | The maintenance is carried out after the components fail. This method is applicable to the components whose service age is difficult to ascertain. | Problems such as interrupting the normal working plan of components and untimely maintenance will occur. | |
| Preventive maintenance | Age dependent maintenance strategy | The maintenance time is determined according to the service age of the components. This method is applicable for components whose service age is known. | Leaves equipment prone to insufficient maintenance. |
| Periodic maintenance strategy | The interval between two maintenances is constant. This method is suitable for components with small fluctuations in degradation rate. | The risk of failure due to an increase in the rate of component degradation cannot be avoided. | |
| Sequential maintenance strategy | The maintenance interval decreases step by step. This method is applicable to components with significant change characteristics of degradation rules. | Prone to a mismatch between maintenance requirements and maintenance operations. | |
| Failure limit strategy | The maintenance time is determined according to the relationship between component reliability and threshold. This method is suitable for components with high reliability requirements. | The threshold is difficult to determine. | |
| Predictive maintenance | The maintenance opportunity is determined according to the predicted component degradation trend. This method is applicable to components whose degradation parameters can be monitored. | It cannot be applied to nonmonitorable components. | |
| Maintenance Strategy | Definition | Characteristics | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Batch maintenance strategy | Carry out preventive maintenance on multiple components of equipment at the same time according to the same maintenance cycle. | It is suitable for equipment with a closed life cycle. This strategy may cause cost waste due to excessive maintenance. | ||
| Opportunity maintenance strategy | When repairing a part of the equipment, other parts of the equipment that need to be repaired soon are also repaired | It may increase the average maintenance cost of components and reduce the effective service time of components. | ||
| Group maintenance strategy | Static grouping | Reparative group | When the faulty components do not affect the normal operation of the equipment, they can be repaired together when the equipment is shut down due to component failure. | It is applicable to multicomponent equipment with a redundant design, and these components can only be repaired. |
| Preventive group | Adjust the maintenance time interval of multiple components to an integer multiple to increase the coincidence probability of component maintenance time. | It is applicable to equipment with a certain multiple relationship between component maintenance intervals. This strategy can reduce the cost of resource preparation. | ||
| Dynamic grouping | Finite time axis | Within a limited time, the maintenance cycle of multiple components is dynamically adjusted and updated. | Only the maintenance methods within a certain period are planned. This strategy is applicable to equipment with a short life and low scrap cost. | |
| Scroll timeline | Under no time limits, the maintenance cycle of multiple components is dynamically adjusted and updated. | It is suitable for equipment with a long life, high scrap cost and complex and changeable service conditions. Maintenance decisions can reflect and track the health status of equipment. | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, J.; Gao, C.; Tang, T. A Review of Sustainable Maintenance Strategies for Single Component and Multicomponent Equipment. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2992. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14052992
Zhao J, Gao C, Tang T. A Review of Sustainable Maintenance Strategies for Single Component and Multicomponent Equipment. Sustainability. 2022; 14(5):2992. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14052992
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Jingyi, Chunhai Gao, and Tao Tang. 2022. "A Review of Sustainable Maintenance Strategies for Single Component and Multicomponent Equipment" Sustainability 14, no. 5: 2992. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14052992
APA StyleZhao, J., Gao, C., & Tang, T. (2022). A Review of Sustainable Maintenance Strategies for Single Component and Multicomponent Equipment. Sustainability, 14(5), 2992. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14052992






