The COVID-19 Infodemic: Mechanism, Impact, and Counter-Measures—A Review of Reviews
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Background and Rationale for This Work
1.2. Definitions
1.3. Research Questions
2. Previous Literature
3. Methods
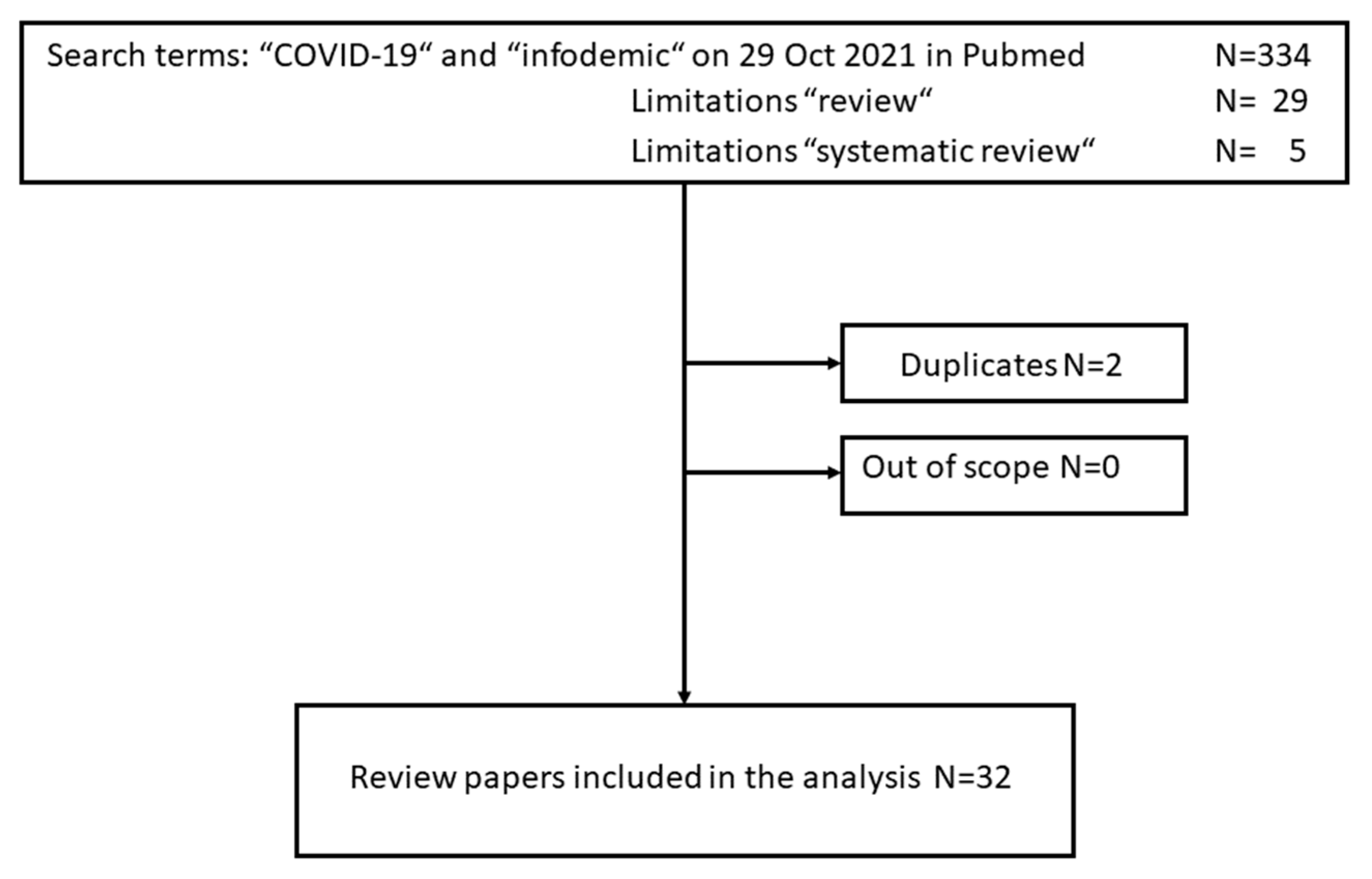
3.1. Review Scope
3.2. Literature Search
3.3. Qualitative Literature Analysis
4. Presentation and Interpretation of Results
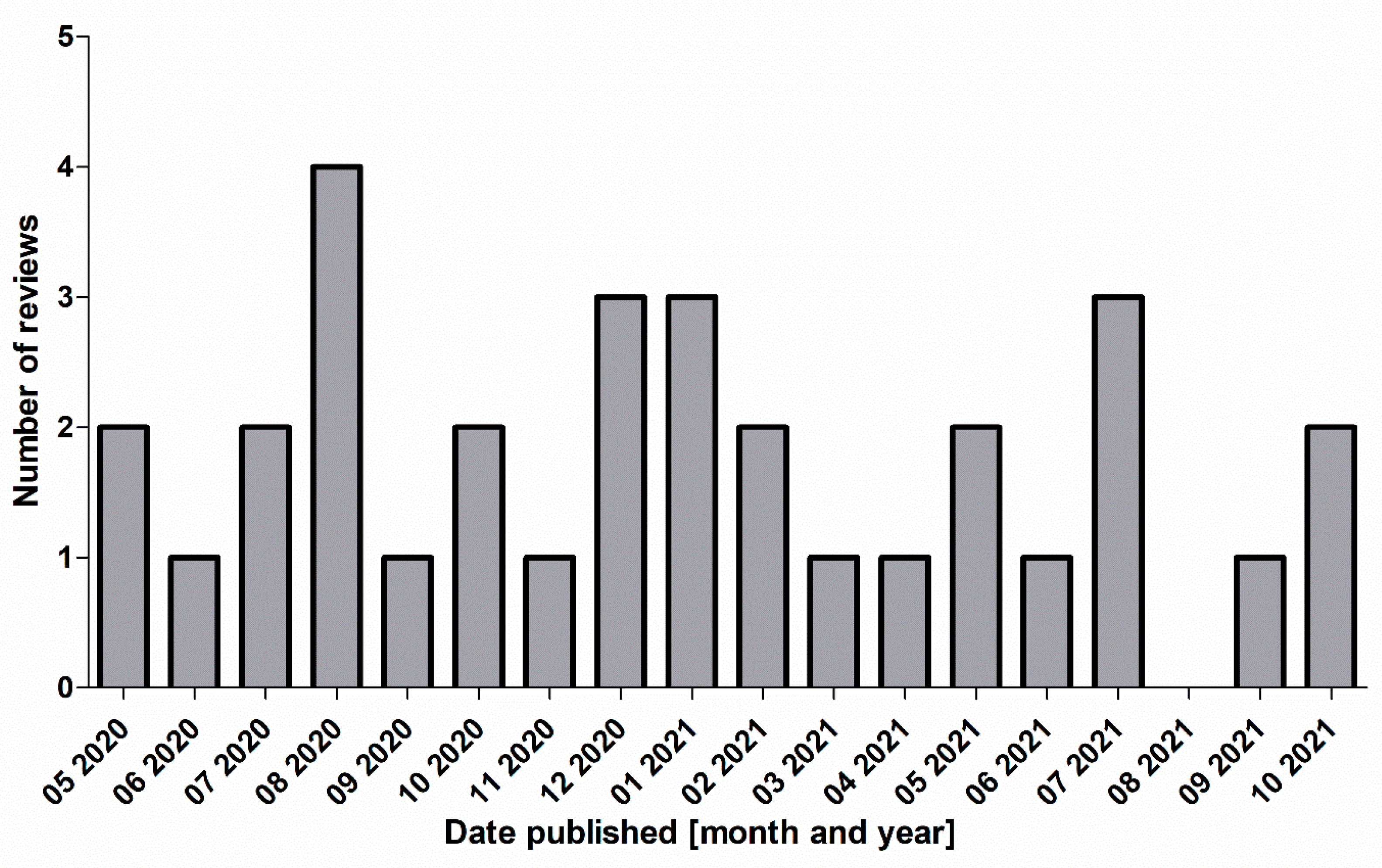
4.1. Global Geographical Distribution of Reviews Included Assessed as Countries of First Authors’ Affiliation
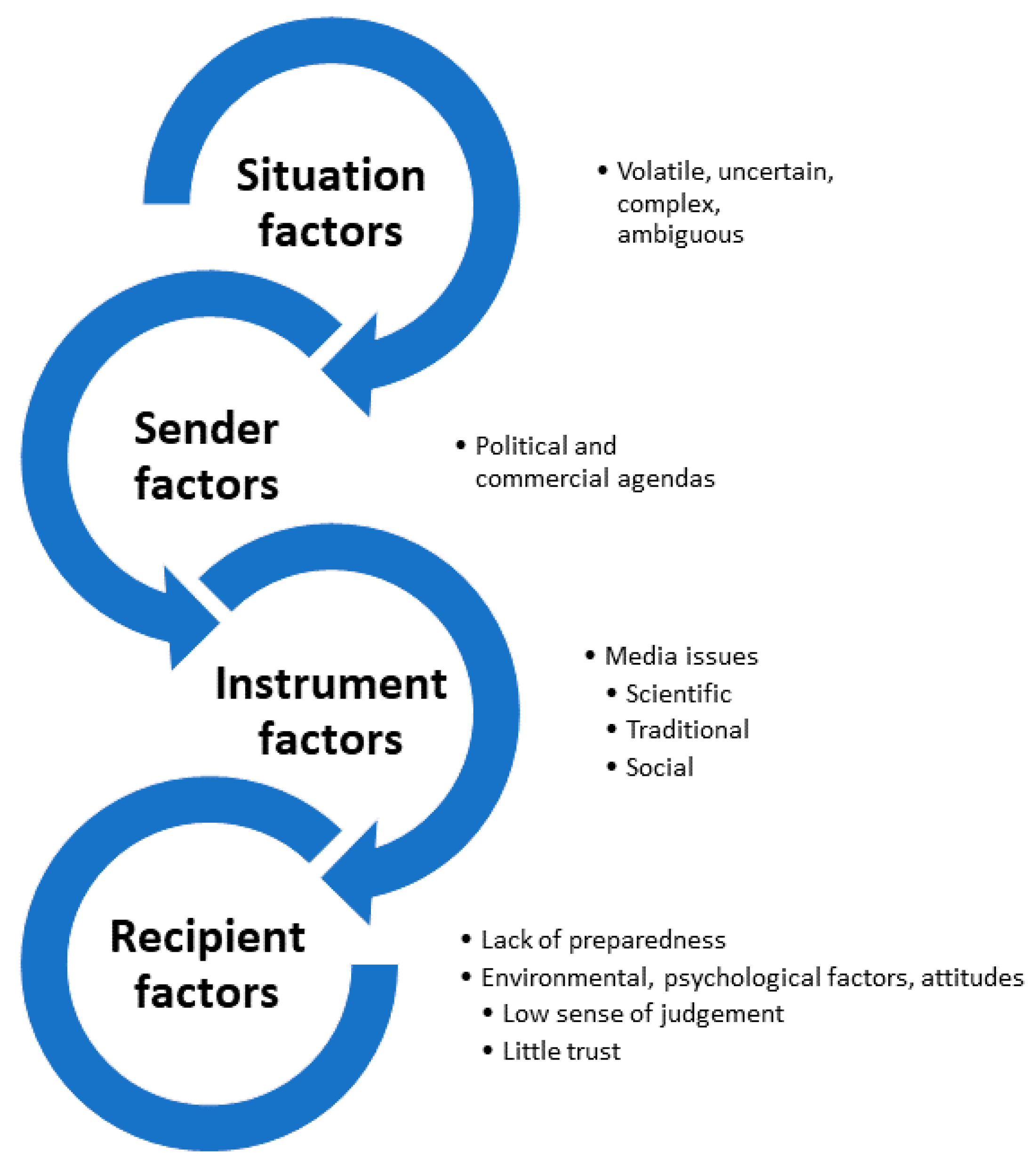
4.2. Mechanism of the Infodemic
4.2.1. Situation Factors
4.2.2. Sender Factors
4.2.3. Instrument Factors
4.2.4. Recipient Factors
4.3. Impact of the Infodemic on Health
4.3.1. Stress
4.3.2. Deception
4.3.3. Violence
4.3.4. Harm
4.4. Measures to Confront the Infodemic by Phase of Disaster Cycle
4.4.1. Pre-Impact Measures
4.4.2. Trans-Impact Measures
4.4.3. Post Impact Measures
4.5. Examples for Infodemics in the Past Other Than COVID-19
4.6. Limitations and Directions for Future Research
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johns Hopkins University. COVID-19 Dashboard by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University (JHU). Available online: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html (accessed on 29 December 2021).
- Schulze, C.; Welker, A.; Kuhn, A.; Schwertz, R.; Otto, B.; Moraldo, L.; Dentz, U.; Arends, A.; Welk, E.; Wendorff, J.J.; et al. Public Health Leadership in a VUCA World Environment: Lessons Learned during the Regional Emergency Rollout of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccinations in Heidelberg, Germany, during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Vaccines 2021, 9, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. COVID-19 Vaccines. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/covid-19-vaccines (accessed on 29 December 2021).
- World Health Organization. Health Topics/Infodemic. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/infodemic#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 12 January 2021).
- United Nations. Universal Declaration of Human Rights. Available online: https://www.un.org/en/about-us/universal-declaration-of-human-rights (accessed on 29 December 2021).
- United Nations. Convention on the Rights of the Child. Available online: https://www.ohchr.org/en/professionalinterest/pages/crc.aspx (accessed on 29 December 2021).
- United Nations. Sustainable Development. Goal 3: Good Health and Well Being. Ensure Healthy Lifes and Promote Well-Being for All at All Ages (Overview). Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal3 (accessed on 4 January 2022).
- United Nations. Sustainable Development. Goal 3: Good Health and Well Being. Ensure Healthy Lifes and Promote Well-Being for All at all Ages (Targets and Indicators). Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal3 (accessed on 4 January 2022).
- Rothkopf, D.J. When the Buzz Bites Back. Available online: https://www.washingtonpost.com/archive/opinions/2003/05/11/when-the-buzz-bites-back/bc8cd84f-cab6-4648-bf58-0277261af6cd/ (accessed on 12 January 2022).
- Pautasso, M. Ten simple rules for writing a literature review. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2013, 9, e1003149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creswell, J.W. Narrative Research. In Qualitative Inquiry & Research Design: Choosing among Five Approaches; Sage: Washington, DC, USA, 2021; pp. 70–76. [Google Scholar]
- Creswell, J.W. Phenomenological Research. In Qualitative Inquiry & Research Design: Choosing among Five Approaches; Sage: Washington, DC, USA, 2021; pp. 76–83. [Google Scholar]
- Kano, M.; Wood, M.M.; Siegel, J.M.; Bourque, L.B. Disaster Research and Epidemiology. In Koenig’s and Schultz’s Disaster Medicine: Principles and Practice; Koenig, K.L., Schultz, C.H., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- La Bella, E.; Allen, C.; Lirussi, F. Communication vs evidence: What hinders the outreach of science during an infodemic? A narrative review. Integr. Med. Res. 2021, 10, 100731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mheidly, N.; Fares, J. Leveraging media and health communication strategies to overcome the COVID-19 infodemic. J. Public Health Policy 2020, 41, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, R.; Bethel, A.; Rogers, M.; Whear, R.; Orr, N.; Shaw, L.; Stein, K.; Coon, J.T. Characteristics, quality and volume of the first 5 months of the COVID-19 evidence synthesis infodemic: A meta-research study. BMJ Evid.-Based Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, H.J. A call to arms: Helping family, friends and communities navigate the COVID-19 infodemic. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 449–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topf, J.M.; Williams, P.N. COVID-19, Social Media, and the Role of the Public Physician. Blood Purif. 2021, 50, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tentolouris, A.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Vlachakis, P.K.; Tsilimigras, D.I.; Gavriatopoulou, M.; Dimopoulos, M.A. COVID-19: Time to flatten the infodemic curve. Clin. Exp. Med. 2021, 21, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loss, J.; Boklage, E.; Jordan, S.; Jenny, M.A.; Weishaar, H.; El Bcheraoui, C. Risk communication in the containment of the COVID-19 pandemic: Challenges and promising approaches. Bundesgesundh. Gesundh. Gesundh. 2021, 64, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, A.; Malik, M.; Raees, V.; Anwar, A. Role of Mass Media and Public Health Communications in the COVID-19 Pandemic. Cureus 2020, 12, e10453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Surgeon General. Confronting Health Misinformation: The U.S. Surgeon General’s Advisory on Building a Healthy Information Environment. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK572169/ (accessed on 7 January 2022).
- Magarini, F.M.; Pinelli, M.; Sinisi, A.; Ferrari, S.; De Fazio, G.L.; Galeazzi, G.M. Irrational Beliefs about COVID-19: A Scoping Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.P.; Kute, V.B.; Agarwal, S.K. “Infodemic” COVID 19: More Pandemic than the Virus. Indian J. Nephrol. 2020, 30, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasidharan, S.; Singh, D.H.; Vijay, S.; Manalikuzhiyil, B. COVID-19: Pan(info)demic. Turk. J. Anaesthesiol. Reanim. 2020, 48, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Su, Y.; Song, L.; Gong, X.; Peng, Y. Stem cell ‘therapy’ advertisements in China: Infodemic, regulations and recommendations. Cell Prolif. 2020, 53, e12937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diethelm, P.; McKee, M. Denialism: What is it and how should scientists respond? Eur. J. Public Health 2009, 19, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, D.C.; Pathak, A.; Chaurasia, R.N.; Joshi, D.; Singh, R.K.; Mishra, V.N. Fighting infodemic: Need for robust health journalism in India. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2020, 14, 1445–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, Y.M.; de Moura, G.A.; Desidério, G.A.; de Oliveira, C.H.; Lourenço, F.D.; de Figueiredo Nicolete, L.D. The impact of fake news on social media and its influence on health during the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review. Z. Gesundh. Wiss. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Naeem, S.; Kamel Boulos, M.N. COVID-19 Misinformation Online and Health Literacy: A Brief Overview. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabarron, E.; Oyeyemi, S.O.; Wynn, R. COVID-19-related misinformation on social media: A systematic review. Bull. World Health Organ. 2021, 99, 455–463a. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, F.A.; Farooq, F. Information Overload and Infodemic in the COVID-19 Pandemic. JPMA J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2020, 70 (Suppl. 3), S162–S165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, N.; Khalid, A.; Turin, T.C. Understanding misinformation infodemic during public health emergencies due to large-scale disease outbreaks: A rapid review. Z. Gesundh. Wiss. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, P.J.; Larson, H.; Dubé, È.; Fisher, A. Vaccine Hesitancy: Drivers and How the Allergy Community Can Help. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 3568–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrams, E.M.; Shaker, M.; Oppenheimer, J.; Davis, R.S.; Bukstein, D.A.; Greenhawt, M. The Challenges and Opportunities for Shared Decision Making Highlighted by COVID-19. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2020, 8, 2474–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, S.; Biswas, P.; Ghosh, R.; Chatterjee, S.; Dubey, M.J.; Chatterjee, S.; Lahiri, D.; Lavie, C.J. Psychosocial impact of COVID-19. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2020, 14, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Siddique, R.; Wang, X.; Zhang, R.; Nabi, G.; Sohail Afzal, M.; Liu, J.; Xue, M. Mental health consequences of infections by coronaviruses including severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Brain Behav. 2021, 11, e01901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Lian, X.; Su, X.; Wu, W.; Marraro, G.A.; Zeng, Y. From SARS and MERS to COVID-19: A brief summary and comparison of severe acute respiratory infections caused by three highly pathogenic human coronaviruses. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, A.; Manchikanti, L. Value and Validity of Coronavirus Antibody Testing. Pain Physician 2020, 23, S381–S390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bórquez, P.B.; Luengo-Charath, M.X.; Anguita, M.V.; Bascuñán, R.M.; Pacheco, M.I.; Michaud Ch, P.; Vacarezza, Y.R. The responsible use and dissemination of information in a pandemic: An ethical imperative. Rev. Chil. Pediatr. 2020, 91, 794–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storeng, K.T.; de Bengy Puyvallée, A. The Smartphone Pandemic: How Big Tech and public health authorities partner in the digital response to COVID-19. Glob. Public Health 2021, 16, 1482–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Jeong, G. Characteristics of the Measurement Tools for Assessing Health Information-Seeking Behaviors in Nationally Representative Surveys: Systematic Review. J. Med. Internet Res. 2021, 23, e27539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, N.; Hogg-Johnson, S.; Mior, S.; Cancelliere, C.; Injeyan, S.; Teodorczyk-Injeyan, J.; Cassidy, J.D.; Taylor-Vaisey, A.; Côté, P. Assessment of Studies Evaluating Spinal Manipulative Therapy and Infectious Disease and Immune System Outcomes: A Systematic Review. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e215493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vériter, S.L.; Bjola, C.; Koops, J.A. Tackling COVID-19 Disinformation: Internal and External Challenges for the European Union. Hague J. Dipl. 2020, 15, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Mechanisms of the Infodemic | Situation factors |
| Sender factors | |
| Instrument factors | |
| Recipient factors | |
| Impact of the Infodemic | Stress |
| Deception | |
| Violence | |
| Harm | |
| Measures to Confront the Infodemic by Phase of Disaster Cycle # | Pre-impact |
| Trans-impact | |
| Post-impact |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ries, M. The COVID-19 Infodemic: Mechanism, Impact, and Counter-Measures—A Review of Reviews. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2605. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14052605
Ries M. The COVID-19 Infodemic: Mechanism, Impact, and Counter-Measures—A Review of Reviews. Sustainability. 2022; 14(5):2605. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14052605
Chicago/Turabian StyleRies, Markus. 2022. "The COVID-19 Infodemic: Mechanism, Impact, and Counter-Measures—A Review of Reviews" Sustainability 14, no. 5: 2605. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14052605
APA StyleRies, M. (2022). The COVID-19 Infodemic: Mechanism, Impact, and Counter-Measures—A Review of Reviews. Sustainability, 14(5), 2605. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14052605






