A Study on the Evaluation of Green Innovation Efficiency and Influencing Factors of the Chinese Tourism Industry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Methods and Data Source
3.1. Super-Efficient SBM Model
3.2. Spatial Correlation Analysis
3.2.1. Global Spatial Autocorrelation-Global Moran’s I Index
3.2.2. Local Spatial Autocorrelation—Local Moran’s I Index
3.3. Geographically Weighted Regression (GWR) Model
3.4. Data Sources
4. Research Design and Result Analysis
4.1. Construction of Green Innovation Efficiency Evaluation Index System of the Tourism Industry and Analysis of Results
4.1.1. Construction of Green Innovation Efficiency Evaluation Index System for the Tourism Industry
- (1)
- Input indicators: Combined with the studies of Liu J [17], Wang YK [24], and Wei ZX [25] et al., the economic and ecological innovation efficiency of tourism industry development can be achieved on the basis of reducing resource consumption by investing in tourism innovation elements of talent, capital, and resources and carrying out tourism innovation activities. Economic efficiency lies in relying on scientific and technological progress to promote green production in the tourism industry, which in turn improves the efficiency of tourism resource utilization. Ecological innovation efficiency lies in the combination of tourism green innovation activities and products to reduce the negative impact of tourism activities on the ecological environment and enhance tourism environmental welfare. The green innovation efficiency of the tourism industry precisely combines tourism economic efficiency and ecological innovation efficiency, thus realizing the high-quality development of the tourism industry. Therefore, this paper selects the number of employees in the tourism industry, research funds in the tourism industry, and the number of tourist attractions of grade 3 or above as the indicators of labor input, capital input, and tourism resource input in the tourism industry based on domestic and foreign studies [26]. At the same time, the greening coverage rate of the city’s built-up area and the number of institutions are introduced as the measurement indicators of the green innovation dimension.
- (2)
- Expected output indicators: the output of green innovation activities carried out by the tourism industry is generally reflected in social and economic benefits. Social benefits include subjective emotions, such as tourists’ satisfaction and willingness to revisit, which are difficult to measure in a standardized way and therefore are not selected. Therefore, this paper only considers the output of economic benefits, so tourism revenue is set as the desired output indicator. In addition, the number of patents applied by tourism is introduced as a measure of innovation benefits.
- (3)
- Non-desired output indicators: environmental pollution is the key issue affecting green innovation in tourism due to the limitation of data calculability and the number of indicators, so this paper selects tourism wastewater discharge and solid waste discharge as non-desired output indicators based on the research of Liu Jia and other scholars [27].
4.1.2. Analysis of Empirical Results
4.2. Spatial Correlation Analysis of Green Innovation Efficiency in Tourism
4.2.1. Global Spatial Correlation Analysis
4.2.2. Local Spatial Correlation Analysis
4.3. Research on Factors Influencing Green Innovation Efficiency of the Tourism Industry in China
4.3.1. Geographically Weighted Regression Model Research Design
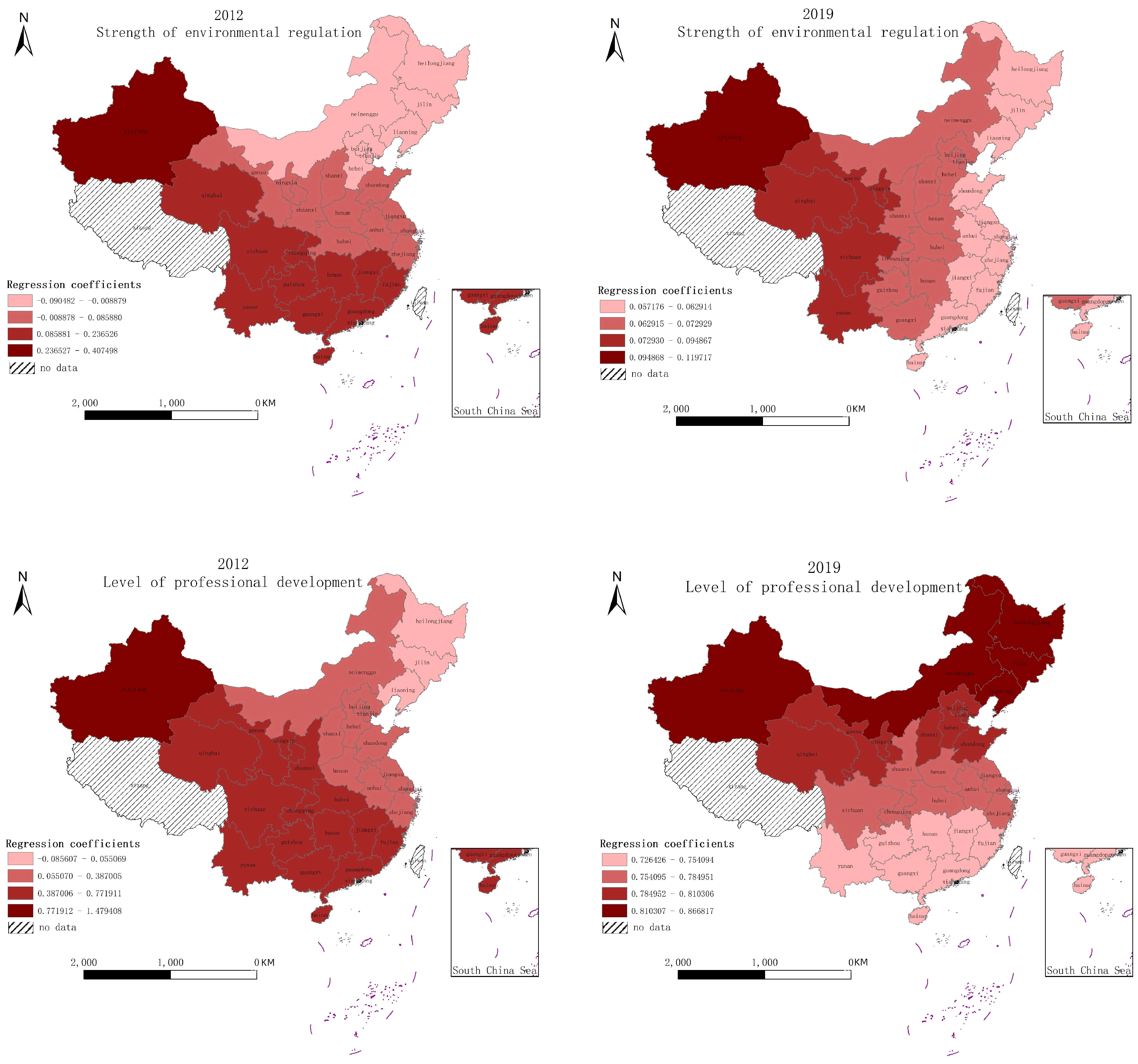
4.3.2. Spatial and Temporal Heterogeneity Analysis of the Factors Influencing Green Innovation Efficiency in China’s Tourism Industry
5. Conclusions and Discussion
5.1. Conclusions
- (1)
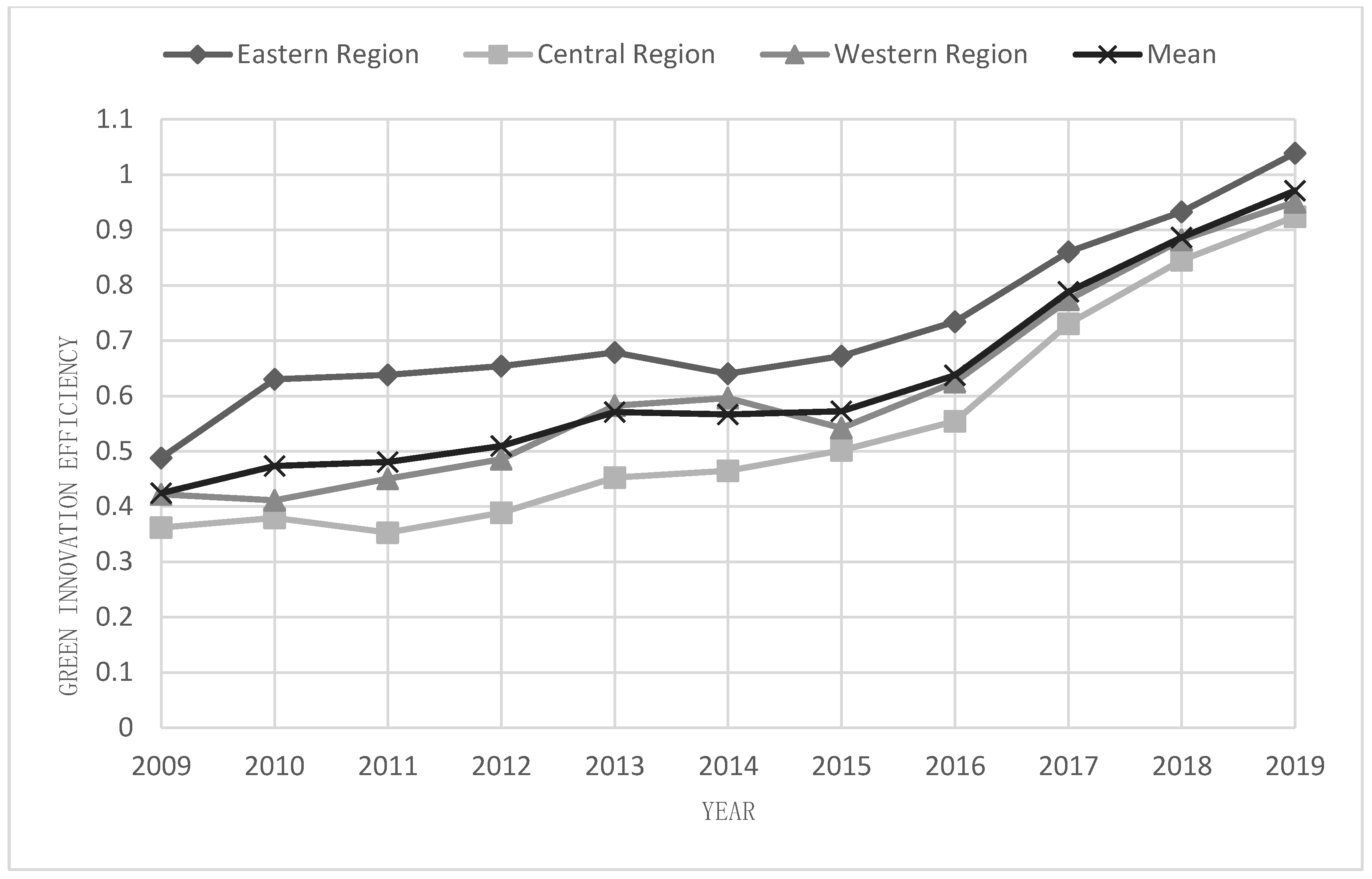
- The green innovation efficiency of China’s tourism industry has been improving in general, and it has achieved rapid growth with the introduction of the five development concepts. From a regional perspective, the average value of the green innovation efficiency of tourism in the eastern region is always higher than that in the central and western areas, as well as the national average, and the gap between the three parts is gradually narrowing. The green innovation efficiency of tourism gradually tends to be balanced.
- (2)
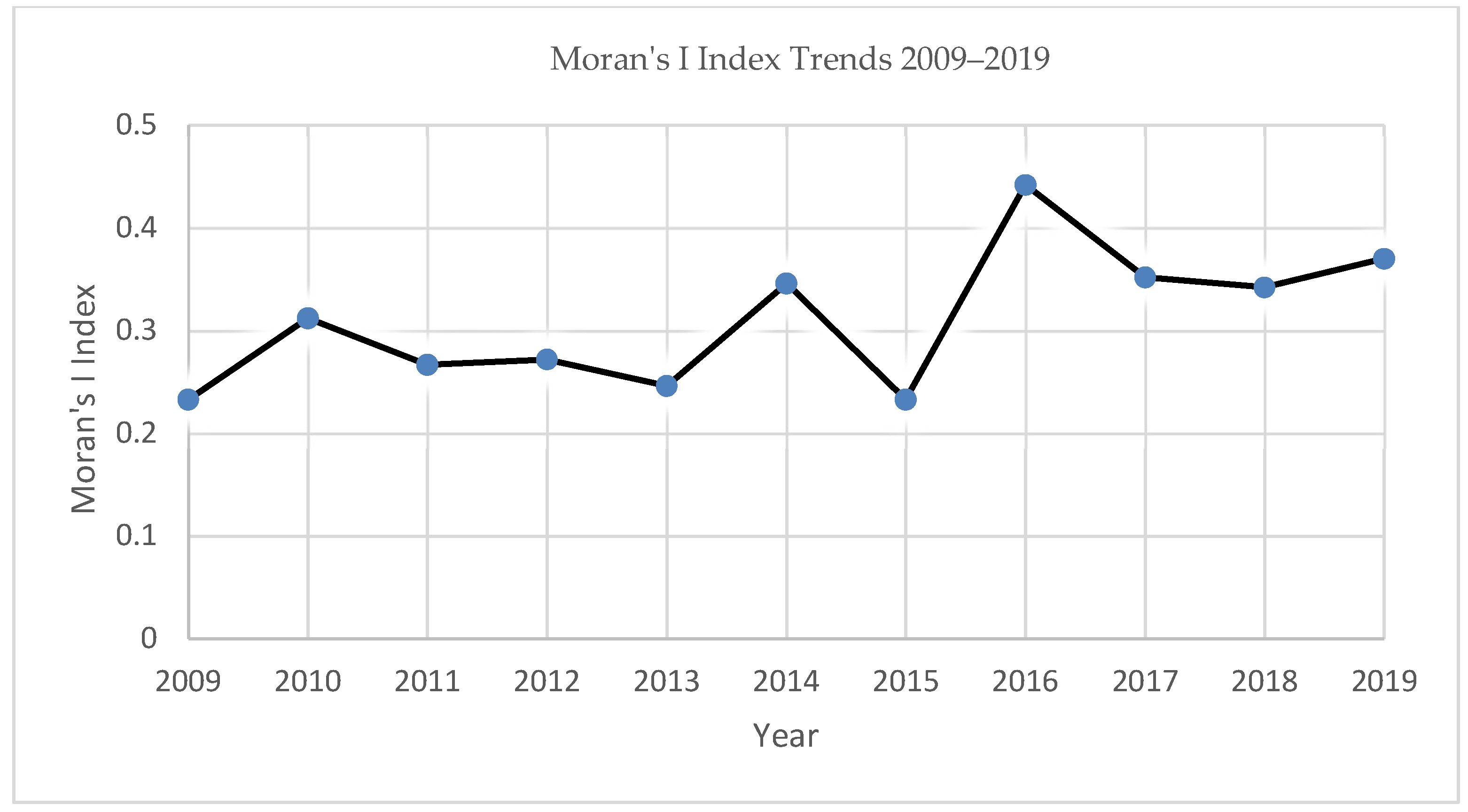
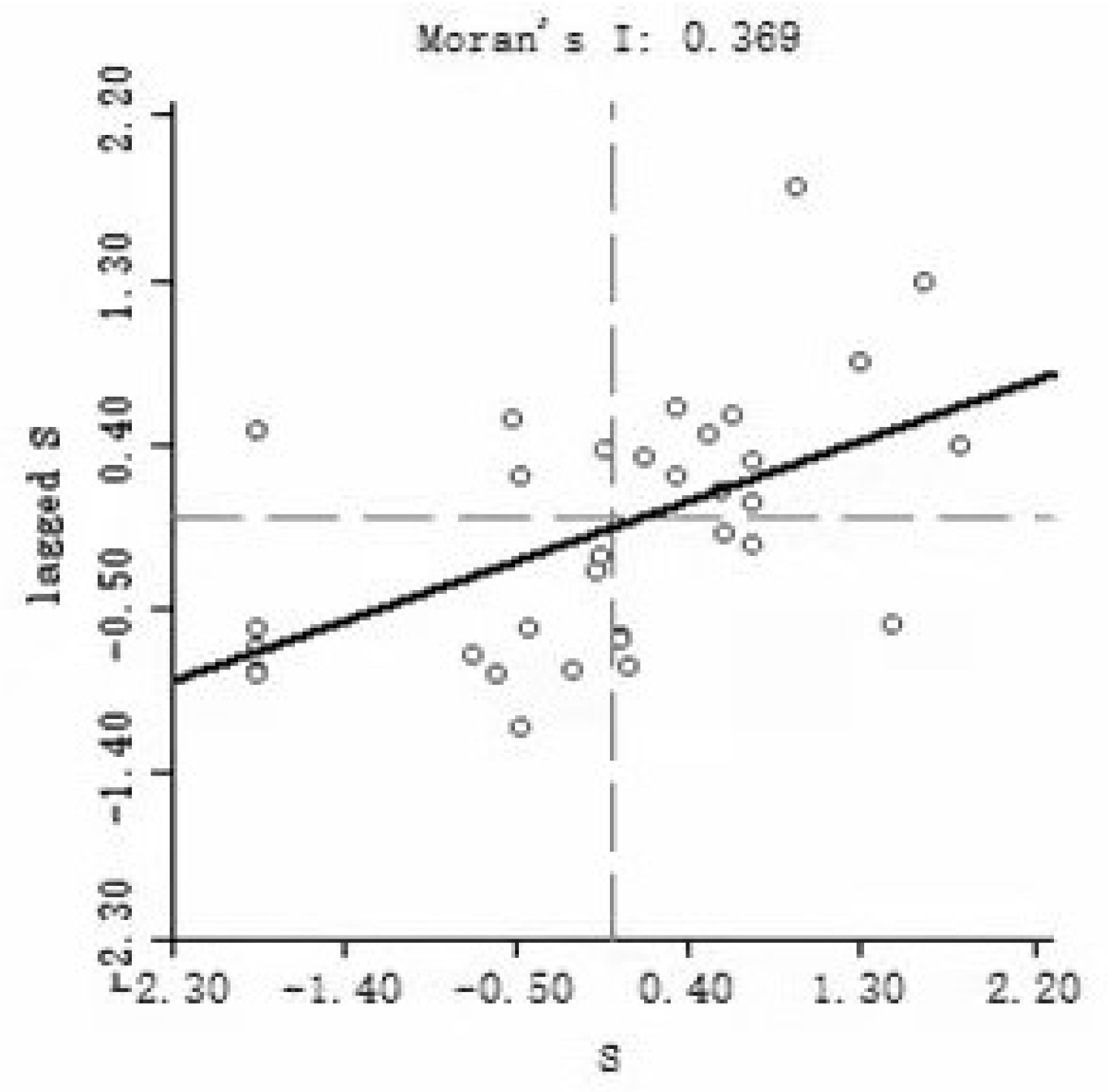
- In terms of spatial distribution, the global Moran index is positive and shows a fluctuating upward trend, which indicates that the spatial aggregation of green innovation efficiency in China’s tourism industry is increasing. In the scatter plot of the mean local Moran index of green innovation efficiency in 30 provinces and cities, 22 provinces and cities in China are distributed in the first and third quadrants, which further leads to a similar conclusion as the global Moran index, i.e., high-high agglomeration and low-low agglomeration are more significant.
- (3)
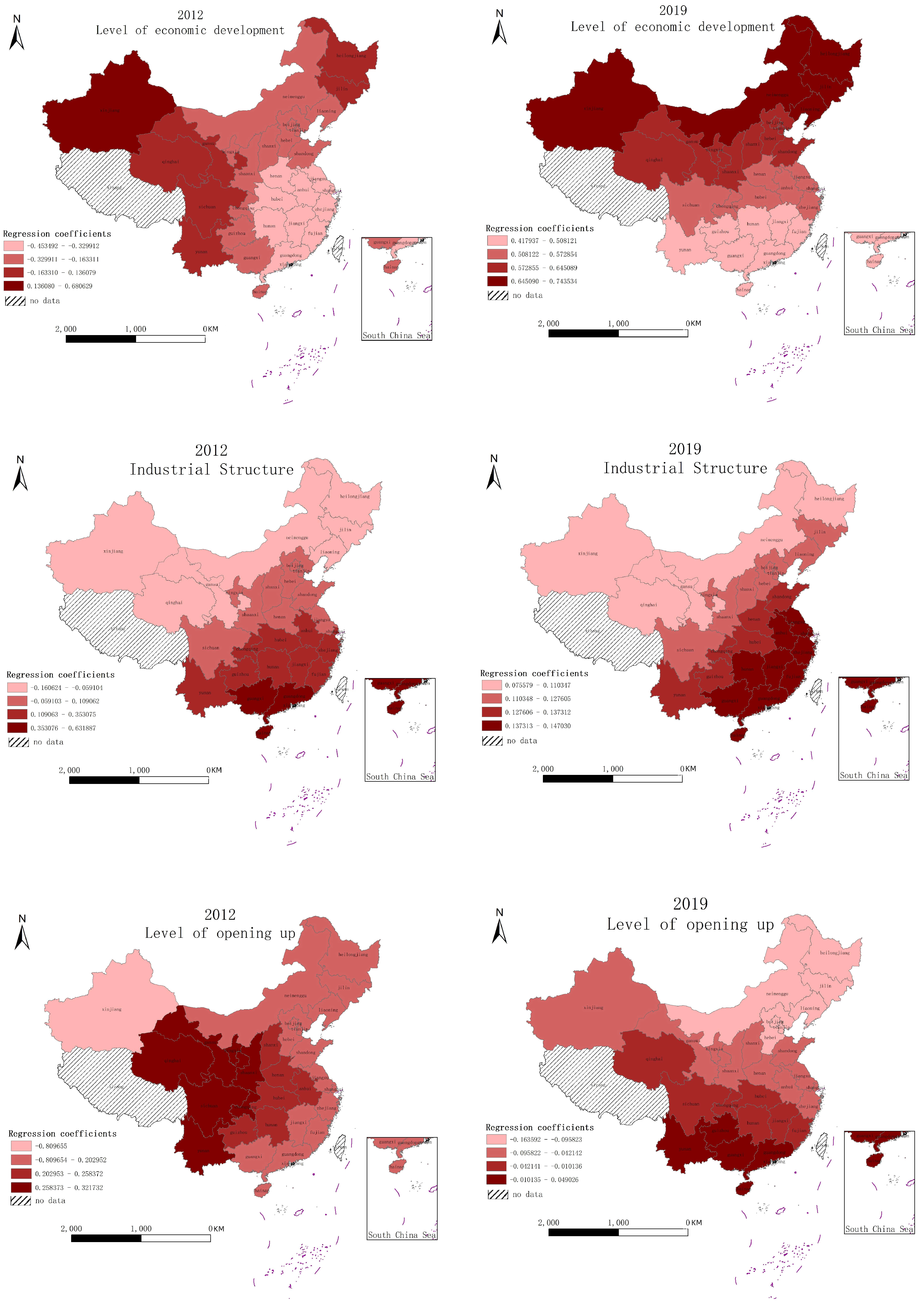
- The green innovation efficiency of China’s tourism industry is influenced by many factors, the strength and tendency of various influencing factors differ from region to region, and the influence on green innovation efficiency of tourism industry has obvious spatial and temporal heterogeneity. Moreover, the level of economic development has a positive influence on green innovation efficiency and gradually decreases from northwest to southeast. The level of economic development has a positive impact on green innovation efficiency and decreases from the northwest to the southeast. The industrial structure and the degree of marketization have a significant positive impact on green innovation efficiency in general, showing a decreasing trend from the southeast to the northwest. The level of openness has a negative impact on the green innovation efficiency of tourism in some regions. The level of professional development of tourism has a significant positive influence on the green innovation efficiency of local tourism, and the influence gradually increases. The intensity of environmental regulation has a U-shaped relationship with local green innovation efficiency, and environmental regulation has not yet played a substantial role in promoting the green innovation efficiency of local tourism.
5.2. Policy Suggestions
5.3. Limitations and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- James, P.; Fussler, C. Driving Eco-Innovation: A Breakthrough Discipline for Innovation and Sustainability; PitanPub: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Z. The Dynamic Value of China’s High-Tech Zones: Direct and Indirect Influence on Urban Ecological Innovation. Land 2022, 11, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, X.L.; Lu, F.; Fan, F. The impact of collaborative innovation on ecological efficiency-Empirical research based on China’s regions. Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 2021, 33, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmaki, A. Regional network governance and sustainable tourism. Tour. Geogr. 2015, 17, 385–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Corte, V.; Del Gaudio, G.; Sepe, F.; Sciarelli, F. Sustainable Tourism in the Open Innovation Realm: A Bibliometric Analysis. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, V.; Sousa, M.J.; Costa, C.; Au-Yong-Oliveira, M. Tourism towards Sustainability and Innovation: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.L.; Liu, Y.; Diao, W.X. Assessing Regional Differences in Green Innovation Efficiency of Industrial Enterprises in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.R.; Jiang, W.L.; Xu, Y.S.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, W. Assessing the corporate green technology progress and environmental governance performance based on the panel data on industrial enterprises above designated size in Anhui Province, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 1151–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Click, B.; Baraniecka, A.; Jefmanski, B. Exploring Supply Chain Collaboration for Green Innovations: Evidence from the High-Tech Industry in Poland. Energies 2022, 15, 1750. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.P.; Wang, S.J.; Sun, S.; Zhu, J. Influence Mechanism of High-Tech Industrial Agglomeration on Green Innovation Performance: Evidence from China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.Y.; Lyu, Y.W.; Shi, F.; Zeng, J.; Liu, C. The Impact of Financial Factor Market Distortion on Green Innovation Efficiency of High-tech Industry. Ekoloji 2019, 28, 3449–3461. [Google Scholar]
- Razzaq, A.; Fatima, T.; Murshed, M. Asymmetric effects of tourism development and green innovation on economic growth and carbon emissions in top 10 GDP countries. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2021, 16, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurley, M.; Koseoglu, M.A. Green innovation research in hospitality and tourism: The construct, antecedents, consequences, and future outlook. Serv. Ind. J. 2021, 41, 734–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.G.; Liao, Y.; Zheng, S.Y.; Shao, X.; Gao, J. The role of green innovation and tourism towards carbon neutrality in Thailand: Evidence from bootstrap ADRL approach. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 292, 112778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Deng, M.R. Institutional support system for green innovation of ecotourism products in the central and western regions. Sci. Technol. Prog. Countermeas. 2006, 2, 108–111. [Google Scholar]
- Liu Jia Song, Q.Y. Spatial network structure and formation mechanism of green innovation efficiency in the Chinese tourism industry. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2018, 28, 127–137. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Xu, W.Q. Spatial and temporal divergence and formation mechanism of green innovation efficiency in China’s coastal tourism industry under carbon emission constraints. Resour. Dev. Mark. 2022, 38, 538–545. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.H.; Xiao, L. The coupled coordination and spatial and temporal divergence of regional eco-efficiency and tourism industry efficiency: A sample of nine cities (states) in Guizhou Province. Ecol. Econ. 2022, 38, 121–127. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Yu, Q.F. Tourism economy in Yangtze River Delta-Eco-efficiency measurement and analysis of influencing factors. J. Shenyang Univ. Technol. 2021, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; An, K. Evaluation of green innovation efficiency and analysis of influencing factors in China’s tourism industry under the goal of “double carbon”. J. Southwest Univ. Natl. 2022, 43, 29–40. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Q. Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA). Sci. Bull. 2000, 1793–1808. [Google Scholar]
- Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Opera Res. 2001, 130, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaoru, T. A Slacks-Based Measure of Super-Efficiency in Data Envelopment Analysis; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; Volume 143. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.K.; Guo, H. Study on the Spatial and Temporal Differentiation and Convergence of Xinjiang Tourism Ecological Efficiency. Geogr. Arid. Areas 2022, 45, 1320–1331. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Z.X.; Guo, W. Study on space-time characteristics and influencing factors of tourism ecological efficiency. Ecol. Econ. 2021, 37, 111–119. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.L.; Lu, C.P.; Mao, J.H.; Sun, D.; Li, H.; Lu, C. Spatial-Temporal Heterogeneity and the Related Influencing Factors of Tourism Efficiency in China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, J.F.; Fu, Z.B. Tourism eco-efficiency of Chinese coastal cities-Analysis based on the DEA-Tobit model. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2017, 148, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.Z.; Cao, Z.X.; Zhang, R.J. Identification of green innovation efficiency and influencing factors in two stages of Chinese high-tech industry. Stat. Decis. Mak. 2022, 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Wang, Z.F. Spatial and temporal evolution of tourism industry efficiency in the Yangtze River Economic Zone under carbon emission constraints and the influencing factors. Yangtze River Basin Resour. Environ. 2021, 30, 280–289. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.; Luo, Y.S.; Lu, Z.N. Environmental regulation, industrial agglomeration and green innovation efficiency. Stat. Decis. Mak. 2021, 37, 53–57. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.Y.; Shang, M.Y.; Zhao, Y.N. Two-way FDI and green innovation efficiency in China in the context of “double-loop”-AS moderating analysis based on the level of marketization. Bus. Res. 2022, 144–152. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Shi, P.; Deng, Z.; Li, X.; Hu, Y. Green productivity measurement and spatial and temporal evolution analysis of tourism in Yangtze River Economic Zone. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2019, 29, 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.F.; Tan, J.X.; Huang, J. Research on the process of regional tourism industry agglomeration and its influencing factors—Take Xiangxi region as an example. J. Tour. 2021, 36, 13–27. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.H. Research on the impact of environmental regulation on economic agglomeration—Based on the perspective of new economic geography. Soft Sci. 2016, 30, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, Y. Economic hierarchy and environmental pollution: A study of ecological Kuznets curve based on carbon emissions. Stat. Decis. Mak. 2021, 37, 146–150. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.H.; Wang, Y.L. Innovation compensation or compliance cost? Pollution halo or pollution paradise?—Testing the threshold effect and spatial spillover effect of the dual hypothesis from the perspective of green total factor productivity. Sci. Technol. Prog. Countermeas. 2018, 35, 46–54. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Li, G.Y. Research on the impact of environmental regulation on the efficiency of green innovation. Res. Financ. Econ. 2018, 42, 52–58. [Google Scholar]
| Primary Indicators | Second-Level Indicators | Tertiary Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| Input indicators | Human input | Number of employees in the tourism industry |
| Financial input | Tourism industry research funds | |
| Resource input | Number of tourism scenic spots above grade 3A | |
| Green Innovation Inputs | Greening coverage rate of built-up areas | |
| Output indicators | Desired Outputs | Number of tourism colleges and universities Total tourism revenue Number of tourism patents |
| Non-desired output indicators | Tourism industry wastewater emissions Tourism solid waste emission |
| Year | Moran’s I | p-Value | Z-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 | 0.233 | 0.006 | 3.216 |
| 2010 | 0.312 | 0.009 | 3.304 |
| 2011 | 0.267 | 0.023 | 2.481 |
| 2012 | 0.272 | 0.016 | 2.366 |
| 2013 | 0.246 | 0.027 | 2.140 |
| 2014 | 0.346 | 0.004 | 2.832 |
| 2015 | 0.233 | 0.031 | 2.001 |
| 2016 | 0.442 | 0.000 | 3.749 |
| 2017 | 0.352 | 0.005 | 2.785 |
| 2018 | 0.342 | 0.002 | 3.318 |
| 2019 | 0.370 | 0.003 | 3.719 |
| Year | ED | IN | FDI | MD | TS | ER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 | 3.29 | 2.25 | 2.84 | 3.03 | 1.22 | 1.28 |
| 2019 | 4.04 | 3.36 | 2.72 | 2.64 | 1.36 | 1.25 |
| GWR Model Parameters | 2012 | 2019 |
|---|---|---|
| Bandwidth | 1,355,374 | 2,535,886 |
| Residual Squares | 0.20 | 0.79 |
| Effective Number | 16.32 | 10.60 |
| Sigma | 0.11 | 0.19 |
| AICc | 15.22 | 3.42 |
| Adjusted R2 | 0.88 | 0.79 |
| Adjusted R2 | 0.81 | 0.69 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, Y.; Zhang, K. A Study on the Evaluation of Green Innovation Efficiency and Influencing Factors of the Chinese Tourism Industry. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16458. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142416458
Zheng Y, Zhang K. A Study on the Evaluation of Green Innovation Efficiency and Influencing Factors of the Chinese Tourism Industry. Sustainability. 2022; 14(24):16458. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142416458
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Yuxiang, and Kegong Zhang. 2022. "A Study on the Evaluation of Green Innovation Efficiency and Influencing Factors of the Chinese Tourism Industry" Sustainability 14, no. 24: 16458. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142416458
APA StyleZheng, Y., & Zhang, K. (2022). A Study on the Evaluation of Green Innovation Efficiency and Influencing Factors of the Chinese Tourism Industry. Sustainability, 14(24), 16458. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142416458





