Factors Influencing Vocational Education and Training Teachers’ Professional Competence Based on a Large-Scale Diagnostic Method: A Decade of Data from China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Conceptual Clarifications and Research Hypothesis
2.1. Conceptual Clarifications
2.1.1. Professional Competence
2.1.2. Vocational Education and Training Teacher
2.1.3. Large-Scale Diagnostic Method
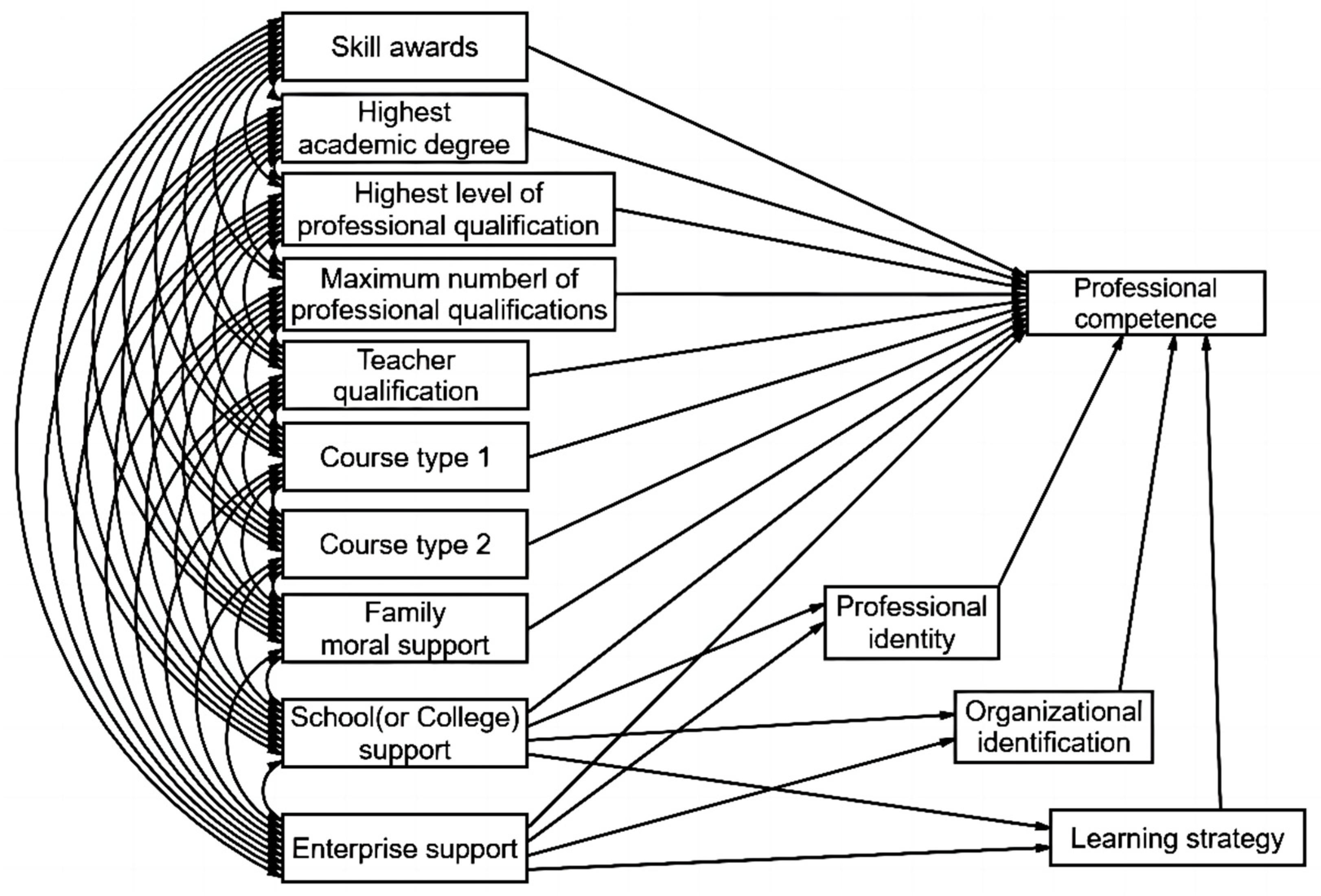
2.2. Research Hypothesis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Participants
3.2. Instruments
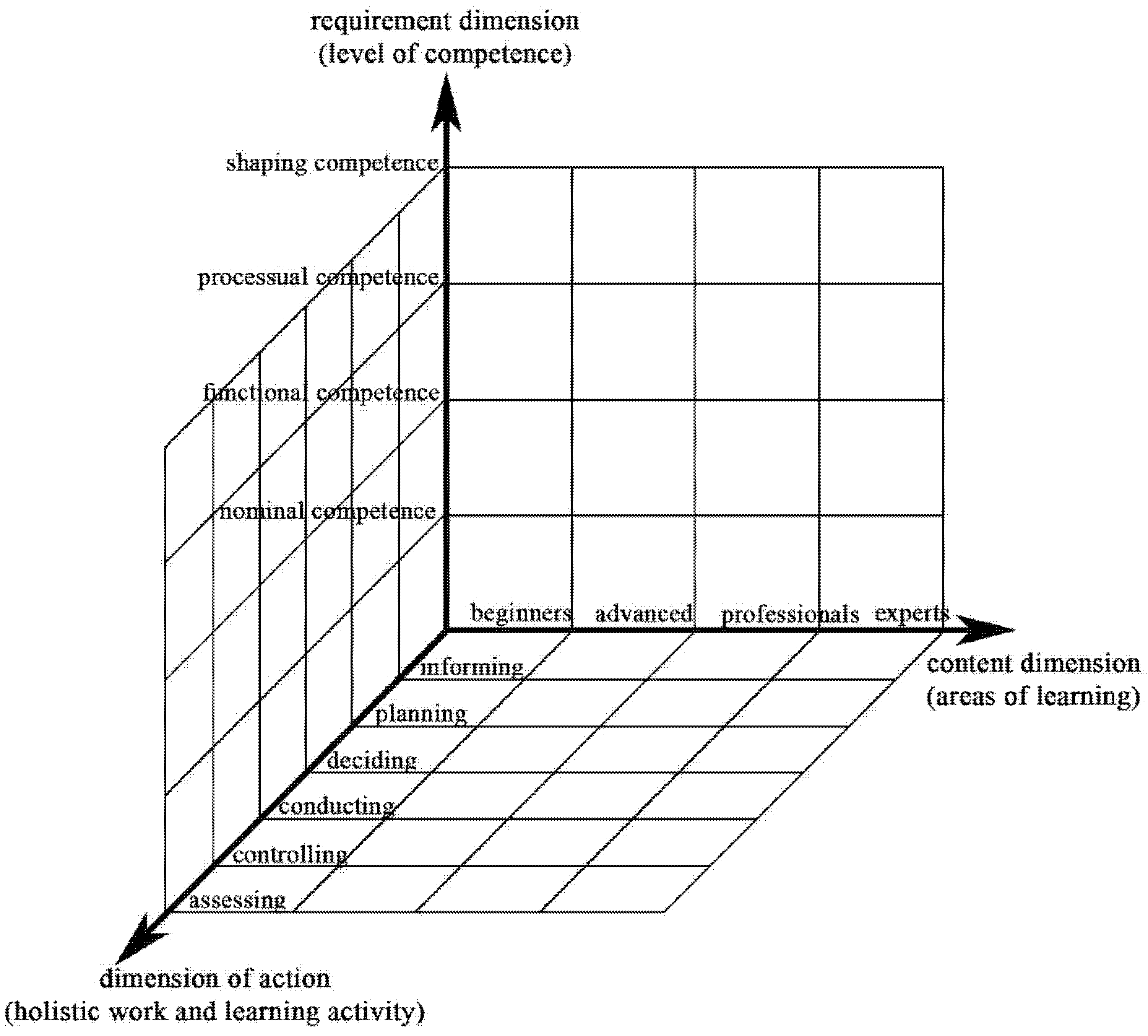
3.2.1. Professional Competence Model and Assessment Criteria for VET Teachers
3.2.2. Comprehensive Diagnostic Tasks
3.2.3. Questionnaires
3.2.4. Difficulty, Discrimination, and Empirical Validity of the Tests
3.3. Procedure
3.4. Data Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Model Fit
4.2. Research Findings
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
7. Research and Implications Limitations
7.1. Implications for Theory
7.2. Implications for Practice
7.3. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The Central People’s Government of the People’s Republic of China. China Has Built the World’s Largest Vocational Education System. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2022-05/29/content_5692904.htm (accessed on 7 July 2022).
- The Central People’s Government of the People’s Republic of China; Ministry of Education Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security; Ministry of Industry and Information Technology. Notice on the Issuance of the Guide to the Development Plan for Manufacturing Talents. Available online: http://www.moe.gov.cn/srcsite/A07/moe_953/201702/t20170214_296162.html (accessed on 21 October 2022).
- Song, J.X. Analysis and choices of testing and evaluation tools of occupational aptitude home and abroad. J. Kunming Metall. Coll. 2014, 30, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.L. The Reflection on the Professional Competence Evaluation of Secondary Vocational School Students. Educ. Teach. Res. 2009, 23, 104–105. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.Y.; Zhao, Z.Q. Review of the German vocational competence assessment ASCOT project. J. Vocat. Educ. 2015, 31, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.L. Construction of the Competency Model for Professional Teachers in Higher Vocational Colleges and its Application. Ph.D. Thesis, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.Q. Research on Vocational Competence Structure of Teachers in Higher Vocational Colleges. Ph.D. Thesis, Northwest University, Xi’an, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z. The current situation of teachers’ qualities and improving strategies in secondary vocational schools. Educ. Res. 2010, 31, 84–88. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.Q.; Huang, F.H. Quality control of professional competence assessment—Taking COMET as an example. Shanghai J. Educ. Eval. 2019, 8, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.X.; Zhao, Z.Q. A study on the construction of a professional competency model for vocational education teachers. J. Vocat. Educ. 2016, 32, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.Q.; Zhuang, R.X. COMET, Giving Professional Competence a Yardstick. Available online: http://www.71.cn/2013/1016/739486.shtml (accessed on 8 July 2022).
- Zhang, Z.X.; Zhao, Z.Q. Current status and prospects of research on professional competence assessment of vocational education teachers. Chin. Vocat. Tech. Educ. 2015, 23, 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Rauner, F.; Heinemann, L.; Piening, D.; Haasler, B.; Maurer, A.; Erdwien, B.; Martens, T.; Katzenmeyer, R.; Baltes, D.; Becker, U.; et al. Messen Beruflicher Kompetenzen Band II: Ergebnisse KOMET 2008; LIT: Berlin, Germany, 2009; pp. 1–225. [Google Scholar]
- Rauner, F.; Heinemann, L.; Maurer, A.; Ji, L.; Zhao, Z.Q. Messen Beruflicher Kompetenzen Band Ⅲ—Drei Jahre KOMET-Testerfahrung; LIT: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 1–257. [Google Scholar]
- Rauner, F.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Ji, L. Messen Beruflicher Kompetenzen; Tsinghua University Publishing House Co., Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2010; pp. 14–22. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.X. Assessment-Based Research on the Professional Competence of Vocational Education and Training Teachers; Tsinghua University Publishing House Co., Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2016; pp. 3–134. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D. International Large Scale Mathematics Assessment Study. Ph.D. Thesis, Shanghai Normal University, Shanghai, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.Q.; Yang, L. Large-scale diagnosis on the vocational ethics development of vocational institution students in China. Commun. Vocat. Educ. 2011, 27, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, F.; Bai, B. Analysis of the problems and factors influencing the capacity development of the vocational education teaching force. Educ. Vocat. 2010, 26, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.F. A research review on vocational teachers’ vocational education competence. J. Hubei Ind. Polytech. 2015, 28, 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, X.C.; He, B.; Peng, Y.H.; Ma, P.T. Hierarchy of influential factors on teachers’ well-being. J. Hunan First Norm. Univ. 2020, 20, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.J. A Study on the Training Path of Teachers’ Vocational Ability Insecondary Vocational Schools. Ph.D. Thesis, Tianjin University of Technology and Education, Tianjin, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.J.; Lu, J.C. A study on the factors influencing the continuous development of teachers’ professional competence. J. Harbin Vocat. Tech. Coll. 2008, 19, 72–73. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Xiao, Y.; Yan, X. A Review of the Research on Teachers’ Professional ldentity in Higher Vocational Colleges. Commun. Vocat. Educ. 2020, 36, 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, A. Problems of and Solutions for Cooperation between Enterprises and Higher Vocational Schools. Ph.D. Thesis, Hebei Normal University, Shijiazhuang, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H. Research on the Problems and Countermeasures of School-Enterprise Cooperation in Higher Vocational Institutions. Ph.D. Thesis, Shandong Normal University, Jinan, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.X. Investigation and Study on the Status of School-Enterprise Cooperation in Women’s Vocational School in Guiyang. Ph.D. Thesis, Guizhou Normal University, Guiyang, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Antera, S. Professional Competence of Vocational Teachers: A Conceptual Review. Vocat. Learn. 2021, 14, 459–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.Y. Professional competence of teachers in vocational institutions: An empirical survey based on 628 secondary and higher vocational teachers. Chin. Vocat. Tech. Educ. 2019, 27, 46–53. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.Y.; Sun, Q.L. A study on teacher role conflict and teacher burnout. Stud. Foreign Educ. 2004, 31, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, L. Research on the Present Situation and Influencing Factors of Social Workers’ Vocational Ability—Based on the Example of 53 Social Organizations in Chengdu. Ph.D. Thesis, Xihua University, Chengdu, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, M.; Hofman, J. Professional Identity in Institutions of Higher-Learning in Israel. High. Educ. 1988, 17, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.-S.; Park, T.-Y.; Koo, B. Identifying Organizational Identification as a Basis for Attitudes and Behaviors: A Meta-Analytic Review. Psychol. Bull. 2015, 141, 1049–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgkinson, G.P.; Ford, J.K. International Review of Industrial and Organizational Psychology; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1995; pp. 1–384. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.L.; Zhao, Y.S. Research on the skills evaluation modes in the reform of vocational education—Taking the predictive validity of COMET skills evaluation method on job performance as the case. Vocat. Tech. Educ. 2022, 43, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.F. On the target of professional development of vocational education teachers from the trails of double qualified teacher policies. Teach. Educ. Res. 2014, 26, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Qiao, Z.H.; Song, H.T. Review of researches on career identity. J. Beijing Norm. Univ. (Soc. Sci.) 2011, 56, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, F.P.; Zhang, N.P. Study on the relationship between organizational identity and professional identity. Commer. Res. 2010, 1, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.H.; Zhao, H.Y. The effects of mentor support on pre-service teachers’ professional efficacy, professional identity and professional commitment. Teach. Educ. Res. 2018, 30, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.X.; Wu, Y.; Wu, F.Y.; Yao, L.H.; Xing, C. Effects of social support on school football teachers’ professional identity: A mediating effect of sense of career calling. J. Wuhan Sports Univ. 2017, 51, 51–81, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.X.; Gao, W.X. A case study research of why young teachers’ professional recognition fluctuated in newly-built public middle school. Teach. Educ. Res. 2020, 32, 75, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Zhu, F.; Lin, S.; Sun, J.; Wu, Y.; Xiao, W. How Is Professional Identity Associated with Teacher Career Satisfaction? A Cross-Sectional Design to Test the Multiple Mediating Roles of Psychological Empowerment and Work Engagement. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, E.M. The reasons of why they want to leave rural school-based on the analysis of teachers’ professional identity. Mod. Educ. Sci. 2017, 34, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canrinus, E.T.; Dalehefte, I.M.; Myhre, S. VET Teachers’ Beliefs on Collaboration, Identity, and Status and Their Relationship with Professional Development. Pedagog. Stud. 2019, 96, 463–480. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, I.; Hur, W.-M.; Kang, S. Employees’ Perceptions of Corporate Social Responsibility and Job Performance: A Sequential Mediation Model. Sustainability 2016, 8, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, D.C. Strategies in Learning and Using a Second Language; Pearson Education Group: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 1–215. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, K.S. Workplace Learning and Pfessional Innovation. Ph.D. Thesis, Northeast University, Chongqing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.Z.; Huang, X.T. Overview of learning strategies research. Educ. Res. 2002, 23, 78–82. [Google Scholar]
- Rauner, F.; Maclean, R. Handbook of Thchnical and Vocational Education and Training Research; Beijing Normal University Publishing Group: Beijing, China, 2017; pp. 86–88. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.G.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Shen, J. The analysis of the present situation and influencing factors of students’ professional competence in secondary vocational education. Mod. Educ. Manag. 2016, 36, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.Q.; Gao, F. Professional competence of students in Chinese vocational colleges and its influencing factors—An analysis on COMET data of five major areas of manufacturing. China Educ. Technol. 2022, 43, 47–55. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Huang, F.H. Development of vocational competency assessment methods. Chin. Vocat. Tech. Educ. 2017, 25, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, H.Z. Quantitative Research and Statistical Analysis; Chongqing University Press: Chongqing, China, 2009; p. 296. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.X.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Tian, J.Y. Research on the professional competence of vocational school and college teachers based on large-scale diagnostics—Data from 36 schools and colleges in five administrative regions. China Educ. Technol. 2021, 42, 55–64. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Q. Research on the construction of vocational school teachers in poor areas from the perspective of precise poverty alleviation—An analysis of a survey based on “job satisfaction of vocational school teachers in S city. ” Soc. Sci. Guangxi 2017, 33, 206–211. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.J. Exploring on reform of accounting practical teaching in vocational and technical institute. J. Beijing Polytech. Coll. 2005, 22, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C. An analysis of teacher-professional development phase of higher vocational educational practice class—A perspective based on development of tasks & attention to contents. Theory Pract. Educ. 2012, 32, 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, G.C. Exploring the factors influencing the professional development of teachers of practical courses in higher education institutions. J. Vocat. Educ. 2011, 27, 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.Q. Two essential features of vocational education engineering courses. Educ. Vocat. 2007, 23, 18–20. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, F.X.; Zhang, C. Interpreting the meaning of “dual-teacher” teachers. Chin. Vocat. Tech. Educ. 2012, 20, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- The Central People’s Government of the People’s Republic of China. State Council on the Issuance of National Vocational Education Reform Notice of the Implementation Programme. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2019-02/13/content_5365341.htm (accessed on 25 July 2022).
- Pan, H.S.; Wang, S.B.; Long, D.Y. The analyses of the status and influence factors of school enterprise cooperation of China higher vocational education. Res. High. Educ. Eng. 2013, 31, 143–148. [Google Scholar]
- The Central People’s Government of the People’s Republic of China. Teachers’ Qualifications Regulations. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/2020-12/26/content_5574844.htm (accessed on 24 July 2022).
- Li, Z.J.; Zhang, B.X. Problems and its countermeasures of teacher certification system construction in China. Educ. Res. 2008, 29, 43–46. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Ma, Y.R. More initiative, higher performance: The role of organisational socialisation and organisational identity. Hum. Resour. Dev. China 2019, 36, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Fit Index | χ² | df | χ2/df | RMSEA | GFI | AGFI | NFI | CFI | IFI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scales | ||||||||||
| Professional identity | 23.423 | 8 | 2.928 | 0.078 | 0.976 | 0.938 | 0.959 | 0.972 | 0.973 | |
| Organizational identification | 42.346 | 9 | 4.705 | 0.108 | 0.959 | 0.903 | 0.944 | 0.955 | 0.955 | |
| Learning strategy | 114.499 | 62 | 1.847 | 0.051 | 0.948 | 0.923 | 0.921 | 0.962 | 0.962 | |
| School support | 34.520 | 7 | 4.931 | 0.111 | 0.963 | 0.889 | 0.965 | 0.972 | 0.972 | |
| Enterprise support | 53.986 | 12 | 4.499 | 0.105 | 0.955 | 0.896 | 0.944 | 0.956 | 0.956 | |
| Family moral support | 12.509 | 4 | 3.127 | 0.082 | 0.984 | 0.941 | 0.983 | 0.988 | 0.988 | |
| χ2 | df | χ2/df | RMSEA | GFI | AGFI | NFI | CFI | IFI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 283.653 | 27 | 10.506 | 0.133 | 0.925 | 0.707 | 0.832 | 0.840 | 0.846 |
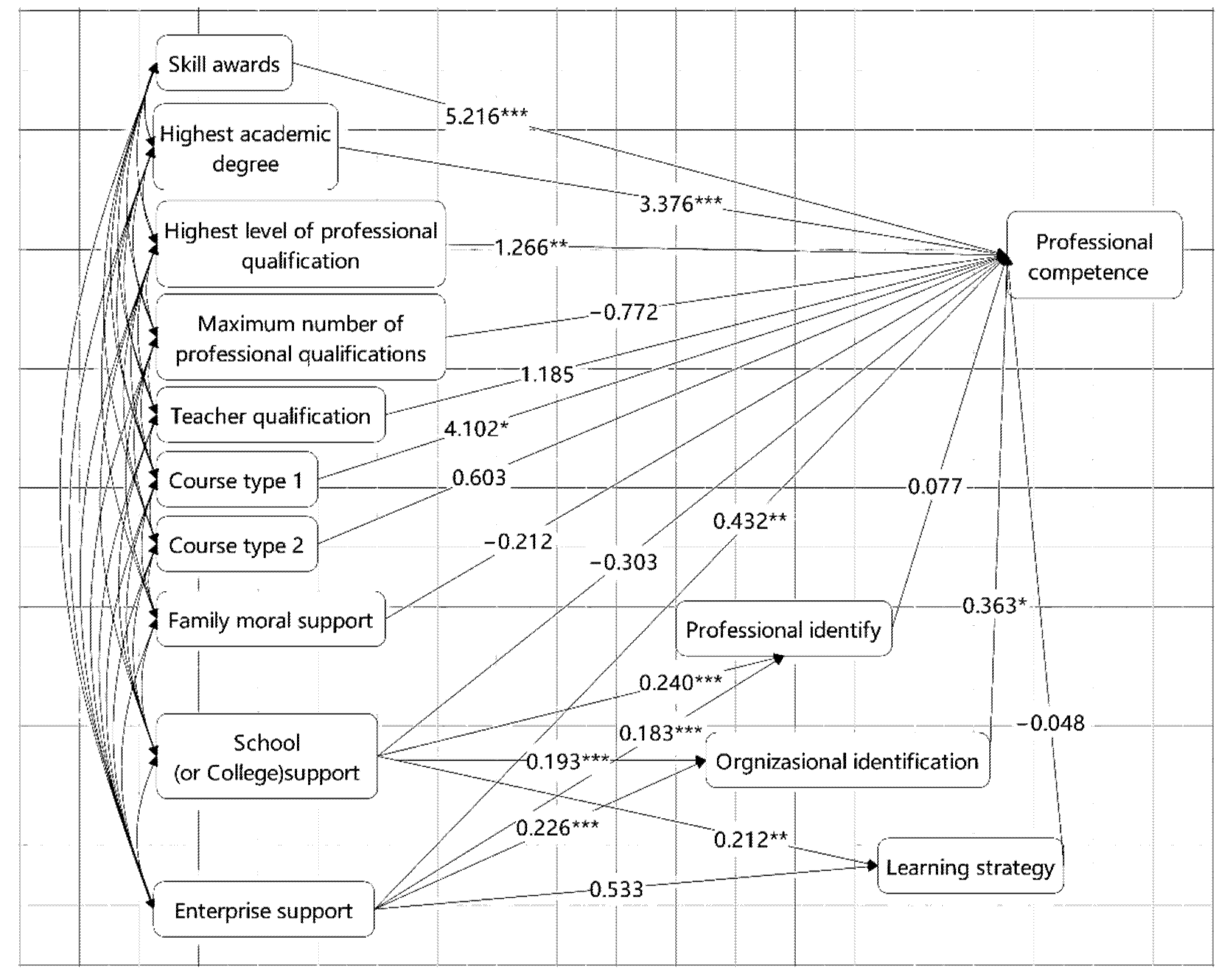
| Hypothesis | Estimate | 95% CI | p | Support or Not Support | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| Direct effects | ||||||
| H1 | Skill awards->PC(professional competence) | 5.216 | 3.319 | 7.161 | 0.000 | √ |
| H2 | Highest degree->PC | 3.376 | 2.012 | 4.810 | 0.000 | √ |
| H3 | Teacher qualification->PC | 1.185 | −2.669 | 5.276 | 0.548 | × |
| H4 | Maximum number of professional qualifications->PC | −0.772 | −2.089 | 0.543 | 0.258 | × |
| H5 | Highest level of professional qualification->PC | 1.266 | 0.619 | 1.883 | 0.001 | √ |
| H6 | School support->PC | −0.303 | −0.576 | −0.034 | 0.026 | √ |
| H7 | Enterprise support->PC | 0.432 | 0.160 | 0.715 | 0.001 | √ |
| H8 | Family moral support->PC | −0.212 | −0.573 | 0.141 | 0.231 | × |
| H9 | Course type 1->PC | 4.102 | 0.813 | 7.270 | 0.016 | √ |
| H10 | Course type 2->PC | 0.603 | −1.811 | 2.955 | 0.643 | × |
| Indirect effects | ||||||
| H11 | School support->organizational identification->PC | 0.070 | 0.009 | 0.145 | 0.210 | √ |
| H12 | Enterprise support->professional identity->PC | 0.014 | −0.055 | 0.091 | 0.675 | × |
| H13 | School support->professional identity->PC | 0.018 | −0.071 | 0.111 | 0.675 | × |
| H14 | Enterprise support->organizational identification->PC | 0.082 | 0.011 | 0.165 | 0.021 | √ |
| H15 | School support->learning strategy->PC | −0.010 | −0.061 | 0.035 | 0.624 | × |
| H16 | Enterprise support->learning strategy->PC | −0.025 | −0.137 | 0.083 | 0.624 | × |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Tian, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, W.; Sun, F.; Que, Y.; He, X. Factors Influencing Vocational Education and Training Teachers’ Professional Competence Based on a Large-Scale Diagnostic Method: A Decade of Data from China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15871. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142315871
Zhang Z, Tian J, Zhao Z, Zhou W, Sun F, Que Y, He X. Factors Influencing Vocational Education and Training Teachers’ Professional Competence Based on a Large-Scale Diagnostic Method: A Decade of Data from China. Sustainability. 2022; 14(23):15871. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142315871
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhixin, Jinyou Tian, Zhiqun Zhao, Wei Zhou, Fangfang Sun, Yongping Que, and Xingguo He. 2022. "Factors Influencing Vocational Education and Training Teachers’ Professional Competence Based on a Large-Scale Diagnostic Method: A Decade of Data from China" Sustainability 14, no. 23: 15871. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142315871
APA StyleZhang, Z., Tian, J., Zhao, Z., Zhou, W., Sun, F., Que, Y., & He, X. (2022). Factors Influencing Vocational Education and Training Teachers’ Professional Competence Based on a Large-Scale Diagnostic Method: A Decade of Data from China. Sustainability, 14(23), 15871. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142315871





