Incorporation of Silver-Doped Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots in Polyvinylidene Fluoride Membrane for Verapamil Removal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Pre-Treatment of Oil Palm Empty Fruit Bunches (EFB)
2.3. Production of Graphite from Oil Palm Empty Fruit Bunches (EFB)
2.4. Production of Graphene Oxide (GO) from Graphite
2.5. Decoration of Silver (Ag) onto GO
2.6. Production of Ag−GOQD from Ag-GO
2.7. Characterization of Ag−GOQD
2.7.1. Morphological Analysis of Ag−GOQD
2.7.2. Elemental Composition Analysis of Ag−GOQD
2.7.3. Determination of Functional Groups of Ag−GOQD
2.7.4. Determination Zeta Potential of Ag−GOQD
2.8. Composite Membrane Fabrication
2.9. Membrane Characterization
2.9.1. Morphological Analysis of Membrane
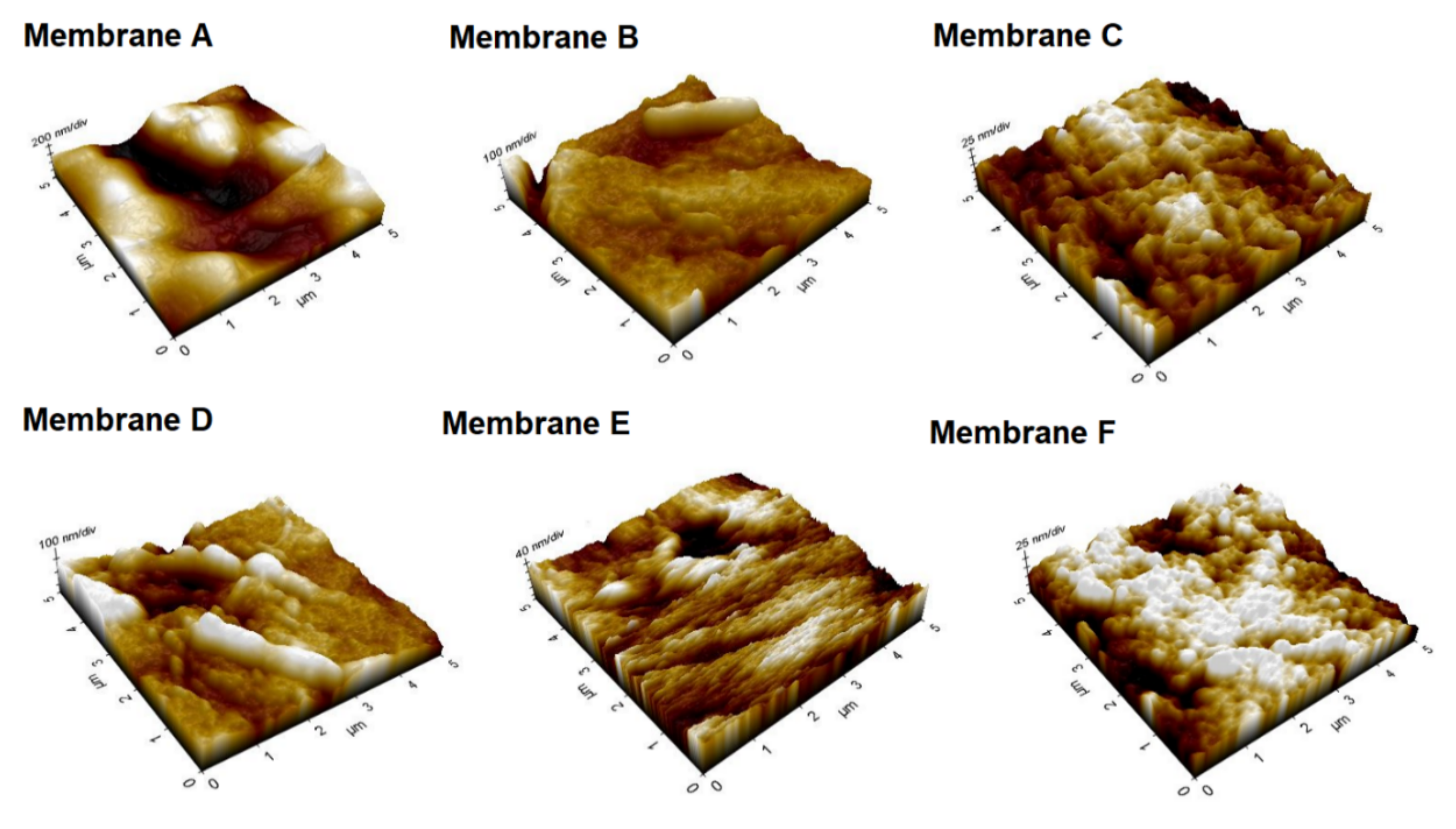
2.9.2. Determination of Membrane Surface Roughness
2.9.3. Determination of Surface Hydrophilicity of Membrane
2.10. Flux and Rejection Test
2.11. Membrane Anti-Fouling Test
2.12. Antibacterial Test
3. Results and Discussion
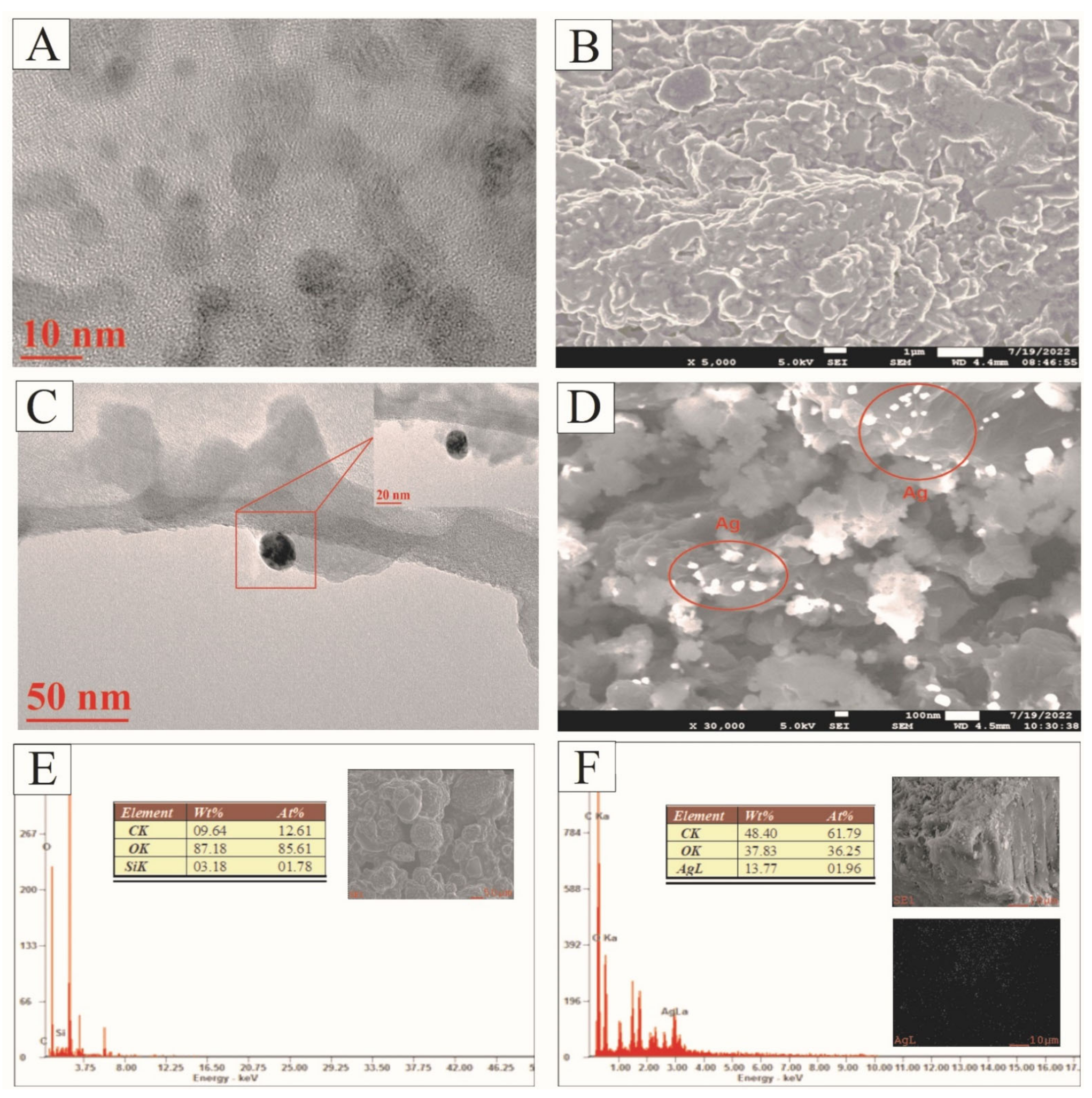
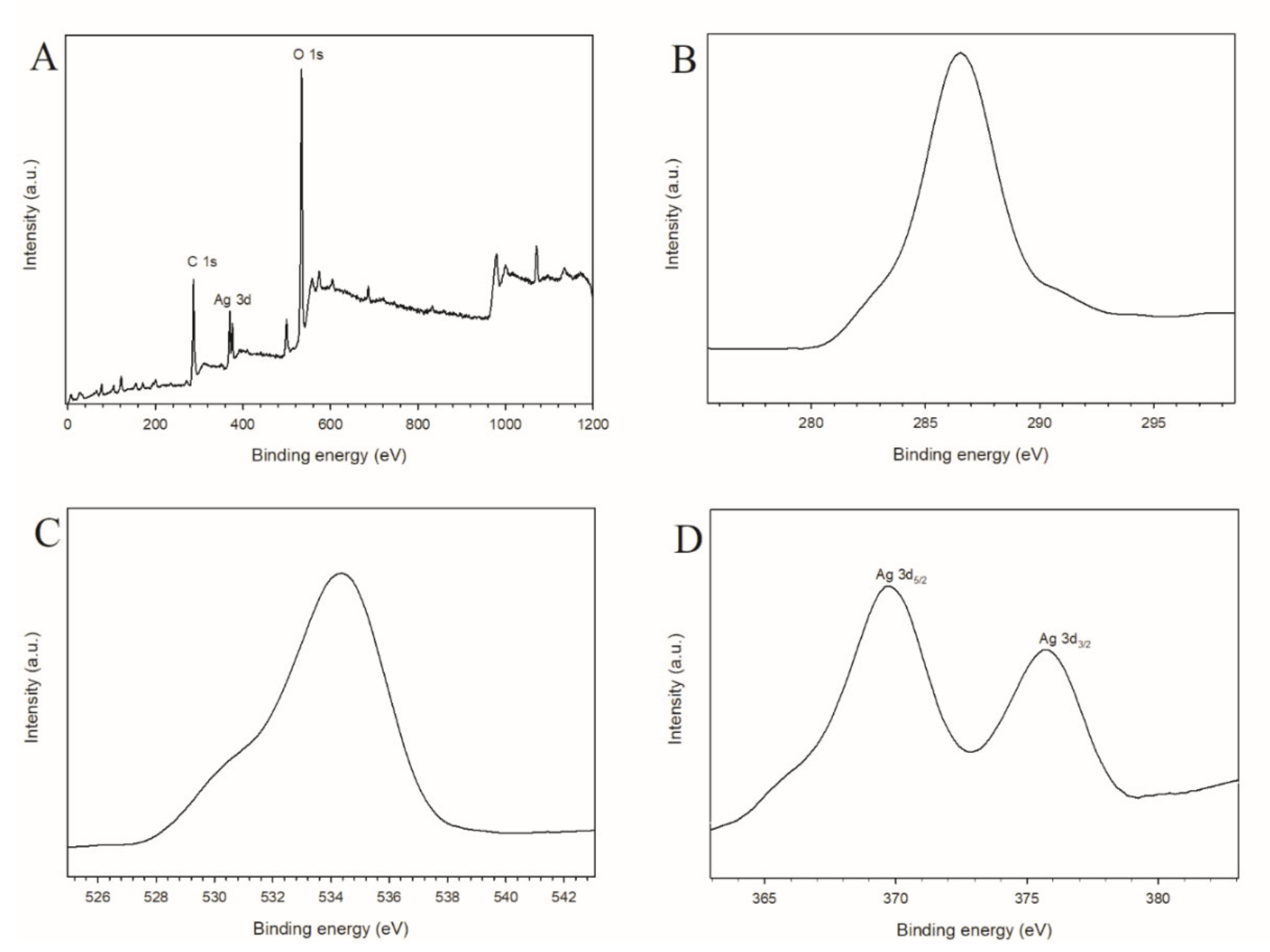
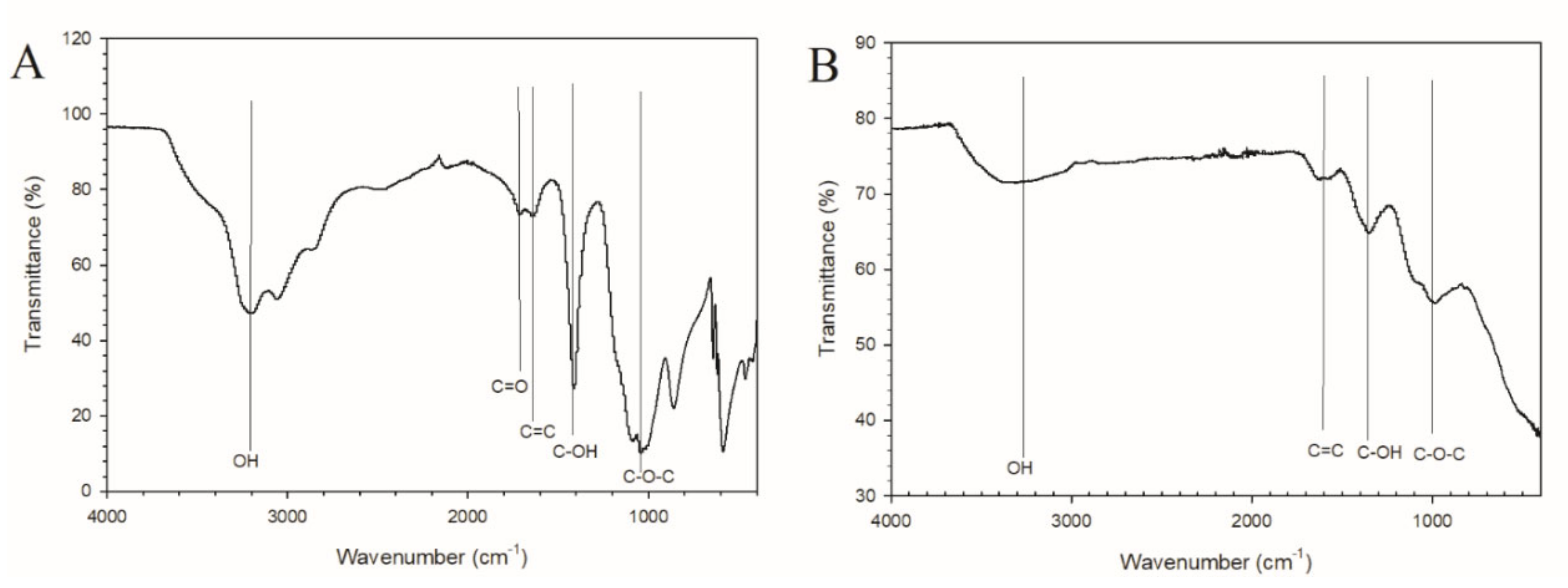
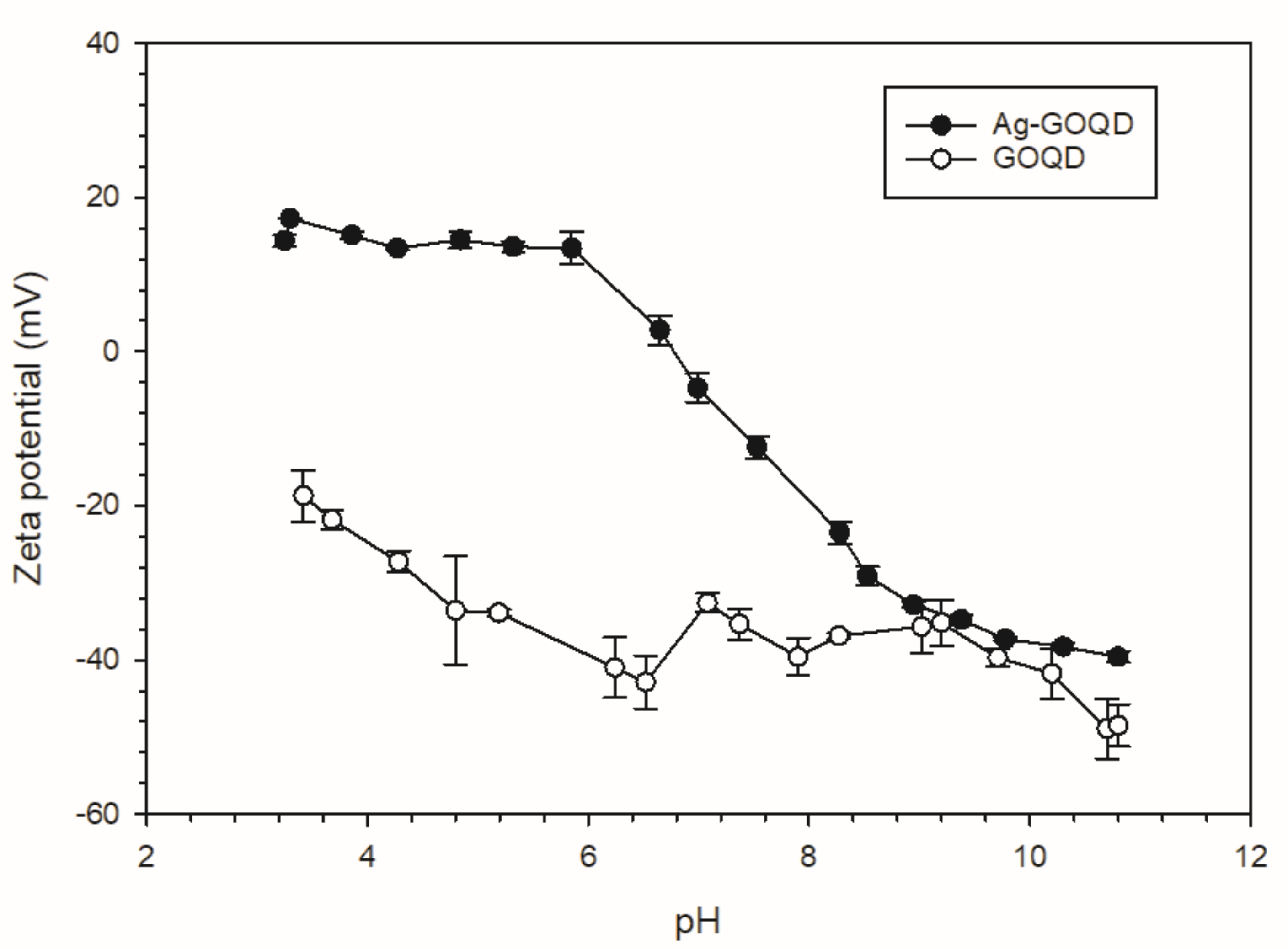
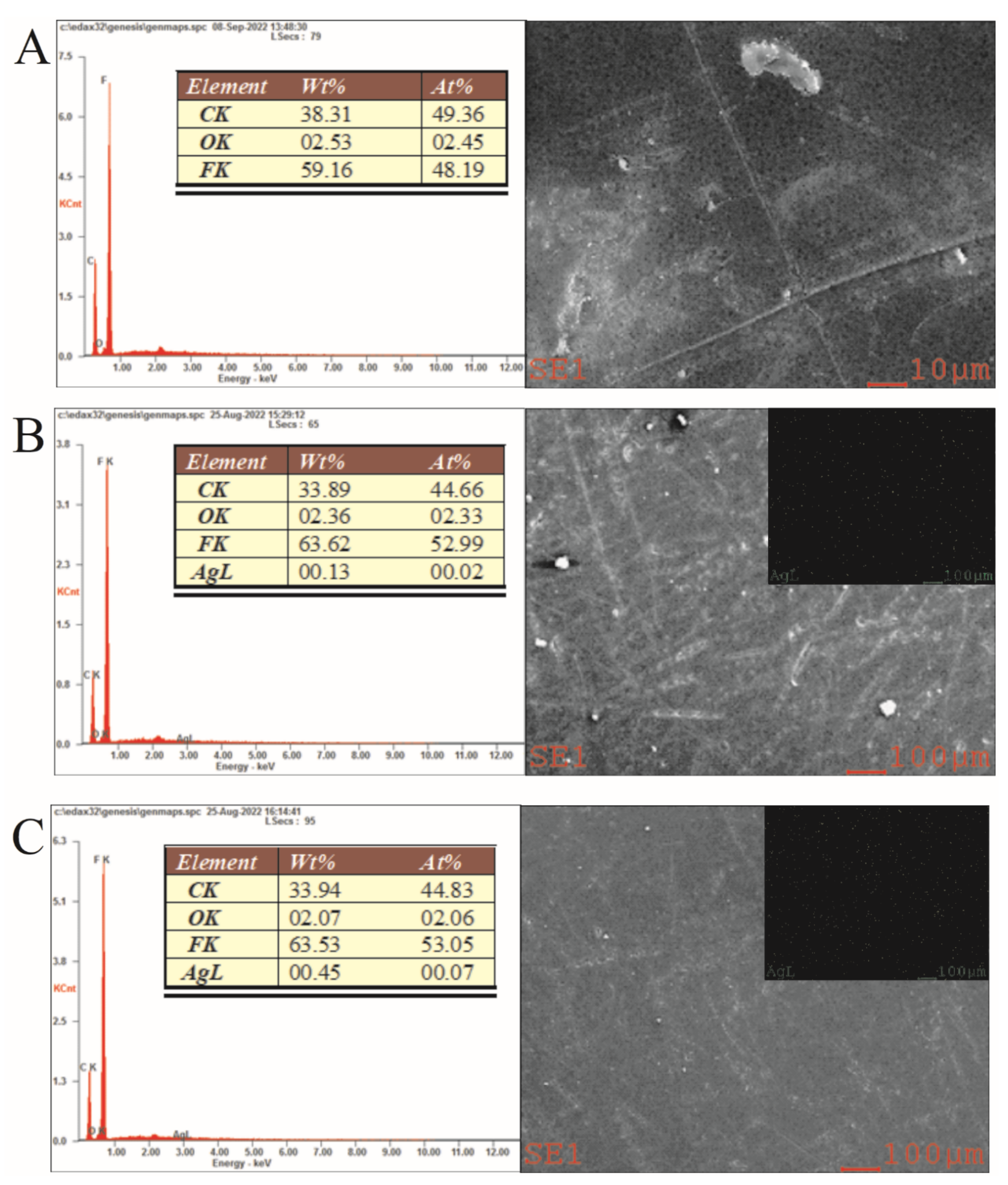
3.1. Characterization of GOQD and Ag−GOQD
3.2. Characterization of Pure PVDF and Ag−GOQD-Incorporated PVDF Membranes
3.3. Performance of Pure PVDF Membrane and Ag−GOQD-Incorporated PVDF Membranes
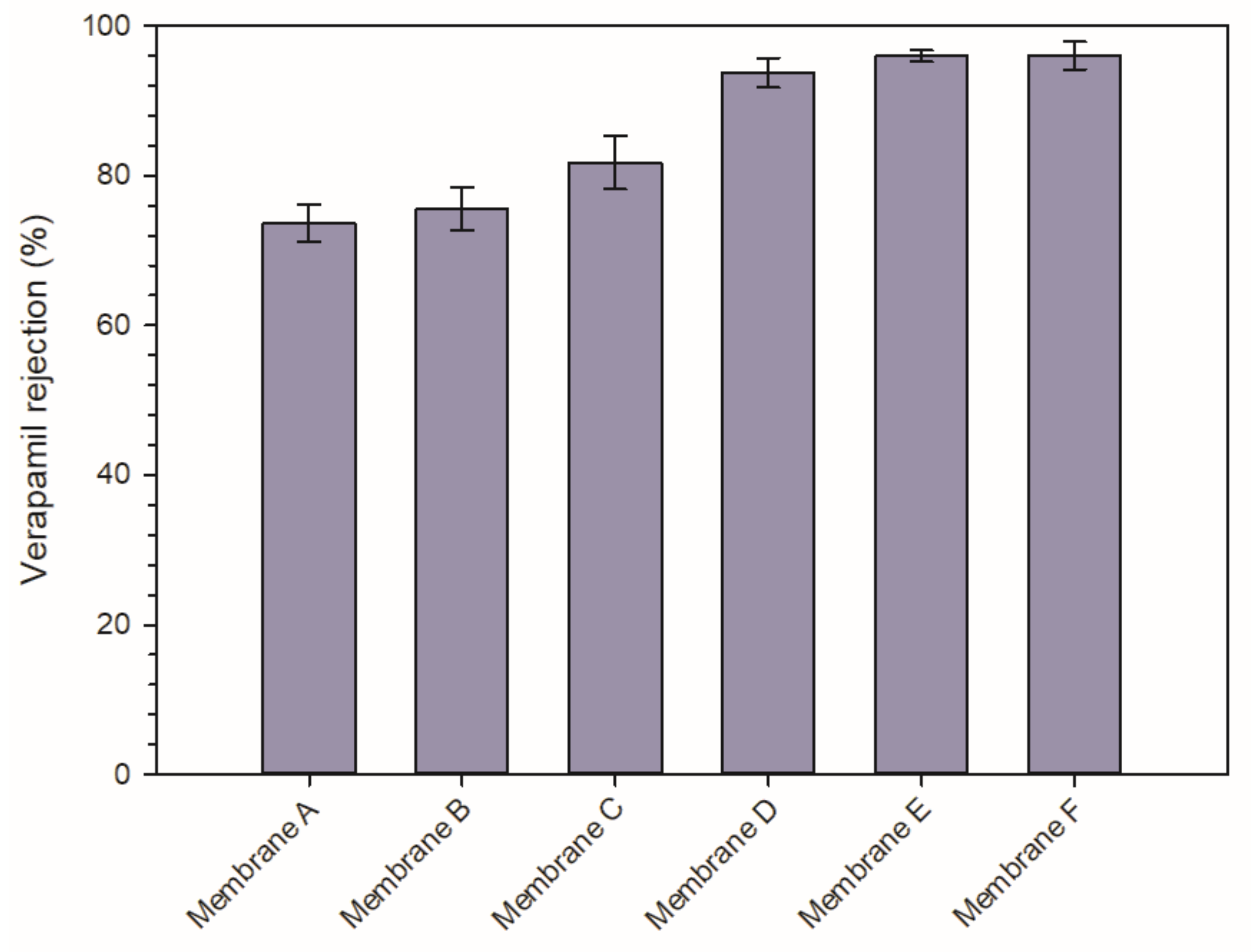
3.3.1. Permeability and Rejection Capability of the PVDF Membranes
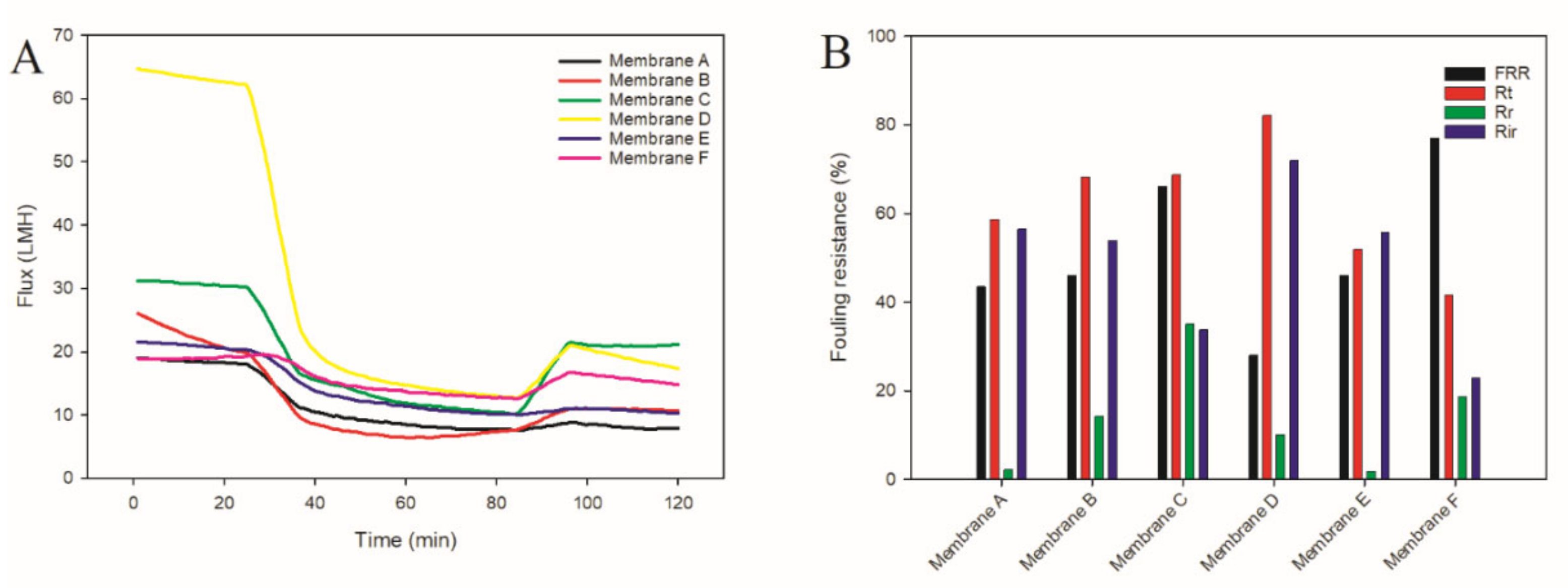
3.3.2. Anti-Fouling Performance
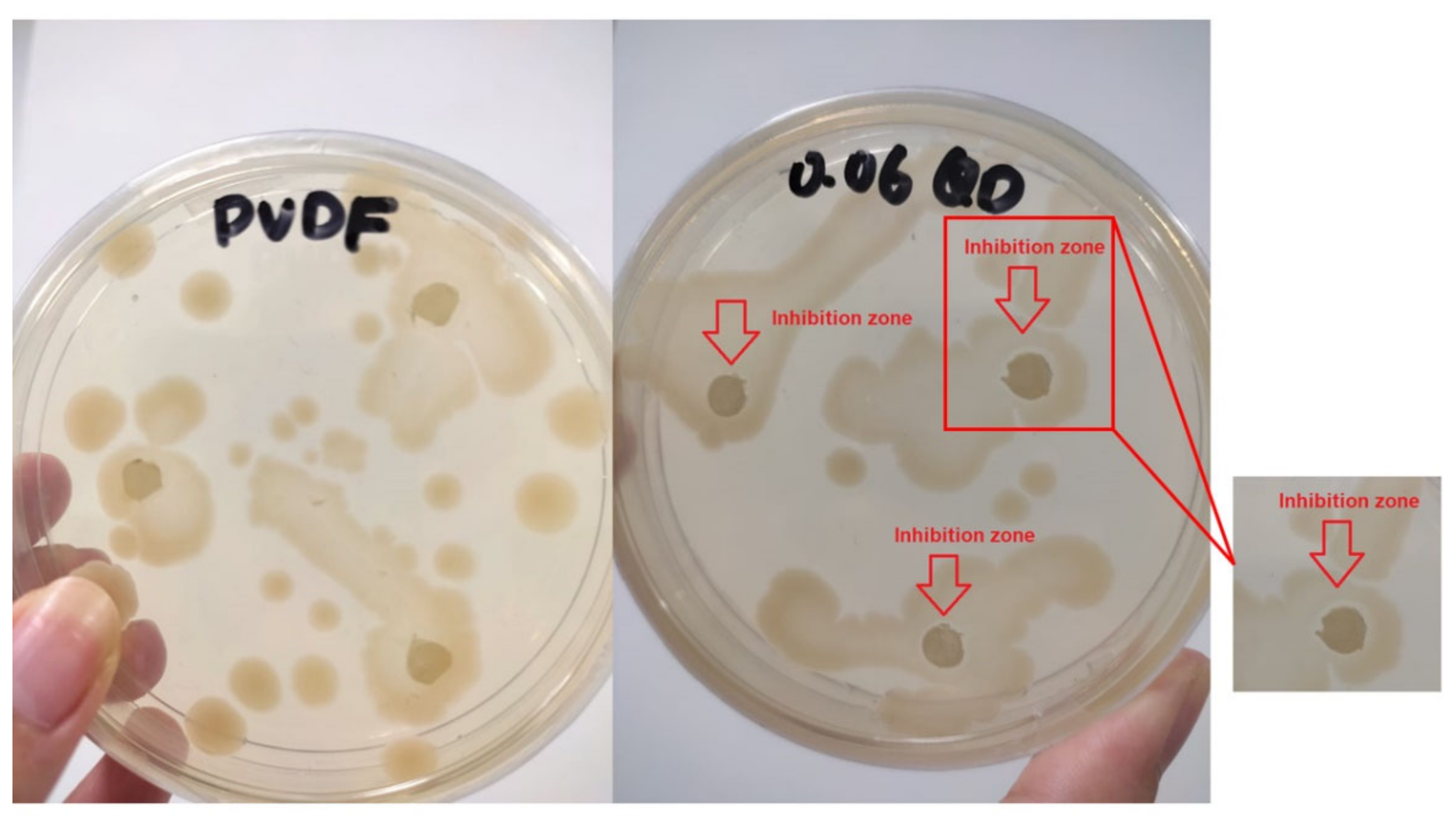
3.3.3. Antibacterial Activity of Pure PVDF and Ag−GOQD-Incorporated PVDF Membranes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kleywegt, S.; Payne, M.; Ng, F.; Fletcher, T. Environmental loadings of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients from manufacturing facilities in Canada. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 646, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.H.M.L.M.; Gros, M.; Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Pena, A.; Barceló, D.; Montenegro, M.C.B.S.M. Contribution of hospital effluents to the load of pharmaceuticals in urban wastewaters: Identification of ecologically relevant pharmaceuticals. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 461–462, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berghmans, S.; Butler, P.; Goldsmith, P.; Waldron, G.; Gardner, I.; Golder, Z.; Richards, F.M.; Kimber, G.; Roach, A.; Alderton, W.; et al. Zebrafish based assays for the assessment of cardiac, visual and gut function—Potential safety screens for early drug discovery. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2008, 58, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.-H.; Li, P.; Randak, T. Ecotoxocological effects of short-term exposure to a human pharmaceutical Verapamil in juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010, 152, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbach, C.; Fedorova, G.; Prokes, M.; Grabicova, K.; Machova, J.; Grabic, R.; Valentova, O.; Kroupova, H.K. Toxic effects, bioconcentration and depuration of verapamil in the early life stages of common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 461–462, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semaan, F.É.; Der, É.; Cavalheiro, É.; Brett, C. Electrochemical Behavior of Verapamil at Graphite–Polyurethane Composite Electrodes: Determination of Release Profiles in Pharmaceutical Samples. Anal. Lett. 2009, 42, 1119–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Zonja, B.; Gonzalez, O.; Sans, C.; Pérez, S.; Barceló, D.; Esplugas, S.; Xu, K.; Qiang, Z. Degradation kinetics and pathways of three calcium channel blockers under UV irradiation. Water Res. 2015, 86, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, S.; Ceriani, E.; Marotta, E.; Giardina, A.; Špatenka, P.; Paradisi, C. Products and mechanism of verapamil removal in water by air non-thermal plasma treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 292, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalova, L.; Siegrist, H.; von Gunten, U.; Eugster, J.; Hagenbuch, M.; Wittmer, A.; Moser, R.; McArdell, C.S. Elimination of Micropollutants during Post-Treatment of Hospital Wastewater with Powdered Activated Carbon, Ozone, and UV. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7899–7908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subedi, B.; Balakrishna, K.; Sinha, R.K.; Yamashita, N.; Balasubramanian, V.G.; Kannan, K. Mass loading and removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products, including psychoactive and illicit drugs and artificial sweeteners, in five sewage treatment plants in India. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2882–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, E.; Ang, W.L.; Ng, C.Y.; Ng, L.Y.; Mohammad, A.W.; Benamor, A. Distinguishing characteristics and usability of graphene oxide based on different sources of graphite feedstock. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 542, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panáček, A.; Kvítek, L.; Prucek, R.; Kolář, M.; Večeřová, R.; Pizúrová, N.; Sharma, V.K.; Nevěčná, T.; Zbořil, R. Silver Colloid Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Their Antibacterial Activity. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 16248–16253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahsani, M.; Hazrati, H.; Javadi, M.; Ulbricht, M.; Yegani, R. Preparation of antibiofouling nanocomposite PVDF/Ag-SiO2 membrane and long-term performance evaluation in the MBR system fed by real pharmaceutical wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 249, 116938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhou, W.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, H.; Gao, B.; Wang, Z. Antibacterial Thin-Film Nanocomposite Membranes Incorporated with Graphene Oxide Quantum Dot-Mediated Silver Nanoparticles for Reverse Osmosis Application. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 8724–8734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Gao, B.; Wang, Y.; Jin, B.; Yue, Q.; Wang, Z. Antibacterial thin film nanocomposite reverse osmosis membrane by doping silver phosphate loaded graphene oxide quantum dots in polyamide layer. Desalination 2019, 464, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalova, L.; Siegrist, H.; Singer, H.; Wittmer, A.; McArdell, C.S. Hospital Wastewater Treatment by Membrane Bioreactor: Performance and Efficiency for Organic Micropollutant Elimination. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 1536–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasir, S.; Hussein, M.Z.; Yusof, N.A.; Zainal, Z. Oil palm waste-based precursors as a renewable and economical carbon sources for the preparation of reduced graphene oxide from graphene oxide. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Dai, J.; Tian, S.; Xie, A.; Dai, X.; Pan, J. Coordination-driven interfacial cross-linked graphene oxide-alginate nacre mesh with underwater superoleophobicity for oil-water separation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 251, 117097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, E.; Ng, L.Y.; Ba-Abbad, M.M.; Mohammad, A.W. Novel nanohybrid polysulfone membrane embedded with silver nanoparticles on graphene oxide nanoplates. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 277, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.R.; Sarma, R.K.; Saikia, R.; Kale, V.S.; Shelke, M.V.; Sengupta, P. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles in an aqueous suspension of graphene oxide sheets and its antimicrobial activity. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2011, 83, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Pan, F.; Yang, L.; Song, Y.; Wu, H.; Cheng, X.; Liu, G.; Yang, H.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Z.; et al. Graphene oxide quantum dots incorporated nanocomposite membranes with high water flux for pervaporative dehydration. J. Memb. Sci. 2018, 563, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Sadanandhan, A.M.; Jain, S.L. Silver doped reduced graphene oxide as a promising plasmonic photocatalyst for oxidative coupling of benzylamines under visible light irradiation. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 9116–9122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xu, A.; Feng, Z.; Long, D.; Chen, X.; Lu, M. pH-dependent fluorescent quenching of graphene oxide quantum dots: Towards hydroxyl. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2020, 260, 114627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colburn, A.; Wanninayake, N.; Kim, D.Y.; Bhattacharyya, D. Cellulose-graphene quantum dot composite membranes using ionic liquid. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 556, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Ma, C.; Zhao, J.; Guo, H.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xing, B. Graphene oxide mediated reduction of silver ions to silver nanoparticles under environmentally relevant conditions: Kinetics and mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 679, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.V.; Huang, N.M.; Lim, H.N.; Marlinda, A.R.; Harrison, I.; Chia, C.H. One-step size-controlled synthesis of functional graphene oxide/silver nanocomposites at room temperature. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 219, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, T.; Xu, H.; Wang, Z. Pressure-assisted preparation of graphene oxide quantum dot-incorporated reverse osmosis membranes: Antifouling and chlorine resistance potentials. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 16896–16905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhu, Y.; Pan, F.; He, G.; Fang, C.; Cao, K.; Xing, R.; Jiang, Z. Fabricating graphene oxide-based ultrathin hybrid membrane for pervaporation dehydration via layer-by-layer self-assembly driven by multiple interactions. J. Memb. Sci. 2015, 487, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeh, S.; Adolfsson, K.H.; Hakkarainen, M. Controlling the cooperative self-assembly of graphene oxide quantum dots in aqueous solutions. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 57425–57432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Hu, R.; Li, J.; Zhu, H. Graphene oxide quantum dots embedded polysulfone membranes with enhanced hydrophilicity, permeability and antifouling performance. Sci. China Mater. 2019, 62, 1177–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Guo, H.; Ma, X.-H.; Lin, C.-E.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, B.; Zhu, B.-K.; Shih, K.; Tang, C.Y. A novel thin-film nano-templated composite membrane with in situ silver nanoparticles loading: Separation performance enhancement and implications. J. Memb. Sci. 2017, 544, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinifard, S.M.; Aroon, M.A.; Dahrazma, B. Application of PVDF/HDTMA-modified clinoptilolite nanocomposite membranes in removal of reactive dye from aqueous solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 251, 117294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Field, R.W.; Zhang, K. Biogenic silver nanocomposite polyethersulfone UF membranes with antifouling properties. J. Memb. Sci. 2014, 471, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraswathi, M.S.S.A.; Rana, D.; Divya, K.; Alwarappan, S.; Nagendran, A. Fabrication of anti-fouling PVDF nanocomposite membranes using manganese dioxide nanospheres with tailored morphology, hydrophilicity and permeation. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 15803–15810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Li, F.; Su, B.; Hu, M.Z.; Gao, X.; Gao, C. Novel graphene quantum dots (GQDs)-incorporated thin film composite (TFC) membranes for forward osmosis (FO) desalination. Desalination 2019, 451, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
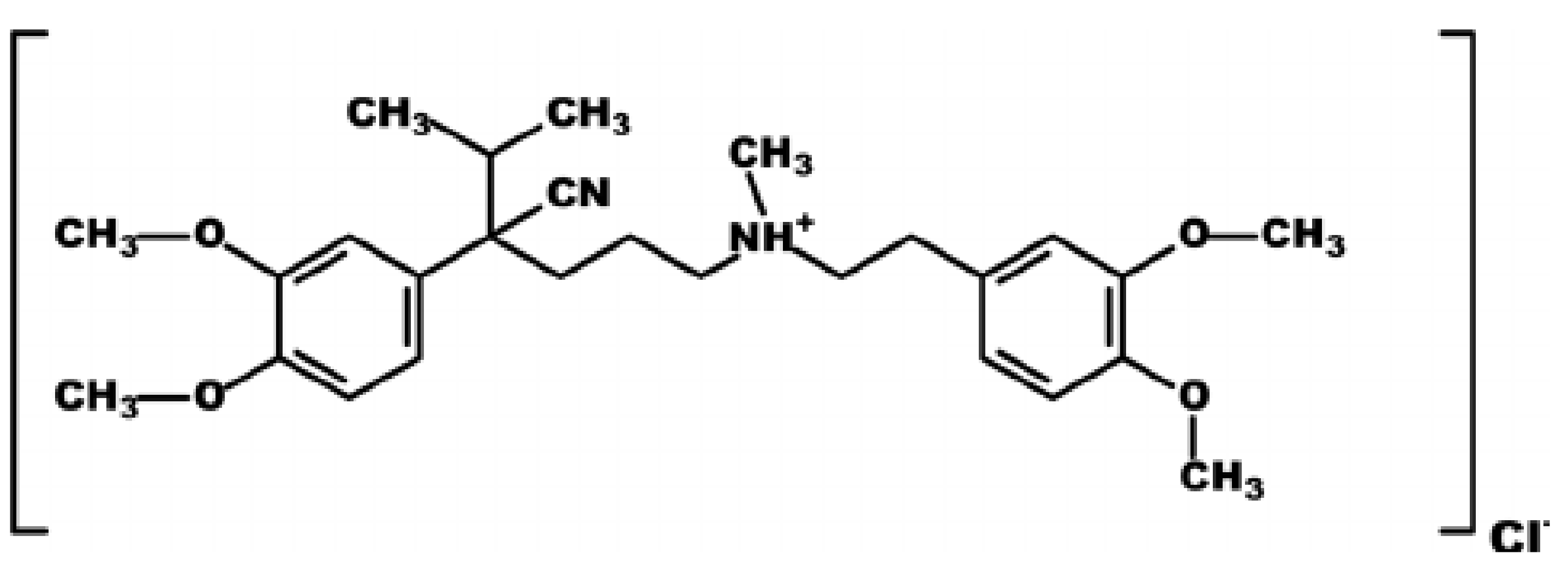


| Sample Labeling | PVDF Beads (wt%) | NMP (wt%) | Ag−GOQD (wt%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Membrane A | 22 | 78 | 0 |
| Membrane B | 22 | 77.98 | 0.02 |
| Membrane C | 22 | 77.96 | 0.04 |
| Membrane D | 22 | 77.94 | 0.06 |
| Membrane E | 22 | 77.92 | 0.08 |
| Membrane F | 22 | 77.9 | 0.1 |
| Membrane | Sa (nm) | Sq (nm) | Sz (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Membrane A | 123.80 | 148.10 | 870.90 |
| Membrane B | 30.10 | 39.70 | 311.30 |
| Membrane C | 16.60 | 20.90 | 148.00 |
| Membrane D | 32.90 | 45.20 | 342.10 |
| Membrane E | 15.40 | 20.40 | 210.20 |
| Membrane F | 13.10 | 16.60 | 120.90 |
| Membrane | Contact Angle (°) |
|---|---|
| Membrane A | 79.06 ± 4.53 |
| Membrane B | 75.10 ± 3.32 |
| Membrane C | 71.66 ± 1.68 |
| Membrane D | 73.06 ± 1.40 |
| Membrane E | 68.37 ± 3.36 |
| Membrane F | 53.60 ± 4.75 |
| Membrane | Pure Water Flux (LMH) |
|---|---|
| Membrane A | 18.9 ± 0.81 |
| Membrane B | 25.89 ± 3.75 |
| Membrane C | 31.64 ± 0.76 |
| Membrane D | 64.52 ± 1.53 |
| Membrane E | 21.37± 2.44 |
| Membrane F | 19.73 ± 2.16 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tay, W.Y.; Ng, L.Y.; Ng, C.Y.; Mahmoudi, E.; Lim, Y.P.; Sim, L.C. Incorporation of Silver-Doped Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots in Polyvinylidene Fluoride Membrane for Verapamil Removal. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15843. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142315843
Tay WY, Ng LY, Ng CY, Mahmoudi E, Lim YP, Sim LC. Incorporation of Silver-Doped Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots in Polyvinylidene Fluoride Membrane for Verapamil Removal. Sustainability. 2022; 14(23):15843. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142315843
Chicago/Turabian StyleTay, Wan Yee, Law Yong Ng, Ching Yin Ng, Ebrahim Mahmoudi, Ying Pei Lim, and Lan Ching Sim. 2022. "Incorporation of Silver-Doped Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots in Polyvinylidene Fluoride Membrane for Verapamil Removal" Sustainability 14, no. 23: 15843. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142315843
APA StyleTay, W. Y., Ng, L. Y., Ng, C. Y., Mahmoudi, E., Lim, Y. P., & Sim, L. C. (2022). Incorporation of Silver-Doped Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots in Polyvinylidene Fluoride Membrane for Verapamil Removal. Sustainability, 14(23), 15843. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142315843










