Global Value Chains and Spatial Spillovers of Economic Growth—Based on the Perspective of Participation and Status Index in Global Value Chain
Abstract
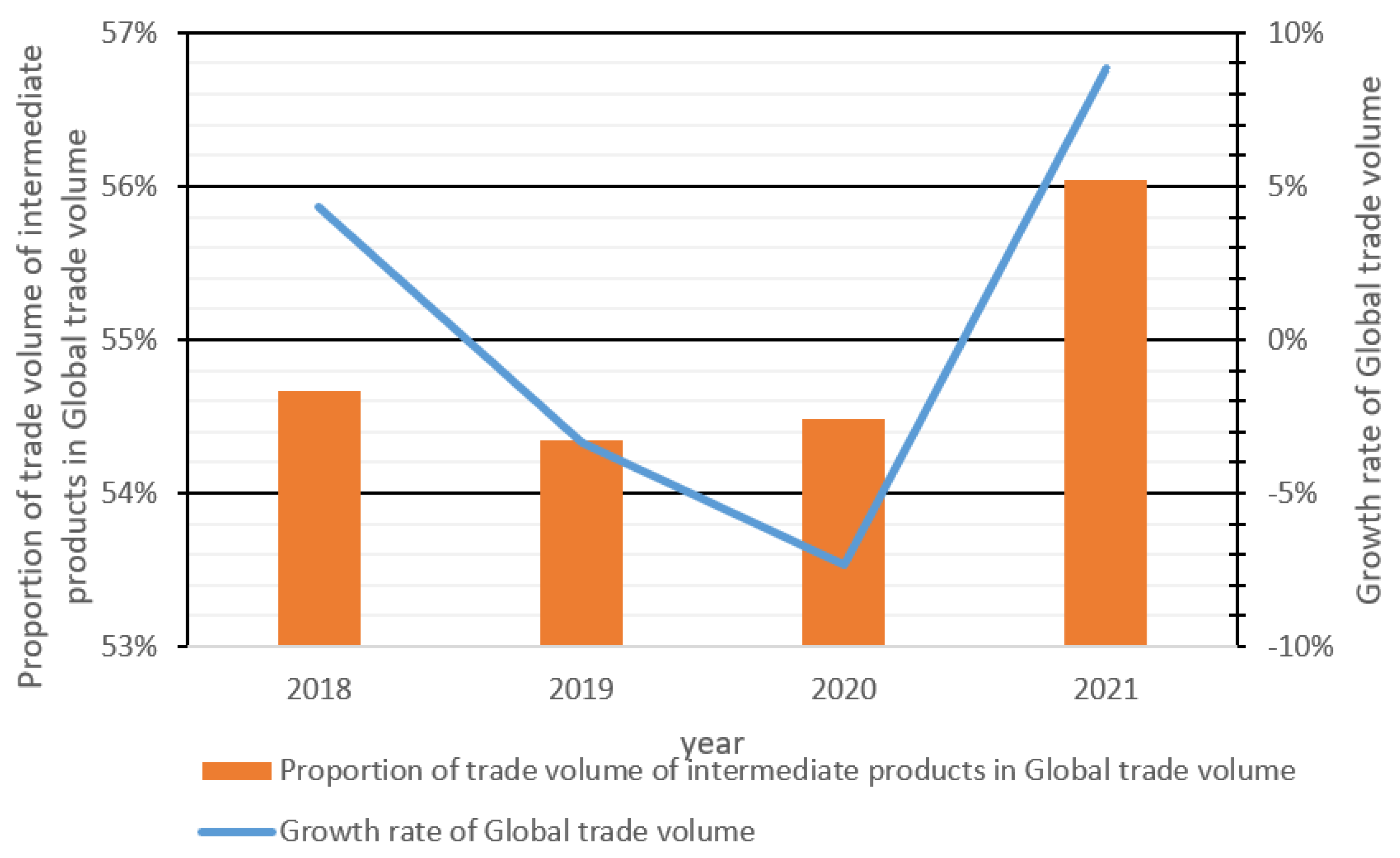
1. Introduction
2. Literature Reviewed
3. Index Measurement and Mechanism Analysis
3.1. Mechanism Analysis
3.2. Participation Index and Status Index of Global Value Chain
3.3. Spatial Characteristics of World Economic Growth
4. Econometric Model and Variable Description
4.1. Setting of Spatial Econometric Model
4.2. Data Sources
5. Empirical Test and Result Analysis
5.1. Economic Growth and Spillover Effects of Global Value Chain Participation
5.2. Economic Growth and Spillover Effects of Global Value Chain Position
6. Main Conclusions and Policy Implications
7. Limitations and Future Research Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- World Bank. World Development Report 2020: Trading for Development in the Age of Global Value Vhains; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Porter, M.E. Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance; New York Free Press: New York, NY, USA, 1985.
- Gereffi, G. Commodity Chains and Global Capitalism; ABC-Clio: Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, J. Danger and Opportunity in the Asia-Pacific. In Economic Dynamism in the Asia Pacific; Thompson, G., Ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 1998; pp. 356–384. [Google Scholar]
- Gereffi, G.; Kaplinsky, R. The Value of Value Chains. IDS Bull. 2001, 32, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, H.; Humphrey, J. Governance and Upgrading: Linking Industrial Cluster and Global Value Chain Research; IDS Working Paper: Brighton, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey, J.; Schmitz, H. How Does Insertion in Global Value Chains Affec Upgrading in Industrial Clusters? Reg. Stud. 2002, 36, 1017–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplinsky, R.; Morris, M. Governance matters in value chains. Dev. Altern. 2003, 9, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Gereffi, G.; Humphrey, J.; Sturgeon, T. The Governance of Global Value Chains. Rev. Int. Polit. Econ. 2003, 11, 5–11. [Google Scholar]
- Sturgeon, T.J. Turnkey Production Networks: A New American Model of Industrial Organization? 1997. Available online: https://escholarship.org/uc/item/2095c9d0 (accessed on 3 July 2022).
- Fujita, M.; Krugman, P.R.; Venables, A. The Spatial Economy: Cities, Regions, and International Trade; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Canils, M.C.J.; Verspagen, B. Barriers to knowledge spillovers and regional convergence in an evolutionary model. J. Evol. Econ. 2001, 11, 307–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Department, E. Upgrade Mechanism and Path of China’s Export Technology Structure in the GVC. Ind. Econ. Res. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bank, T.W. Inclusive Global Value Chains: Policy Options in Trade and Complementary Areas for GVC Integration by Small and Medium Enterprises and Low-Income Developing Countries; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin, J.R.; Yan, B. Global Value Chains and the Productivity of Canadian Manufacturing Firms; Statistics Canada, Analytical Studies Branch: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, E.; Yi, K.M. Global Value Chains and Inequality with Endogenous Labor Supply. J. Int. Econ. 2018, 115, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z. Global Value Chains (GVCs) and Economic Growth: A Non- linear Analysis. Singap. Econ. Rev. 2021, 67, 985–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Anwar, S. Immigrant Diversity, Institutional Quality, and GVC Position. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplinsky, R. Globalization, Poverty and Inequality: Between a Rock and a Hard Place; Polity Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplinsky, R. (§) Export processing zones in the dominican republic: Transforming manufactures into commodities. World Dev. 1993, 21, 1851–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplinsky, R.; Morris, M.; Readman, J. The globalisation of product markets and immiserising growth: Lessons from the South African furniture industry. World Dev. 2002, 30, 1159–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplinsky, R.; Terheggen, A.; Tijaja, J.P. China as a fifinal market: The gabon timber and Thai Cassava value chains. World Dev. 2011, 39, 1177–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollen, J.; Romagosa, H.R. Trade Wars: Economic Impacts of Us Tariff Increases and Retaliations: An International Perspective. CPB Background Document. June 2018. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/328761235 (accessed on 16 August 2022).
- Ran, C.; Byeongho, L. Economic Effects of US-China Decoupling on Global Value Chain. Korea Int. Commer. Rev. 2021, 37, 261–280. [Google Scholar]
- McKibbin, W. The Global Macroeconomic Impacts of COVID-19: Seven Scenarios. Asian Econ. Pap. 2021, 20, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, N. Economic Effects of Coronavirus Outbreak (COVID-19) on the World Economy. SSRN Electron. J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobler, W. Cellular Geography. In Philosophy in Geography; Gale, S., Olsson, G., Eds.; Reidel Dortrecht, 1979; pp. 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L.; Griffith, D.A. Do Spatial Effects really matter in Regression Analysis? Pap. Reg. Sci. 1988, 65, 11–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L. Lagrange Multiplier Test Diagnostics for Spatial Dependence and Spatial Heterogeneity. Geogr. Anal. 1988, 20, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L. Local Indicators of Spatial Association—LISA. Geogr. Anal. 2010, 27, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xin, L.; Li, J.; Sun, H. The Impact of Renewable Energy Technology Innovation on Industrial Green Transformation and Upgrading: Beggar Thy Neighbor or Benefiting Thy Neighbor. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L. Thirty years of spatial econometrics. Pap. Reg. Sci. 2010, 89, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, L.; Sun, H.; Xia, X. Spatial–temporal differentiation and dynamic spatial convergence of inclusive low-carbon development: Evidence from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danni, S.U.; Shao, C. Global Value Chain, Regional Economic Growth and Spatial Spillover. J. Int. Trade 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Genqiang, L.I. National Value Chain and Global Value Chain in Chinese Regions: Regional Interaction and Value-added Gains. Econ. Res. J. 2018, 53, 171–186. [Google Scholar]
- Ivarsson, I.; Alvstam, C.G. Supplier Upgrading in the Home-furnishing Value Chain: An Empirical Study of IKEA’s Sourcing in China and South East Asia. World Dev. 2010, 38, 1575–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, D.; Chiara, F. FDI spillovers at different levels of industrial and spatial aggregation: Evidence from the electricity sector. Energy Policy 2013, 61, 1490–1502. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.M.; Li, C.Y.; School, B. The Impact of International Knowledge Spillovers on the Value Chain Upgrading in China’s Manufacturing Industry. Econ. Rev. J. 2019, 115–129. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J. Technology spillover in the transnational outsourcing system and technological innovation in the host country. China Soc. Sci. 2013, 108–125. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, P.; Peng, G. Research on Technology Spillover’s Bridge Effect between Bidirectional FDI and GVC Position—A Case of Chinese Manufacturing Industry. Am. J. Ind. Bus. Manag. 2019, 9, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, L.; Nie, M.; Management, S.O. Learning Disabilities and Breakthrough Path in Captive GVC. Sci. Sci. Manag. S.T. 2013, 116–122. [Google Scholar]
- Bo, W.U.; Shengxiao, L.I. Does Global Value Chain Embeddedness Impede Functional Upgrading of Developing Country? An Empirical Research on Shaoxing Textile Industrial Cluster. Sci. Sci. Manag. S.T. 2010, 31, 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Rong-Jian, Y.U. A Coevolution Analysis on OEM/ODMs GVC Upgrading Mechanism and Its Application to Strategies—Dyadic Perspective. China Ind. Econ. 2010, 2, 16–25. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao-Yan, H.U.; Jiang, G.; Economics, S.O. Influence of China's Outward Foreign Direct Investment on Production Scale and Structure of Global Value Chain. West Forum 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piermartini, R.; Rubinova, S. How much do global value chains boost innovation? Can. J. Econ.-Rev. Can. D Econ. 2021, 54, 892–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomstrom, M.; Persson, H. Foreign investment and spillover efficiency in an underdeveloped economy: Evidence from the Mexican manufacturing industry. World Dev. 1983, 11, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitzer, J.; Geishecker, I.; Görg, H. Productivity spillovers through vertical linkages: Evidence from 17 OECD countries. Econ. Lett. 2008, 99, 328–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitken, B.J.; Harrison, A.E. Do Domestic Firms Benefit from Direct Foreign Investment? Evidence from Venezuela. Am. Econ. Rev. 1999, 89, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beugelsdijk, S.; Smeets, R.; Zwinkels, R. The impact of horizontal and vertical FDI on host's country economic growth. Int. Bus. Rev. 2008, 17, 452–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demena, B.A.; van Bergeijk, P.A.G. A meta-analysis of FDI and productivity spillovers in developing countries. J. Econ. Surv. 2017, 31, 546–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danni, S.U.; Shao, C. Spatial spillover of global value chain productivity effect. China Ind. Econ. 2017, 94–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, H.; Ishii, J.; Yi, K.M. The nature and growth of vertical specialization in world trade. J. Int. Econ. 2001, 54, 75–96. [Google Scholar]
- Fally, T. Production Staging: Measurement and Facts. Univ. Colo. Boulder 2012, 155–168. [Google Scholar]
- Antras, P.; Chor, D.; Fally, T.; Hillberry, R. Measuring the Upstreamness of Production and Trade Flows; Social Science Electronic Publishing: Rochester, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Koopman, R.; Powers, W.; Wang, Z.; Wei, S.J. Give Credit Where Credit Is Due: Tracing Value Added in Global Production Chains. NBER Work. Pap. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopman, R.; Wang, Z.; Wei, S.J. Tracing Value-added and Double Counting in Gross Exports. Am. Econ. Rev. 2014, 104, 459–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wei, S.J.; Zhu, K.F. Quantifying International Production Sharing at the Bilateral and Sector Levels. NBER Work. Pap. 2014, 19677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeSage, J.R. Pace, Introduction to Spatial Econometrics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z. Spatial econometric analysis of influencing factors of industrial structure upgrading in China. Stat. Res. 2015, 32, 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, J.E.; van Wincoop, E. Gravity with Gravitas: A Solution to the Border Puzzle. Am. Econ. Rev. 2003, 93, 170–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.S.; Tenreyro, S. The log of gravity. Rev. Econ. Stat. 2006, 88, 641–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos Silva, J.M.C.; Tenreyro, S. The log of gravity at 15. Port. Econ. J. 2022, 21, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helpman, E.; Krugman, P. Trade Policy and Market Structure; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Shelburne, R.C. Bilateral intra-industry trade in a multi-country Helpman-Krugman model. Int. Econ. J. 2002, 16, 53–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Year | Moran’s I | Z-Value | p-Value | Year | Moran’s I | Z-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 0.579 | 4.793 | 0.000 | 2008 | 0474 | 4.038 | 0.000 |
| 2001 | 0.570 | 4.726 | 0.000 | 2009 | 0.497 | 4.194 | 0.000 |
| 2002 | 0.561 | 4.661 | 0.000 | 2010 | 0.505 | 4.254 | 0.000 |
| 2003 | 0.555 | 4.618 | 0.000 | 2011 | 0.500 | 4.224 | 0.000 |
| 2004 | 0.538 | 4.491 | 0.000 | 2012 | 0.481 | 4.073 | 0.000 |
| 2005 | 0.519 | 4.354 | 0.000 | 2013 | 0.474 | 4.022 | 0.000 |
| 2006 | 0.507 | 4.270 | 0.000 | 2014 | 0.473 | 4.003 | 0.000 |
| 2007 | 0.492 | 4.157 | 0.000 |
| Binary Space Weight | Geospatial Weight | Spatial Weight of Economic Gravity Model | Weight of Bilateral Trade Gravity Model | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| λ | 0.322 *** (3.67) | 12.34 *** (5.33) | 0.844 *** (18.16) | 0.820 *** (15.61) |
| lngvcpt | 1.346 *** (5.49) | 0.880 *** (2.96) | 0.324 ** (2.33) | 0.281 * (1.82) |
| lnopen | −0.412 *** (−2.70) | −0.434 *** (−3.05) | −0.480 *** (−3.13) | −0.437 *** (−2.78) |
| lngov | 0.373 * (1.78) | 0.219 (1.07) | −0.151 (−0.84) | −0.130 (−0.67) |
| lnurban | 0.524 (1.15) | 1.229 *** (2.77) | 0.060 (0.14) | 0.109 (0.27) |
| lnrd | 0.333 *** (4.73) | 0.339 *** (5.02) | 0.201 *** (2.66) | 0.201 *** (2.68) |
| lnfdi | −0.019 *** (−3.29) | −0.014 ** (−2.13) | −0.014 ** (−2.52) | −0.014 ** (−2.50) |
| lnhk | 0.602 *** (8.35) | 0.653 *** (8.51) | 0.599 *** (9.62) | 0.579 *** (9.35) |
| lnins | 4.322 *** (3.54) | 5.899 *** (5.11) | 5.154 *** (4.36) | 5.223 *** (4.59) |
| lninf | −0.416 *** (−2.78) | −0.327 (−1.16) | −0.0697 (−1.52) | −0.069 * (−1.69) |
| Constant term | −15.67 *** (−2.60) | −27.44 *** (−5.07) | −24.44 *** (−4.95) | −24.89 *** (−5.17) |
| R2 | 0.569 | 0.443 | 0.806 | 0.850 |
| Obs | 630 | 630 | 630 | 630 |
| Binary Space Weight | Geospatial Weight | Spatial Weight of Economic Gravity Model | Weight of Bilateral Trade Gravity Model | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| lngvcpt | 0.948 *** (3.07) | 0.693 ** (2.25) | −0.146 (−0.67) | −0.173 (−0.73) |
| lnopen | −0.342 ** (−2.53) | −0.367 ** (−2.55) | −0.457 *** (−3.06) | −0.409 *** (−2.71) |
| lngov | 0.396 * (1.88) | 0.212 (1.09) | −0.0928 (−0.52) | −0.070 (−0.37) |
| lnurban | 0.290 (0.79) | 0.794 * (1.80) | 0.016 (0.04) | 0.058 (0.14) |
| lnrd | −0.020 *** (−3.34) | −0.014 ** (−2.11) | −0.013 ** (−2.31) | −0.012 ** (−2.24) |
| lnfdi | 0.336 *** (6.43) | 0.318 *** (4.85) | 0.183 ** (2.46) | 0.182 ** (2.46) |
| lnhk | 0.632 *** (9.75) | 0.648 *** (8.22) | 0.576 *** (9.69) | 0.563 *** (9.39) |
| lnins | 4.312 *** (3.38) | 6.332 *** (4.87) | 5.329 *** (4.46) | 5.429 *** (4.66) |
| lninf | −0.200 *** (−2.62) | −0.123 * (−1.84) | −0.082 (−1.61) | −0.077 * (−1.75) |
| Constant term | −14.88 *** (−2.72) | −26.06 *** (−4.63) | −23.51 *** (−4.79) | −23.97 *** (−4.92) |
| 1.034 *** (4.55) | 36.56 *** (6.09) | 0.975 *** (3.60) | 0.986 *** (3.46) | |
| 0.189 *** (4.64) | 4.759 *** (6.16) | 0.749 *** (11.30) | 0.704 *** (10.10) | |
| Direct effect | 1.032 *** (3.46) | 0.718 ** (2.29) | −0.051 (−0.23) | −0.093 (−0.40) |
| Indirect effect | 1.168 *** (5.47) | 1.306 *** (6.99) | 3.534 *** (3.51) | 2.912 *** (4.11) |
| Total effect | 2.200 *** (11.60) | 2.024 *** (9.79) | 3.483 *** (3.53) | 2.819 *** (4.31) |
| R2 | 0.887 | 0.912 | 0.792 | 0.843 |
| Obs | 630 | 630 | 630 | 630 |
| Binary Space Weight | Geospatial Weight | Spatial Weight of Economic Gravity Model | Weight of Bilateral Trade Gravity Model | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| λ | 0.458 *** (6.31) | 0.738 *** (15.99) | 0.898 *** (29.79) | 0.874 *** (24.61) |
| lngvcpt | 0.030 * (1.76) | 0.020 * (1.74) | 0.020 (1.59) | 0.020 (1.57) |
| lnopen | −0.071 (−0.55) | −0.334 *** (−2.60) | −0.421 *** (−3.15) | −0.395 *** (−2.85) |
| lngov | 0.950 *** (3.96) | −0.046 (−0.24) | −0.098 (−0.56) | −0.104 (−0.56) |
| lnurban | 0.789 (1.10) | 0.258 (0.73) | 0.134 (0.34) | 0.179 (0.48) |
| lnrd | 0.321 *** (3.46) | 0.161 ** (2.21) | 0.182 ** (2.57) | 0.182 ** (2.55) |
| lnfdi | −0.016 *** (−2.77) | −0.0132 ** (−2.40) | −0.013 ** (−2.33) | −0.013 ** (−2.32) |
| lnhk | 0.664 *** (7.23) | 0.571 *** (9.50) | 0.614 *** (9.11) | 0.588 *** (8.96) |
| lnins | 5.975 *** (4.35) | 5.153 *** (4.77) | 5.584 *** (4.42) | 5.541 *** (4.64) |
| lninf | −0.511 ** (−2.45) | −0.0621 (−1.56) | −0.070 (−1.56) | −0.068 * (−1.67) |
| Constant term | −29.89 *** (−4.36) | −25.03 *** (−5.56) | −28.07 *** (−5.46) | −27.75 *** (−5.66) |
| R2 | 0.490 | 0.873 | 0.807 | 0.841 |
| Obs | 630 | 630 | 630 | 630 |
| Binary Space Weight | Geospatial Weight | Spatial Weight of Economic Gravity Model | Weight of Bilateral Trade Gravity Model | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| lngvcpt | 0.030 * (1.86) | 0.022 * (1.93) | 0.020 *** (3.18) | 0.012 *** (3.20) |
| lnopen | −0.0887 (−0.69) | −0.358 *** (−2.73) | −0.420 *** (−9.07) | −0.404 *** (−8.78) |
| lngov | 0.950 *** (4.05) | −0.035 (−0.19) | −0.114 (−1.32) | −0.086 (−1.01) |
| lnurban | 0.816 (1.16) | 0.201 (0.56) | 0.134 (0.84) | 0.154 (0.97) |
| lnrd | −0.017 *** (−2.92) | −0.014 *** (−2.65) | −0.013 *** (−3.45) | −0.013 *** (−3.31) |
| lnfdi | 0.318 *** (3.63) | 0.163 ** (2.31) | 0.182 *** (6.09) | 0.179 *** (6.04) |
| lnhk | 0.671 *** (7.40) | 0.575 *** (9.71) | 0.611 *** (22.60) | 0.593 *** (21.79) |
| lnins | 5.952 *** (4.13) | 5.235 *** (4.79) | 5.541 *** (9.65) | 5.589 *** (9.77) |
| lninf | −0.475 ** (−2.23) | −0.0621 (−1.56) | −0.071 ** (−1.98) | −0.068 ** (−2.02) |
| Constant term | −30.07 *** (−4.30) | −24.83 *** (−5.54) | −27.78 *** (−11.25) | −27.94 *** (−11.45) |
| 0.042 *** (2.83) | 0.092 ** (2.51) | −0.017 (−0.93) | 0.036 ** (1.98) | |
| 0.470 *** (6.59) | 0.737 *** (16.15) | 0.890 *** (39.40) | 0.889 *** (40.99) | |
| Direct effect | 0.041 ** (2.16) | 0.032 ** (2.20) | 0.021 ** (2.20) | 0.033 *** (3.13) |
| Indirect effect | 0.081 *** (2.69) | 0.428 ** (2.05) | 0.024 (0.12) | 0.500 * (1.94) |
| Total effect | 0.122 *** (2.72) | 0.460 ** (2.10) | 0.044 (0.22) | 0.532 ** (2.00) |
| R2 | 0.493 | 0.865 | 0.808 | 0.827 |
| Obs | 630 | 630 | 630 | 630 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Men, K.; Sun, H.; Kou, M. Global Value Chains and Spatial Spillovers of Economic Growth—Based on the Perspective of Participation and Status Index in Global Value Chain. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15518. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142315518
Men K, Sun H, Kou M. Global Value Chains and Spatial Spillovers of Economic Growth—Based on the Perspective of Participation and Status Index in Global Value Chain. Sustainability. 2022; 14(23):15518. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142315518
Chicago/Turabian StyleMen, Keping, Hui Sun, and Minglong Kou. 2022. "Global Value Chains and Spatial Spillovers of Economic Growth—Based on the Perspective of Participation and Status Index in Global Value Chain" Sustainability 14, no. 23: 15518. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142315518
APA StyleMen, K., Sun, H., & Kou, M. (2022). Global Value Chains and Spatial Spillovers of Economic Growth—Based on the Perspective of Participation and Status Index in Global Value Chain. Sustainability, 14(23), 15518. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142315518






