Effect of Dimpled Rib with Arc Pattern on Hydrothermal Characteristics of Al2O3-H2O Nanofluid Flow in a Square Duct
Abstract
1. Introduction
- To investigate the effect of arc rib pitch, arc flow attack angle, dimpled arc rib, and volume fraction on and with nanofluid flow in a ribbed square duct.
- To determine the prolific dimpled rib with arc pattern and flow parameters for nanofluid flow in a ribbed square duct by considering the thermal-hydraulic performance.
2. Rib Parameters
3. Experimental Setup
4. Nanofluid Preparation and Its Thermo-Physical Properties
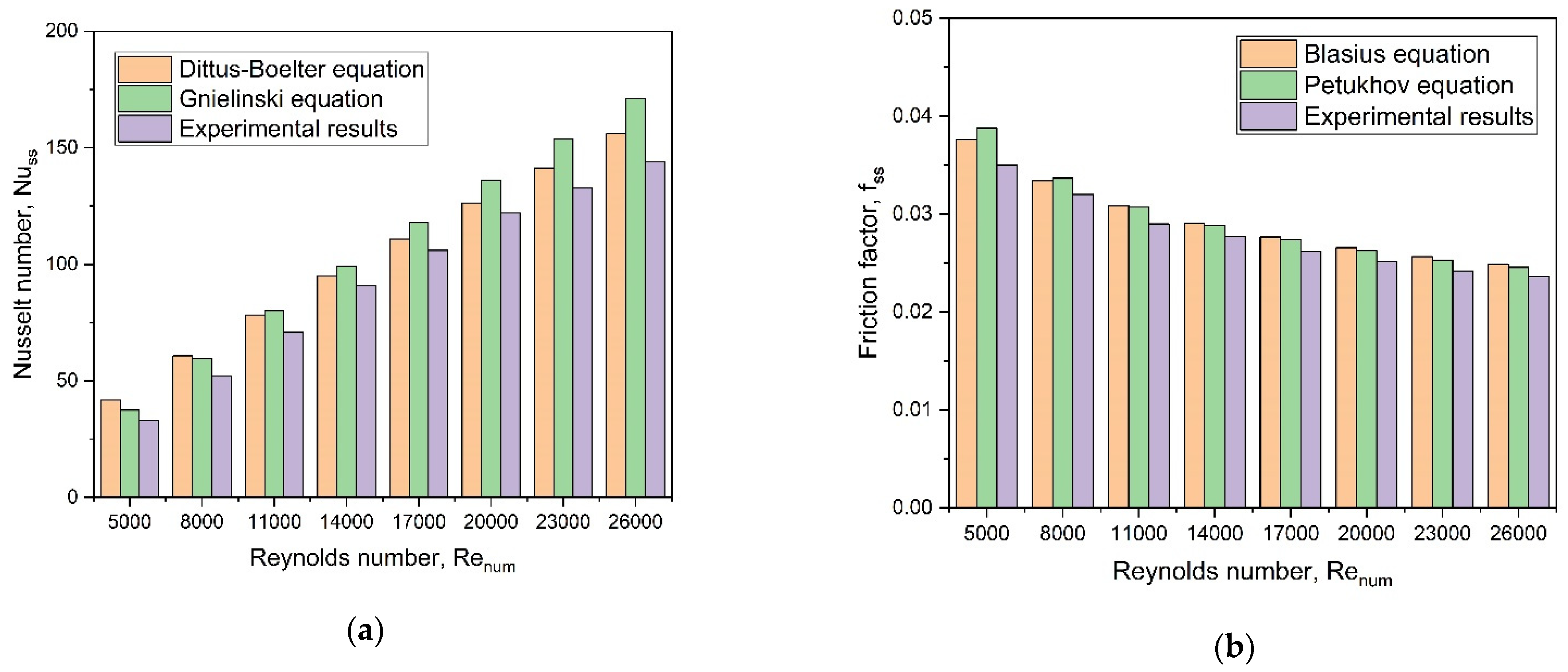
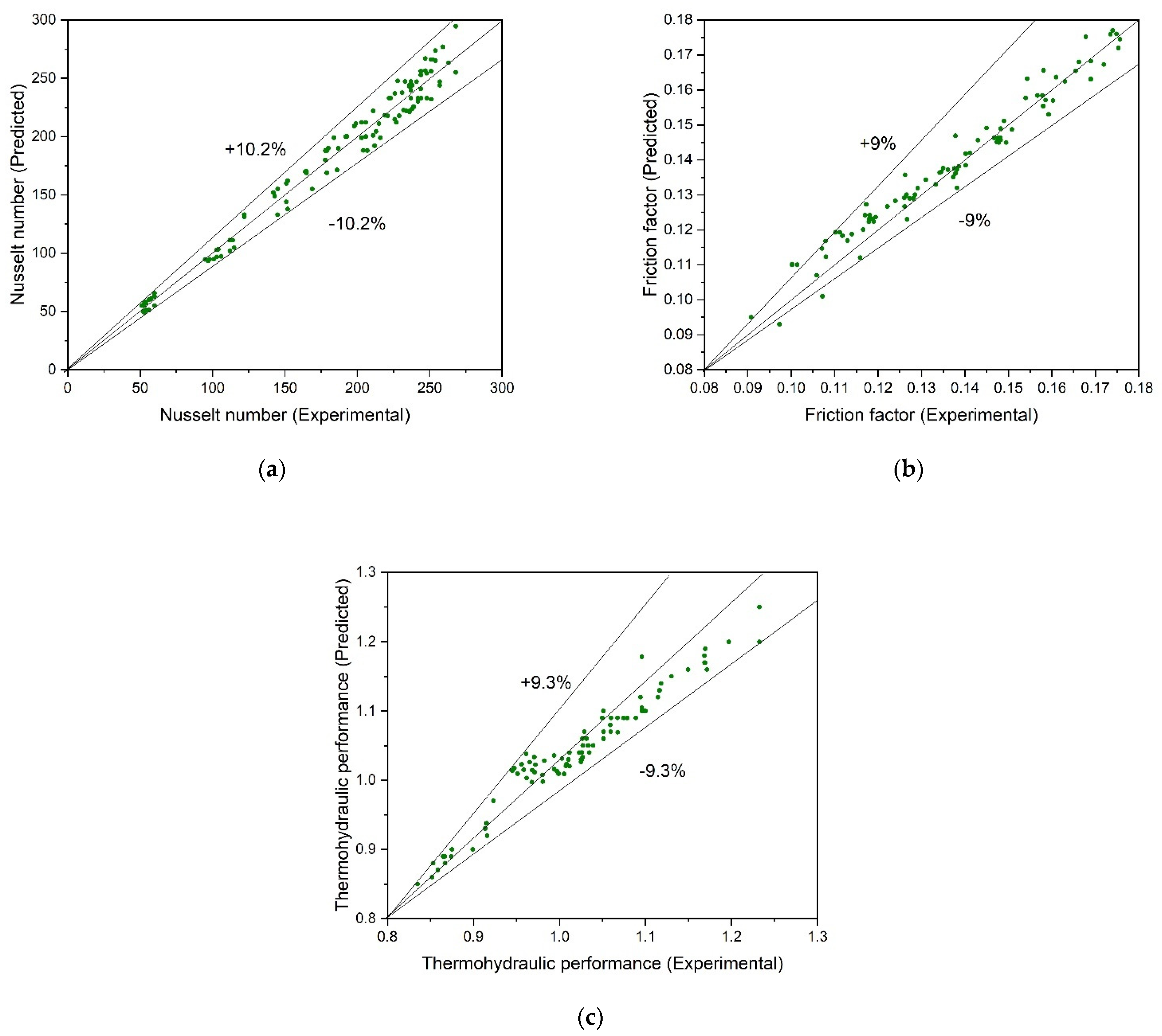
5. Validation of Experimental Setup
6. Data Reduction
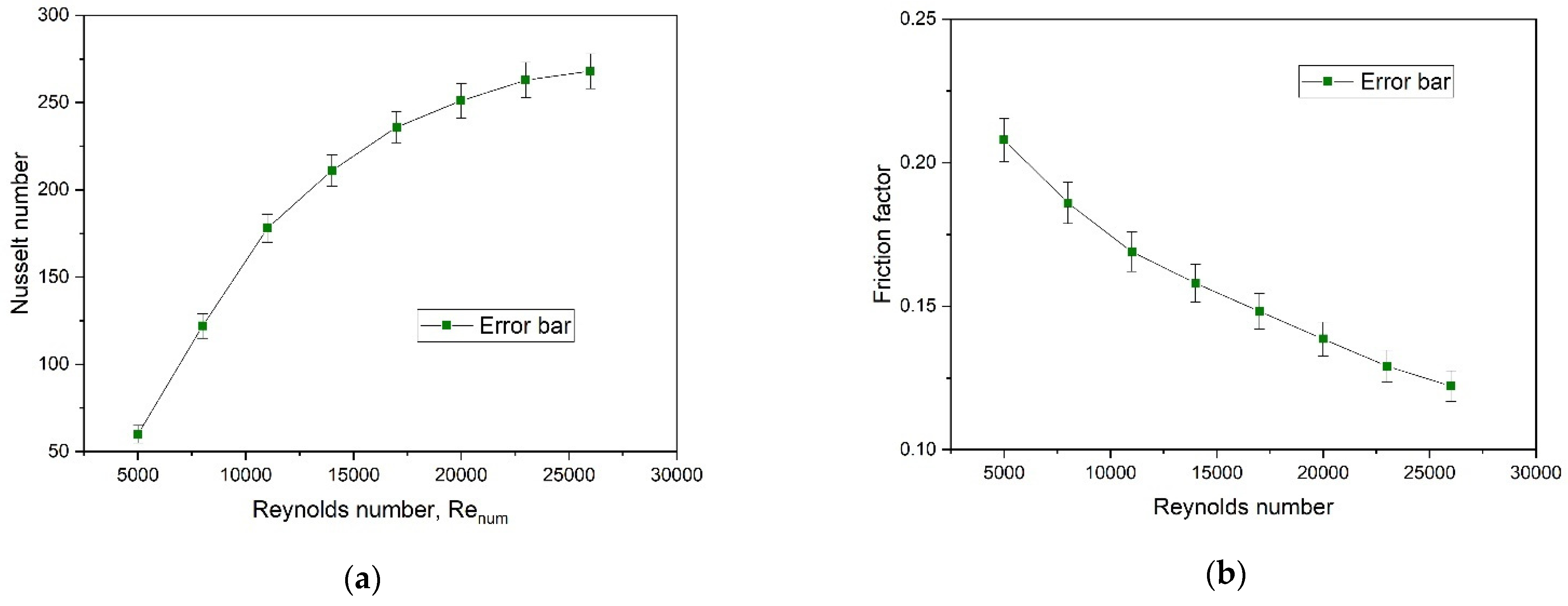
7. Uncertainty Analysis
- Uncertainty in
- Uncertainty in
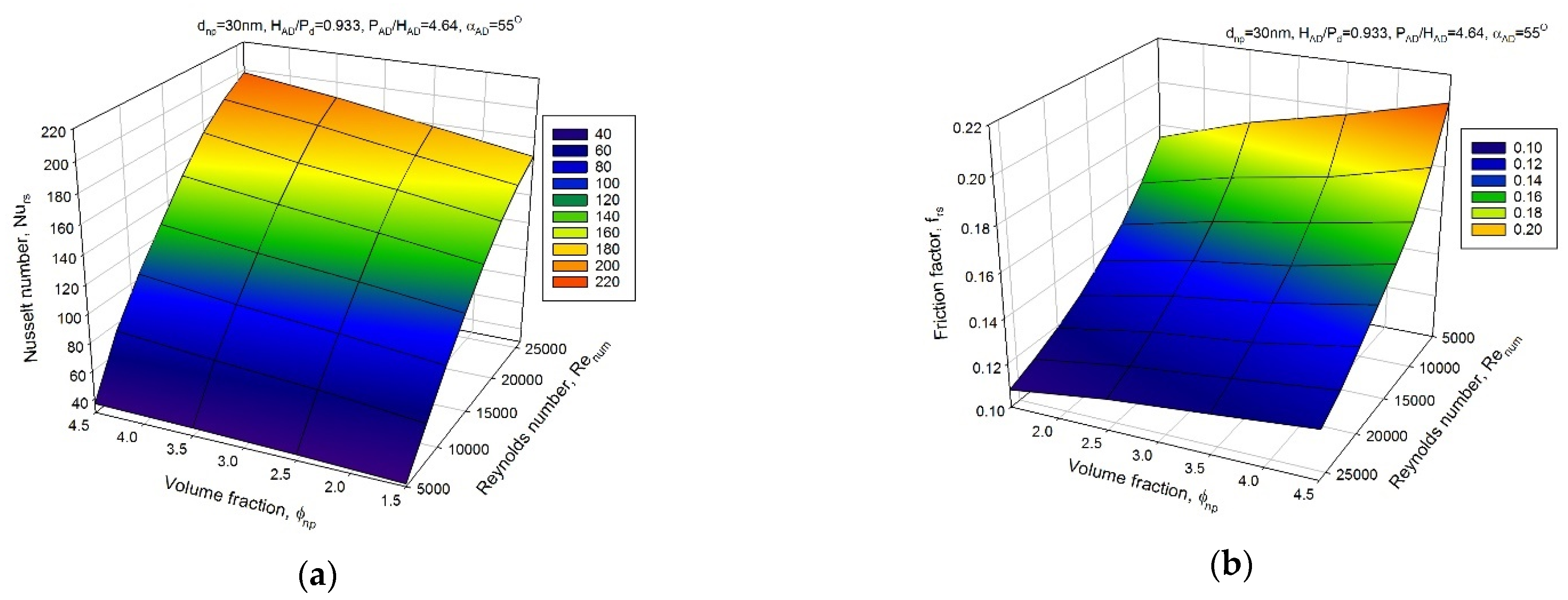
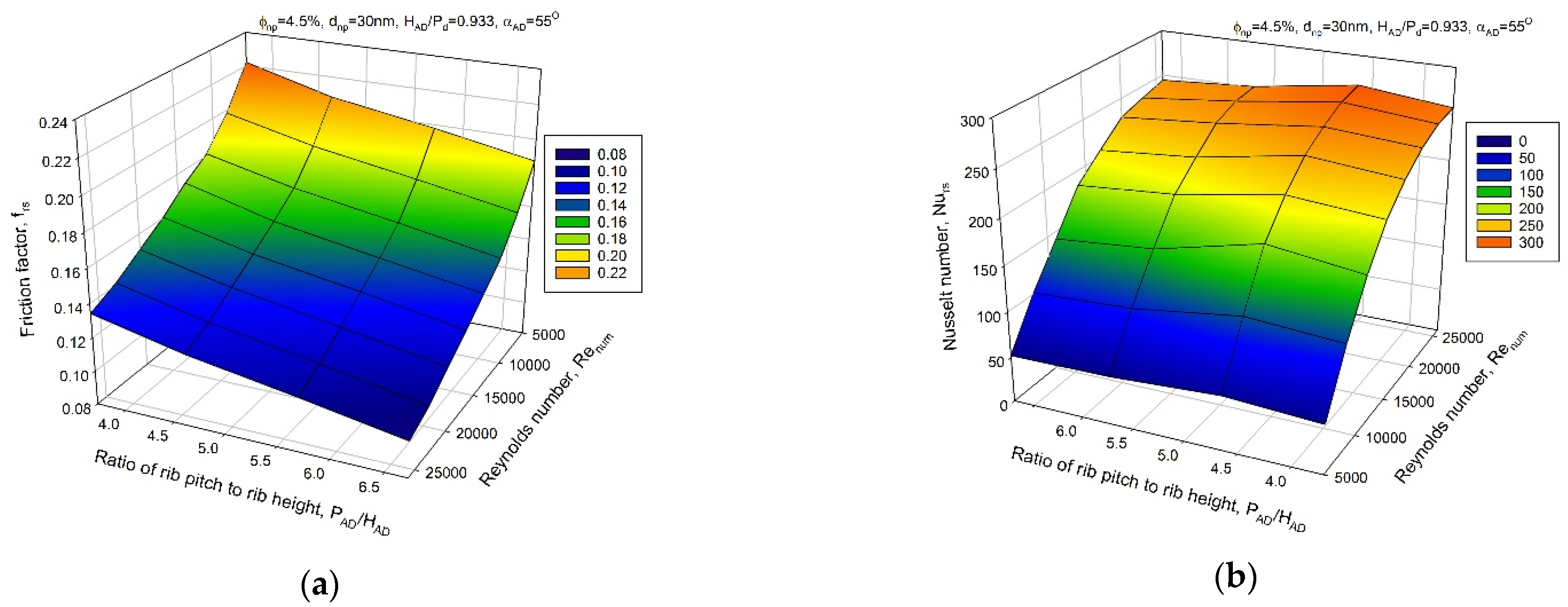
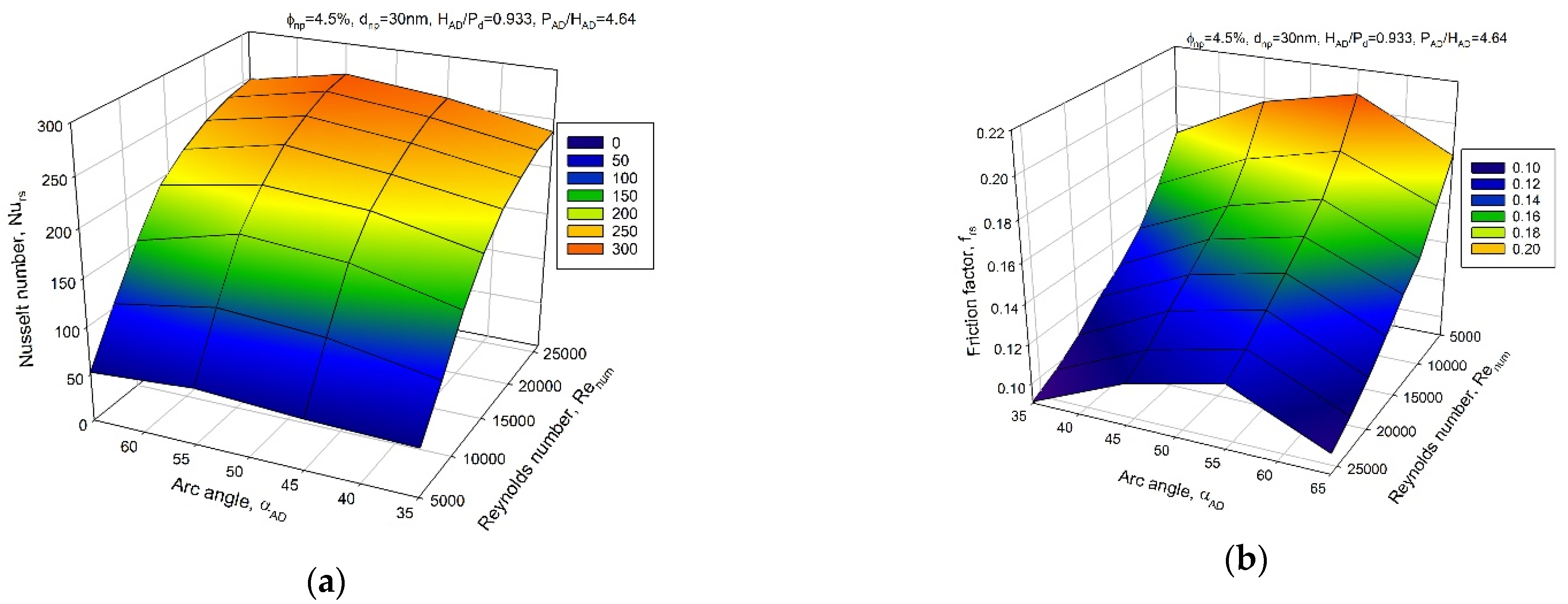
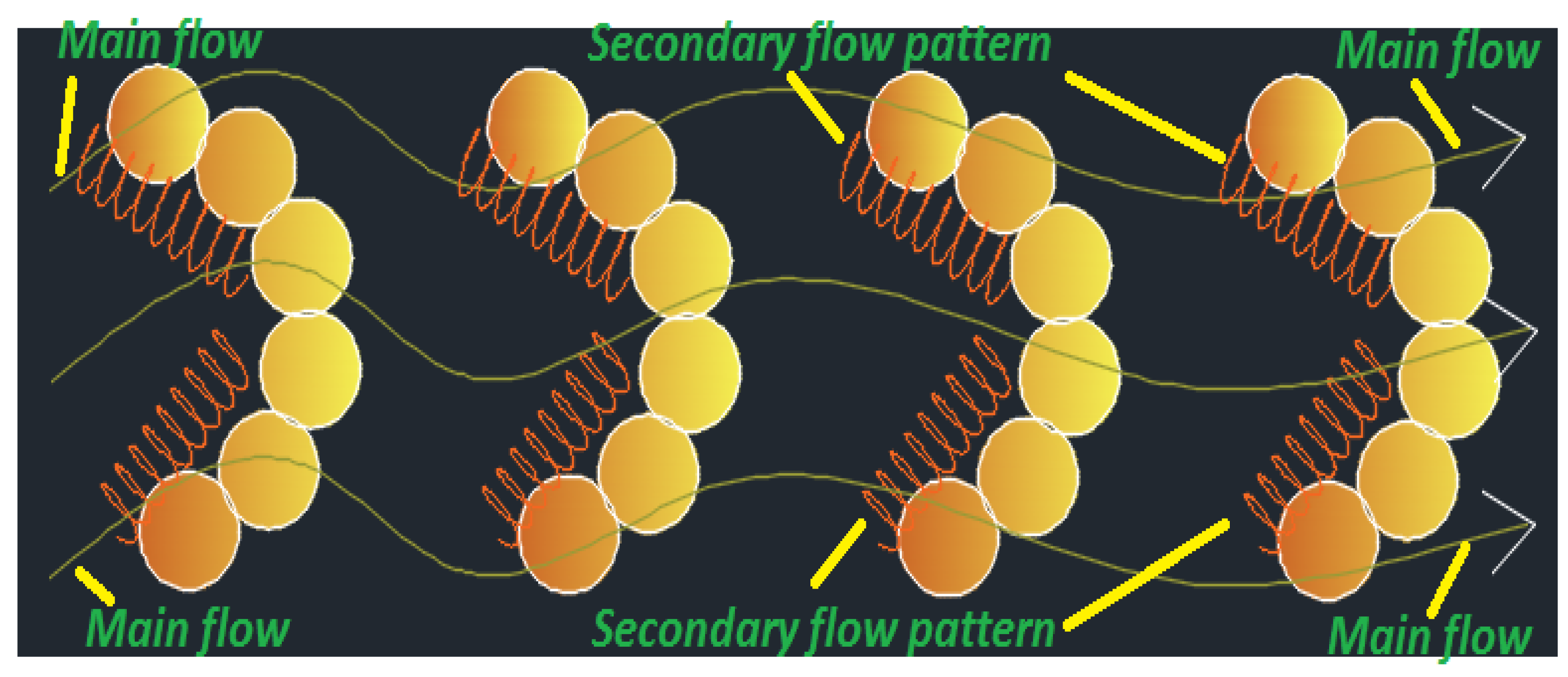
8. Results and Discussion
9. Correlations for Nusselt Number and Friction Factor
10. Conclusions
- Dimpled arc rib pitch, dimpled arc rib height, dimpled arc angle and volume fraction of nanofluid strongly affected the flow pattern and augmented the thermal-hydraulic performance of the square duct.
- In general, the and all tend to upsurge with the upsurge in nanoparticle concentration, attaining the highest value of nanoparticle concentration of 4.5% gives the highest values of both the and for the range of parameters investigated.
- A ratio of dimpled arc rib height to print diameter of 0.933 gives the highest value of and , whereas a ratio of dimpled arc rib height to print diameter of 1.133 gives the highest value of the .
- A relative dimpled arc rib height of 4.64 gives the highest value of both the and , whereas a relative dimpled arc rib height of 3.71 gives the highest value of the .
- In general, the value of , and have been found to increase with increases in the values of dimpled arc angle. Attaining the maximum value of dimpled arc angle of 55° gives the highest values of , and given the set of parameters examined.
- The maximum value of the thermal-hydraulic performance parameter occurs at of 4.5%, of 30 nm, of 0.933, of 4.64 and of 55° for of 11,000. The thermal-hydraulic performance characteristics’ maximum value was discovered to be 1.23 for -based nanofluid flow in a dimpled rib with arc pattern square duct for the range of parameters investigated.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Specific heat | |
| Nanoparticle diameter | |
| Hydraulic diameter | |
| Convective heat transfer coefficient | |
| dimpled-arc-rib-height | |
| dimpled-rib-pitch | |
| print diameter | |
| Prandtl number | |
| Nusselt number of rough surface | |
| Friction factor of rough surface | |
| Thermal conductivity | |
| Greek symbols | |
| Duct length | |
| Mass flow rate | |
| Reynolds number | |
| Pressure drop across the duct | |
| Fluid velocity | |
| dimpled arc angle | |
| Volume fraction | |
| Thermohydraulic performance parameter | |
| Nanofluid density | |
| Dynamic viscosity | |
References
- Kumar, S.; Shandilya, M.; Chauhan, A.; Maithani, R.; Kumar, A. Experimental Analysis of Zinc Oxide/Water/Ethylene Glycol-Based Nanofluid in a Square Duct Roughened with Inclined Ribs. J. Enhanc. Heat Transf. 2020, 27, 687–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godson, L.; Raja, B.; Lal, D.M.; Wongwises, S. Enhancement of heat transfer using nanofluids—An overview. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, M.J.; Sandeep, N.; Saleem, S. Free convective MHD Cattaneo-Christov flow over three different geometries with thermophoresis and Brownian motion. Alex. Eng. J. 2017, 56, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.K.; Reji Kumar, R.; Kalidasan, B.; Laghari, I.A.; Samykano, M.; Kothari, R.; Abusorrah, A.M.; Sharma, K.; Tyagi, V.V. Utilization of solar energy for wastewater treatment: Challenges and progressive research trends. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 297, 113300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Gupta, S.K.; Sharma, V.K. Application of phase change material for thermal energy storage: An overview of recent advances. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 44, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogungbemi, A.T.; Adun, H.; Adedeji, M.; Kavaz, D.; Dagbasi, M. Does Particle Size in Nanofluid Synthesis Affect Their Performance as Heat Transfer Fluid in Flat Plate Collectors?—An Energy and Exergy Analysis. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arıkan, E.; Abbasoğlu, S.; Gazi, M. Experimental Performance Analysis of Flat Plate Solar Collectors Using Different Nanofluids. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazem, H.A.; Chaichan, M.T.; Al-Waeli, A.H.A.; Jarimi, H.; Ibrahim, A.; Sopian, K. Effect of Temperature on the Electrical and Thermal Behaviour of a Photovoltaic/Thermal System Cooled Using SiC Nanofluid: An Experimental and Comparison Study. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giwa, S.O.; Sharifpur, M.; Ahmadi, M.H.; Meyer, J.P. Magnetohydrodynamic convection behaviours of nanofluids in non-square enclosures: A comprehensive review. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 2020, 1–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseema; NawazishMehdia, S.; Hussain, M.M.; Basha, S.K.; Samad, M.A. Heat Enhancement of Heat Exchanger Using Aluminium Oxide(Al2O3), Copper Oxide(CuO)Nano Fluids with Different Concentrations. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5 Pt 1, 6481–6488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, A.; Coulombe, S.; Kietzig, A. Boiling heat transfer enhancement with stable nanofluids and laser textured copper surfaces. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 126, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dormohammadi, R.; Farzaneh-Gord, M.; Ebrahimi-Moghadam, A.; Ahmadi, M.H. Heat transfer and entropy generation of the nanofluid flow inside sinusoidal wavy channels. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 269, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehzad, N.; Zeeshan, A.; Ellahi, R.; Vafai, K. Convective heat transfer of nanofluid in a wavy channel: Buongiorno’s mathematical model. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 222, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Hatami, M.; Zhou, J.; Jing, D. Natural convection heat transfer in a nanofluid-filled cavity with double sinusoidal wavy walls of various phase deviations. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 115, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifpur, M.; Solomon, A.B.; Ottermann, T.L.; Meyer, J.P. Optimum concentration of nanofluids for heat transfer enhancement under cavity flow natural convection with TiO2—Water. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 98, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, A.B.; Sharifpur, M.; Ottermann, T.; Grobler, C.; Joubert, M.; Meyer, J.P. Natural convection enhancement in a porous cavity with Al2O3-Ethylene glycol/water nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 108, 1324–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbadeen, I.; Sharifpur, M.; Slabber, J.; Meyer, J. Experimental study on natural convection of MWCNT-water nanofluids in a square enclosure. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 88, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodsinezhad, H.; Sharifpur, M.; Meyer, J.P. Experimental investigation on cavity flow natural convection of Al2O3–Water nanofluids. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 76, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joubert, J.; Sharifpur, M.; Solomon, A.B.; Meyer, J. Enhancement in heat transfer of a ferrofluid in a differentially heated square cavity through the use of permanent magnets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 443, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoury, D.; Doshmanziari, F.I.; Kiani, A.; Chamkha, A.J. Heat transfer and flow characteristics of Al2O3/water nanofluid in various heat exchangers: Experiments on counter flow. Heat Transf. Eng. 2020, 41, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayeli, P.; Hesami, H.; Besharati-Foumani, H.; Niajalili, M. Al2O3–Water nanofluid heat transfer and entropy generation in a ribbed channel with wavy wall in the presence of magnetic field. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A Appl. 2018, 73, 604–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, B.-H.; Kang, H.U.; Kim, S.H. Effect of alumina nanoparticles in the fluid on heat transfer in double-pipe heat exchanger system. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2008, 25, 966–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Flow and heat transfer of nanofluid over an exponentially shrinking porous sheet with heat and mass fluxes. Propuls. Power Res. 2018, 7, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Qiu, T. Heat transfer performance assessment of hybrid nanofluids in a parallel channel under identical pumping power. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2017, 168, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshvaght-Aliabadi, M.; Hormozi, F. Investigation on Heat Transfer and Pressure Drop of Copper–Water Nanofluid Flow in Plain and Perforated Channels. Exp. Heat Transf. 2015, 29, 427–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Y.; Li, Q. Investigation on Convective Heat Transfer and Flow Features of Nanofluids. J. Heat Transf. 2003, 125, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.; Liu, R.; Wang, J.; Du, M. The characteristics of convective heat transfer in microchannel heat sinks using Al2O3 and TiO2 nanofluids. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 76, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parashar, A.K.; Gupta, A. Investigation of the effect of bagasse ash, hooked steel fibers and glass fibers on the mechanical properties of concrete. Mater. Today Proc. 2001, 44, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekiciler, R.; Çetinkaya, M.S.A. A comparative heat transfer study between monotype and hybrid nanofluid in a duct with various shapes of ribs. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2021, 23, 100913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Feng, L.; Altanji, M.; Sharma, K.; Nisar, K.S.; Khorasani, S. Proposing novel “L” shaped fin to boost the melting performance of a vertical PCM enclosure. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2021, 28, 101465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çobanoğlu, N.; Banisharif, A.; Estellé, P.; Karadeniz, Z.H. The developing flow characteristics of water—Ethylene glycol mixture based Fe3O4 nanofluids in eccentric annular ducts in low temperature applications. Int. J. Thermofluids 2022, 14, 100149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinoth, R.; Sachuthananthan, B.; Vadivel, A.; Balakrishnan, S.; Raj, A.G.S. Heat transfer enhancement in oblique finned curved microchannel using hybrid nanofluid. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2023, 183, 107848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, K.; Shibata, A.; Torii, S. An experimental and numerical study of turbulent heat transfer enhancement for graphene nanofluids produced by pulsed discharge. Int. J. Thermofluids 2022, 16, 100219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.; Huang, S.; Lai, C.-M. Enhancing laminar forced convection heat transfer by using Al2O3/PCM nanofluids in a concentric double-tube duct. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 35, 102147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalili, B.; Aghaee, N.; Jalili, P.; Ganji, D.D. Novel usage of the curved rectangular fin on the heat transfer of a double-pipe heat exchanger with a nanofluid. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 35, 102086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Nunayon, S.S.; Jin, X.; Lai, A.C. Pressure drop and nanoparticle deposition characteristics for multiple twisted tape inserts with partitions in turbulent duct flows. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 193, 121474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omri, M.; Smaoui, H.; Frechette, L.; Kolsi, L. A new microchannel heat exchanger configuration using CNT-nanofluid and allowing uniform temperature on the active wall. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 32, 101866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers. Methods of Testing to Determine the Thermal Performance of Solar Collectors; Technical Report ASHRAE-93-1986/XAB; ASHRAE: Washington, DC, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, C.; Wei, L.; Li, Z. An experimental investigation of forced convective cooling performance of a microchannel heat sink with Al2O3/water nanofluid. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2010, 30, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajjha, R.S.; Das, D.K. Experimental determination of thermal conductivity of three nanofluids and development of new correlations. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2009, 52, 4675–4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyf, H.R.; Mohammadian, S.K. Thermal and Hydraulic Performance of Counterflow Microchannel Heat Exchangers with and without Nanofluids. J. Heat Transf. 2011, 133, 081801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanaki, S.; Mohammed, H.; Abdollahi, A.; Wahid, M. Effect of nanoparticle shapes on the heat transfer enhancement in a wavy channel with different phase shifts. J. Mol. Liq. 2014, 196, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittus, F.W.; Boelter, L.M.K. Heat transfer in automobile radiators of the tubular type. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 1930, 12, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Das, R.K.; Kulkarni, K. Computational and experimental assessment of solar air heater roughened with six different baffles. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2021, 27, 101350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S. Calculation of flat-plate collector loss coefficients. Sol. Energy 1975, 17, 79–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, R.; Eckert, E. Application of rough surfaces to heat exchanger design. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1972, 15, 1647–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| S.N. | Parameters | Ranges |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | 0.533–1.133 | |
| 2. | 3.71–6.71 | |
| 3. | 35°–65° | |
| 4. | 1.5–4.5% | |
| 5. | 30 nm | |
| 6. | 5000–26,000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumar, A.; Maithani, R.; Sharma, S.; Kumar, S.; Sharifpur, M.; Alam, T.; Gupta, N.K.; Eldin, S.M. Effect of Dimpled Rib with Arc Pattern on Hydrothermal Characteristics of Al2O3-H2O Nanofluid Flow in a Square Duct. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14675. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142214675
Kumar A, Maithani R, Sharma S, Kumar S, Sharifpur M, Alam T, Gupta NK, Eldin SM. Effect of Dimpled Rib with Arc Pattern on Hydrothermal Characteristics of Al2O3-H2O Nanofluid Flow in a Square Duct. Sustainability. 2022; 14(22):14675. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142214675
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar, Anil, Rajesh Maithani, Sachin Sharma, Sunil Kumar, Mohsen Sharifpur, Tabish Alam, Naveen Kumar Gupta, and Sayed M. Eldin. 2022. "Effect of Dimpled Rib with Arc Pattern on Hydrothermal Characteristics of Al2O3-H2O Nanofluid Flow in a Square Duct" Sustainability 14, no. 22: 14675. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142214675
APA StyleKumar, A., Maithani, R., Sharma, S., Kumar, S., Sharifpur, M., Alam, T., Gupta, N. K., & Eldin, S. M. (2022). Effect of Dimpled Rib with Arc Pattern on Hydrothermal Characteristics of Al2O3-H2O Nanofluid Flow in a Square Duct. Sustainability, 14(22), 14675. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142214675










