Investigation of Radon in Groundwater and the Corresponding Human-Health Risk Assessment in Northeastern Saudi Arabia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
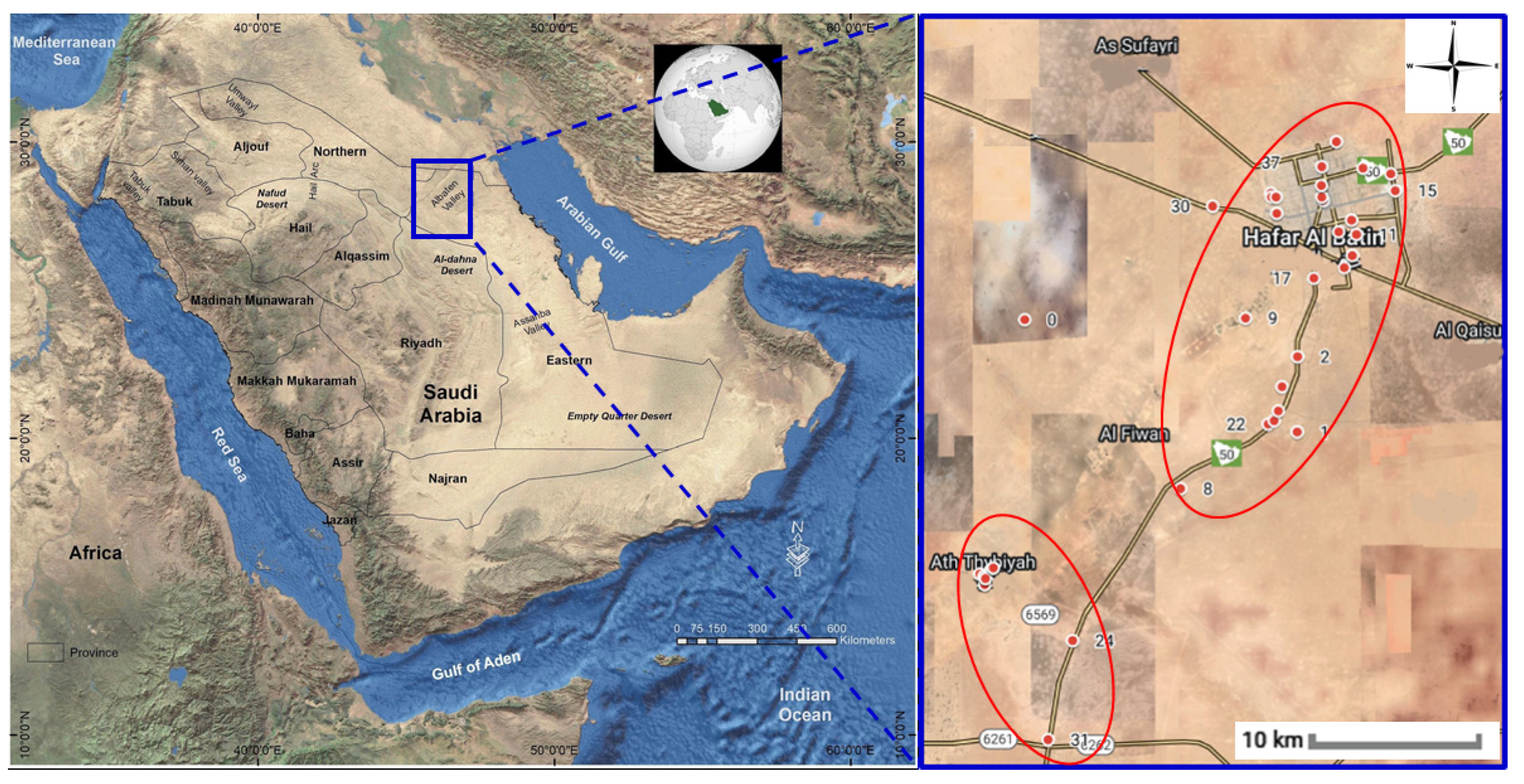
2.1. The Study Area
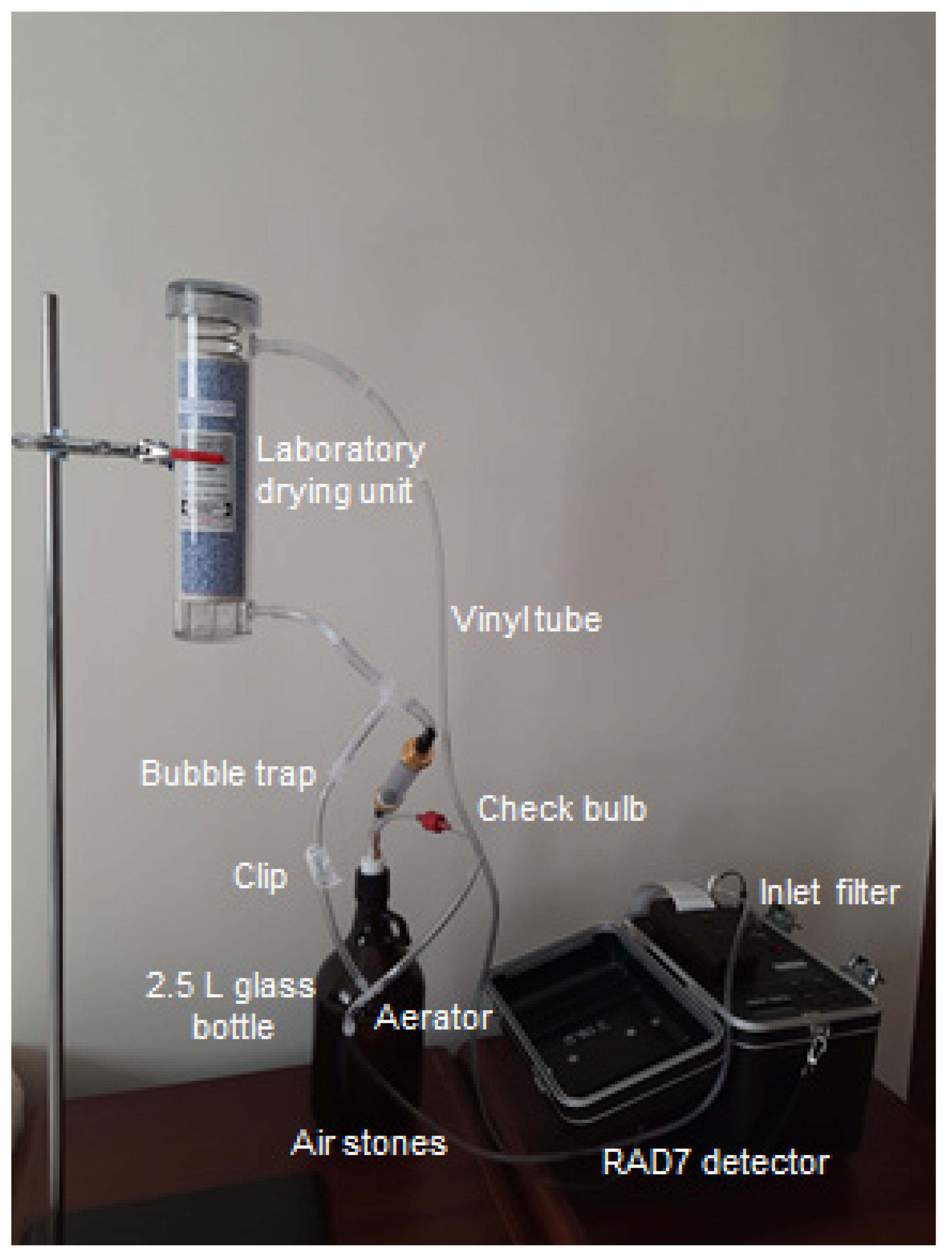
2.2. Radon Measurement
2.3. Sampling Method
2.4. Dose Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UNSCEAR. Sources, Effects and Risks of Ionizing Radiation; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 1988; Volume 199. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. National primary drinking water regulations; Radionuclides, proposed rule. Fed. Reg. 1991, 56, 33050–33127. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, J.D. Lung cancer risk and effective dose coefficients for radon: UNSCEAR review and ICRP conclusions. J. Radiol. Prot. 2021, 41, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Küçükönder, E.; Gümbür, S. Radon Gas Measurement in Water Samples in Kahramanmaras Province of Turkey. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2022, 233, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirmarche, M.; Harrison, J.D.; Laurier, D.; Paquet, F.; Blanchardon, E.; Marsh, J.W. ICRP Publication 115. Lung cancer risk from radon and progeny and statement on radon. Ann. ICRP 2010, 40, 1–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleissa, K.A.; Alghamdi, A.S.; Almasoud, F.I.; Islam, M.S. Measurement of radon levels in groundwater supplies of Riyadh with liquid scintillation counter and the associated radiation dose. Radiation Prot. Dosim. 2012, 154, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, R.; Bala, P. Estimation of annual effective dose due to Radon level in indoor air and soil gas in Hamirpur district of Himachal Pradesh. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 142, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, J.D.; Balonov, M.; Bochud, F.; Martin, C.; Menzel, H.G.; Ortiz-Lopez, P.; Smith-Bindman, R.; Simmonds, J.R.; Wakeford, R. ICRP Publication 147: Use of Dose Quantities in Radiological Protection. Ann. ICRP 2021, 50, 9–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petoussi-Henss, N.; Satoh, D.; Endo, A.; Eckerman, K.; Bolch, W.; Hunt, J.; Jansen, J.T.M.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, C.; Saito, K.; et al. ICRP Publication 144: Dose Coefficients for External Exposures to Environmental Sources. Ann. ICRP 2020, 49, 11–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Mehta, K.; Narang, S.; Kumar, A. Dose estimation from the exposure to radon, thoron and their progeny concentrations in the environs of Kangra area, Himachal Himalayas, India. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 11, 100409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maringer, F.J.; Baumgartner, A.; Rechberger, F.; Seidel, C.; Stietka, M. Activity measurement and effective dose modelling of natural radionuclides in building material. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2013, 81, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Radon in Workplaces: Implementing the Requirements in Council Directive 2013/59/Euratom; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Desalination for Safe Water Supply: Guidance for the Health and Environmental Aspects Applicable to Desalination; World Health Organization (WHO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2007.
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; Volume 216, pp. 303–304.
- WHO. The World Health Organization (2009) WHO Handbook on Indoor Radon; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009; ISBN 978-92-4-154767-3.
- Malik, M.F.I.; Rabaiee, N.A.; Jaafar, M.S. Determination of radon concentration in water using RAD7 with RAD H2 accessories. In Proceedings of the National Physics Conference 2014 (PERFIK 2014), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 1 April 2015; p. 120005. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Exposure to Radon in Drinking Water Supplies. Off. J. Eur. Comm. 2001, 344, 85–88. [Google Scholar]
- Hopke, P.K.; Borak, T.B.; Doull, J.; Cleaver, J.E.; Eckerman, K.F.; Gundersen, L.C.S.; Harley, N.H.; Hess, C.T.; Kinner, N.E.; Kopecky, K.J.; et al. Health Risks Due to Radon in Drinking Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 921–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Simone, G.; Galli, G.; Lucchetti, C.; Tuccimei, P. Calibration of Big Bottle RAD H2O set-up for radon in water using HDPE bottles. Radiat. Meas. 2015, 76, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobbágy, V.; Altzitzoglou, T.; Malo, P.; Tanner, V.; Hult, M. A brief overview on radon measurements in drinking water. J. Environ. Radioact. 2017, 173, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuelhia, E. Evaluation of annual effective dose from indoor radon concentration in Eastern Province, Dammam, Saudi Arabia. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2017, 140, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuelhia, E. Assessment of radiation dose from radon ingestion and inhalation in commercially bottled drinking water and its annual effective dose in Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2019, 29, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, N.F. Determine the Contaminations of Radon in the Drinking Water Using NTDs (CR-39) and RAD7 Detectors. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2021, 46, 6061–6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, T.; Adel, A.; Baloch, M.A.; Alsagabi, S.F.; Alssalim, Y.A.; Alslamah, A.S.; Alkhomashi, N. Natural radioactivity measurements and age-dependent dose assessment in groundwater from Al-Zulfi, Al-Qassim and Al-Majmaah regions, Saudi Arabia. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2018, 318, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, P. Saudi Arabia: An Environmental Overview; CRC Press: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsharhan, A.S.; Rizk, Z.A.; Nairn, A.E.M.; Bakhit, D.W.; Alhajari, S.A. Preface. In Hydrogeology of An Arid Region: The Arabian Gulf and Adjoining Areas; Alsharhan, A.S., Rizk, Z.A., Nairn, A.E.M., Bakhit, D.W., Alhajari, S.A., Eds.; Elsevier Science B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrani, S.A. Radon concentration values in the field: Correlation with underlying geology. Radiat. Meas. 1999, 31, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Taher, A.M.; Abojassim, A.A.; Najam, L.A.; Mraity, H.A.A.B. Assessment of Annual effective Dose for Different Age Groups based on Radon Concentrations in the Groundwater of Qassim, Saudi Arabia. Iran. J. Med. Phys. 2020, 17, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binesh, A.; Mohammadi, S.; Mowlavi, A.; Parvaresh, P. Evaluation of the radiation dose from radon ingestion and inhalation in drinking water. Int. J. Water Resour. Environ. Eng. 2010, 2, 174–178. [Google Scholar]
- Alzurfi, S.; Abojassim, A.; Mraity, H. Monthly Monitoring of Physicochemical and Radiation Properties of Kufa River, Iraq. Pak. J. Sci. Ind. Res. Ser. A Phys. Sci. 2018, 61, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNSCEAR. Sources and Effects of Ionizing Radiation, United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (UNSCEAR) 1993 Report: Report to the General Assembly, with Scientific Annexes; UNSCEAR: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, M.N.; Chowdhury, M.I.; Kamal, M.; Ghose, S.; Islam, M.N.; Anwaruddin, M. Radiological Assessment of Drinking Water of the Chittagong Region of Bangladesh. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 1999, 82, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNSCEAR. The General Assembly with Scientific Annex; UNSCEAR: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- El-Taher, A. Annual effective dose exposure in ground water from Qassim area, Saudi J. Environmen. Sci. Techn 2012, 5, 475–481. [Google Scholar]
- IAEA. WHO—International Basic Standards for Protection against Ionizing Radiation and for the Safety of Radiation Sources. In Safety Series; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- UNSCEAR. United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (2019) UNSCEAR 2019 Report, Annex B—Lung Cancer from Exposure to Radon; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Aljaloud, K.B.; ElBatouti, M. Statistical analysis of 222Rn concentration in Zamzam and other water sources in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Jaseem, Q.K.; Almasoud, F.I.; Ababneh, A.M.; Al-Hobaib, A.S. Radiological assessment of water treatment processes in a water treatment plant in Saudi Arabia: Water and sludge radium content, radon air concentrations and dose rates. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 563–564, 1030–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althoyaib, S.; El-Taher, A. Natural radioactivity measurements in groundwater from Al-Jawa, Saudi Arabia. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2015, 304, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Taher, A.; Al-Turki, A. Radon activity measurements in irrigation water from Qassim Province by RAD7. J. Environ. Biol. 2016, 37, 1299–1302. [Google Scholar]
- Tayyeb, Z.; Kinsara, A.; Farid, S. A study on the radon concentrations in water in Jeddah (Saudi Arabia) and the associated health effects. J. Environ. Radioact. 1998, 38, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Araby, E.H.; Soliman, H.A.; Abo-Elmagd, M. Measurement of radon levels in water and the associated health hazards in Jazan, Saudi Arabia. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2019, 12, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalım, H.A.; Sandıkcıoğlu, A.; Ünal, R.; Orhun, Ö. Measurements of radon concentrations in well waters near the Akşehir fault zone in Afyonkarahisar, Turkey. Radiat. Meas. 2007, 42, 505–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrani, D. Natural radioactivity in Algerian bottled mineral waters. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2002, 252, 597–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahesh, H.; Avadhani, D.; Karunakara, N.; Somashekarappa, H.; Narayana, Y.; Siddappa, K. 222Rn concentration in ground waters of coastal Karnataka and Kaiga of south west coast of India. Health Phys. 2001, 81, 724–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moldovan, M.; Nita, D.C.; Cucos-Dinu, A.; Dicu, T.; Bican-Brişan, N.; Cosma, C. Radon concentration in drinking water and supplementary exposure in Băiţa-Ştei mining area, Bihor county (Romania). Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2014, 158, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idriss, H.; Salih, I.; Sam, A. Study of radon in ground water and physicochemical parameters in Khartoum state. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2011, 290, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakootian, M.; Nejhad, Y.S. Determination of radon concentration in drinking water of Bam villages and evaluation of the annual effective dose. Int. J. Radiat. Res. 2017, 15, 81. [Google Scholar]
- Xinwei, L. Analysis of radon concentration in drinking water in Baoji (China) and the associated health effects. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2006, 121, 452–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hystad, P.; Brauer, M.; Demers, P.A.; Johnson, K.C.; Setton, E.; Cervantes-Larios, A.; Poplawski, K.; McFarlane, A.; Whitehead, A.; Nicol, A.M. Geographic variation in radon and associated lung cancer risk in Canada. Can. J. Public Health 2014, 105, e4–e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmehdi, H.; Dalah, E.; Bakhronov, K. Measurements of Radon Concentration in Water in the United Arab Emirates and the Associated Health Effects. In Proceedings of the 2019 Advances in Science and Engineering Technology International Conferences (ASET), Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 26 March–10 April 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seoud, M. Measurement of Radon-222 Concentration in Bottled Natural Mineral Drinking Water in Kuwait Using the Nuclear Track Detector (CR-39). Int. J. Phys. 2017, 5, 201–207. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, F.A.; El-Kamel, A.H.; Harb, S.; Zahran, A.M.; Abbady, A.A. Natural radioactivity of ground water in some areas in Aden governorate South of Yemen Region. Radiat. Prot. Environ. 2013, 36, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bataina, B.A.; Ismail, A.M.; Kullab, M.K.; Abumurad, K.M.; Mustafa, H. Radon measurements in different types of natural waters in Jordan. Radiat. Meas. 1997, 28, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abojassim, A. Radon Concentrations Measurement for Drinking Water in Kufa City /Iraq Using Active Detecting Method. Adv. Phys. Theor. Appl. 2014, 26, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Leggett, R.; Eckerman, K. Dosimetric Significance of the ICRP’s Updated Guidance and Models, 1989–2003, and Implications for U.S. Federal Guidance; United States Department of Energy: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample No. | Purpose of Use | Depth of Well | CRn (Bq/L) | Sample No. | Purpose of Use | Depth of Well | CRn (Bq/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H01 | Domestic use | Shallow | 0.29 | H21 | Domestic use | Shallow | 0.27 |
| H02 | Domestic use | Shallow | 0.03 | H22 | Domestic use | Shallow | 0.23 |
| H03 | Drinking and domestic | Deep | 2.11 | H23 | Domestic use | Shallow | 0.34 |
| H04 | Drinking and domestic | Deep | 1.15 | H24 | Domestic use | Shallow | 1.69 |
| H05 | Drinking and domestic | Deep | 1.00 | H25 | Domestic use | Shallow | 2.17 |
| H06 | Drinking and domestic | Deep | 0.89 | H26 | Drinking and domestic | Deep | 1.99 |
| H07 | Drinking and domestic | Deep | 0.67 | H27 | Drinking and domestic | Deep | 1.67 |
| H08 | Drinking and domestic | Shallow | 1.02 | H28 | Drinking and domestic | Deep | 2.04 |
| H09 | Drinking and domestic | Shallow | 1.27 | H29 | Domestic use | Shallow | 0.60 |
| H10 | Domestic use | Shallow | 3.20 | H30 | Domestic use | Shallow | 0.67 |
| H11 | Drinking and domestic | Deep | 1.67 | H31 | Domestic use | Shallow | 1.51 |
| H12 | Drinking and domestic | Deep | 0.17 | H32 | Drinking and domestic | Deep | 1.21 |
| H13 | Domestic use | Shallow | 0.65 | H33 | Domestic use | Shallow | 1.20 |
| H14 | Domestic use | Shallow | 0.85 | H34 | Drinking and domestic | Deep | 1.73 |
| H15 | Domestic use | Shallow | 0.46 | H35 | Domestic use | Shallow | 1.38 |
| H16 | Domestic use | Shallow | 0.32 | H36 | Domestic use | Shallow | 1.99 |
| H17 | Domestic use | Shallow | 0.13 | H37 | Domestic use | Shallow | 1.67 |
| H18 | Domestic use | Shallow | 0.52 | H38 | Domestic use | Shallow | 0.57 |
| H19 | Drinking and domestic | Deep | 2.95 | Max | 3.20 | ||
| H20 | Domestic use | Shallow | 1.80 | Min | 0.03 | ||
| Average | 1.16 | ||||||
| Depth of the shallow well: ~400 m | S. D | 0.79 | |||||
| Depth of the deep well: 800 m and above | |||||||
| Location | Water Type | Radon Concentration, CRn (Bq/L) |
|---|---|---|
| Sharjah, UAE | Groundwater | 0.05–1.82 [51] |
| Kuwait City, Kuwait | Drinking-bottle water | 1.02–6.05 [52] |
| Aden, Yemen | Groundwater | 0.33–2.67 [53] |
| Afyonkarahisar, Turkey | Well water | 0.70–31.70 [43] |
| Jordan | Well water | 3.10–5.10 [54] |
| Algeria | Drinking-bottle water | 2.6–14.0 [44] |
| Kufa, Iraq | Drinking water | 0.0039–0.221 [55] |
| Karnataka, India | Groundwater | 0.14–25.40 [45] |
| Baita Stei, Romania | Well water | 4.78–35.50 [46] |
| Khartoum, Sudan | Groundwater | 1.58–345.10 [47] |
| Bam village, Iran | Drinking water | 1.20–9.88 [48] |
| Baoji, China | Drinking water | 30.0–127.0 [49] |
| Al-Jawa, Saudi Arabia | Groundwater | 1.45–9.15 [39] |
| Al-Qassim, Saudi Arabia | Groundwater | 0.76–4.69 [34] |
| Jeddah, Saudi Arabia | Groundwater | 0.92–2.12 [41] |
| Dammam, Saudi Arabia | Drinking water | 0.11–9.20 [22] |
| Jazan, Saudi Arabia | Groundwater | 1.74–4.32 [42] |
| Hafr Al Batin, Saudi Arabia | Groundwater | 0.03–3.20 (present study) |
| Sample No. | AED for Ingestion (μSv/y) | AED for Inhalation (μSv/y) | Total Dose (μSv/y) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AEDing (≤1 year) | AEDing (2–17 year) | AEDing (≥17 year) | AEDinh (≥17 year) | AEDT | |
| H01 | 1.51 | 0.56 | 0.73 | 0.72 | 1.45 |
| H02 | 0.14 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.13 |
| H03 | 11.16 | 4.11 | 5.39 | 5.32 | 10.71 |
| H04 | 6.08 | 2.24 | 2.94 | 2.90 | 5.84 |
| H05 | 5.29 | 1.95 | 2.56 | 2.52 | 5.08 |
| H06 | 4.71 | 1.73 | 2.27 | 2.24 | 4.52 |
| H07 | 3.54 | 1.30 | 1.71 | 1.69 | 3.40 |
| H08 | 5.40 | 1.99 | 2.61 | 2.57 | 5.18 |
| H09 | 6.72 | 2.47 | 3.24 | 3.20 | 6.45 |
| H10 | 16.93 | 6.23 | 8.18 | 8.06 | 16.24 |
| H11 | 8.83 | 3.25 | 4.27 | 4.21 | 8.48 |
| H12 | 0.91 | 0.33 | 0.44 | 0.43 | 0.87 |
| H13 | 3.44 | 1.27 | 1.66 | 1.64 | 3.30 |
| H14 | 4.50 | 1.65 | 2.17 | 2.14 | 4.31 |
| H15 | 2.45 | 0.90 | 1.19 | 1.17 | 2.35 |
| H16 | 1.67 | 0.62 | 0.81 | 0.80 | 1.60 |
| H17 | 0.70 | 0.26 | 0.34 | 0.33 | 0.67 |
| H18 | 2.76 | 1.01 | 1.33 | 1.31 | 2.64 |
| H19 | 15.61 | 5.74 | 7.54 | 7.43 | 14.97 |
| H20 | 9.52 | 3.50 | 4.60 | 4.54 | 9.14 |
| H21 | 1.44 | 0.53 | 0.70 | 0.69 | 1.39 |
| H22 | 1.21 | 0.45 | 0.59 | 0.58 | 1.16 |
| H23 | 1.82 | 0.67 | 0.88 | 0.87 | 1.75 |
| H24 | 8.94 | 3.29 | 4.32 | 4.26 | 8.58 |
| H25 | 11.48 | 4.22 | 5.54 | 5.47 | 11.01 |
| H26 | 10.53 | 3.87 | 5.08 | 5.01 | 10.10 |
| H27 | 8.83 | 3.25 | 4.27 | 4.21 | 8.48 |
| H28 | 10.79 | 3.97 | 5.21 | 5.14 | 10.35 |
| H29 | 3.17 | 1.17 | 1.53 | 1.51 | 3.05 |
| H30 | 3.54 | 1.30 | 1.71 | 1.69 | 3.40 |
| H31 | 7.99 | 2.94 | 3.86 | 3.81 | 7.66 |
| H32 | 6.40 | 2.36 | 3.09 | 3.05 | 6.14 |
| H33 | 6.35 | 2.34 | 3.07 | 3.02 | 6.09 |
| H34 | 9.15 | 3.37 | 4.42 | 4.36 | 8.78 |
| H35 | 7.30 | 2.69 | 3.53 | 3.48 | 7.00 |
| H36 | 10.53 | 3.87 | 5.08 | 5.01 | 10.10 |
| H37 | 8.83 | 3.25 | 4.27 | 4.21 | 8.48 |
| H38 | 3.02 | 1.11 | 1.46 | 1.44 | 2.89 |
| Max | 16.93 | 6.23 | 8.18 | 8.06 | 16.24 |
| Min | 0.14 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.13 |
| Average | 6.14 | 2.26 | 2.96 | 2.92 | 5.89 |
| S. D | 4.18 | 1.54 | 2.02 | 1.99 | 4.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mamun, A.; Alazmi, A.S. Investigation of Radon in Groundwater and the Corresponding Human-Health Risk Assessment in Northeastern Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14515. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142114515
Mamun A, Alazmi AS. Investigation of Radon in Groundwater and the Corresponding Human-Health Risk Assessment in Northeastern Saudi Arabia. Sustainability. 2022; 14(21):14515. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142114515
Chicago/Turabian StyleMamun, Al, and Amira Salman Alazmi. 2022. "Investigation of Radon in Groundwater and the Corresponding Human-Health Risk Assessment in Northeastern Saudi Arabia" Sustainability 14, no. 21: 14515. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142114515
APA StyleMamun, A., & Alazmi, A. S. (2022). Investigation of Radon in Groundwater and the Corresponding Human-Health Risk Assessment in Northeastern Saudi Arabia. Sustainability, 14(21), 14515. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142114515









