The Need for a Proper Waste Management Plan for the Construction Industry: A Case Study in Lebanon
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Data Analysis
3.1. Reliability of Results
3.2. Demographic Background of Respondents
3.3. Quantitative Data Analysis
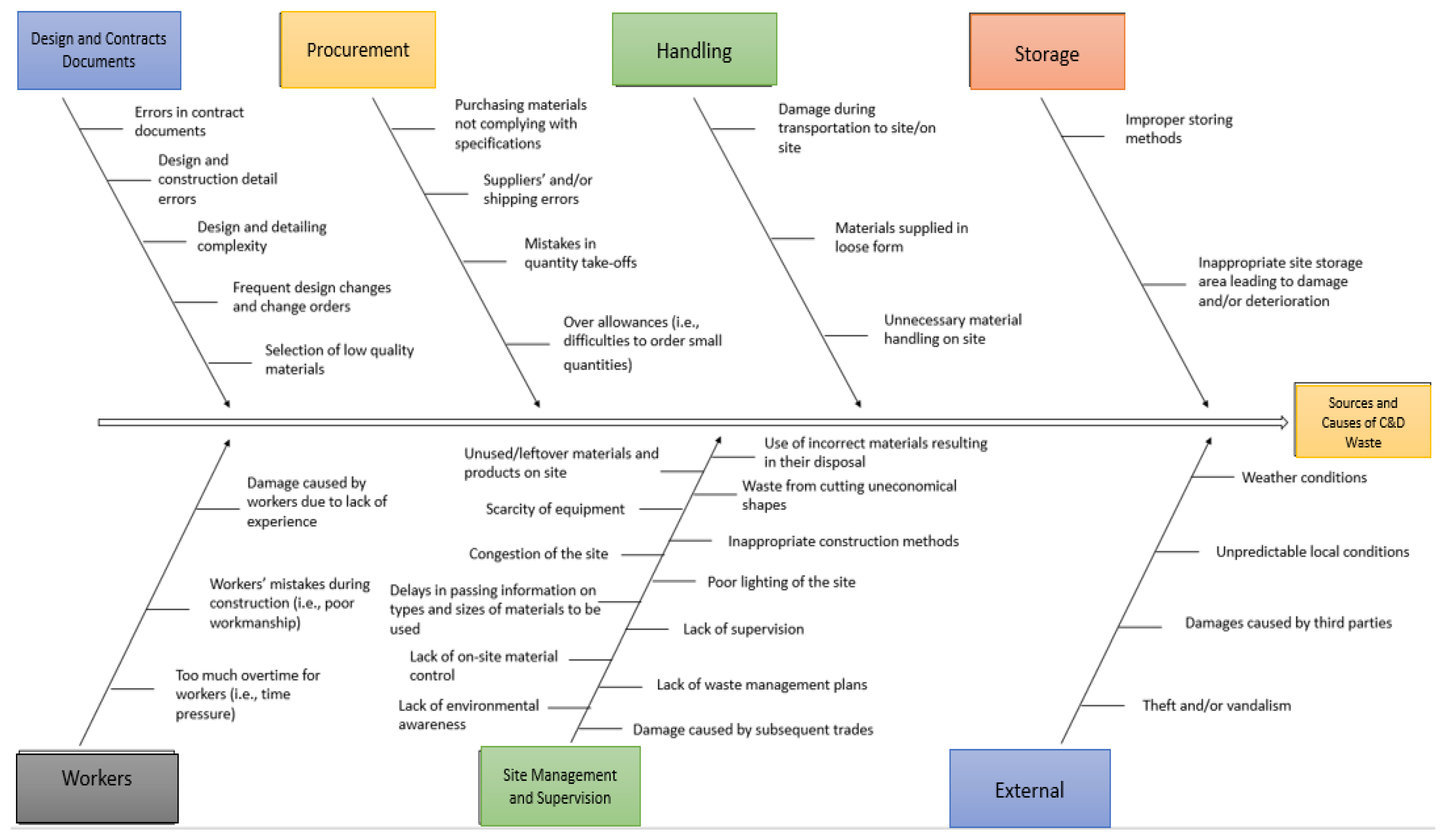
3.3.1. Sources and Causes of C&D Waste
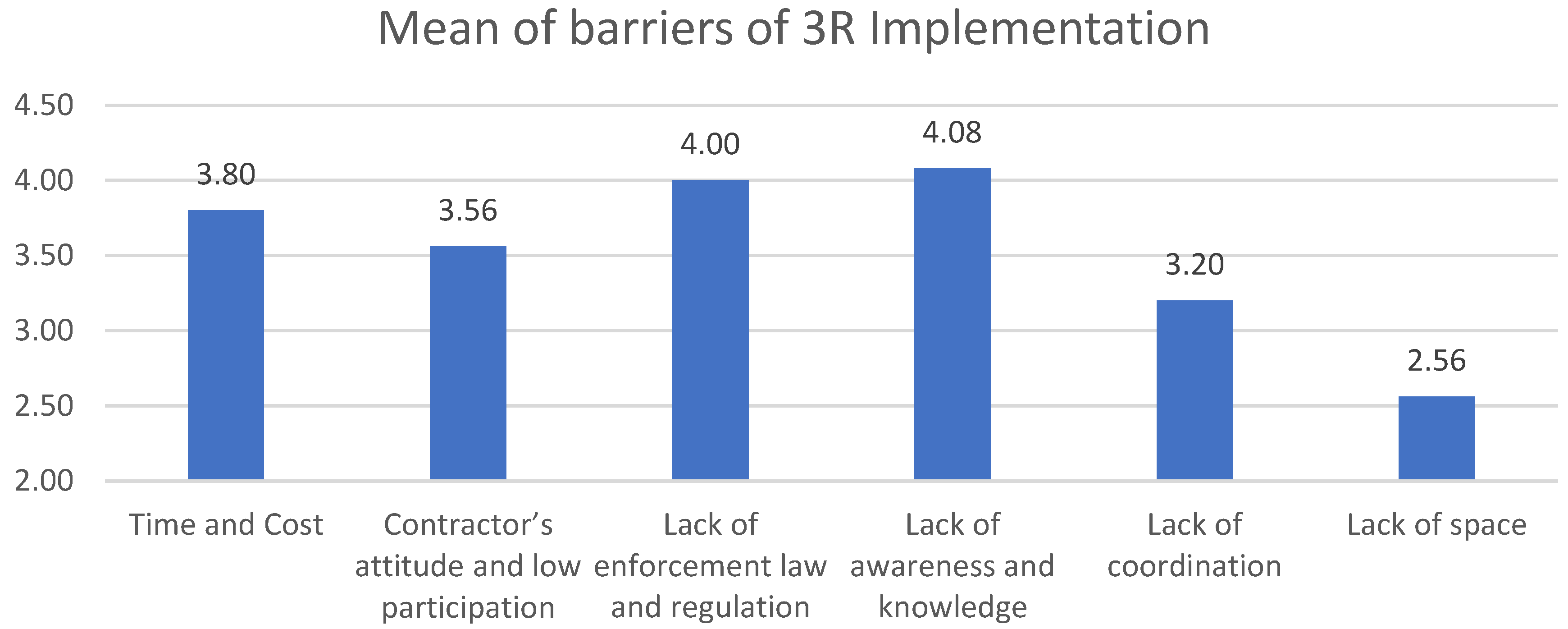
3.3.2. Barriers for Implementing 3R
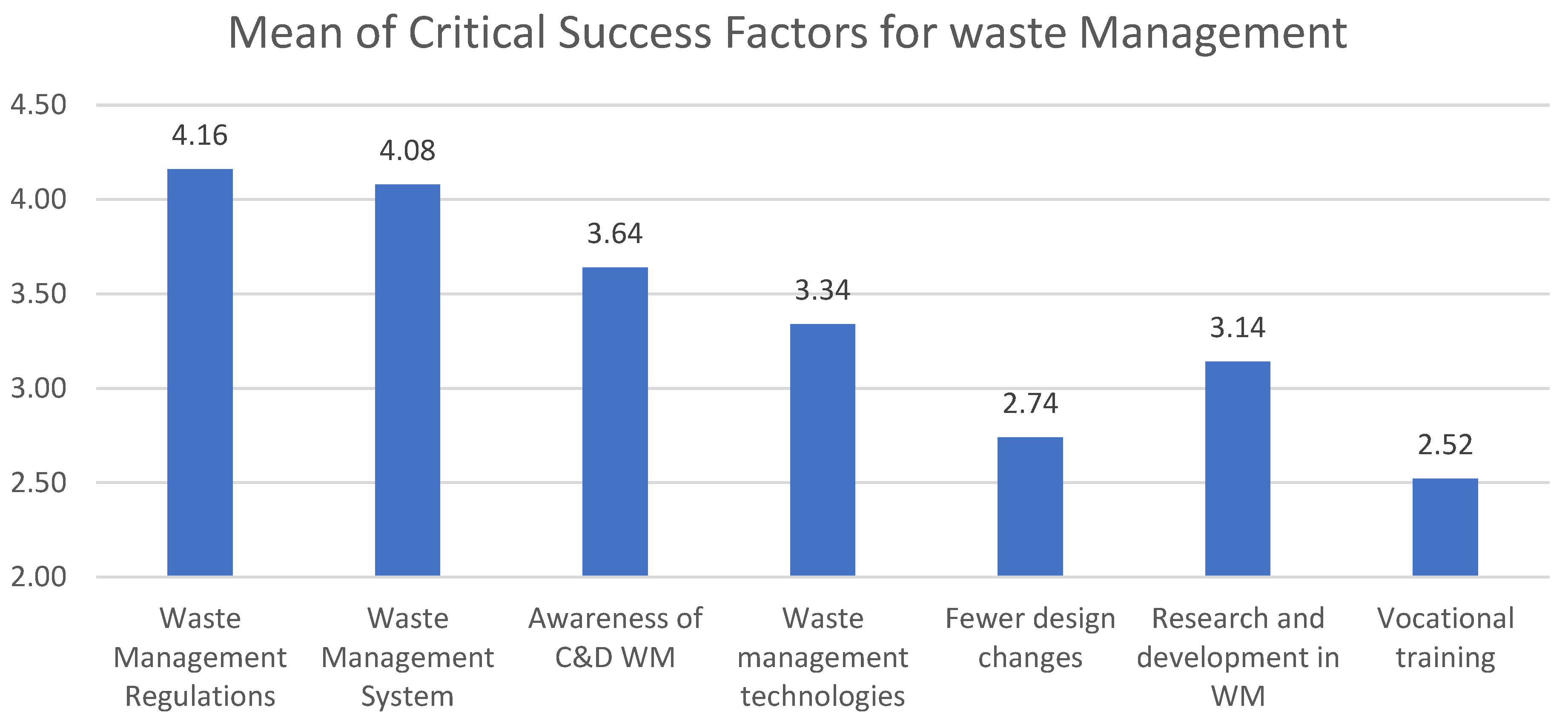
3.3.3. Critical Success Factors for (CWM) Construction Waste Management
3.3.4. Advantages of Construction Waste Management
3.4. Qualitative Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
- The main source and cause of construction and demolition waste in Lebanon is site management and supervision and the worker-related factors with the mean value of 4.24.
- The main barrier for implementing 3R is lack of awareness and knowledge and lack of law enforcementand regulation with a 4.08 mean value.
- The results revealed that the main critical success factor for construction waste management is waste management regulations and the waste management system with 4.16 and 4.08 values, respectively.
- The main advantage of the construction waste management is the factor denoted as “Reduction in negative environmental impact due to waste” with a mean value of 4.34.
- We should implement construction waste-sorting procedures onsite and manage the amount of waste and compare it with the ex-determined targets to identify and handle potential sources of waste.
- We should enhance the skills of construction site workers and manage the team by providing them with necessary training courses.
- We should note that external factors and their natual effects are beyond human control, but waste caused by external factors can be mitigated by including this cause in the project risk assessment process and implementing a mitigation strategy.
- We should provide training and educational programs on environmental management to raise awareness and knowledge on the implementation of 3R and conduct awareness campaigns to encourage and motivate contractors to practice 3R in the construction industry.
- We should provide subsidies to contractors in order to reduce the CW by implementing the 3R strategy to improve the CWM plan. This also implies that the application of additional charges as penalties for sending construction waste to a landfill instead of recycling and reusing this waste would be effective.
Limitations and Future Improvement
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yukalang, N.; Clarke, B.; Ross, K. Solid Waste Management Solutions for a Rapidly Urbanizing Area in Thailand: Recommendations Based on Stakeholder Input. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.; Singhal, S.; Jain, N.K. Construction and demolition waste (C&DW) in India: Generation rate and implications of C&DW recycling. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2018, 21, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laquatra, J.; Pierce, M. Waste Management at the Construction Site. Integr. Waste Manag. 2011, 1, 281–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana Yesmin Global Waste Crisis: A Rising Threat to Environment. Available online: https://moderndiplomacy.eu/2019/12/26/global-waste-crisis-a-rising-threat-to-environment/ (accessed on 5 November 2020).
- McGrath, M. US Top of the Garbage Pile in Global Waste Crisis, BBC News: London, UK, 2019.
- Ioppolo, G.; Heijungs, R.; Cucurachi, S.; Kleijn, R. Urban Metabolism: Many Open Questions for Future Answers. In Pathways to Environmental Sustainability; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S. The Impact of C & D Waste on Indian Environment: A Critical Review. Civ. Eng. Res. J. 2018, 5, 555658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafourian, K.; Kabirifar, K.; Mahdiyar, A.; Yazdani, M.; Ismail, S.; Tam, V.W.Y. A Synthesis of Express Analytic Hierarchy Process (EAHP) and Partial Least Squares-Structural Equations Modeling (PLS-SEM) for Sustainable Construction and Demolition Waste Management Assessment: The Case of Malaysia. Recycling 2021, 6, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, F.D.S.; Mendes, J.C.; Morais, L.J.B.; Silva, J.S.; Peixoto, R.A.F. Mapping and recycling proposal for the construction and demolition waste generated in the Brazilian Amazon. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 176, 105896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, M.; Kabirifar, K.; Frimpong, B.E.; Shariati, M.; Mirmozaffari, M.; Boskabadi, A. Improving construction and demolition waste collection service in an urban area using a simheuristic approach: A case study in Sydney, Australia. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 280, 124138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Li, X.; Zhu, X.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Li, C. Impact of Recycler Information Sharing on Supply Chain Performance of Construction and Demolition Waste Resource Utilization. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortaheb, M.M.; Mahpour, A. Integrated Construction Waste management, a holistic approach. Sci. Iran. 2016, 23, 2044–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Han, Y.; Zheng, H.; Huang, Y.; Li, X. Considering Consumers’ Green Preferences and Government Subsidies in the Decision Making of the Construction and Demolition Waste Recycling Supply Chain: A Stackelberg Game Approach. Buildings 2022, 12, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esa, M.R.; Halog, A.; Rigamonti, L. Developing strategies for managing construction and demolition wastes in Malaysia based on the concept of circular economy. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2016, 19, 1144–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathanson, J.A. Solid-Waste Management; Encyclopedia Britannica: Chicago, IL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Amasuomo, E.; Baird, J. The Concept of Waste and Waste Management. J. Manag. Sustain. 2016, 6, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, C. Advantages and Disadvantages of Waste Management-WiseStep. Available online: https://content.wisestep.com/advantages-disadvantages-waste-management/ (accessed on 16 November 2020).
- Ghiani, G.; Laganà, D.; Manni, E.; Musmanno, R.; Vigo, D. Operations research in solid waste management: A survey of strategic and tactical issues. Comput. Oper. Res. 2014, 44, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tam, V.W.; Zuo, J.; Zhu, J. Designers’ attitude and behaviour towards construction waste minimization by design: A study in Shenzhen, China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 105, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narcis, N.; Ray, I.; Hosein, G. Construction and Demolition Waste Management Actions and Potential Benefits: A Perspective from Trinidad and Tobago. Buildings 2019, 9, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newaz, M.T.; Davis, P.; Sher, W.; Simon, L. Factors affecting construction waste management streams in Australia. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2020, 22, 2625–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Jha, K.N.; Vyas, G. Proposing building information modeling-based theoretical framework for construction and demolition waste management: Strategies and tools. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2020, 22, 2345–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, H.H.; Goh, K.C.; Seow, T.W.; Said, N.S.; Ang, S.E.P. Challenges in Adopting 3R Concept in the Heritage Building Restoration. Int. J. Civ. Environ. Eng. 2015, 9, 142–149. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, H. The 3R Initiative for Sustainable Development; IGES: Kathmandu, Nepal, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Woodward, R. Lea Engineering Analysis of Solid Waste Management; Louisiana State University and Agricultural & Mechanical College: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Memon, M.A. Integrated solid waste management based on the 3R approach. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2010, 12, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annabel Bhamani Kajornboon Using Interviews as Research Instruments. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Using-interviews-as-research-instruments-Kajornboon/57e187565ff9c19fb9d7673b964cd77f485bcab0 (accessed on 19 January 2020).
- Kabirifar, K.; Mojhatedi, M.; Wang, C.; Tam, V.W.Y. Construction and demolition waste management contributing factors coupled with reduce, reuse, and recycle strategies for effective waste management: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, R. Builders’ Guidebook to Reducing, Reusing and Recycling res I den TI a L Construction Waste in Wisconsin; 1993. Available online: https://silo.tips/download/recycling-res-i-den-ti-a-l (accessed on 16 November 2020).
- Hu, Y. Minimization Management of Construction Waste. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/5893453 (accessed on 16 November 2020).
- Kulatunga, U.; Amaratunga, D.; Haigh, R.; Rameezdeen, R. Attitudes and perceptions of construction workforce on construction waste in Sri Lanka. Manag. Environ. Qual. Int. J. 2006, 17, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondinel-Oviedo, D.R. Construction and demolition waste management in developing countries: A diagnosis from 265 construction sites in the Lima Metropolitan Area. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2021, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massoud, M.; El-Fadel, M.; Malak, A.A. Assessment of public vs private MSW management: A case study. J. Environ. Manag. 2003, 69, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srour, I.; Chehab, G.; Awwad, E.; Oswald Chong, W. Use of Sustainable Techniques in Lebanese Construction Industry. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/268409054_Use_of_Sustainable_Techniques_in_Lebanese_Construction_Industry (accessed on 16 November 2020).
- Nasr, D.; Massoud, M.; Khoury, R.; Kabakian, V. Environmental Impacts of Reconstruction Activities: A Case of Lebanon. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2009, 3, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BBC What We Know about the Beirut Explosion. BBC News 2020. Available online: https://www.bbc.com/news/world-middle-east-53668493./ (accessed on 6 November 2020).
- Ghanimeh, S.; Jawad, D.; Semaan, P. Quantification of Construction and Demolition Waste: A Measure toward Effective Modeling. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7560117/ (accessed on 20 November 2020).
- Abbas, I. (PDF) Solid Waste Management in Lebanon: Challenges and Recommendations. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/320190830_Solid_Waste_Management_in_Lebanon_Challenges_and_Recommendations (accessed on 7 July 2021).
- Abbas, I.; Chaaban, J.; Al-Rabaa, A.-R.; Shaar, A. Solid Waste Management in Lebanon: Challenges and Recommendations JEWM Solid Waste Management in Lebanon: Challenges and Recommendations. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/331378505_Solid_Waste_Management_in_Lebanon_Challenges_and_Recommendations_JEWM_Solid_Waste_Management_in_Lebanon_Challenges_and_Recommendations (accessed on 22 November 2020).
- Shooshtarian, S.; Maqsood, T.; Caldera, S.; Ryley, T. Transformation towards a circular economy in the Australian construction and demolition waste management system. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 30, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May 2016, N.N. 18; 10:59 Shehayyeb Announces “Permanent” Closure of Naameh Dump at Midnight. Available online: https://www.naharnet.com/stories/en/209519 (accessed on 25 October 2020).
- Van Gelder, M.M.H.J.; Bretveld, R.W.; Roeleveld, N. Web-based Questionnaires: The Future in Epidemiology? Am. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 172, 1292–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fincham, J.E. Response Rates and Responsiveness for Surveys, Standards, and the Journal. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2008, 72, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwin, K. (PDF) Reliability and Validity of Research Instruments Correspondence to Kubaiedwin@yahoo.com. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/335827941_Reliability_and_Validity_of_Research_Instruments_Correspondence_to_kubaiedwinyahoocom (accessed on 14 November 2020).
- Taherdoost, H. Validity and Reliability of the Research Instrument; How to Test the Validation of a Questionnaire/Survey in a Research. SSRN Electron. J. 2018, 5, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, G.; Damci, A.; Turkoglu, H.; Gurgun, A.P. Identification of Root Causes of Construction and Demolition (C&D) Waste: The Case of Turkey. Procedia Eng. 2017, 196, 948–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäckle, A.; Lynn, P.; Sinibaldi, J.; Tipping, S. The Effect of Interviewer Experience, Attitudes, Personality and Skills on Respondent Co-operation with Face-to-Face Surveys. Surv. Res. Methods 2012, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostertagova, E.; Ostertag, O. Methodology and Application of One-Way ANOVA. Available online: http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajme/1/7/21 (accessed on 8 November 2020).
- Singhal, R.; Rana, R. Chi-square test and its application in hypothesis testing. J. Pract. Cardiovasc. Sci. 2015, 1, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, B.-G.; Ng, W.J. Project management knowledge and skills for green construction: Overcoming challenges. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2013, 31, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y. Withdrawn: A case-study of critical success factors for construction and demolition waste management: The pearl river delta region of china. Waste Manag. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, D.W.; Kumaraswamy, M.M. An evaluation of construction time performance in the building industry. Build. Environ. 1996, 31, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rifai, J.A.-R.; Amoudi, O. Understanding the Key Factors of Construction Waste in Jordan. Jordan J. Civ. Eng. 2016, 10, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafourian, K.; Ismail, S.; Mohamed, Z. Construction and Demolition Waste: Its Origins and Causes. Adv. Sci. Lett. 2018, 24, 4132–4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagdi, N.; Aggarwal, V.; Sherwal, N. Management of Construction Waste in India: A Case of Green Technology. Glob. J. Manag. Bus. Stud. 2013, 3, 361–364. [Google Scholar]
- Ametepey, O.; Aigbavboa, C.; Ansah, K. Barriers to Successful Implementation of Sustainable Construction in the Ghanaian Construction Industry. Procedia Manuf. 2015, 3, 1682–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, L.S.; Tan, L.W.; Seow, T.W. Constraints to 3R construction waste reduction among contractors in Penang. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 4–5 December 2017, Langkawi, Malaysia; 140, p. 012103. [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Yuan, H. Exploring critical success factors for waste management in construction projects of China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2010, 55, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagapan, S.; Abdul Rahman, I.; Hameed Memon, A. Identifying Causes of Construction Waste-Case of Central Region of Peninsula Malaysia. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/256838800_Identifying_Causes_of_Construction_Waste_-Case_of_Central_Region_of_Peninsula_Malaysia (accessed on 9 October 2020).
- Papargyropoulou, E.; Dr, P.; Preece, C.; Adila, A.; Abdullah, B. Sustainable Construction Waste Management in Malaysia: A Contractor’s Perspective; Management and Innovation for a Sustainable Built Environment MISBE: Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mawed, M. Construction and demolition waste management in the uae: Application and obstacles. Int. J. Geomate 2020, 18, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EJOLT Naameh Landfill, Lebanon|EJAtlas. Available online: https://ejatlas.org/conflict/naameh-landfill-lebanon (accessed on 26 October 2020).
- Nagapan, S.; Abdul Rahman, I. Construction Waste Management: Malaysian Perspective. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/258224407_CONSTRUCTION_WASTE_MANAGEMENT_Malaysian_Perspective (accessed on 12 October 2020).
- Hwang, B.; Yeo, Z.B. Perception on benefits of construction waste management in the Singapore construction industry. Eng. Constr. Arch. Manag. 2011, 18, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hintons, H. How Can Recycling Help to Improve Your Business’ Brand Value. Available online: https://www.hintonswaste.co.uk/news/can-recycling-help-improve-business-brand-value/ (accessed on 23 November 2020).





| Cronbach’s Alpha Value | Internal Consistency |
|---|---|
| α > 0.9 | Excellent |
| 0.8 < α < 0.9 | Good |
| 0.7 < α < 0.8 | Acceptable |
| 0.6 < α < 0.7 | Questionable |
| 0.5 < α < 0.6 | Poor |
| α < 0.5 | Unacceptable |
| Items | Respondents | |
|---|---|---|
| Number | % | |
| Business category | ||
| Consultant | 10 | 20 |
| Contractor | 12 | 24 |
| Academics | 8 | 16 |
| Engineer | 18 | 36 |
| Other | 2 | 4 |
| Years of experience | ||
| <5 years | 22 | 44 |
| 5–10 years | 10 | 20 |
| 11–20 years | 9 | 18 |
| >20 years | 9 | 18 |
| Work nature | ||
| Public sector | 17 | 34 |
| Private sector | 33 | 66 |
| Survey Sections | Suggestions | Categories |
|---|---|---|
| Construction and demolition waste |
| Worker-related Factors |
| ||
| ||
| Site management and supervision | |
| ||
| ||
| ||
| ||
| ||
| ||
| External factors | |
| ||
| ||
| ||
| Handling factor | |
| Suggested barriers for implementing 3R |
| Time and cost |
| Contractor’s attitude | |
| Suggested critical success Factors for construction waste management |
| Awareness of C&D waste management |
| Waste management system | |
| Waste management regulations | |
| Suggested advantage of construction waste management |
| Waste disposal saving |
| Reduction in negative environmental impact due to waste |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saad, A.; Bal, M.; Khatib, J. The Need for a Proper Waste Management Plan for the Construction Industry: A Case Study in Lebanon. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12783. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912783
Saad A, Bal M, Khatib J. The Need for a Proper Waste Management Plan for the Construction Industry: A Case Study in Lebanon. Sustainability. 2022; 14(19):12783. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912783
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaad, Ali, Menoka Bal, and Jamal Khatib. 2022. "The Need for a Proper Waste Management Plan for the Construction Industry: A Case Study in Lebanon" Sustainability 14, no. 19: 12783. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912783
APA StyleSaad, A., Bal, M., & Khatib, J. (2022). The Need for a Proper Waste Management Plan for the Construction Industry: A Case Study in Lebanon. Sustainability, 14(19), 12783. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912783








