Impact of Resource-Saving and Environment-Friendly Society Construction on Sustainability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Theoretical Analysis and Hypotheses
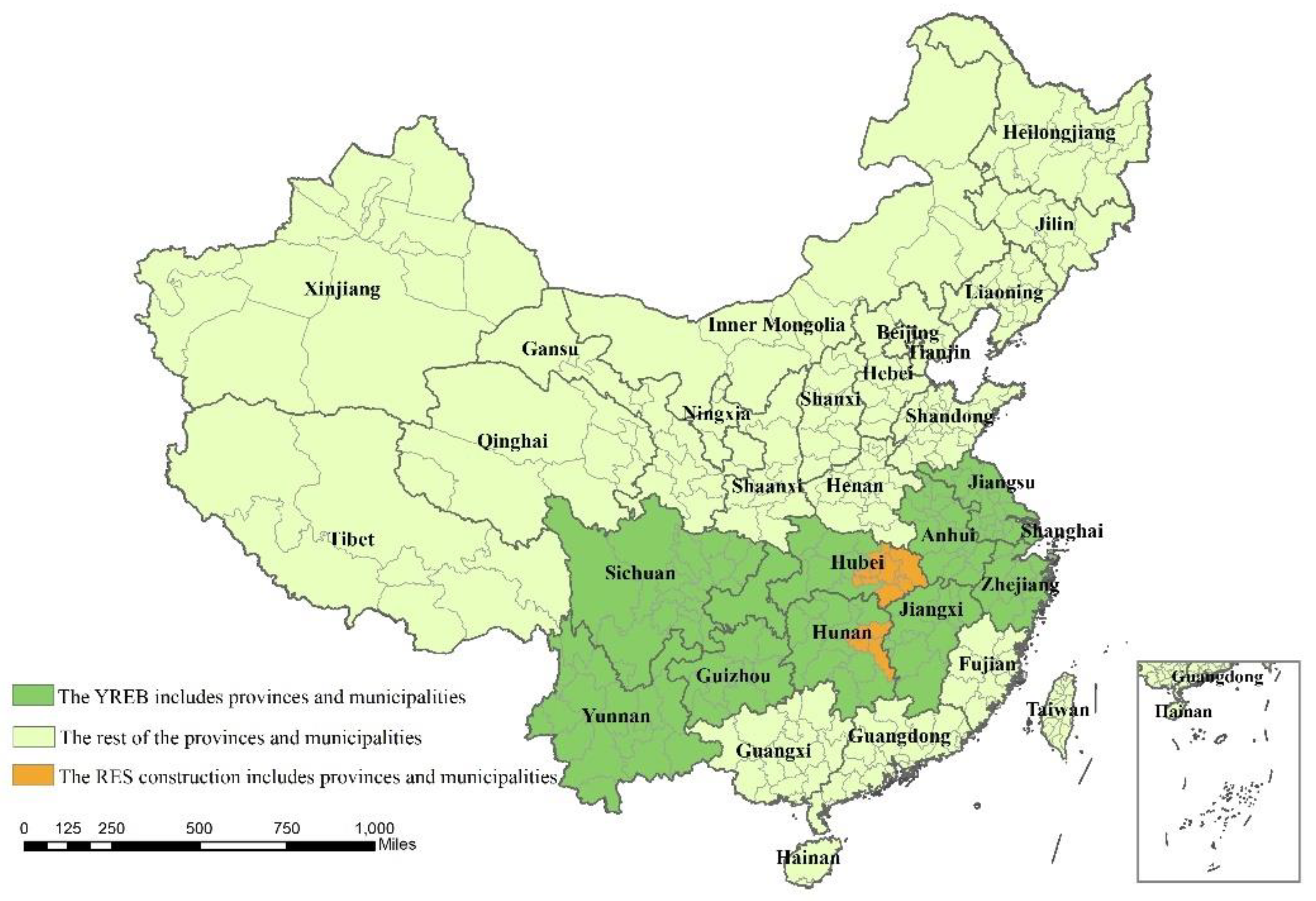
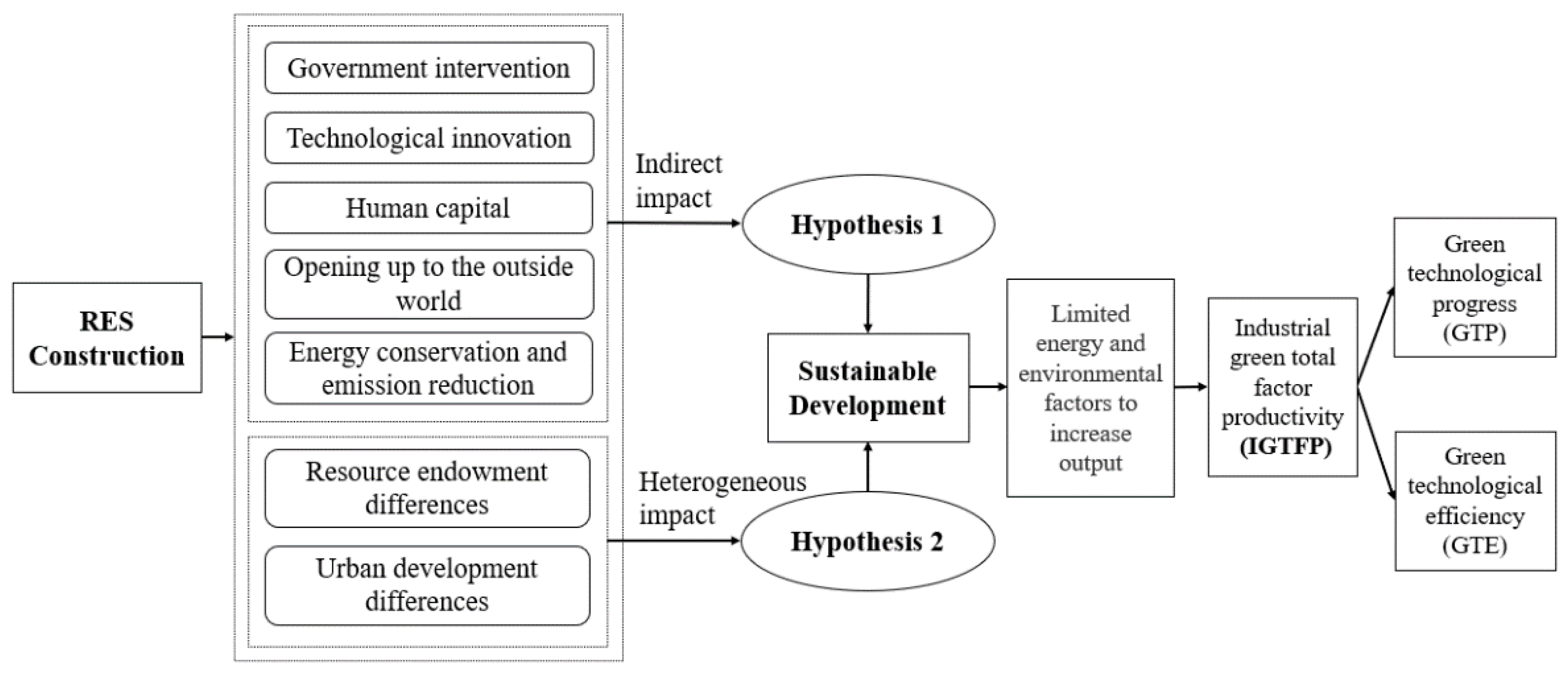
3.1. Possible Impact Mechanism of RES Construction
- (1)
- Effects of government intervention
- (2)
- Effects of technological innovation
- (3)
- Effects of human capital
- (4)
- Effects of opening up to the outside world
- (5)
- Effects of energy saving and emissions reduction
3.2. Impact of Heterogeneity on Effects of RES Policies
4. Research Design
4.1. Model Design
4.1.1. SBM-GML Index
- (1)
- Global directional SBM
- (2)
- GML index
4.1.2. Difference-in-Differences (DID) Method
4.1.3. Propensity Score Matching (PSM) Method
4.1.4. Mediating Effect Model
4.1.5. Triple Difference (DDD) Method
4.2. Variables and Measurements
4.2.1. Dependent Variable (Sustainable Development)
4.2.2. Independent Variables
4.2.3. Control Variables
4.3. Data Sources
5. Empirical Results
5.1. Evolution Characteristics of IGTFP
5.2. Propensity Score Matching and Balance Test
5.3. Baseline Regressive Results
5.3.1. Impact of RES Construction on Sustainable Development
5.3.2. Impact of RES Construction on GTP and GTE
5.4. Robustness Tests
5.4.1. Counterfactual Test
5.4.2. Effects of Environmental Policy in Other Regions
5.4.3. Changing the Sample Time Window
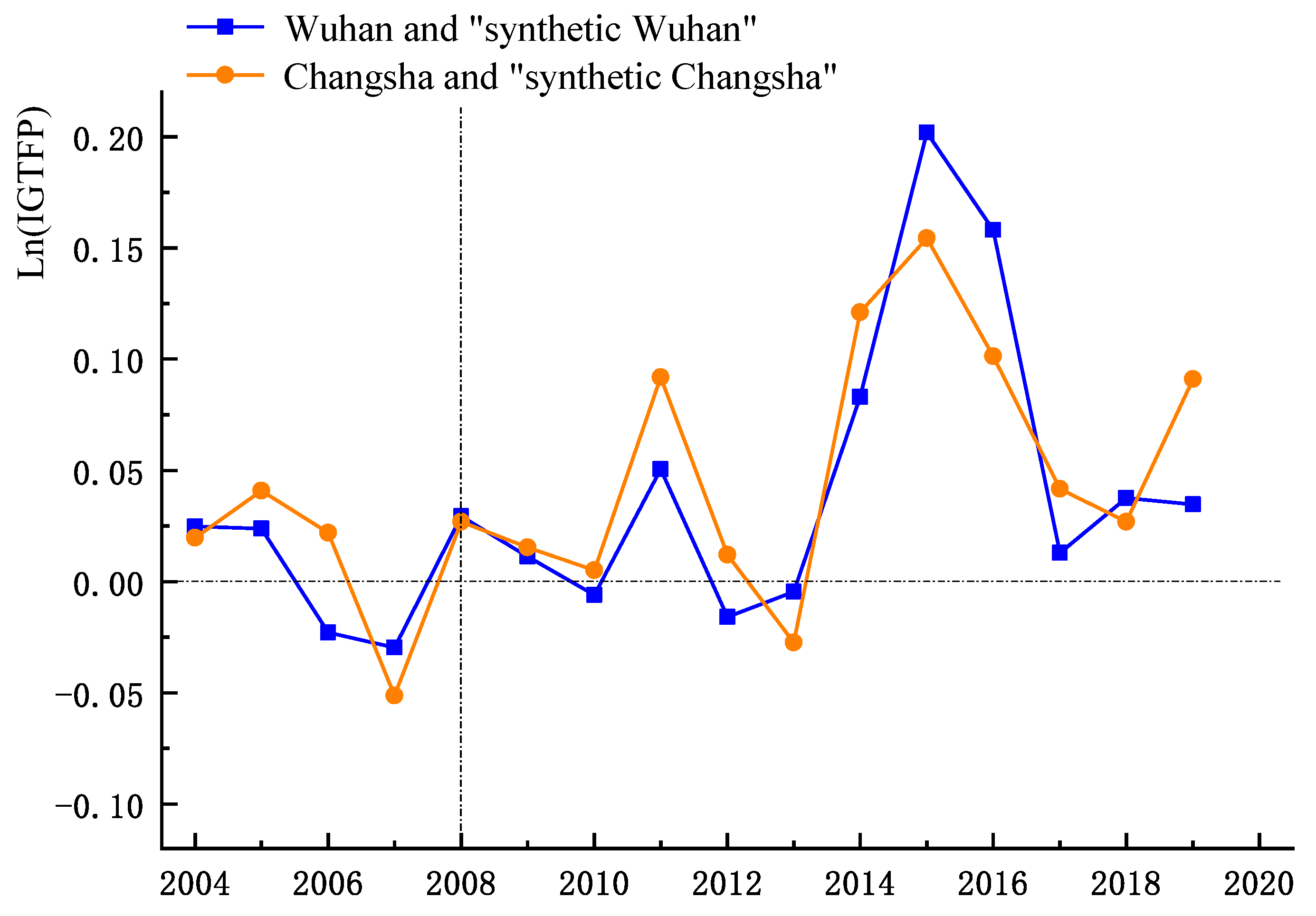
5.4.4. Synthetic Control Method
6. Further Analysis
6.1. Mediating Effect Test
6.2. Heterogeneous Analysis
6.2.1. Degree of Heterogeneity in Urban Resource Dependency
6.2.2. Degree of Heterogeneity of Urban Development
7. Discussion and Conclusions
7.1. Discussion
7.2. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Okereke, C.; Coke, A.; Geebreyesus, M.; Ginbo, T.; Wakeford, J.J.; Mulugetta, Y. Governing green industrialization in Africa, Assessing key parameters for a sustainable socio-technical transition in the context of Ethiopia. World Dev. 2019, 115, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. The Sustainable Development Goals. 2019. Available online: https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/sustainable-development-goals/ (accessed on 21 July 2022).
- Salvia, A.L.; Leal Filho, W.; Brandli, L.L.; Griebeler, J.S. Assessing research trends related to Sustainable Development Goals, local and global issues. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 208, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Yuan, H. Is China’s River Chief Policy effective? Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Tang, D.; Kong, H.; Boamah, V. Impact of Industrial Structure Upgrading on Green Total Factor Productivity in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Wang, L.; Yao, F. Industrial green total factor productivity based on an MML index in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 30673–30696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solow, R. Technical change and the aggregate production function. Rev. Econ. Stat. 1957, 39, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krugman, P. The myth of Asia’s miracle. Foreign Aff. 1994, 73, 62–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A. The tyranny of numbers, confronting the statistical realities of the east Asian growth experience. Q. J. Econ. 1995, 110, 641–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgenson, D.; Kevin, J.U.S. economic growth at the industry level. Am. Econ. Rev. 2000, 90, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinji, K.; Shunsuke, M. Environmental productivity in China. Econ. Bull. 2004, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Z.; Li, L.; Liu, J. The emissions reduction effect and technical progress effect of environmental regulation policy tools. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 149, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ji, J.; Zhang, Y. Nonlinear effects of environmental regulations on economic outcomes. Manag. Environ. Qual. 2018, 30, 368–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horbach, J.; Rennings, K. Environmental innovation and employment dynamics in different technology fields—An analysis based on the German Community Innovation Survey 2009. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 57, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Lee, C.C. How does green finance affect green total factor productivity? Evidence from China. Energy Econ. 2022, 107, 105863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Y. China’s agricultural green total factor productivity based on carbon emission, An analysis of evolution trend and influencing factors. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 278, 123692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K. A slack-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2001, 130, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuyama, H.; Weber, W.L. A directional slacks-based measure of technical inefficiency. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2009, 43, 274–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D. A global Malmquist-Luenberger productivity index. J. Product. Anal. 2009, 34, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Hu, R.; Mao, H.; Chen, S. How crop insurance influences agricultural green total factor productivity, Evidence from Chinese farmers. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 321, 128977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Y.; Duncan, A.A. Growth of Green Total Factor Productivity and Its Determinants of Cities in China, A Spatial Econometric Approach. Emerg. Mark. Financ. Trade 2018, 53, 2123–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picazo-Tadeo, A.J.; Beltrán-Esteve, M.; Gómez-Limón, J.A. Assessing eco-efficiency with directional distance functions. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2012, 220, 798–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wu, S. Effects of local and civil environmental regulation on green total factor productivity in China, A spatial Durbin econometric analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 153, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y. Research on the green total factor productivity and its influencing factors based on system GMM model. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2020, 11, 3497–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Li, X. Can Industrial Agglomeration Facilitate Green Development? Evidence From China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 745465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Luan, R.; Yang, Z.; Li, C. Does directed technological change get greener, Empirical evidence from Shangha’s industrial green development transformation. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 69, 758–770. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Quan, Y.; Li, X.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Song, W.; Lu, J.; Wu, G. Characterizing and analyzing the sustainability and potential of China’s cities over the past three decades. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Hong, C.; Zho, Y. Multi-Scale Evaluation of Suzhou City’s Sustainable Development Level Based on the Sustainable Development Goals Framework. Sustainability 2020, 12, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caiado, R.; Dias, R.; Mattos, L.; Quelhas, O.; Leal, W. Towards sustainable development through the perspective of eco-efficiency—A systematic literature review. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 890–904. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Bossink, B.; Chen, Q. Efficiency Evaluation of Regional Sustainable Innovation in China, A Slack-Based Measure (SBM) Model with Undesirable Outputs. Sustainability 2020, 12, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Wang, C.; Quan, Y.; Wu, G.; Zhao, J. Urban sustainable development efficiency towards the balance between nature and human well-being, Connotation, measurement, and assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 178, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Chen, W.; Cheng, J. Effects of urbanization on energy efficiency in China, New evidence from short run and long run efficiency models. Energy Policy 2021, 147, 111858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; He, Q.; Guo, T.; Zhu, J.; Yu, B. Measurement Method and Empirical Research on the Sustainable Development Capability of a Regional Industrial System Based on Ecological Niche Theory in China. Sustainability 2015, 6, 8485–8509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, H.; Xiong, S.; Li, K.; Jia, P. Electricity price and industrial green productivity, Does the “low-electricity price trap” exist? Energy 2020, 207, 118239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Q. Which factors stimulate industrial green total factor productivity growth rate in China? An industrial aspect. Greenh. Gases-Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funtowicz, S.; Ravetz, J. Science for the post-normal age. Futures 1993, 25, 739–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravetz, J.; Funtowicz, S. Post-Normal Science—An insight now maturing. Futures 1999, 31, 641–646. [Google Scholar]
- Funtowicz, S.; Ravetz, J. The worth of a songbird, Ecological economics as a post-normal science. Ecol. Econ. 1994, 10, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funtowicz, S.; Ravetz, J. A new scientific methodology for global environmental issues. In Ecological Economics: The Science and Management of Sustainability; Costanza, R., Ed.; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 137–152. [Google Scholar]
- Munda, G. Social multi-criteria evaluation, Methodological foundations and operational consequences. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2004, 158, 662–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F. The impact of China’s low-carbon city pilot policy on carbon emissions, based on the multi-period DID model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Yi, J.; Dai, S.; Xiong, Y. Can low-carbon city construction facilitate green growth? Evidence from China’s pilot low-carbon city initiative. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 231, 1158–1170. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Jiang, P.; Wang, D.; Wu, J. Can smart city construction facilitate green total factor productivity? A quasi-natural experiment based on China’s pilot smart city. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 69, 102809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Zhao, D. Knowledge accumulation, development potential and efficiency evaluation, an example using the Hainan free trade zone. J. Knowl. Manag. 2018, 23, 1673–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Green economy on small and Medium Enterprise’s sustainable development analysis-for example to Changsha-zhuzhou-xiangtan city cluster. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 291–294, 1537–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Wan, X.; Ma, H. Assessing green development efficiency of municipalities and provinces in China integrating models of super-efficiency DEA and Malmquist index. Sustainability 2015, 7, 4492–4510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, X.; Hu, D. Assessment of sustainable development, A case study of Wuhan as a pilot city in China. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 50, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T. Evaluation on ecological security and optimize on ecological system in key district of Changzhutan Urban Agglomeration. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Forum on Energy, Environment Science and Materials, Shenzhen, China, 25–26 September 2015; Volume 40, pp. 432–436. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, R. Performance of Carbon Emissions of “Two Oriented Society” Pilot Policy in Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan—Based on Difference in Difference Method. Soft Sci. 2016, 30, 51–55. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Xiao, B.; Song, L. Emission reduction and energy-intensity enhancement, The expected and unexpected consequences of China’s coal consumption constraint policy. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 271, 122691. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Xiang, B.; Li, W. The treatment effect of the Shanxi Comprehensive Reform Area policy on PM2.5 concentrations, A study based on a quasi-experiment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 29, 9065–9079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Wang, Z.; Liu, S. The policy outcomes of low-carbon city construction on urban green development, Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment conducted in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 66, 102699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Zhang, Z.; Fei, Y. How to Evaluate the Green and High-Quality Development Path? An FsQCA Approach on the China Pilot Free Trade Zone. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, R.; Guo, H.; Zheng, D.; Chang, R.; Na, S. Research on the Measurement, Evolution, and Driving Factors of Green Innovation Efficiency in Yangtze River Economic Belt, A Super-SBM and Spatial Durbin Model. Complexity 2020, 2020, 8094247. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, L.; Peng, F.; Zhu, Y.; Pan, A. Harmony in Diversity, Can the One Belt One Road Initiative Promote China’s Outward Foreign Direct Investment? Sustainability 2018, 10, 3264. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, C.; Luo, K.; Kong, Y.; Lin, H.; Ren, Y. Evaluating Performance and Elucidating the Mechanisms of Collaborative Development within the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 471. [Google Scholar]
- Macfarlane, R.; Wood, L.; Campbell, M. Healthy Toronto by Design, Promoting a healthier built environment. Can. J. Public Health-Rev. Can. Sante Publique 2015, 106, ES5–ES8. [Google Scholar]
- Tortajada, C.; Castelan, E. Water management for a megacity, Mexico City Metropolitan Area. Ambio 2003, 32, 124–129. [Google Scholar]
- Nunez Collado, J.; Wang, H. Slum upgrading and climate change adaptation and mitigation: Lessons from Latin America. Cities 2020, 104, 102791. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Hu, S. How Does Technological Innovation Mediate the Relationship between Environmental Regulation and High-Quality Economic Development? Empirical Evidence from China. Sustainability 2020, 13, 2231. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, C.; Huang, J.; Wang, M. The sustainability of China’s metal industries, features, challenges and future focuses. Resour. Policy 2019, 60, 215–224. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, G. Is knowledge spillover from human capital investment a catalyst for technological innovation? The curious case of fourth industrial revolution in BRIGS economies. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2021, 162, 120327. [Google Scholar]
- Yeo, Y.; Lee, J. Revitalizing the race between technology and education, Investigating the growth strategy for the knowledge-based economy based on a CGE analysis. Technol. Soc. 2020, 62, 101295. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Q. The influence of foreign direct investment and trade opening on green total factor productivity in the equipment manufacturing industry. Appl. Econ. 2021, 53, 6641–6654. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, B.; Gao, J.; Pan, L.; Chen, Y. Research on the Impact Factors of Green Economy of China-From the Perspective of System and Foreign Direct Investment. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8741. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Liao, W. Resource-Exhausted City Transition to continue industrial development. China Econ. Rev. 2021, 67, 101623. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.; Wang, D.; Meng, P.; Yang, J.; Pang, M.; Wang, L. Research on Resource Curse Effect of Resource-Dependent Cities, Case Study of Qingyang, Jinchang and Baiyin in China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 91. [Google Scholar]
- Song, W.; Ye, C.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, W. Do China’s Urban-Environmental Quality and Economic Growth Conform to the Environmental Kuznets Curve? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 18, 13420. [Google Scholar]
- Song, M.; Li, H. Total factor productivity and the factors of green industry in Shanxi Province, China. Growth Chang. 2019, 51, 488–504. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Li, Y. Green development of China’s Pan-Pearl River Delta mega-urban agglomeration. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15717. [Google Scholar]
- Abadie, A.; Diamond, A.; Hainmueller, J. Comparative Politics and the Synthetic Control Method. Am. J. Political Sci. 2015, 59, 495–510. [Google Scholar]
| Variables | Observations | Mean | Std. Dev. | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IGTFP | 1680 | 1.01 | 0.22 | 0.24 | 4.24 |
| GDP | 1680 | 3236.08 | 4592.97 | 130.42 | 38,155.32 |
| TI | 1680 | 69.44 | 109.38 | 0.01 | 1238.60 |
| IS | 1680 | 0.46 | 0.21 | 0.03 | 4.76 |
| HC | 1680 | 160,589.64 | 223,365.13 | 4481.00 | 907,426.00 |
| FDI | 1680 | 50.91 | 86.91 | 0.22 | 1090.41 |
| POP | 1680 | 753.24 | 2953.87 | 117.84 | 71,023.00 |
| UB | 1680 | 115.02 | 157.18 | 4.17 | 1066.54 |
| FAN | 1680 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.06 | 2.52 |
| Year | Total Sample | East | Central | West | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IGTFP (1) | GTP (2) | GTE (3) | IGTFP (4) | GTP (5) | GTE (6) | IGTFP (7) | GTP (8) | GTE (9) | IGTFP (10) | GTP (11) | GTE (12) | |
| 2005 | 1.018 | 1.010 | 1.007 | 0.760 | 0.634 | 1.200 | 0.747 | 0.963 | 0.701 | 1.366 | 1.273 | 1.073 |
| 2006 | 1.033 | 0.983 | 1.054 | 0.972 | 1.077 | 0.902 | 0.765 | 0.940 | 0.814 | 0.752 | 0.831 | 0.905 |
| 2007 | 0.977 | 0.940 | 1.038 | 1.122 | 1.060 | 1.059 | 1.102 | 1.000 | 1.050 | 1.458 | 1.308 | 1.114 |
| 2008 | 0.980 | 0.967 | 1.014 | 1.005 | 1.023 | 0.982 | 0.802 | 0.780 | 1.028 | 0.923 | 0.908 | 1.017 |
| 2009 | 0.944 | 0.812 | 1.154 | 0.870 | 0.898 | 0.970 | 1.590 | 1.142 | 1.392 | 0.822 | 0.893 | 0.921 |
| 2010 | 1.024 | 1.000 | 1.006 | 0.957 | 0.936 | 1.022 | 0.837 | 0.747 | 1.120 | 1.193 | 1.182 | 1.010 |
| 2011 | 0.984 | 1.048 | 0.935 | 0.991 | 0.786 | 1.260 | 0.969 | 1.028 | 0.942 | 0.851 | 0.880 | 0.967 |
| 2012 | 0.996 | 1.056 | 0.940 | 0.474 | 1.806 | 0.263 | 1.058 | 1.062 | 0.997 | 1.159 | 1.179 | 0.983 |
| 2013 | 0.941 | 0.990 | 0.954 | 1.006 | 1.015 | 0.991 | 1.041 | 1.114 | 0.935 | 0.987 | 0.963 | 1.025 |
| 2014 | 0.998 | 0.982 | 1.015 | 0.990 | 1.020 | 0.971 | 0.935 | 0.901 | 1.039 | 0.805 | 0.797 | 1.009 |
| 2015 | 0.938 | 1.051 | 0.887 | 0.967 | 0.992 | 0.975 | 1.298 | 1.229 | 1.056 | 1.558 | 1.548 | 1.007 |
| 2016 | 1.002 | 1.034 | 0.979 | 0.943 | 0.921 | 1.024 | 1.009 | 1.010 | 0.999 | 0.674 | 0.959 | 0.702 |
| 2017 | 0.937 | 0.987 | 0.946 | 1.101 | 1.105 | 0.996 | 0.960 | 0.961 | 1.000 | 0.807 | 1.023 | 0.789 |
| 2018 | 1.014 | 1.101 | 1.003 | 1.037 | 1.012 | 1.025 | 1.135 | 1.133 | 1.002 | 0.915 | 1.000 | 0.916 |
| 2019 | 1.015 | 1.045 | 0.980 | 1.051 | 0.998 | 1.053 | 1.067 | 1.248 | 0.856 | 0.834 | 0.945 | 0.883 |
| Mean | 0.987 | 1.000 | 0.994 | 0.933 | 0.995 | 0.938 | 1.001 | 1.009 | 0.993 | 0.975 | 1.028 | 0.949 |
| Variables | Logit Estimation | Type | Mean | Std. Dev. (%) | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | p Value | Experimental | Control | ||||
| TI | 0.005 *** (0.001) | 0.000 | Unmatched Matched | 114.392 115.081 | 62.485 115.13 | 44.2 −6.4 | 0.000 0.525 |
| FDI | −0.033 *** (0.098) | 0.053 | Unmatched Matched | 3.085 3.140 | 3.330 3.200 | −16.7 −7.5 | 0.001 0.276 |
| IS | 1.257 ** (0.535) | 0.019 | Unmatched Matched | 0.490 0.492 | 0.457 0.500 | 19.5 −2.7 | 0.145 0.478 |
| HC | 0.265 ** (0.139) | 0.057 | Unmatched Matched | 10.895 10.881 | 11.159 10.951 | −20.9 8.5 | 0.064 0.346 |
| FAN | 4.634 *** (0.729) | 0.000 | Unmatched Matched | 0.304 0.263 | 0.165 0.258 | 49.9 1.6 | 0.000 0.895 |
| POP | 0.209 (0.224) | 0.352 | Unmatched Matched | 6.292 6.291 | 6.209 6.332 | 15.8 −6.8 | 0.027 0.198 |
| UB | 0.341 *** (0.098) | 0.056 | Unmatched Matched | 3.887 3.871 | 4.185 3.967 | −30.0 −9.5 | 0.011 0.208 |
| GDP | 0.115 * (0.202) | 0.045 | Unmatched Matched | 7.309 7.289 | 7.452 7.291 | −12.9 0.9 | 0.044 0.245 |
| Constant | 0.082 *** (1.536) | 0.009 | |||||
| R2 | 0.157 | ||||||
| Variables | DID (1) | PSM-DID (2) | PSM-DID (Total) (3) | PSM-DID (Central) (4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.027 * (0.025) | 0.029 * (0.038) | 0.040 ** (0.047) | 0.044 * (0.052) | |
| TI | 0.013 (0.000) | 0.039 ** (0.001) | 0.083 * (0.000) | |
| IS | −0.012 (0.041) | −0.048 (0.060) | −0.031 (0.106) | |
| FDI | 0.108 ** (0.007) | 0.161 ** (0.015) | 0.203 ** (0.015) | |
| HC | −0.021 (0.009) | 0.051 * (0.023) | 0.074 * (0.021) | |
| POP | −0.088 (0.016) | 0.091 (0.038) | 0.270 * (0.038) | |
| FAN | −0.014 (0.051) | −0.025 ** (0.073) | −0.051 * (0.075) | |
| UB | 0.096 (0.012) | 0.015 (0.035) | 0.027 (0.034) | |
| GDP | 0.116 (0.014) | 0.117 (0.039) | 0.158 (0.025) | |
| Constant | 1.278 *** (0.107) | 1.032 *** (0.027) | 1.297 *** (0.240) | 1.707 *** (0.255) |
| City and Year FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| R2 | 0.018 | 0.024 | 0.031 | 0.053 |
| N | 1680 | 1360 | 1360 | 608 |
| Variables | Total Sample | Central Region | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) GTE | (2) GTP | (3) GTE | (4) GTP | |
| −0.008 * (0.005) | 0.023 * (0.015) | −0.005 * (0.012) | 0.010 * (0.012) | |
| Control variables | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Constant | 1.261 *** (0.264) | 1.052 *** (0.080) | 0.817 *** (0.093) | 1.900 *** (0.281) |
| City and Year FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| R2 | 0.033 | 0.044 | 0.083 | 0.064 |
| N | 1360 | 1360 | 608 | 608 |
| Variable | Treatment Year | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (1) 2009 | (2) 2010 | (3) 2006 | |
| −0.075 (0.046) | −0.106 (0.051) | 0.062 (0.037) | |
| Constant | 1.191 *** (0.086) | 1.237 *** (0.097) | 1.152 *** (0.069) |
| Control variables | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| City and Year FE | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| R2 | 0.026 | 0.037 | 0.021 |
| N | 1680 | 1680 | 1680 |
| Variables | Two Control Zones Policy (1) | Low-Carbon City Pilot Policy (2) | Emission-Trading System (3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.041 ** (0.023) | 0.040 ** (0.028) | 0.039 ** (0.022) | |
| Constant | 1.110 *** (0.067) | 1.333 *** (0.188) | 1.252 *** (0.154) |
| Control Variables | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| City and Year FE | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| R2 | 0.060 | 0.074 | 0.068 |
| N | 1680 | 1680 | 1680 |
| Variables | 2004 to 2012 | 2004 to 2014 | 2004 to 2016 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.132 * (0.030) | 0.090 ** (0.071) | 0.086 ** (0.050) | |
| Constant | 1.128 *** (0.052) | 1.291 *** (0.123) | 1.231 *** (0.093) |
| Control Variables | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| City and Year FE | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| R2 | 0.051 | 0.043 | 0.036 |
| N | 945 | 1155 | 1365 |
| Variables | TI (1) | FAN (2) | FDI (3) | HC (4) | ES (5) | PM (6) | IGTFP (7) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.175 *** (10.016) | 0.267 ** (0.019) | 0.020 * (0.128) | 0.061 ** (0.104) | −0.110 *** (0.072) | −0.098 *** (0.011) | 0.031 * (0.026) | |
| TI | 0.013 *** (4.945) | ||||||
| FAN | −0.002 ** (0.028) | ||||||
| FDI | 0.082 (0.192) | ||||||
| HC | 0.004 * (0.156) | ||||||
| ES | 0.010 *** (0.107) | ||||||
| PM | 0.101 *** (0.017) | ||||||
| Constant | 4.619 *** (4.664) | 0.126 *** (0.077) | 2.556 *** (0.521) | 3.168 *** (0.424) | 0.363 *** (0.291) | 0.967 *** (0.045) | 1.193 *** (0.092) |
| Control variables | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| City and Year FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| R2 | 0.320 | 0.086 | 0.189 | 0.475 | 0.590 | 0.544 | 0.683 |
| N | 1680 | 1680 | 1680 | 1680 | 1680 | 1680 | 1680 |
| Variables | Resource-Exhausted Cities (1) | First-Tier Cities (2) | Second-Tier Cities (3) | Third-Tier Cities (4) | Below Third-Tier Cities (5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −0.029 ** (0.079) | |||||
| 0.053 ** (0.034) | |||||
| 0.044 ** (0.024) | |||||
| −0.036 (0.020) | |||||
| −0.018 (0.023) | |||||
| RD | 0.065 (0.001) | 0.041 (0.001) | 0.061 (0.001) | 0.035 (0.001) | 0.041 (0.001) |
| FAN | −0.190 (0.785) | −0.031 (0.052) | −0.002 (0.049) | −0.008 (0.049) | −0.003 (0.049) |
| FDI | 0.260 (0.023) | 0.092 ** (0.008) | 0.107 ** (0.007) | 0.115 *** (0.008) | 0.102 ** (0.008) |
| HC | −0.075 (0.026) | 0.030 (0.009) | 0.023 (0.009) | 0.027 (0.009) | 0.026 (0.009) |
| IS | −0.415 (0.159) | −0.013 (0.052) | −0.011 (0.041) | −0.013 (0.041) | −0.008 (0.041) |
| EB | 0.581 (0.046) | 0.090 * (0.011) | 0.080 (0.012) | 0.087 (0.012) | 0.088 (0.012) |
| POP | 0.319 (0.029) | 0.086 (0.016) | 0.097 (0.016) | 0.090 * (0.016) | 0.086 (0.016) |
| GDP | 0.248 (0.040) | 0.125 * (0.014) | 0.138 * (0.014) | 0.120 (0.014) | 0.122 (0.014) |
| Constant | 0.641 *** (0.257) | 1.319 *** (0.109) | 1.325 *** (0.110) | 1.309 *** (0.110) | 1.302 *** (0.118) |
| City and Year FE | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| R2 | 0.267 | 0.021 | 0.021 | 0.018 | 0.017 |
| N | 1680 | 1680 | 1680 | 1680 | 1680 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Z.; Zhang, J. Impact of Resource-Saving and Environment-Friendly Society Construction on Sustainability. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11139. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141811139
Sun Z, Zhang J. Impact of Resource-Saving and Environment-Friendly Society Construction on Sustainability. Sustainability. 2022; 14(18):11139. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141811139
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Zhenglin, and Jinyue Zhang. 2022. "Impact of Resource-Saving and Environment-Friendly Society Construction on Sustainability" Sustainability 14, no. 18: 11139. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141811139
APA StyleSun, Z., & Zhang, J. (2022). Impact of Resource-Saving and Environment-Friendly Society Construction on Sustainability. Sustainability, 14(18), 11139. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141811139





