How New Urbanization Affects Tourism Eco-Efficiency in China: An Analysis Considering the Undesired Outputs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Tourism Eco-Efficiency
2.2. New Urbanization
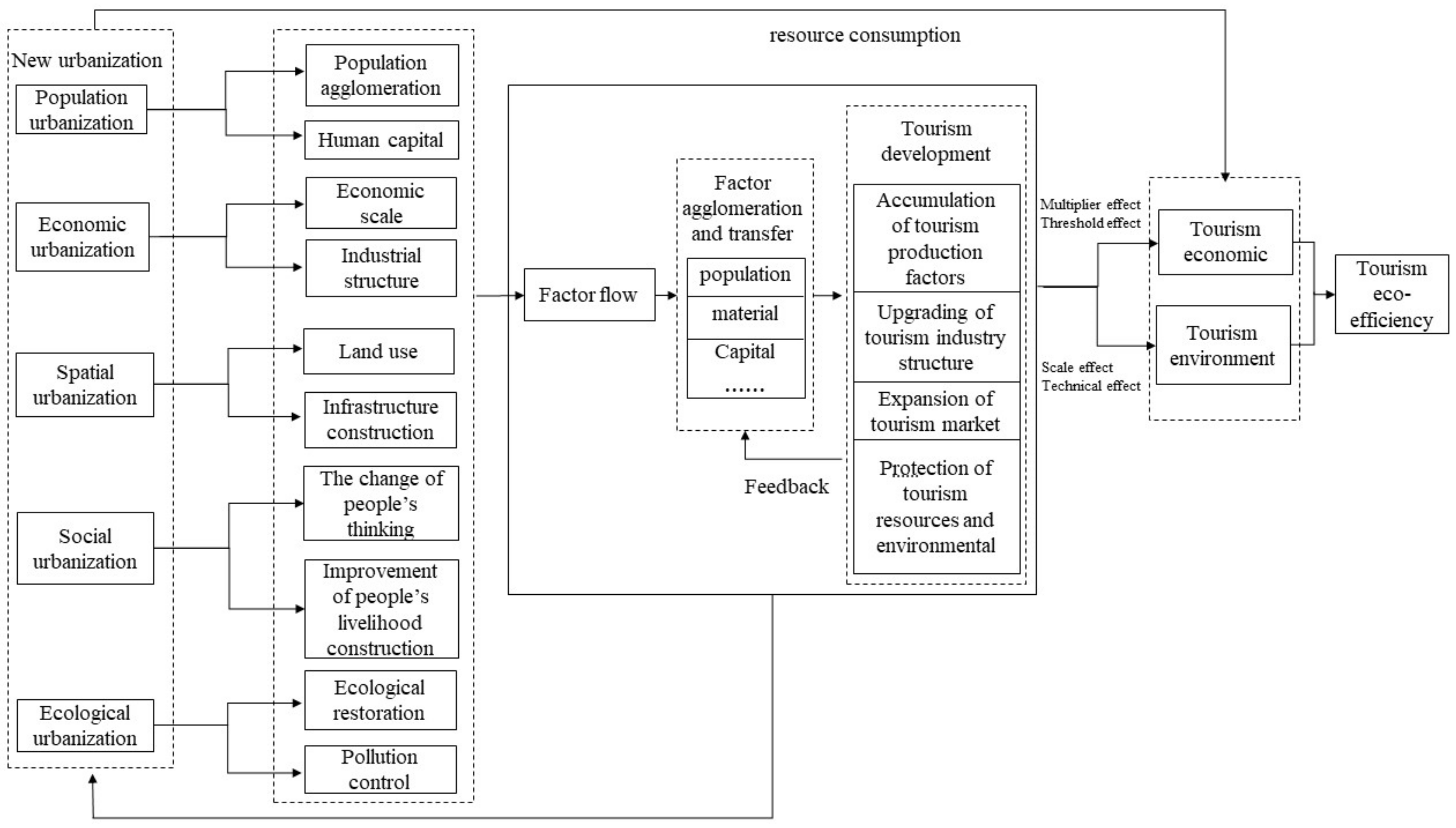
2.3. Impact Mechanism of New Urbanization on Tourism Eco-Efficiency
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Index System Construction
3.1.1. Index System of Tourism Eco-Efficiency
3.1.2. Index System of New Urbanization
3.2. Research Methods
3.2.1. Super-SBM Model
3.2.2. Entropy Method
| Normalization of indicators: | (7) | |
| Calculate the entropy of each indicator: | ||
| Calculate the entropy redundancy of each indicator: | ||
| Calculate the weight of each indicator: | ||
| Entropy: |
3.2.3. Panel Vector Autoregression Model
3.2.4. Ordinary Least Square Model
3.2.5. Geographically Weighted Regression Model
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Measurement of Tourism Eco-Efficiency
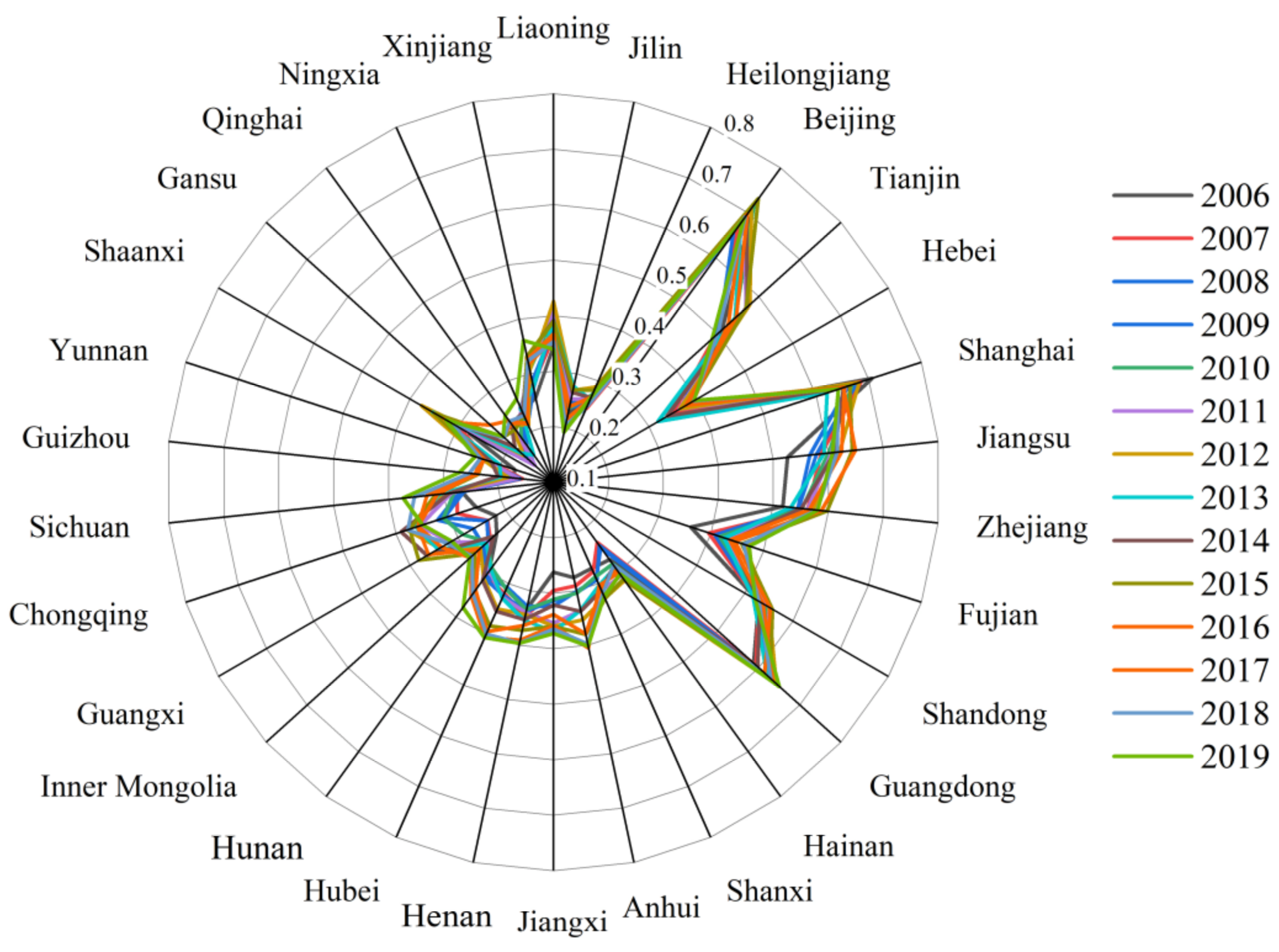
4.2. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Tourism Eco-Efficiency
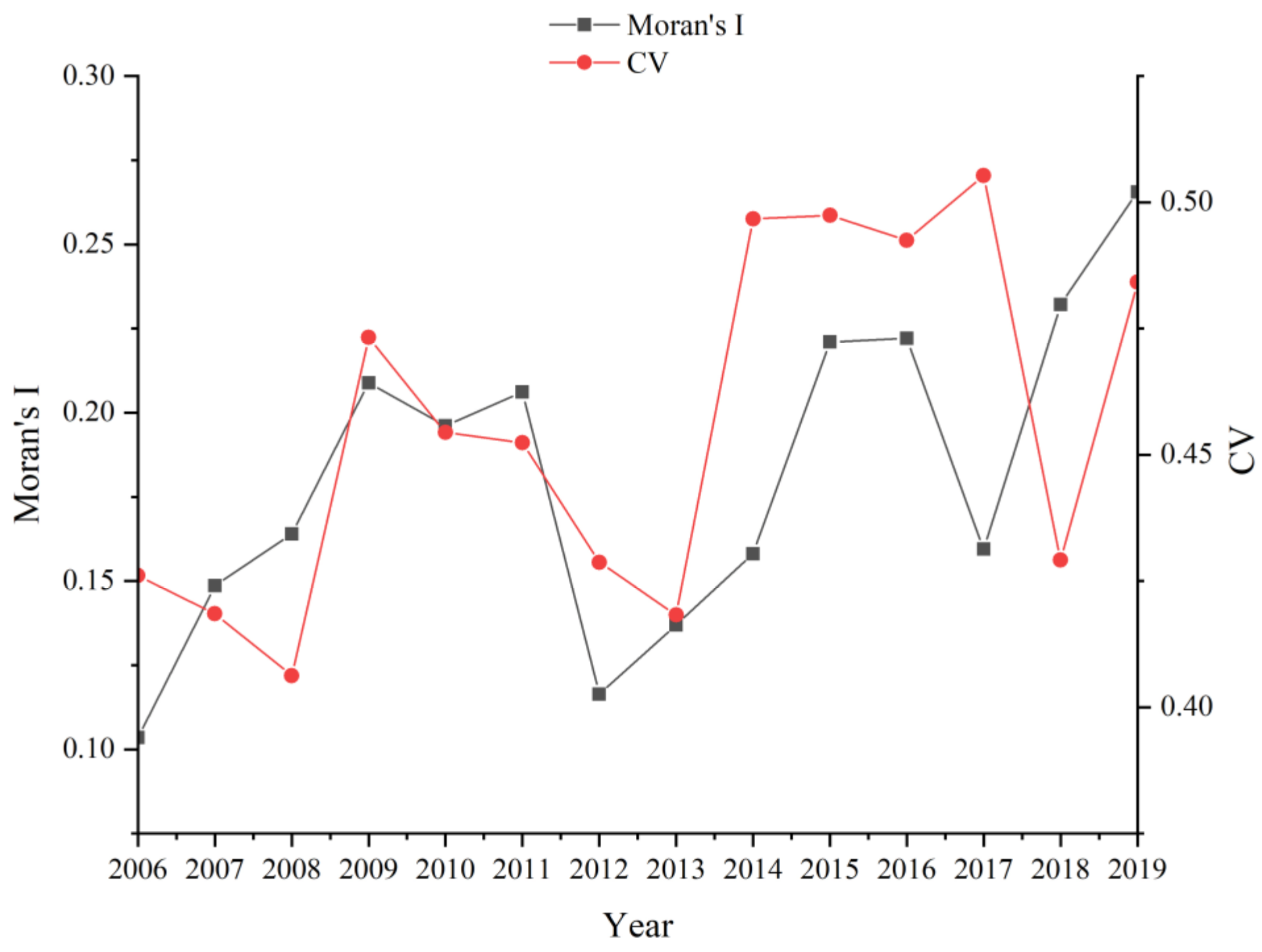
4.2.1. General Characteristics of Temporal and Spatial Distribution of Tourism Eco-Efficiency in China
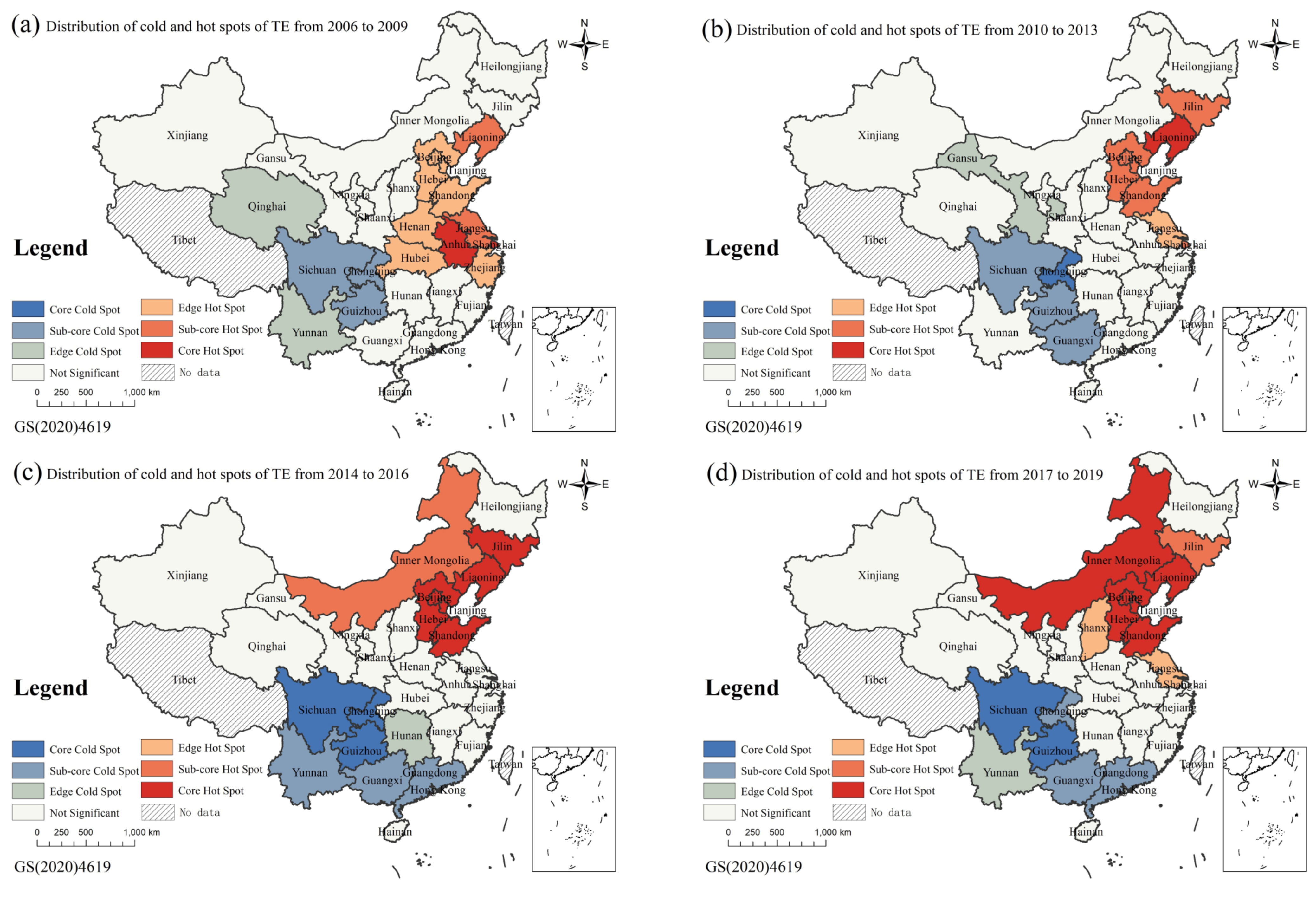
4.2.2. Local Spatial Evolution Characteristics of Tourism Eco-Efficiency
4.3. The Level of New Urbanization
4.4. The Interactive Response of Tourism Eco-Efficiency and New Urbanization
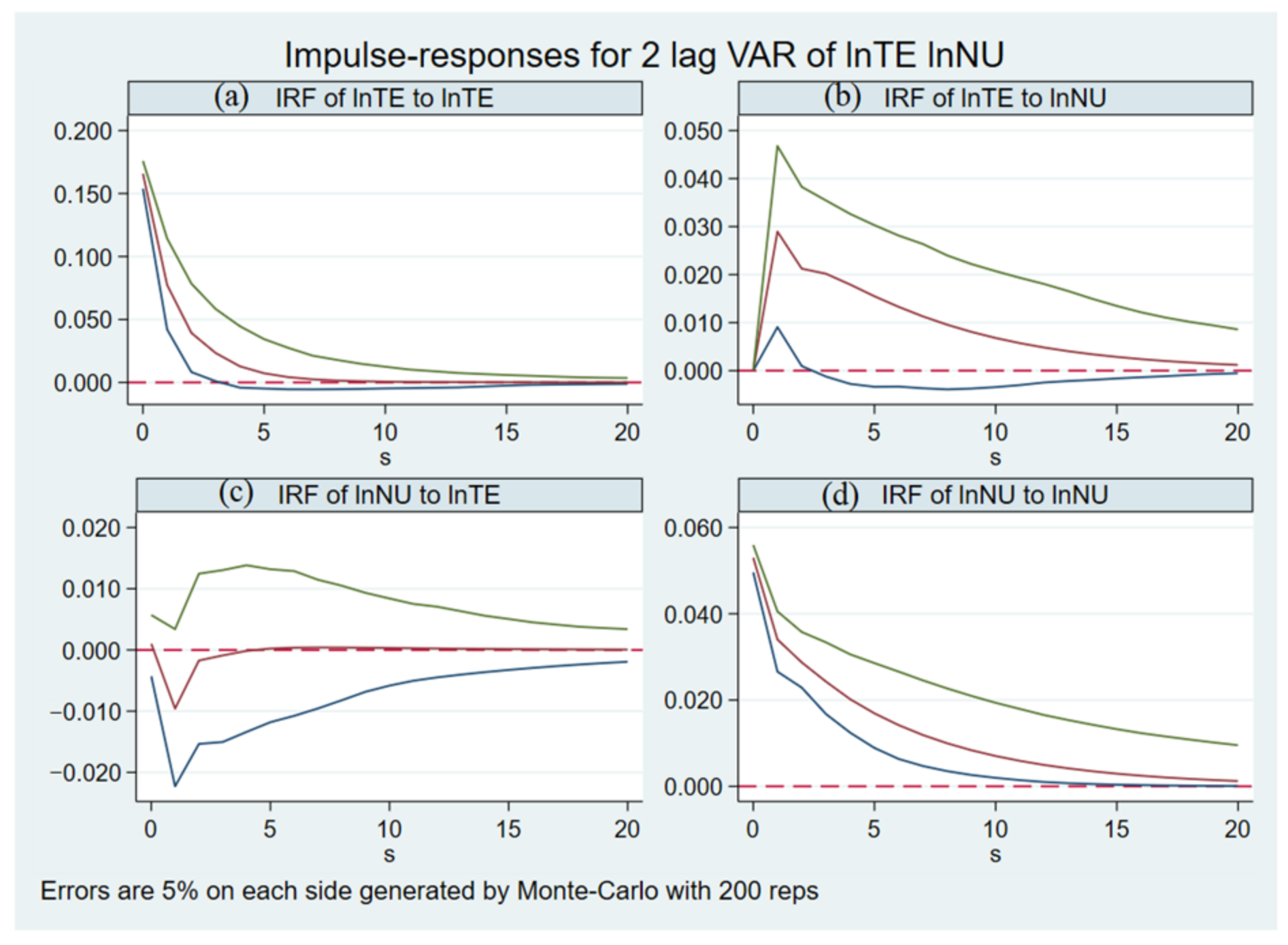
4.4.1. Impulse Response Analysis
4.4.2. Analysis of Variance Decomposition
4.5. The Impact of the Internal Structure of New Urbanization on Tourism Eco-Efficiency
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- (1)
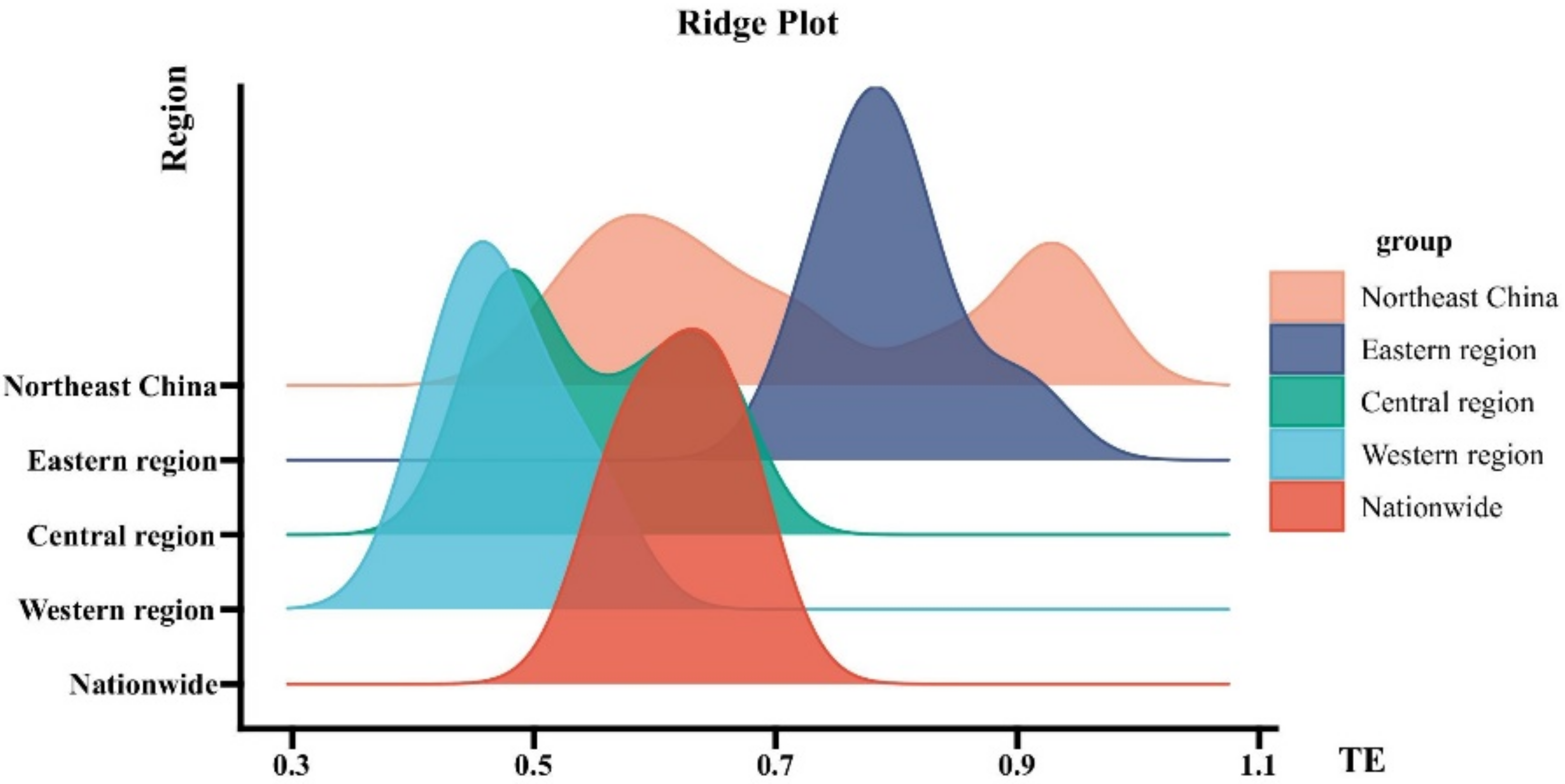
- China’s TE showed a slight fluctuation and upward trend. During the study period, the four major economic regions were in a state of fluctuation. Furthermore, the TE of the eastern and northeastern regions of China had a certain leading edge, but the northeast region fluctuated greatly, followed by the central region and finally the western region.
- (2)
- The agglomeration characteristics of China’s TE changed from high in the east and low in the west to low in the south and high in the north, but the balance point remained in Henan, indicating that it is in a dynamic equilibrium on the whole. The eco-efficiency of regional tourism showed a trend that the strong become weaker and the weak become stronger, and the regional differences first increased and then decreased, which is in line with the law of “unbalanced growth theory” and the goal of coordinated regional development in China.
- (3)
- The impact of NU on TE was one-way, and the dynamic response of TE had obvious regional specificity, especially in the eastern region, because economic urbanization had a great impact on the improvement of TE.
- (4)
- From the national level and the eastern region, the response of TE was the largest in the first year after the disturbance of NU, and the impact was long term. Moreover, the contribution rate of NU to developed economic regions reached 35%.
- (5)
- Among the key influencing factors of the impact of NU on TE, urban registered unemployment rate, urban population density, and per capita road area had a negative impact on TE. The proportion of the total output value of secondary and tertiary industries in GDP, the popularization rate of water and gas, the area of park green space per capita, the harmless treatment rate of domestic waste, and the comprehensive utilization rate of industrial solid waste had a positive impact on TE. It was found that ecological factors are becoming more and more important.
7. Limitations and Recommendations for Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Newman, P. Green Urbanism and its Application to Singapore. Environ. Urban. ASIA 2010, 1, 149–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deilmann, C.; Lehmann, I.; Reißmann, D.; Hennersdorf, J. Data envelopment analysis of cities—Investigation of the ecological and economic efficiency of cities using a benchmarking concept from production management. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 67, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkis, J.; Cordeiro, J.J. Ecological modernization in the electrical utility industry: An application of a bads–goods DEA model of ecological and technical efficiency. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2011, 219, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lin, B. Ecological total-factor energy efficiency of China’s heavy and light industries: Which performs better? Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 72, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tittonell, P. Ecological intensification of agriculture—sustainable by nature. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2014, 8, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilli, G.; Tyllianakis, E.; Luisetti, T.; Ferrini, S.; Turner, R.K. Prospective tourist preferences for sustainable tourism development in Small Island Developing States. Tour. Manag. 2020, 82, 104178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Jia, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, C.; Zhang, S. Space–time evolution of the ecological security of regional urban tourism: The case of Hubei Province, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaobin, M.; Biao, S.; Guolin, H.; Xing, Z.; Li, L. Evaluation and spatial effects of tourism ecological security in the Yangtze River Delta. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 131, 108190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, M.; Alam, M.; Hafeez, M.H. Effect of tourism on environmental pollution: Further evidence from Malaysia, Singapore and Thailand. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 190, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonn, M.A.; Chang, H.; Cho, M. The environment and perceptions of wine consumers regarding quality, risk and value: Reputations of regional wines and restaurants. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2020, 45, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.; Bonn, M.A.; Li, J. Examining Risk-Reduction Behavior Toward Water Quality Among Restaurant Guests. Cornell Hosp. Q. 2020, 61, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, L. Ecological efficiency management of tourism scenic spots based on carbon footprint analysis. Int. J. Low-Carbon Technol. 2020, 15, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.M.; Amelung, B.; Cohen, S.; Eijgelaar, E.; Gössling, S.; Higham, J.; Leemans, R.; Peeters, P.; Ram, Y.; Scott, D. On climate change skepticism and denial in tourism. J. Sustain. Tour. 2014, 23, 4–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikkemaat, B.; Peters, M.; Bichler, B.F. Innovation research in tourism: Research streams and actions for the future. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2019, 41, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmeen, H.; Tan, Q.; Zameer, H.; Tan, J.; Nawaz, K. Exploring the impact of technological innovation, environmental regulations and urbanization on ecological efficiency of China in the context of COP21. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 274, 111210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Huang, C. How does urbanization affect carbon emission efficiency? Evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 272, 122828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, M.A.; Tapia, J.; Gallardo, C.; Núñez, P.; Varas-Belemmi, K. Loss of coastal ecosystem spatial connectivity and services by urbanization: Natural-to-urban integration for bay management. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 276, 111297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Shi, X.; Phillips, T.K.; Du, P.; Gao, W. The Coupling Coordinated Development of Urban Environment Towards Sustainable Urbanization: An Empirical Study of Shandong Peninsula, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Li, X.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Lu, S. Coupling and coordinated development of new urbanization and agro-ecological environment in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 776, 145837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, Z.; Ning, X.; Li, L. Gauging the impacts of urbanization on CO2 emissions from the construction industry: Evidence from China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 288, 112440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B. Ecological effects of new-type urbanization in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 135, 110239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brida, J.G.; Gómez, D.M.; Segarra, V. On the empirical relationship between tourism and economic growth. Tour. Manag. 2020, 81, 104131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaltegger, S.; Sturm, A. kologische Rationalitt (German/in English: Environmental rationality). Die Unternehm. 1990, 4, 117–131. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, M.; Sun, M.; Li, J. Impact of environmental regulation policy on ecological efficiency in four major urban agglomerations in eastern China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 130, 108002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Zhang, J.; Lu, L.; Tang, G.; Yan, B.; Xiao, X.; Han, Y. Eco-efficiency and its determinants at a tourism destination: A case study of Huangshan National Park, China. Tour. Manag. 2016, 60, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gössling, S.; Peeters, P.; Ceron, J.-P.; Dubois, G.; Patterson, T.; Richardson, R.B. The eco-efficiency of tourism. Ecol. Econ. 2005, 54, 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Ji, X. Spatial-temporal differences and evolution of eco-efficiency in China’s forest park. Urban For. Urban Green. 2020, 57, 126894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Li, P.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, Y. GHG Emission-Based Eco-Efficiency Study on Tourism Itinerary Products in Shangri-La, Yunnan Province, China. Curr. Issues Tour. 2008, 11, 604–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brida, J.G.; Deidda, M.; Pulina, M. Tourism and transport systems in mountain environments: Analysis of the economic efficiency of cableways in South Tyrol. J. Transp. Geogr. 2014, 36, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepal, R.; al Irsyad, M.I.; Nepal, S.K. Tourist arrivals, energy consumption and pollutant emissions in a developing economy–implications for sustainable tourism. Tour. Manag. 2018, 72, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Fu, Z. Tourism eco-efficiency of Chinese coastal cities—Analysis based on the DEA-Tobit model. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2017, 148, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, J.; Yuan, W.; Dai, J.; Tan, T.; He, L. Eco-efficiency, eco-productivity and tourism growth in China: A non-convex metafrontier DEA-based decomposition model. J. Sustain. Tour. 2020, 28, 663–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C. Dictionnaire de Démographie; Blackwell: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, H.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, K. Evolutionary overview of urban expansion based on bibliometric analysis in Web of Science from 1990 to 2019. Habitat Int. 2019, 95, 102100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, F.; Wang, W.; Xiao, R. Effects of rapid urbanization on ecological functional vulnerability of the land system in Wuhan, China: A flow and stock perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 248, 119284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, Q. Analysis and forecasts of investment scale and structure in upstream sector for oil companies based on system dynamics. Resour. Sci. 2011, 26, 1323–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Tian, H.; Chen, G.; Chappelka, A.; Xu, X.; Ren, W.; Hui, D.; Liu, M.; Lu, C.; Pan, S.; et al. Impacts of urbanization on carbon balance in terrestrial ecosystems of the Southern United States. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 164, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Deng, X.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z. Exploring the relationship between urbanization and urban eco-efficiency: Evidence from prefecture-level cities in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 195, 1487–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Cui, Z.; Hu, C. Does the New Urbanization Influence Air Quality in China? Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Liu, C.; Xia, Y.; Da, B. Examining the coordination between urbanization and eco-environment using coupling and spatial analyses: A case study in China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 1163–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Zhuo, H.; Song, H.; Wang, J.; Ren, L. Examination of a coupling coordination relationship between urbanization and the eco-environment: A case study in Qingdao, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 23981–23993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wang, B. How does the new-type urbanisation affect CO2 emissions in China? An empirical analysis from the perspective of technological progress. Energy Econ. 2019, 80, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Xu, P.; Huang, Z. Impact of urbanization on ecological efficiency in China: An empirical analysis based on provincial panel data. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hou, G.; Huang, Z.; Zhong, Y. Spatial-Temporal Differences and Influencing Factors of Tourism Eco-Efficiency in China’s Three Major Urban Agglomerations Based on the Super-EBM Model. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, J.; He, L.; Liu, Y.; Shao, Y. Evaluation on development efficiency of low-carbon tourism economy: A case study of Hubei Province, China. Socio-Economic Plan. Sci. 2018, 66, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becken, S.; Patterson, M. Measuring National Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Tourism as a Key Step Towards Achieving Sustainable Tourism. J. Sustain. Tour. 2006, 14, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Shang, J.; Shi, C.; Liu, Z.; Bi, K. Decoupling indicators of CO2 emissions from the tourism industry in China: 1990–2012. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 46, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, J.; Dai, J.; Ma, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X. How to decouple tourism growth from carbon emissions? A case study of Chengdu, China. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2021, 39, 100849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Fang, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhu, F. Tourism Eco-Efficiency Measurement, Characteristics, and Its Influence Factors in China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, B. New urbanization path planning based on cluster calculation. Clust. Comput. 2018, 22, 6827–6835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, J. The effect of urbanization on environmental pollution in rapidly developing urban agglomerations. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 237, 117649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, J. Examining the influences of urbanization on carbon dioxide emissions in the Yangtze River Delta, China: Kuznets curve relationship. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 675, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neto, J.Q.F.; Walther, G.; Bloemhof, J.; van Nunen, J.; Spengler, T. A methodology for assessing eco-efficiency in logistics networks. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2009, 193, 670–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebolledo-Leiva, R.; Angulo-Meza, L.; Iriarte, A.; González-Araya, M.C.; Vásquez-Ibarra, L. Comparing two CF+DEA methods for assessing eco-efficiency from theoretical and practical points of view. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 659, 1266–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.-Y.; Pratt, S. The Economic, Carbon Emission, and Water Impacts of Chinese Visitors to Taiwan. J. Travel Res. 2014, 53, 733–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of super-efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2002, 143, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H.; Peng, H.; Zhang, Z.; Ke, Q.; Bu, S. Spatial-temporal patterns and characteristics of ecological function between 2009 and 2015 in China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 116, 106478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, I.; Zicchino, L. Financial development and dynamic investment behavior: Evidence from panel VAR. Q. Rev. Econ. Finance 2006, 46, 190–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Huang, Y. The correlation between HSR construction and economic development—Empirical study of Chinese cities. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2019, 126, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Geng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Kang, X.; Shi, X.; Zhang, J. Ecological trap in tourism-urbanization: Simulating the stagnation and restoration of urbanization from the perspective of government incentives. Ecol. Econ. 2021, 185, 107054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, C.-H. Evaluation and drive mechanism of tourism ecological security based on the DPSIR-DEA model. Tour. Manag. 2019, 75, 609–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanta, K.; Sharma, L.K. Assessing the impacts of urbanization on the thermal environment of Ranchi City (India) using geospatial technology. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2017, 8, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Alam, K. Clean energy, population density, urbanization and environmental pollution nexus: Evidence from Bangladesh. Renew. Energy 2021, 172, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Wang, F.; Sun, Q.; Wang, X.; Guo, S. Comprehensive evaluation and prediction of tourism ecological security in droughty area national parks—A case study of Qilian Mountain of Zhangye section, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 16816–16829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Wu, X.; Zheng, Q.; Lyu, N. Ecological security evaluations of the tourism industry in Ecological Conservation Development Areas: A case study of Beijing’s ECDA. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 197, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charara, N.; Cashman, A.; Bonnell, R.; Gehr, R. Water use efficiency in the hotel sector of Barbados. J. Sustain. Tour. 2011, 19, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, J.; Williams, P.; Haider, W. Moving towards more eco-efficient tourist transportation to a resort destination: The case of Whistler, British Columbia. Res. Transp. Econ. 2010, 26, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.; Williams, P. Tourism destination water management strategies: An eco-efficiency modelling approach. Leisure 2007, 31, 427–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitivattananon, V.; Srinonil, S. Enhancing coastal areas governance for sustainable tourism in the context of urbanization and climate change in eastern Thailand. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2019, 10, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Measurement Target | Indicator Type | Indicator Name | Primary | Main Data Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tourism eco-efficiency (TE) | Input indicators | Labor input | Number of people employed in tourism | China Tourism Statistical Yearbook, China Tourism Yearbook |
| Capital input | Tourism fixed asset investment | China Statistical Yearbook | ||
| Energy input | Total tourism energy consumption | China Statistical Yearbook, China Tertiary Industry Statistical Yearbook | ||
| Desirable output indicator | Total tourism economy | Total tourism revenue | China Tourism Statistical Yearbook China Tourism Yearbook, provincial Statistical Yearbook | |
| Undesirable output indicator | Tourism environmental pollution | Tourism CO2 emissions | China Tourism Statistical Yearbook China Tourism Yearbook, Tourism Sample Survey Data, China Traffic Statistical Yearbook, provincial Statistical Yearbook |
| Target Layer | Rule Layer | Index Layer | Attribute | Weight | Main Data Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comprehensive development level of new urbanization (NU) | Population urbanization | Proportion of urban population in total permanent population | + | 0.0231 | China Statistical Yearbook, China Tertiary Industry Statistical Yearbook, provincial Statistical Yearbook |
| Proportion of employed persons in tertiary industry | + | 0.0521 | |||
| Registered urban unemployment rate | − | 0.0607 | |||
| Economic urbanization | GDP per capita | + | 0.0748 | ||
| Proportion of total output value of secondary and tertiary industries in GDP | + | 0.0189 | |||
| Local fiscal revenue per capita | + | 0.1443 | |||
| Living expenditure of urban residents per capita | + | 0.1059 | |||
| Spatial urbanization | Urban population density | + | 0.0521 | ||
| Built-up urban area | + | 0.0620 | |||
| Road area per capita | + | 0.0251 | |||
| Social urbanization | Water penetration rate | + | 0.0473 | ||
| Gas penetration rate | + | 0.0241 | |||
| Beds in medical institutions | + | 0.0569 | |||
| Number of internet access ports | + | 0.0711 | |||
| Proportion of education expenditure in government expenditure | + | 0.0351 | |||
| Ecological urbanization | Afforestation coverage rate of built-up area | + | 0.0413 | ||
| Park green space area per capita | + | 0.0342 | |||
| Harmless treatment rate of household garbage | + | 0.0276 | |||
| Comprehensive utilization rate of industrial solid waste | + | 0.0432 |
| Region | 2006 | 2010 | 2014 | 2019 | Average | Region | 2006 | 2010 | 2014 | 2019 | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 1.0295 | 1.0708 | 1.1513 | 1.1945 | 1.1143 | Henan | 0.7517 | 0.5495 | 0.5154 | 0.4722 | 0.6036 |
| Tianjin | 1.3816 | 1.2432 | 1.1300 | 1.4880 | 1.2331 | Hubei | 0.4854 | 0.4558 | 0.4463 | 0.4519 | 0.4654 |
| Hebei | 0.5565 | 0.4605 | 0.4231 | 0.5051 | 0.4940 | Hunan | 0.4751 | 0.4558 | 0.4022 | 0.4786 | 0.4703 |
| Shanxi | 1.0318 | 0.4203 | 0.5657 | 1.1202 | 0.7487 | Guangdong | 1.0811 | 0.6351 | 0.7039 | 0.6605 | 0.7467 |
| Inner Mongolia | 0.4622 | 0.5637 | 1.1542 | 1.0301 | 0.8284 | Guangxi | 0.4711 | 0.3519 | 0.3469 | 0.4379 | 0.3988 |
| Liaoning | 0.4690 | 0.3971 | 0.3908 | 1.0829 | 0.6865 | Hainan | 0.4253 | 0.3112 | 0.2901 | 0.3697 | 0.3220 |
| Jilin | 0.6777 | 0.6255 | 1.0215 | 1.0021 | 0.8667 | Chongqing | 0.5284 | 0.3947 | 0.3982 | 0.5231 | 0.4361 |
| Heilongjiang | 0.6357 | 0.6361 | 0.5177 | 0.4138 | 0.6008 | Sichuan | 0.4831 | 0.4071 | 0.4348 | 0.4313 | 0.4369 |
| Shanghai | 1.0171 | 1.1467 | 1.1434 | 1.0902 | 1.1021 | Guizhou | 0.4833 | 0.5974 | 0.4745 | 0.4733 | 0.5429 |
| Jiangsu | 1.0977 | 1.1643 | 1.0458 | 1.0978 | 1.1077 | Yunnan | 0.4031 | 0.3251 | 0.3269 | 0.3289 | 0.3693 |
| Zhejiang | 0.6680 | 0.7890 | 0.5924 | 0.6509 | 0.6784 | Shaanxi | 0.4239 | 0.3666 | 0.3410 | 0.3807 | 0.3745 |
| Anhui | 0.5802 | 0.5310 | 0.4022 | 0.5838 | 0.5051 | Gansu | 0.5304 | 0.3881 | 0.3239 | 0.4181 | 0.4122 |
| Fujian | 1.1357 | 0.5835 | 0.4395 | 0.5375 | 0.6292 | Qinghai | 0.5400 | 0.4189 | 0.4701 | 0.2664 | 0.5601 |
| Jiangxi | 0.4346 | 0.4703 | 0.4225 | 0.5410 | 0.5048 | Ningxia | 0.3525 | 0.4570 | 0.4509 | 0.6340 | 0.4644 |
| Shandong | 0.5653 | 0.4922 | 0.5888 | 0.5094 | 0.5309 | Xinjiang | 0.3827 | 0.3700 | 0.3502 | 0.4823 | 0.3878 |
| Region | Provinces and Cities |
|---|---|
| Northeast China | Liaoning, Jilin, Heilongjiang |
| Eastern China | Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Fujian, Shandong, Guangdong, Hainan |
| Central China | Shanxi, Anhui, Jiangxi, Henan, Hubei, Hunan |
| Western China | Inner Mongolia, Guangxi, Chongqing, Sichuan, Guizhou, Yunnan, Shaanxi, Gansu, Qinghai, Ningxia, Xinjiang |
| Nationwide | Eastern Region | Central Region | Western Region | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chi-sq | p-Value | Chi-sq | p-Value | Chi-sq | p-Value | Chi-sq | p-Value | |
| Equation lnTE/Excluded lnNU | 6.3030 | 0.043 | 12.174 | 0.002 | 0.61011 | 0.435 | 2.9476 | 0.229 |
| Equation lnNU/Excluded lnTE | 3.5751 | 0.167 | 0.35124 | 0.839 | 0.08971 | 0.765 | 3.9981 | 0.136 |
| Nationwide | Eastern Region | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Period | lnTE | lnNU | lnTE | lnNU |
| 1 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| 2 | 97.6 | 2.4 | 90.1 | 9.9 |
| 3 | 96.5 | 3.5 | 83.3 | 16.7 |
| 4 | 95.4 | 4.6 | 78.1 | 21.9 |
| 5 | 94.7 | 5.3 | 74.3 | 25.7 |
| 10 | 92.9 | 7.1 | 66.7 | 33.3 |
| 15 | 92.6 | 7.4 | 65.3 | 34.7 |
| 20 | 92.6 | 7.4 | 65.0 | 35.0 |
| 25 | 92.6 | 7.4 | 64.9 | 35.1 |
| Dimension | 2006 | 2019 | Factors | 2006 | 2019 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | Coefficient | Coefficient | VIF | Coefficient | VIF | ||
| Population urbanization | 0.199565 * | 0.225851 * | Proportion of urban population in total permanent population | 0.1114 * | 76.2581 | 0.1227 * | 37.9070 |
| Proportion of employed persons in tertiary industry | 0.0424 * | 8.7832 | 0.0467 * | 7.5526 | |||
| Registered urban unemployment rate | 0.0956 * | 4.6955 | 0.1053 * | 2.3221 | |||
| Economic urbanization | 0.603064 * | 0.673458 * | GDP per capita | 0.1373 * | 76.2581 | 0.1512 * | 18.8918 |
| Proportion of total output value of secondary and tertiary industries in GDP | 0.0347 * | 7.8492 | 0.0382 * | 2.6713 | |||
| Local fiscal revenue per capita | 0.2647 * | 50.8541 | 0.2914 * | 25.4607 | |||
| Living expenditure of urban residents per capita | 0.1943 * | 21.9205 | 0.2140 * | 25.8037 | |||
| Spatial urbanization | 0.124309 * | 0.179521 * | Urban population density | 0.0956 * | 2.1698 | 0.1052 * | 1.9793 |
| Built-up urban area | 0.1138 * | 40.1680 | 0.1253 * | 19.5404 | |||
| Road area per capita | 0.0460 * | 8.16403 | 0.0507 * | 5.4727 | |||
| Social urbanization | 0.275655 * | 0.345117 * | Water penetration rate | 0.0869 * | 10.1859 | 0.0956 * | 4.7905 |
| Gas penetration rate | 0.0442 * | 13.1810 | 0.0487 * | 2.8137 | |||
| Beds in medical institutions | 0.1044 * | 20.3901 | 0.1150 * | 11.2501 | |||
| Number of internet access ports | 0.1304 * | 40.8299 | 0.1436 * | 22.1668 | |||
| Proportion of government’s education expenditure | 0.0644 * | 3.6143 | 0.0709 * | 9.9185 | |||
| Ecological urbanization | 0.197794 * | 0.154883 * | Afforestation coverage rate of built-up area | 0.0758 * | 7.6195 | 0.0835 * | 8.5107 |
| Park green space area per capita | 0.0628 * | 7.6864 | 0.0691 * | 3.8030 | |||
| Harmless treatment rate of household garbage | 0.0506 * | 2.8357 | 0.0557 * | 4.9206 | |||
| Comprehensive utilization rate of industrial solid waste | 0.0793 * | 8.7708 | 0.0874 * | 6.9126 | |||
| Key Factors | Northeast China | Eastern Region | Central Region | Western Region | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2006 | 2019 | 2006 | 2019 | 2006 | 2019 | 2006 | 2019 | |
| Registered urban unemployment rate | 0.4045 * | −0.0108 * | 0.5604 * | −0.0108 * | 0.6065 * | −0.0108 * | 0.7187 * | −0.0108 * |
| Proportion of total output value of secondary and tertiary industries in GDP | -- | 0.2883 * | -- | 0.2887 * | -- | 0.2888 * | -- | 0.2888 * |
| Urban population density | −0.0745 * | −0.0667 * | −0.1655 * | −0.0667 * | −0.1568* | −0.0667 * | −0.1061 * | −0.0668 * |
| Road area per capita | -- | −0.4044 * | -- | −0.4042 * | -- | −0.4042 * | -- | −0.4042 * |
| Water penetration rate | -- | 0.4800 * | -- | 0.4799 * | -- | 0.4798 * | -- | 0.4798 * |
| Gas penetration rate | -- | 0.382587 * | -- | 0.382845 * | -- | 0.3829 * | -- | 0.3830 * |
| Proportion of government’s education expenditure | −0.1582 * | -- | −0.2321 * | -- | −0.2080 * | −0.0939 * | -- | |
| Park green space area per capita | -- | 0.4332 * | -- | 0.4331 * | 0.4331 * | -- | 0.4330 * | |
| Harmless treatment rate of household garbage | 0.5737 * | 0.2542 * | 0.4856 * | 0.2542 * | 0.4414 * | 0.2542 * | 0.2819 * | 0.2543 * |
| Comprehensive utilization rate of industrial solid waste | -- | 0.0056 * | -- | 0.0055 * | -- | 0.0054 * | -- | 0.0053 * |
| Average | 0.1864 * | 0.1716 * | 0.1621 * | 0.1717 * | 0.1708 * | 0.1717 * | 0.2001 * | 0.1717 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, F.; Yang, X.; Wu, J.; Ma, D.; Xiao, Y.; Gong, G.; Zhang, J. How New Urbanization Affects Tourism Eco-Efficiency in China: An Analysis Considering the Undesired Outputs. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10820. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710820
Zhang F, Yang X, Wu J, Ma D, Xiao Y, Gong G, Zhang J. How New Urbanization Affects Tourism Eco-Efficiency in China: An Analysis Considering the Undesired Outputs. Sustainability. 2022; 14(17):10820. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710820
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Fengtai, Xingyu Yang, Jianfeng Wu, Dalai Ma, Yuedong Xiao, Guofang Gong, and Junyi Zhang. 2022. "How New Urbanization Affects Tourism Eco-Efficiency in China: An Analysis Considering the Undesired Outputs" Sustainability 14, no. 17: 10820. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710820
APA StyleZhang, F., Yang, X., Wu, J., Ma, D., Xiao, Y., Gong, G., & Zhang, J. (2022). How New Urbanization Affects Tourism Eco-Efficiency in China: An Analysis Considering the Undesired Outputs. Sustainability, 14(17), 10820. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710820








