Evaluation and Countermeasures of High-Quality Development of China’s Marine Economy Based on PSO-SVM
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data Sources
2.1. Evaluation Index System of Marine Economic Growth Quality
2.2. Methods
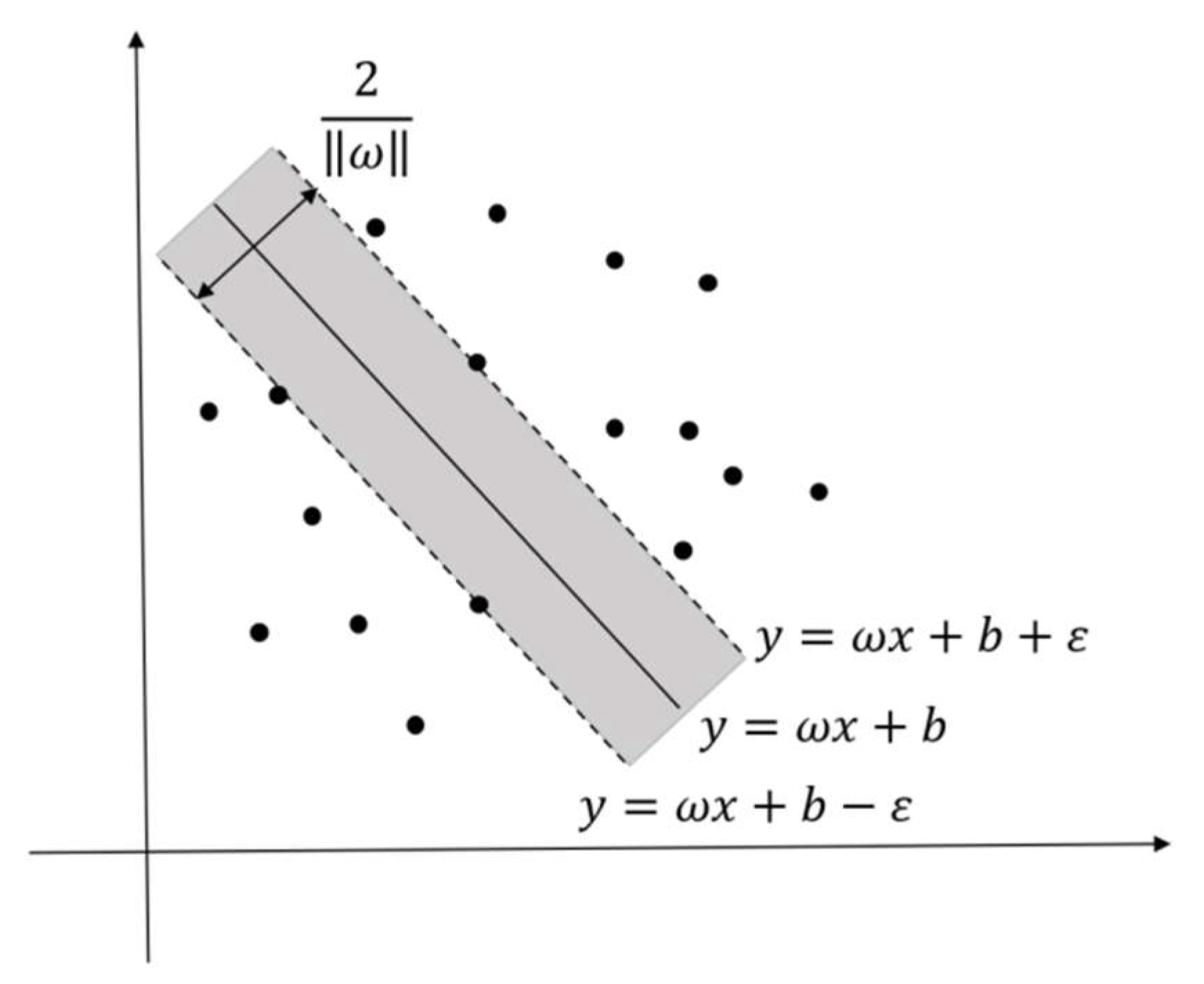
2.2.1. PSO Algorithm and SVM Model
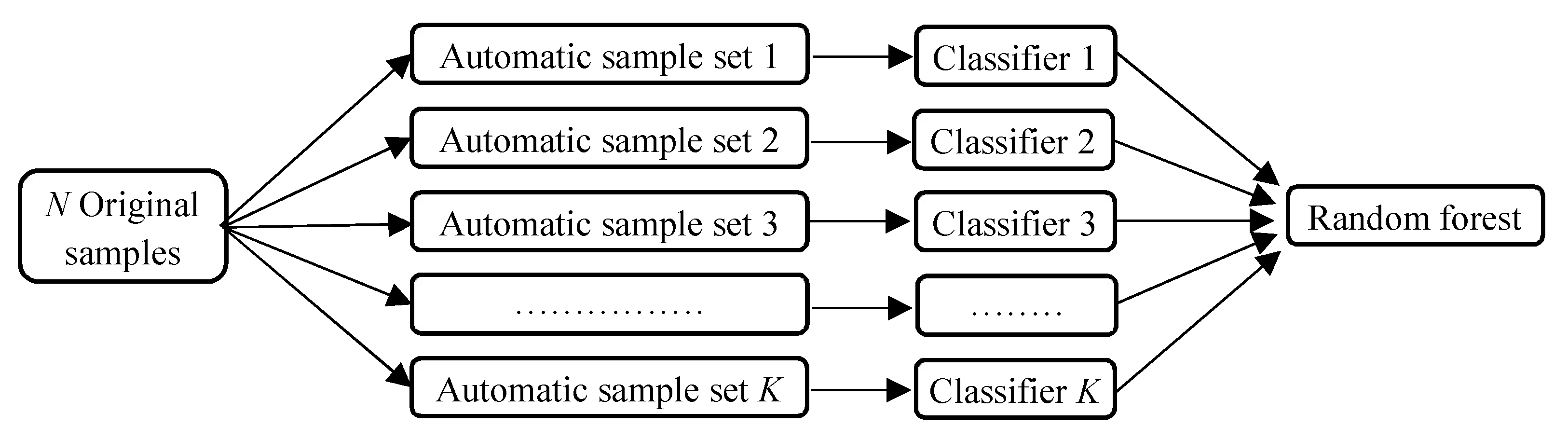
2.2.2. Random Forest Model
3. Analysis of the Results
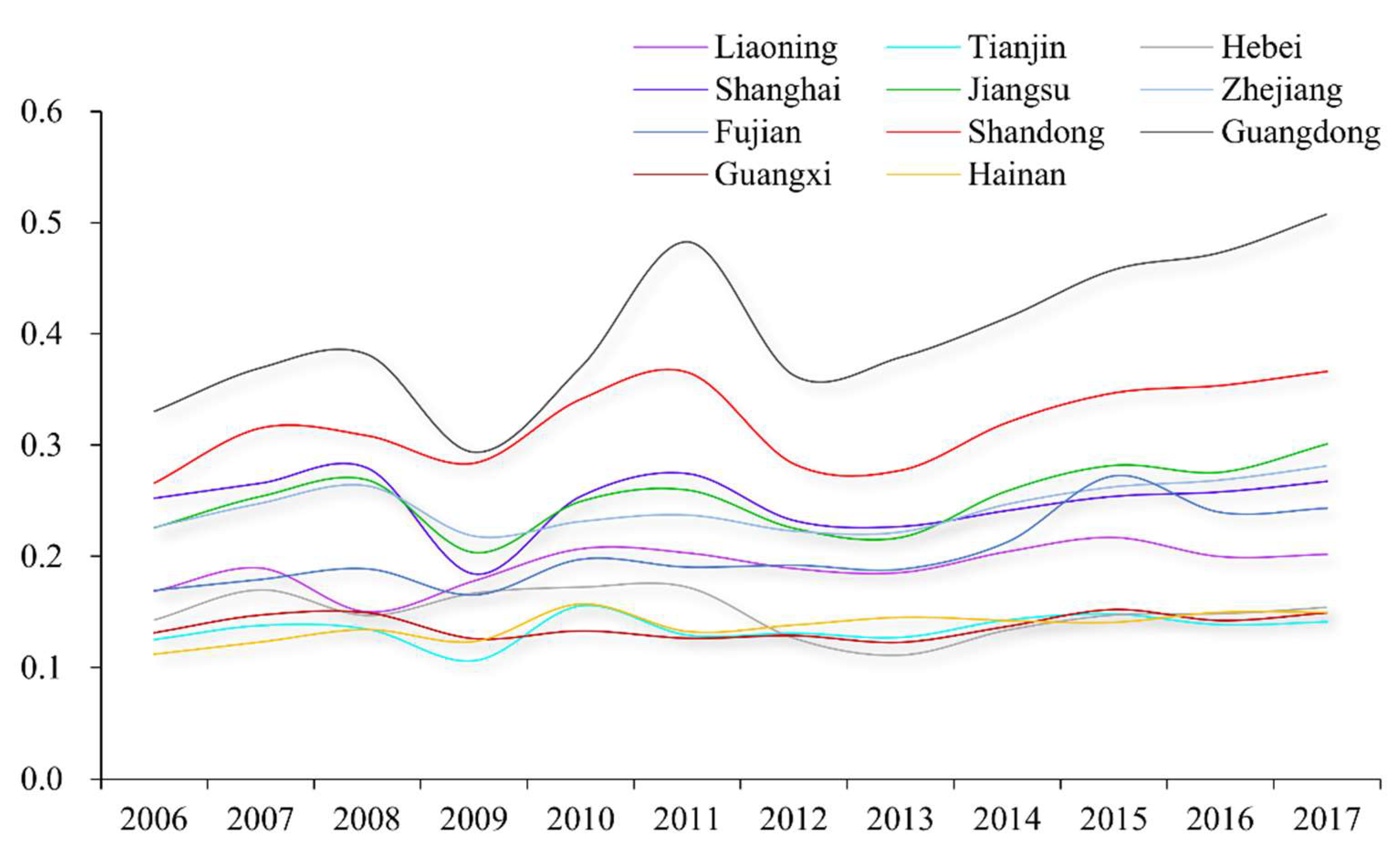
3.1. High-Quality Development Level of Marine Economy
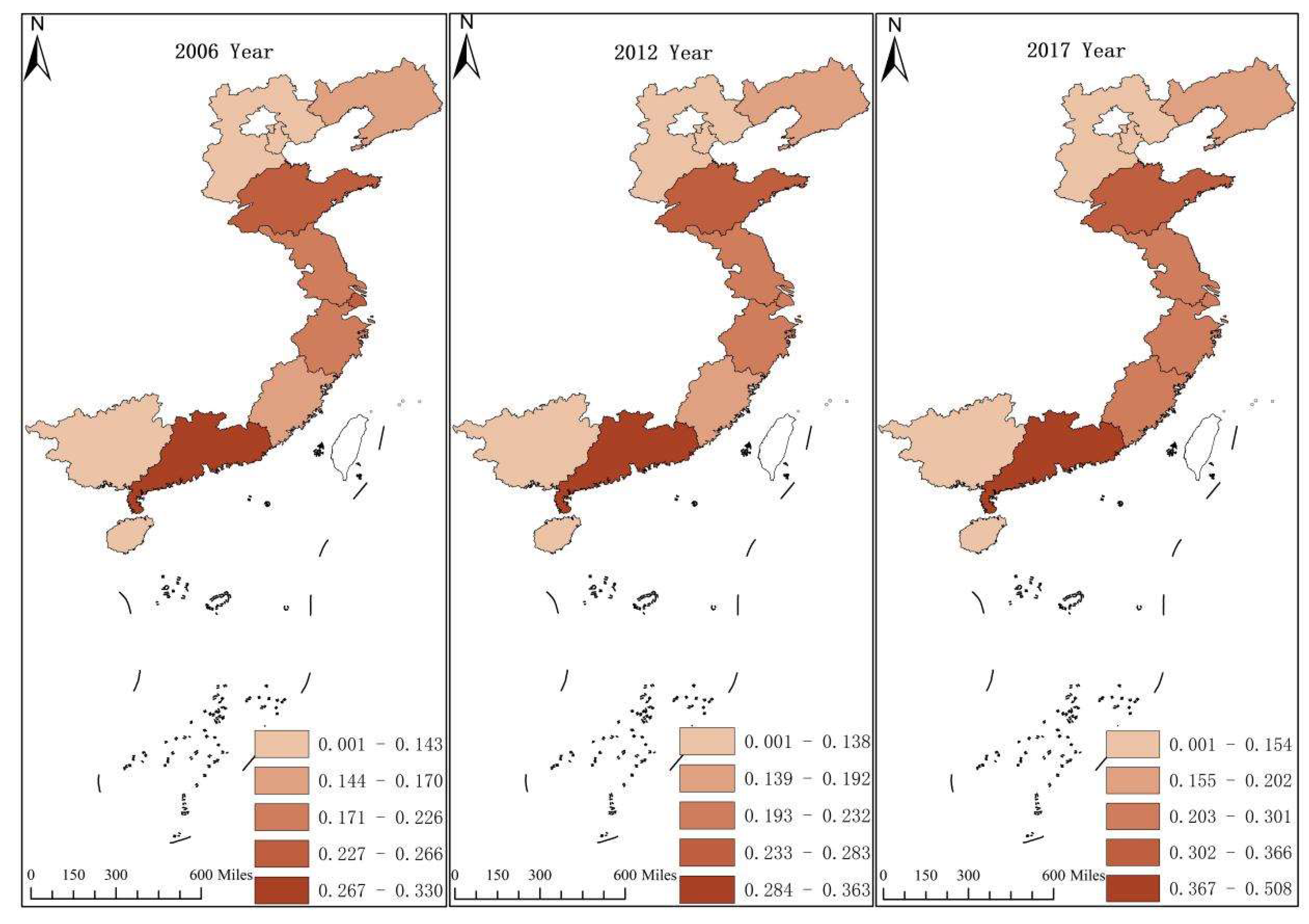
3.2. Temporal and Spatial Evolution of High-Quality Development of Marine Economy
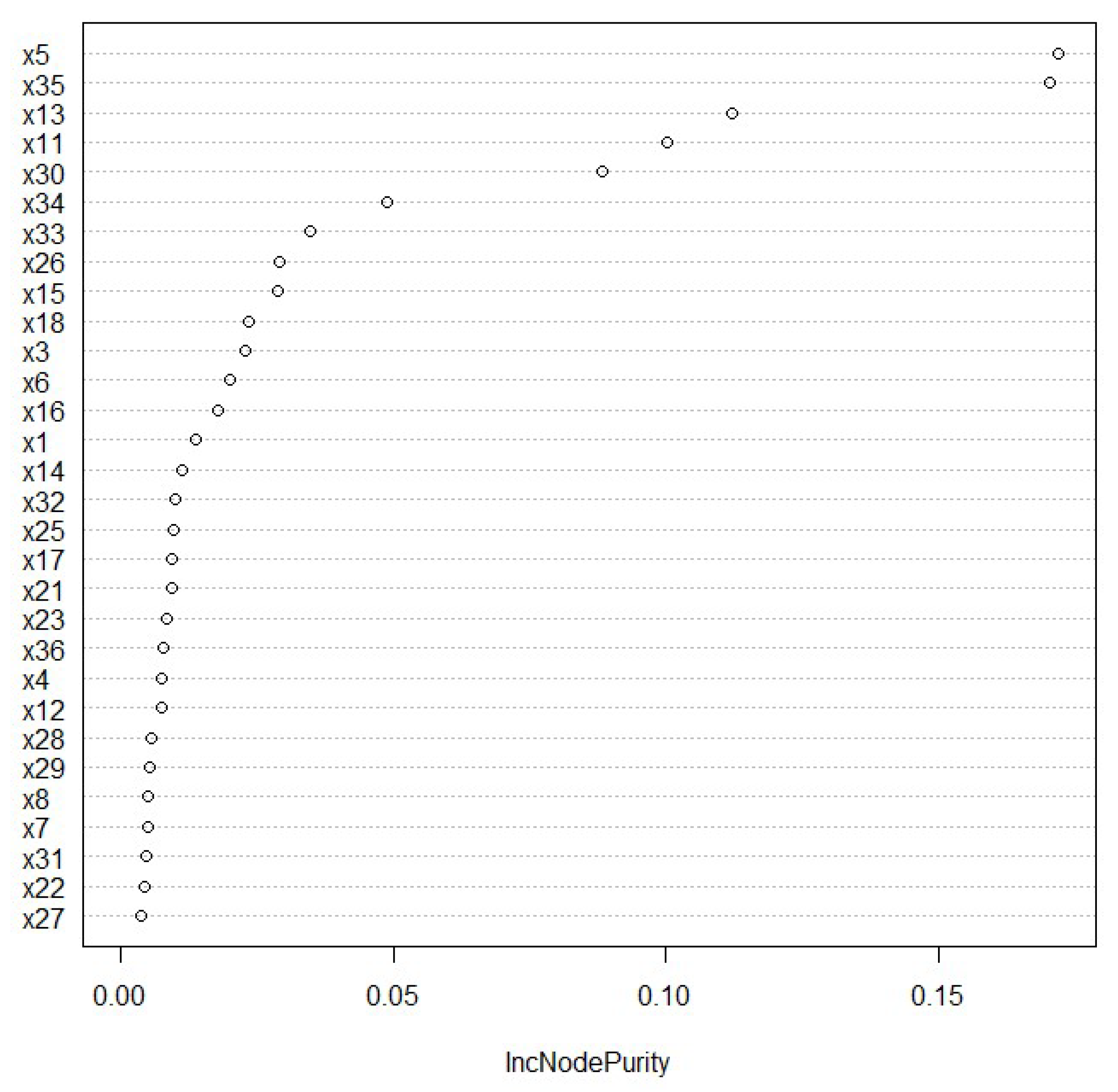
3.3. Driving Factors and Regulation Methods of High-Quality Development of Marine Economy
3.4. Regulation Methods of Main Driving Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yan, Y.; Tsydypova, A.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation of marine economic efficiency of China’s coastal provinces based on DEA model. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 112 (Suppl. 1), 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, Q.B.; Lv, D.H. Research on measurements and response relationship between carrying capacity of marine region and marine economic benefits in China. Ecol. Econ. 2019, 35, 126–133+169. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Bao, W.; Shi, L. Governance mechanism and performance of marine eco-economic system: Evidence from China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wang, J.; Xu, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, L. Evaluation of the comprehensive benefit of various marine exploitation activities in China. Mar. Policy 2020, 116, 103924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Xiao, J. Evaluation of green development level of Marine economy in Guangdong province based on entropy method. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1774, 012012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Ji, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation of China’s marine economic efficiency under environmental constraints—An empirical analysis of China’s eleven coastal regions. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 184, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.G.; Shen, T.Y. Does Technological innovation promotethe high quality development of China’s marine economy—Empirical test based on effect of technological innovation on GTFP. Sci. Technol. Prog. Policy 2020, 37, 105–112. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Han, Z.L.; Hu, W.; Zhong, J.Q. Sustainable development of marine eco-economics based on an emergy analysis in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 2563–2574. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.H.; Lu, B.B.; Yin, K.D. Financial development, productivity, and high-quality development of the marine economy. Mar. Policy 2021, 130, 104553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhao, L.; Sun, H.; Liu, W. Comprehensive evaluation and main influencing factors of sustainable development of marine economy based on GRA and LWCI models. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 104 (Suppl. 1), 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Xu, M.; Wang, J.; Xie, S. Regional disparities in China’s marine economy. Mar. Policy 2017, 82, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Xu, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, L. Evaluation of China’s marine economic growth quality based on set pair analysis. Mar. Policy 2021, 126, 104405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.T. A study on marine eco-economic quality assessment—A case study of 11 coastal provinces and cities. Territ. Nat. Resour. Study 2019, 6, 62–63. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Sun, H.H.; Wang, R.J. Audit evaluation and driving force analysis of marine economic development quality. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Hu, D. Construction and empirical study of the evaluation index system for high-quality development of marine economy in Guangdong Province based on five new development concepts. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1629, 012030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A.; Guan, H.; Sun, Z. Understanding high-quality development of marine economy in China: A literature review. Mar. Econ. Manag. 2019, 2, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.L.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, Y.M. Research progress of the indicators systems and evaluating methods for the high quality development of marine economy. Mar. Econ. 2020, 10, 3–16. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ding, L.L. Research on the connotation and evaluation system of high-quality development of marine economy. J. Ocean. Univ. China 2020, 3, 12–20. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.Y.; Ma, Y.Y.; Lin, H.L. Using the entropy and TOPSIS models to evaluate sustainable development of islands: A case in China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Lin, Z.; He, G. Measurement and influencing factors of green total factor productivity of marine economy in China. Forum Sci. Technol. China 2015, 2, 72–78. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winfield, M.; Dolter, B. Energy, economic and environmental discourses and their policy impact: The case of Ontario’s green energy and green economy act. Energy Policy 2014, 68, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, W.; Sun, X.; Jiang, P.; Wang, L. Analysis of the environmental sustainability of a megacity through a cobenefits indicator system—the case of Shanghai. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steven, A.E. Toward a recycling society:Ecological sanitation closing the loop to food security. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 43, 177–187. [Google Scholar]
- Bushra, W.; Faisal, K.; Brian, V. Linkage-based frameworks for sustainability assessment: Making a case for driving force-pressure-state-exposure-effect-action (DPSEEA) frameworks. Sustainability 2009, 1, 441–463. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.S.; Ouyang, Z.Y. Social-economic-natural complex ecosystem and sustainability. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2012, 27, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Sun, H.; Ma, M.; Lu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Liu, W. Vulnerability assessment of marine economic system based on comprehensive index and catastrophe progression model. Ecosyst. Health Sustain. 2020, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.L.; Yang, Y.; Li, H. Bidirectional Evaluation and Difference of High-quality Development Level of Regional Marine Economy. Econ. Geogr. 2021, 41, 31–39. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Y. Construction and comprehensive evaluation of high-quality development index system of marine economy. Stat. Decis. 2021, 37, 169–173. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, G.; Lin, Z.; Huihui, S.; Guangxi, C.; Wei, L. Evaluation and driving force analysis of marine sustainable development based on the grey relational model and path analysis. J. Resour. Ecol. 2020, 11, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.Y.; Chen, Q. Estimation and evaluation of China’s provincial marine economic growth quality—Empirical analysis based on five development concepts. Sci. Technol. Econ. 2020, 33, 91–95. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Gao, S.; Liu, J.; Liu, W. Research on comprehensive benefits and reasonable selection of marine resources development types. Open Geosci. 2022, 14, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Miao, J.; Mu, H.; Xu, J.; Zhai, N. Sustainable development in marine economy: Assessing carrying capacity of Shandong province in China. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2022, 216, 105981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, Q.B.; Yu, Z.; Xu, L.X. Spatial-temporal coordination mode of marine economic development under the background of high quality growth: Based on the empirical study of prefecture-level cities in circum-Bohai Sea. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2019, 39, 1621–1630. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cao, N.G.; Zhao, L.; Jia, J.Q. Quality measurement and influencing factor analysis of China’s marine economic development based on RESSIC framework. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2021, 37, 106–112. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.T.; Zhao, L.; Cao, N.G. Evolution characteristics of spatial correlation network of the high-quality development of China’s marine economy. Areal Res. Dev. 2022, 41, 7–13. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.; Yan, B. Research on driving factors of high-quality development of marine economy based on PVAR model. J. Ocean. Univ. China 2021, 4, 46–58. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ning, L.; Song, Z.M. Dynamic Relationship Between Marine Science and Technology Innovation, Marine Total Factor Productivity and Marine Economic Development:Empirical Analysis Based on Panel Vector Autoregressive Model. Sci. Technol. Manag. Res. 2020, 40, 164–170. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, W.L.; Zhang, J.L.; Nie, Z.W. Research on the Connotation and Index System of High Quality Development of Marine Economy in Tianjin City. Nat. Resour. Econ. China 2020, 33, 34–42+62. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bo, L.; Tian, C.; Shi, Z.; Han, Z. Spatial characteristics and influencing factors of marine economic growth quality in Liaoning coastal areas. Prog. Geogr. 2019, 38, 1080–1092. [Google Scholar]
- Zeyu, W.; Zhen, Z.; Zenglin, H.; Caizhi, S.; Yingrui, L. Response measures of the marine economy to regional economic development. Resour. Sci. 2016, 38, 1832–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Han, Z.L.; Sun, C.Z.; Peng, F. Coordination between quality and scale of marine economy under the background of the new normal in China. Areal Res. Dev. 2015, 34, 1–7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Di, Q.B.; Gao, G.Y.; Yu, Z. Evaluation and influencing factors of high-quality development of marine economy in China. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2022, 42, 650–661. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gai, M.; He, Y.N.; Ke, L.N. Research on the development quality of China’s marine economy. J. Nat. Resour. 2022, 37, 942–965. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Long, R.Y.; Zhu, C.G.; Sun, X.X.; Pan, K.Y. Comprehensive measurement of the index system for marine economy high-quality development in Jiangsu province. Econ. Geogr. 2020, 40, 104–113. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Tian, C.; Shi, Z.; Han, Z. Evolution and differentiation of high-quality development of marine economy: A case study from China. Complexity 2020, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Fu, Q.; Zou, Y.; Hu, X. Evaluation of livable city based on GIS and PSO-SVM: A case study of hunan province. Int. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 2021, 35, 2159030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Shi, S. Multiple birth support vector machine based on dynamic quantum particle swarm optimization algorithm. Neurocomputing 2022, 480, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Shi, W.; Yuen, K.F.; Xiao, Y.; Li, K.X. Oil tanker risks on the marine environment: An empirical study and policy implications. Mar. Policy 2019, 108, 103655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, L.; Zheng, J.; Wang, J.; Yuan, Y.; Lv, Z.; Wei, Y.; Han, Q.; Gao, J.; Liu, W. China’s public firms’ attitudes towards environmental protection based on sentiment analysis and random forest models. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Han, L.M. Impacts of marine industrial structure changes on marine economic growth for 11 coastal provinces in China. Resour. Sci. 2017, 39, 1182–1193. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.D.; Zhu, B.Y.; Yang, M.Y. Has marine technology innovation promoted the high-quality development of the marine economy?—Evidence from coastal regions in China. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2021, 209, 105695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, B. Spatio-temporal evolutionary characteristics and type classification of marine economy resilience in China. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2022, 217, 106016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.M.; Liu, C.; Mamonov, K.A.; Jun, D. Measurement of coordinated and coupled development and evaluation of sustainable development for marine economic-ecological complex system. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2021, 2021, 2043635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
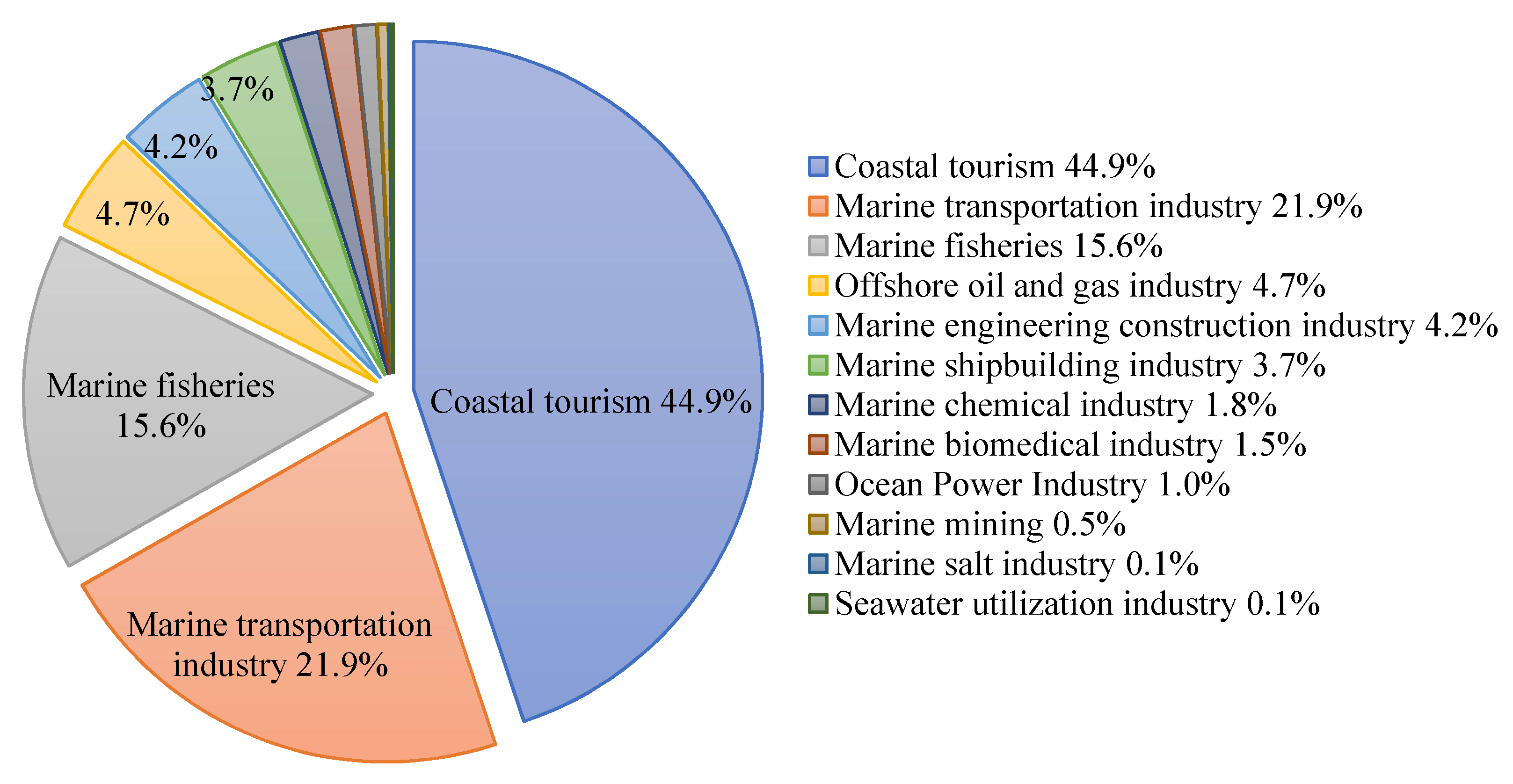

| Six Aspects | Sort | Coastal Area Indicators | Entropy Weight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Economic vitality in coastal areas | ×1 | GDP of coastal areas (CNY 100 million) | 0.0186 |
| ×2 | Growth rate of GDP in coastal areas (%) | 0.0021 | |
| ×3 | Gross marine product (CNY 100 million) | 0.0228 | |
| ×4 | GDP of major marine industries in coastal areas (CNY 100 million) | 0.0198 | |
| ×5 | Gross product value of marine scientific research, education, management, and service industry (CNY 100 million) | 0.0379 | |
| ×6 | Gross product value of marine-related industries (CNY 100 million) | 0.0214 | |
| Structural optimization in coastal areas | ×7 | Proportion of marine gross product to coastal area gross product (%) | 0.0176 |
| ×8 | Proportion of marine primary industry in total marine production (%) | 0.0254 | |
| ×9 | Proportion of marine secondary industry output value in total marine production (%) | 0.0072 | |
| ×10 | Proportion of marine tertiary industry output value in total marine production (%) | 0.0068 | |
| ×11 | Proportion of major marine industries in the added value of marine and related industries (%) | 0.0084 | |
| ×12 | Proportion of marine scientific research, education, and management services in the added value of marine and related industries (%) | 0.0135 | |
| Openness level in coastal areas | ×13 | Total import and export of goods (USD 1 million) | 0.0337 |
| ×14 | Port cargo throughput (10,000 tons) | 0.0180 | |
| ×15 | Port passenger throughput (10,000 people) | 0.0395 | |
| ×16 | Ocean freight volume (10,000 tons) | 0.0222 | |
| ×17 | Cargo Turnover Volume (10,000 tons) | 0.0306 | |
| ×18 | Port standard container throughput (10,000 TEUs) | 0.0317 | |
| Social livelihood in coastal areas | ×19 | Per capita disposable income of urban residents (CNY) | 0.0132 |
| ×20 | Per capita disposable income of rural residents (CNY) | 0.0141 | |
| ×21 | Number of Employed Persons (10,000 people) | 0.0238 | |
| ×22 | Number of health institutions (number) | 0.0263 | |
| ×23 | General public budget expenditure (CNY 10,000) | 0.0996 | |
| ×24 | Fixed asset investment of the whole society (CNY 100 million) | 0.0205 | |
| Green development in coastal areas | ×25 | Area of marine nature reserves (km2) | 0.1159 |
| ×26 | Total wetland area (1000 hm2) | 0.0175 | |
| ×27 | Water resources per capita (m3/person) | 0.0366 | |
| ×28 | Water consumption per capita (m3/person) | 0.0186 | |
| ×29 | Comprehensive utilization of general industrial solid waste (tons) | 0.0765 | |
| ×30 | Total wastewater discharge (10,000 tons) | 0.0168 | |
| Innovation drive in coastal areas | ×31 | Number of employees in marine scientific research institutions (person) | 0.0180 |
| ×32 | Total revenue of marine scientific research institutions (CNY 10,000) | 0.0460 | |
| ×33 | Number of marine scientific research institutions (number) | 0.0159 | |
| ×34 | Number of scientific and technological projects in marine scientific research institutions (items) | 0.0293 | |
| ×35 | Marine scientific research institutions publish scientific papers (articles) | 0.0242 | |
| ×36 | Number of colleges and universities (number) | 0.0098 |
| Province | 2017/2006 | Sort | 2017/2012 | Sort |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | 53.69% | 1 | 39.98% | 1 |
| Jiangsu | 33.30% | 5 | 33.60% | 2 |
| Shandong | 37.69% | 3 | 29.29% | 3 |
| Fujian | 43.46% | 2 | 26.62% | 4 |
| Zhejiang | 24.47% | 6 | 26.25% | 5 |
| Hebei | 8.07% | 10 | 22.22% | 6 |
| Guangxi | 13.57% | 8 | 15.95% | 7 |
| Shanghai | 6.03% | 11 | 15.25% | 8 |
| Hainan | 33.68% | 4 | 8.49% | 9 |
| Tianjin | 12.70% | 9 | 7.70% | 10 |
| Liaoning | 19.75% | 7 | 6.76% | 11 |
| Factors | Importance | Sort | Factors | Importance | Sort |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ×5 | 0.1719 | 1 | ×21 | 0.0094 | 19 |
| ×35 | 0.1704 | 2 | ×23 | 0.0085 | 20 |
| ×13 | 0.1121 | 3 | ×36 | 0.0079 | 21 |
| ×11 | 0.1003 | 4 | ×4 | 0.0076 | 22 |
| ×30 | 0.0884 | 5 | ×12 | 0.0075 | 23 |
| ×34 | 0.0487 | 6 | ×28 | 0.0058 | 24 |
| ×33 | 0.0347 | 7 | ×29 | 0.0055 | 25 |
| ×26 | 0.0291 | 8 | ×8 | 0.0052 | 26 |
| ×15 | 0.0289 | 9 | ×7 | 0.0052 | 27 |
| ×18 | 0.0234 | 10 | ×31 | 0.0048 | 28 |
| ×3 | 0.0229 | 11 | ×22 | 0.0046 | 29 |
| ×6 | 0.0201 | 12 | ×27 | 0.0039 | 30 |
| ×16 | 0.0178 | 13 | ×9 | 0.0027 | 31 |
| ×1 | 0.0140 | 14 | ×20 | 0.0025 | 32 |
| ×14 | 0.0113 | 15 | ×19 | 0.0025 | 33 |
| ×32 | 0.0099 | 16 | ×10 | 0.0025 | 34 |
| ×25 | 0.0097 | 17 | ×2 | 0.0020 | 35 |
| ×17 | 0.0095 | 18 | ×24 | 0.0014 | 36 |
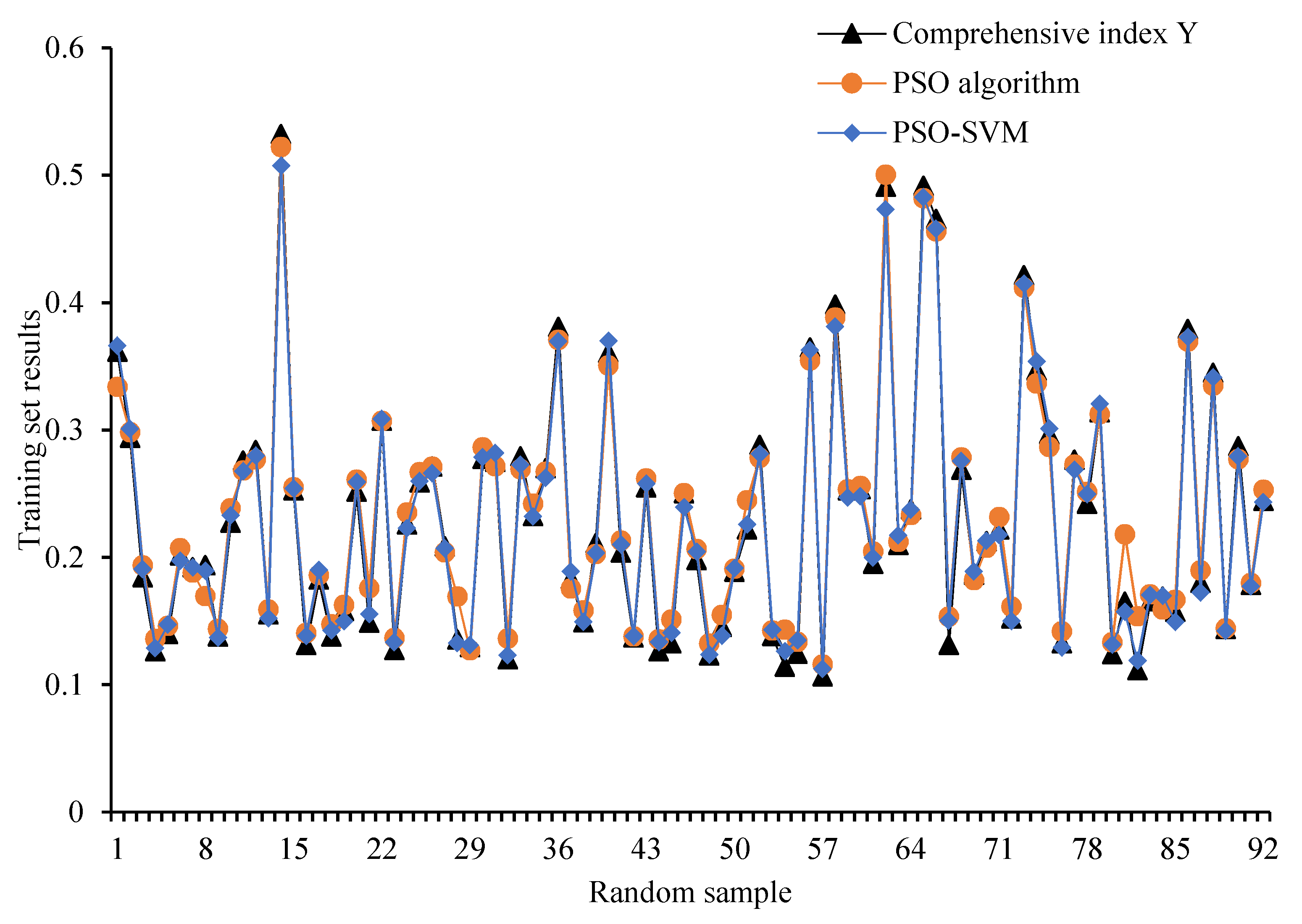
| Source of Difference | SS | df | MS | F | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSR of index Y and PSO | 0.0018 | 1 | 0.0018 | 0.2451 | 0.6209 |
| MSE of index Y and PSO | 1.9484 | 262 | 0.0074 | ||
| MSR of index Y and PSO-SVM | 0.0000 | 1 | 1.040 × 10−5 | 0.0014 | 0.9707 |
| MSE of index Y and PSO-SVM | 2.0123 | 262 | 0.0077 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, S.; Sun, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, W. Evaluation and Countermeasures of High-Quality Development of China’s Marine Economy Based on PSO-SVM. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10749. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710749
Gao S, Sun H, Wang J, Liu W. Evaluation and Countermeasures of High-Quality Development of China’s Marine Economy Based on PSO-SVM. Sustainability. 2022; 14(17):10749. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710749
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Sheng, Huihui Sun, Jingyi Wang, and Wei Liu. 2022. "Evaluation and Countermeasures of High-Quality Development of China’s Marine Economy Based on PSO-SVM" Sustainability 14, no. 17: 10749. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710749
APA StyleGao, S., Sun, H., Wang, J., & Liu, W. (2022). Evaluation and Countermeasures of High-Quality Development of China’s Marine Economy Based on PSO-SVM. Sustainability, 14(17), 10749. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710749






