Estimation of the Value of Forest Ecosystem Services in Pudacuo National Park, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
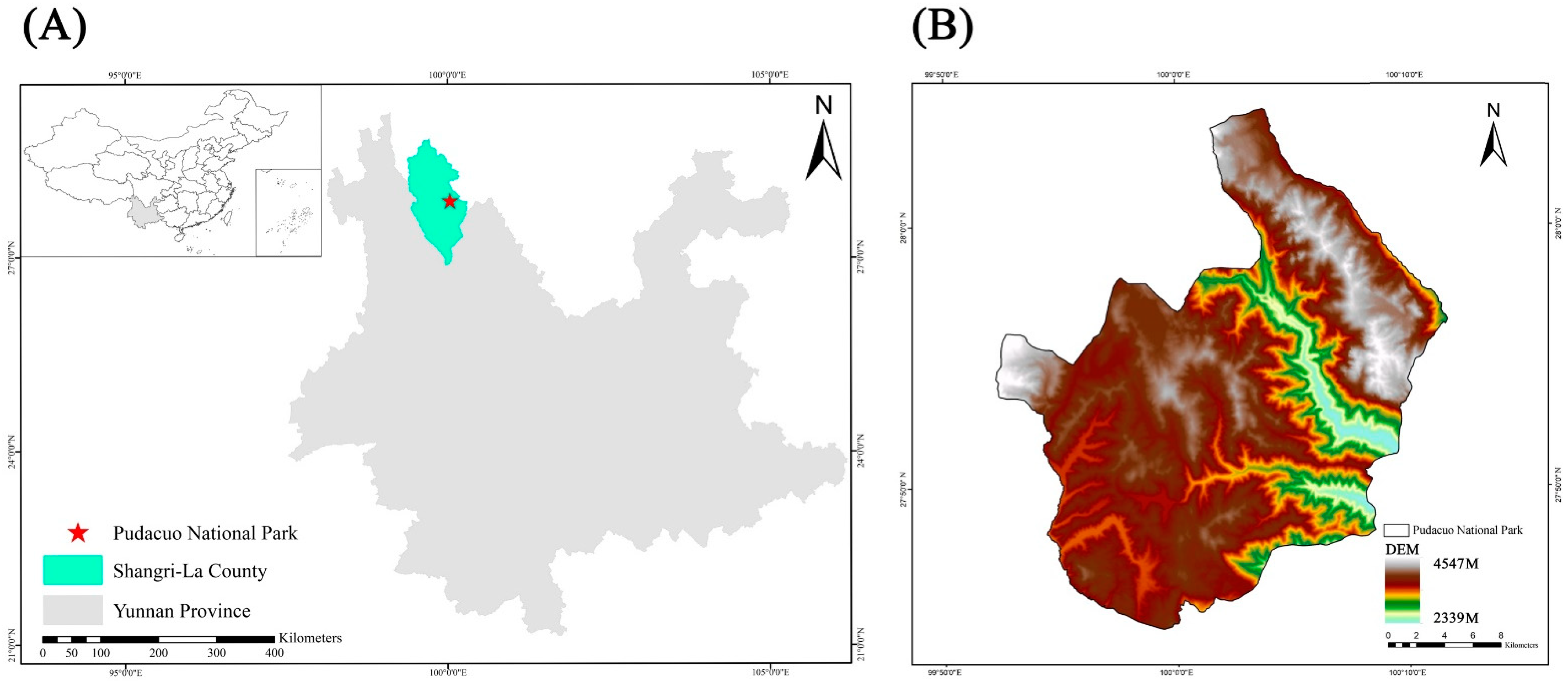
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Preprocessing
2.2.1. Data Sources
2.2.2. Preprocessing
2.3. Assessment Methodology and Indicator Selection
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Different Forest-Stand Types
3.2. The Value of Forest Ecosystem Services
3.3. Value of Ecosystem Services per Unit Area of Different Forest−Stand Types
4. Discussion
4.1. Assessing the Value of Forest Ecosystem Services Using Multidisciplinary Cross-Sectional Research and Multisource Data
4.2. The Relationship between Forest Ecosystems and Ecological Compensation
4.3. Analysis of Uncertainties
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daily, G.C.; Soederqvist, T.; Aniyar, S.; Arrow, K.; Dasgupta, P.; Ehrlich, P.R.; Folke, C.; Jansson, A.M.; Jansson, B.O.; Kautsky, N. The Value of Nature and the Nature of Value. Science 2000, 289, 395–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chisholm, R.A. Trade-offs between ecosystem services: Water and Carbon in a Biodiversity Hotspot. Ecol. Econ. 2010, 69, 1973–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onaindia, M.; Beatriz, F.; Madariaga, I.; Rodríguez-Loinaz, G. Co-benefits and Trade-offs between Biodiversity, Carbon Storage and Wwater Flow Regulation. For. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 289, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronald, C.; Francisco, E.; Daniel, M.L.; Amr, A.E. Analyzing Trade-Offs, Synergies, and Drivers among Timber Production, Carbon Sequestration, and Water Yield in Pinus Elliotii Forests in Southeastern USA. Forests 2014, 5, 1409–1431. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, T.; Ouyang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Wang, X.; Miao, H. Forest Ecosystem Services and Their Valuation in China. J. Nat. Resour. 2004, 4, 480–491. [Google Scholar]
- Constanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; De, G.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’neill, R.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The Value of the World’s Ecosystem Services and Nature Capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Lu, S.; Jin, F.; Chen, L.; Rao, L.; Lu, G. The assessment of the Forest Ecosystem Services Evaluation in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2005, 8, 2096–2102. [Google Scholar]
- He, A. Discussion on the Forest Public Function Economic Valuation Assessment in Japan. Cent. South For. Inventry Plan. 2002, 2, 48–54. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, F.; Lu, S.; Yu, X.; Rao, L.; Zhang, Z.; Mao, F. Preliminary Study on Evaluation Index System of Forest Ecosystem Services in China. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2005, 3, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, Z.; Wang, X.; Miao, H. A Primary Study on Chinese Terrestrial Ecosystem Services and Their Ecological Economic Values. Acta Ecol. Sin. 1999, 19, 607–613. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhou, G. Estimation of Ecosystem Services of Major Forest in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 1999, 23, 426–432. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Wang, N.; Du, A.; Kong, L.; Xu, W.; Ouyang, Z. Experiences, Achievement, Problems and Recommendations of the First Batch of China’s National Park System Pilots. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 8839–8850. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, A.; Hendrayana, Y.; Ramadani, D.; Umiyati, S. Composition of Vegetation Types and Structures in Gunung Ciremai National Park Forest. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 748, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyanta, R.; Proborini, M.; Dalem, A. Phosphate Solvent Fungi Exploration and Identification in West Bali National Park Forest Area. Metamorf. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 6, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ye, W. Experience in the Pudacuo National Park System Pilot in Shangri-La, Yunnan. Biodivers. Sci. 2021, 29, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yu, X.; Yu, G. A Case Study of International Ecosystem Assessment. Adv. Earth Sci. 2008, 11, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar]
- Levin, P.; Kelble, C.; Shuford, R.; Ainsworth, C.; deReynier, Y.; Dunsmore, R.; Fogarty, M.; Holsman, K.; Howell, E.; Monaco, M.; et al. Guidance for Implementation of Integrated Ecosystem Assessments: A US Perspective. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2014, 5, 1198–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey-Collas, M. Why the Omplex Nature of Integrated Ecosystem Assessments Requires A Flexible and Adaptive Approach. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2014, 5, 1174–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LY/T1721-2008; Specifications for Assessment of Forest Ecosystem Services in China. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2008.
- GB/T 38582 2020; Specifications for Assessment of Forest Ecosystem Services in China. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Feng, X.; Fu, B.; Yang, X.; Lv, Y. Remote Sensing of Ecosystem Services: An Opportunity for Spatially Explicit Assessment. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2010, 20, 522–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, H.; Li, Y.; Robinson, B.E.; Liu, G.; Ma, D.; Wang, F.; Lu, F.; Ouyang, Z.; Daily, G.C. Using Ecosystem Service Trade-offs to Inform Water Conservation Policies and Management Practices. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2016, 14, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runting, R.; Bryan, B.; Dee, L.; Maseyk, F.; Mandle, L.; Hamel, P.; Wilson, K.; Yetka, K.; Possingham, H.; Rhodes, J. Incorporating Climate Change into Ecosystem Service Assessments and Decisions: A Review. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martínez-Sastre, R.; Ravera, F.; González, J.A.; Santiago, C.L.; Bidegain, I.; Munda, G. Mediterranean Landscapes under Change: Combining Social Multicriteria Evaluation and the Ecosystem Services Framework for Land Use Planning. Land Use Policy 2017, 67, 472–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Dong, X.; Liu, H.; Wei, H.; Fan, W.; Lu, N.; Xu, Z.; Ren, J.; Xing, K. Linking Land Use Change, Ecosystem Services and Human Well-being: A Case Study of the Manas River Basin of Xinjiang, China. Ecosyst. Serves 2017, 27, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, R.; Zhang, C.; He, Z.; Zheng, H.; Yang, R.; Chen, Y.; Feng, P.; Sina, Q.; Zhao, D.; Yixi, Y.; et al. Population Spatial Distribution Pattern and Association of Abies Georgei in Shangri-La Potatso National Park. Chin. J. Ecol. 2021, 40, 3860–3869. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Fan, Z.; Fu, P.; Shankar, P.; Tang, H. Radial Growth Responses of Four Coniferous Species to Climate Change in the Potatso National Park, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 32, 3548–3556. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, Z.; Liao, S.; Wu, W.; Li, L.; Liu, W. Remote sensing estimation of forest aboveground biomass in Potatso National Park using GF-1 images. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 37, 216–223. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Gong, A.; Ning, D.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Xiang, B. Characteristics of Soil Erosion and Nutrient Loss in Yunnan Province Based on RUSLE Model. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 35, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, K. Soil Erosion Forecasting Models; Science and Technology of China Press: Beijing, China, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, X. Vegetation Geography and Dominant Phytochemical Composition of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Wen, L.; Huang, L. Changes of Net Primary Productivity of vegetation from 1996 to 2015 in Shangri-La Region China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 266–276. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.; Liu, G.; Xu, S. Biomass and Net Production of Forest Vegetation in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 1996, 16, 497–508. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Q.; Tian, K. Study on the Characteristics of Runoff and Sediment Production on Slope Land of Plateau Wetland Napa Lake. J. Yunnan Agric. Univ. 2011, 26, 81–85. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, C. Forest Biomass Estimation in Shangri-La County Based on Remote Sensing. Ph.D. Thesis, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B. The Research on Services and Values of Forestry Ecosystem of the Emphasied Public Warfare Forest-Taking Ji Gong Shan Nature Researve as an Example. Bachelor’s Thesis, Henan Agricultural University, Zhengzhou, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z. The Study on the Variation of Air Negative Oxygen Ion Content in Different Forest Parts. Bachelor’s Thesis, Central South University of Forestry and Technology, Changsha, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Deng, Z.; Bei, R. Study on the Effect of Absorption and Purification Air Pollution of 10 Common Greening Species at Different Polluted Area in Kunming. J. Southwest For. Univ. 2016, 36, 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, A. Analysis on the Characteristics of Soil Physical and Chemical Properties and Soil Quality along the Altitude Gradient in the East and West Slopes of Ailao Mountains National Nature Reserve. Bachelor’s Thesis, Yunnan Normal University, Kunming, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, L.; Huang, D. Guide to Fertilizer Use; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z. Vegetation of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Zhu, Y. Vegetation of Yunnan; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Fan, L.; Liu, S.; Sun, T. Evaluation of Forest Ecosystem Services Value in Shanxi Province. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 4732–4740. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Q.; Li, J.; Xu, Z.; Han, Y. Assessment of Service Functions Value of the Natural Forest Protection Program in Xinjiang. J. Northwest For. Univ. 2018, 33, 289–296. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, R.; Wang, B.; Niu, X.; Gu, J.; Dang, J.; Xu, Y. Assessment on the Atmosphere Purification Function of Forest Ecosystem in Shanxi Province. J. Northwest For. Univ. 2017, 32, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Shi, X.; Shi, W. Evaluation of Water Retention Services of Forest Ecosystems in Fujian Province: Comparison between Results from the InVEST Model and Meta-analysis. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 1349–1361. [Google Scholar]
- Bo, X.; Mi, W.; Xu, H.; Dong, J. Estimating of Ecological Service Value for Different Wetland Types Based on Multi-source Data Fusion in Ningxia Plain. J. Zhejiang Univ. 2016, 42, 228–244. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Gao, H.; Yang, J.; Xi, J.; Li, X.; Ge, Q. Valuation of Nansihu Lake Wetland Ecosystem Services Based on Multi-Sources Data Fusion. Resour. Sci. 2014, 36, 840–847. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, Y.; Meng, S.; Shi, K.; Yu, T.; Wang, X.; Niu, X.; Zhao, D.; Liu, L.; Feng, M.; Qin, X.; et al. Forest Coverage Monitoring in the Natural Forest Protection Project Area of China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 5080–5092. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Wang, B.; Niu, X.; Song, Q. Spatial Pattern of the Ecosystem Service Function of Forests in Jinan City. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 6477–6486. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Guo, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhang, J. Assessment of Forest Ecosystem Service Function Value in Guizhou. Guizhou Agric. Sci. 2014, 42, 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Adhikari, R.K.; Kindu, M.; Pokharel, R.; Castro, L.M. Knoke Financial Compensation for Biodiversity Conservation in Ba Be National Park of Northern Vietnam. J. Nat. Conserv. 2017, 35, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Shen, H.; Yang, M. Studies on Ecosystem Service Value and Ecological Compensation Strategy in Lishui River Basin. Res. Environ. Sci. 2016, 29, 774–782. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Wang, X.; Luo, L.; Gong, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Bachagha, N. A Systematic Review on the Methods of Ecosystem Services Value Assessment. Chin. J. Ecol. 2018, 37, 1233–1245. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, M.; Wu, S.; Yin, Y.; Pan, T. Accounting for Eco-compensation in the Three-river Headwaters Region Based on Ecosystem Service Value. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 227–236. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Q. Study on the Spatial Selection of Ecologica1Compensation Objects: A Case Study of Water Conservation of Grasslands in Gannan Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture. J. Nat. Resour. 2010, 25, 415–425. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C. Study on the Service Function and Compensation Mechanism of Ecological Forest in Hunan Province. Ph.D. Thesis, Hunan Agricultural University, Changsha, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]



| Name of Data | Unit | Source of Data |
|---|---|---|
| Soil-erosion modulus on wooded and unwooded land in forest stands | t·hm−2·a−1 | Reference [29] |
| The soil in forest stands contains N, P, K, and organic matter | % | 2021 Report on the Comprehensive Scientific Study of Shangri-La’s Pudacuo National Park, Reference [30]. |
| Elemental N, P, and K contents of forest | % | References [31,32] |
| Net productivity of forest stands | t·hm−2·a−1 | Reference [33] |
| Precipitation outside the forest | mm·a−1 | Reference [31] |
| Evapotranspiration from forest stands | mm·a−1 | Reference [31] |
| Rapid surface runoff from forest stands | mm·a−1 | Reference [34] |
| Carbon sequestration in forest soils | t·hm−2·a−1 | Reference [35] |
| Amount of sulfur dioxide, fluoride, and nitrogen oxides absorbed by forest stands | kg·hm−2·a−1 | Reference [36] |
| Negative-oxygen-ion concentration in forest stands | pcs·cm−3 | Reference [37] |
| Forest-stand height | m | 2021 Report on the Comprehensive Scientific Study of Shangri-La’s Pudacuo National Park |
| Negative-oxygen-ion life | min | Reference [19] |
| Dust-holding capacity | t·hm−2·a−1 | References [36,38] |
| Soil consolidation prices | yuan·m−3 | Reference [19]. The price of soil consolidation instead of the cost of excavating and transporting a unit volume of soil is RMB 12.6 yuan/m3. |
| Soil capacity | g·cm−3 | Reference [39] |
| Diammonium phosphate fertilizer prices | yuan·t−1 | National Price List of Agricultural Production Materials, published by the Price Monitoring Centre of the National Development and Reform Commission of China in January–December 2020. |
| Potassium chloride fertilizer prices | yuan·t−1 | |
| Organic-matter fertilizer prices | yuan·t−1 | |
| Nitrogen content of diammonium phosphate fertilizer | % | Reference [40] |
| Phosphorus content of diammonium phosphate fertilizer | % | |
| Potassium chloride fertilizer with the potassium content | % | |
| Water-transaction costs, water-purification costs | yuan·m−3 | Water-resource-transaction costs, water-purification costs, instead of reservoir-construction-unit reservoir-capacity investment costs (compensation for land demolition and relocation, construction costs, maintenance costs, etc.), China Water Resources Yearbook 1993–1999, China Statistical Abstract 2019. |
| Negative-oxygen-ion generation costs | yuan·pcs−1 | Reference [9] |
| Sulfur dioxide, fluoride, nitrogen oxides, and stagnant dust clean-up costs | yuan·kg−1 | Notice on the Implementation Plan for the Adjustment of the Sewage Charge Levy Standard, issued by the Yunnan Provincial Department of Environmental Protection, Reference [9]. |
| Solid carbon prices | yuan·t−1 | International carbon tax law. 2020 USD:RMB, exchange rate of 1:6.86, Swedish carbon-tax rate: USD 129.7/t, equivalent to RMB 889.74/t |
| Oxygen prices | yuan·t−1 | Oxygen Market Annual Report 2019–2020. The price of oxygen was RMB 594.8/t. |
| The value of forest tourism and leisure industries, and forest rehabilitation and healing industries | yuan·a−1 | Courtesy of Pudacuo National Park Authority |
| Service Features | Evaluation Indicators | Evaluation Methods | Functional-Volume-Calculation Formula | Value-Quantity-Calculation Formula |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | E1 | OC | ||
| E2 | OC | |||
| E3 | ||||
| E4 | ||||
| E5 | ||||
| Ⅱ | F1 | SP | ||
| F2 | ||||
| F2 | ||||
| Ⅲ | G1 | WB | ||
| G2 | ||||
| Ⅳ | H1 | OC | ||
| H2 | ||||
| H3 | ||||
| Ⅴ | I1 | SP | ||
| I2 | ||||
| I3 | ||||
| I4 | ||||
| I5 | ||||
| Ⅵ | J1 | MV |
| Vegetation Type | Dominant Species |
|---|---|
| Sclerophyllous evergreen broad-leaved forest | Quercus pannosa Hand.-Mazz., Quercus guyavifolia H. Léveillé, Quercus senescens Hand.-Mazz., Quercus aquifolioides Rehd. et Wils. |
| Deciduous broad-leaved forest | Betula platyphylla Suk., Betula albo-sinensis Burkill, Populus rotundifolia var. duclouxiana (Dode) Gomb., Acer sterculiaceum subsp. franchetii (Pax) A. E. Murray, Acer davidii Franch., Salix takasagoalpina Koidz., Hippophae rhamnoides L. Pinus yunnanensis Franch. |
| Warm coniferous forest | Pinus yunnanensis Franch., Pinus armandii Franch., Taxus yunnanensis W.C.Cheng and L.K.Fu. |
| Temperate coniferous forest | Tsuga dumosa (D. Don) Eichler, Pinus densata Mast., Abies ernestii var. salouenensis (Borderes-Rey et Gaussen) Cheng et L. K. Fu, Juniperus tibetica Komarov, Picea likiangensis (Franch) Pritz, Abies georgei Orr, Larix potaninii var. australis A. Henry ex Handel-Mazzetti. |
| Scrub | Rhododendron hippophaeoides Balf. F. et W. W. Smith, Rhododendron telmateium Balf. F. et W. W. Smith, Rhododendron alutaceum Balf. F. et W. W. Smith, Rhododendron rubiginosum Franch., Caragana franchetiana Kom., Juniperus squamata Buchanan-Hamilton ex D. Don, Spiraea myrtilloides Rehd., Berberis dictyophylla Franch., Daphne aurantiaca Diels. |
| Meadow | Carex atrata L., Rheum alexandrae Batal., Carex forrestii Kukenth. |
| Type of Forest Stand | Value of Forest Ecosystem Services (106 yuan·a−1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil Conservation | Forest Nutrient Retention | Water Conservation | Carbon Fixation and Oxygen Released | Atmosphere Environmental Purification | Forest Health Care | |
| Deciduous broad-leaved forest | 5.61 | 3.18 | 23.94 | 202.67 | 0.67 | |
| Warm coniferous forest | 20.70 | 7.91 | 90.38 | 1207.02 | 3.82 | |
| Temperate coniferous forest | 48.96 | 16.14 | 96.00 | 1967.39 | 4.40 | |
| Sclerophyllous evergreen broad-leaved forest | 11.42 | 0.96 | 49.03 | 387.33 | 1.40 | |
| Scrub | 2.20 | 0.85 | 6.71 | 26.83 | 0.13 | |
| Meadow | 26.20 | 3.86 | 74.04 | 61.88 | 1.24. | |
| Total | 115.12 | 32.93 | 340.12 | 3853.15 | 11.67 | 144.44 |
| Total value | 4497.47 | |||||
| Type of Forest Stand | Value of Forest Ecosystem Services per Unit Area (yuan·hm−2·a−1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil Conservation | Forest Nutrient Retention | Water Conservation | Carbon Fixation and Oxygen Released | Atmosphere Environmental Purification | Total | |
| Deciduous broad-leaved forest | 1336.09 | 756.69 | 5696.08 | 48,213.51 | 159.65 | 56,162.02 |
| Warm coniferous forest | 1305.02 | 499.13 | 5696.09 | 76,069.44 | 240.79 | 83,810.47 |
| Temperate coniferous forest | 2905.06 | 957.95 | 5696.09 | 116,725.20 | 261.16 | 126,545.46 |
| Sclerophyllous evergreen broad-leaved forest | 1327.15 | 111.97 | 5696.09 | 44,991.54 | 163.08 | 52,289.83 |
| Scrub | 1874.85 | 729.89 | 5696.12 | 22,775.98 | 114.00 | 31,190.84 |
| Meadow | 2015.97 | 297.57 | 5696.09 | 4760.54 | 95.84 | 12,866.01 |
| Total | 10,764.14 | 3353.20 | 34,176.56 | 313,536.21 | 1034.52 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Kou, W.; Ma, X.; Wei, X.; Gong, M.; Yin, X.; Li, J.; Li, J. Estimation of the Value of Forest Ecosystem Services in Pudacuo National Park, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10550. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710550
Chen Y, Kou W, Ma X, Wei X, Gong M, Yin X, Li J, Li J. Estimation of the Value of Forest Ecosystem Services in Pudacuo National Park, China. Sustainability. 2022; 14(17):10550. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710550
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yue, Weili Kou, Xianguang Ma, Xiaoyan Wei, Maojia Gong, Xiong Yin, Jingting Li, and Jianqiang Li. 2022. "Estimation of the Value of Forest Ecosystem Services in Pudacuo National Park, China" Sustainability 14, no. 17: 10550. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710550
APA StyleChen, Y., Kou, W., Ma, X., Wei, X., Gong, M., Yin, X., Li, J., & Li, J. (2022). Estimation of the Value of Forest Ecosystem Services in Pudacuo National Park, China. Sustainability, 14(17), 10550. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710550






