Soil Erosion Processes and Geographical Differentiation in Shaanxi during 1980–2015
Abstract
:1. Introduction
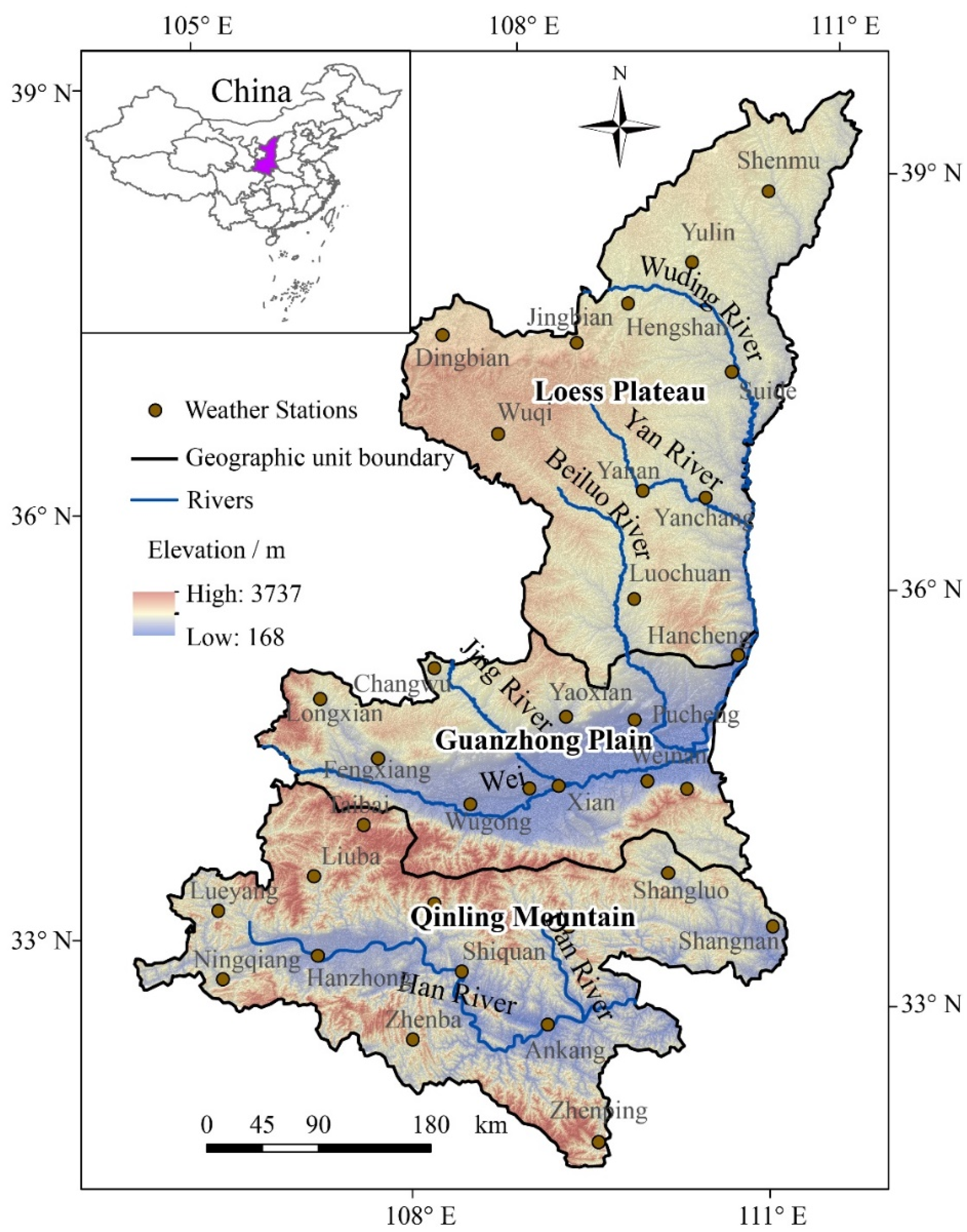
2. Environment Setting
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Data Sources
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Soil Erosion Simulation of RUSLE Model
3.2.2. Time Series and Spatial Analysis
4. Results
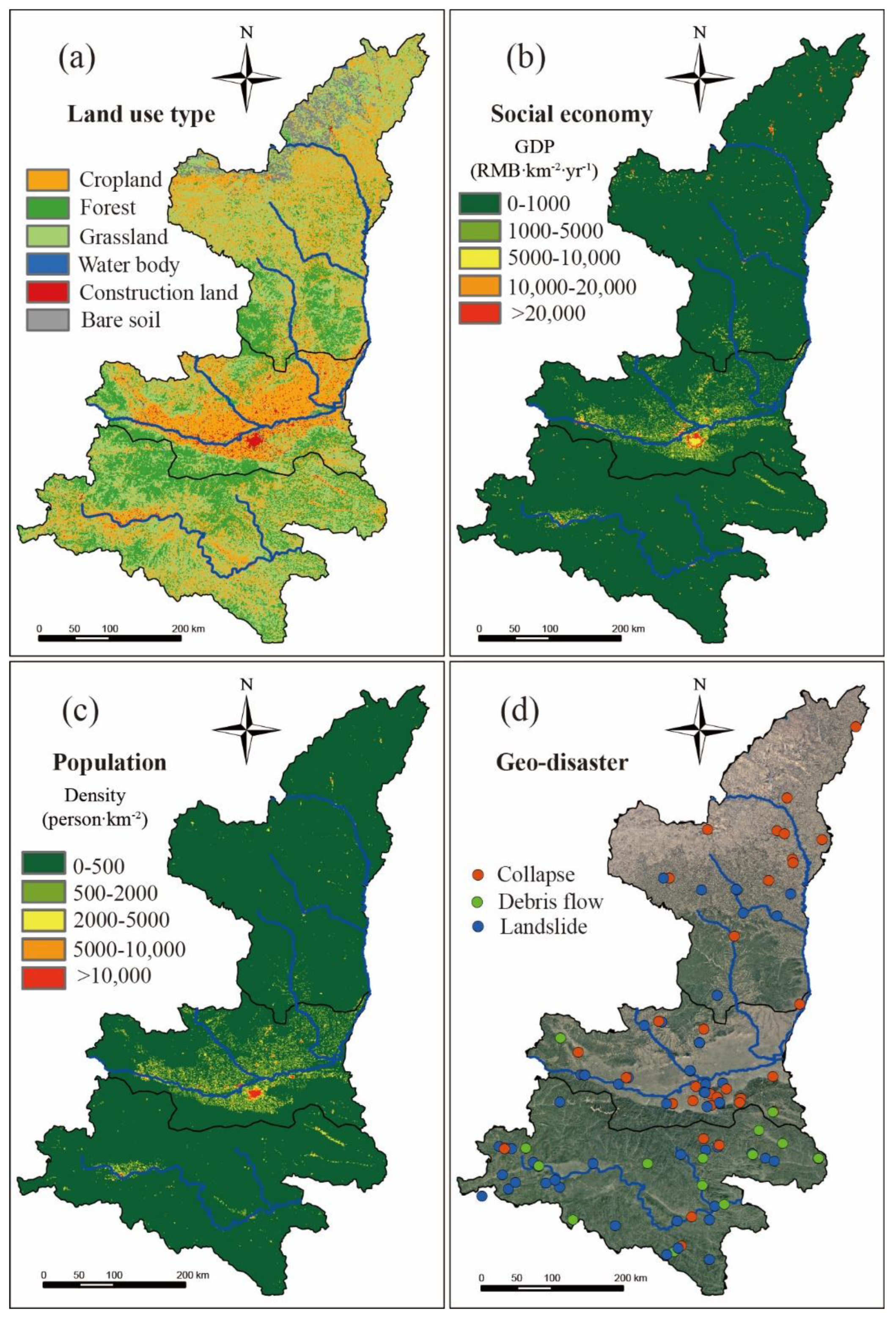
4.1. Changes in Environmental Factors
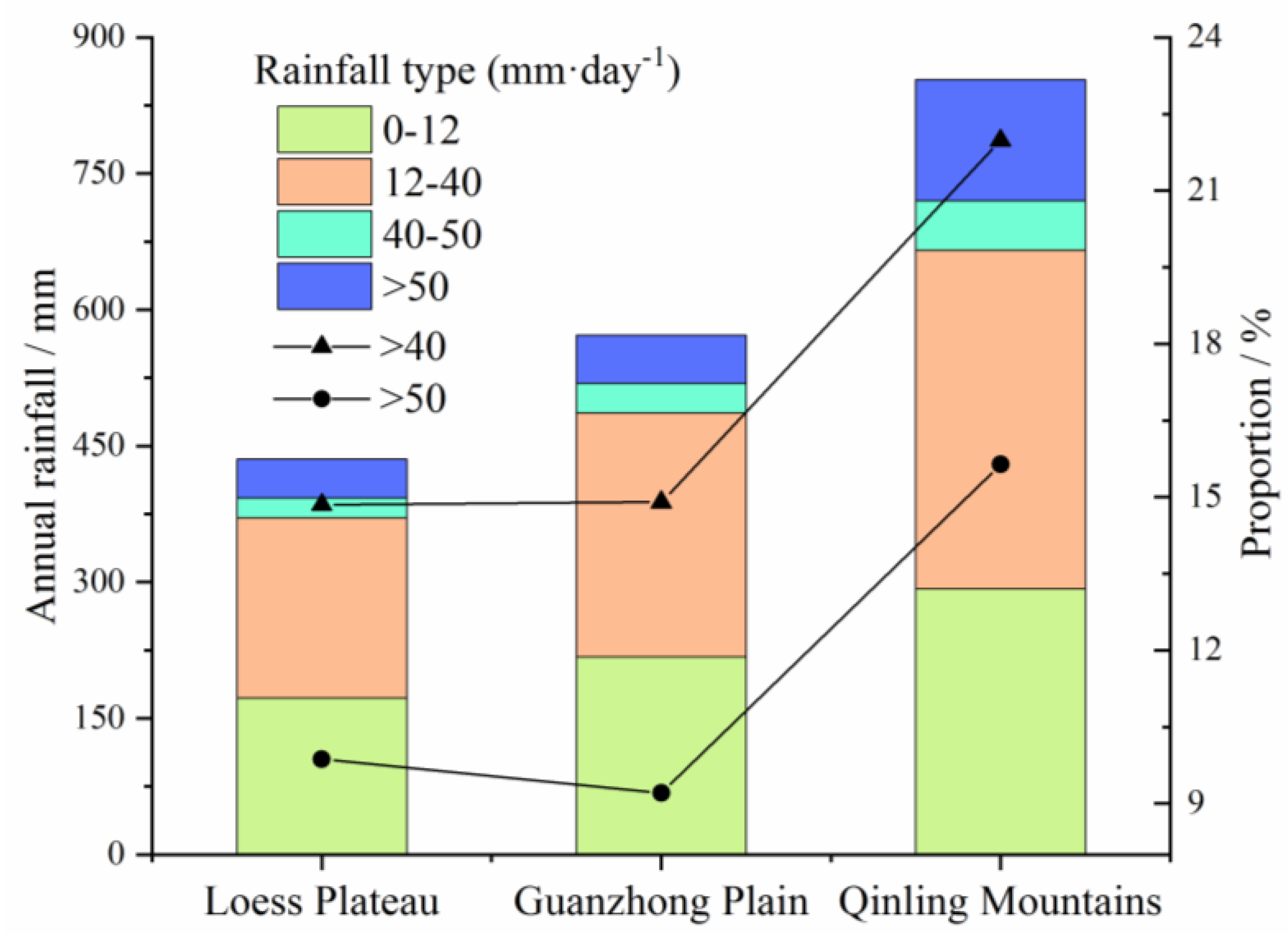
4.1.1. Precipitation Change
4.1.2. Vegetation Change
4.1.3. Human Activities Change
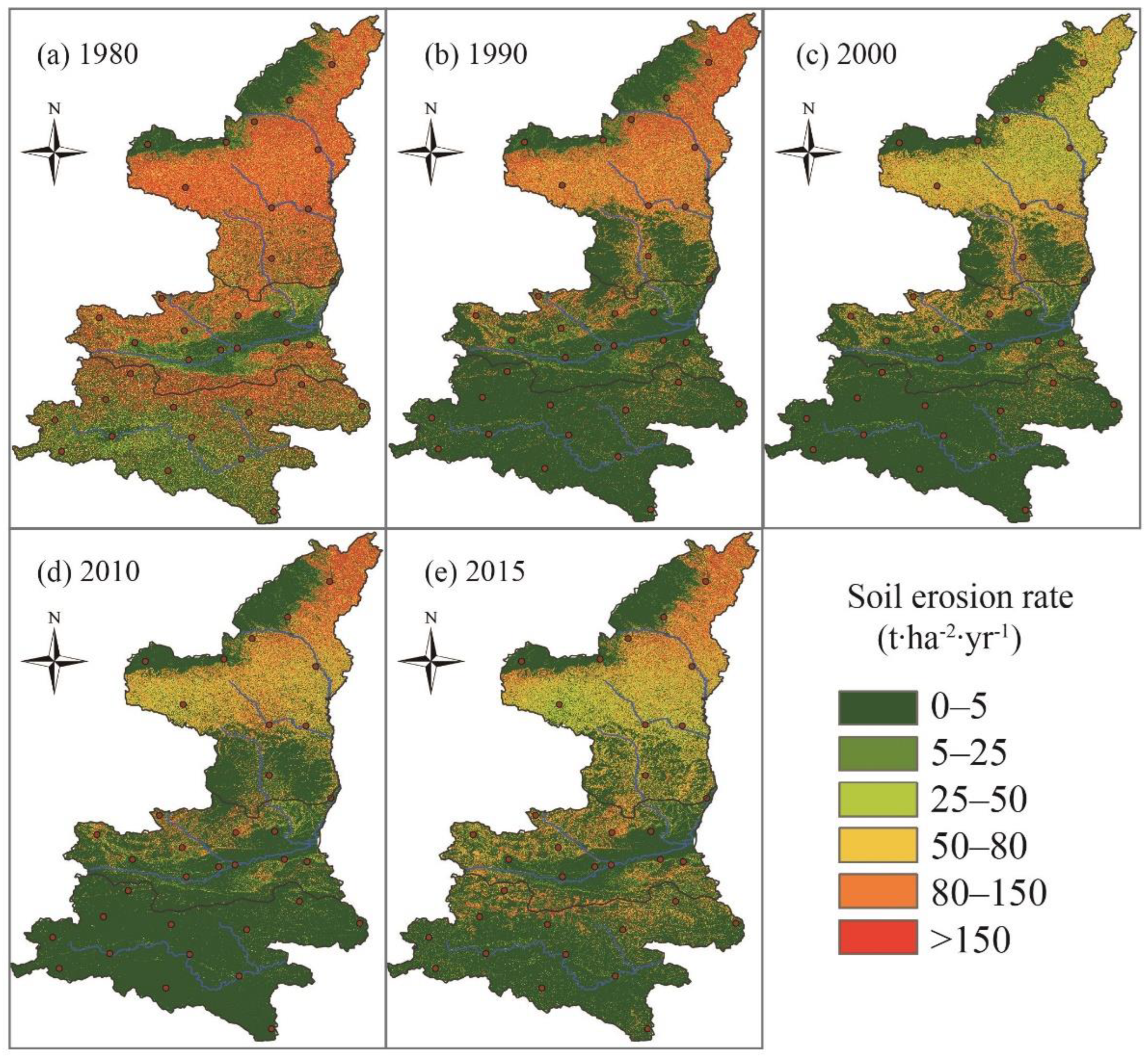
4.2. Dynamic Changes of Soil Erosion Simulation Result by RUSLE Model
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ochoa, P.A.; Fries, A.; Mejía, D.; Burneo, J.I.; Ruíz-Sinoga, J.D.; Cerdà, A. Effects of climate, land cover and topography on soil erosion risk in a semiarid basin of the Andes. Catena 2016, 140, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhatu, A.; Speranza, C.I.; Zeleke, G.; Roth, V.; Lemann, T.; Herweg, K.; Hurni, H. Interrelationships between terrace development, topography, soil erosion, and soil dislocation by tillage in Minchet Catchment, Ethiopian Highlands. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 3584–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haregeweyn, N.; Tsunekawa, A.; Nyssen, J.; Poesen, J.; Tsubo, M.; Tsegaye Meshesha, D.; Schütt, B.; Adgo, E.; Tegegne, F. Soil erosion and conservation in Ethiopia. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2015, 39, 750–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, S.W.; Mello, C.R.; Chou, S.C.; Curi, N.; Norton, L.D. Soil erosion risk associated with climate change at Mantaro River basin, Peruvian Andes. Catena 2016, 147, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Fang, H.Y. Impacts of climate change on water erosion: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 163, 94–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wei, W.; Chen, L.D. Effects of terracing practices on water erosion control in China: A meta-analysis. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 173, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.F.; Zhao, C.Y.; Zhu, J.T. Aggravated risk of soil erosion with global warming—A global meta-analysis. Catena 2021, 200, 105129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, M.Q.; Sun, R.H.; Chen, L.D. A global comparison of soil erosion associated with land use and climate type. Geoderma 2019, 343, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuepper, D.; Borrelli, P.; Finger, R. Countries and the global rate of soil erosion. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 3, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaezi, A.R.; Zarrinabadi, E.; Auerswald, K. Interaction of land use, slope gradient and rain sequence on runoff and soil loss from weakly aggregated semi-arid soils. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 172, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ruiz, J.M.; Beguería, S.; Nadal-Romero, E.; González-Hidalgo, J.C.; Lana-Renault, N.; Sanjuán, Y. A meta-analysis of soil erosion rates across the world. Geomorphology 2015, 239, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.F.; Overeem, I.; Kettner, A.J.; Zhou, Y.J.; Lu, X.X. Air Temperature Regulates Erodible Landscape, Water, and Sediment Fluxes in the Permafrost-Dominated Catchment on the Tibetan Plateau. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2020WR028193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, G.R.; Ovenden, M.; Sharma, K.; Rowlands, W.; Gibson, A.; Wells, T. Soil erosion—The impact of grazing and regrowth trees. Geoderma 2020, 361, 114102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, P.; Robinson, D.A.; Fleischer, L.R.; Lugato, E.; Ballabio, C.; Alewell, C.; Meusburger, K.; Modugno, S.; Schutt, B.; Ferro, V.; et al. An assessment of the global impact of 21st century land use change on soil erosion. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benaud, P.; Anderson, K.; Evans, M.; Farrow, L.; Glendell, M.; James, M.R.; Quine, T.A.; Quinton, J.N.; Rawlins, B.; Jane Rickson, R.; et al. National-scale geodata describe widespread accelerated soil erosion. Geoderma 2020, 371, 114378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, X.P.; Abla, M.; Lü, D.; Yan, R.; Ren, Q.F.; Ren, Z.Y.; Yang, Y.H.; Zhao, W.H.; Lin, P.F.; et al. Effects of vegetation and rainfall types on surface runoff and soil erosion on steep slopes on the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2018, 170, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.M.; Zhou, J.; Peart, M.R.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Q.F. Sensitivity of hydrogeomorphological hazards in the Qinling Mountains, China. Quat. Int. 2012, 282, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.F.; He, H.M.; Wang, J.J.; Bai, C.Y.; Zhang, C.J. Vegetation Restoration and Its Environmental Effects on the Loess Plateau. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Brandt, M.; Zhao, M.F.; Tong, X.W.; Xing, K.X.; Xue, F.; Kang, M.Y.; Wang, L.H.; Jiang, Y.; Fensholt, R. Major forest increase on the Loess Plateau, China (2001–2016). Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 4080–4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.Y.; Yang, D.; Zhang, P.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Song, M.; Huang, Y.C.; Jing, W.L. Multi-Scenario Simulation of Land Use Changes with Ecosystem Service Value in the Yellow River Basin. Land 2022, 11, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrière, N.; Locatelli, B.; Laumonier, Y.; Freycon, V.; Bernoux, M. Soil erosion in the humid tropics: A systematic quantitative review. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 203, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.Y.; Jia, H.; Chen, H.; Liu, D.; Zhang, H. Landscape Sustainability in the Loess Hilly Gully Region of the Loess Plateau: A Case Study of Mizhi County in Shanxi Province, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.L.; Yu, J.S.; Jiang, H.; Sun, W.C.; Li, Z.J. Roles of soil erodibility, rainfall erosivity and land use in affecting soil erosion at the basin scale. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 174, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.P.; Zhang, H.P.; Chen, L.; Zhao, J.F. Influence of the South-North Water Diversion Project and the mitigation projects on the water quality of Han River. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 406, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statistics, N.B.O. Statistical Yearbook of China-2018; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2018. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.L.; Zhang, M.J.; Wang, S.J.; Wang, B.L.; Li, F.; Che, Y.J. Changes in precipitation extremes over Shaanxi Province, northwestern China, during 1960–2011. Quat. Int. 2013, 313–314, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.J.; Van Rompaey, A.; Wang, J.A. Detecting the impact of the “Grain for Green” program on the mean annual vegetation cover in the Shaanxi province, China using SPOT-VGT NDVI data. Land Use Policy 2009, 26, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.J.; Jiao, J.Y.; Rayburg, S.; Wang, Q.L.; Su, Y. Soil erosion resistance of “Grain for Green” vegetation types under extreme rainfall conditions on the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2016, 141, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Y.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yu, L.; Li, H.C.; Bai, Y.Q. Assessment of the cropland classifications in four global land cover datasets: A case study of Shaanxi Province, China. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soksamnang, K.; He, H.M.; Zhao, H.F.; Jing, Z.W. Analysis of Rainfall Erosivity Change and Its Impacts on Soil Erosion on the Loess Plateau over More than 50 Years. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 25, 1–7, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Liang, X.Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, H.; Mao, N.Z. A Quantitative Assessment of Comprehensive Ecological Risk for a Loess Erosion Gully: A Case Study of Dujiashi Gully, Northern Shaanxi Province, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kateb, H.E.; Zhang, H.F.; Zhang, P.C.; Mosandl, R. Soil erosion and surface runoff on different vegetation covers and slope gradients: A field experiment in Southern Shaanxi Province, China. Catena 2013, 105, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Q.S.; Gao, Z.Q.; Ning, J.C.; Bi, X.L.; Wang, Q.X. Impact of progressive urbanization and changing cropping systems on soil erosion and net primary production. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 75, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnell, P.I.A. Applying the RUSLE and the USLE-M on hillslopes where runoff production during an erosion event is spatially variable. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 3328–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; McCool, D.K.; Yoder, D.C. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); USDA Agriculture Handbook: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Ganasri, B.P.; Ramesh, H. Assessment of soil erosion by RUSLE model using remote sensing and GIS—A case study of Nethravathi Basin. Geosci. Front. 2016, 7, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Zhang, X.P.; Yan, S.J.; Chen, H. Estimating soil erosion response to land use/cover change in a catchment of the Loess Plateau, China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2018, 6, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.Y.; Shao, Q.Q.; Liu, J.Y.; Zhai, J. Assessing the effects of land use and topography on soil erosion on the Loess Plateau in China. Catena 2014, 121, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Wang, Z.J.; Yang, R.; Yao, J. SpatioTemporal Variation Characteristics of Soil Erosion in Southern Shaanxi Region Based on RUSLE. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 25, 1–11, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, L.; Yang, Q.K.; Xie, H.X.; Wang, C.M.; Guo, W.L. GIS and CSLE Based Quantitative Assessment of Soil Erosion in Shaanxi China. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2009, 23, 61–66, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.F.; Yao, S.B.; Ding, Z.M.; Hou, M.Y.; Deng, Y.J.; Liu, G.Q. The Grain for Green project, geographical features and soil erosion: Taking 107 counties in Shaanxi Province as examples. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 301–312, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.F.; Chen, J.N.; Zhao, G.J.; Holden, J.; Liu, B.T.; Chan, F.K.S.; Hu, J.F.; Wu, P.L.; Mu, X.M. Determining the drivers and rates of soil erosion on the Loess Plateau since 1901. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 823, 153674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.B.; Xie, Y.; Liu, B.Y. Rainfall erosivity estimation using daily rainfall amounts. Geogr. Res. 2002, 22, 705–711, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Williams, J.R.; Jones, C.A.; Dyke, P.T. A modelling approach to determining the relationship between erosion and soil productivity. Trans. Am. Soc. Agric. Eng. 1984, 27, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.Y.; Nearing, M.A.; Risse, M. Slope gradient effects on soil loss for steep slopes. Trans. Am. Soc. Agric. Eng. 1994, 37, 1835–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.L. Effect of Vegetation Changes on Soil Erosion on the Loess Plateau. Pedosphere 2006, 16, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.F.; Ding, S.W.; Shi, Z.H.; Huang, L.; Zhang, G.Y. Study of applying USLE and geographical information system IDRISI to predict soil erosion in small watershed. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2000, 14, 19–24, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.T.; Han, J.C.; Huang, Y.F.; Fassnacht, S.R.; Xie, S.; Lv, E.Z.; Chen, M. Vegetation response to climate conditions based on NDVI simulations using stepwise cluster analysis for the Three-River Headwaters region of China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 92, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods; Griffin: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Z.J.; Duan, X.W.; Liu, B.; Hu, J.M.; He, J.N. The spatial distribution and temporal variation of rainfall erosivity in the Yunnan Plateau, Southwest China: 1960–2012. Catena 2016, 145, 291–300. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, X.W.; Gu, Z.J.; Li, Y.G.; Xu, H.J. The spatiotemporal patterns of rainfall erosivity in Yunnan Province, southwest China: An analysis of empirical orthogonal functions. Glob. Planet. Change 2016, 144, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisi, O.; Ay, M. Comparison of Mann–Kendall and innovative trend method for water quality parameters of the Kizilirmak River, Turkey. J. Hydrol. 2014, 513, 362–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Fu, B.J.; Gao, G.Y.; Lü, Y.H.; Liu, Y.; Lü, N.; Wang, S. Effects of precipitation and restoration vegetation on soil erosion in a semi-arid environment in the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2016, 137, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.P.; Ren, Y.L.; Jiao, P.; Xiao, P.; Li, Z. Changes in rainfall erosivity from combined effects of multiple factors in China’s Loess Plateau. Catena 2022, 216, 106373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.O.; Zheng, F.L.; Wen, L.L.; Han, Y.; Hu, W. Impacts of rainfall intensity and slope gradient on rill erosion processes at loessial hillslope. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 155, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, J.M.; Bai, Z.K.; Lv, C.J. Effects of vegetation on runoff and soil erosion on reclaimed land in an opencast coal-mine dump in a loess area. Catena 2015, 128, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Deng, J.; Chai, X.; Mu, X.; Zhao, G.; Shao, H.; Sun, W. Dynamic sediment discharge in the Hekou-Longmen region of Yellow River and soil and water conservation implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 578, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Huang, C.C.; Pang, J.L.; Zha, X.C.; Zhou, Y.L.; Yin, S.Y.; Wang, J. Comparative study of the modern flood slackwater deposits in the upper reaches of Hanjiang and Weihe River Valleys, China. Quat. Int. 2012, 282, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.X.; Wang, Y.M.; Istanbulluoglu, E.; Bai, T.; Huang, Q.; Yang, D.W.; Huang, S.Z. Impact of climate change and human activities on runoff in the Weihe River Basin, China. Quat. Int. 2015, 380–381, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.J.; Wang, L.; Wei, A.S.; Gao, J.B.; Lu, Y.L.; Zhou, J.B. Land-use change from arable lands to orchards reduced soil erosion and increased nutrient loss in a small catchment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Region | 1980 | 1990 | 2000 | 2010 | 2015 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loess Plateau | 37.04 | 45.14 | 53.77 | 57.87 | 56.91 |
| Guanzhong Plain | 43.75 | 65.58 | 63.19 | 64.80 | 64.20 |
| Qinling Mountains | 54.11 | 76.52 | 76.91 | 78.14 | 76.76 |
| Average | 44.59 | 59.08 | 64.08 | 66.58 | 64.28 |
| Land Use Type | 2015 | Grand Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Farmland | Forestland | Grassland | Water Body | Construction Land | Unutilized Land | |||
| 1980 | Farmland | 67,827.30 | 894.30 | 1411.40 | 175.54 | 1289.12 | 75.99 | 71,673.64 |
| Forestland | 168.52 | 45,852.00 | 404.70 | 8.40 | 60.40 | 35.53 | 46,529.54 | |
| Grassland | 1237.92 | 967.31 | 74,448.10 | 94.69 | 247.08 | 194.69 | 77,189.80 | |
| Water body | 218.71 | 12.31 | 86.61 | 1507.50 | 12.14 | 6.65 | 1843.93 | |
| Construction land | 75.89 | 0.74 | 4.51 | 0.62 | 2101.23 | 0.03 | 2183.02 | |
| Unutilized land | 290.03 | 110.04 | 1332.82 | 24.36 | 131.98 | 4493.90 | 6383.13 | |
| Grand total | 69,818.36 | 47,836.71 | 77,688.14 | 1811.10 | 3841.95 | 4806.79 | 205,803.06 | |
| Region | 1980 | 1990 | 2000 | 2010 | 2015 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loess Plateau | 110.70 | 78.80 | 38.22 | 48.91 | 46.72 |
| Guanzhong Plain | 70.80 | 23.26 | 19.97 | 18.30 | 24.40 |
| Qinling Mountains | 25.89 | 7.78 | 4.09 | 1.63 | 13.02 |
| Average | 86.76 | 42.75 | 22.96 | 22.96 | 30.59 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, J.; Lin, Y.; Zhao, H.; He, H. Soil Erosion Processes and Geographical Differentiation in Shaanxi during 1980–2015. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10512. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710512
Lin J, Lin Y, Zhao H, He H. Soil Erosion Processes and Geographical Differentiation in Shaanxi during 1980–2015. Sustainability. 2022; 14(17):10512. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710512
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Jifeng, Yunhong Lin, Hongfei Zhao, and Hongming He. 2022. "Soil Erosion Processes and Geographical Differentiation in Shaanxi during 1980–2015" Sustainability 14, no. 17: 10512. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710512
APA StyleLin, J., Lin, Y., Zhao, H., & He, H. (2022). Soil Erosion Processes and Geographical Differentiation in Shaanxi during 1980–2015. Sustainability, 14(17), 10512. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710512






