Abstract
Geological disasters caused by surface deformation are common, especially in urban areas, which seriously impede urbanization’s sustainable development. Monitoring and analysis with high spatial and temporal resolution are particularly important to assess the risk of geological disasters caused by urban deformation. This study uses Sentinel-1A satellite imagery to obtain the surface deformation time series of Nanchang City based on SBAS-InSAR and PS-InSAR techniques and is combined with wavelet period analysis and gray correlation analysis to determine the correlation between deformation area and climate environment. This study shows that there was a large-scale subsidence trend in the central urban area of Nanchang in those two years, and an uplift trend in the agro-ecological areas in the southeast. A periodic analysis further shows that the areas with larger changes in surface deformation are more affected by changes in precipitation. This study, integrated with external data, examines the possibility of subsidence disasters occurring along subway lines in areas with large deformation magnitudes from multiple angles.
1. Introduction
The problem of urban surface deformation is a common problem in today’s world, which seriously threatens the basic buildings of the city and our personal safety [1,2,3]. The causes of urban surface deformation include human factors and natural factors [4,5,6]. Human factors are mainly caused by the construction needs of urbanization, which can be traced back for a long time. Periods of rapid development of bridges and tall buildings were in the 19th and 20th centuries, respectively [7,8]. In the 21st century, above-ground space is gradually being crowded, and the construction of underground space facilities such as basements, subways, and pipeline burials has accelerated the progress of urbanization [9,10]. Moreover, several natural phenomena such as rainfall infiltration, landslides, earthquakes, storms, and flooding may contribute to increasing ground deformation hazards [11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18]. The phenomenon of urban surface deformation has also become more severe, which seriously affects the stability of urban public infrastructure and directly damages the sustainable development of the local economy and environment [19,20].
Monitoring surface deformation is the key to disaster prevention and mitigation [21]. Three-dimensional laser scanning methods, photogrammetry, conventional geodetic technology, etc. can meet the needs of small-scale monitoring [22,23,24,25]. For large areas, methods such as Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) and Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry (InSAR) are required [26]. The data of discrete monitoring points obtained by traditional geodetic methods and GNSS technology cannot meet large-scale and full coverage monitoring needs. InSAR technology is a satellite-based geodetic survey method with a large-scale, all-day/all-weather monitoring capability [27,28]. InSAR technology can accurately measure the spatial position of the ground by using the parameters of the radar satellite and the spatial geometric position relationship [29]. Differential Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar Technology (DInSAR) can obtain small deformations at a certain position at different times through differential means [28,30]. To obtain the cumulative deformation value from the time series, Time Series Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar technologies (TS-InSAR) have been proposed; these include Berardino’s Small Baseline Subsets Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar technology (SBAS-InSAR) based on DInSAR, and the Permanent Scatterer Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar technology (PS-InSAR), which was proposed by A. Ferretti, C. Prati, and F. Rocca [1,31]. TS-InSAR reduces the atmospheric decorrelation, the estimation of the topographic phase, and other limitations of conventional InSAR, and improves the time and space resolution. Therefore, TS-InSAR technologies has been widely used in the monitoring of urban surface deformation [32,33].
Nanchang City is located in Jiangxi Province, China, at the confluence of the Ganjiang River and the Fuhe River. It is a typical alluvial plain. Nanchang City can be roughly divided into three areas, namely the central urban area, the ecological agriculture area, and the natural area. The central urban area is the main area of Nanchang’s urbanization development in recent years, and there have been many surface collapses caused by subway construction and operation. According to reports, in May 2016, Nanchang City Subway Line 2 experienced a pavement collapse caused by a surge of water and sand; in July 2018, the Nanchang City Subway shield construction caused a 10 square meter collapse near Qingshan Lake. Moreover, Nanchang City is located at the confluence of the Ganjiang River and Fuhe River, which is a typical alluvial plain. Changes in the water level of the Ganjiang River are affected by local precipitation. The increase in precipitation has promoted the increase in surface water. Sufficient surface water is added to the groundwater, causing the groundwater levels to rise. The raised groundwater levels reduce the stress between the groundwater and the ground and raises the ground surface. When the amount of precipitation is low, resulting in insufficient groundwater replenishment, the drop in the groundwater table increases the stress between the groundwater and the ground, resulting in land subsidence [34,35]. Monitoring large-scale surface deformation over a long period of time, analyzing the temporal and spatial evolution of areas with large subsidence levels, and analyzing the impact of natural environment and human activities on surface deformation is more conducive to local government management of cities [36]. Most of the current research on surface deformation in Nanchang is based on geological data, combined with the spatial distribution and magnitude of experimental processing results, to speculate on the influencing factors of surface deformation [37,38,39,40]. However, there is uncertainty in inferring influencing factors only from spatial distribution and magnitude. Considering the period, this study further determines the influencing factors of surface deformation.
Based on the SBAS and PS-InSAR technologies, this study uses the Senitinel-1A satellite image to obtain the surface deformation time-series of Nanchang City. The influence of natural topography, precipitation, human activities, and other factors on the surface deformation of Nanchang City was revealed, and the evolution of dangerous subsidence areas was analyzed and combined with external data. The study consists of four parts: (1) using SBAS and PS-InSAR techniques to obtain long-term surface deformation values; (2) multi-angle mutual verification of the deformation results to ensure the reliability of InSAR results; (3) use of wavelet analysis and grey correlation analysis to evaluate the degree of correlation between precipitation and surface deformation; and (4) combining the external data to analyze the temporal and spatial evolution of subway lines in areas with large deformation amplitudes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Nanchang, located in the north of central Jiangxi Province, is an important central city in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River in China. It covers an area of about 7402.36 square kilometers. Its geographic location is shown in Figure 1. Nanchang City is located in the alluvial plain of the lower reaches of the Ganjiang River and the Fuhe River, and the terrain is high in the west and low in the east. The main urban area in the central part is mostly soft siltstone, with soft and fragile soil layers [41,42]. The northeast region is relatively flat, while the northwest region is hilly. The region has subtropical humid monsoon climate, with an annual precipitation of 1600–1800 mm and a well-developed water system. At the same time, as an important transportation hub connecting the economic zone on the west bank of the Straits, the Pearl River Delta, and the Yangtze River Delta, Nanchang has experienced rapid urbanization and transportation development in recent years.
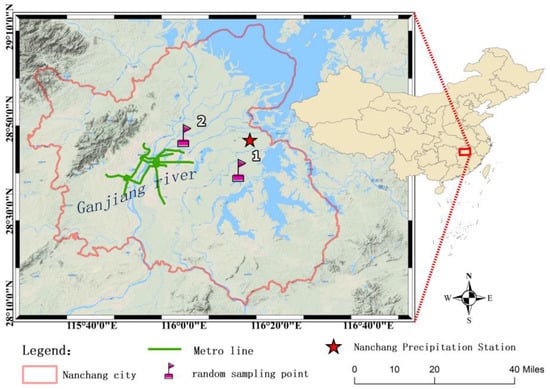
Figure 1.
Location of Nanchang City.
2.2. Data Sources
The data used in this study are: the SAR data set of the European Space Agency Earth Observation Satellite Series Sentinel-1, the 30-m spatial resolution ALOS World 3D 30 m DEM provided by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency, the Precise orbital data provided by Copernicus POD Service, the optical image of the sky map, and the American Institute of Physics provided global regional rainfall data.
As shown in Figure 2, the area of Nanchang City occupies the coverage of two radar images. Therefore, we selected 50 Sentinel-1A SLC images from 25 time-series from January 2019 to January 2021. The study used ascending-orbit SAR data with relative orbit number 40.
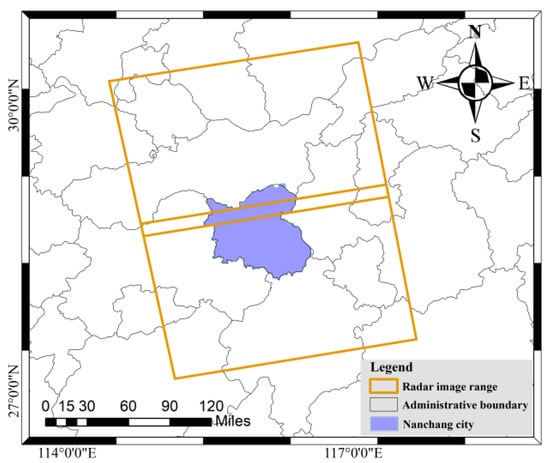
Figure 2.
Radar image coverage. The yellow border is the coverage of a single radar image.
The 30m DEM collected by the Panchromatic Stereo Mapper on the Japanese ALOS satellite using the L-band was used to remove the topographic phase and geocoding during the research process. The higher the resolution of the DEM, the fewer the data hole regions. The use of a high-resolution DEM enables better removal of the topographic phase from the interferogram. The Copernicus POD Service provides Precise orbit data for image co-registration and interferogram generation, avoiding large residual fringes in the interferogram generation.
To analyze and more intuitively understand the main causes of surface deformation in Nanchang, we downloaded the corresponding time series of precipitation data sets from the American Institute of Physics, and downloaded the optical images of the relevant areas in the map software (GGGIS).
2.3. Technical Method
2.3.1. Technical Process
As shown in Figure 3, the whole study consists of three main steps: (1) using InSAR technology to obtain the deformation results of long time-series in the study area and carry out cross-validation to prove the reliability of the method; (2) the time-series analysis, grey correlation degree, and wavelet analysis method are used to evaluate the correlation degree between precipitation and settlement area; and (3) based on the external data and the deformation profile along the subway calculated by the InSAR results, the temporal and spatial evolution process of the area with large settlement along the Nanchang subway is analyzed.
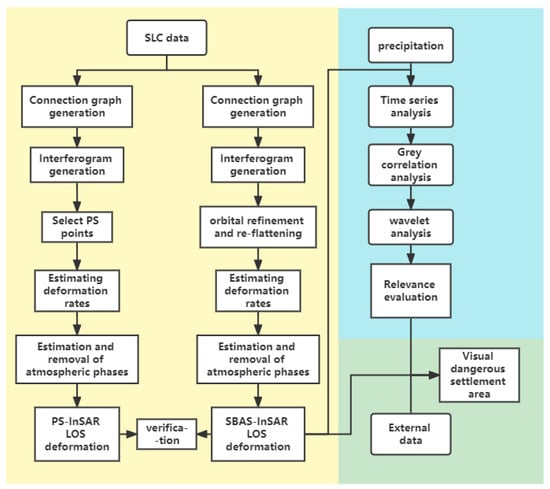
Figure 3.
Flowchart of the proposed methodology.
2.3.2. InSAR Technology
PS-InSAR and SBAS are two common TS-InSAR technologies. The basic principles of the two are as follows:
The analysis object of PS-InSAR technology is the Permanent Scatterer (PS), which still maintains high coherence over a long time interval and is less affected by the atmosphere [43]. The processing of PS-InSAR consists of six steps: (1) Select the master image to pair with other images to generate the connection graph; (2) differential interferometry for all interferometric pairs is performed, including registration, interferogram generation, amplitude dispersion index calculation, etc; (3) select PS points based on the amplitude departure index; (4) the estimation of deformation rate and residual elevation information from all differential interferograms using a linear model; (5) atmospheric phase removal using temporal high-pass filtering and spatial low-pass filtering; and (6) geocoding to obtain line-of-sight topographic variables is done [44].
The processing of SBAS consists of six steps: (1) Generate the connection graph based on the set values of the temporal and spatial baselines to divide multiple SAR images of the same study area into multiple subsets; (2) interferogram generation, including removal of flattening and topographic effects, filtering, and phase unwrapping is performed [45]; (3) select high-coherence points for orbital refinement and re-flattening; (4) estimating deformation rates using Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) is performed; (5) the estimation and removal of atmospheric phases using spatial low-pass filtering and temporal high-pass filtering is done; and (6) geocoding to obtain line-of-sight topographic variables is done [46].
The InSAR processing software used in this study is SARscape. In SBAS data processing, to ensure the accuracy of the data and the coordination of space, the time baseline threshold used is 120 days and the space baseline threshold is 45%. A total of 86 pairs of interference pairs are obtained. The connection graph of SBAS technology is shown in Figure 4a. To better connect a group of high-coherence pixels and other isolated high-coherence regions, the selected phase unwrapping method is Delaunay MCF. Nanchang City has dense hydrology and vegetation coverage. After a large number of experiments, the phase unwrapping coherence threshold of 0.35 is used, and pixels with coherence values smaller than 0.35 were not unwrapped, which ensures the reliability of the deformation results and the spatial distribution density.
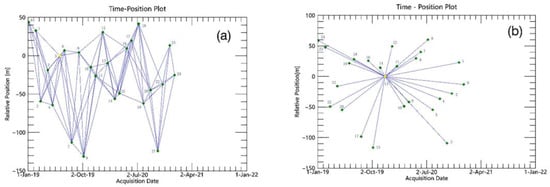
Figure 4.
Time space baseline connection diagram. The numbers 0–24 in the graph represent time series. (a) SBAS connection diagram. (b) PS-InSAR connection diagram.
In the process of PS-InSAR data processing, the image of 5 December 2019 is automatically selected as the main image according to the influence of time baseline, spatial baseline, and Doppler center. The connection graph of PS-InSAR technology is shown in Figure 4b, and the yellow dot is the main image.
The SBAS technique uses the Delaunay MCF phase unwrapping method to smooth the elevation information of the entire surface, while the phase unwrapping of PS InSAR preserves the elevation information by analyzing the permanent scatterers separately. Therefore, the elevation accuracy obtained by PS-InSAR in this study will be higher than that of SBAS [47,48]. However, similar to the surface settlement caused by the change in groundwater level, it belongs to a non-linear deformation. The PS-InSAR technique does not recognize the non-linear motion of the PS point, which is considered to be the atmospheric contribution [49]. In addition, the results obtained by PS-InSAR are discrete points, while SBAS is used to obtain spatially continuous deformation results. The applicability of SBAS technology will be higher, therefore, in the subsequent time series analysis, this study uses the results of SBAS for analysis and description.
2.3.3. Grey Relational Analysis Method
The grey relational analysis method is an analytical method that can evaluate the relative strength of an item affected by other factors in a grey system. This method does not require the size of the sample and whether the sample is regular or not. Before the grey relational analysis, the evaluation quantity needs to be dimensionless to reduce the difference of the absolute value of the data. Each item is brought into the following Formula (1) to obtain the grey relational coefficient. The average value of the relational coefficient of each sequence is the gray relational degree between the sequence and the reference sequence.
2.3.4. Wavelet Analysis Method
The wavelet analysis is based on a suitable wavelet function, which calculates the wavelet coefficients through wavelet transformation and gradually refines the signal to obtain any details of the signal, and then analyzes the time-frequency variation characteristics of the signal time-series. Wavelet analysis is particularly suitable for dealing with signals whose properties change with time uncertainty. This study uses wavelet variance to analyze the periodic components of surface deformation and precipitation changes in the study area.
The Cmor wavelet used in this study is a complex morlet wavelet, and its expression is shown in Formula (2).
where is the bandwidth parameter and is the wavelet center frequency.
After scaling and shifting the generating function , the obtained wavelet sequence is shown in Formula (3).
where is the subwavelet, a is the scaling factor, and b is the translation factor.
In this study, the time-series is discrete data, and it is represented by a function, f(kt), then its continuous wavelet transform coefficient is shown in Formula (4).
where is the wavelet transform coefficient, f(kt) is a signal, and is the complex conjugate of .
The square value of the wavelet transform coefficient is integrated in the range of b, and the wavelet variance is obtained as shown in Formula (5), which can intuitively reflect the main time scale of the signal.
2.3.5. Kriging Interpolation
Kriging interpolation is an interpolation method based on the theory that the spatial property z has the same distribution at each point. This means that for any point (x, y), the value z(x, y) of the point is composed of the regional average value c and the random deviation R(x, y) of the point, which can be expressed by Formula (6).
where R(x, y) represents the deviation at point (x, y), and its mean is 0.
To obtain the change of precipitation in Nanchang in 2020 relative to that in 2019, this study obtained the precipitation data around Nanchang provided by American Physical Research with a spatial resolution of 2.5°. According to the Kriging interpolation method, the precipitation data of Nanchang in 2019 and 2020 were obtained, respectively. Through the difference, the change in precipitation in Nanchang in 2020 relative to that in 2019 was obtained.
3. Results and Accuracy Assessments
3.1. InSAR Results
The line of sight deformation rates of Nanchang retrieved by InSAR technology is shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6, respectively. A positive value of the rate indicates that the surface deformation trend is upward along the radar line of sight, and a negative value indicates that the surface deformation trend is downward along the radar line of sight. The deformation results obtained by using SBAS technology range from −56.5 mm/year to 51.9 mm/year. The range of deformation results obtained by using PS-InSAR technology is between −24.3 mm/year and 24.4 mm/year.
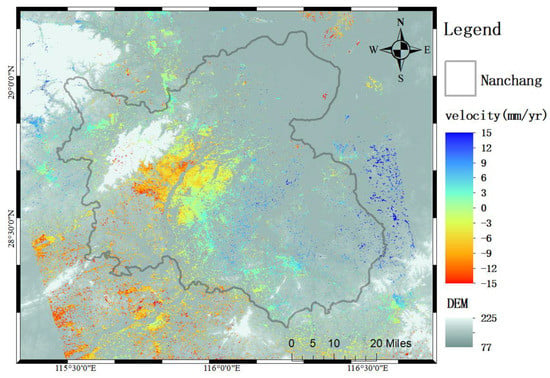
Figure 5.
The subsidence rate of Nanchang City is inverted by the SBAS method. The base map is DEM.
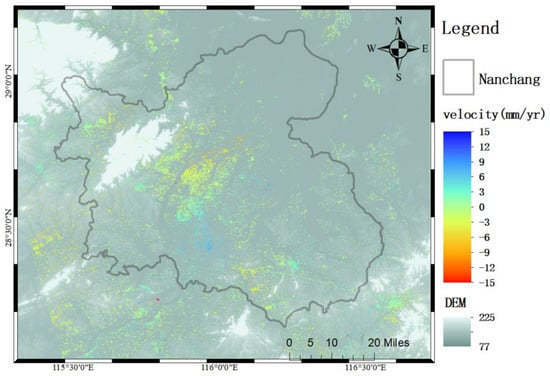
Figure 6.
The subsidence rate of Nanchang City is inverted by the PS-InSAR method. The base map is DEM.
It is worth noting that this study converts the vector point velocities of PS-InSAR to raster velocities. The number of PS points obtained in this study is small. The output resolution of Figure 5 and Figure 6 is 100 dpi. If 500 dpi is used for the output, the PS-InSAR results in Figure 6 will show less coverage.
The results of SBAS and PS-InSAR indicate that in the two years from 2019 to 2020, the uneven surface deformation areas in Nanchang are mainly distributed in the three areas A, B, and C, as shown in Figure 7. The deformation rate in Figure 7 is the result of SBAS.
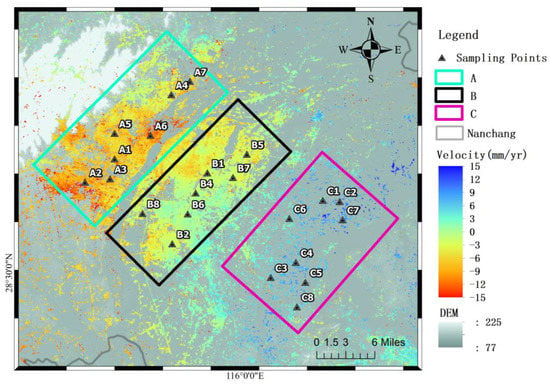
Figure 7.
The uneven surface deformation area in Nanchang City. The colour boundaries are three unevenly deformed regions. The black triangles in the frame are sampling points.
3.2. Accuracy Assessment of InSAR Results
3.2.1. Spatial Consistency
It can be seen from Figure 5 and Figure 6 that the area of surface subsidence and uplift in Nanchang calculated by the two methods are similar, both of which show the phenomenon of slowly changing from subsidence to uplift from the northwest to the southeast. The subsidence areas obtained by the two technologies are mainly concentrated in the urban areas on both sides of the Ganjiang River, while the uplifted areas are mainly concentrated in the ecological agriculture area in the southeast of Nanchang City.
3.2.2. Time-Series Consistency
The time-series deformation of the points with the same name of the two technologies is compared and analyzed, as shown in Figure 8. The results obtained by SBAS and PS-InSAR have similar cumulative deformations at the end.
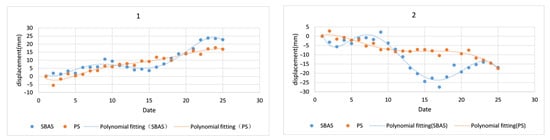
Figure 8.
Time-series diagram of SBAS and PS-InSAR technology. (1,2) are the time-series deformation diagram of the average value of ten pixels around two random sampling points.
3.2.3. Correlation
From the distribution range of the deformation rate results in Figure 5 and Figure 6, it can be preliminarily seen that the two techniques are in good agreement. To further verify the reliability of SBAS and PS-InSAR, this study uniformly extracted 1000 points of the same location in SBAS and PS-InSAR. Combining the annual average deformation rates calculated by the two technologies, the correlation diagram shown in Figure 9 is obtained. The points in the figure are evenly distributed, and the correlation coefficient R between the two technologies is 0.74, which has a strong correlation.
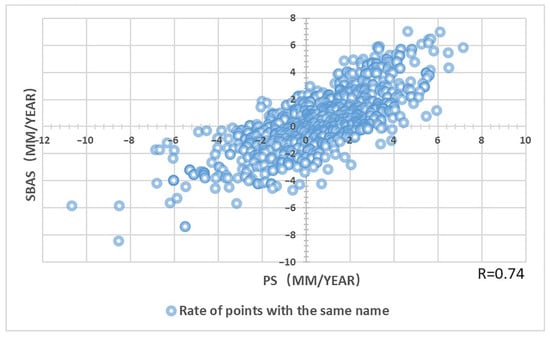
Figure 9.
The correlation between PS-InSAR and SBAS points of the same name. There are 1000 points of the same location.
3.2.4. Normal Curve Analysis
By performing the difference statistics for all points with the same location the two technologies are obtained, and their normal curves can be calculated to obtain a normal distribution diagram, as shown in Figure 10. It can be seen from the figure that the difference between the measured values of SBAS and PS-InSAR basically conform to the normal distribution, that is, the results obtained by SBAS and PS-InSAR have strong consistency.
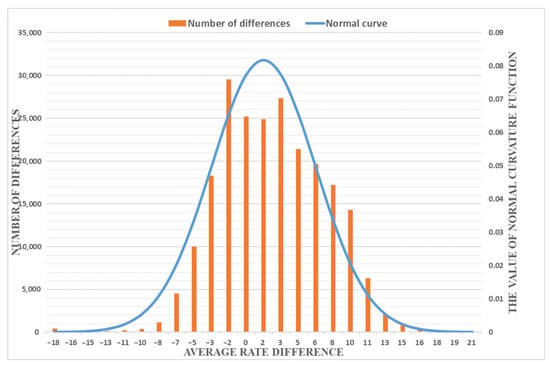
Figure 10.
Normal curve statistics of PS-InSAR and SBAS results. The orange histogram is the difference of the points with the same location, and the blue curve is the normal curve.
3.2.5. Error Analysis
The accuracy of InSAR results is further assessed using error analysis. Based on the same location points of PS-InSAR and SBAS annual average deformation results, the accuracy is evaluated by using the two indexes of mean error and average error in Formulas (7) and (8). The obtained medium error is ±4.853 mm/year, and the average error is ±3.847 mm/year. It can be seen that InSAR technology has good reliability in relative accuracy.
In summary, the annual average displacement map obtained by the SBAS and PS-InSAR methods have strong consistency, which proves the reliability of the monitoring results of the two methods.
3.3. Deformation Results along Metro Lines
The distribution of the Nanchang Subway is shown in Figure 11. Area A and area B are the main areas of Nanchang City’s urban construction, including all subway operating lines in Nanchang City. Figure 11b–e represent the deformation rate diagrams within the 1-km buffer zone around Metro Line 1, Line 2, Line 3, and Line 4, respectively.
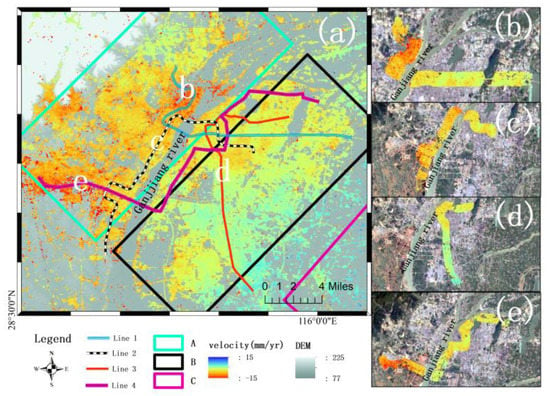
Figure 11.
1000-m buffer zone along Nanchang Metro. (a) Distribution map of four subway lines in Nanchang. (b) Metro Line 1. (c) Metro Line 2. (d) Metro Line 3. (e) Metro Line 4.
3.3.1. Metro Line 2
The displacement around the station of Metro Line 2 north of Ganjiang River is shown in Figure 12a. The cumulative deformation values of these subway stations are shown in Figure 12b, where it can be seen that the subsidence of Wolong Mountain Station is larger than that of its neighboring National Sports Center Station and Lingbei Station. Figure 12c,d are historical optical images of 9 January 2019 and 13 January 2021 that were downloaded from World Imagery (https://livingatlas.arcgis.com/wayback, accessed on 6 January 2022), respectively.
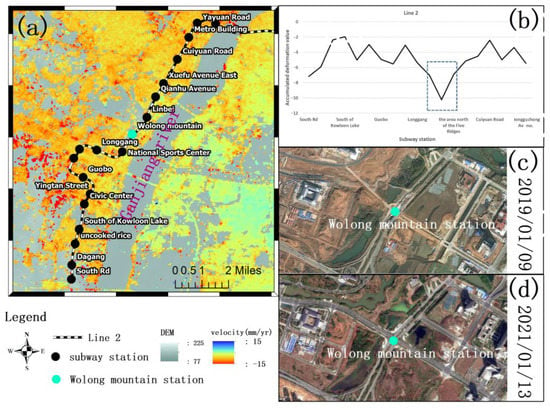
Figure 12.
Cumulative deformation profile view of Metro Line 2 stations. (a) The location of the station to the north of Ganjiang River in Metro Line 2. (b) Cumulative shape variables of stations north of Ganjiang River in Metro Line 2. (c) 9 January 2019 Optical History Image. (d) 13 January 2021 Optical History Image.
3.3.2. Metro Line 4
The displacement around the station of Metro Line 4 north of Ganjiang River is shown in Figure 13a. The cumulative deformation values of these subway stations are show in Figure 13b, where it shows that the cumulative subsidence of Baima Mountain Station, Yufeng Street Station, Huangxi Station, Zhongbao Station, and Lizhuang Mountain Station over the past two years is between −11.5 mm and −15 mm. The accumulated subsidence of West Railway Station South Square Station, Huaiyushan Avenue Station, and Anfeng Station after Lizhuang Mountain Station are between −5.5 mm and −6.5 mm. This indicates that there is obvious uneven subsidence between Lizhuang Mountain Station and West Station South Square Station. The historical images of the two stations and surrounding areas are shown in Figure 13c,d.
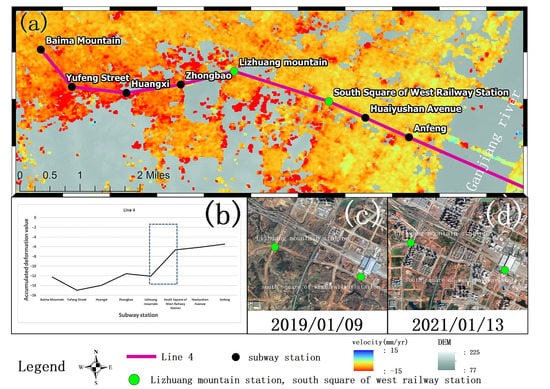
Figure 13.
Cumulative deformation profile view of Metro Line 4 stations. (a) The location of the station to the north of Ganjiang River in Metro Line 4. (b) Cumulative shape variables of stations north of Ganjiang River in Metro Line 4. (c) 9 January 2019 Optical History Image. (d) 13 January 2021 Optical History Image.
3.4. Time-Series Results of Precipitation and Surface Displacement
To analyze the impact of precipitation on surface deformation, we selected the global regional rainfall data provided by the American Institute of Physics and downloaded the monthly average precipitation of Nanchang Station from January 2019 to January 2021 for statistics, and obtained, as shown in Figure 14, the monthly mean precipitation—indicated by the black broken line. It can be clearly seen from the figure that in the past two years, the rainfall in Nanchang has shown seasonal periodic changes, and the annual rainfall in 2020 is more than that in 2019.
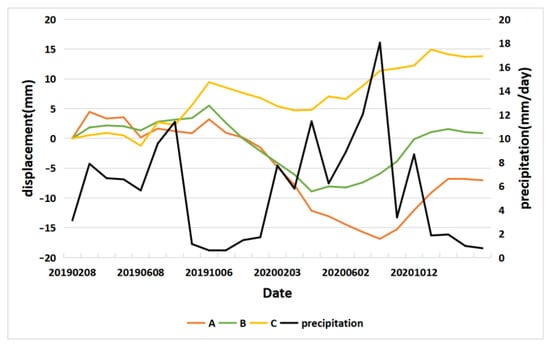
Figure 14.
Time-series analysis graph. A–C represent the time series averages of the sampling points for each region in Figure 7.
In the three regions A, B, and C in Figure 7, the sampling points represented by the black triangles in the figure are selected. The average time-series surface deformation of the sampling points in areas A, B, and C are shown as orange, green, and yellow dashes in Figure 14. It can be seen that the surface deformation changes with the change of precipitation. From July to October 2019, when the precipitation dropped significantly, the surface deformation showed a sinking signal. When the precipitation increased significantly from January to August 2020, the surface deformation showed an upward trend. This shows that in regions A, B, and C with different deformation signals, most of the time-series deformation trends of the surface are still very similar.
3.5. Results of Grey Relational Analysis
As shown in Figure 7, eight sampling points are randomly selected in the three regions, A, B, and C, respectively. The time-series surface deformation of the sampling points is processed as dimensionless, and the grey relational analysis is carried out with the rainfall, respectively. The closer the gray correlation degree is to 1, the better the correlation between the two time-series. The analysis results are shown in Table 1, and the grey relational degree is as high as 0.89 or more. In the case of removing the linear trend of surface deformation, its grey correlation with precipitation has increased.

Table 1.
Grey relational degree of each sampling point.
3.6. Results of Wavelet Period Analysis
As shown in the contour plot of the wavelet coefficient real-part of the precipitation in Figure 15a and the real-part contour plot of the wavelet coefficient at the sampling point A1 in Figure 15b, the precipitation and sampling point A1 have a maximum time around the 24th time scale. Moreover, the periodicity of the span and the energy intensity changes the most on the 24th time scale. Consequently, the first main period is on the 24th time scale. In the same way, the periodicity with the second largest time span is around the 9th time scale, and the energy intensity change is the largest on the 9th time scale, so the second main period is on the 9th time scale. In the variance diagram of Figure 15c, the first and second maximum values of precipitation and sampling point A1 are on the 24th and 9th time scales, respectively, which confirms the accuracy of the time scale of the main cycle. In the energy line chart at the 24th time scale in Figure 15d, both sampling point A1 and the period of precipitation are 16 time-series’, about one year. In the energy line chart of the 9th time scale in Figure 15e, the period of both sampling point #2 and precipitation is 6 time-series’, which is about five months.
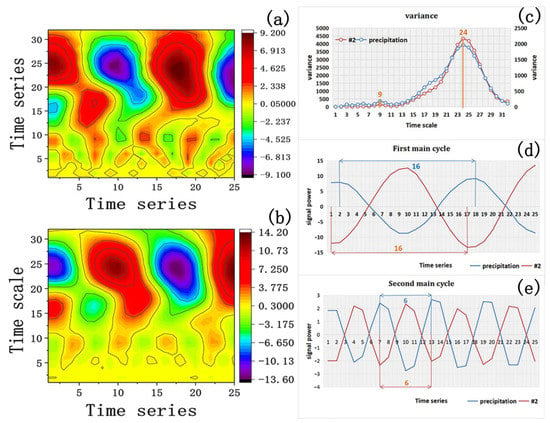
Figure 15.
Wavelet periodic analysis. (a) Wavelet real-part periodic contour map of precipitation; (b) Sampling point A1 wavelet real-part periodic contour map; (c) Precipitation and sampling point A1 variance map; (d) Energy line chart of the 24th time span; (e) Energy line chart of the 9th time span.
3.7. Kriging Interpolation
The change of precipitation in Nanchang in 2020 relative to 2019 is shown in Figure 16. It can be seen from the figure that the precipitation in Nanchang in 2020 is higher than that in 2019.
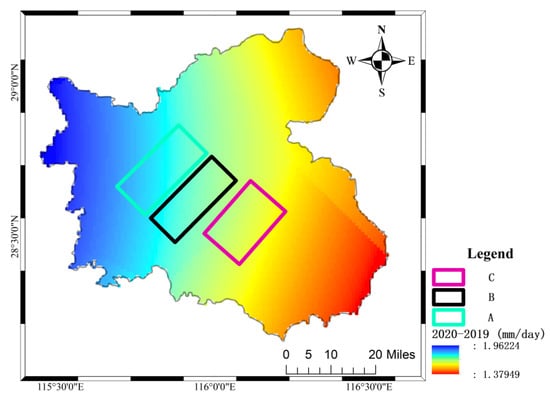
Figure 16.
Changes in the precipitation of Nanchang City in 2020 relative to 2019.
4. Discussion
4.1. Seasonal Water Level Changes
From the time-series results of precipitation and surface displacement, we can see that the trend of surface deformation in regions A, B, and C is similar to that of precipitation. In order to further illustrate the relationship between precipitation and surface deformation, the grey relational analysis method is used. In the case of removing the linear trend of surface deformation, its grey correlation with precipitation has increased, indicating that the similarity of time-series trends in regions A, B, and C has a strong correlation with precipitation.
To prove the accuracy of the high grey relational degree obtained by the grey relational analysis method, the wavelet analysis method was used to mine the periodic information of surface deformation and precipitation. It can be seen from Figure 15 that the surface deformation and precipitation of sampling point A1 have the same periodic signal, which proves the reliability of the grey correlation analysis and proves that the surface deformation of the time-series of regions A, B, and C is affected by precipitation.
4.2. Influence of Groundwater
Area C is dominated by agricultural farming, and urban construction is sparse. Due to this, it is unlikely that the large-scale surface deformation in this area is mainly caused by engineering construction. However, the agricultural irrigation water in this area is mainly pumped groundwater. Therefore, the surface deformation may be caused by the change in groundwater level. The altitudes of the three areas, A, B, and C, decrease one by one. As a result, most of the surface water will converge in area C of Nanchang City.
In 2020, Mo Ying et al. used Sentinel-1A data from January 2016 to July 2018 to obtain subsidence signals in the ecological agriculture area in the southeast of Nanchang City through SBAS and PS-InSAR technologies [50]. We downloaded and got statistics for precipitation data from 2016 to 2020, as shown in Figure 17, where the value in the colored dotted box is the average daily precipitation value during the year. From the figure, it can be seen from 2016 to 2018 that the precipitation in Nanchang City has been decreasing year by year. The lack of surface water and the need for agricultural irrigation led to a drop in groundwater levels in this ecological agricultural area from 2016 to 2018, which caused surface subsidence.
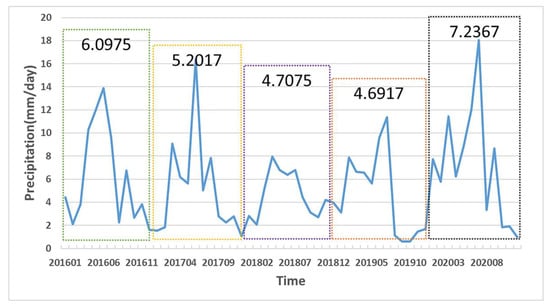
Figure 17.
Precipitation at Nanchang Station from 2016 to 2020. The number in the box is the average annual precipitation.
From 2019 to 2020, the increase in precipitation brought sufficient surface water, which can be continuously replenished to groundwater, and alleviated the subsidence caused by the lack of groundwater before. Therefore, area C has a large-scale uplift signal. The experimental results calculated by Mo Ying are consistent with our results and analysis. Therefore, the surface deformation of area C is mainly affected by the groundwater level, and from 2019 to 2020, the irrigation water is less than the groundwater replenishment, thereby causing the surface deformation to rebound and showing an uplift trend.
4.3. The Impact of Urban Construction
As shown in Figure 7 and Figure 16, the increased precipitation amplitudes in areas A, B, and C decreased in turn, while the deformation signals in areas A, B, and C gradually changed from subsidence to uplift. The eastern part A and the middle B area of Nanchang are places with high rainfall and more adequate groundwater replenishment, but the subsidence in this area is larger. After investigation, areas A and B are areas with more frequent urban construction. During the construction process, a large amount of groundwater was extracted to avoid the working principle of underwater operations, resulting in a drop in the groundwater level, compression of the above-ground soil layers, and surface subsidence.
Areas A and B are the main areas of the Nanchang Subway, and it is necessary to evaluate the stability of the subway lines in this area. It can be seen from Figure 11a that the subsidence along the subway line is mainly concentrated in the north of the Ganjiang River. The reason for this phenomenon is that the soil around the Ganjiang River is relatively soft, and the urban construction of Nanchang City in the past two years has also been mainly concentrated in the newly-built areas north of the Ganjiang River. The more frequent the construction of the city, the greater the subsidence of the surface. Therefore, a series of maintenance needs to be carried out in the cross-river part of the subway line to prevent the uneven deformation of the subway facilities from breaking.
4.3.1. Metro Line 2
It can be seen from the optical images in Figure 12c,d that during the past two years, the surrounding areas are being greened while the new roads are being built around the Wolongshan Station. The increase in plant coverage results in spatial decoherence of the SBAS imagery and a decrease in the coverage of the extracted deformation results. The construction of highways requires an anhydrous working environment, and the extraction of groundwater aggravates the surface subsidence. Therefore, the magnitude of the surface subsidence of Wolongshan Station will be relatively large, and the coverage of the deformation area extracted by SBAS is relatively small.
4.3.2. Metro Line 4
According to reports, the first phase of Nanchang Metro Line 4 starts at Baima Mountain Station and ends at Yuweizhou Station. The length of the line is 39.60 km. The section from Baima Mountain Station to the western part of Lizhuang Mountain is an elevated line with a length of 5.49 km. The rest are underground lines, about 33.91 km. Each section of the elevated section of Metro Line 4 completed the box girder work from July 2020 to October 2020. The construction time is within the monitoring scope of this study. Thus, the substantial subsidence from Baima Station to Lizhuang Mountain Station may be related to the construction of the viaduct. To prevent the subsequent construction of subways and viaducts from having a significant impact on ground subsidence, it is necessary to increase the maintenance structures from Lizhuang Mountain Station to West Station South Square Subway Station, and continue to monitor the surface deformation in this area.
5. Conclusions
Using SBAS technology and PS-InSAR technology, we interfered with 25 Sentinel-1A radar images of Nanchang from January 2019 to January 2021 and obtained the surface deformation rate map within this time span. The results obtained by the two techniques were cross-validated from various perspectives to prove the reliability of the results. The results of SBAS show that the surface deformation in Nanchang ranges from −56.5 mm/year to 51.9 mm/year.
The relationship between deformation and precipitation is refined by using grey correlation analysis and wavelet period analysis. The research shows that the change periods of the three ABC regions with different deformation variables are all affected by the periodic changes of precipitation. Area A is located to the north of the Ganjiang River where the clay layer is thick, and urban construction compresses the clay layer and causes settlement. Area B has a thin underground clay layer, small demand for agricultural irrigation, and the first and second main periods of deformation are the same as changes in precipitation, so the periodic change of precipitation is the main factor for surface deformation in area B. Area C is located in the eco-agricultural area in the southeast of Nanchang City, where the demand for irrigation is large and the increase in precipitation replenishes the groundwater, thereby causing the surface to uplift.
The study also identified several areas of uneven subsidence along the subway north of the Ganjiang River, where dangerous subsidence may exist. Further investigations are needed to increase the understanding of these subsidence factors-induced subsidence in order to avoid ground collapse events in cities.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.H. and B.C.; methodology, B.H.; software, Z.Z.; validation, J.Y. and J.N.; formal analysis, B.C.; investigation, J.Y.; resources, B.H.; data curation, B.C.; writing—original draft preparation, B.C.; writing—review and editing, B.H.; visualization, J.N.; supervision, X.D.; project administration, B.H.; funding acquisition, J.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is funded by the National Key R & D Program of China (2017YFA0603103), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41204012, 41974009, 41431070, 41590854 and 41674006), the Science and Technology Plan Project in Fujian Province under grant (2017Y3004), the Key Research Program of Frontier Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) (Grant Nos. QYZDB-SSW-DQC027 and QYZDJ-SSW-DQC042), the State Key Laboratory of Geodesy and Earth’s Dynamics Foundation of China under grant (SKLGED2020-2-3-E), project funded by Guangzhou Science and Technology planning program (202102080682).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Sentinel-1 satellite data is freely available from the European Space Agency (https://scihub.copernicus.eu/dhus/#/home, accessed on 20 January 2022). AW3D30DEM is freely provided by JAXA (https://www.eorc.jaxa.jp/ALOS/en/aw3d30/data/index.htm, accessed on 20 January 2022). The precipitation data were provided free of charge by the American Institute of Physics (https://psl.noaa.gov/data/gridded/index.html, accessed on 20 January 2022).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xinyu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, G.; Tian, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, S. Comprehensive framework for the integration and analysis of geo-environmental data for urban geohazards. Earth Sci. Inform. 2021, 14, 2387–2399. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.J.; Zhai, G.; Zhou, S.; Lu, Y.; Chen, W.; Liu, H. How Can Cities Adapt to a Multi-Disaster Environment? Empirical Research in Guangzhou (China). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, H.; Bürgmann, R.; Xu, X.; Fielding, E.; Liu, Z. Machine-Learning Characterization of Tectonic, Hydrological and Anthropogenic Sources of Active Ground Deformation in California. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2021, 126, e2021JB022373. [Google Scholar]
- Kemal, E.M.; Sultan, M.; Alakhras, K.; Sataer, G.; Gozi, S.; Al-Marri, M.; Gebremichael, E. Countrywide Monitoring of Ground Deformation Using InSAR Time Series: A Case Study from Qatar. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 702. [Google Scholar]
- Polcari, M.; Albano, M.; Montuori, A.; Bignami, C.; Tolomei, C.; Pezzo, G.; Falcone, S.; la Piana, C.; Doumaz, F.; Salvi, S.; et al. InSAR Monitoring of Italian Coastline Revealing Natural and Anthropogenic Ground Deformation Phenomena and Future Perspectives. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H. The past and present of super high-rise construction. Technol. Dev. Enterp. 2019, 3, 34–36. [Google Scholar]
- Editorial Department of China Journal of Highway and Transport. Review on China’s Bridge Engineering Research: 2021. China J. Highw. Transp. 2021, 34, 1–97. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Wang, Y. Long-Term Ground Settlements over Mined-Out Region Induced by Railway Construction and Operation. Sustainability 2019, 11, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klug, D.R. Underground construction industry has been on wild ride recently. Min. Eng. 2010, 62, 1–2. Available online: https://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-foreign_other_thesis/020411812878.html (accessed on 4 January 2021).
- Massimiliano, A.; Fausto, G.; Mauro, R. Scaling properties of rainfall induced landslides predicted by a physically based model. Geomorphology 2014, 213, 38. [Google Scholar]
- Chuanhao, P.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, K.; Jiang, Y.; Hao, L.; Liu, J.; Chen, W.; Kou, P. Characterizing the Topographic Changes and Land Subsidence Associated with the Mountain Excavation and City Construction on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1556. [Google Scholar]
- Gudjónsdóttir, S.R.; Ilyinskaya, E.; Hreinsdóttir, S.; Bergsson, B.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Michalczewska, K.; Aiuppa, A.; Óladóttir, A.A. Gas emissions and crustal deformation from the Krýsuvík high temperature geothermal system, Iceland. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2020, 391, 106350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Catalano, S.; Pavano, F.; Romagnoli, G.; Tortorici, G. Late Quaternary tectonics and active ground deformation in the Catania urban area (eastern Sicily): New constraints from a geological investigation. Tectonophysics 2017, 712–713, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardizzone, F.; Rossi, M.; Calò, F.; Paglia, L.; Manunta, M.; Mondini, A.C.; Zeni, G.; Reichenbach, P.; Lanari, R.; Guzzetti, F. Preliminary analysis of a correlation between ground deformations and rainfall: The Ivancich landslide, central Italy. In Proceedings of the SAR Image Analysis, Modeling, and Techniques XI, Prague, Czech Republic, 26 October 2011; Volume 8179. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, K.; Xu, P.; Cao, C.; Zheng, L.; Liu, Y.; Dong, X. Preliminary Identification of Geological Hazards from Songpinggou to Feihong in Mao County along the Minjiang River Using SBAS-InSAR Technique Integrated Multiple Spatial Analysis Methods. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Ding, Q.; Zhang, L.; Wang, M.; Wang, Q. Analysis of Land Surface Deformation in Chagan Lake Region Using TCPInSAR. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.; Park, H.; Jeong, S. Settlement Behavior of Shallow Foundations in Unsaturated Soils under Rainfall. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakon, M.; Perissin, D.; Lazecky, M.; Papco, J. Infrastructure Non-linear Deformation Monitoring Via Satellite Radar Interferometry. Procedia Technol. 2014, 16, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, Y.; Xu, G.; Kaufmann, H.; Wang, J.; Ma, H.; Liu, T. Integration of InSAR and LiDAR Technologies for a Detailed Urban Subsidence and Hazard Assessment in Shenzhen, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldow, J.S. Monitoring Growth of the Daisetta, Texas Sinkhole with Terrestrial Laser Scanning, Close Range Digital Photography, and GPS. Houst. Geol. Soc. Bull. 2009, 51, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Hu, J.; Sun, Q. Estimating Actual 2D Ground Deformations Induced by Underground Activities with Cross-Heading InSAR Measurements. J. Sens. 2017, 2017, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gutiérrez, F.; Benito-Calvob, A.; Domingo Carbonela, G.D.; Sevil, J.; Guerrero, J.; Martínez-Fernández, A.; Karamplaglidisb, T.; García-Arnay, Á.; Fabregata, I. Review on sinkhole monitoring and performance of remediation measures by high-precision leveling and terrestrial laser scanner in the salt karst of the Ebro Valley, Spain. Eng. Geol. 2019, 248, 283–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eboigbe, M.A.; Kidner, D.B. Assessment of the precision of a smart-phone pole photogrammetry for a second-order cliff surface deformation studies. ISPRS-Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2020, XLIV-M-2-2020, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Xie, T.; Yang, X. Application of Ground-based Three-dimensional Laser Scanning in Landslide Monitoring. Resources 2020, 5, 131–134. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, P.; Wang, W.; Zhang, B.; Wang, J.; Shi, G.; Huang, G.; Chen, F.; Jiang, L.; Lin, H. Remotely sensing large- and small-scale ground subsidence: A case study of the Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area of China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 232, 111282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Li, Z.; Hu, J. Research Progress and Methods of InSAR for Deformation Monitoring. Acta Geod. Et Cartogr. Sin. 2017, 46, 1717–1733. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Q.; Perissin, D.; Lin, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W. Subsidence Monitoring of Tianjin Suburbs by TerraSAR-X Persistent Scatterers Interferometry. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 1642–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabu, D.; Small, D.; Schubert, A.; Hanssen, R.F. High-precision positioning of radar scatterers. J. Geod. 2016, 90, 403–422. [Google Scholar]
- Keiding, M.; Árnadóttir, T.; Jónsson, S.; Decriem, J.; Hooper, A. Plate boundary deformation and man-made subsidence around geothermal fields on the Reykjanes Peninsula, Iceland. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2010, 194, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Costantini, M.; Franceschetti, G.; Iodice, A.; Pietranera, L.; Rizzo, V. Use of differential SAR interferometry in monitoring and modelling large slope instability at Maratea (Basilicata, Italy). Eng. Geol. 2003, 68, 31–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, A.; Calò, F. A Review of Interferometric Synthetic Aperture RADAR (InSAR) Multi-Track Approaches for the Retrieval of Earth’s Surface Displacements. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bürgmann, R.; Rosen, P.A.; Fielding, E.J. Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry to Measure Earth’s Surface Topography and Its Deformation. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2000, 28, 169–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.R.; Shi, Z.H.; Cai, C. Soil erosion hazard evaluation—An integrated use of remote sensing, GIS and statistical approaches with biophysical parameters towards management strategies. Ecol. Model. 2009, 220, 1724–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, D.L.; Hudnut, K.W.; Ingebritsen, S.E.; Phillips, S.P.; Peltzer, G.; Rogez, F.; Rosen, P.A. Detection of aquifer system compaction and land subsidence using interferometric synthetic aperture radar, Antelope Valley, Mojave Desert, California. Water Resour. Res. 1998, 34, 2573–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A. A multi-temporal InSAR method incorporating both persistent scatterer and small baseline approaches. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huaqi, G.; Jierong, C.; Ting, L. Application of PS-InSAR in Surface Deformation Monitoring in Nanchang. Jiangxi Sci. 2019, 37, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, J.; Nie, Y.; Luo, Y.; Li, Y. Land Subsidence Monitoring in Nanchang Central City Based on SBAS-InSAR. Urban Geotech. Investig. Surv. 2019, 2, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Liu, F.; Tu, L. Study on surface deformation monitoring of Nanchang based on D-InSAR technology. Miner. Resour. Geol. 2019, 33, 546–550+556. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Xia, Y. Monitoring and Analysis of Land Subsidence Along Nanchang Metro Line Based on InSAR Technology. Beijing Surv. Mapp. 2019, 33, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, F.; Liu, X.; Huang, C.; Yuan, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, F. Hydrogeological features of water supply in city center of Nanchang City. J. Nanchang Inst. Technol. 2018, 37, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, P.; Li, X. Analysis of Engineering Geology, Hydrogeology and Geological Conditions along Rail Transit Lines in Nanchang City. Constr. Mater. Decor. 2017, 47, 231–232. [Google Scholar]
- Hooper, A.; Zebker, H.; Segall, P.; Kampes, B. A new method for measuring deformation on volcanoes and other natural terrains using InSAR persistent scatterers. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L23611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco, J.M.D.; Foumelis, M.; Stewart, C.; Hooper, A. Measuring Urban Subsidence in the Rome Metropolitan Area (Italy) with Sentinel-1 SNAP-StaMPS Persistent Scatterer Interferometry. Remote Sens. 2019, 2, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Usai, S. A least squares database approach for SAR interferometric data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, H.; Zhu, J.; Li, Z.; Ding, X. Ground Subsidence Monitoring in Mining Area Using DInSAR SBAS Algorithm. Acta Geod. Et Cartogr. Sin. 2011, 40, 52–58. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.S.; Kim, D.-J.; Kim, S.-W.; Won, J.-S.; Moon, W.M. Monitoring of urban land surface subsidence using PSInSAR. Geosci. J. 2007, 11, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, H. Complex Urban Infrastructure Deformation Monitoring Using High Resolution PSI. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C. Nonlinear subsidence rate estimation using permanent scatterers in differential SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 2202–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ying, M.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, L. Land Subsidence Monitoring of Nanchang Area Based on Sentinel-1A Using Time Series InSAR Technology. J. Geod. Geodyn. 2020, 40, 270–275. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).