Multi-Scenario Simulation of Ecosystem Service Values in the Guanzhong Plain Urban Agglomeration, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Ecological Response to Land Use Changes
2.2. Land Use Simulation
2.3. Quantification of Ecosystem Service Values
3. Materials and Methods
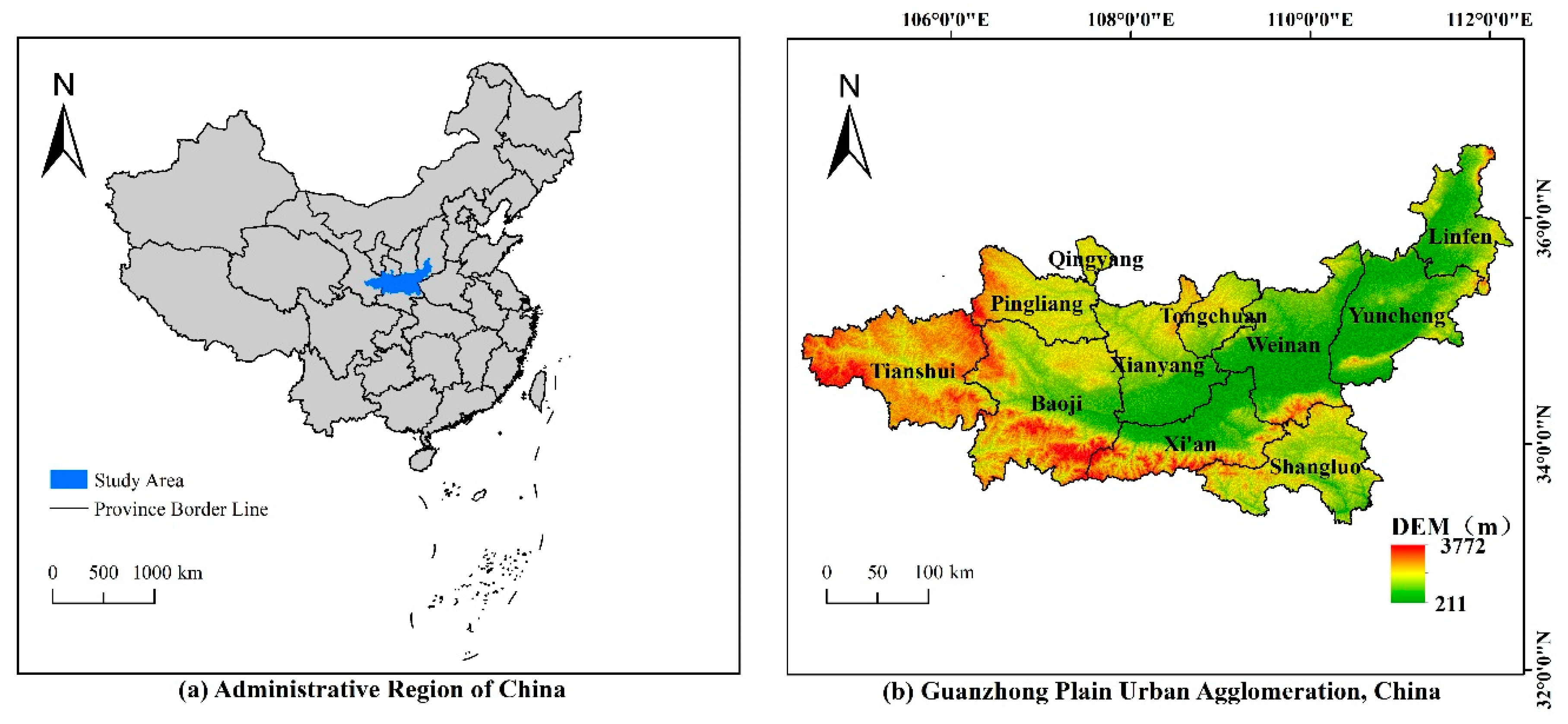
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Data Sources
3.3. Methodology Flow
3.4. Future Land Use Simulation
3.4.1. PLUS Model
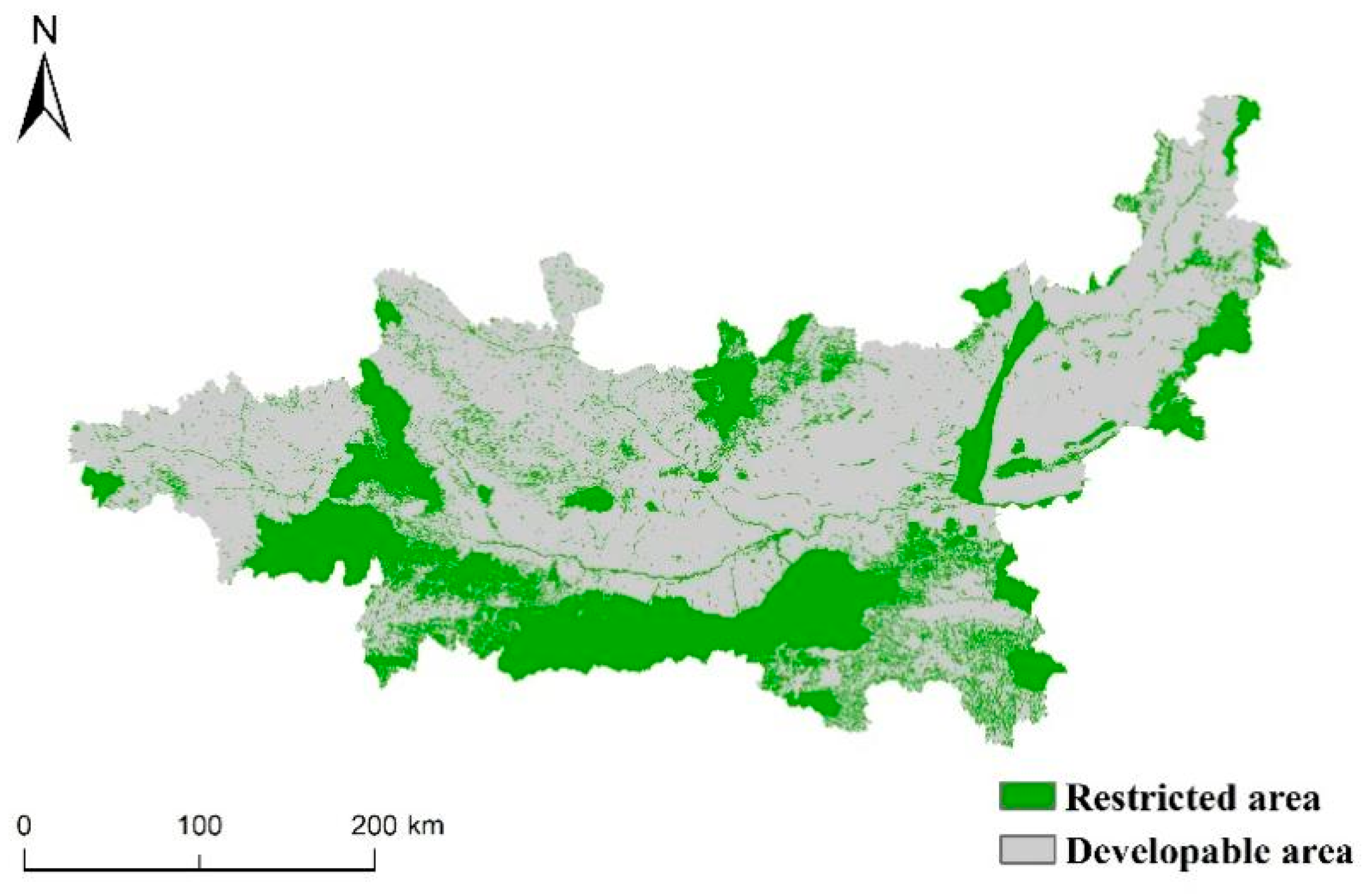
3.4.2. Multi-Scenario Simulation Settings
- (1)
- BAU scenario
- (2)
- ED scenario
- (3)
- EC scenario
3.5. Valuation of Ecosystem Services
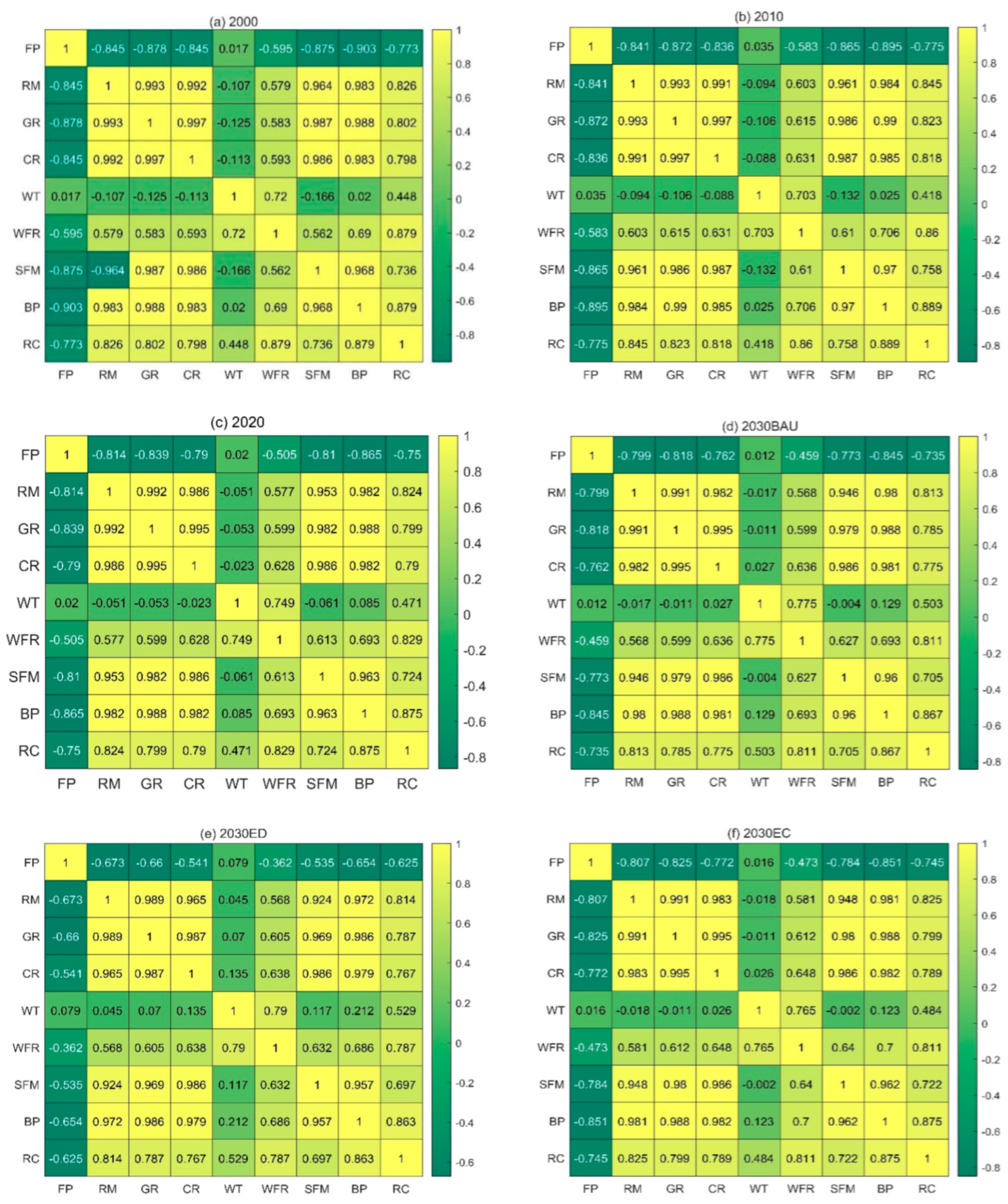
3.6. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis
4. Results
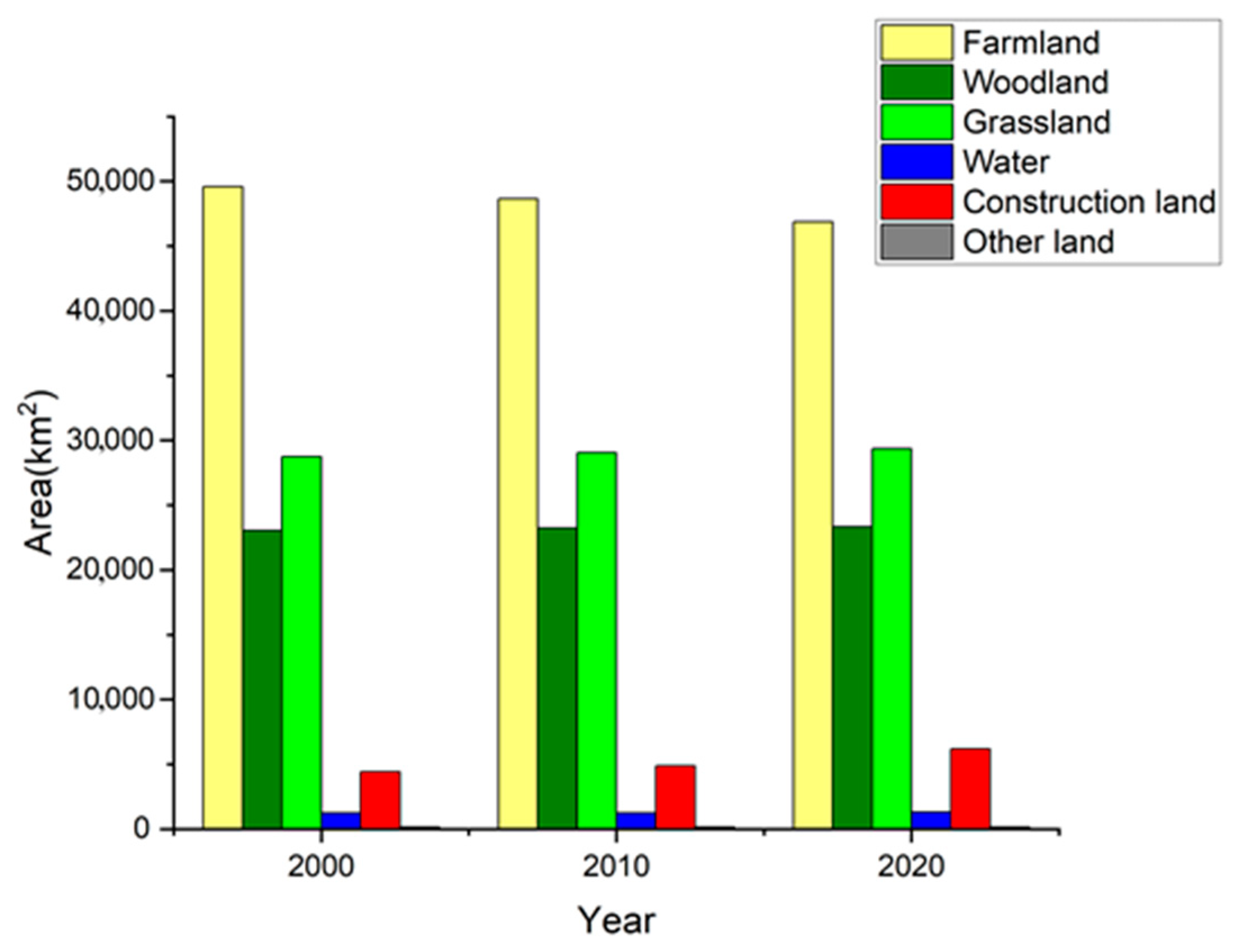
4.1. Land Use Change Characteristics
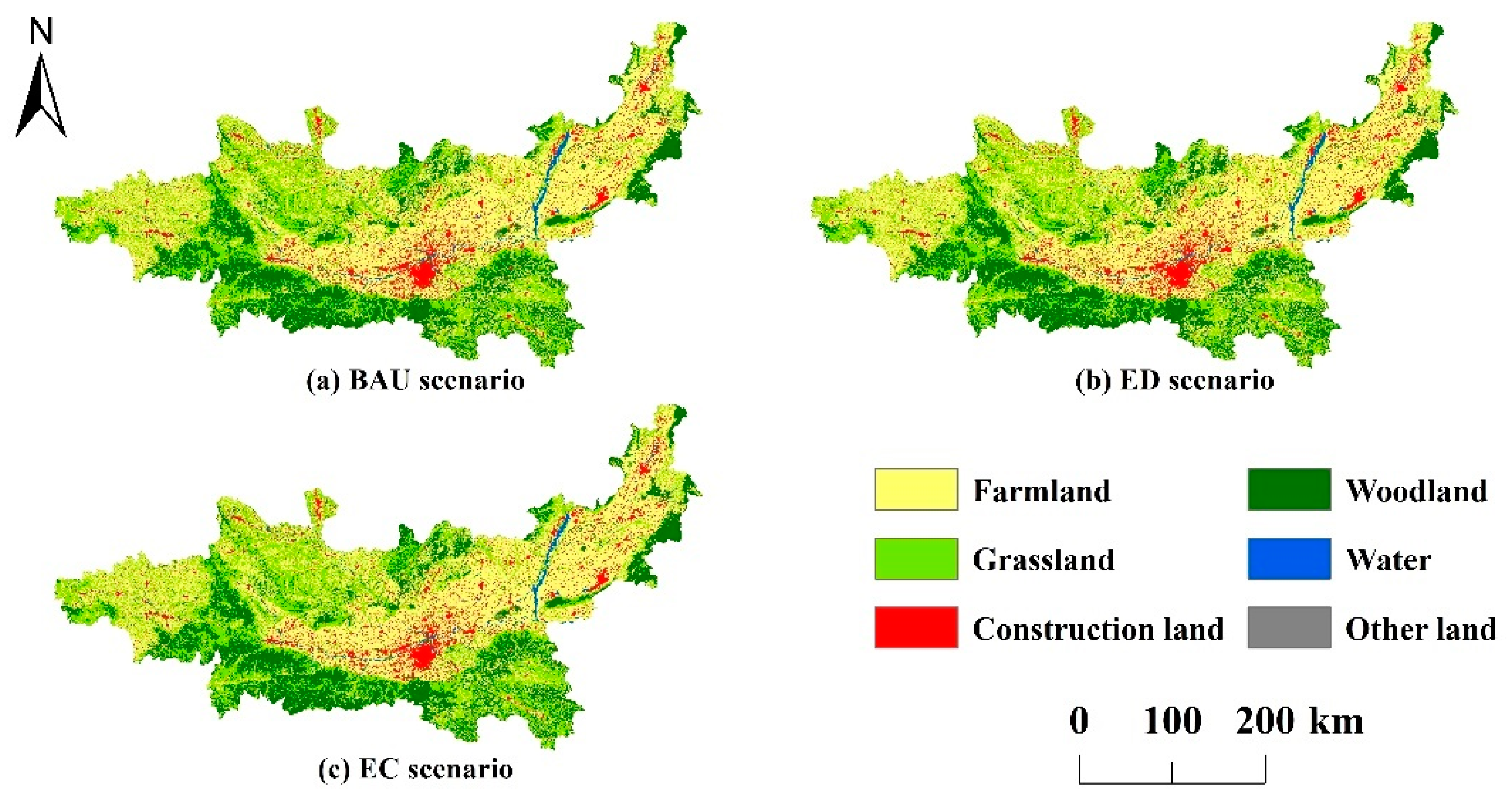
4.2. Multi-Scenario Land Use Simulation
4.3. Spatial and Temporal Variation of Ecosystem Service Values
4.3.1. Total ESVs and Variations of Each Ecosystem Service
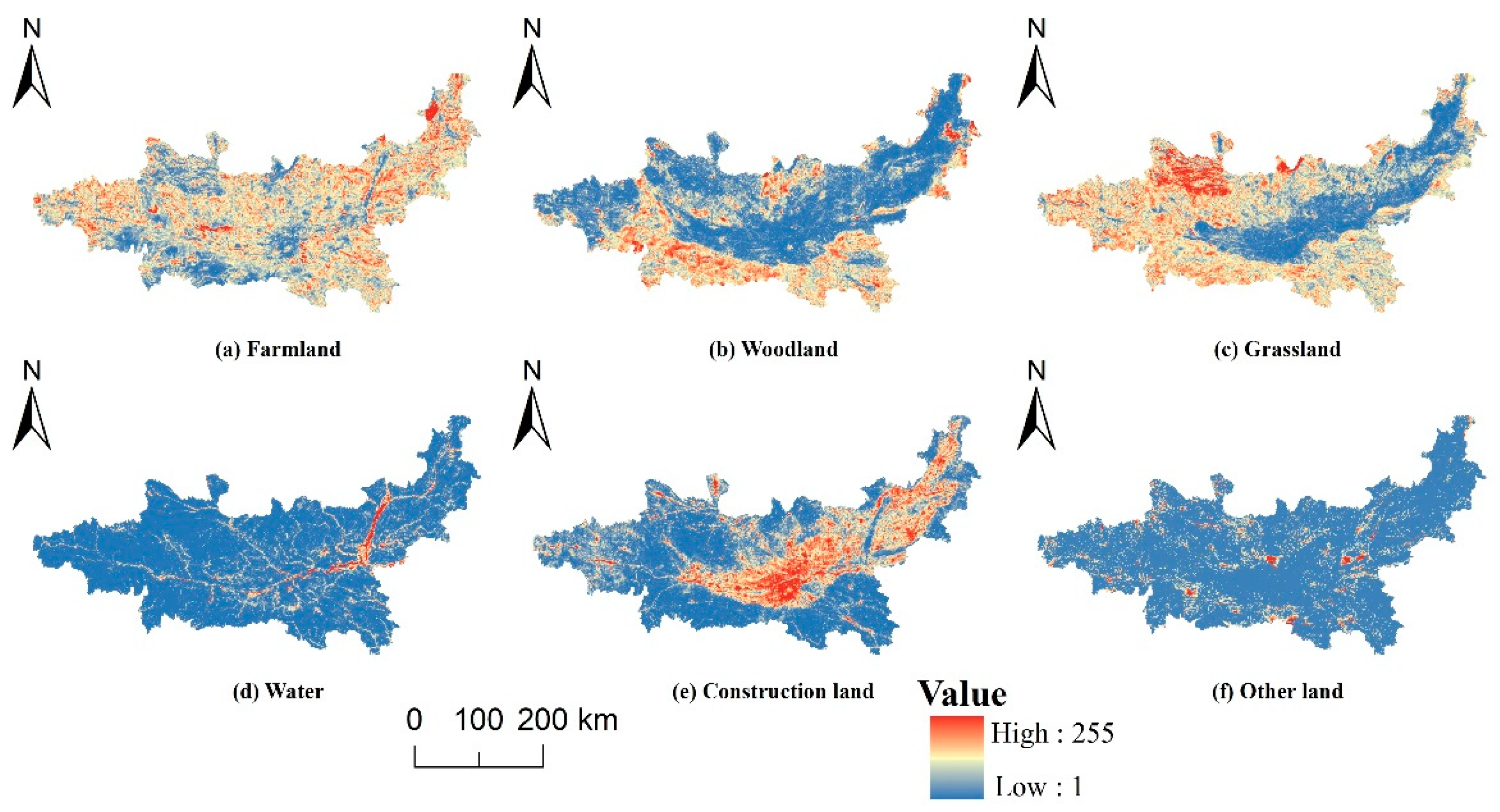
4.3.2. Spatial Distribution and Trade-Offs of Different ESVs in Different Scenarios
5. Discussion
5.1. Feasibility of PLUS Model Application
5.2. Land Use Change Patterns and ESV Trade-Offs
5.3. Policy Implications
5.4. Establishment of Smart and Sustainable Cities
5.5. Limitations and Future Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; de Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; Oneill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.L.; Zhang, Y.W.; Choi, Y.; Li, F.Q. A Scientometrics Review on Land Ecosystem Service Research. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, W.B.; Jiang, W.; Du, H.Y.; Chen, R.S.; Cai, Y.L. Assessing Ecosystem Services Supply-Demand (Mis)Matches for Differential City Management in the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C. Chinas Urban Agglomeration and Metropolitan Area Construction under the New Development Pattern. Econ. Geogr. 2021, 41, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Wang, S.S.; Zou, Y.T. Construction of an ecological security pattern based on ecosystem sensitivity and the importance of ecological services: A case study of the Guanzhong Plain urban agglomeration, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Tang, H.P.; Liang, H.G. A theoretical framework for researching cultural ecosystem service flows in urban agglomerations. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 28, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Wu, L.F.; Li, F.Z.; Lin, C.S. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Ecosystem Services and the Driving Factors in Urban Agglomerations: Evidence from 12 National Urban Agglomerations in China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 804969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, X.; Tang, L.S.; Wei, X.; Li, Y.H. Spatial interaction between urbanization and ecosystem services in Chinese urban agglomerations. Land Use Pol. 2021, 109, 105587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.N.; He, Y.Y.; Xu, H.L.; Zhu, C.M.; Dong, B.Y.; Lin, Y.; Si, B.; Deng, J.S.; Wang, K. Impacts of Urban Expansion Forms on Ecosystem Services in Urban Agglomerations: A Case Study of Shanghai-Hangzhou Bay Urban Agglomeration. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Wang, X.X.; Pei, L.; Su, Y.; Zhang, D.M.; Wang, Y. Identifying the spatiotemporal dynamic of PM2.5 concentrations at multiple scales using geographically and temporally weighted regression model across China during 2015–2018. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 141765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, H.; Cheng, Y. Why is it crucial to evaluate the fairness of natural capital consumption in urban agglomerations in terms of ecosystem services and economic contribution? Sust. Cities Soc. 2021, 65, 102644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.Y.; Shang, J.; Ali, R.; Rehman, R.U. The Coupling Coordinated Relationship Between New-type Urbanization, Eco-Environment and its Driving Mechanism: A Case of Guanzhong, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 638891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.X.; Zhang, L.W.; Li, X.P.; Wang, Z.Z.; Wang, H.; Jiao, L. Spatial expansion effects on urban ecosystem services supply-demand mismatching in Guanzhong Plain Urban Agglomeration of China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 806–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, J.A.; De Fries, R.; Asner, G.P.; Barford, C.; Bonan, G.; Carpenter, S.R.; Chapin, F.S.; Coe, M.T.; Daily, G.C.; Gibbs, H.K.; et al. Global consequences of land use. Science 2005, 309, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lugeri, F.R.; Farabollini, P. Discovering the Landscape by Cycling: A Geo-Touristic Experience through Italian Badlands. Geosciences 2018, 8, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruban, D.A. Quantification of geodiversity and its loss. Proc. Geol. Assoc. 2010, 121, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brilha, J. Geoconservation and protected areas. Environ. Conserv. 2002, 29, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monkkonen, P.; Comandon, A.; Escamilla, J.A.M.; Guerra, E. Urban sprawl and the growing geographic scale of segregation in Mexico, 1990–2010. Habitat Int. 2018, 73, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kong, X.S.; Fu, M.X.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Jiang, P. Ecological effects of land-use change on two sides of the Hu Huanyong Line in China. Land Use Pol. 2022, 113, 105895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.Y.; Tian, Y.Y.; Jiang, G.H. Spatio-temporal investigation of the interactive relationship between urbanization and ecosystem services: Case study of the Jingjinji urban agglomeration, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 95, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, A.L.; Wang, J.; MacLachlan, I.; Zhu, L.K. Modeling the trade-offs between urban development and ecological process based on landscape multi-functionality and regional ecological networks. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2020, 63, 2357–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Deng, X.Z. Land-use/land-cover change and ecosystem service provision in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 576, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, F.H.; Lai, X.H.; Ouyang, W.; Xu, Y.M.; Wei, X.F.; Song, K.Y. Effects of Land Use Changes on the Ecosystem Service Values of a Reclamation Farm in Northeast China. Environ. Manag. 2012, 50, 888–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambin, E.F.; Turner, B.L.; Geist, H.J.; Agbola, S.B.; Angelsen, A.; Bruce, J.W.; Coomes, O.T.; Dirzo, R.; Fischer, G.; Folke, C.; et al. The causes of land-use and land-cover change: Moving beyond the myths. Glob. Environ. Chang.-Hum. Policy Dimens. 2001, 11, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.M.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y. Unraveling land system vulnerability to rapid urbanization: An indicator-based vulnerability assessment for Wuhan, China. Environ. Res. 2022, 211, 112981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.; Zhiyuan, R. Variations in Ecosystem Service Value in Response to Land use Changes in the Loess Plateau in Northern Shaanxi Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2011, 5, 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Kindu, M.; Schneider, T.; Teketay, D.; Knoke, T. Changes of ecosystem service values in response to land use/land cover dynamics in Munessa-Shashemene landscape of the Ethiopian highlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 547, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.A.; Costanza, R.; Troy, A.; D’Aagostino, J.; Mates, W. Valuing New Jersey’s Ecosystem Services and Natural Capital: A Spatially Explicit Benefit Transfer Approach. Environ. Manag. 2010, 45, 1271–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.X.; Wei, H.J.; Xue, D.; Liu, M.X.; Cai, E.X.; Chen, W.Q.; Feng, X.W.; Li, J.W.; Lu, J.; Guo, Y.L. Trade-Off and Projecting Effects of Land Use Change on Ecosystem Services under Different Policies Scenarios: A Case Study in Central China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.L.; Liu, Y.Q.; Hou, X.G.; Li, T.T.; Li, Y.R. Effects of land use transitions due to rapid urbanization on ecosystem services: Implications for urban planning in the new developing area of China. Habitat Int. 2014, 44, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.Y.; Ye, X.Y.; Qi, Z.F.; Zhang, H. Impacts of land use/land cover change and socioeconomic development on regional ecosystem services: The case of fast-growing Hangzhou metropolitan area, China. Cities 2013, 31, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Lan, H.F.; Zhang, X.S.; He, Y. Confirmatory Analysis of the Effect of Socioeconomic Factors on Ecosystem Service Value Variation Based on the Structural Equation Model-A Case Study in Sichuan Province. Land 2022, 11, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aburas, M.M.; Ahamad, M.S.S.; Omar, N.Q. Spatio-temporal simulation and prediction of land-use change using conventional and machine learning models: A review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Z.; Jiang, Y.Y.; He, T.; Lu, Y.S.; Xv, X.L.; Yang, J. Land use change simulation: Progress, challenges, and prospects. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Hou, Y.; Wang, B.; Bi, X.; Li, B.; Zhang, X.S. Scenario analysis of ecosystem service changes and interactions in a mountain-oasis-desert system: A case study in Altay Prefecture, China. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Li, S.; Liu, Z. Multi-Scenario Simulation and Prediction of Regional Habitat Quality Based on a System Dynamic and Patch-Generating Land-Use Simulation Coupling Model: A Case Study of Jilin Province. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.J.; Wu, H.Q.; Fan, X.; Jia, H.T.; Dong, T.; He, P.X.; Baqa, M.F.; Jiang, P.G. Trade-Offs and Synergies of Multiple Ecosystem Services for Different Land Use Scenarios in the Yili River Valley, China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, D.; Palka, G.; Hersperger, A.M. Effect of Zoning Plans on Urban Land-Use Change: A Multi-Scenario Simulation for Supporting Sustainable Urban Growth. Sust. Cities Soc. 2021, 69, 102833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Wang, J.; Li, C.X.; Shen, W.N.; Song, Z.Y.; Nie, C.J.; Zhang, X.R. Land use change simulation and spatial analysis of ecosystem service value in Shijiazhuang under multi-scenarios. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 31043–31058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.Z.; He, J.H.; Liu, D.F.; Wang, J.W. Predicting the joint effects of future climate and land use change on ecosystem health in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Appl. Geogr. 2020, 124, 102293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.F.; Jiang, W.G.; Ling, Z.Y.; Hou, P.; Deng, Y.W. Evaluating the potential impacts of land use changes on ecosystem service value under multiple scenarios in support of SDG reporting: A case study of the Wuhan urban agglomeration. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 307, 127321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Wang, J.; Xiong, N.N.; Sun, L.; Xu, J.Q. Impacts of Land Use Changes on Net Primary Productivity in Urban Agglomerations under Multi-Scenarios Simulation. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Qi, W.; Yu, X.Y. Impacts of land use change on ecosystem services in the intensive agricultural area of North China based on Multi-scenario analysis. Alex. Eng. J. 2021, 60, 1703–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsova, D.; Shuster, W.; Wang, X.H. A cellular automata model of land cover change to integrate urban growth with open space conservation. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 99, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verburg, P.H.; Soepboer, W.; Veldkamp, A.; Limpiada, R.; Espaldon, V.; Mastura, S.S.A. Modeling the spatial dynamics of regional land use: The CLUE-S model. Environ. Manag. 2002, 30, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.P.; Liang, X.; Li, X.; Xu, X.C.; Ou, J.P.; Chen, Y.M.; Li, S.Y.; Wang, S.J.; Pei, F.S. A future land use simulation model (FLUS) for simulating multiple land use scenarios by coupling human and natural effects. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 168, 94–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Guan, Q.F.; Clarke, K.C.; Liu, S.S.; Wang, B.Y.; Yao, Y. Understanding the drivers of sustainable land expansion using a patch-generating land use simulation (PLUS) model: A case study in Wuhan, China. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2021, 85, 101569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, P.; Xia, J.; Wang, W.; Cai, W.; Chen, N.; Hu, S.; Luo, X.; Li, J.; Zhan, C. Land use/land cover prediction and analysis of the middle reaches of the Yangtze River under different scenarios. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.D.; Yang, M.Y.; Li, Z.B.; Wang, B.Q. How Will Rwandan Land Use/Land Cover Change under High Population Pressure and Changing Climate? Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, Y.M.; Gao, B.P.; Zheng, K.J.; Wu, Y.; Li, C. Multi-scenario simulation of ecosystem service value for optimization of land use in the Sichuan-Yunnan ecological barrier, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 132, 108328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.Y.; He, Y.; Li, Y.L. Urban Spatial Development Based on Multisource Data Analysis: A Case Study of Xianyang City’s Integration into Xi’an International Metropolis. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.D.; Zhang, C.X.; Zhang, L.M.; Chen, W.H.; Li, S.M. Improvement of the Evaluation Method for Ecosystem Service Value Based on Per Unit Area. J. Nat. Resour. 2015, 8, 1243–1254. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, G.P.; Swinton, S.M. Reconciling agricultural productivity and environmental integrity: A grand challenge for agriculture. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2005, 3, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.A.; Li, W.H.; Xie, G.D. Ecosystem services research in China: Progress and perspective. Ecol. Econ. 2010, 69, 1389–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; de Groot, R.; Sutton, P.; van der Ploeg, S.; Anderson, S.J.; Kubiszewski, I.; Farber, S.; Turner, R.K. Changes in the global value of ecosystem services. Glob. Environ. Chang.-Hum. Policy Dimens. 2014, 26, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.D.; Lu, C.X.; Leng, Y.F.; Zheng, D.U.; Li, S.C. Ecological assets valuation of the Tibetan Plateau. J. Nat. Resour. 2003, 18, 189–196. [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar, M.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Gao, G.L.; Gulzar, Q.; Hussain, A. Assessment of spatiotemporal variations of ecosystem service values and hotspots in a dryland: A case-study in Pakistan. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 1383–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Gan, X.Y.; Dai, W.N.; Huang, Y. Construction of an Ecological Security Pattern and the Evaluation of Corridor Priority Based on ESV and the “Importance-Connectivity” Index: A Case Study of Sichuan Province, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Mo, W.B.; Li, M.H.; Zhang, X.; Chen, M.; Li, F.; Gao, W.C. A Study on the Spatio-Temporal Land-Use Changes and Ecological Response of the Dongting Lake Catchment. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, H.B.; Yan, J.J.; Xu, H.L.; Guo, B.; Zhang, Q.Q. Estimates of shifts in ecosystem service values due to changes in key factors in the Manas River basin, northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.J.; Hua, L.; Zhang, X.S.; Yuan, X.Y.; Li, J.H. Evaluation of ESV Change under Urban Expansion Based on Ecological Sensitivity: A Case Study of Three Gorges Reservoir Area in China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, D.H.; Lu, L.; Yu, H. Multi-Scenario Simulation of the Impact of Urban Land Use Change on Ecosystem Service Value in Shenzhen. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 2086–2097. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, Y.D.; Chang, Y.Q.; Cheng, X.Y.; Wang, D. Land-use changes and ecosystem services under different scenarios in Nansi Lake Basin, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.H.; Zhong, Q.L.; Cheng, D.L.; Xu, C.B.; Chang, Y.N.; Lin, Y.Y.; Li, B.Y. Landscape ecological risk projection based on the PLUS model under the localized shared socioeconomic pathways in the Fujian Delta region. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, J.P.; Xiong, N.N.; Liang, B.Y.; Wang, Z.; Cressey, E.L. Spatial and Temporal Variation, Simulation and Prediction of Land Use in Ecological Conservation Area of Western Beijing. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wei, T.X.; Li, Y.R. Simulation and Spatio-Temporal Variation Characteristics of LULC in the Context of Urbanization Construction and Ecological Restoration in the Yellow River Basin. Sustainability 2022, 14, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.C.; Wang, P.; Xiong, P.S.; Li, C.H.; Quan, B. Spatial Pattern Simulation of Land Use Based on FLUS Model under Ecological Protection: A Case Study of Hengyang City. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.D.; Xiao, Y.; Zhen, L.; Lu, C. Study on ecosystem services value of food production in China. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2005, 13, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Tian, J.; Li, J. Ecosystem services value change in Qinglong County from dynamically adjusted value coefficients. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2015, 23, 373–381. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.M.; Tang, H.N.; Lei, J.R.; Song, X.Q. Spatial autocorrelation in land use type and ecosystem service value in Hainan Tropical Rain Forest National Park. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D. An assessment of surface and zonal models of population. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 1996, 10, 973–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Gao, B.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, K.; Wu, Y. Dynamic Simulation of Landscape Ecological Risk in Mountain Towns Based on Plus Model. J. Zhejiang AF Univer. 2022, 39, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.Y.; Gong, J.; Guldmann, J.M.; Yang, J.X.; Zhang, Z. Simulation of Land-Use Spatiotemporal Changes under Ecological Quality Constraints: The Case of the Wuhan Urban Agglomeration Area, China, over 2020-2030. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. Measurement of Observer Agreement for Categorical Data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, L.F.; Liu, X.; Tong, D.; Liu, Z.X.; Yin, L.R.; Zheng, W.F. Forecasting Urban Land Use Change Based on Cellular Automata and the PLUS Model. Land 2022, 11, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Wu, T.; Wu, X.C.; Luigi, S.; Wang, Y.Q. Simulation of Urban Land Expansion Under Ecological Constraints in Harbin-Changchun Urban Agglomeration, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 438–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.X.; Wu, J.Y. Land Use Transformation and Eco-Environmental Effects Based on Production-Living-Ecological Spatial Synergy: Evidence from Shaanxi Province, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 41492–41504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zhang, X. Analysis on the Spatiotemporal Evolution of Land Use Transformation and Its Ecological Environment Effect in Shaanxi Province. Res. Soil Water Cons. 2021, 28, 356. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. Ecosystem Service Value(Esv)and Spatial-Temporal Difference of Urban Agglomeration in Guanzhong Plain from 1995 to 2015. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. Edit. 2020, 47, 615. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.Y.; Chen, B.W.; Huang, X.J.; Wei, Y.H.D. Effect of land-use change and optimization on the ecosystem service values of Jiangsu province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubiszewski, I.; Muthee, K.; Rasheed, A.R.; Costanza, R.; Suzuki, M.; Noel, S.; Schauer, M. The costs of increasing precision for ecosystem services valuation studies. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 135, 108551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.F.; Zhu, J.T.; Zhang, H.B.; Yan, W.; Zhao, C.Y. Trade-offs and synergies in ecosystem service values of inland lake wetlands in Central Asia under land use/cover change: A case study on Ebinur Lake, China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 24, e01253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Liu, C.; Shan, L.; Lin, J.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, G. Spatial-Temporal Responses of Ecosystem Services to Land Use Transformation Driven by Rapid Urbanization: A Case Study of Hubei Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 19, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, D.F.; Wan, J.Y.; Bai, L.N.; lv, L.T. Multi-Scale Analysis of Ecosystem Service Trade-Offs/Synergies in Yanshan-Taihang Mountains Area. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2022, 38, 409–417. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Xu, G.; Li, A.; Liu, Y.; Hu, C. Evaluation and Trade-Off of Ecosystem Services in the Qingyijiang River Basin. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 9315–9327. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Qu, M.; Wang, C.; Zhao, J.; Cao, Y. Quantifying landscape pattern and ecosystem service value changes: A case study at the county level in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 23, e01110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Blanc, D. Towards Integration at Last? The Sustainable Development Goals as a Network of Targets. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 23, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenmenger, N.; Pichler, M.; Krenmayr, N.; Noll, D.; Plank, B.; Schalmann, E.; Wandl, M.T.; Gingrich, S. The Sustainable Development Goals prioritize economic growth over sustainable resource use: A critical reflection on the SDGs from a socio-ecological perspective. Sustain. Sci. 2020, 15, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Feng, C.C.E.; Xu, N.Y.; Guo, L. Spatial heterogeneous relationship between ecosystem services and human disturbances: A case study in Chuandong, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 137818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, M.; Roseland, M.; Ferguson, K.; Perl, A. Seeking urban sustainability on the world stage. Habitat Int. 2008, 32, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabareen, Y.R. Sustainable urban forms-Their typologies, models, and concepts. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 2006, 26, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caragliu, A.; Del Bo, C.; Nijkamp, P. Smart Cities in Europe. J. Urban Technol. 2011, 18, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, L.; Bolici, R.; Deakin, M. The First Two Decades of Smart-City Research: A Bibliometric Analysis. J. Urban Technol. 2017, 24, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibri, S.E.; Krogstie, J. Smart sustainable cities of the future: An extensive interdisciplinary literature review. Sust. Cities Soc. 2017, 31, 183–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Sun, Z.; Jiang, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, P.; Tao, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, N. Big Earth Data Supports Sustainable Cities and Communities: Progress and Challenges. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2021, 36, 914–922. [Google Scholar]
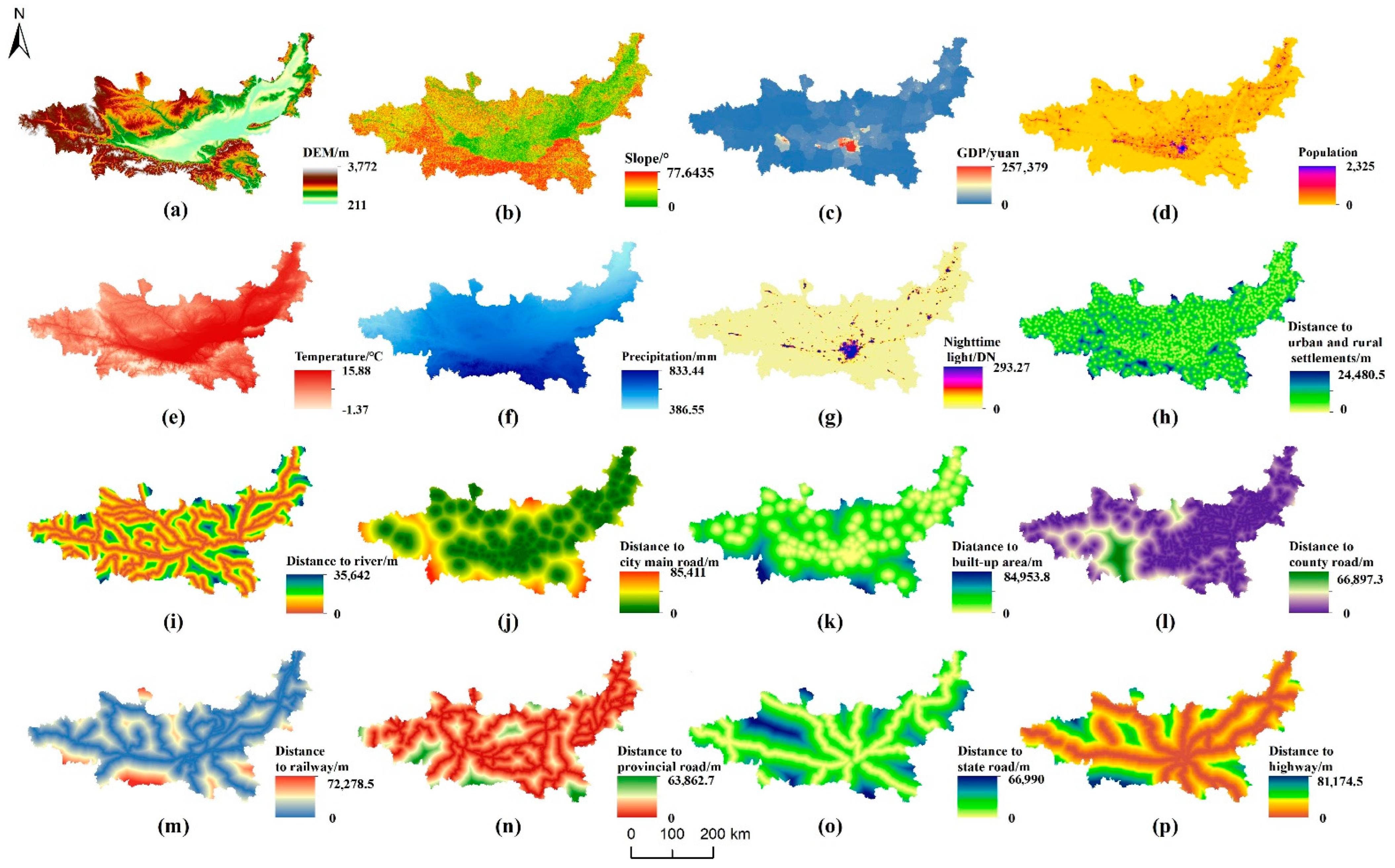



| Data Type | Data Source | Website | Spatial Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Slope | Calculated with DEM from ArcGIS | / | 30 m |
| GDP grid | RESD | https://www.resdc.cn/, accessed on 15 April 2022 | 1000 m |
| Annual average precipitation | |||
| Annual average temperature | |||
| Railway | API interface of AMap | https://lbs.amap.com/, accessed on 15 April 2022 | Vector |
| State road | |||
| Highway | |||
| Provincial road | |||
| City main road | |||
| County road | |||
| Urban and rural settlement | NCSGI | https://www.webmap.cn/, accessed on 15 April 2022 | Vector |
| Built-up area | |||
| River | |||
| Population density | WorldPop | http://www.worldpop.org, accessed on 15 April 2022 | 100 m |
| NPP-VIIRS nighttime light image | Earth Observation Group | https://eogdata.mines.edu/products/vnl, accessed on 15 April 2022 | 500 m |
| Primary Classification | Secondary Classification | Farmland | Woodland | Grassland | Water | Construction Land | Other Land |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Provisioning services | Food production | 1057.68 | 105.77 | 317.30 | 105.77 | 10.58 | 10.58 |
| Raw material | 105.77 | 2749.97 | 52.88 | 10.58 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Regulating services | Gas regulation | 528.84 | 3701.88 | 846.14 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Climate regulation | 941.34 | 2855.74 | 951.91 | 486.53 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Waste treatment | 1734.60 | 1385.56 | 1385.56 | 19,228.62 | −2601.89 | 10.58 | |
| Water flow regulation | 634.61 | 3384.58 | 846.14 | 21,555.52 | −7943.18 | 31.73 | |
| Supporting services | Soil fertility maintenance | 1544.21 | 4124.95 | 2062.48 | 10.58 | 21.15 | 21.15 |
| Biodiversity protection | 750.95 | 3448.04 | 1152.87 | 2633.62 | 359.61 | 359.61 | |
| Cultural services | Recreation and culture | 10.58 | 1353.83 | 42.31 | 4590.33 | 10.58 | 10.58 |
| Period | Land Use Types | Farmland | Woodland | Grassland | Water | Construction Land | Other Land | Transfer Out |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000~2010 | Farmland | 48,256.30 | 187.27 | 615.12 | 109.07 | 459.14 | 6.49 | 1377.09 |
| Woodland | 51.05 | 22,921.05 | 69.72 | 6.40 | 17.48 | 1.56 | 146.22 | |
| Grassland | 256.46 | 129.32 | 28,361.06 | 20.46 | 21.08 | 1.56 | 428.88 | |
| Water | 108.15 | 7.78 | 18.86 | 1113.46 | 2.58 | 1.47 | 138.84 | |
| Construction land | 13.51 | 1.17 | 3.68 | 0.55 | 4383.12 | 0.04 | 18.95 | |
| Other land | 8.29 | 4.17 | 10.66 | 0.04 | 0.62 | 136.67 | 23.79 | |
| Transfer In | 437.46 | 329.72 | 718.04 | 136.52 | 500.91 | 11.13 | - | |
| 2010~2020 | Farmland | 45,482.36 | 260.65 | 1305.63 | 122.51 | 1508.63 | 13.46 | 3210.89 |
| Woodland | 144.11 | 22,738.86 | 315.51 | 8.33 | 34.06 | 7.89 | 509.89 | |
| Grassland | 889.81 | 325.14 | 27,748.15 | 26.04 | 73.41 | 15.36 | 1329.75 | |
| Water | 67.10 | 3.75 | 31.07 | 1117.27 | 28.49 | 2.09 | 132.50 | |
| Construction land | 326.02 | 8.59 | 15.25 | 6.19 | 4527.64 | 0.33 | 356.38 | |
| Other land | 2.88 | 0.79 | 0.00 | 15.98 | 3.84 | 120.76 | 23.49 | |
| Transfer In | 1429.91 | 598.92 | 1667.46 | 179.05 | 1648.43 | 39.14 | - |
| Different Scenarios | Farmland | Woodland | Grassland | Water | Construction Land | Other Land | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BAU scenario | Farmland | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Woodland | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Grassland | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Water | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Construction land | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| Other land | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| ED scenario | Farmland | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Woodland | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Grassland | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Water | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Construction land | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| Other land | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| EC scenario | Farmland | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Woodland | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Grassland | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| Water | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| Construction land | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| Other land | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Different Scenarios | Farmland | Woodland | Grassland | Water | Construction Land | Other Land |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BAU scenario | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.9 | 0.1 |
| ED scenario | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.1 |
| EC scenario | 0.5 | 1 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.1 |
| Scenarios | Farmland | Woodland | Grassland | Water | Construction Land | Other Land |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BAU scenario | 45,333.58 | 23,381.52 | 29,670.14 | 1333.23 | 7320.40 | 169.62 |
| ED scenario | 47,050.41 | 22,849.78 | 27,898.48 | 1156.53 | 8121.29 | 132.01 |
| EC scenario | 45,233.17 | 23,694.21 | 32,243.73 | 1311.02 | 7257.18 | 169.18 |
| ESV/ CNY 100 million | Year/Scenario | Farmland | Woodland | Grassland | Water | Construction Land | Other Land | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Changing rate/% | 2000 | 362.46 | 532.53 | 220.12 | 60.87 | −44.63 | 0.07 | 1131.42 |
| 2010 | 355.60 | 536.77 | 222.33 | 60.75 | −49.52 | 0.06 | 1125.99 | |
| 2020 | 342.61 | 538.80 | 224.93 | 63.01 | −62.62 | 0.07 | 1106.80 | |
| 2030 BAU | 331.32 | 540.35 | 227.20 | 64.82 | −74.25 | 0.08 | 1089.52 | |
| 2030 ED | 343.87 | 528.07 | 213.64 | 56.23 | −82.38 | 0.06 | 1059.49 | |
| 2030 EC | 330.59 | 547.58 | 246.91 | 63.74 | −73.61 | 0.08 | 1115.29 | |
| 2000–2010 | −1.89 | 0.80 | 1.00 | −0.20 | −10.96 | −14.29 | −0.48 | |
| 2010–2020 | −3.65 | 0.38 | 1.17 | 3.72 | −26.45 | 16.67 | −1.70 | |
| 2000–2020 | −5.48 | 1.18 | 2.19 | 3.52 | −40.31 | 0.00 | −2.18 | |
| 2020-BAU | −3.30 | 0.29 | 1.01 | 2.87 | −18.57 | 14.29 | −1.56 | |
| 2020-ED | 1.26 | −10.73 | −11.29 | −6.78 | −19.76 | −0.01 | −47.31 | |
| 2020-EC | −12.02 | 8.78 | 21.98 | 0.73 | −10.99 | 0.01 | 8.49 |
| Ecosystem Service Type | 2000 | 2010 | 2020 | BAU | Variation | ED | Variation | EC | Variation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Food production | 64.19 | 63.32 | 61.57 | 60.06 | −1.51 | 61.24 | −0.33 | 60.80 | −0.77 |
| Raw material | 70.15 | 70.57 | 70.64 | 70.68 | 0.04 | 69.30 | −1.34 | 71.66 | 1.02 |
| Gas regulation | 135.85 | 136.28 | 135.95 | 135.63 | −0.32 | 133.08 | −2.87 | 138.92 | 2.97 |
| Climate regulation | 140.46 | 140.37 | 139.30 | 138.34 | −0.96 | 136.66 | −2.64 | 141.58 | 2.28 |
| Waste treatment | 170.41 | 168.13 | 163.17 | 158.73 | −4.44 | 153.04 | −10.13 | 162.30 | −0.87 |
| Water flow regulation | 125.82 | 122.21 | 112.41 | 103.61 | −8.80 | 91.23 | −21.18 | 106.80 | −5.61 |
| Soil fertility maintenance | 231.03 | 230.94 | 229.29 | 227.82 | −1.47 | 224.64 | −4.65 | 234.26 | 4.97 |
| Biodiversity protection | 154.77 | 155.19 | 155.14 | 155.07 | −0.07 | 152.30 | −2.84 | 158.96 | 3.82 |
| Recreation and culture | 38.73 | 38.98 | 39.32 | 39.59 | 0.27 | 38.01 | −1.31 | 40.02 | 0.70 |
| Year | Moran’s I | Z-score | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 0.6979 | 83.9632 | 0.0000 |
| 2010 | 0.7049 | 84.8010 | 0.0000 |
| 2020 | 0.7057 | 84.8883 | 0.0000 |
| 2030BAU | 0.7087 | 85.2570 | 0.0000 |
| 2030ED | 0.5755 | 69.2342 | 0.0000 |
| 2030EC | 0.7122 | 85.6717 | 0.0000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, S.; Su, H. Multi-Scenario Simulation of Ecosystem Service Values in the Guanzhong Plain Urban Agglomeration, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8812. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148812
Yang S, Su H. Multi-Scenario Simulation of Ecosystem Service Values in the Guanzhong Plain Urban Agglomeration, China. Sustainability. 2022; 14(14):8812. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148812
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Shuo, and Hao Su. 2022. "Multi-Scenario Simulation of Ecosystem Service Values in the Guanzhong Plain Urban Agglomeration, China" Sustainability 14, no. 14: 8812. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148812
APA StyleYang, S., & Su, H. (2022). Multi-Scenario Simulation of Ecosystem Service Values in the Guanzhong Plain Urban Agglomeration, China. Sustainability, 14(14), 8812. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148812






