How Does Retailer-Oriented Remanufacturing Affect the OEM’s Quality Choice?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature
2.1. Remanufacturing Supply-Chain Management
2.2. Environmental Impact of Remanufacturing
2.3. Quality Decision in Supply-Chain Operation
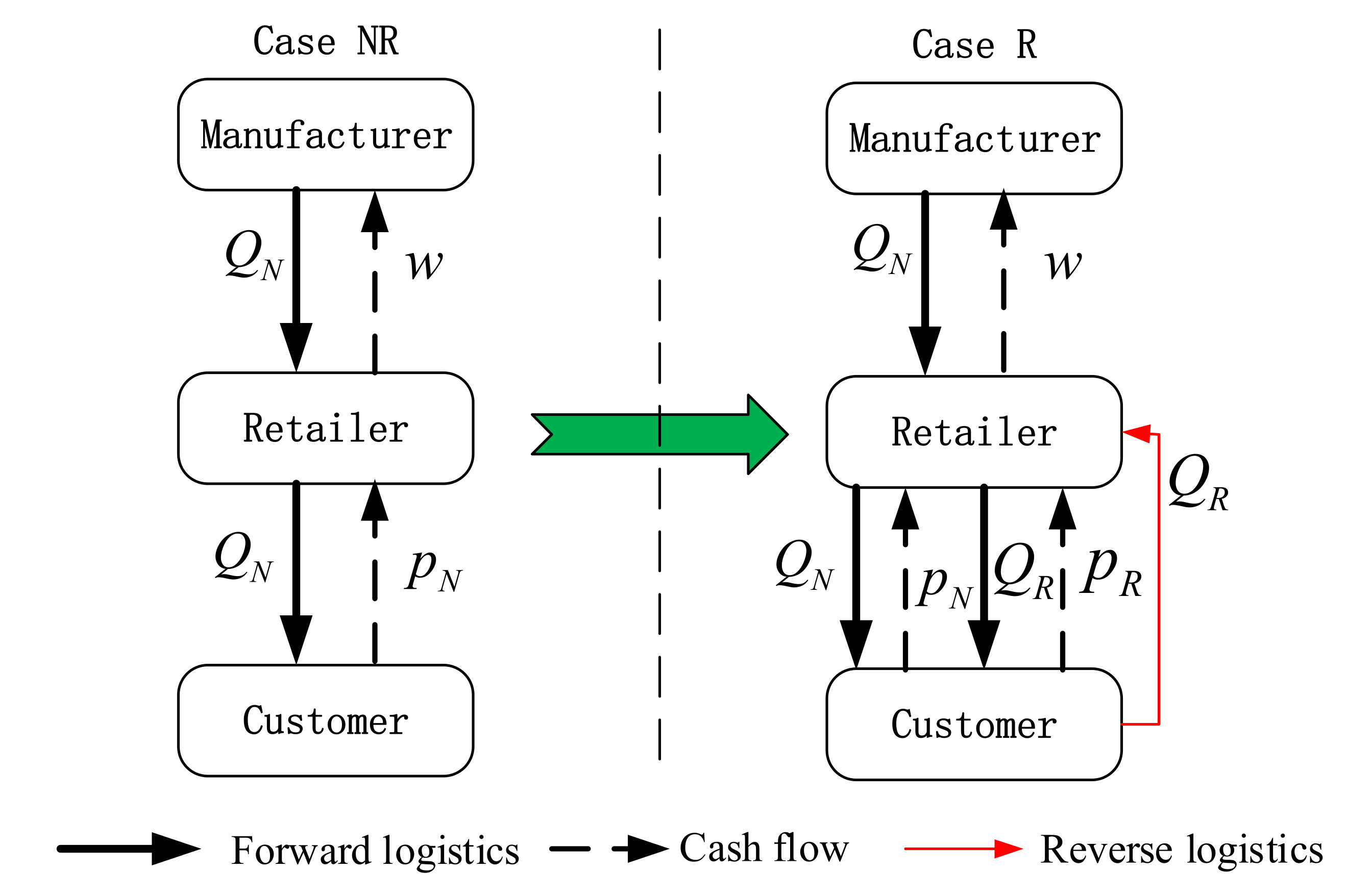
3. Model and Equilibrium Results
3.1. Model Description
3.1.1. Customer Choice Behavior
3.1.2. Demand Functions
3.1.3. Cost Functions
3.2. Model and Equilibrium Result
3.2.1. Basic Model without Remanufacturing (Model NR)
3.2.2. Retailer Developed Remanufacturing (Model R)
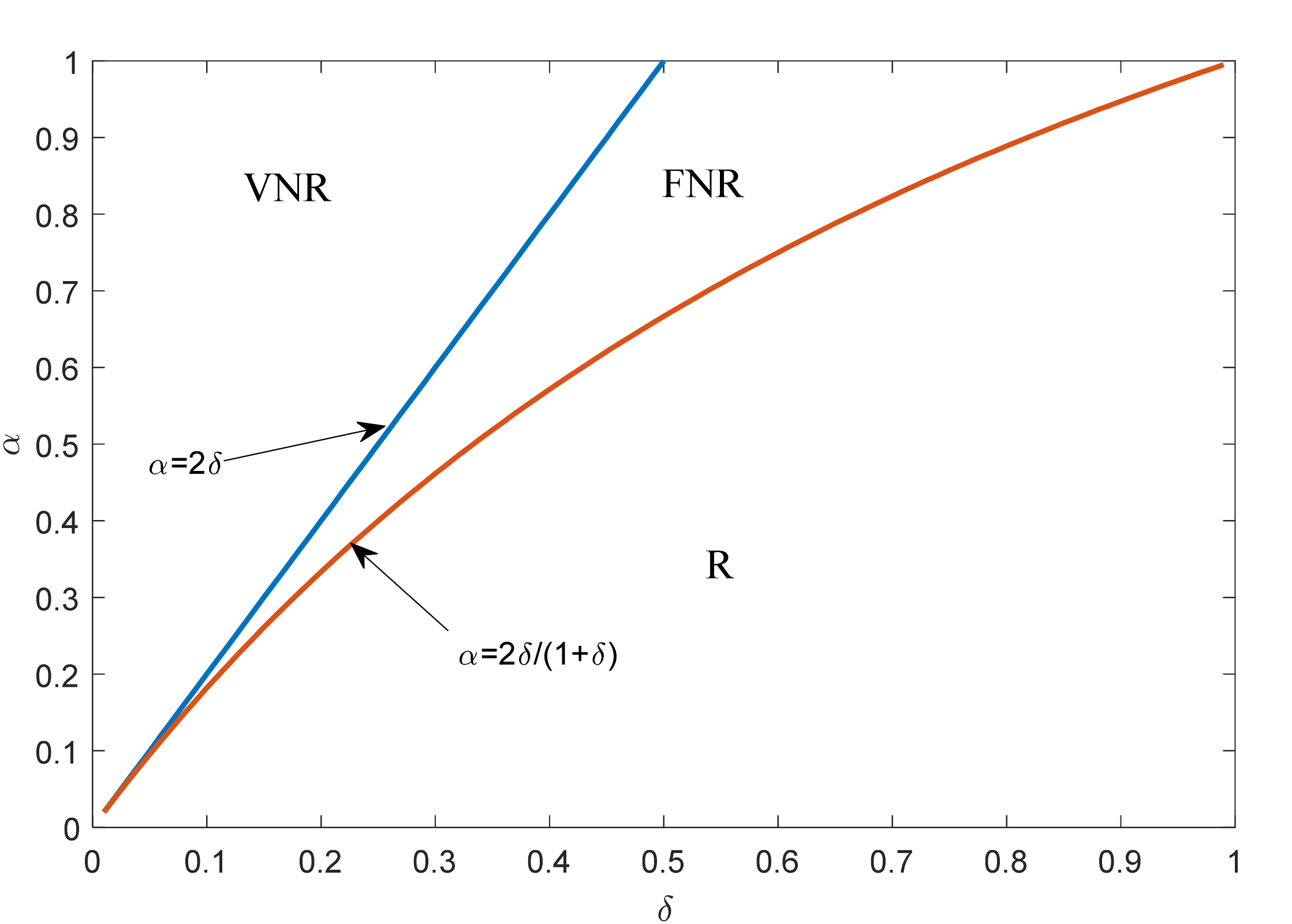
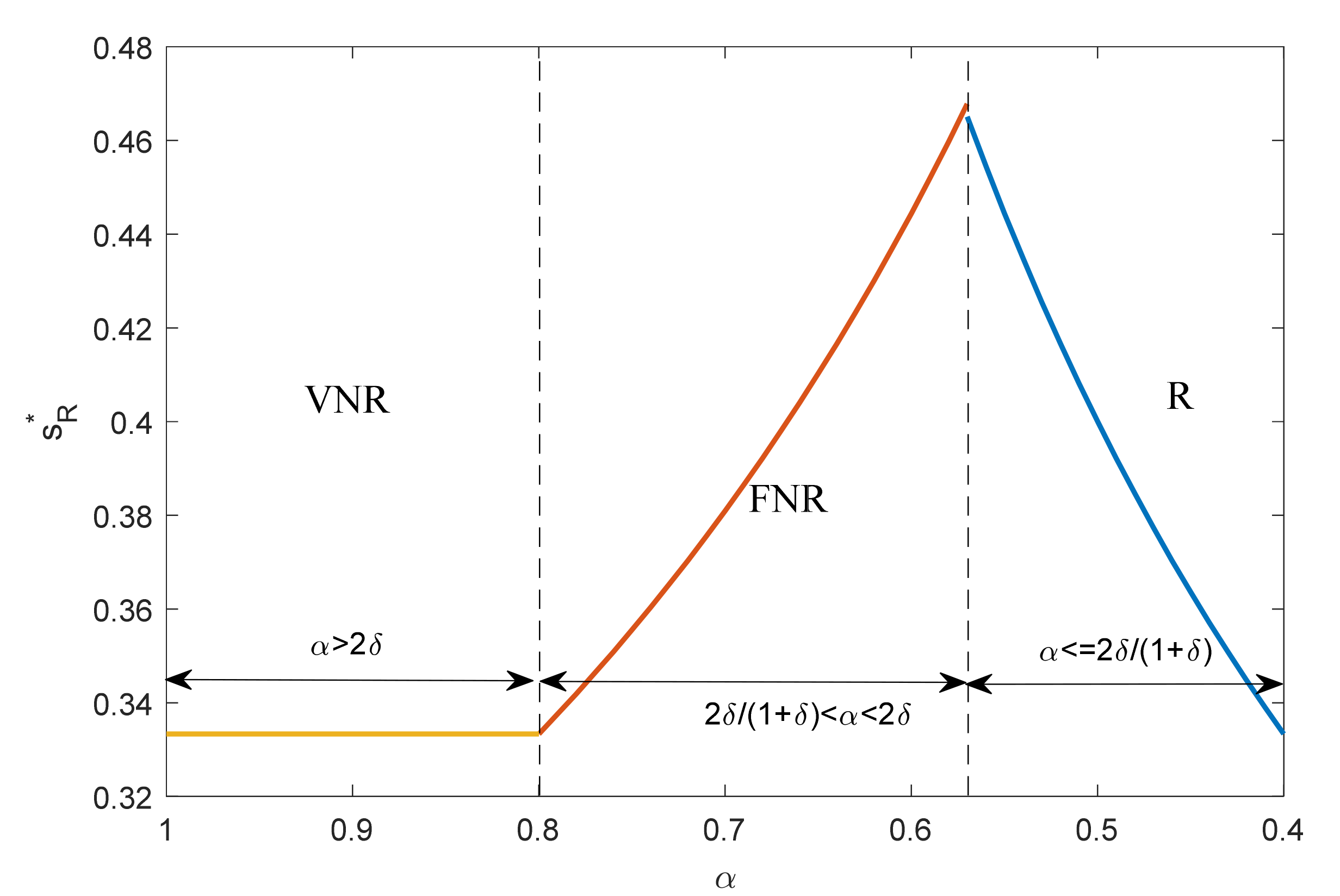
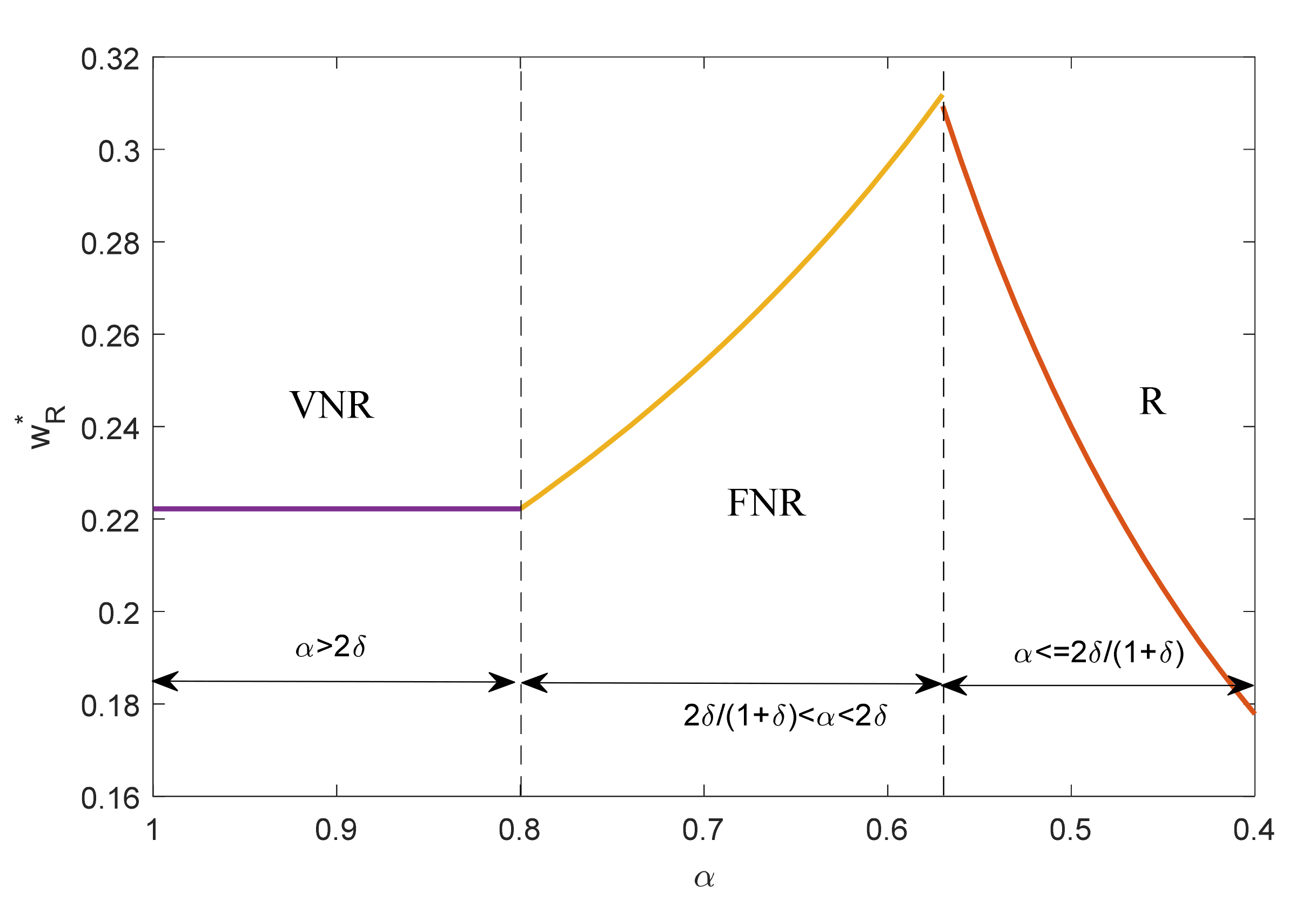
4. Equilibrium Result Analysis
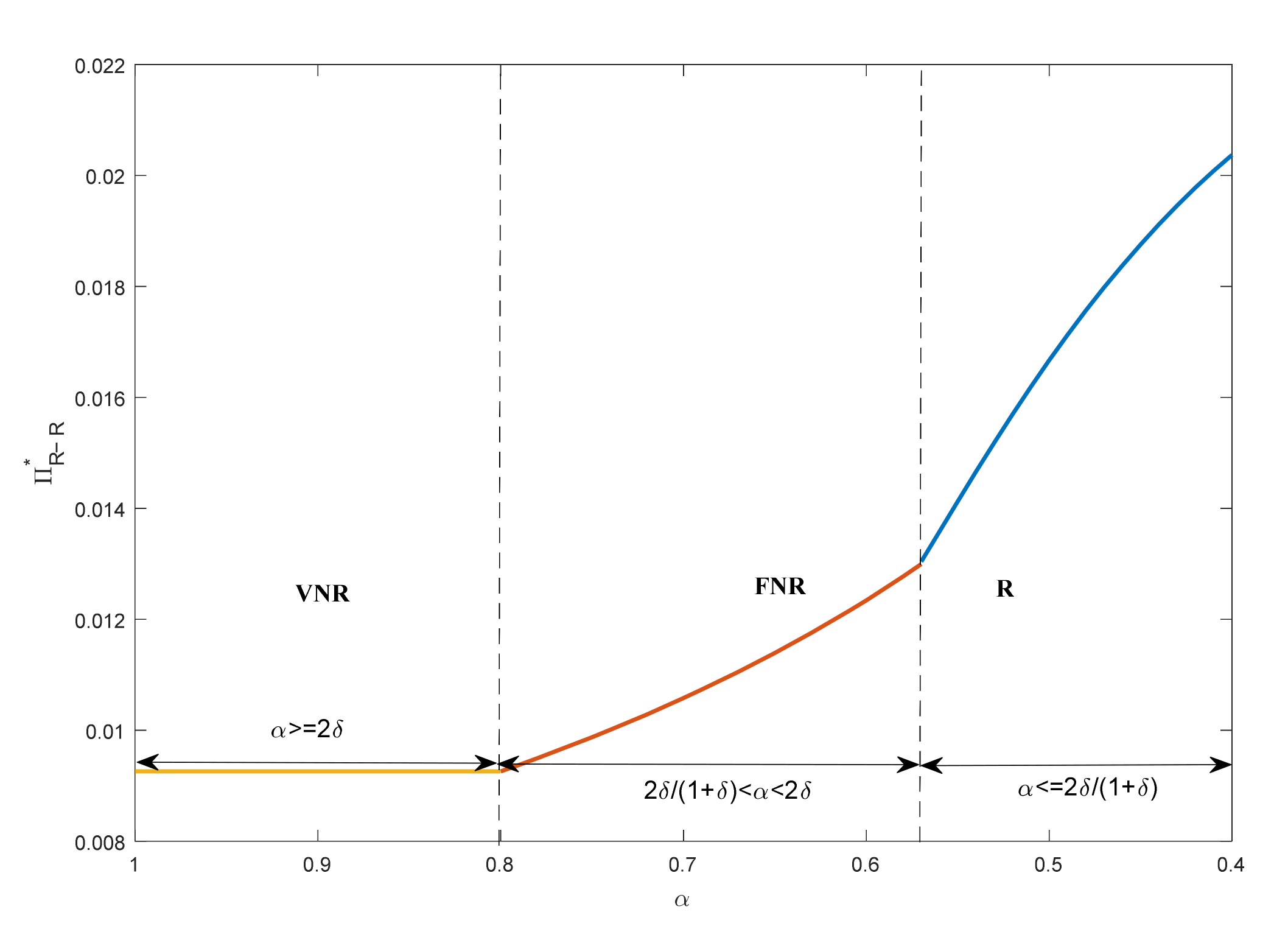
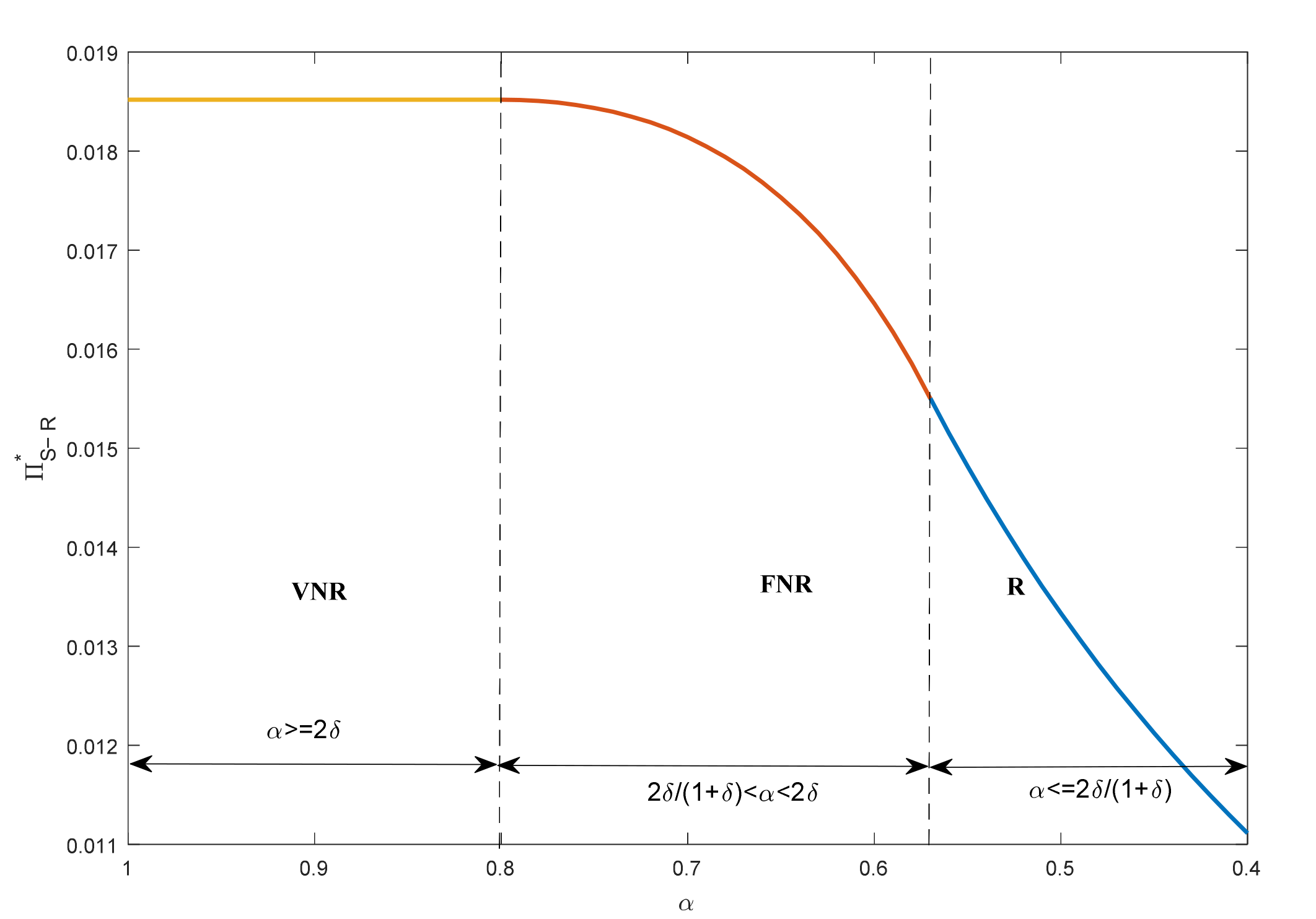
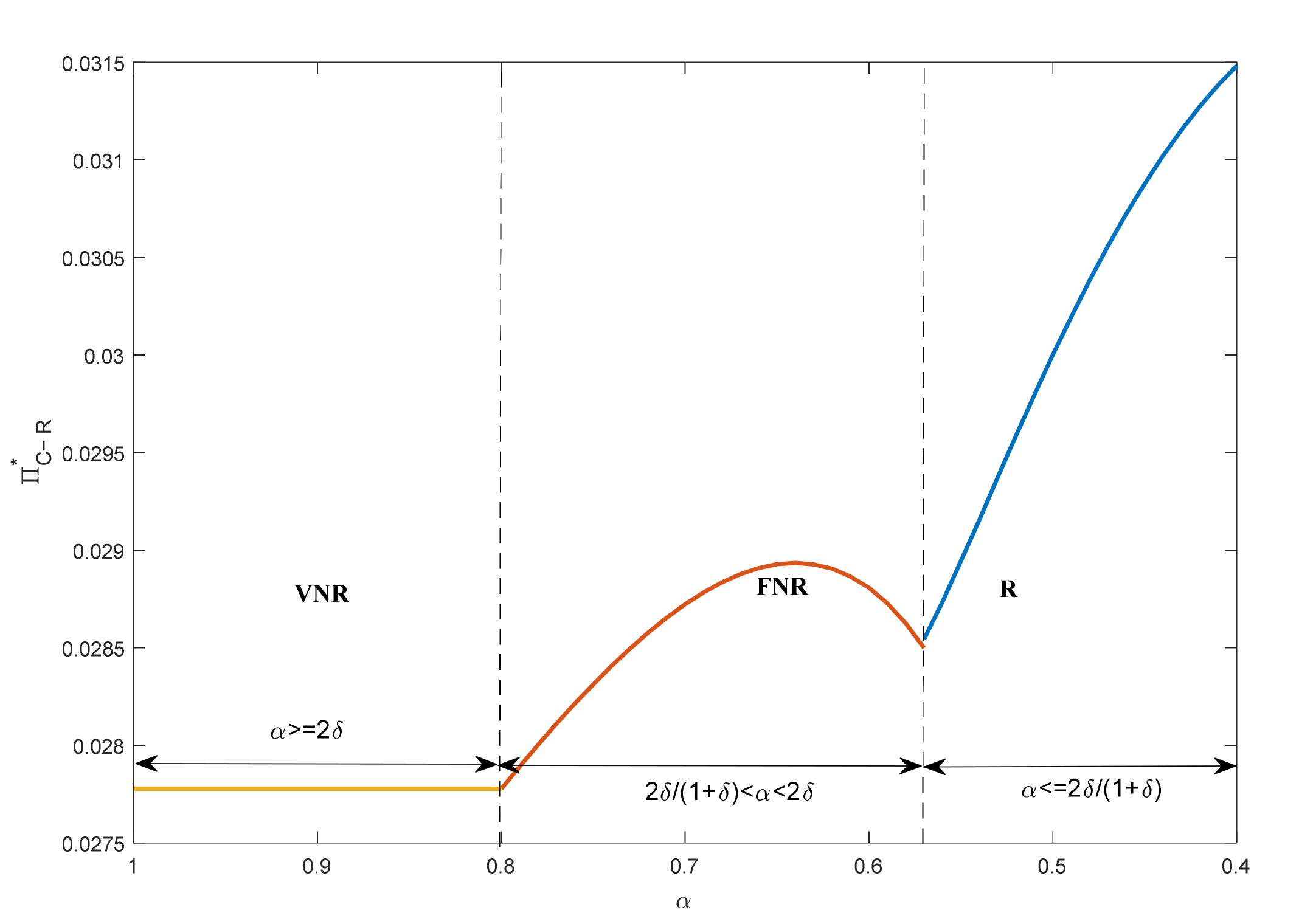
4.1. Operation Decision and Profits
4.2. Customer Surplus and Social Welfare
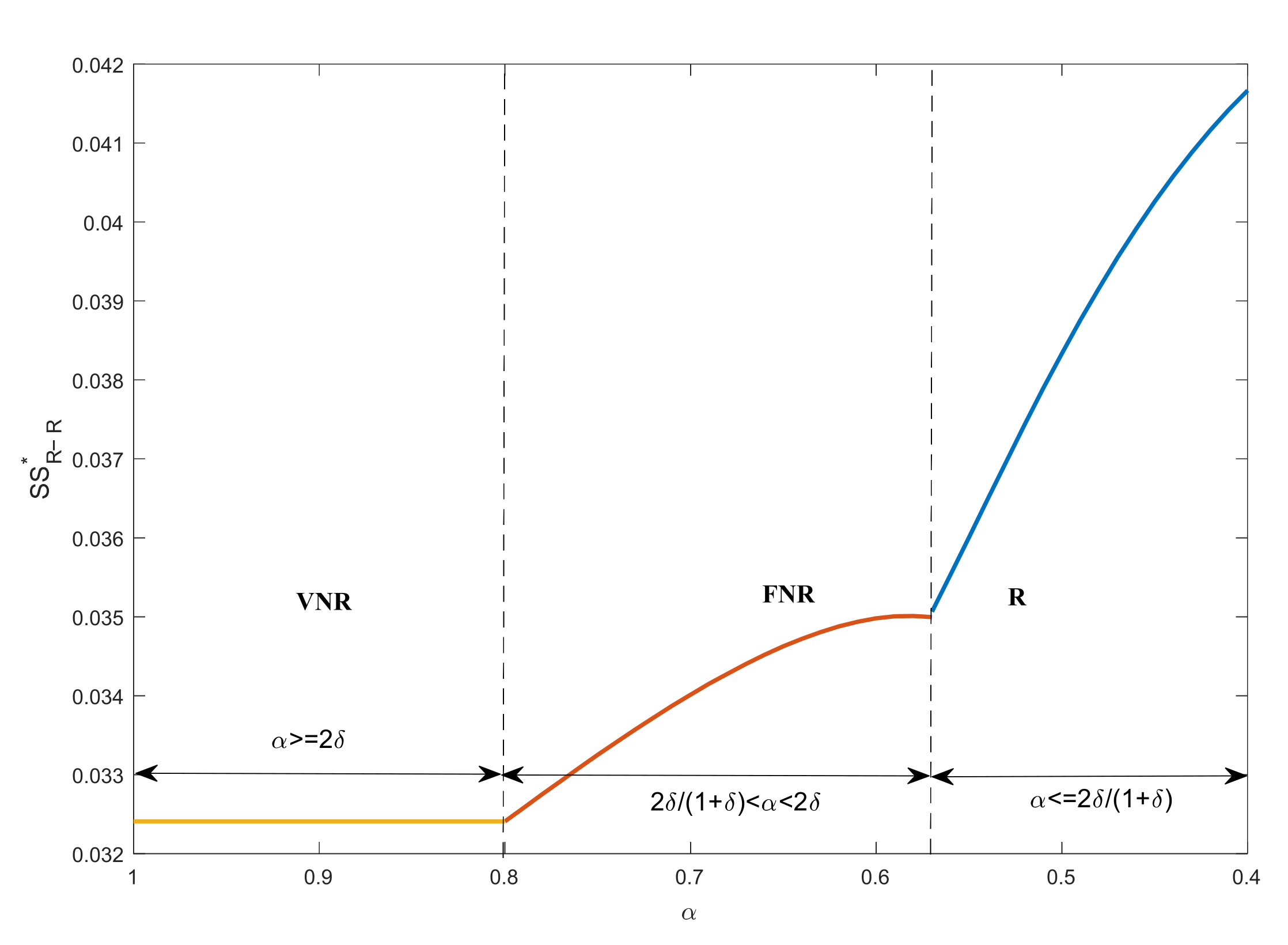
4.3. Environmental Impact
5. Conclusions and Managerial Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Huang, Z.; Shao, W.; Meng, L.; Zhang, G.; Qiang, Q. Pricing Decision for a Closed-Loop Supply Chain with Technology Licensing under Collection and Remanufacturing Cost Disruptions. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, J. Fairness Concern in Remanufacturing Supply Chain—A Comparative Analysis of Channel Members’ Fairness Preferences. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atasu, A.; Guide, V.D.R.; Van Wassenhove, L.N. So What If Remanufacturing Cannibalizes My New Product Sales? Calif. Manag. Rev. 2010, 52, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giutini, R.; Gaudette, K. Remanufacturing: The next great opportunity for boosting US productivity. Bus. Horiz. 2003, 46, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Han, H.; Wang, H. Pricing and effort decisions in a closed-loop supply chain under different channel power structures. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 2043–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guide, V.D.R.; Harrison, T.P.; Van Wassenhove, L.N. The challenge of closed-loop supply chains. INFORMS J. Appl. Anal. 2003, 33, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, M.E.; Souza, G.C. Closed-Loop Supply Chains—New Developments to Improve the Sustainability of Business Practices; Taylor & Francis Group: Oxford, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov, A.; Blass, V.; Raz, G. Economic and Environmental Assessment of Remanufacturing Strategies for Product + Service Firms. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2014, 23, 744–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, W.M.; Lund, R.T. Remanufacturing: Operating Practices and Strategies; Boston University: Boston, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, P.; Huang, M.; Guo, L.; Shi, T. Dual recycling channel decision in retailer oriented closed-loop supply chain for construction machinery remanufacturing. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 137, 1393–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Örsdemir, A.; Kemahlıoğlu-Ziya, E.; Parlaktürk, A.D. Competitive quality choice and remanufacturing. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2014, 23, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atasu, A.; Souza, G.C. How does product recovery affect quality choice? Prod. Oper. Manag. 2013, 22, 991–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Chai, J.; Li, H.; Yan, W.; Chen, H. Implications of product upgrading confronting supplier remanufacturing. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2020, 58, 5870–5892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Wang, F.; Lai, X.; Hong, J. How Does Licensing Remanufacturing Affect the Supply Chain Considering Customer Environmental Awareness? Sustainability 2019, 11, 1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atasu, A.; Sarvary, M.; Van Wassenhove, L.N. Remanufacturing as a Marketing Strategy. Manag. Sci. 2008, 54, 1731–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Chang, C. The co-opetitive strategy of a closed-loop supply chain with remanufacturing. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2012, 48, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Wang, J.; Deng, G.; Chen, H. Third-party remanufacturing mode selection: Outsourcing or authorization? Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2016, 87, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savaskan, R.C.; Bhattacharya, S.; Van Wassenhove, L.N. Closed-loop supply chain models with product remanufacturing. Manag. Sci. 2004, 50, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbey, J.D.; Meloy, M.G.; Guide, V.D.R.; Atalay, S. Remanufactured products in closed-loop supply chains for consumer goods. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2015, 24, 488–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, S.K.; Sarmah, S.P. Price and service co-opetiton under uncertain demand and condition of used items in a remanufacturing system. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2016, 173, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Cao, J.; Kumar, S. Government regulation and enterprise decision in China remanufacturing industry: Evidence from evolutionary game theory. Energy Ecol. Environ. 2021, 6, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Webster, S. Competition in remanufacturing and the effects of government subsidies. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2008, 111, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; He, Y.; Xu, H. Channel structure and pricing in a dual-channel closed-loop supply chain with government subsidy. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2019, 213, 108–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Li, G.; Zhou, Y.; Fernandes, K.; Harrison, R.; Xiong, Z. Dynamic pricing models for used products in remanufacturing with lost-sales and uncertain quality. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2014, 147, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.H.; Wu, H.Y.; Yang, Q.X.; Shang, J. Collection channel and production decisions in a closed-loop supply chain with remanufacturing cost disruption. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2017, 55, 1147–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Chen, W.; Liu, B.; Chen, X. Economic lot scheduling problem in a remanufacturing system with returns at different quality grades. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 170, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghdadi, E.; Shafiee, M.; Alkali, B. Upgrading Strategy, Warranty Policy and Pricing Decisions for Remanufactured Products Sold with Two-Dimensional Warranty. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cui, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, D.; Xu, F. Optimisation of reverse supply chain with used-product collection effort under collector’s fairness concerns. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2019, 59, 652–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M. Development of a simulation model for reuse businesses and case studies in Japan. J. Clean. Prod. 2010, 18, 1284–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, R.; Subramanyam, R. Key factors in the market for remanufactured products. Manuf. Serv. Oper. Manag. 2012, 14, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, W.; Xiong, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Guo, N. Bricks vs. clicks: Which is better for marketing remanufactured products? Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2015, 242, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yenipazarli, A. Managing new and remanufactured products to mitigate environmental damage under emissions regulation. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2016, 249, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, J.Q.; Bloemhof, J. An Analysis of the Eco-Efficiency of Remanufactured Personal Computers and Mobile Phones. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2012, 21, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Chhajed, D.; Petruzzi, N.C.; Yalabik, B. Quality design and environmental implications of green consumerism in remanufacturing. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2015, 162, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaowanapong, J.; Jongwanich, J.; Ijomah, W. Factors influencing a firm’s decision to conduct remanufacturing: Evidence from the Thai automotive parts industry. Prod. Plan. Control. 2017, 28, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, W.; Ryan, C. Eco-efficiency gains from remanufacturing: A case study of photocopier remanufacturing at Fuji Xerox Australia. J. Clean. Prod. 2001, 9, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellofs, L.L.; Jacobson, R. Market Share and Customers’ Perceptions of Quality: When Can Firms Grow Their Way to Higher versus Lower Quality? J. Mark. 1999, 63, 16–25. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, R.; Biswas, I.; Kumar, S. Pricing decisions for three-echelon supply chain with advertising and quality effort-dependent fuzzy demand. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2019, 57, 2715–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Yue, W.; Wang, S.; Lai, K.K. Quality investment and price decision in a risk-averse supply chain. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2011, 214, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Wang, H.; Shang, J. Contract design for two-stage supply chain coordination: Integrating manufacturer-quality and retailer-marketing efforts. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2013, 146, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.C.; Liu, Y.T. Quality investment and inspection policy in a supplier–manufacturer supply chain. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 202, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldman, J.; Gaalman, G. A model of strategic product quality and process improvement incentives. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2014, 149, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Ma, S.; Guan, X.; Xiao, L. Timing of sales commitment in a supply chain with manufacturer-quality and retailer-effort induced demand. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2018, 195, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, J.; Tang, W. Joint dynamic pricing and investment strategy for perishable foods with price-quality dependent demand. Ann. Oper. Res. 2014, 226, 397–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Symbol | Definition |
|---|---|
| The consumers willing to pay for the new product | |
| The valuation of the remanufactured products relative to the new products | |
| The quality level of the new products | |
| The ratio of unit variable cost of remanufactured product to new product | |
| The wholesale price of the new products | |
| The quantity of the new products | |
| The price of the new products | |
| The quantity of the remanufactured products | |
| The price of the remanufactured products |
| Variable | Equilibrium Result |
|---|---|
| Variable | Equilibrium Result | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Range | |||
| 0 | 0 | ||
| NA | NA | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhong, Q. How Does Retailer-Oriented Remanufacturing Affect the OEM’s Quality Choice? Sustainability 2022, 14, 8028. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14138028
Zou Z, Wang C, Zhong Q. How Does Retailer-Oriented Remanufacturing Affect the OEM’s Quality Choice? Sustainability. 2022; 14(13):8028. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14138028
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Zongbao, Cong Wang, and Qinjia Zhong. 2022. "How Does Retailer-Oriented Remanufacturing Affect the OEM’s Quality Choice?" Sustainability 14, no. 13: 8028. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14138028
APA StyleZou, Z., Wang, C., & Zhong, Q. (2022). How Does Retailer-Oriented Remanufacturing Affect the OEM’s Quality Choice? Sustainability, 14(13), 8028. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14138028





