Continuance Usage Intention toward E-Payment during the COVID-19 Pandemic from the Financial Sustainable Development Perspective Using Perceived Usefulness and Electronic Word of Mouth as Mediators
Abstract
1. Introduction
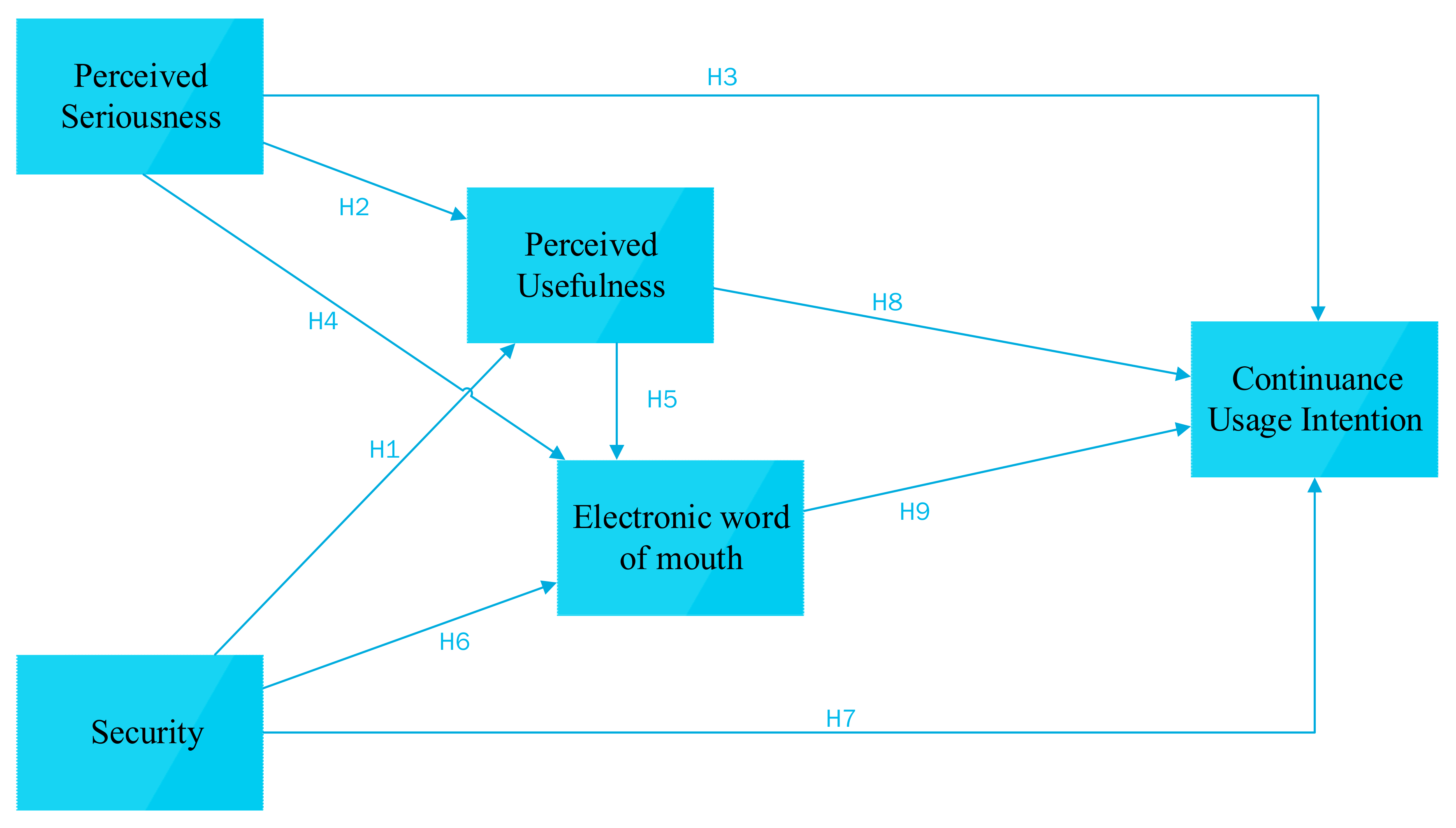
2. Literature Review and Hypotheses Development
2.1. Technology Acceptance Model
2.2. Health Belief Model
2.3. Security and Perceived Usefulness
2.4. Perceived Seriousness, Perceived Usefulness, and Continuance Usage Intention
2.5. Perceived Seriousness and Electronic Word of Mouth
2.6. Perceived Usefulness and Electronic Word of Mouth
2.7. Security, Electronic Word of Mouth, and Continuance Usage Intention
2.8. Perceived Usefulness and Continuance Usage Intention
2.9. Electronic Word of Mouth and Continuance Usage Intention
3. Research Method
3.1. Questionnaire Design
3.2. Sample Characteristics
3.3. Reliability and Validity Analysis
4. Research Results
4.1. Structural Equation Modeling
4.2. Verification of the Hypothesis Results
4.3. Mediation Effect Analysis
5. Conclusions
5.1. Theoretical and Practical Implications
5.2. Managerial Implications
6. Limitations and Future Research Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lerner, J.; Tufano, P. The Consequences of Financial Innovation: A Counterfactual Research Agenda. Annu. Rev. Financ. Econ. 2011, 3, 41–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyelami, L.O.; Adebiyi, S.O.; Adekunle, B.S. Electronic payment adoption and consumers’ spending growth: Empirical evidence from Nigeria. Future Bus. J. 2020, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statista. Digital Payments Report 2020. Available online: https://www.statista.com/study/41122/fintech-report-digitalpayments/ (accessed on 19 November 2021).
- Euromonitor International Ltd. Available online: https://www.euromonitor.com/our-expertise/via (accessed on 16 October 2021).
- Zhao, Y.; Bacao, F. How Does the Pandemic Facilitate Mobile Payment? An Investigation on Users’ Perspective under the COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Financial Supervisory Commission. Available online: https://www.fsc.gov.tw/ch/home.jsp?id=96andparentpath=0,2andmcustomize=news_view.jspanddataserno=202108120001andtoolsflag=Yanddtable=News (accessed on 5 May 2022).
- Kim, E.-A. Social Distancing and Public Health Guidelines at Workplaces in Korea: Responses to Coronavirus Disease-19. Saf. Health Work. 2020, 11, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puriwat, W.; Tripopsakul, S. Explaining an adoption and continuance intention to use contactless payment technologies: During the COVID-19 pandemic. Emerg. Sci. J. 2021, 5, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daragmeh, A.; Sági, J.; Zéman, Z. Continuous Intention to Use E-Wallet in the Context of the COVID-19 Pandemic: Integrating the Health Belief Model (HBM) and Technology Continuous Theory (TCT). J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2021, 7, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, F.D. A Technology Acceptance Model for Empirically Testing New End-User Information Systems: Theory and Results. Ph.D. Thesis, Sloan School of Management, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, F.D. Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Q. 1989, 13, 319–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.; Todd, P.A. Understanding information technology usage: A test of competing models. J. Inf. Syst. 1995, 6, 144–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Davis, F.D. A theoretical extension of the technology acceptance model: Four longitudinal field studies. Manag. Sci. 2000, 46, 186–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstock, I.M. Why people use health services. Milbank Q. 1966, 44, 94–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z. How to persuade adolescents to use nutrition labels: Effects of health consciousness, argument quality, and source credibility. Asian J. Commun. Feb. 2015, 19, 84–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Zhou, J.; Zuo, M. Understanding older adults’ intention to share health information on social media: The role of health belief and information processing. Internet Res. 2020, 31, 100–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahadzadeh, A.S.; Sharif, S.P.; Ong, F.S.; Khong, K.W. Integrating health belief model and technology acceptance model: An investigation of health-related internet use. J. Med. Internet Res. 2015, 17, e3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahadzadeh, A.S.; Sharif, S.P.; Ong, F.S. Online health information seeking among women: The moderating role of health consciousness. Online Inf. Rev. 2018, 42, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Davis, F.D. A model of the antecedents of perceived ease of use: Development and test. Decis. Sci. 1996, 27, 451–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.W.; Kim, Y.G. Extending the TAM for a World-Wide-Web context. Inf. Manag. 2001, 38, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Heijden, H. Factors influencing the usage of websites: The case of a generic portal in the Netherlands. Inf. Manag. 2003, 40, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, H.P. Extended technology acceptance model of Internet utilization behavior. Inf. Manag. 2004, 41, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, P.C. Security as an extension to TAM model: Consumers’ intention to use a single platform E-Payment. Asia-Pacific J. Manag. Res. Innov. 2017, 13, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Mirusmonov, M.; Lee, I. An empirical examination of factors influencing the intention to use mobile payment. Hum. Comput. Interact. 2010, 26, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, P.C. The significance of e-business and knowledge-based customer relationship in the e-market place environment. INTI J. 2006, 2, 552–559. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J. Analysis of health consumers’ behavior using self-tracker for activity, sleep, and diet. Telemed. e-Health 2014, 20, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.C. Remote health monitoring adoption model based on artificial neural networks. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champion, V.L.; Skinner, C.S. The health belief model. Health Educ. Behav. 2008, 4, 45–65. [Google Scholar]
- Glanz, K.; Rimer, B.K.; Viswanath, K. Health Behavior and Health Education: Theory, Research, and Practice, 4th ed.; John Wiley and Sons.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 230–240. [Google Scholar]
- Langley, D.J.; Wijn, R.; Epskamp, S.; van Bork, R. Encouraging vaccination behavior through online social media. Lect. Notes Control. Inf. Sci. 2016, 19, 307–318. [Google Scholar]
- Grajales, F.J., III; Sheps, S.; Ho, K.; Novak-Lauscher, H.; Eysenbach, G. Social media: A review and tutorial of applications in medicine and health care. J. Med. Internet Res. 2014, 16, e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betsch, C.; Sachse, K. Dr. Jekyll or Mr. Hyde? (How) the internet influences vaccination decisions: Recent evidence and tentative guidelines for online vaccine communication. Vaccine 2012, 30, 3723–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houston, T.K.; Sands, D.Z.; Nash, B.R.; Ford, D.E. Experiences of physicians who frequently use e-mail with patients. Health Commun. 2003, 4, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstock, I.M.; Strecher, V.J.; Becker, M.H. The health belief model and HIV risk behavior change. In Preventing AIDS: Theories and Methods of Behavioral Interventions; DiClemente, R.J., Peterson, J.L., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1994; pp. 5–24. [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka, I. A dynamic theory of organizational knowledge creation. Organ. Sci. 1994, 5, 14–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sussman, S.W.; Siegal, W.S. Informational influence in organizations: An integrated approach to knowledge adoption. Inf. Syst. Res. 2003, 14, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, C.M.; Lee, M.K.; Thadani, D.R. The impact of positive electronic word-of-mouth on consumer online purchasing decision. In Proceedings of the 2rd World Summit on the Knowledge Society (WSKS 2009), Chania, Greece, 16–18 September 2009; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 501–510. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.R.; Zhang, W. Informational influence of online customer feedback: An empirical study. J. Database Mark. Cust. Strategy Manag. 2010, 17, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cheung, C.M.; Lee, M.K.; Rabjohn, N. The impact of electronic word-of-mouth: The adoption of online opinions in online customer communities. Internet Res. 2008, 18, 229–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, K.Y.; Heng, C.S.; Lin, Z. Social media brand community and consumer behavior: Quantifying the relative impact of user-and marketer-generated content. Inf. Syst. Res. 2013, 24, 88–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, H.; Ahn, J.; Choi, Y. Helpfulness of online consumer reviews: Readers’ objectives and review cues. Int. J. Electron. Commer. 2012, 17, 99–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Mafe, C.; Bigné-Alcañiz, E.; Currás-Pérez, R. The effect of emotions, eWOM quality, and online review sequence on consumer intention to follow advice obtained from digital services. J. Serv. Manag. 2020, 31, 468–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, M.Y.; Luo, C.; Sia, C.L.; Chen, H. Credibility of electronic word-of-mouth: Informational and normative determinants of on-line consumer recommendations. Int. J. Electron. Commer. 2009, 13, 9–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.J.; Kim, K.K.; Benayad, A.; Yoon, S.M.; Park, H.K.; Jung, I.S.; Jin, M.H.; Jeong, H.K.; Kim, J.M.; Choi, J.Y.; et al. Efficient reduction of graphite oxide by sodium borohydride and its effect on electrical conductance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 1987–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.W.; Weng, C.C.; Lai, C.L.; Ku, C.J. Multiple channels with overlapping data sub-channel method for mobile ad hoc networks. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, Hong Kong, China, 11–15 March 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, P. Online Reviews: Do Consumers Use Them? Adv. Consum. Res. 2001, 28, 129–134. [Google Scholar]
- Bueno, S.; Gallego, M.D. eWOM in C2C platforms: Combining IAM and customer satisfaction to examine the impact on purchase intention. J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2021, 16, 1612–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muda, M.; Hamzah, M.I. Should I suggest this YouTube clip? The impact of UGC source credibility on eWOM and purchase intention. J. Res. Interact. Mark. 2021, 15, 441–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.; Park, S.; Shin, N. Sustainable Development of a Mobile Payment Security Environment Using Fintech Solutions. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, D.; Gupta, A.; Gupta, S. E-Commerce Security Challenges: A Review. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Innovative Computing and Communications (ICICC), New Delhi, India, 19–20 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.W. Cyber security issues and challenges in E-commerce. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Digital Strategies for Organizational Success, Gwalior, India, 5–7 January 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, P.C.; Zainal, A.A. Perceived risk as an extension to TAM model: Consumers’ intention to use a single platform e-payment. J. Aust. Stud. 2015, 9, 323–330. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, H.K.; Lettice, F.; Durowoju, O.A. Decision Making for Supply Chain Integration (Decision Engineering); Springer: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kamran, A.; Hanifa, S.; Paul, K. RFID applications: An introductory and exploratory study. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2010, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, P.C. The chip technology management implication in the era of globalization: Malaysian consumers’ perspective. Asia Pacific Bus. Rev. 2007, 3, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Smart Card Alliance. Mobile Operator Needs And Roles. In Smart Card Alliance Proximity Mobile Payments: Leveraging NFC and the Contactless Financial Payments Infrastructure; A Smart Card Alliance Contactless Payments Council White Paper; Smart Card Alliance: Township, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 22–27. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, D.; Shuo, Z.; Luo, G.; Chen, Z.; Ling, X. Analyze mobile payment based on RFID. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 10, 950–955. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, H.Y. Factors influencing consumer perceptions of brand trust online. J. Prod. Brand. Manag. 2004, 13, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, H. What determines Turkish customer’s acceptance of internet banking? Int. J. Bank Mark. 2008, 26, 353–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petty, R.E.; Cacioppo, J.T.; Schumann, D. Central and Peripheral Routes to Advertising Effectiveness: The Moderating Role of Involvement. J. Consum. Res. 1983, 10, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H. User acceptance of mobile library applications in academic Libraries: An application of the technology acceptance model. J. Acad. Librariansh. 2016, 42, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Gan, L.; Yan, D. Study on influence factors model of technology acceptance in digital library based on user cognition and TAM. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Management and Service Science, Wuhan, China, 16 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- George, J.F. Influences on the intent to make internet purchases. Internet Res. 2002, 12, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawashdeh, A.M.; Elayan, M.B.; Alhyasat, W.; Shamout, M.D. Electronic human resources management perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use and continuance usage intention: The mediating role of user satisfaction in Jordanian hotels sector. Int. J. Qual. Res. 2021, 15, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Lim, W.M.; Pandey, N.; Christopher Westland, J. 20 years of electronic commerce research. Electron. Commer. Res. 2021, 21, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmel, J.; Alon, I.; Vega, D. Alkosto faces up to Amazon in Colombia’s e-commerce market. Glob. Bus. Organ. Excell. 2019, 38, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandonde, F.A. A PESTLE analysis of international retailing in the East African Community. Glob. Bus. Organ. Excell. 2019, 38, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hride, F.T.; Ferdousi, F.; Jasimuddin, S.M. Linking perceived price fairness, customer satisfaction, trust, and loyalty: A structural equation modeling of Facebook-based e-commerce in Bangladesh. Glob. Bus. Organ. Excell. 2022, 41, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, C.M.; Xiao, B.S.; Liu, I.L. Do actions speak louder than voices: The signaling role of social information cues in influencing consumer purchase decisions. Decis. Support Syst. 2014, 65, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filieri, R.; McLeay, F. E-WOM and accommodation. An analysis of the factors that influence travelers’ adoption of information from online reviews. J. Travel Res. 2014, 53, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filieri, R. What makes online reviews helpful? A diagnosticity-adoption framework to explain informational and normative influences in e-WOM. J. Bus. Res. 2015, 68, 1261–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, S.; Wang, F. Online review helpfulness: Impact of reviewer profile image. Decis. Support Syst. 2017, 96, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Jiang, B.; Guo, R. Factors Affecting Public Adoption of COVID-19 Prevention and Treatment Information During an Infodemic: Cross-sectional Survey Study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2021, 23, e23097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viglia, G.; Furlan, R.; Ladron-de-Guevara, A. Please: Talk about it! When hotel popularity boosts preferences. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2014, 42, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nantembelele, F.A.; Gopal, S. Assessing the challenges to e-commerce adoption in Tanzania. Glob. Bus. Organ. Excell. 2018, 37, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.M.; Ahmed, P.K.; Ali, M.Y. Giving electronic word of mouth (eWOM) as a prepurchase behavior: The case of online group buying. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 146, 582–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.Z.; Zhao, S.J.; Cheung, C.M.; Lee, M.K. Examining the influence of online reviews on consumers’ decision-making: A heuristic-systematic model. Decis. Support Syst. 2014, 67, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudeshia, C.; Kumar, A. Social eWOM: Does it affect the brand attitude and purchase intention of brands? Manag. Res. Rev. 2017, 40, 310–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filieri, R.; McLeay, F.; Tsui, B.; Lin, Z. Consumer perceptions of information helpfulness and determinants of purchase intention in online consumer reviews of services. Inf. Manag. 2018, 55, 956–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sook Lee, M.; An, H. A study of antecedents influencing eWOM for online lecture website: Personal interactivity as moderator. Online Inf. Rev. 2018, 42, 1048–1064. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, S.; Bhatti, S.H.; Hwang, Y. E-service quality and actual use of e-banking: Explanation through the Technology Acceptance Model. Inf. Dev. 2020, 36, 503–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casalo, L.V.; Flavián, C.; Guinalíu, M. The role of security, privacy, usability, and reputation in the development of online banking. Online Inf. Rev. 2007, 31, 583–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyette, I.; Ricard, L.; Bergeron, J.; Marticotte, F. e-WOM Scale: Word-of-mouth measurement scale for e-services context. Can. J. Adm. Sci. 2010, 27, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, J.C.; Chiu, C.M.; Martínez, F.J. Understanding e-learning continuance intention: An extension of the Technology Acceptance Model. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2006, 64, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M. Situational interest: Its multifaceted structure in the secondary school mathematics classroom. J. Educ. Psychol. 1993, 85, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, D.L. Revisiting sample size and number of parameter estimates: Some support for the N: Q hypothesis. Struct. Equ. Model. 2003, 10, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error: Algebra and statistics. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 3, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F., Jr.; Anderson, R.E.; Babin, B.J.; Black, W.C. Multivariate Data Analysis, 7th ed.; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kline, R.B. Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling, 3rd ed.; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hoyle, R.H. Structural Equation Modeling: Concepts, Issues, and Applications; Sage: Riverside County, CA, USA, 1995; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Boomsma, A. Reporting analyses of covariance structures. Struct. Equ. Model. 2000, 7, 461–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, J.B. Core reporting practices in structural equation modeling. Res. Soc. Adm. Pharm. 2008, 4, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gefen, D.; Straub, D.; Boudreau, M.C. Structural Equation Modeling and Regression: Guidelines for Research Practice. Commun. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2000, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.T.; Bentler, P.M. Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Struct. Equ. Model. 1999, 6, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, W.J.; Xia, W.; Torkzadeh, G.A. A Confirmatory Factor Analysis of the End-User Computing Satisfaction Instrument. MIS Q. 1994, 18, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etezadi-Amoli, J.; Farhoomand, A.F. A structural model of end user computing satisfaction and user performance. Inf. Manag. 1996, 30, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, E. Model fit evaluation in multilevel structural equation models. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayduk, L.A. Structural Equation Modeling with LISREL: Essentials and Advances; The Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Baron, R.M.; Kenny, D.A. The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1986, 51, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preacher, K.J.; Rucker, D.D.; Hayes, A.F. Addressing moderated mediation hypotheses: Theory, methods, and prescriptions. Multivar. Behav. Res. 2007, 42, 185–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, A.F.; Scharkow, M. The relative trustworthiness of inferential tests of the indirect effect in statistical mediation analysis: Does method really matter? Psychol. Sci. 2013, 24, 1918–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A.F. Beyond Baron and Kenny: Statistical mediation analysis in the new millennium. Commun. Monogr. 2009, 76, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillard, A.J.; Couper, M.P.; Zikmund-Fisher, B.J. Perceived risk of cancer and patient reports of participation in decisions about screening: The DECISIONS study. Med. Decis. Making. 2010, 30, 96S–105S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Park, H.A. Development of a health information technology acceptance model using consumers’ health behavior intention. J. Med. Internet Res. 2012, 14, e133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| N | % | |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | ||
| Male | 214 | 55.3 |
| Female | 173 | 44.7 |
| Total | 387 | 100.0 |
| Age | ||
| 18–24 y | 48 | 12.4 |
| 25–34 y | 44 | 11.4 |
| 35–44 y | 95 | 24.5 |
| 45–54 y | 108 | 27.9 |
| 55–64 y | 87 | 22.5 |
| Over 65 y | 5 | 1.3 |
| Total | 387 | 100.0 |
| Education | ||
| General and vocational high school or below | 13 | 3.4 |
| Bachelor | 195 | 50.4 |
| Master | 162 | 41.9 |
| PhD | 17 | 4.4 |
| Total | 387 | 100.0 |
| Occupation | ||
| Student | 42 | 10.9 |
| Professionals | 58 | 15.0 |
| Business services | 168 | 43.4 |
| Soldiers, civil servants, and teachers | 70 | 18.1 |
| Manufacturing | 35 | 9.0 |
| Administrative associate | 14 | 3.6 |
| Total | 387 | 100.0 |
| E-payment usage frequency during the COVID-19 pandemic | ||
| 10 times or less | 145 | 37.5 |
| 11–20 times | 92 | 23.8 |
| 21–30 times | 46 | 11.9 |
| 31–40 times | 41 | 10.6 |
| 41–50 times | 16 | 4.1 |
| 51 times or more | 47 | 12.1 |
| Total | 387 | 100.0 |
| Increase in usage after COVID-19 | ||
| Yes | 294 | 76 |
| No | 93 | 24 |
| Total | 387 | 100 |
| Construct | Item | Model Parameter Estimates | Item Reliability | Residuals | Convergent Validity | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unstd. | S.E. | t-Value | p | Std. | SMC | 1-SMC | CR | AVE | ||
| SECU 2 | SECU1 | 1 | 0.705 | 0.497 | 0.503 | 0.929 | 0.687 | |||
| SECU3 | 1.371 | 0.084 | 16.366 | *** 1 | 0.863 | 0.745 | 0.255 | |||
| SECU4 | 1.161 | 0.081 | 14.278 | *** | 0.751 | 0.564 | 0.436 | |||
| SECU5 | 1.523 | 0.093 | 16.335 | *** | 0.873 | 0.762 | 0.238 | |||
| SECU6 | 1.54 | 0.093 | 16.536 | *** | 0.89 | 0.792 | 0.208 | |||
| SECU7 | 1.447 | 0.089 | 16.243 | *** | 0.872 | 0.760 | 0.240 | |||
| PU 2 | PU2 | 1 | 0.795 | 0.632 | 0.368 | 0.936 | 0.746 | |||
| PU3 | 1.249 | 0.062 | 20.256 | *** | 0.88 | 0.774 | 0.226 | |||
| PU4 | 1.221 | 0.062 | 19.858 | *** | 0.871 | 0.759 | 0.241 | |||
| PU5 | 1.228 | 0.06 | 20.616 | *** | 0.902 | 0.814 | 0.186 | |||
| PU6 | 1.184 | 0.06 | 19.616 | *** | 0.866 | 0.750 | 0.250 | |||
| PER 2 | PER1 | 1 | 0.707 | 0.500 | 0.500 | 0.870 | 0.577 | |||
| PER2 | 1.259 | 0.079 | 15.853 | *** | 0.859 | 0.738 | 0.262 | |||
| PER3 | 1.095 | 0.083 | 13.215 | *** | 0.757 | 0.573 | 0.427 | |||
| PER4 | 1.227 | 0.085 | 14.364 | *** | 0.847 | 0.717 | 0.283 | |||
| PER5 | 1.059 | 0.099 | 10.694 | *** | 0.596 | 0.355 | 0.645 | |||
| eWOM 2 | eWOM2 | 1 | 0.754 | 0.569 | 0.431 | 0.943 | 0.625 | |||
| eWOM 4 | 1.097 | 0.059 | 18.595 | *** | 0.875 | 0.766 | 0.234 | |||
| eWOM 5 | 1.107 | 0.068 | 16.233 | *** | 0.786 | 0.618 | 0.382 | |||
| eWOM 6 | 1.018 | 0.062 | 16.438 | *** | 0.793 | 0.629 | 0.371 | |||
| eWOM 7 | 0.699 | 0.05 | 14.02 | *** | 0.692 | 0.479 | 0.521 | |||
| eWOM 11 | 1.084 | 0.059 | 18.253 | *** | 0.869 | 0.755 | 0.245 | |||
| eWOM 12 | 0.955 | 0.064 | 14.966 | *** | 0.736 | 0.542 | 0.458 | |||
| eWOM 13 | 0.945 | 0.065 | 14.623 | *** | 0.718 | 0.516 | 0.484 | |||
| eWOM 14 | 1.143 | 0.064 | 17.754 | *** | 0.848 | 0.719 | 0.281 | |||
| eWOM 16 | 0.926 | 0.055 | 16.869 | *** | 0.813 | 0.661 | 0.339 | |||
| CI 2 | CI1 | 1 | 0.891 | 0.794 | 0.206 | 0.897 | 0.745 | |||
| CI2 | 0.991 | 0.037 | 26.46 | *** | 0.918 | 0.843 | 0.157 | |||
| CI3 | 0.915 | 0.05 | 18.367 | *** | 0.774 | 0.599 | 0.401 | |||
| Cronbach’s Alpha | CR | AVE | eWOM | SECU | PU | PER | CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| eWOM 3 | 0.948 | 0.943 | 0.625 | 0.791 1 | ||||
| SECU 3 | 0.928 | 0.929 | 0.687 | 0.488 2 | 0.829 1 | |||
| PU 3 | 0.935 | 0.936 | 0.746 | 0.529 2 | 0.420 2 | 0.864 1 | ||
| PER 3 | 0.858 | 0.870 | 0.577 | 0.233 2 | 0.043 2 | 0.158 2 | 0.759 1 | |
| CI 3 | 0.886 | 0.897 | 0.745 | 0.727 2 | 0.393 2 | 0.426 2 | 0.165 2 | 0.863 1 |
| R2 (PU) = 0.196, R2 (eWOM) = 0.391, R2 (CI) = 0.531 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regression Path | β | B | S.E. | C.R. | p Value | Hypothesis | Confirmed (Y/N) | ||
| PU 2 | ← | SECU 2 | 0.414 | 0.457 | 0.062 | 7.379 | 0.000 *** 1 | H1 | Y |
| PU | ← | PER 2 | 0.140 | 0.119 | 0.044 | 2.724 | 0.006 ** 1 | H2 | Y |
| CI 2 | ← | PER | −0.003 | −0.003 | 0.048 | −0.071 | 0.943 | H3 | N |
| eWOM 2 | ← | PER | 0.161 | 0.167 | 0.048 | 3.444 | 0.000 *** 1 | H4 | Y |
| eWOM | ← | PU | 0.366 | 0.45 | 0.066 | 6.854 | 0.000 *** 1 | H5 | Y |
| eWOM | ← | SECU | 0.328 | 0.444 | 0.072 | 6.172 | 0.00 0 *** 1 | H6 | Y |
| CI | ← | SECU | 0.040 | 0.058 | 0.070 | 0.825 | 0.409 | H7 | N |
| CI | ← | PU | 0.048 | 0.063 | 0.065 | 0.965 | 0.334 | H8 | N |
| CI | ← | eWOM | 0.682 | 0.727 | 0.067 | 10.862 | 0.000 *** 1 | H9 | Y |
| Goodness-of-fit statistic | |||||||||
| χ2 (chi-square) = 367, χ2/df = 3.061, GFI = 0.831, AGFI = 0.80, RMSEA = 0.073, and CFI = 0.916 SRMR = 0.0569 | |||||||||
| Path | Bootstrap 5000 Confidence Interval 2 | |||
| Effect | BootSE | LLCI | ULCI | |
| Total indirect effect | ||||
| PER 1 → CI 1 | 0.153 | 0.039 | 0.078 | 0.230 |
| Indirect effects | ||||
| Path 1 3 | 0.008 | 0.006 | 0.000 | 0.027 |
| Path 2 3 | 0.041 | 0.017 | 0.009 | 0.078 |
| Path 3 3 | 0.103 | 0.031 | 0.045 | 0.167 |
| Direct effect | ||||
| PER → CI | −0.011 | 0.033 | −0.077 | 0.054 |
| Path | Bootstrap 5000 Confidence Interval | |||
| Effect | BootSE | LLCI | ULCI | |
| Total indirect effect | ||||
| SECU 1 → CI | 0.357 | 0.043 | 0.276 | 0.448 |
| Indirect effects | ||||
| Path 4 3 | 0.024 | 0.017 | −0.008 | 0.062 |
| Path 5 3 | 0.109 | 0.023 | 0.070 | 0.160 |
| Path 6 3 | 0.224 | 0.041 | 0.146 | 0.310 |
| Direct effect | ||||
| SECU→CI | 0.068 | 0.0430 | −0.016 | 0.152 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, T.-L.; Lin, T.T.; Hsu, S.-Y. Continuance Usage Intention toward E-Payment during the COVID-19 Pandemic from the Financial Sustainable Development Perspective Using Perceived Usefulness and Electronic Word of Mouth as Mediators. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7775. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137775
Liu T-L, Lin TT, Hsu S-Y. Continuance Usage Intention toward E-Payment during the COVID-19 Pandemic from the Financial Sustainable Development Perspective Using Perceived Usefulness and Electronic Word of Mouth as Mediators. Sustainability. 2022; 14(13):7775. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137775
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Tsai-Ling, Tyrone T. Lin, and Shu-Yen Hsu. 2022. "Continuance Usage Intention toward E-Payment during the COVID-19 Pandemic from the Financial Sustainable Development Perspective Using Perceived Usefulness and Electronic Word of Mouth as Mediators" Sustainability 14, no. 13: 7775. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137775
APA StyleLiu, T.-L., Lin, T. T., & Hsu, S.-Y. (2022). Continuance Usage Intention toward E-Payment during the COVID-19 Pandemic from the Financial Sustainable Development Perspective Using Perceived Usefulness and Electronic Word of Mouth as Mediators. Sustainability, 14(13), 7775. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137775








