Does the Pilot Free Trade Zone Promote the Quality of Urban Economic Growth: An Empirical Research Based on Quasi-Natural Experiment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review, Policy Background and Mechanism Analysis
2.1. Literature Review
2.2. Policy Background
2.3. Mechanism Analysis
3. Model Setting, Variable Selection and Data Interpretation
3.1. Model Setting
3.2. Variable Selection
3.2.1. Explained Variable
3.2.2. Explanatory Variables
3.2.3. Control Variable
4. Empirical Analysis
4.1. Basic Regression Analysis
4.2. Dynamic Effects Analysis
4.3. Parallel Trend Test
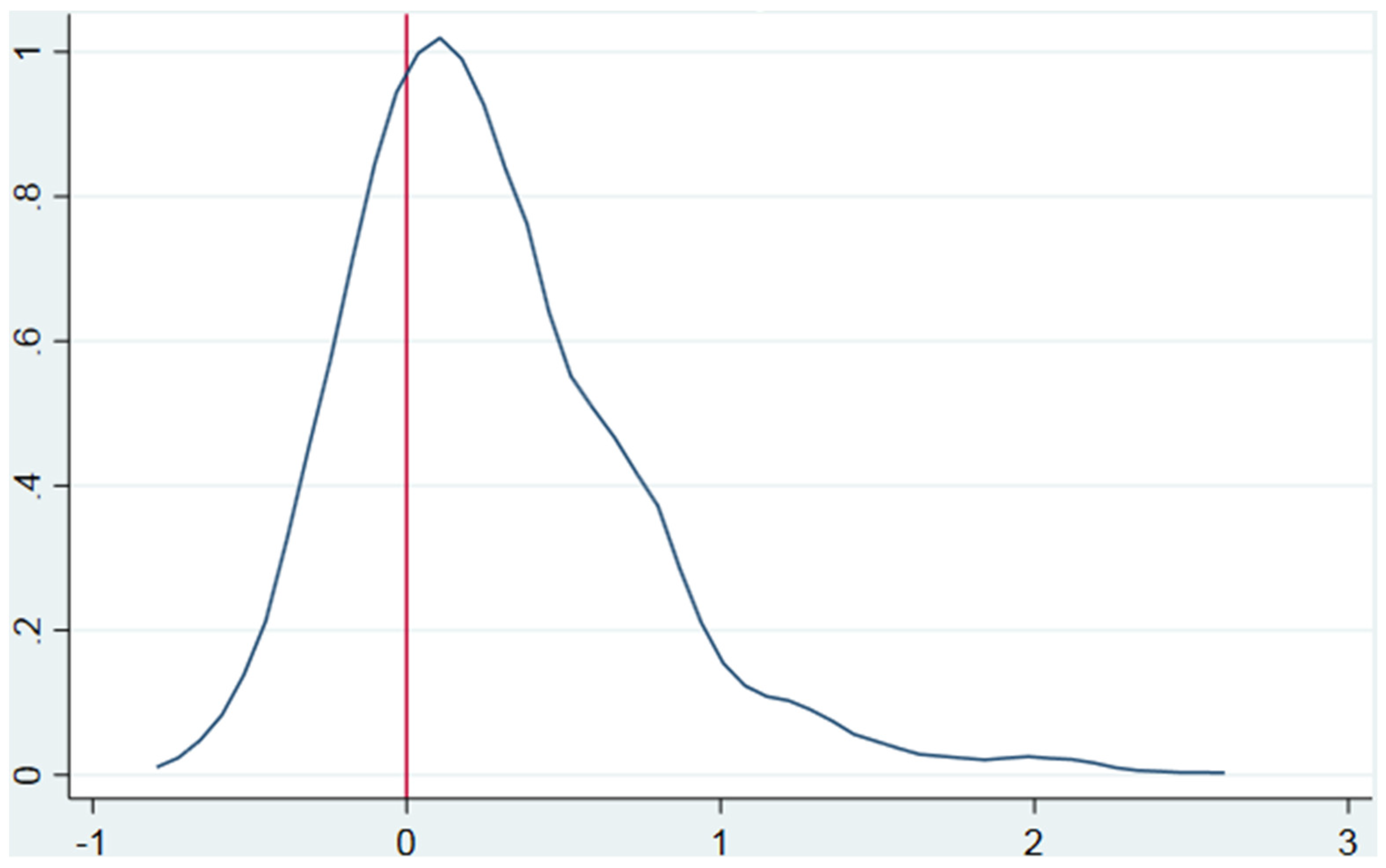
4.4. Robustness Check
5. Further Discussion
5.1. Mediation Test
5.2. Heterogeneity Test
5.2.1. Developmental Orientation Heterogeneity
5.2.2. Location Distribution Heterogeneity
5.2.3. Batch Heterogeneity
6. Conclusions and Policy Implications
6.1. Conclusions
6.2. Policy Implications
6.3. Study Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kong, Q.; Peng, D.; Ni, Y.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Z. Trade openness and economic growth quality of China: Empirical analysis using ARDL model. Finance Res. Lett. 2021, 35, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Su, K.; Wang, S. Does the Digital Economy Promote Industrial Structural Upgrading?—A Test of Mediating Effects Based on Heterogeneous Technological Innovation. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Le, Y.; Xia, B.; Skitmore, M. Causes of business-to-government corruption in the tendering process in China. J. Manag. Eng. 2017, 11, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Liu, X.; Chu, F.; Zhang, E.; Chu, C.B. Service-oriented robust worker scheduling with motivation effects. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2021, 59, 2328–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Yu, J. Gender gap, capital accumulation and the demographic transition. Econ. Transit. 2017, 63, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-C. Why do people adopt cloud services? Gender differences. Soc. Sci. Inf. 2015, 4, 55–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Nie, R. Enterprise investment, local government intervention and coal overcapacity: The case of China. Energ. Policy 2017, 101, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Z. Research onthe Effects of Free Trade Area on Local Economy—Based on the “Counter-Factual” Thinking. J. Int. Trade 2017, 2, 3–15. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, X. Pilot Free Trade Zones and Economic Growth: An Empirical Research Based on Quasi—Natural Experiment. Econ. Rev. 2018, 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Yang, Z. Does the Construction of the Pilot Free Trade Zones Bring Regional Radiation Effects—Empirical Research Based on the Yangtze River Delta, Pearl River Delta, and Beijing—Tianjin—Hebei Regions. J. Int. Trade 2020, 9, 65–80. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, L.; Feng, X. Has the Pilot Free Trade Zone Contributed to Steady Economic Growth in the Region?—Based on Data Envelopment Analysis and Difference in Difference Method Verification. Inq. Into Econ. Issues 2020, 4, 131–141. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, N.; Zhou, X.; Ling, J. Study on Economic Growth Effect of Shanghai Pilot Free Trade ZoneBased on Counterfactual Analysis with Panel Data. J. Int. Trade 2015, 14–24. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Yuan, B.; Cui, Q. Does the pilot free trade zone policy attract the entering of foreign-invested enterprises? The evidence from China. Appl Econ Lett 2021, 28, 1162–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, H.; Gao, W. Do the Pilot Free Trade Zones Cause the Effects of Institutional Dividends? Evidence from Shanghai PFTZ. J. Financ. Econ. 2017, 43, 48–59. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Wang, J. Innovative Performance Promotion Effect of Free-Trade Zone—Evidence from the Quasi-Experiment of the Shanghai Free-Trade Zone. Res. Econ. Manag. 2018, 39, 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Lv, C. Impact Analysis of Free Trade Zones in Regional Economies—A Comparative Study Based on Synthetic Control Method. J. Int. Trade 2018, 3, 51–66. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Zheng, J. How Does the Setting Up of Pilot Free Trade Zone Affect the Trade Pattern Transformation?—Evidence from the Guangdong Pilot Free Trade Zone. J. Int. Trade 2017, 6, 71–82. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Zhao, T. Has the Pilot Free Trade Zone Promoted the Upgrading of Industrial Structure? An Empirical Analysis Based on China ( Shanghai) Pilot Free Trade Zone. J. Cent. Univ. Financ. Econ. 2019, 8, 118–128. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Li, L. Study on the Policy Effect of Free Trade Zone on Industrial Structure Upgrading—A Quasi-Natural Experiment Based on Shanghai Free Trade Zone. Econ. Surv. 2019, 36, 79–86. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Peng, Y.; Shen, Y. China (Shanghai) Pilot Free Trade Zone: Realizing the Replicability and Promotion of National Strategy. Intertrade 2013, 12, 4–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y. Free Trade Pilot Zone Experiment and Construction of Opening Economic System. Acad. Mon. 2014, 46, 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- David, N.; William, W. Employment Effects of Minimum and Subminimum Wages: Panel Data on State Minimum Wage Laws. Ind. Labor Relat. Rev. 1992, 23, 1026–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Jajri, I.; Ismail, R. Impact of labour quality on labour productivity and economic growth. Afr. J. Bus. Manag. 2010, 4, 486–495. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Chen, D. Air Pollution, Government Regulations and High-quality Economic Development. Econ. Res. J. 2018, 53, 20–34. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, T.; Levine, R.; Levkov, A. Big Bad Banks? The Winners and Losers from Bank Deregulation in the United States. J. Financ. 2010, 65, 1637–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, P.; Lu, Y.; Wang, J. Does flattening government improve economic performance? Evidence from China. J. Dev. Econ. 2016, 123, 18–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantoni, D.; Chen, Y.; Yang, D.; Yuchtman, N.; Zhang, Y.J. Curriculum and Ideology. J. Polit. Econl. 2017, 125, 338–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Variable | Variable Meaning | Mean | Std. Dev. | Max | Maximum | Obs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pro | labor productivity | 18.77 | 8.76 | 1.36 | 97.09 | 1650 |
| Pro_fix | Revised labor productivity | 4.78 | 5.19 | 0.19 | 55.1 | 1650 |
| FTZ | pilot free trade zones | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0 | 1 | 1650 |
| lngov | Government R&D expenditure | 14.58 | 0.71 | 12.27 | 18.24 | 1650 |
| lnfin | Loan balance of financial institutions | 16 | 1.02 | 13.67 | 20.33 | 1650 |
| lnedu | The number of universities | 1.18 | 0.91 | 0 | 4.21 | 1650 |
| lnfra | Logarithmic highway mileage | 6.83 | 0.88 | 2.64 | 9.6 | 1650 |
| lninter | Logarithmic number of Internet users | 3.76 | 0.92 | 0 | 8.55 | 1650 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pro | Pro_fix | Pro | Pro_fix | |
| FTZ | 3.103 ** | 4.288 *** | 2.393 * | 3.817 *** |
| (1.396) | (1.191) | (1.362) | (1.078) | |
| lngov | 3.919 * | 2.314 *** | ||
| (2.165) | (0.555) | |||
| lnfin | 0.774 | −0.751 * | ||
| (1.916) | (0.439) | |||
| lnedu | −1.892 * | 0.0986 | ||
| (1.103) | (0.205) | |||
| lnfra | −0.360 | −0.323 | ||
| (0.580) | (0.200) | |||
| lninter | −0.296 | 0.522 *** | ||
| (0.666) | (0.169) | |||
| _cons | 15.59 *** | 2.896 *** | −45.53 | −14.19 * |
| (0.248) | (0.220) | (50.48) | (8.481) | |
| Time fixed effect | be | be | be | be |
| Individual effect | be | be | be | be |
| Control variable | no | no | be | be |
| N | 1650 | 1650 | 1650 | 1650 |
| R2 | 0.433 | 0.433 | 0.445 | 0.453 |
| (1) | (2) | |
|---|---|---|
| Pro_fix | Pro_fix | |
| After 1 | 0.424 | 0.313 |
| (0.348) | (0.381) | |
| After 2 | 3.400 *** | 2.843 *** |
| (0.990) | (0.901) | |
| After 3 | 6.515 *** | 5.931 *** |
| (1.555) | (1.479) | |
| After 4 | 5.770 *** | 5.227 *** |
| (1.141) | (1.026) | |
| After 5 | 6.365 *** | 5.607 *** |
| (0.447) | (0.456) | |
| Time fixed effect | be | be |
| Individual effect | be | be |
| Control variable | no | be |
| N | 1650 | 1650 |
| R2 | 0.481 | 0.495 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pro_fix | Pro_fix | Pro_fix | Pro_fix | Pro_fix | Pro_fix | |
| The Top 20 Cities Are the Control Group | The Top 30 Cities Are the Control Group | The Top 40 Cities Are the Control Group | ||||
| FTZ | 3.351 ** | 1.657 * | 3.508 *** | 1.963 ** | 3.648 *** | 2.394 ** |
| (1.261) | (0.899) | (1.244) | (0.931) | (1.226) | (0.947) | |
| Time fixed effect | be | be | be | be | be | be |
| Individual effect | be | be | be | be | be | be |
| Control variable | no | be | no | be | no | be |
| N | 320 | 320 | 420 | 420 | 520 | 520 |
| R2 | 0.425 | 0.483 | 0.421 | 0.484 | 0.428 | 0.482 |
| (1) | (2) | |
|---|---|---|
| Pro_fix | Pro_fix | |
| FTZ | 4.283 *** | 3.746 *** |
| (1.199) | (1.024) | |
| Time fixed effect | be | be |
| Individual effect | be | be |
| Control variable | no | be |
| N | 740 | 740 |
| R2 | 0.416 | 0.447 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pro_fix | Pro_fix | Pro_fix | Pro_fix | Pro_fix | Pro_fix | Pro_fix | Pro_fix | |
| FTZ | 4.288 *** | 4.308 *** | 3.817 *** | 3.838 *** | ||||
| (1.191) | (1.211) | (1.078) | (1.094) | |||||
| HTZ | 0.293 | 0.368 | 0.329 | 0.393 | ||||
| (0.469) | (0.474) | (0.492) | (0.488) | |||||
| FTZ_HTZ | 4.505 *** | 4.032 *** | ||||||
| (1.212) | (1.099) | |||||||
| Time fixed effect | be | be | be | be | be | be | be | be |
| Individual effect | be | be | be | be | be | be | be | be |
| Control variable | no | no | no | no | be | be | be | be |
| N | 1650 | 1650 | 1650 | 1650 | 1650 | 1650 | 1650 | 1650 |
| R2 | 0.433 | 0.369 | 0.434 | 0.437 | 0.453 | 0.454 | 0.404 | 0.456 |
| Market (1) | Market (2) | Pro_fix (3) | Pro_fix (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FTZ | −0.0615 *** (0.0147) | −0.0725 *** (0.0214) | 4.228 *** | 3.720 *** |
| (1.183) | (1.058) | |||
| fiscal | −0.981 *** (0.310) | −1.339 *** (0.351) | ||
| Time fixed effect | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Individual effect | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Control variable | no | yes | no | yes |
| N | 1650 | 1650 | 1650 | 1650 |
| R2 | 0.498 | 0.520 | 0.437 | 0.461 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pro_fix | Pro_fix | Pro_fix | Pro_fix | Pro_fix | Pro_fix | Pro_fix | Pro_fix | |
| Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration | Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration | Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area | Chengdu-Chongqing Urban Agglomeration | Urban Agglomeration in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River | Central Plains Urban Agglomeration | Urban Agglomeration on the West Coast of the Straits | Liaozhongnan City Groups | |
| FTZ | 4.601 *** | 4.495 *** | 9.041 *** | −0.524 *** | 2.547 *** | 0.0741 | 2.375 *** | −0.214 |
| (0.125) | (0.254) | (2.031) | (0.129) | (0.138) | (0.504) | (0.787) | (0.451) | |
| Time fixed effect | be | be | be | be | be | be | be | be |
| Individual effect | be | be | be | be | be | be | be | be |
| Control variable | be | be | be | be | be | be | be | be |
| N | 1510 | 1510 | 1520 | 1510 | 1510 | 1520 | 1520 | 1520 |
| R2 | 0.538 | 0.539 | 0.461 | 0.529 | 0.534 | 0.531 | 0.536 | 0.532 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pro_fix | Pro_fix | Pro_fix | Pro_fix | |
| Coastal FTZ | Non-Coastal FTZ | |||
| FTZ | 4.818 ** | 3.615 ** | 0.233 | 0.303 |
| (1.641) | (1.208) | (0.582) | (0.578) | |
| Time fixed effect | be | be | be | be |
| Individual effect | be | be | be | be |
| Control variable | no | be | no | be |
| N | 120 | 120 | 1530 | 1530 |
| R2 | 0.409 | 0.422 | 0.510 | 0.534 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pro_fix | Pro_fix | Pro_fix | Pro_fix | Pro_fix | Pro_fix | |
| The First Batch of FTZ | The Second Batch of FTZ | The Third Batch of FTZ | ||||
| FTZ | 5.087 *** | 4.495 *** | 5.957 *** | 5.422 *** | 0.230 | 0.295 |
| (0.0809) | (0.254) | (1.659) | (1.564) | (0.489) | (0.490) | |
| Time fixed effect | be | be | be | be | be | be |
| Individual effect | be | be | be | be | be | be |
| Control variable | no | be | no | be | no | be |
| N | 1540 | 1540 | 1580 | 1580 | 1590 | 1590 |
| R2 | 0.521 | 0.539 | 0.442 | 0.455 | 0.520 | 0.538 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, T.; He, F. Does the Pilot Free Trade Zone Promote the Quality of Urban Economic Growth: An Empirical Research Based on Quasi-Natural Experiment. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7352. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127352
Zhao T, He F. Does the Pilot Free Trade Zone Promote the Quality of Urban Economic Growth: An Empirical Research Based on Quasi-Natural Experiment. Sustainability. 2022; 14(12):7352. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127352
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Tingru, and Feng He. 2022. "Does the Pilot Free Trade Zone Promote the Quality of Urban Economic Growth: An Empirical Research Based on Quasi-Natural Experiment" Sustainability 14, no. 12: 7352. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127352
APA StyleZhao, T., & He, F. (2022). Does the Pilot Free Trade Zone Promote the Quality of Urban Economic Growth: An Empirical Research Based on Quasi-Natural Experiment. Sustainability, 14(12), 7352. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14127352





