The Role of Pedagogical Agents in Personalised Adaptive Learning: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Reviews on Pedagogical Agents in Personalised Adaptive Learning
“If the agents can do half of my routine tasks, that would be nice...as an academic, I can spend that valuable spare time for more productive activities. I don’t mind if those routine tasks are handled by agents.”
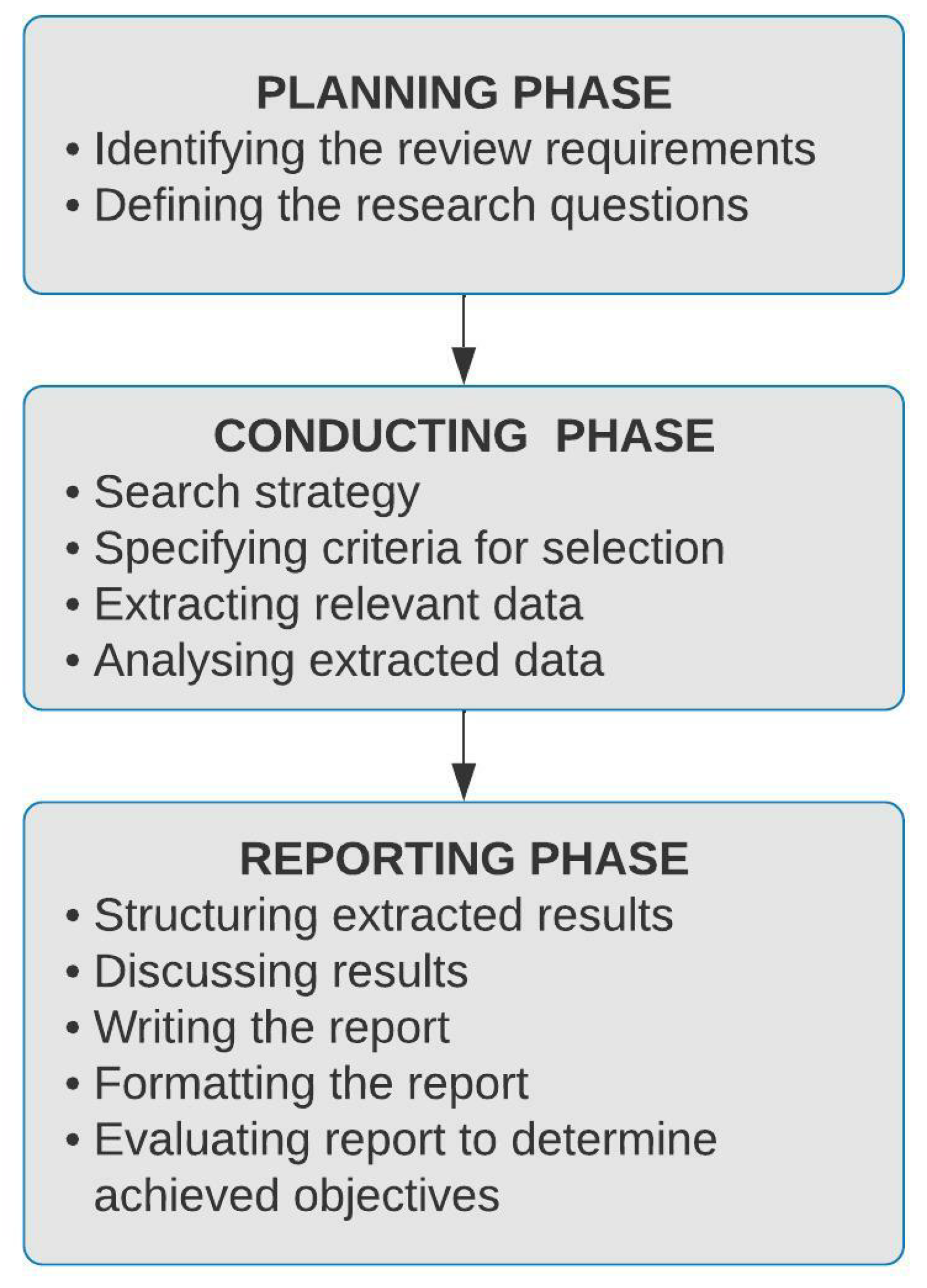
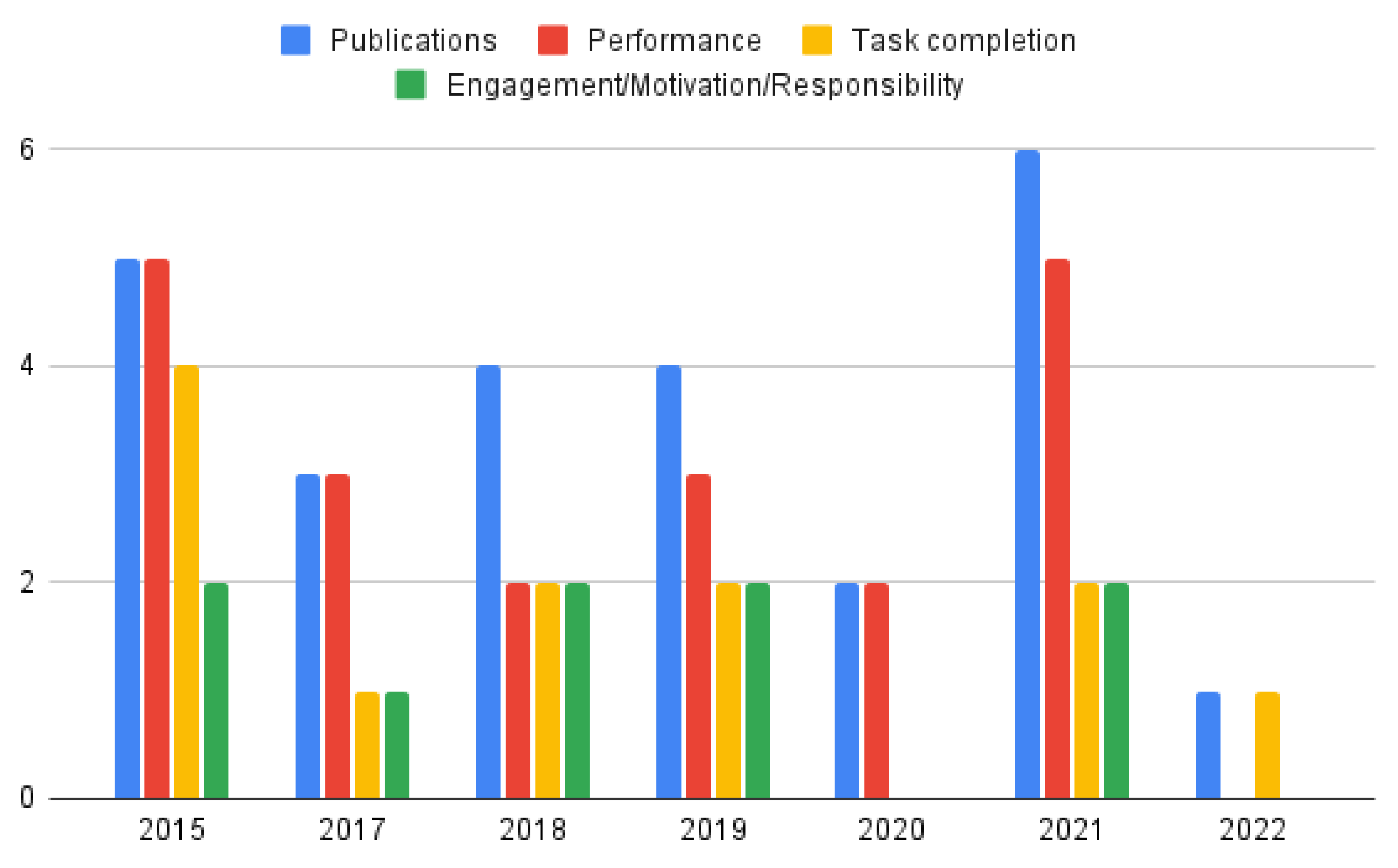
3. Research Methodology
3.1. Planning the Review
- To define the roles pedagogical agents play in PAL systems.
- To investigate the projected outcomes of including pedagogical agents in PAL environments.
Specifying the RQs
3.2. Conducting the Review
3.2.1. Search Strategy
3.2.2. Criteria for Study Selection
- Articles published between 2015 and 2022
- Articles written in English
- Articles that performed some form of real-time personalisation during learning according to the learner’s preferences
- Articles that incorporated pedagogical agents in the personalisation of learning
- Articles that appeared in conference proceedings and scholarly journals
- Books
- PowerPoint presentations or publications that just include abstracts
- Articles with inaccessible texts
- Articles in which the agent roles are not clearly established
- Articles that lack real-time personalisation
4. Agent Theories in Personalised Adaptive Learning
“an entity that functions continuously and autonomously in an environment in which other processes take place and other agents exist.”[15]
“an encapsulated computer system that is situated in some environment and that is capable of flexible, autonomous action in that environment in order to meet its design objectives.”[16]
“a system situated within and a part of an environment that senses that environment and acts on it, in pursuit of its own agenda and so as to effect what it senses in the future.”[17]
- Autonomy: the ability to exert some control over their behaviour and internal condition without the need for direct intervention.
- Reactivity: the capacity to detect changes in their surroundings and respond appropriately.
- Pro-activity: the ability to not just be reactive but also to engage in goal-directed behaviour
- Continuity: the capacity to run constantly or just when necessary,
- Social capacity: the ability to engage with other agents (through agent-communication language in a multi-agent system architecture) and humans (through natural language).
5. Discussions
5.1. Adaptive Roles
5.1.1. Adaptive Presentation
5.1.2. Adaptive Navigation
5.1.3. Adaptive Information Filtering
5.2. Intelligent Roles
5.2.1. Intelligent Tutoring
5.2.2. Intelligent Monitoring
5.2.3. Intelligent Collaborative Learning
5.3. Expected Outcomes
5.3.1. Improved Performance
5.3.2. Task Completion
5.3.3. Enhanced Engagement, Motivation, Responsibility
6. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FSLS | Felder Silverman Learning Style |
| IEEE | Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers |
| ITS | Intelligent Tutoring System |
| MAS | Multi-Agent System |
| MOOC | Massive Open Online Course |
| PAL | Personalised Adaptive Learning |
| PALS | Personalised Adaptive Learning System |
| VLE | Virtual Learning Environment |
References
- Peng, H.; Ma, S.; Spector, J.M. Personalized Adaptive Learning: An Emerging Pedagogical Approach Enabled by a Smart Learning Environment. Lect. Notes Educ. Technol. 2019, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becta. Personalising Learning: The Opportunities Offered by Technology Introduction; Becta: Coventry, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Office of Educational Technology. Reimagining the Role of Technology in Education: 2017 National Education Technology Plan Update; Office of Educational Technology: Washington, DC, USA, 2017.
- Becker, S.A.; Brown, M.; Dahlstrom, E.; Davis, A.; DePaul, K.; Diaz, V.; Pomerantz, J. NMC Horizon Report: 2018 Higher Education Edition; EDUCAUSE: Louisville, CO, USA, 2018; p. 60. [Google Scholar]
- Pugliese, L. Adaptive Learning Systems: Surviving the Storm. Available online: https://er.educause.edu/articles/2016/10/adaptive-learning-systems-surviving-the-storm (accessed on 16 August 2021).
- Brusilovsky, P.; Peylo, C. Adaptive and Intelligent Web-based Educational Systems. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. (IJAIED) 2003, 13, 159–172. [Google Scholar]
- Vandewaetere, M.; Desmet, P.; Clarebout, G. The contribution of learner characteristics in the development of computer-based adaptive learning environments. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2011, 27, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassi, R.; Daradoumis, T.; Xhafa, F.; Caballe, S.; Sula, A. Software Agents in Large Scale Open E-learning: A Critical Component for the Future of Massive Online Courses (MOOCs). In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Intelligent Networking and Collaborative Systems, Salerno, Italy, 10–12 September 2014; pp. 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veletsianos, G.; Russell, G.S. Pedagogical Agents. In Handbook of Research on Educational Communications and Technology; Spector, J.M., Merrill, M.D., Elen, J., Bishop, M.J., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchenham, B.; Charters, S. Guidelines for Performing Systematic Literature Reviews in Software Engineering; Keele University: Newcastle, UK; Durham University: Durham, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmood, A.K.; Ferneley, E. The use of animated agents in e-learning environments: An exploratory, interpretive case study. ALT-J 2006, 14, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y. Pedagogical Agents. In Encyclopedia of Educational Technology; Spector, M., Ed.; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2015; pp. 561–567. [Google Scholar]
- Martha, A.S.D.; Santoso, H. The Design and Impact of the Pedagogical Agent: A Systematic Literature Review. J. Educ. Online 2019, 16, n1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papoutsi, F.; Rangoussi, M. Pedagogical Agents in E-learning: A review of recent (2009–2019) research results. In Proceedings of the 24th Pan-Hellenic Conference on Informatics, Athens, Greece, 20–22 November 2020; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoham, Y. Agent-oriented programming. Artif. Intell. 1993, 60, 51–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooldridge, M. Agent-based software engineering. IEEE Proc. Softw. Eng. 1997, 144, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franklin, S.; Graesser, A. Is It an agent, or just a program? A taxonomy for autonomous agents. In Intelligent Agents III Agent Theories, Architectures, and Languages; Müller, J.P., Wooldridge, M.J., Jennings, N.R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; pp. 21–35. [Google Scholar]
- Baylor, A.L. Intelligent agents as cognitive tools. Educ. Technol. 1999, 39, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Gulz, A. Social enrichment by virtual characters—Differential benefits. J. Comput. Assist. Learn. 2005, 21, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusilovsky, P. Adaptive and Intelligent Technologies for Web-based Eduction. Künstliche Intell. 1999, 13, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Rani, M.; Nayak, R.; Vyas, O.P. An ontology-based adaptive personalized e-learning system, assisted by software agents on cloud storage. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2015, 90, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palomino, C.E.G.; Silveira, R.A.; Nakayama, M.K. Using agent-based adaptive learning environments for knowledge sharing management. Int. J. Knowl. Learn. 2015, 10, 278–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowri, R.; Kanmani, S. Self-adaptive agent-based tutoring system. Int. J. Adapt. Innov. Syst. 2015, 2, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooshyar, D.; Ahmad, R.; Yousefi, M.; Yusop, F.; Horng, S.J. A flowchart-based intelligent tutoring system for improving problem-solving skills of novice programmers. J. Comput. Assist. Learn. 2015, 31, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, M.C.; Azevedo, R. Motivation matters: Interactions between achievement goals and agent scaffolding for self-regulated learning within an intelligent tutoring system. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2015, 52, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bendou, K.; Megder, E.; Cherkaoui, C. Animated Pedagogical Agents to Assist Learners and to keep them motivated on Online Learning Environments (LMS or MOOC). Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2017, 168, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oskouei, R.J.; Kor, N.M. Proposing a Novel Adaptive Learning Management System: An Application of Behavior Mining & Intelligent Agents. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput. 2017, 23, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciloglugil, B.; Inceoglu, M.M. An Agents and Artifacts Metamodel Based E-Learning Model to Search Learning Resources. In ICCSA; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Graesser, A.C.; Hu, X.; Nye, B.D.; VanLehn, K.; Kumar, R.; Heffernan, C.; Heffernan, N.; Woolf, B.; Olney, A.M.; Rus, V.; et al. ElectronixTutor: An intelligent tutoring system with multiple learning resources for electronics. Int. J. STEM Educ. 2018, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nye, B.D.; Pavlik, P.I.; Windsor, A.; Olney, A.M.; Hajeer, M.; Hu, X. SKOPE-IT (Shareable Knowledge Objects as Portable Intelligent Tutors): Overlaying natural language tutoring on an adaptive learning system for mathematics. Int. J. STEM Educ. 2018, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciloglugil, B.; Inceoglu, M.M. A Learner Ontology Based on Learning Style Models for Adaptive E-Learning. In International Conference on Computational Science and Its Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meleško, J.; Kurilovas, E. Adaptive Tutoring System With Application of Intelligent Agents. Int. J. Smart Educ. Urban Soc. 2018, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, S.; Saeed, F.; Mathkour, H.; Arafah, M.A. Continuous improvement of deaf student learning outcomes based on an adaptive learning system and an Academic Advisor Agent. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2019, 92, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korovin, M.; Borgest, N. Multi-agent Approach Towards Creating an Adaptive Learning Environment. In Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Volume 836, pp. 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diego, M.; Carlos, G.; Jose, A. Adaptive learning objects in the context of eco-connectivist communities using learning analytics. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, S.; Jiang, L.; Xu, J.; Tham, B.J.K.; Qiu, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Murnane, E.L.; Brunskill, E.; Landay, J.A. QuizBot: A Dialogue-based Adaptive Learning System for Factual Knowledge. In Proceedings of the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Scotland, UK, 4–9 May 2019; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Ghouch, N.; En-Naimi, E.M.; Kouissi, M. Implementation of an adaptive learning system based on agents and web services. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 2020, 15, 162–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nihad, E.G.; Mohamed, K.; El Mokhtar, E.N. Designing and modeling of a multi-agent adaptive learning system (MAALS) using incremental hybrid case-based reasoning (IHCBR). Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2020, 10, 1980–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apoki, U.C. The Design of WASPEC: A Fully Personalised Moodle System Using Semantic Web Technologies. Computers 2021, 10, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, A.H.; Viecelli, K.; do Prado, H.A.; Ferneda, E.; Thalheimer, J.; da Rocha Fernandes, A.M. An Adaptive and Proactive Interface Agent for Interactivity and Decision-Making Improvement in a Collaborative Virtual Learning Environment. In Enterprise Information Systems; Filipe, J., Śmiałek, M., Brodsky, A., Hammoudi, S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Swizterland, 2021; pp. 612–634. [Google Scholar]
- González-Castro, N.; Muñoz-Merino, P.J.; Alario-Hoyos, C.; Kloos, C.D. Adaptive learning module for a conversational agent to support MOOC learners. Australas. J. Educ. Technol. 2021, 37, 24–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciloglugil, B.; Alatli, O.; Inceoglu, M.M.; Erdur, R.C. A Multi-agent Based Adaptive E-Learning System. In Computational Science and Its Applications—ICCSA 2021; Gervasi, O., Murgante, B., Misra, S., Garau, C., Blečić, I., Taniar, D., Apduhan, B.O., Rocha, A.M.A.C., Tarantino, E., Torre, C.M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Swizterland, 2021; pp. 693–707. [Google Scholar]
- Mota Lopes, A.M.; De Magalhaes Netto, J.F. Designing Pedagogical Agents Toward the Recommendation and Intervention Based on Students’ Actions in an ITS. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference (FIE), Lincoln, NE, USA, 13–16 October 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, T.; Du, Y.; Li, T. Curriculum-Oriented Multi-goal Agent for Adaptive Learning. In Web and Big Data. APWeb-WAIM 2020 International Workshops; Chen, Q., Li, J., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 104–115. [Google Scholar]
- Viswanathan, N.; Meacham, S.; Adedoyin, F.F. Enhancement of online education system by using a multi-agent approach. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2022, 3, 100057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusilovsky, P. Adaptive Hypermedia. User Model. User-Adapt. Interact. 2001, 11, 87–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusilovsky, P. Adaptive navigation support. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 4321 LNCS, pp. 263–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Felder, R.M. Matters of styles. ASEE Prism 1996, 6, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, P.M. The learning styles myth is thriving in higher education. Front. Psychol. 2015, 6, 1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, P.M.; Miah, M. Evidence-based higher education—Is the learning styles ’myth’ important? Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
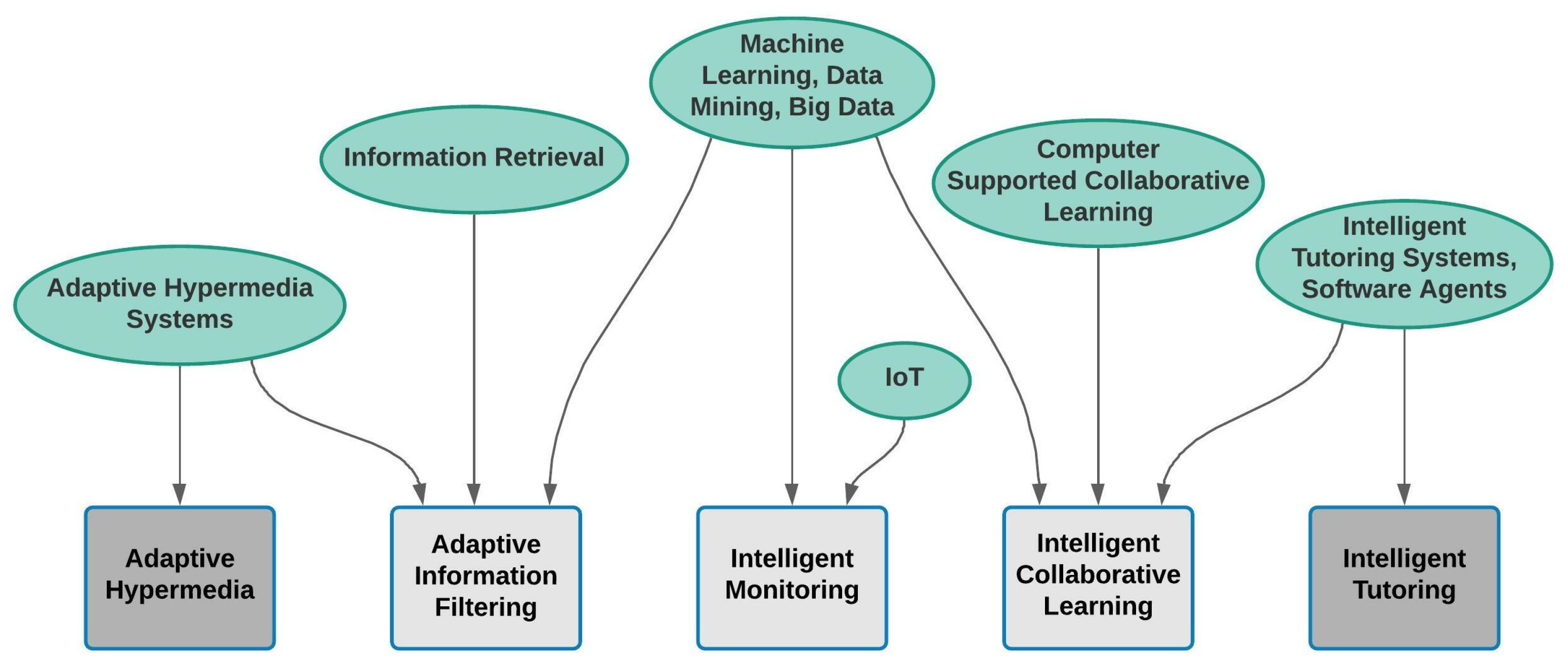
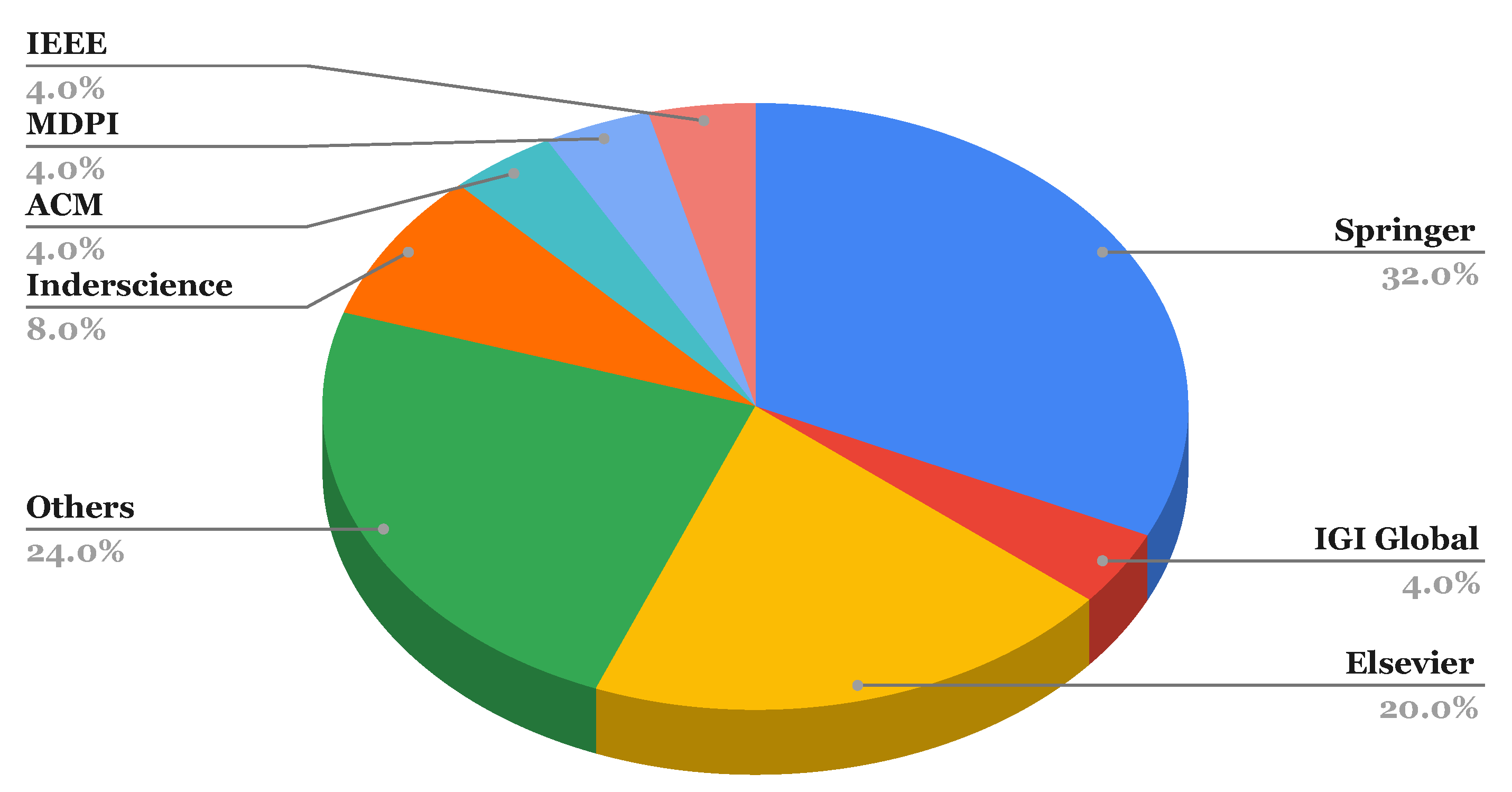
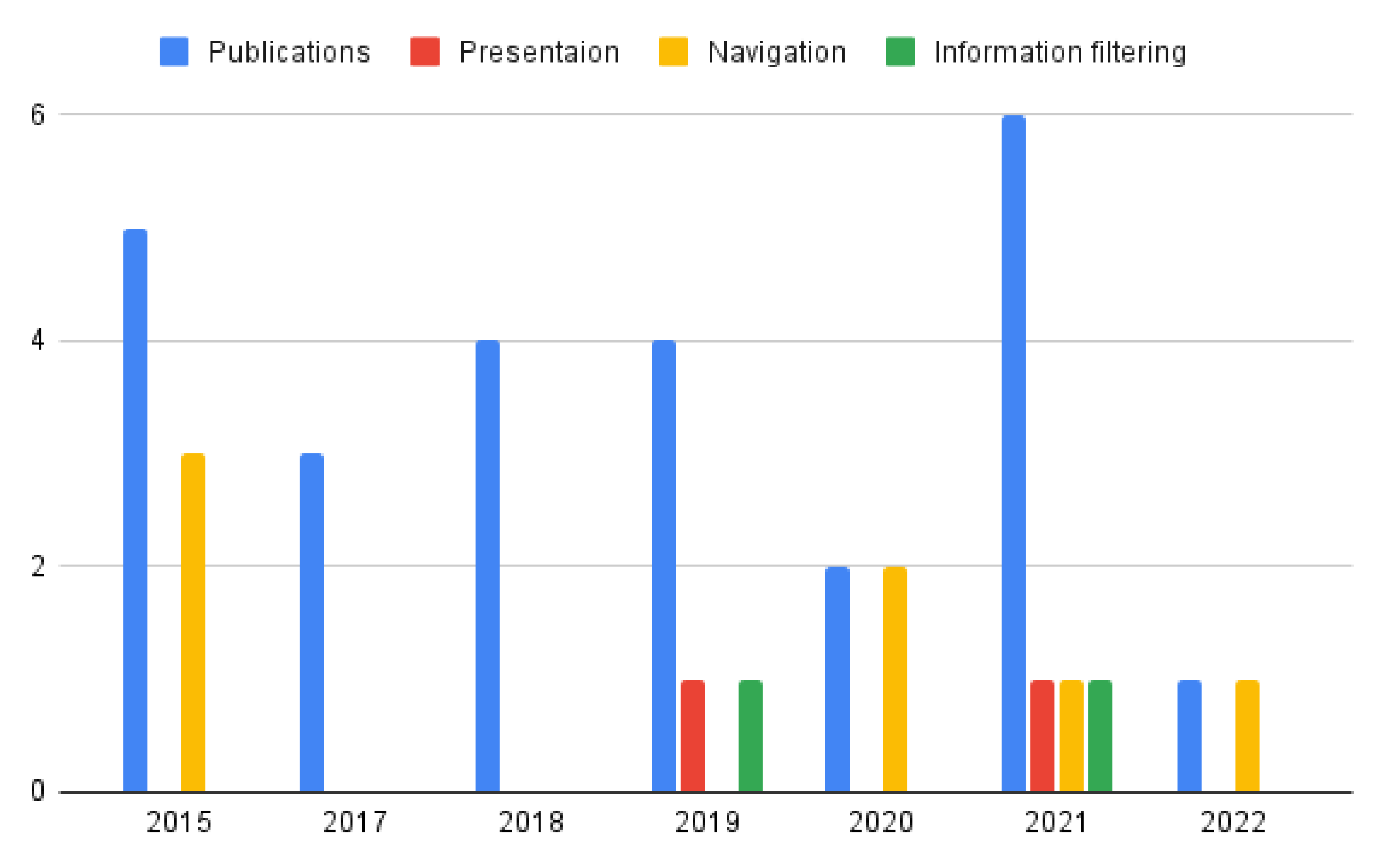

| Technologies | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Adaptivity | Presentation | The adaptive presentation technology, which is derived from the field of adaptive hypermedia, delivers a non-static website that dynamically adapts to fit the learner model’s objectives, knowledge, and other preferences [20]. |
| Navigation | Adaptive navigation is a technique that is also associated with adaptive hypermedia. Adaptive navigation provides assistance in an educational hyperspace by modifying the look of visible hyperlinks. The primary aim is to provide the ideal path across the learning space based on the learner model’s needs, preferences, and goals [20]. | |
| Information Filtering | Information filtering arose from the field of information retrieval, and it assists a user in finding relevant information in a large body of information. In scenarios such as web searches, results are generated by sorting and filtering information based on the user’s choices. Adaptive information filtering can be either content-based or collaborative. | |
| Intelligence | Monitoring | The lack of feedback from learners makes it difficult for remote teachers to customise their instructions to the learners’ requirements in e-learning. Using artificial intelligence approaches, intelligent monitoring technologies assist the remote teacher in keeping track of the learner’s reactions. Intelligent monitoring, which primarily employs data mining and machine learning, attempts to give teacher support in e-learning environments [6]. |
| Collaborative Learning | Before the internet, collaborative learning technology was formed by combining Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning (CSCL) with Intelligent Tutoring Systems [6,20]. The goal of artificial intelligence approaches is to improve learning experiences through collaborative strategies such as group creation, peer aid, collaboration support, and virtual students. | |
| Tutoring | Intelligent tutoring, which was originally used in ITS, tries to assist the student in the learning process by utilising artificial intelligence. Curriculum sequencing, intelligent solution analysis, and problem-solving assistance are all examples of help [6]. |
| Year | Ref. | Design | Publication |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | [21] | Empirical | Knowledge-Based Systems |
| [22] | Conceptual | International Journal of Knowledge and Learning | |
| [23] | Empirical | International Journal of Adaptive and Innovative Systems | |
| [24] | Empirical | Journal of Computer Assisted Learning | |
| [25] | Empirical | Computers in Human Behavior | |
| 2017 | [26] | Conceptual | International Journal of Computer Applications |
| [27] | Empirical | Intelligent Automation & Soft Computing | |
| [28] | Conceptual | Computational Science and Its Applications—ICCSA 2017 | |
| 2018 | [29] | Empirical | Interservice/Industry Training, Simulation, and Education Conference |
| [30] | Empirical | International Journal of STEM Education | |
| [31] | Conceptual | International Conference on Computational Science and Its Applications | |
| [32] | Conceptual | International Journal of Smart Education and Urban Society (IJSEUS) | |
| 2019 | [33] | Conceptual | Computers in Human Behavior |
| [34] | Conceptual | XVIII International Conference on Data Science and Intelligent Analysis of Information | |
| [35] | Conceptual | Heliyon | |
| [36] | Empirical | 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems | |
| 2020 | [37] | Empirical | International Journal of Emerging Technology in Learning |
| [38] | Conceptual | International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering | |
| 2021 | [39] | Empirical | Computers |
| [40] | Empirical | International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems | |
| [41] | Empirical | Australasian Journal of Educational Technology | |
| [42] | Conceptual | International Conference on Computational Science and Its Applications | |
| [43] | Conceptual | Proceedings - Frontiers in Education Conference, FIE | |
| [44] | Empirical | Asia-Pacific Web (APWeb) and Web-Age Information Management (WAIM) Joint International Conference on Web and Big Data | |
| 2022 | [45] | Empirical | Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence |
| Ref. | Agent Roles | Outcomes | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adaptive Roles | Intelligent Roles | ||||||||
| P | N | IF | M | CL | T | P | TC | E/M/R | |
| [21] | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ |
| [22] | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ |
| [23] | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ |
| [24] | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ |
| [25] | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| [26] | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| [27] | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ |
| [28] | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ |
| [29] | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ |
| [30] | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ |
| [31] | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ |
| [32] | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ |
| [33] | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ |
| [34] | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ |
| [35] | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ |
| [36] | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ |
| [37] | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ |
| [38] | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ |
| [39] | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ |
| [40] | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ |
| [41] | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ |
| [42] | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ |
| [43] | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ |
| [44] | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ |
| [45] | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Apoki, U.C.; Hussein, A.M.A.; Al-Chalabi, H.K.M.; Badica, C.; Mocanu, M.L. The Role of Pedagogical Agents in Personalised Adaptive Learning: A Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6442. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116442
Apoki UC, Hussein AMA, Al-Chalabi HKM, Badica C, Mocanu ML. The Role of Pedagogical Agents in Personalised Adaptive Learning: A Review. Sustainability. 2022; 14(11):6442. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116442
Chicago/Turabian StyleApoki, Ufuoma Chima, Aqeel M. Ali Hussein, Humam K. Majeed Al-Chalabi, Costin Badica, and Mihai L. Mocanu. 2022. "The Role of Pedagogical Agents in Personalised Adaptive Learning: A Review" Sustainability 14, no. 11: 6442. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116442
APA StyleApoki, U. C., Hussein, A. M. A., Al-Chalabi, H. K. M., Badica, C., & Mocanu, M. L. (2022). The Role of Pedagogical Agents in Personalised Adaptive Learning: A Review. Sustainability, 14(11), 6442. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116442







