Green Synthesis of Ag-Au Bimetallic Nanocomposites Using Waste Tea Leaves Extract for Degradation Congo Red and 4-Nitrophenol
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
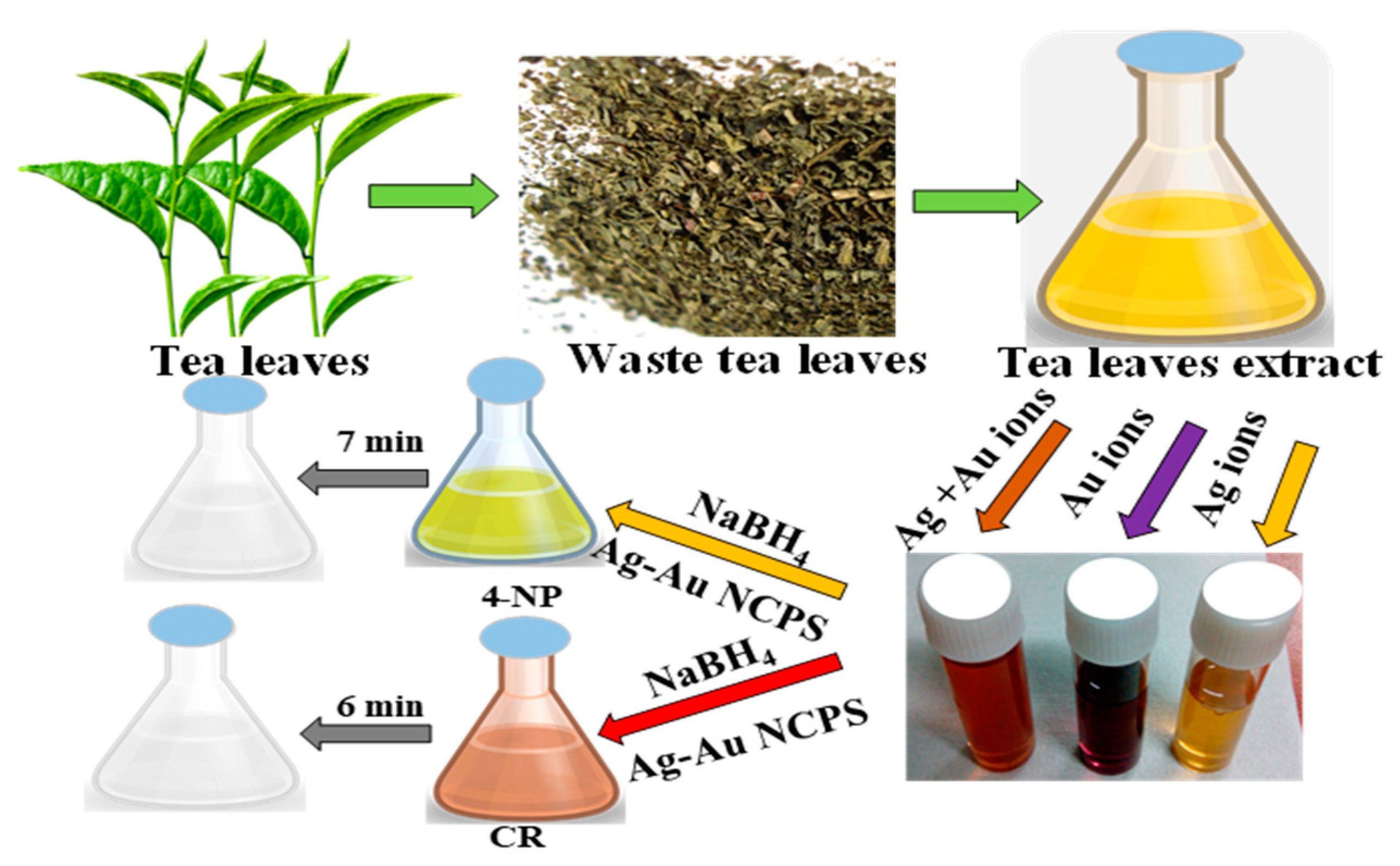
2.2. Preparation of Waste Leaves Extract
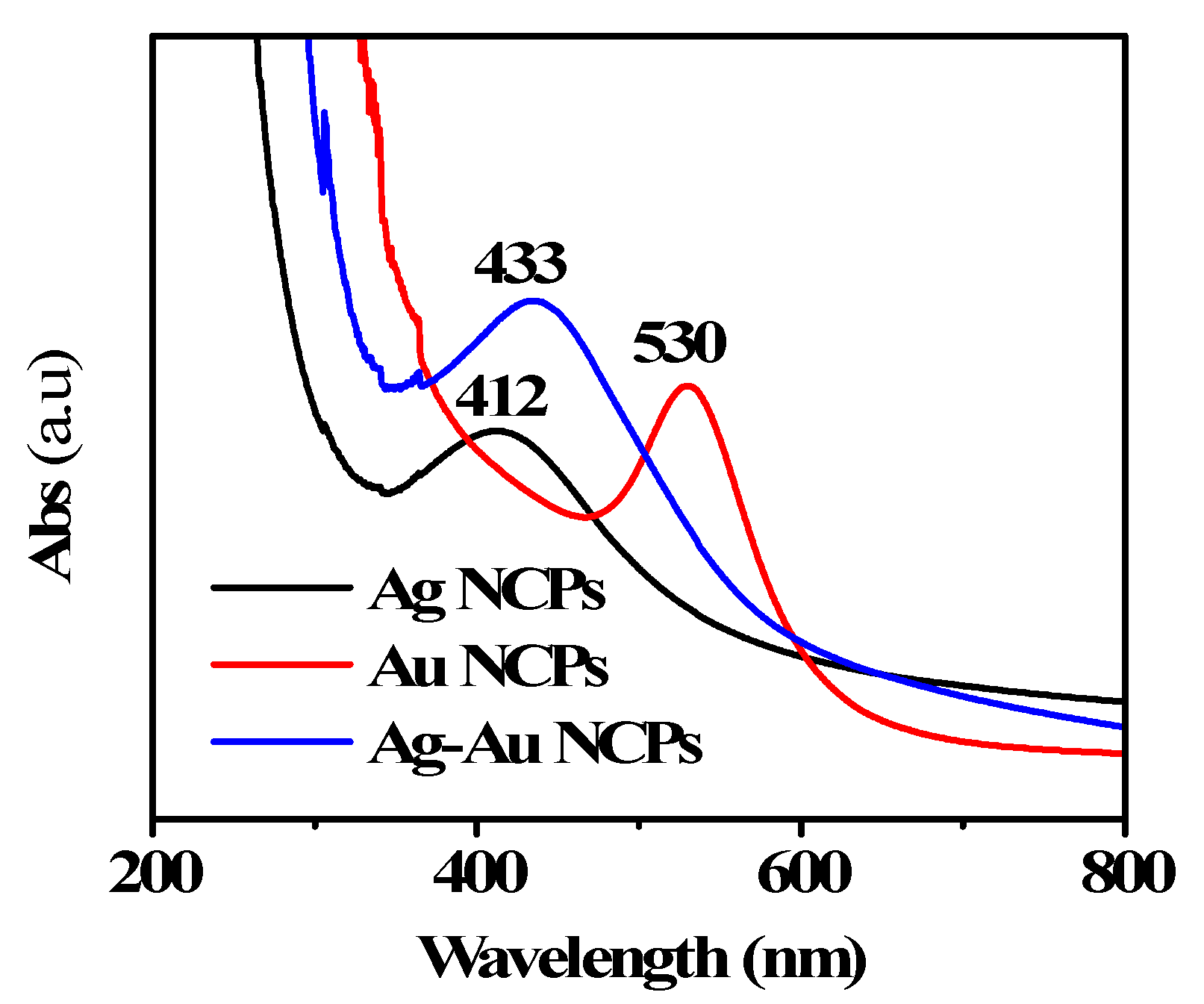
2.3. Synthesis of Ag-Au Nanocomposites
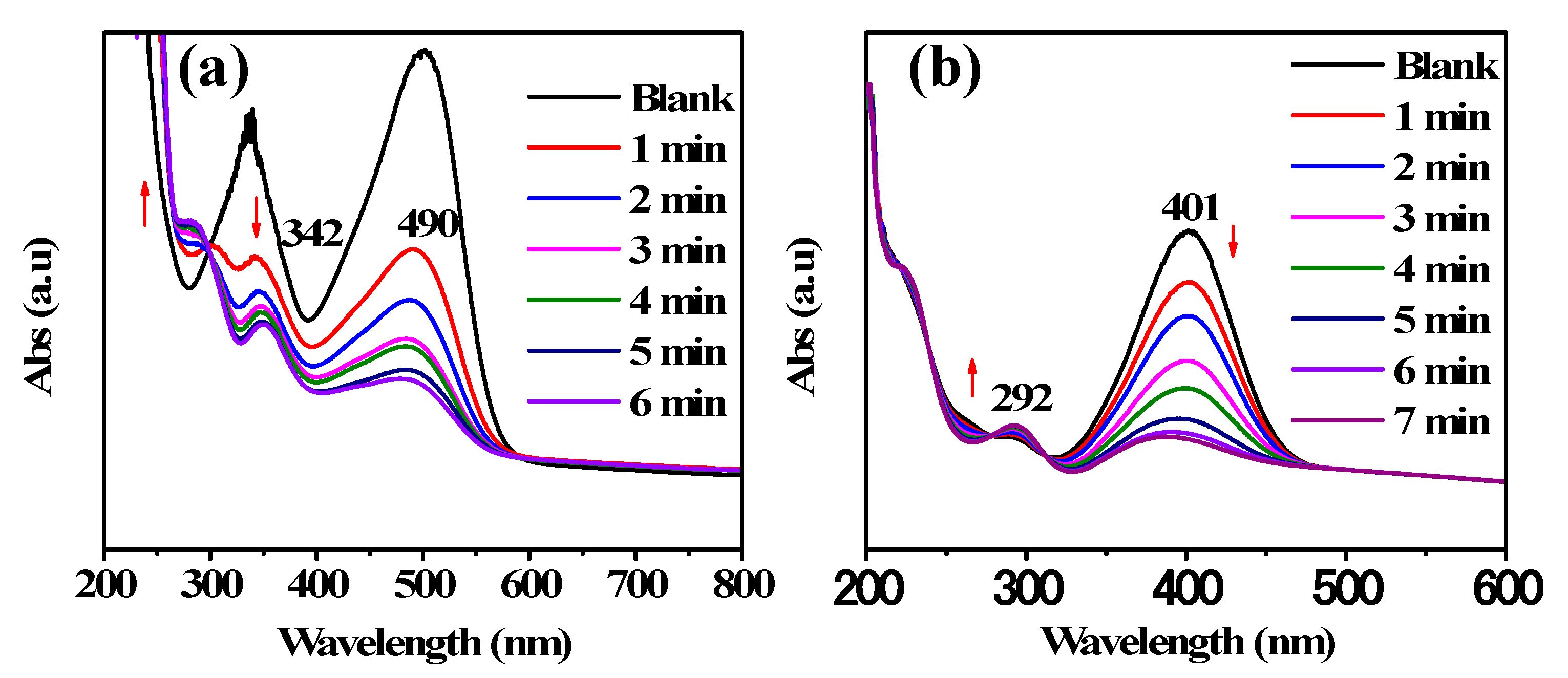
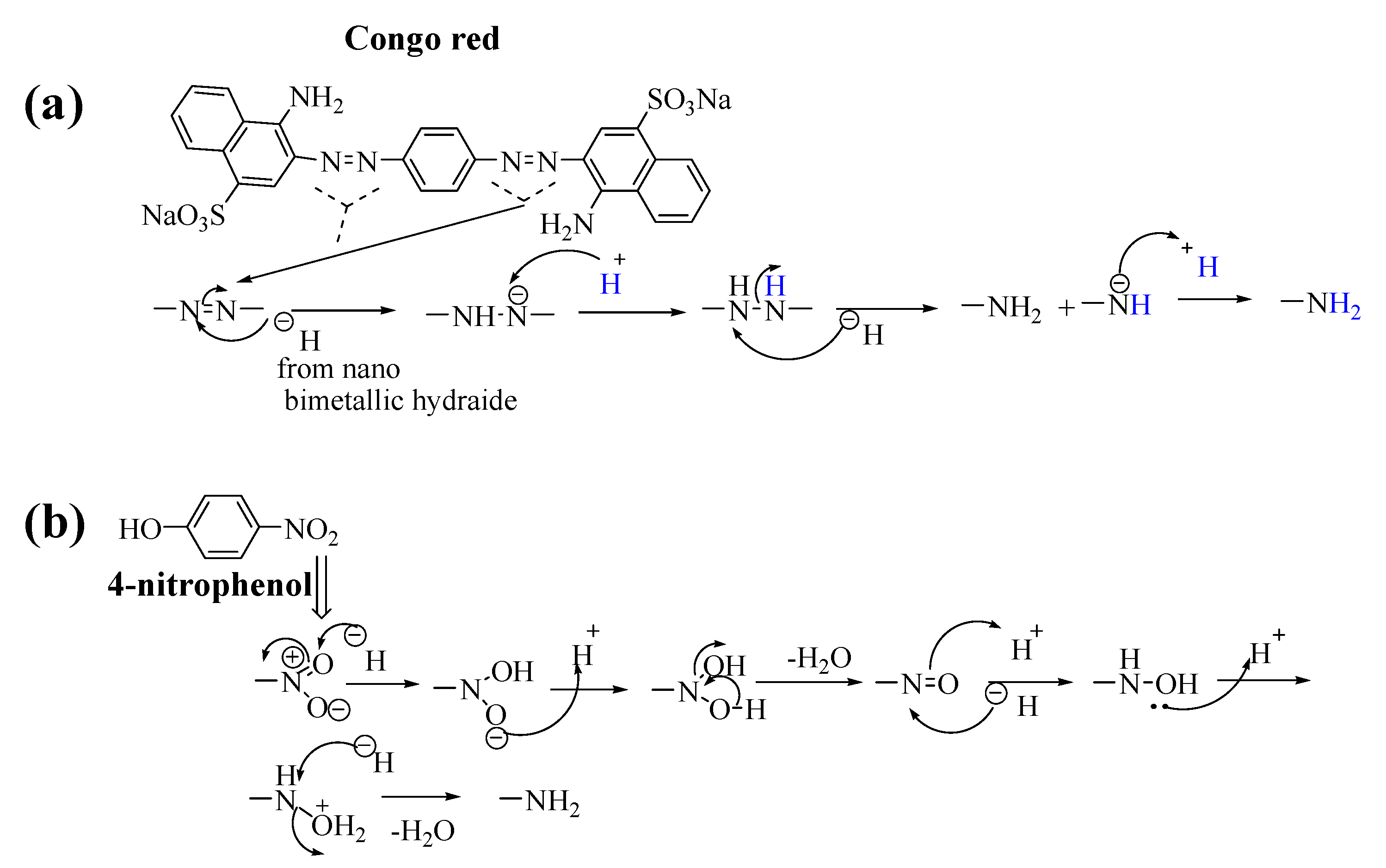
2.4. Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol and Congo Red Azo Dye
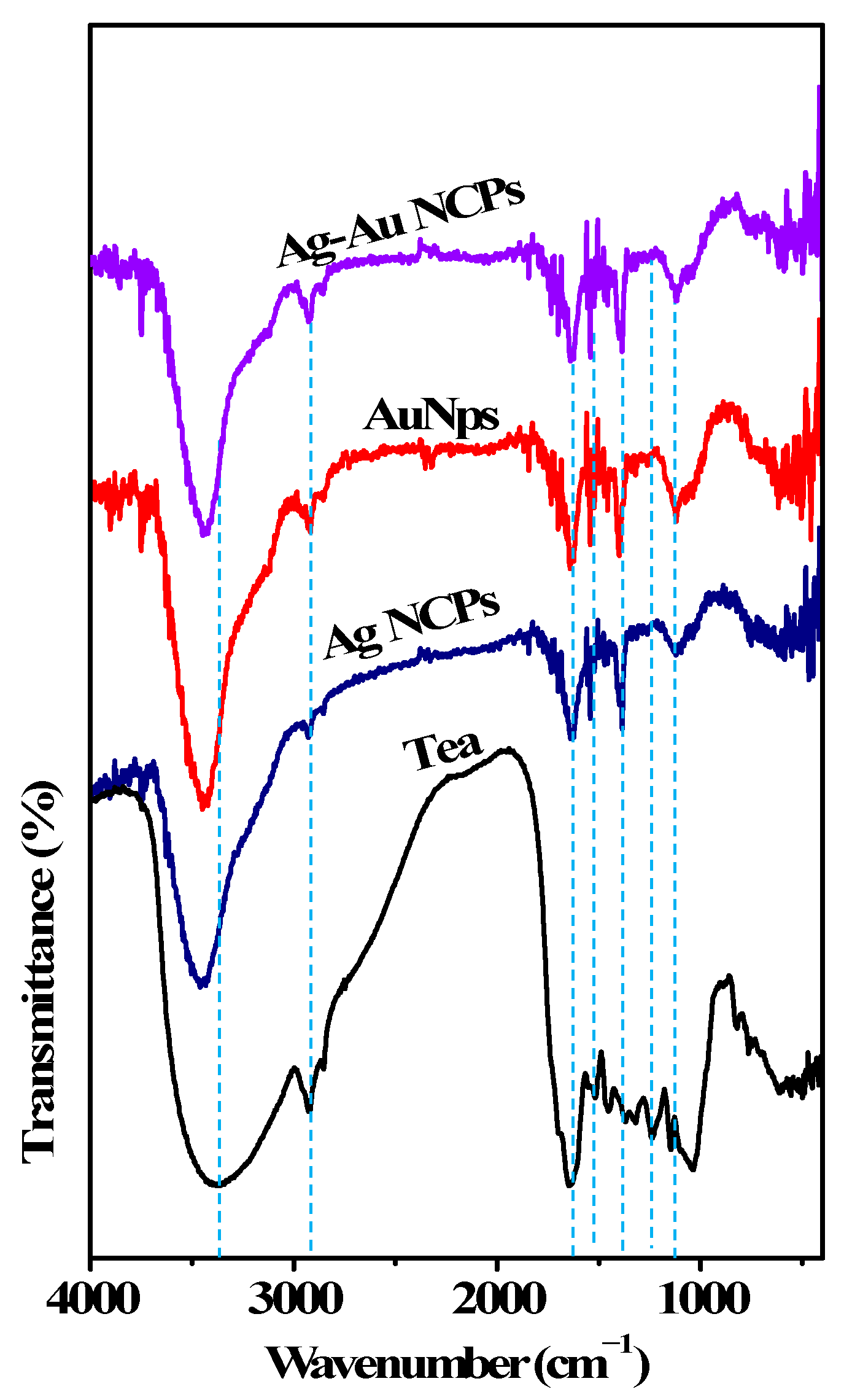
2.5. Material Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jing, Z.; Dai, X.; Xian, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhong, H.; Li, Y. Novel Ternary heterogeneous reduction graphene oxide (RGO)/BiOCl/TiO2 nanocomposites for enhanced adsorption and visible-light induced photocatalytic activity toward organic contaminants. Materials 2020, 13, 2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, K.S.; Parales, R.E. Nitroaromatic compounds, from synthesis to biodegradation, Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2010, 74, 250–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Lv, G.; He, L.; Sun, X. New insight into photodegradation mechanisms, kinetics and health effects of p-nitrophenol by ozonation in polluted water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Ali, N.; Khan, A.; Khan, S.; Khan, S.; Khan, H.; Xiaoqi, S.; Ahmad, W.; Uddin, S.; Ali, N.; et al. Chitosan-capped ternary metal selenide nanocatalysts for efficient degradation of Congo red dye in sunlight irradiation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 167, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salleh, M.A.M.; Mahmoud, D.K.; Karim, W.A.W.A.; Idris, A. Cationic and anionic dye adsorption by agricultural solid wastes: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2011, 280, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.A.; de Vito, S.C. Predicting azo dye toxicity. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1993, 23, 249–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argumedo-Delira, R.; Gómez-Martínez, M.J.; Uribe-Kaffure, R. Trichoderma biomass as an alternative for removal of congo red and malachite green industrial dyes. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Zhang, Y.; Fatehi, P. Sulfomethylated kraft lignin as a flocculant for cationic dye. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 503, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culp, S.J.; Beland, F.A. Malachite green: A toxicological review. J. Am. Coll. Toxicol. 1996, 15, 219–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, A.; Ali, N.; Khan, A.; Bilal, M.; Malik, S.; Ali, N.; Khan, H. Chitosan-zinc sulfide nanoparticles, characterization and their photocatalytic degradation efficiency for azo dyes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 153, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wekoye, J.N.; Wanyonyi, W.C.; Wangila, P.T.; Tonui, M.K. Kinetic and equilibrium studies of Congo red dye adsorption on cabbage waste powder. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2020, 2, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Guo, J.; Yu, X.; Peng, L.; Han, B.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Adsorption of phosphate and photodegradation of cationic dyes with BiOI in phosphate-cationic dye binary system. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 223, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, K.; Guyer, G.T.; Keskinler, B.; Dizge, N. Investigation of segregated wastewater streams reusability with membrane process for textile industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 1437–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Du, J.; Shen, L.; Chen, W. In situ decoration of Ag nanoparticles on hierarchical TiO2 nanowire nanofibers with enhanced catalytic activity used for the removal of 4-nitrophenol. J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 2021, 149, 109784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasmal, D.; Maity, J.; Kolya, H.; Tripathy, T. Study of congo red dye removal from its aqueous solution using sulfated acrylamide and N, N- dimethyl acrylamide grafted amylopectin. J. Water Process Eng. 2017, 18, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolya, H.; Kuila, T.; Kim, N.H.; Lee, J.H. Bioinspired silver nanoparticles/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol, organic dyes and act as energy storage electrode material. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 173, 106924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolya, H.; Tripathy, T. Hydroxyethyl Starch-g-Poly-(N,N-dimethylacrylamide-co-acrylic acid): An efficient dye removing agent. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 4265–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyganowski, P. Fully recyclable gold-based nanocomposite catalysts with enhanced reusability for catalytic hydrogenation of p-nitrophenol. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 612, 125995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolya, H.; Maiti, P.; Pandey, A.; Tripathy, T. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles with antimicrobial and azo dye (Congo red) degradation properties using Amaranthus gangeticus Linn leaf extract. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, K.; Farooqi, Z.H.; Begum, R.; Irfan, A. Removal of Congo red dye from aqueous medium by its catalytic reduction using sodium borohydride in the presence of various inorganic nano-catalysts: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 187, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Sun, Z.; Chen, M.; Chen, C.; Chen, Q. Metal-free catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol to 4-aminophenol by N-doped graphene. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 3260–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Feng, X.; Huang, D.; Yang, G.; Astruc, D. Basic concepts and recent advances in nitrophenol reduction by gold- and other transition metal nanoparticles. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 287, 114–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamaila, S.; Sajjad, A.K.L.; Ryma, N.-A.; Farooqi, S.A.; Jabeen, N.; Majeed, S.; Farooq, I. Advancements in nanoparticle fabrication by hazard free eco-friendly green routes. Appl. Mater. Today. 2016, 5, 150–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Patil, S.; Ahire, M.; Kitture, R.; Gurav, D.D.; Jabgunde, A.M.; Kale, S.; Pardesi, K.; Shinde, V.; Bellare, J.; et al. Gnidia glauca flower extract mediated synthesis of gold nanoparticles and evaluation of its chemocatalytic potential. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2012, 10, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahar, K.N.; Rahaman, M.H.; Khan, G.M.A.; Islam, M.K.; Al-Reza, S.M. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Citrus sinensis peel extract and its antibacterial potential. Asian J. Green Chem. 2021, 5, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundarrajan, S.K.; Pottail, L. Green synthesis of bimetallic Ag@Au nanoparticles with aqueous fruit latex extract of Artocarpus heterophyllus and their synergistic medicinal efficacies. Appl. Nanosci. 2021, 11, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Zhao, B.; Xing, Y.; Shi, Y.; Fu, Y.; Liu, Z. Green synthesis of proanthocyanidins-functionalized Au/Ag bimetallic nanoparticles. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2021, 14, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, A.; Bhattarai, A.; Yadav, A.K.; Adhikari, J.; Singh, M.; Giri, B. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using tea leaves from three different elevations. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 4239–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, N.A.; Mondal, S.; Basu, S.; Laskar, R.A.; Mandal, D. Biogenic synthesis of Au and Ag nanoparticles using aqueous solutions of Black Tea leaf extracts. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2009, 71, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tounekti, T.; Joubert, E.; Hernández, I.; Munné-Bosch, S. Improving the polyphenol content of tea, CRC. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2013, 32, 192–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onitsuka, S.; Hamada, T.; Okamura, H. Preparation of antimicrobial gold and silver nanoparticles from tea leaf extracts. Colloids Surf. B. Biointerfaces 2019, 173, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, T.; Kolya, H.; Jana, S.; Senapati, M. Green synthesis of Ag-Au bimetallic nanocomposites using a biodegradable synthetic graft copolymer; hydroxyethyl starch-g-poly (acrylamide-co-acrylic acid) and evaluation of their catalytic activities. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 87, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, G.; Hu, Y. Fabrication of bimetallic nanoparticles modified hollow nanoporous carbons derived from covalent organic framework for efficient degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berahim, N.; Basirun, W.J.; Leo, B.F.; Johan, M.R. Synthesis of Bimetallic Gold-Silver (Au-Ag) Nanoparticles for the Catalytic Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol to 4-Aminophenol. Catalyst 2018, 8, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diem, P.N.H.; Phuong, T.N.M.; Hien, N.Q.; Quang, D.T.; Hoa, T.T.; Cuong, N.D. Silver, gold, and silver-gold bimetallic nanoparticle-decorated dextran: Facile synthesis and versatile tunability on the antimicrobial activity. J. Nanomater. 2020, 2020, 7195048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elemike, E.E.; Onwudiwe, D.C.; Fayemi, O.E.; Botha, T.L. Green synthesis and electrochemistry of Ag, Au, and Ag–Au bimetallic nanoparticles using golden rod (Solidago canadensis) leaf extract. Appl. Phys. A. 2019, 125, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arie, A.A.; Tekin, B.; Demir, E.; Demir-Cakan, R. Utilization of The Indonesian’s spent tea leaves as promising porous hard carbon precursors for anode materials in sodium ion batteries. Waste Biomass Valoris. 2020, 11, 3121–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benakashani, F.; Allafchian, A.R.; Jalali, S.A.H. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Capparis spinosa L. leaf extract and their antibacterial activity. Karbala Int. J. Mod. Sci. 2016, 2, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sl No | IR Peak at (cm−1) | Assignment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tea | Ag NCPs | Au NCPs | Ag-Au NCPs | ||
| 1. | 3380 | 3459 | 3442 | 3428 | –OH stretching |
| 2. | 2926 | 2928 | 2918 | 2928 | –CH2 asymmetric stretching |
| 3. | 1637 | 1637 | 1637 | 1637 | C=O stretching vibration |
| 4. | 1454 | 1543 | 1543 | 1543 | -CH2 bending, ring stretch, C=C, C-O |
| 5. | 1238 | 1385 | 1396 | 1385 | -C(O)-O stretching vibration and –OH in plane vibrations |
| 6. | 1149 | 1116 | 1116 | 1116 | -C-O stretching of 2° alcohols |
| 7. | 1043 | …. | …. | …. | -C-O-C, anhydride, stretching |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, C.-W.; Kolya, H. Green Synthesis of Ag-Au Bimetallic Nanocomposites Using Waste Tea Leaves Extract for Degradation Congo Red and 4-Nitrophenol. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3318. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13063318
Kang C-W, Kolya H. Green Synthesis of Ag-Au Bimetallic Nanocomposites Using Waste Tea Leaves Extract for Degradation Congo Red and 4-Nitrophenol. Sustainability. 2021; 13(6):3318. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13063318
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Chun-Won, and Haradhan Kolya. 2021. "Green Synthesis of Ag-Au Bimetallic Nanocomposites Using Waste Tea Leaves Extract for Degradation Congo Red and 4-Nitrophenol" Sustainability 13, no. 6: 3318. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13063318
APA StyleKang, C.-W., & Kolya, H. (2021). Green Synthesis of Ag-Au Bimetallic Nanocomposites Using Waste Tea Leaves Extract for Degradation Congo Red and 4-Nitrophenol. Sustainability, 13(6), 3318. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13063318







