CEO Overconfidence and Corporate Governance in Affecting Australian Listed Construction and Property Firms’ Trading Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Overconfidence
2.2. Corporate Governance and Overinvestment
3. Method
- Model 1:where represents property acquisition level in year t.
- Model 2:where is the sales of property, and is the Total Assets in year t.
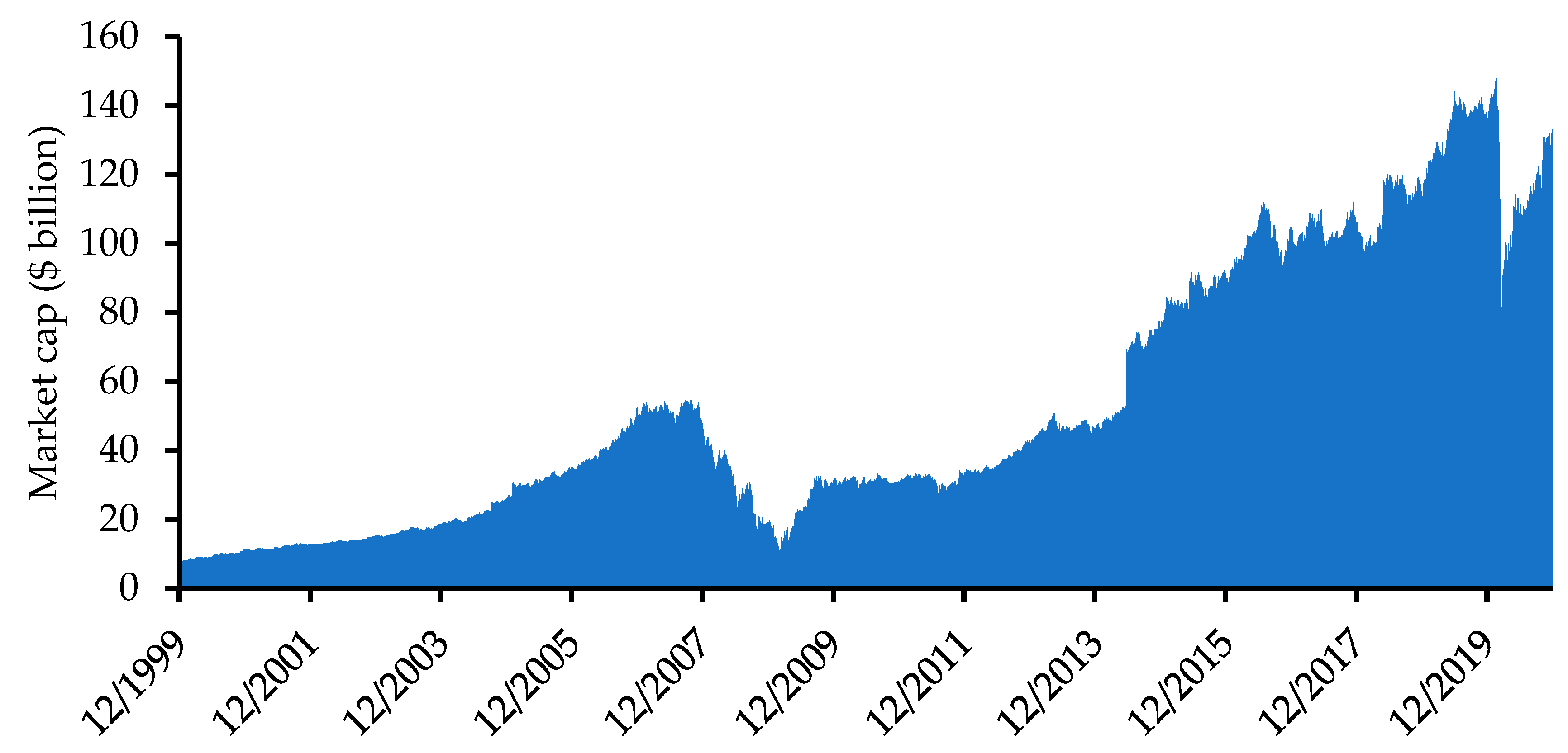
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- PCA (n.d.) About Our Industry. Available online: https://campaign.propertycouncil.com.au/our-campaign (accessed on 23 June 2020).
- EPRA. Global Real Estate Total Markets Table; European Public Real Estate Association: Brussels, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- EPRA. EPRA Global REIT Survey 2019; European Public Real Estate Association: Brussels, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.L. Oceania. In the Routledge REITs Research Handbook; Routledge: London, UK, 2018; pp. 257–278. [Google Scholar]
- PCA. Stapled Structures Consultation Paper; Law Council of Australia Limited: Canberra, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.L.; Stevenson, S.; Lee, M.L. Low-frequency volatility of real estate securities and macroeconomic risk? Account. Financ. 2018, 58, 311–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozza, D.R.; Seguin, P.J. Focus, transparency and value: The REIT evidence. Real Estate Econ. 1999, 27, 587–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, G.; Peng, H.-W. The impact of the global financial crisis on A-REITs. Pac. Rim Prop. Res. J. 2009, 15, 453–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JLL. Transparency: Data, Disclosure and Disruption; Global Research; Jones Lang LaSalle: Chicago, IL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Newell, G.; Lee, C.L. Influence of the corporate social responsibility factors and financial factors on REIT performance in Australia. J. Prop. Investig. Financ. 2012, 30, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westermann, S.; Niblock, S.J.; Kortt, M.A. Does it pay to be responsible? Evidence on corporate social responsibility and the investment performance of Australian REITs. Asia Pac. J. Account. Econ. 2019, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Tan KJ, K.; Faff, R.W. CEO overconfidence and corporate debt maturity. J. Corp. Financ. 2016, 36, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmendier, U.; Tate, G.; Yan, J. Overconfidence and early-life experiences: The effect of managerial traits on corporate financial policies. J. Financ. 2011, 66, 1687–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrand, C.M.; Zechman, S.L. Executive Overconfidence and the Slippery Slope to Financial Misreporting. J. Account. Econ. 2012, 53, 311–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gervais, S.; Heaton, J.B.; Odean, T. Overconfidence, compensation contracts, and capital budgeting. J. Financ. 2011, 66, 1735–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, T.C.; Gallmeyer, M.; Johnson, S.A.; Rutherford, J.; Stanley, B.W. CEO optimism and forced turnover. J. Financ. Econ. 2011, 101, 695–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galasso, A.; Simcoe, T.S. CEO overconfidence and innovation. Manag. Sci. 2011, 57, 1469–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herz, H.; Schunk, D.; Zehnder, C. How do judgmental overconfidence and overoptimism shape innovative activity? Games Econ. Behav. 2014, 84, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Invernizzi, A.C.; Menozzi, A.; Passarani, D.A.; Patton, D.; Viglia, G. Entrepreneurial overconfidence and its impact upon performance. Int. Small Bus. J. Res. Entrep. 2017, 35, 709–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.; Novoselov, K.E.; Wang, R. Does accounting conservatism mitigate the shortcomings of CEO overconfidence? Account. Rev. 2017, 92, 77–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevelyan, R. Optimism, overconfidence and entrepreneurial activity. Manag. Decis. 2008, 46, 986–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.-S.; Ferris, S.P.; Jayaraman, N.; Sabherwal, S. Overconfidence, Corporate governance, and global CEO turnover. In Advances in Financial Economics; Emerald Group Publishing Limited: Bradford, UK, 2013; Volume 16, pp. 101–136. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, K.K.; Wong, S.K.; Chau, K.W. Institutions and capital structure: The case of Chinese property firms. J. Real Estate Financ. Econ. 2018, 56, 352–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lee, C.L.; Chan, N. The asymmetric effect of institutional quality on Chinese outward real estate investment. Int. J. Strateg. Prop. Manag. 2019, 23, 435–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPRA. EPRA Global REIT Survey 2016; European Public Real Estate Association: Brussels, Belgium, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Akimov, A.; Lee, C.L.; Stevenson, S. Interest rate sensitivity in European public eeal estate markets. J. Real Estate Portf. Manag. 2020, 25, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Lee, C.L.; Newell, G. Varying interest rate sensitivity of different property sectors: Cross-country evidence from REITs. J. Prop. Invest. Financ. 2021. ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Wang, C.C.; Lee, G.L. A framework for developing green building rating tools based on Pakistan’s local context. Buildings 2021, 11, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, K.; Titman, S. Market efficiency in an irrational world. Financ. Anal. J. 1999, 55, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chui, A.C.; Titman, S.; Wei, K.J. Intra-industry momentum: The case of REITs. J. Financ. Mark. 2003, 6, 363–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichholtz, P.; Yönder, E. CEO overconfidence, REIT investment activity and performance. Real Estate Econ. 2015, 43, 139–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.J.K. Why do overconfident REIT CEOs issue more debt? Mechanisms and value implications. Abacus 2017, 53, 319–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yung, K.; Li, D.D.; Sun, Q.S. CEO overconfidence and financial policies of real estate investment trusts (REITs). J. Prop. Res. 2015, 32, 384–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao XH, H.; Li, S.H. Investor overconfidence and trading activity in the Asia Pacific REIT markets. J. Risk Financ. Manag. 2020, 13, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.X.; Li, S.H. CEO Overconfidence in Real Estate Markets: A Curse or A Blessing? J. Account. Res. 2016, 51, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Cloutier, E. The new norm: ESG as a material risk and opportunity for real estate. Real Estate Issues 2020, 44, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.; Wu, Z. ESG disclosure, REIT debt financing and firm value. J. Real Estate Financ. Econ. 2021, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Zha, G.; Lee, C.L.; Tang, Q. Does corporate green ranking reflect carbon-mitigation performance? J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 123601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.H.; Byun, J.; Choi, P.M.S. Managerial overconfidence, corporate social responsibility activities, and financial constraints. Sustainability 2020, 12, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, T.; Qiao, Y. The effect of air pollution on corporate social responsibility performance in high energy-consumption industry: Evidence from Chinese listed companies. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 280, 124345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, D.S.; Lee, C.K. Switching behaviour in property related professional services. J. Prop. Res. 2009, 26, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worzala, E.; Sirmans, G.; Zietz, E. Risk and return perceptions of institutional investors. J. Real Estate Portf. Manag. 2000, 6, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.L.; Reed, R.; Robinson, J. An Investigation on the Risk Perceptions of Australian Property Fund Managers. Pac. Rim Prop. Res. J. 2008, 14, 199–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.L. Volatility transmission in Australian REIT futures. J. Real Estate Portf. Manag. 2009, 15, 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; He, S.; Sun, C.; Zhang, H.; Hu, L.; Kang, M. Do landscape amenities impact private housing rental prices? A hierarchical hedonic modeling approach based on semantic and sentimental analysis of online housing advertisements across five Chinese megacities. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 58, 126968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lee, C.L. The value of air quality in housing markets: A comparative study of housing sale and rental markets in China. Energy Policy. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Chung, C.Y. CEO overconfidence, leadership ethics, and institutional investors. Sustainability 2017, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao HX, H.; Li, S.H. Overconfidence and real estate research: A survey of the literature. Singap. Econ. Rev. 2016, 61, 1650015. [Google Scholar]
- Billett, M.T.; Qian, Y. Are overconfident CEOs born or made? Evidence of self-attribution bias from frequent acquirers. Manag. Sci. 2008, 54, 1037–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Stevenson, S. The substitutability of REITs and value stocks. Appl. Financ. Econ. 2007, 17, 541–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bondt, W.F.M.; Thaler, R. Does the stock market overreact? J. Financ. 2005, 40, 793–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benos, A.V. Aggressiveness and survival of overconfident traders. J. Financ. Mark. 1998, 1, 353–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, H.K.; Nofsinger, J.R. Psychological biases of investors. Financ. Serv. Rev. 2002, 11, 97. [Google Scholar]
- Hirshleifer, D.; Luo, G.Y. On the survival of overconfident traders in a competitive securities market. J. Financ. Mark. 2001, 4, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, M.; Weber, M. Overconfidence and trading volume. Geneva Risk Insur. Rev. 2007, 32, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakalaki, M.; Richardson, C.; Bastounis, M. Association of economic internality with saving behavior and motives, financial confidence, and attitudes toward state intervention. J. Appl. Soc. Psychol. 2005, 35, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Wang, Z.; Li, K. Financial literacy overconfidence and stock market participation. Soc. Indic. Res. 2014, 119, 1233–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, K.; Hirshleifer, D.; Subrahmanyam, A. Investor psychology and security market under- and overreactions. J. Financ. 1998, 53, 1839–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, B.M.; Odean, T. Trading is hazardous to your wealth: The common stock investment performance of individual investors. J. Financ. 2000, 55, 773–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janus, T.; Jinjarak, Y.; Uruyos, M. Sovereign default risk, overconfident investors and diverse beliefs: Theory and evidence from a new dataset on outstanding credit default swaps. J. Financ. Stab. 2013, 9, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Scheinkman, J.A.; Xiong, W. Overconfidence and speculative bubbles. J. Political Econ. 2003, 111, 1183–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiller, R.J. From efficient markets theory to behavioral finance. J. Econ. Perspect. 2003, 17, 83–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odean, T. Volume, volatility, price, and profit when all traders are above average. J. Financ. 1998, 53, 1887–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statman, M.; Thorley, S.; Vorkink, K. Investor overconfidence and trading volume. Rev. Financ. Stud. 2006, 19, 1531–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.B.; Ferreira, D. A theory of friendly boards. J. Financ. 2007, 62, 217–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmendier, U.; Tate, G. CEO overconfidence and corporate investment. J. Financ. 2005, 60, 2661–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmendier, U.; Tate, G. Who makes acquisitions? CEO overconfidence and the market’s reaction. J. Financ. Econ. 2008, 89, 20–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, A.D.; Hartzell, J.C. Is There a Disposition Effect in Corporate Investment Decisions? Evid. Real Estate Invest. Trust. 2010. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=1031010 (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- Jensen, M.C. Agency costs of free cash flow, corporate finance, and takeovers. Am. Econ. Rev. 1986, 76, 323–329. [Google Scholar]
- Griffin, J.M.; Nardari, F.; Stulz, R.M. Do investors trade more when stocks have performed well? Evidence from 46 countries. Rev. Financ. Stud. 2007, 20, 905–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cariola, A.; La Rocca, M.; La Rocca, T. Overinvestment and underinvestment problems: Determining factors, consequences and solutions. Corp. Ownersh. Control. 2005, 5, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jensen, M.C.; Meckling, W.H. Theory of the firm: Managerial behavior, agency costs and ownership structure. J. Financ. Econ. 1976, 3, 305–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degryse, H.; De Jong, A. Investment Spending in the Netherlands: Asymmetric Information or Managerial Discretion? KU Leuven: Leuven, Belgium, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, J.C. Agency, information and corporate investment. In Handbook of the Economics of Finance; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; Volume 1, pp. 111–165. [Google Scholar]
- ASX Corporate Governance Council. Corporate Governance Principles and Recommendations, 2nd ed.; ASX Corporate Governance Council: Sydney, Australia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, J.; Kent, P.; Stewart, J. Corporate governance and company performance in Australia. Aust. Account. Rev. 2010, 20, 372–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Country | Number of REITs | Sector Mkt Cap (USD Billion) | % of Global REIT Index |
|---|---|---|---|
| US | 192 | 1163.18 | 64.98% |
| Japan | 66 | 128.43 | 8.23% |
| Australia | 46 | 99.82 | 5.91% |
| UK | 55 | 76.24 | 4.79% |
| Singapore | 35 | 61.64 | 2.26% |
| Canada | 46 | 61.16 | 3.23% |
| France | 29 | 57.72 | 1.77% |
| Hong Kong | 9 | 37.45 | 2.25% |
| Netherland | 5 | 26.75 | 1.83% |
| Spain | 72 | 26.74 | 0.67% |
| Model | R Square | Adjusted R Square | Std. Error of the Estimate |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.8169 | 0.7467 | 1.0164 |
| Variable | Coefficient | Std. Error | T-Statistic | Prob. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 2.5099 | 5.5991 | 0.4482 | 0.6544 |
| CEO Shares | 0.2377 | 0.1594 | 1.4913 | 0.1372 |
| CASH | −0.2043 | 0.0933 | −2.1891 ** | 0.0296 |
| FUNDS_FROM_OPERATIONS | −0.1349 | 0.2383 | −0.5659 | 0.5720 |
| MV | 0.9954 | 0.3057 | 3.2560 *** | 0.0013 |
| DEBT RATIO | 1.7564 | 1.0819 | 1.6234 | 0.1058 |
| Model | R Square | Adjusted R Square | Std. Error of the Estimate |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 0.6738 | 0.5135 | 1.4638 |
| Variable | Coefficient | Std. Error | T-Statistic | Prob. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 6.7518 | 10.2246 | 0.6603 | 0.5099 |
| CEO Shares | −0.3586 | 0.2703 | −1.3264 | 0.1864 |
| CASH | 0.5108 | 0.1509 | 3.3850 *** | 0.0009 |
| FUNDS_FROM_OPERATIONS | 0.0226 | 0.2663 | 0.0848 | 0.9325 |
| TA | 0.0867 | 0.5586 | 0.1553 | 0.8767 |
| DEBT RATIO | −0.5153 | 1.7917 | −0.2876 | 0.7740 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hijjawi, M.; Lee, C.L.; Marzuki, J. CEO Overconfidence and Corporate Governance in Affecting Australian Listed Construction and Property Firms’ Trading Activity. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10920. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131910920
Hijjawi M, Lee CL, Marzuki J. CEO Overconfidence and Corporate Governance in Affecting Australian Listed Construction and Property Firms’ Trading Activity. Sustainability. 2021; 13(19):10920. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131910920
Chicago/Turabian StyleHijjawi, Mahmoud, Chyi Lin Lee, and Jufri Marzuki. 2021. "CEO Overconfidence and Corporate Governance in Affecting Australian Listed Construction and Property Firms’ Trading Activity" Sustainability 13, no. 19: 10920. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131910920
APA StyleHijjawi, M., Lee, C. L., & Marzuki, J. (2021). CEO Overconfidence and Corporate Governance in Affecting Australian Listed Construction and Property Firms’ Trading Activity. Sustainability, 13(19), 10920. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131910920






