Bayesian Updates for an Extreme Value Distribution Model of Bridge Traffic Load Effect Based on SHM Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Modeling Method for Extreme Traffic Load Effect
2.1. The GPD Model for Peaks-Over-Threshold Traffic Load Effect
2.2. The Filtered Poisson Process Model for the Traffic Load Effect Stochastic Process
2.3. Probability Model for Extreme Traffic Load Effect
2.4. Parameter Estimation Based on Bridge Health Monitoring Data
3. Bayesian Updates for the Extreme Traffic Load Effect Model
- EvaluateSince the GEV distribution parameters can be calculated by GPD distribution parameters (see Equation (11)), only need to be chosen as the model parameters . At the beginning, several methods can be used to evaluate the original , such as Jeffreys prior of flat priors, even if no monitoring data are obtained. When the new monitoring data are gathered, the previous posterior distribution becomes the new priors.
- EvaluateIt is very difficult to evaluate by direct numerical integration, but the Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) algorithm provides a good solution to this problem. The basic idea of the MCMC algorithm is to simulate the Markov Chain, whose stationary distribution is . Next, can be sampled based on the stationary distribution.
- Model updateThe posterior distribution, , contains the information from the new data and also the prior information from . Therefore, the mean values of are chosen as the updated model of parameters .
4. Application to a CFST Arch Bridge
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flint, M.M.; Fringer, O.; Billington, S.L.; Freyberg, D.; Diffenbaugh, N.S. Historical Analysis of Hydraulic Bridge Collapses in the Continental United States. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2017, 23, 4017005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, F.Y.; Zhang, M.J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.R. Recent Highway Bridge Collapses in China: Review and Discussion. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 2016, 30, 4016030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leahy, C.; Obrien, E.; O’Connor, A. The Effect of Traffic Growth on Characteristic Bridge Load Effects. Transp. Res. Procedia 2016, 14, 3990–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strauss, A.; Frangopol, D.M.; Kim, S. Use of monitoring extreme data for the performance prediction of structures: Bayesian updating. Eng. Struct. 2008, 30, 3654–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frangopol, D.M.; Strauss, A.; Kim, S. Use of monitoring extreme data for the performance prediction of structures: General approach. Eng. Struct. 2008, 30, 3644–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Sun, L.; Xia, Y.; He, T. Vibration-Based Seismic Damage States Evaluation for Regional Concrete Beam Bridges Using Random Forest Method. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; You, J. Truck Loads and Bridge Capacity Evaluation in China. J. Bridge Eng. 2009, 14, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Cai, C.S.; Pan, F.; Yu, Y. Estimation of extreme structural response distributions for mean recurrence intervals based on short-term monitoring. Eng. Struct. 2016, 126, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Phares, B.M. Automated bridge load rating determination utilizing strain response due to ambient traffic trucks. Eng. Struct. 2016, 117, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sung, Y.-C.; Lin, T.-K.; Chiu, Y.-T.; Chang, K.-C.; Chen, K.-L.; Chang, C.-C. A bridge safety monitoring system for prestressed composite box-girder bridges with corrugated steel webs based on in-situ loading experiments and a long-term monitoring database. Eng. Struct. 2016, 126, 571–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martucci, D.; Civera, M.; Surace, C. The Extreme Function Theory for Damage Detection: An Application to Civil and Aerospace Structures. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.-Y.; Schmidt, F.; Toutlemonde, F.; Jacob, B. A mixture peaks over threshold approach for predicting extreme bridge traffic load effects. Probabilistic Eng. Mech. 2016, 43, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Obrien, E.J.; Schmidt, F.; Hajializadeh, D.; Zhou, X.-Y.; Enright, B.; Caprani, C.C.; Wilson, S.; Sheils, E. A review of probabilistic methods of assessment of load effects in bridges. Struct. Saf. 2015, 53, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, Y.; Li, S.; Li, H.; Guo, Z. A novel Bayesian extreme value distribution model of vehicle loads incorporating de-correlated tail fitting: Theory and application to the Nanjing 3rd Yangtze River Bridge. Eng. Struct. 2014, 59, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprani, C.C.; Obrien, E.J.; Lipari, A. Long-span bridge traffic loading based on multi-lane traffic micro-simulation. Eng. Struct. 2016, 115, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.S.; Szerszen, M.M. Bridge load and resistance models. Eng. Struct. 1998, 20, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.S.; Ferrand, D.M. Truck Load Models for Bridges. In Building on the Past: Securing the Future (Proceeding of the 2004 Structures Congress); George, E.B., Ed.; ASCE: Nashville, TN, USA, 2004; Volume 137, p. 122. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, S.F.; Bez, R. Site specific probability distribution of extreme traffic action effects. Probabilistic Eng. Mech. 1999, 14, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, A.; O’Brien, E.J. Traffic load modelling and factors influencing the accuracy of predicted extremes. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2005, 32, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miao, T.; Chan, T.H.T. Bridge live load models from WIM data. Eng. Struct. 2002, 24, 1071–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, F.; Moutinho, C.; Hu, W.-H.; Cunha, Á.; Caetano, E. Weigh-in-motion implementation in an old metallic railway bridge. Eng. Struct. 2016, 123, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, C.; Li, H.; Ou, J. Traffic load modeling based on structural health monitoring data. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2011, 7, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, C. Damage cross detection between bridges monitored within one cluster using the difference ratio of projected strain monitoring data. Struct. Health Monit. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, Y. Damage detection of bridges monitored within one cluster based on the residual between the cumulative distribution functions of strain monitoring data. Struct. Health Monit. 2020, 19, 1764–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Lee, J.; Kong, J. Performance Degradation Model for Concrete Deck of Bridge Using Pseudo-LSTM. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.Y.; Schmidt, F.; Jacob, B.; Toutlemonde, F. Accurate and Up-to-Date Evaluation of Extreme Load Effects for Bridge Assessment. TRA-Transp. Res. Arena 2014, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Wu, J. Modeling stochastic live load for long-span bridge based on microscopic traffic flow simulation. Comput. Struct. 2011, 89, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.S. Live load model for highway bridges. Struct. Saf. 1993, 13, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotz, S.; Nadarajah, S. Extreme Value Distributions: Theory and Applications; World Scientific Publishing Company: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Caprani, C.C.; Obrien, E.J.; McLachlan, G.J. Characteristic traffic load effects from a mixture of loading events on short to medium span bridges. Struct. Saf. 2008, 30, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obrien, E.J.; Enright, B.; Getachew, A. Importance of the Tail in Truck Weight Modeling for Bridge Assessment. J. Bridg. Eng. 2010, 15, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, G.; Lei, W. Modeling method for extreme traffic-load effect probabilistic model of an existing bridge. J. Harbin Eng. Univ. 2013, 34, 995–999. [Google Scholar]
- Jonathan, P.; Randell, D.; Wadsworth, J.; Tawn, J. Uncertainties in return values from extreme value analysis of peaks over threshold using the generalised Pareto distribution. Ocean Eng. 2021, 220, 107725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, F.; Zhou, X.Y.; Toutlemonde, F. A Peaks-Over-Threshold Analysis of Extreme Traffic Load Effects on Bridges. In Proceedings of the Young Research Seminar, Lyon, France, 5–7 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ashkar, F.; El Adlouni, S.-E. Adjusting for small-sample non-normality of design event estimators under a generalized Pareto distribution. J. Hydrol. 2015, 530, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Soares, C.G. Bayesian analysis of short term extreme mooring tension for a point absorber with mixture of gamma and generalised pareto distributions. Appl. Ocean Res. 2021, 110, 102556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J.; Katafygiotis, L. Updating Models and Their Unvertainties I: Baysian Statistical Framework. J. Eng. Mech. 1998, 1244, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ni, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, C. Bayesian approaches for evaluating wind-resistant performance of long-span bridges using structural health monitoring data. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2021, 28, e2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.W.; Zhang, C. A Bayesian approach for condition assessment and damage alarm of bridge expansion joints using long-term structural health monitoring data. Eng. Struct. 2020, 212, 110520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton, D.A.; Clifton, L.; Hugueny, S.; Wong, D.; Tarassenko, L. An Extreme Function Theory for Novelty Detection. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2012, 7, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañellas, B.; Orfila, A.; Méndez, F.J.; Menéndez, M.; Gómez-Pujol, L.; Tintoré, J. Application of a POT model to estimate the extreme significant wave height levels around the Balearic Sea (Western Mediterranean). J. Coast. Res. 2007, 50, 329–333. [Google Scholar]
- Ribatet, M.; Sauquet, E.; Grésillon, J.-M.; Ouarda, T.B. A regional Bayesian POT model for flood frequency analysis. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2006, 21, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, J.; Ren, W.-X. Threshold selection for extreme value estimation of vehicle load effect on bridges. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2018, 14, 1550147718757698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davison, A.C.; Smith, R.L. Models for Exceedances over High Thresholds. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1990, 52, 393–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, G. Study on the environmental load criteria of existing structure safety evaluation. Ind. Constr. 1995, 25, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, J.; Xu, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, K.; Sun, H.; Li, Y. Typical diseases of a long-span concrete-filled steel tubular arch bridge and their effects on vehicle-induced dynamic response. Front. Struct. Civ. Eng. 2020, 14, 867–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worden, K.; Manson, G.; Sohn, H.; Farrar, C.R. Extreme Value Statistics from Differential Evolution for Damage Detection. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Modal Analysis Conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 3 February 2005. [Google Scholar]
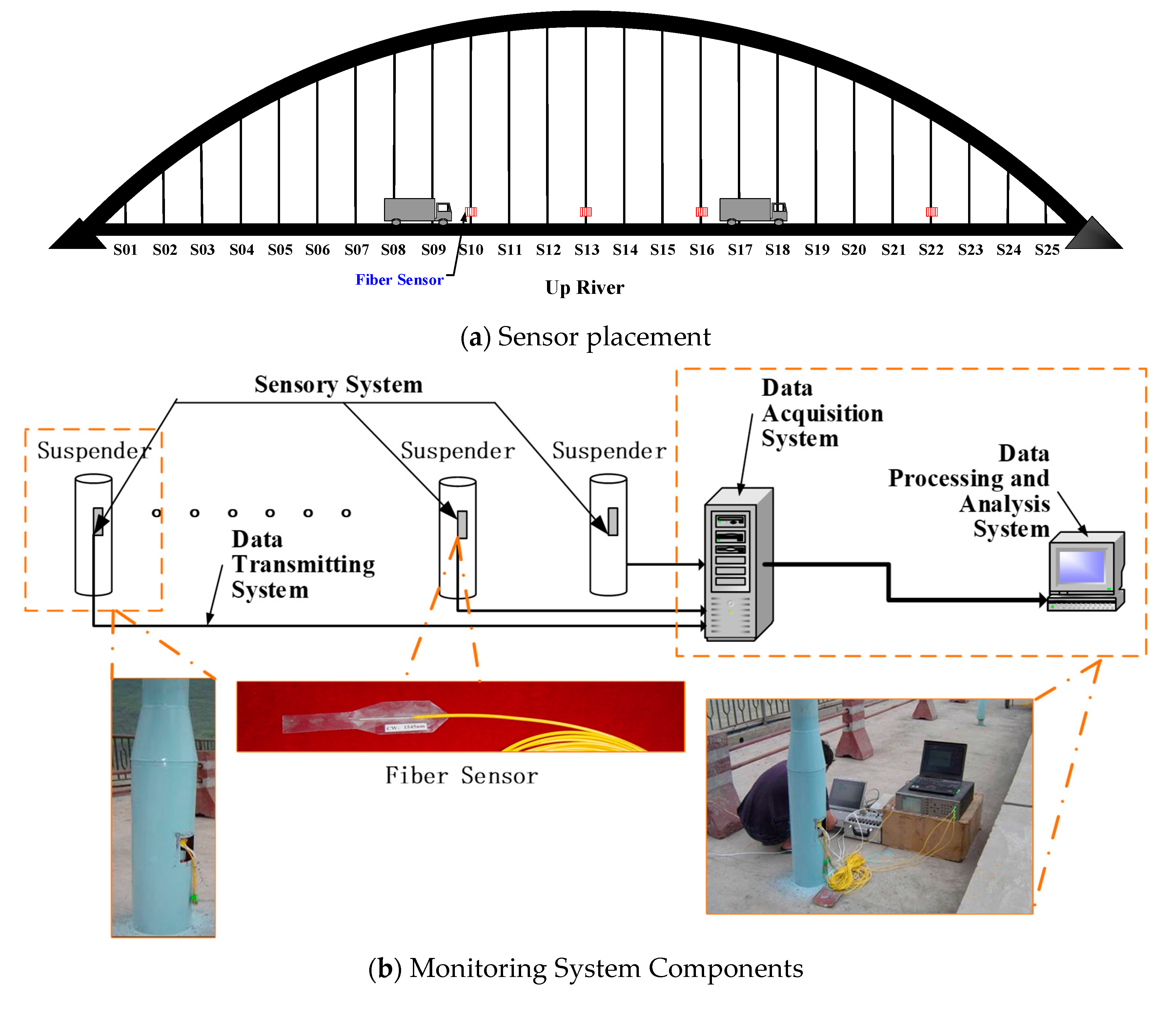
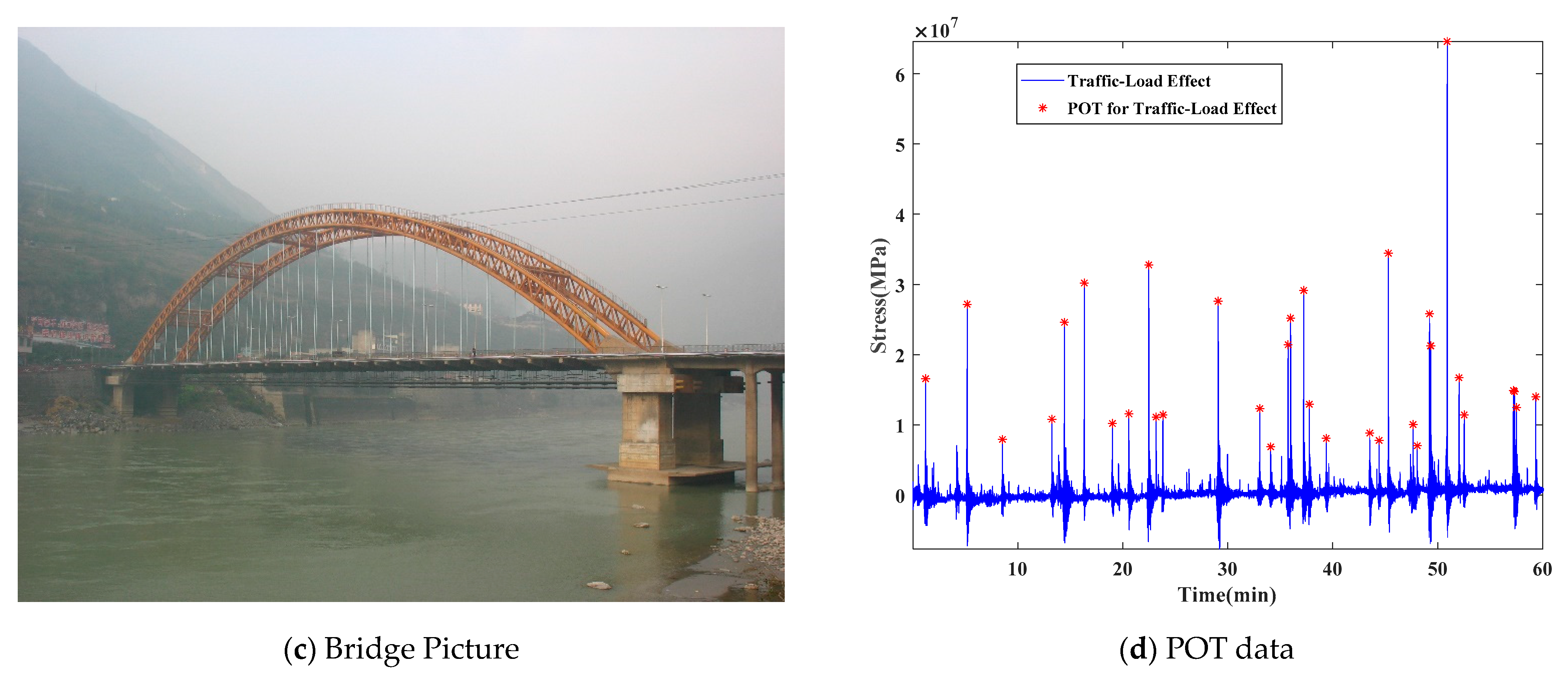

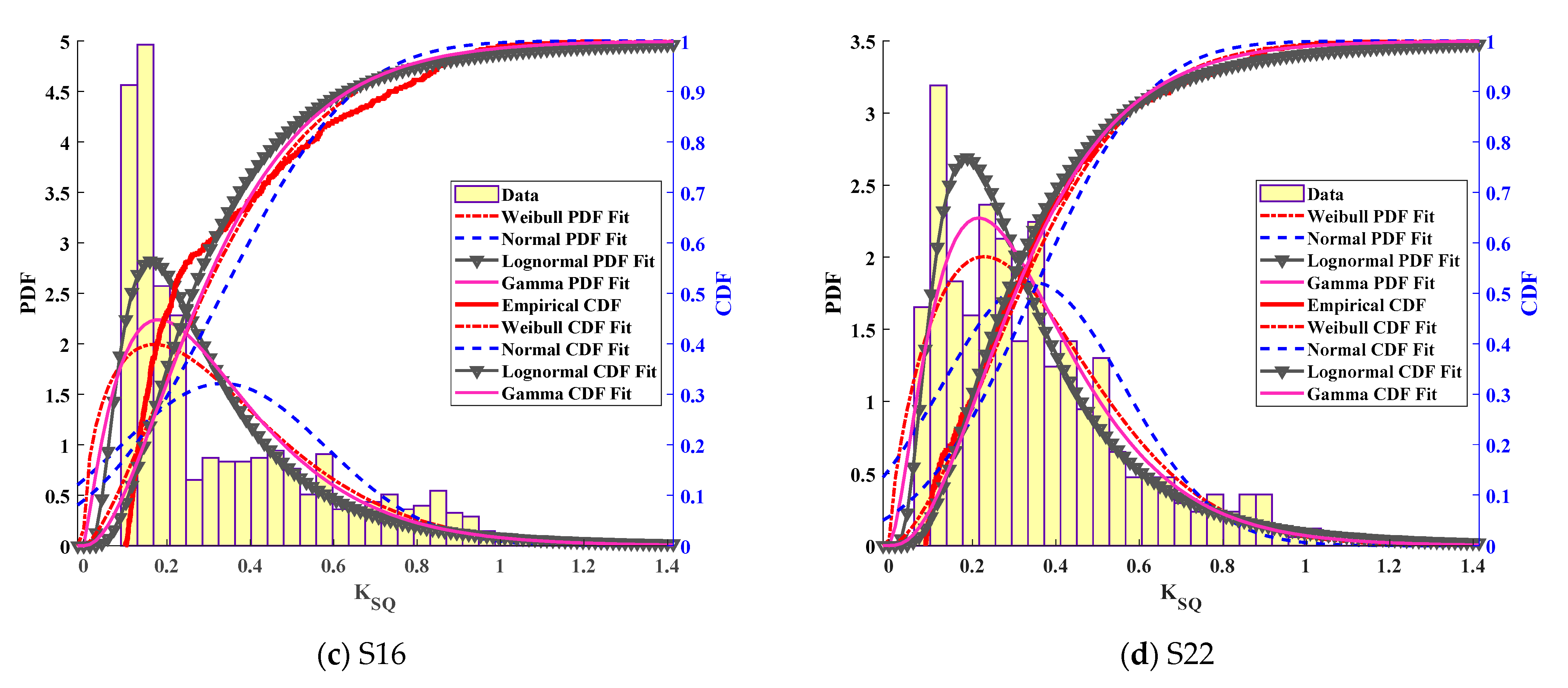
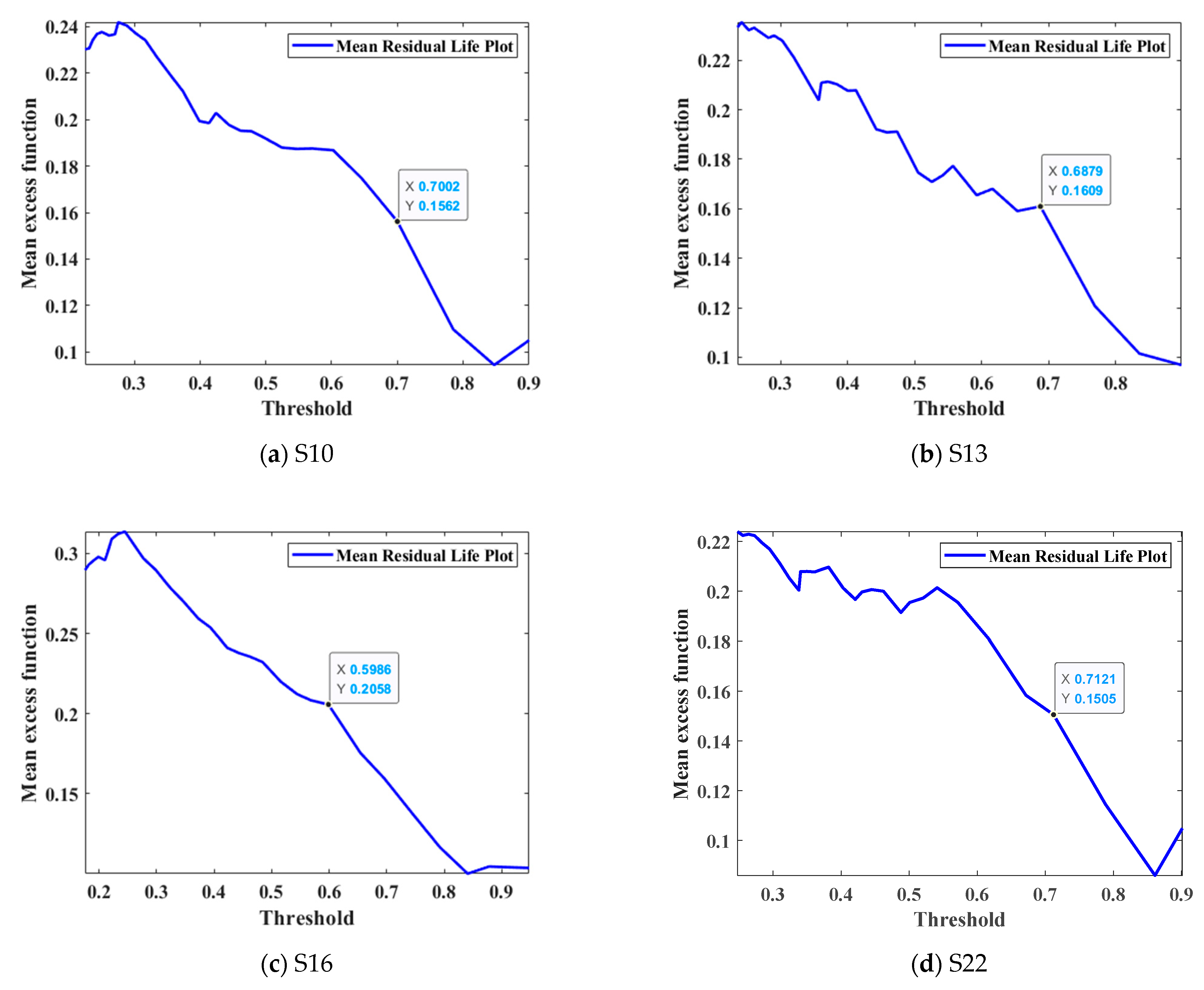
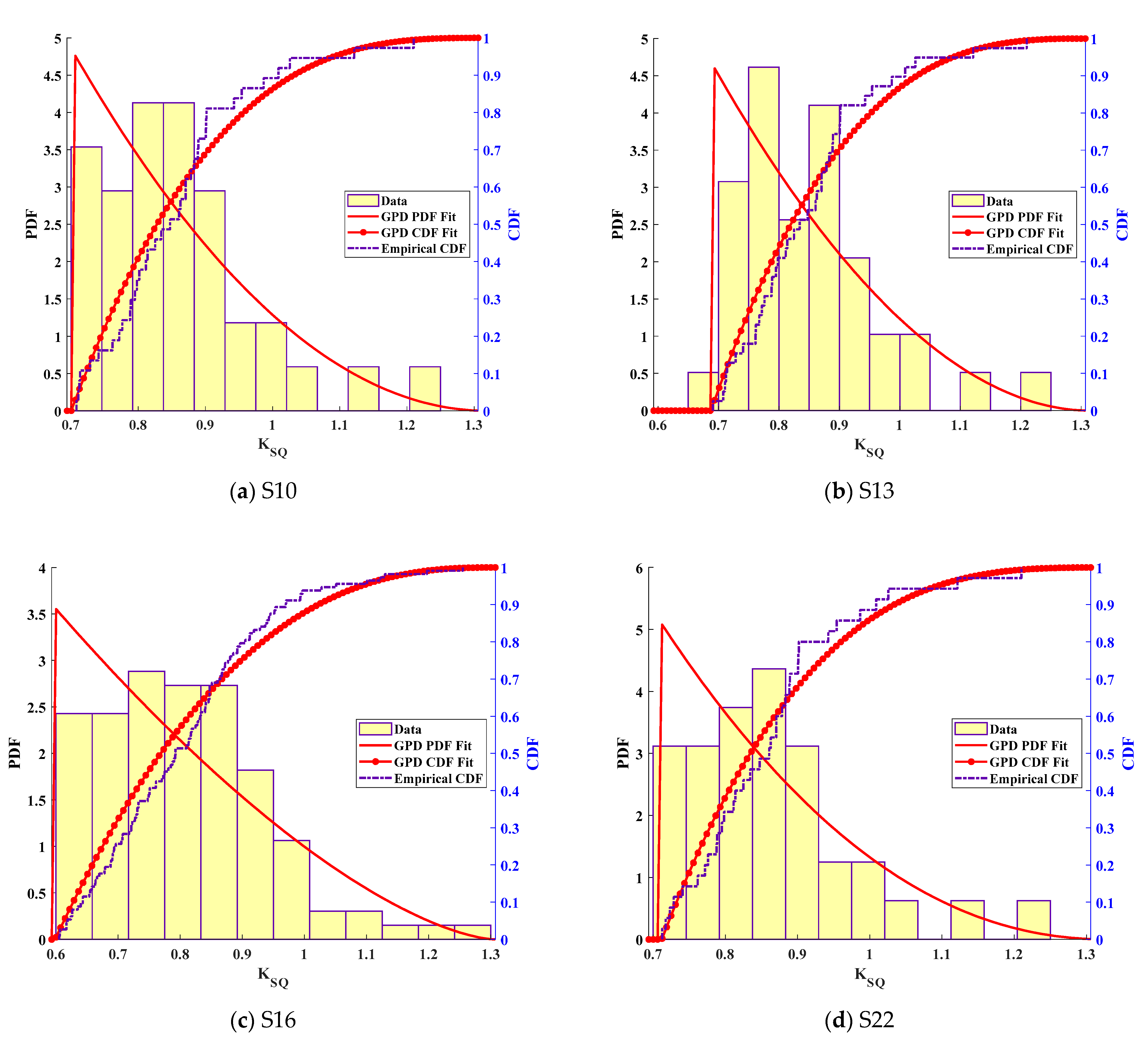
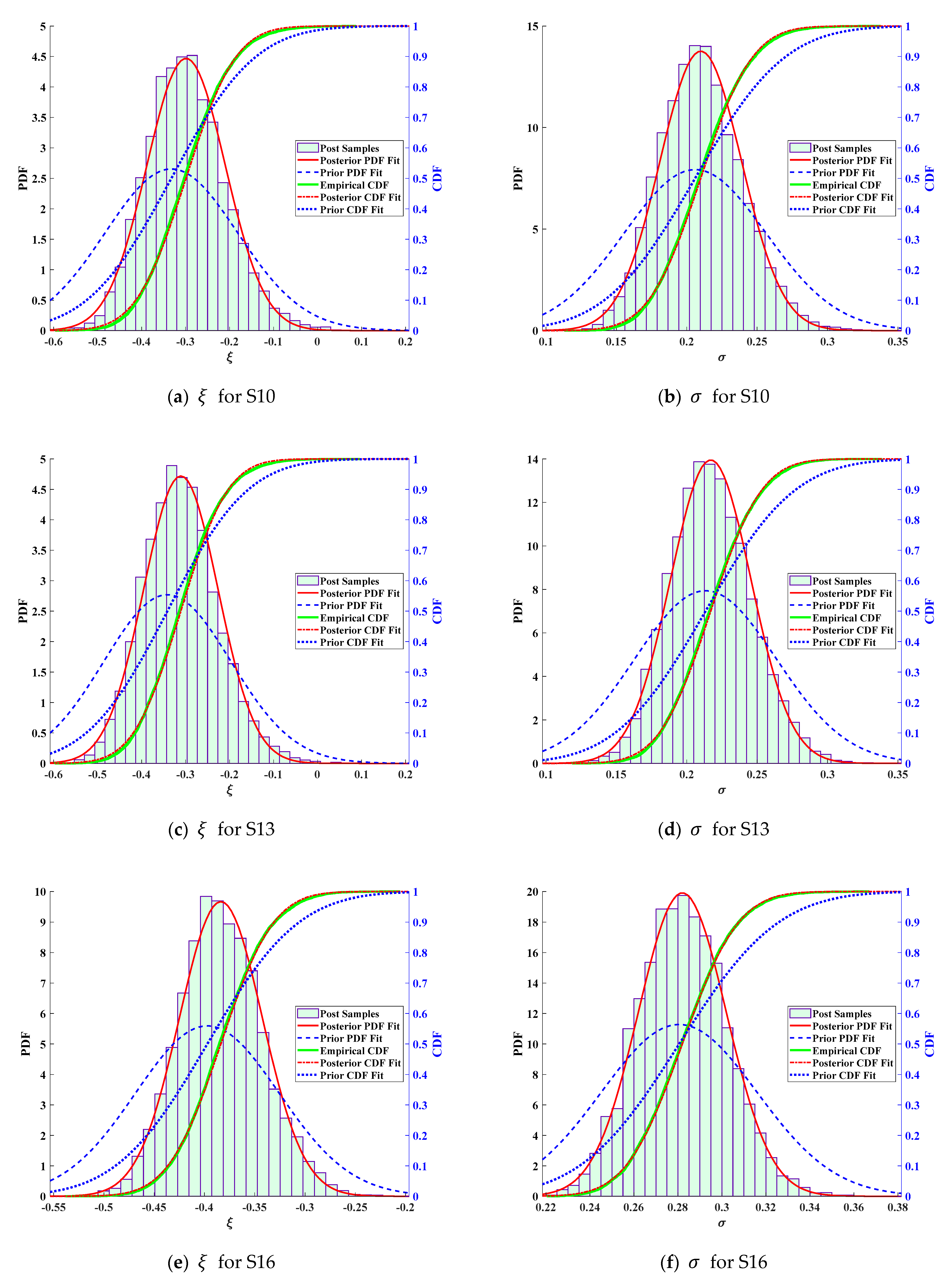
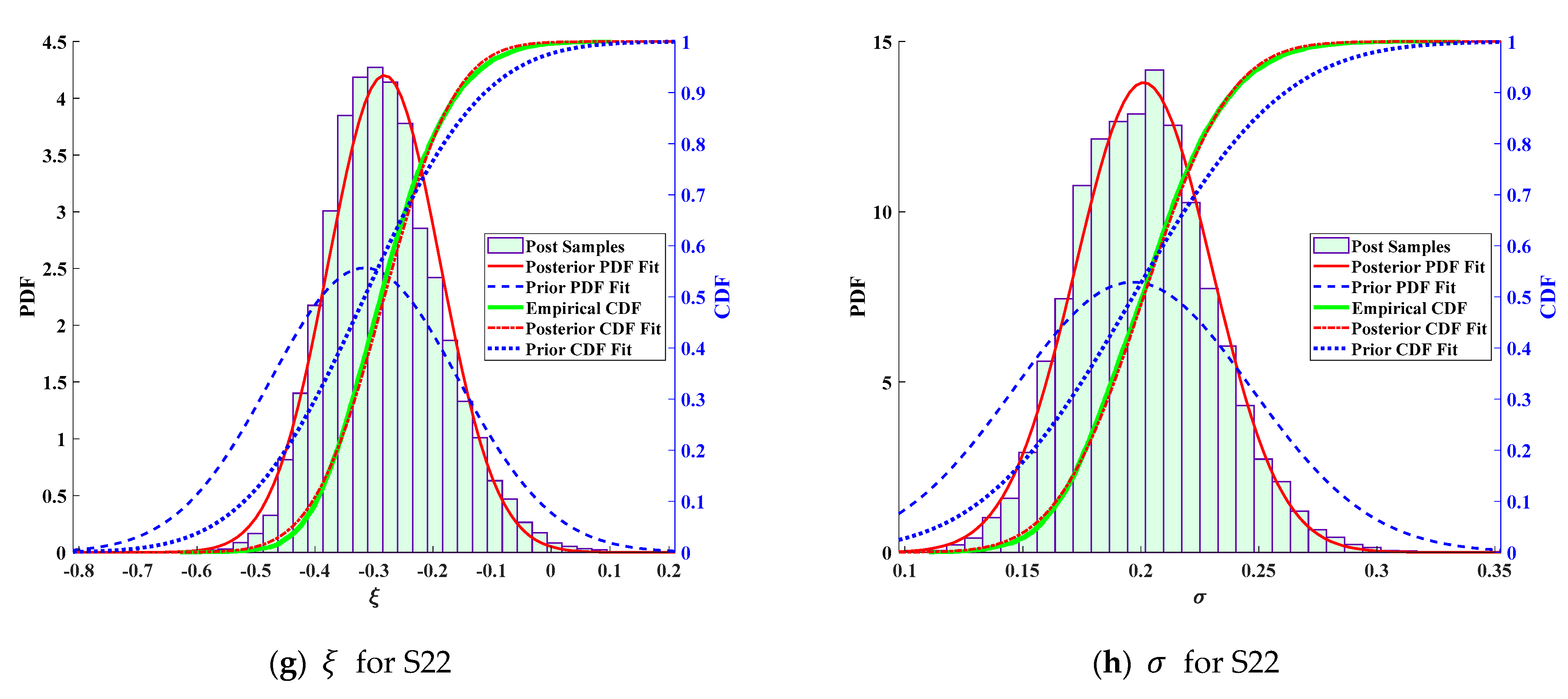
| Suspender | GEV | Suspender | GEV | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Estimate | Mean | S.D. | Parameter | Estimate | Mean | S.D. | ||
| S10 | 1.3141 | 1.3198 | 0.0957 | S16 | 1.3023 | 1.3050 | 0.0813 | ||
| −0.3324 | −0.3972 | ||||||||
| 0.0019 | 0.0010 | ||||||||
| S13 | 1.3071 | 1.3127 | 0.0977 | S22 | 1.3265 | 1.3284 | 0.0938 | ||
| −0.3415 | −0.3160 | ||||||||
| 0.0019 | 0.0025 | ||||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, X.; Duan, G.; Lan, C. Bayesian Updates for an Extreme Value Distribution Model of Bridge Traffic Load Effect Based on SHM Data. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8631. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13158631
Gao X, Duan G, Lan C. Bayesian Updates for an Extreme Value Distribution Model of Bridge Traffic Load Effect Based on SHM Data. Sustainability. 2021; 13(15):8631. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13158631
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Xin, Gengxin Duan, and Chunguang Lan. 2021. "Bayesian Updates for an Extreme Value Distribution Model of Bridge Traffic Load Effect Based on SHM Data" Sustainability 13, no. 15: 8631. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13158631
APA StyleGao, X., Duan, G., & Lan, C. (2021). Bayesian Updates for an Extreme Value Distribution Model of Bridge Traffic Load Effect Based on SHM Data. Sustainability, 13(15), 8631. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13158631





