Is There Coupling Effect between Financial Support and Improvement of Human Settlement? A Case Study of the Middle and Lower Regions of the Yangtze River, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Reviews
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Data Source
3.2. Indicators Selection
3.3. Research Methods
3.3.1. Entropy Method
3.3.2. Coupling Coordination Model
3.3.3. Spatial Autocorrelation Model
3.4. Coupling Characteristics Classification
3.4.1. Types of Coupling
3.4.2. Types of Coupling and Coordination
4. Result Analysis
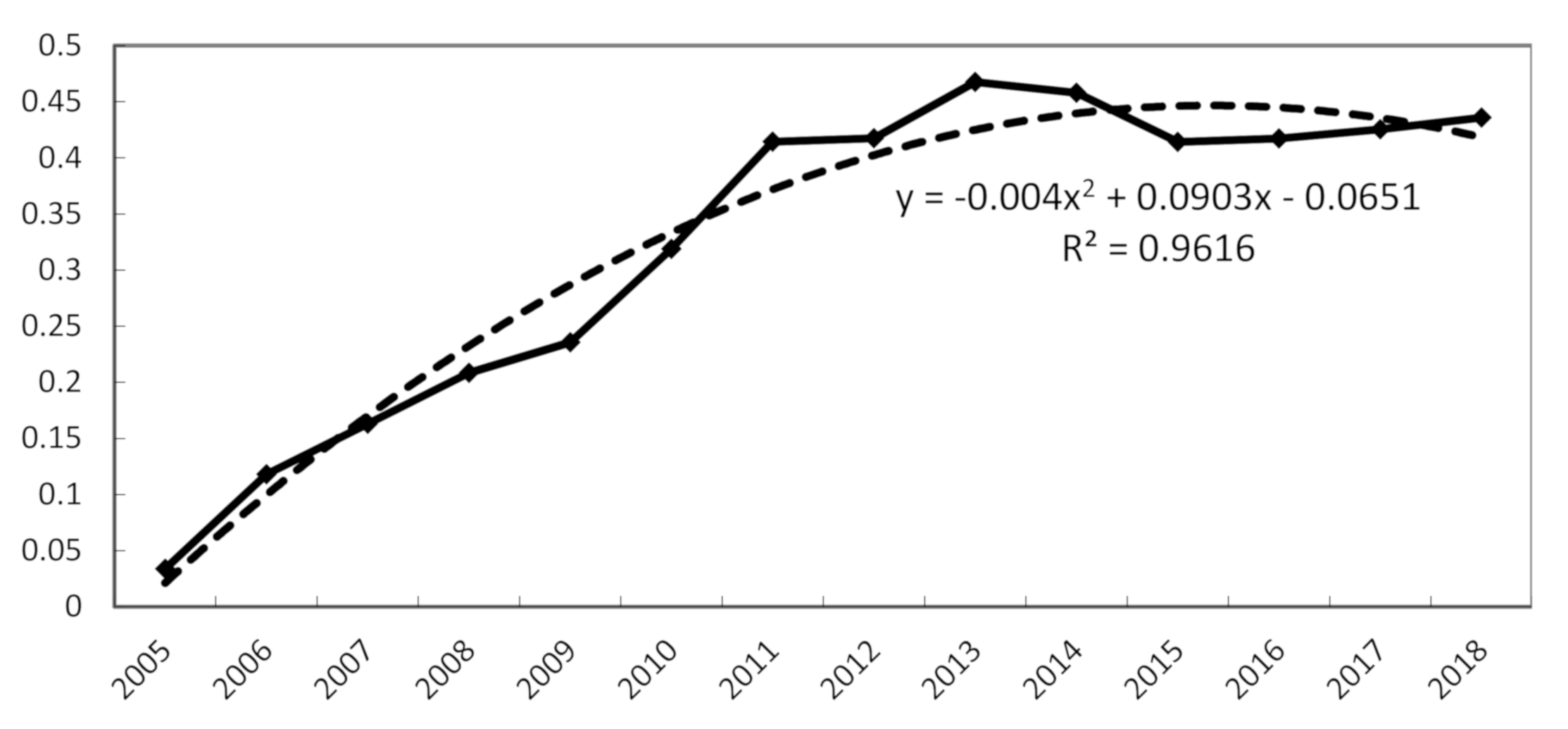
4.1. Analysis of Coupling Degree and Its Type Evolution Characteristics
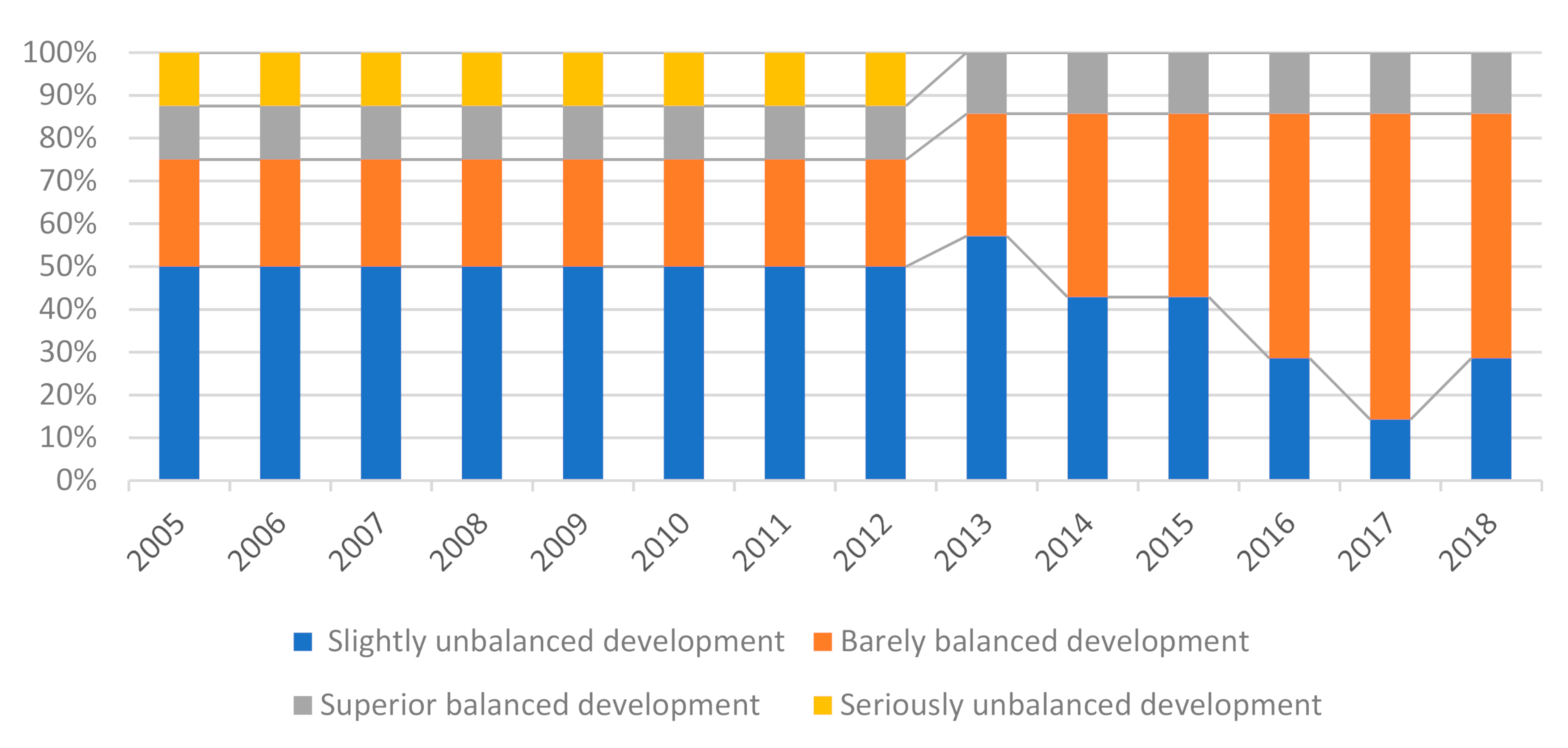
4.2. Analysis of Coordination Degree and Its Type Evolution Characteristics
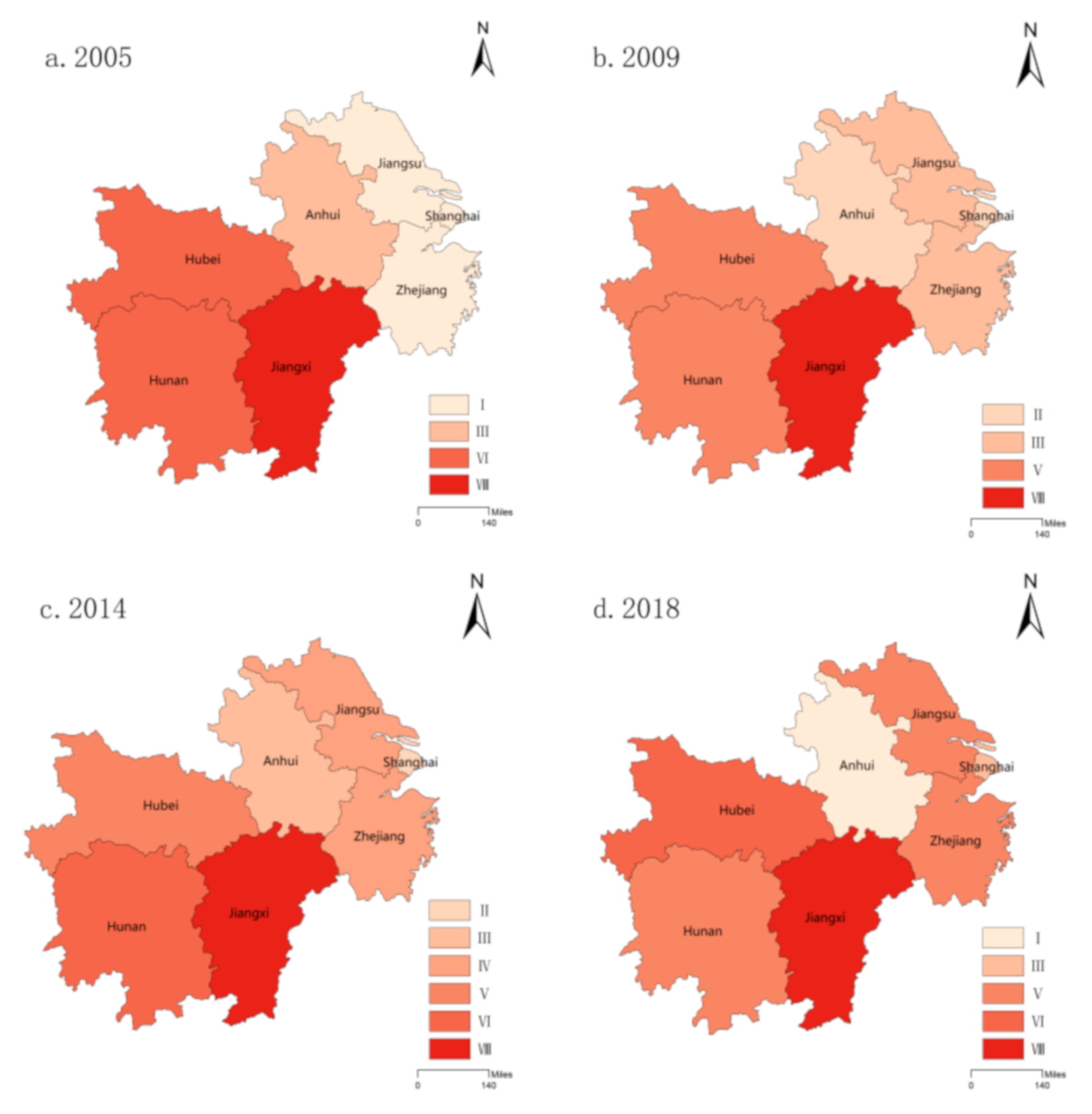
4.3. Analysis of Provincial Spatial Autocorrelation and Its Type Evolution
5. Results Discussion
6. Conclusions and Policy Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guan, J.; Kirikkaleli, D.; Bibi, A.; Zhang, W. Natural resources rents nexus with financial development in the presence of globalization: Is the “resource curse” exist or myth? Resour. Policy 2020, 66, 101641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Ozturk, I. Examining foreign direct investment and environmental pollution linkage in Asia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 27, 7244–7255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.C.; Ouyang, Z.Y.; Shen, X.; Deng, H.B.; Zhao, J.Z. Problems and strategies for the establishment of integrated ecosystem management information system in the west of China. In Proceedings of the Third Ecological Summit, Beijing, China, 22–27 May 2007; pp. 70–71. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, J.; Wang, G.; Ding, Y.; Liu, S. The land ecological evolutional patterns in the source areas of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers in the past 15 years, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 116, 137–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Q.H.; Li, M.Z.; Li, H. Research on Spatial Coupling Coordinated Development Between Financial Agglomeration, Regional Innovation and Ecological Efficiency of Yangtze River Economic Belt. J. Ind. Technol. Econ. 2019, 38, 68–76. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, J.V.; Wang, H.G. Urbanization and city growth: The role of institutions. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2007, 37, 283–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francescato, G. The Significance of Architectural Theory for Environmental Design. Res. Adv. Environ. Behav. Design 1991, 3, 3–52. [Google Scholar]
- William, J.R. On the Rank-Size Distribution for Human Settlements. J. Reg. Sci. 2002, 42, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Stidger, R.W. Rough roads in the city:How less-than-smooth surfaces affect traffic satefety and city liability. Better Roads 2003, 73, 30–36. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, J.; Hokao, K. Residential environmental evaluation of local cities considering regional characteristic and personal residential preference-a case study of Saga City, Japan. J. Environ. Sci. 2004, 16, 138–144. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoodi, M.; Rafieian, M.; Shayan, S. Land Use Planning in the Urban Sensitive Areas Case Study, Farahzad Valley Stream-Tehran. Urban—Reg. Stud. Res. 2013, 16, 47–64. [Google Scholar]
- Talen, E. Neighborhood-Level Social Diversity: Insights from Chicago. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 2006, 72, 431–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hruska, K. Notes on the evolution and organization of the urban ecosystem. Urban Ecosyst. 2006, 9, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnstein, S.R. A Ladder of Citizen Participation. J. Am. Inst. Plan. 1969, 35, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, M.; Ulgiati, S. Emergy-based indices and ratios to evaluate sustainability: Monitoring economies and technology toward environmentally sound innovation. Ecol. Eng. 1997, 9, 51–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, T.R. City size and the urban heat island. Atmos. Environ. 1973, 7, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, R.B.; Gustafson, E.J.; Radeloff, V.C.; Potts, R.S. The relationship between environmental amenities and changing human Settlement patterns between 1980 and 2000 in the Midwestern USA. Landsc. Ecol. 2005, 20, 773–789. [Google Scholar]
- Aitken, S.C. Person-environment theories in contemporary perceptual and behavioural geography I: Personality, attitudinal and spatial choice theories. Prog. Hum. Geogr. 1991, 15, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.K.; McChesney, R.; Munroe, D.K.; Irwi, E.G. Spatial characteristics of exurban settlement pattern in the United States. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2008, 90, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Zhang, W.Z.; Zhan, D.S.; Li, X.L. Quantitative evaluation of human settlement environment and influencing factors in the BohaiRim area. Progress in Geography. Prog. Geography. 2017, 36, 1562–1570. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, Y.; Bu, Y. A Coordinated Assessment between Green Finance and Ecological Environment along the Yangtze River Basin. E3S Web Conf. 2020, 194, 05038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Gu, G.F.; Lu, J.; Wang, J.K. Spatial pattern and regional disparity of regional economic integration and ecology environmental stress in China. World Reg. Stud. 2014, 23, 111–121. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.F. Empirical Research on Spatial Measurement of Financial Agglomeration and Regional Ecological Efficiency. Stat. Decis. 2016, 3, 149–153. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.X.; He, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.; Jia, W.Q. SD Simulation of the Spatial Panel Data of Financial Agglomeration, Economic Development and Eco-efficiency. Syst. Eng. 2017, 35, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Holtz-Eakin, D.; Selden, T.M. Stoking the fires? CO2 emissions and economic growth. J. Public Econ. 1995, 57, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, X.; Chen, M.; Chen, M.-Y. Coupling and Coordination Development of Australian Energy, Economy, and Ecological Environment Systems from 2007 to 2016. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.-H. Housing Finance and Urban Infrastructure Finance. Urban Stud. 1997, 34, 1597–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.E. Financing Urban Development in China. Chin. Econ. 2009, 42, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Shi, Q.; Huang, X. An Analysis of the Support Effect of Rural Financial Development on Rural Infrastructure Construction. J. Agrotech. Econ. 2011, 11, 34–44. [Google Scholar]
- Tomal, M. Analysing the coupling coordination degree of socio-economic-infrastructural development and its obstacles: The case study of Polish rural municipalities. Appl. Econ. Lett. 2020, 28, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, C.K.Y.; Sarpca, S.; Yilmaz, K. Public housing units vs. housing vouchers: Accessibility, local public goods, and welfare. J. Hous. Econ. 2012, 21, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.X.; Shen, K.R. The Impact of Urban Land Quota Allocation on China’s Housing Market. Econ. Res. J. 2019, 54, 116–132. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Q.M.; Nie, J. Coupled and Coordinated Development Evaluation of Health Investment and Health Benefits. Chin. Health Econ. 2016, 35, 68–70. [Google Scholar]
- Zhi, I.; Liang, L.E.I. Environmental Effect of Local Government’s Expenditure on Energy Saving# br# and Environmental Protection. J. Beijing Univ. Posts Telecommun. 2018, 20, 89. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, C.; Hongru, W.; Zhiliang, N. Registration System Reform, Fiscal Expenditure Responsibility and Life Satisfaction of Rural Residents. Public Financ. Res. 2017, 4, 64–74. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.N.; Zhou, H.X.; Chen, G.H. The Optimal Infrastructure Investment Scale and Order: Some Empirical Evidence from Panel Data in China. Econ. Rev. 2011, 4, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S. A Comparative Analysis of Wages Level of Private Enterprises in 30 Provincial Administrative Regions in China Based on Principal Component Analysis. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Forum on Decision Sciences; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.M.; Li, X.X.; Zhang, J. Coordinated Development of Human Settlement and Economy in County-level Cities in the Yellow River Basin. J. Landsc. Res. 2010, 2, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Ding, Z.; Meng, Y.; Li, Q. Regional Sustainable Assessment at City Level Based on CSDIS (China Sustainable Development Indicator System) Concept in the New Era, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 976–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, Y.; Liu, X. Comprehensive Land Carrying Capacities of the Cities in the Shandong Peninsula Blue Economic Zone and their Spatio-Temporal Variations. Sustainability 2019, 11, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, X. Investigation of a coupling model of coordination between urbanization and the environment. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 98, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jin, C.; Lu, M.; Lu, Y. Assessing the suitability of regional human settlements environment from a different preferences perspective: A case study of Zhejiang Province, China. Habitat Int. 2017, 70, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Zhang, X.; Elahi, E.; Wan, A. Evolution of spatial–temporal characteristics and financial development as an influencing factor of green ecology. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Zhang, X.L.; Yin, X. Evaluation of rural human settlements quality and its spatial pattern in Jiangsu Province. Econ. Geogr. 2015, 35, 138–144. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Pan, Y.C.; Tang, L.N. Spatiotemporal Coupling Characteristics of Agricultural Development and Farmers’ Income at County-level in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Econ. Geogr. 2017, 37, 141–147. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Peng, B.; Wei, G.; Elahi, E. Comprehensive Evaluation and Spatial Difference Analysis of Regional Ecological Carrying Capacity: A Case Study of the Yangtze River Urban Agglomeration. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, Y.; Fan, X.; Guo, Y.; Li, S.; Huang, H. Multi-objective optimization of injection-molded plastic parts using entropy weight, random forest, and genetic algorithm methods. J. Polym. Eng. 2020, 40, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, J.; Feng, L.; Dong, X.; Zhu, X.; Li, C. Exploring coupling coordination between urbanization and ecosystem quality (1985–2010): A case study from Lianyungang City, China. Front. Earth Sci. 2015, 10, 527–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhou, L.; Chen, Y.; An, Y.; Hou, C. Degree of coupling and coordination of eco-economic system and the influencing factors: A case study in Yanchi County, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China. J. Arid. Land 2017, 9, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Ge, Y.; Liu, Q.; Liu, X. The spatial differentiation of the coupling relationship between urbanization and the eco-environment in countries globally: A comprehensive assessment. Ecol. Model. 2017, 360, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| System Indicators | Primary Indicators | Secondary Indicators | Unit | Literature Basis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| financial support | Fiscal expenditure | Medical hygiene (X1) | 100 million yuan | Tang and Nie (2016) [33] |
| Energy saving and environmental protection expenditure (X2) | Zhi and Liang (2018) [34] | |||
| Urban and rural community expenditure (X3) | Qian et al. (2017) [35] | |||
| House insurance (X4) | Qian et al. (2017) [35] | |||
| Financial institution loan | Water conservancy, environment and public facilities management (X5) | Zhang et al. (2011) [36] | ||
| Resident services, repairs and other service industries (X6) | Zheng (2020) [37] | |||
| Health and social work (X7) | Qian et al. (2017) [35] | |||
| Transportation and Post (X8) | Zhang et al. (2011) [36] | |||
| improvement of human settlement | infrastructure | Hospital beds per 1000 people (Y1) | Zhu et al. (2010) [38] | |
| Average number of students in colleges and universities per 100,000 population (Y2) | Wei et al. (2020) [39] | |||
| Road area per capita (Y3) | m2 | Cui et al. (2019) [40] | ||
| Number of buses per 10,000 people (Y4) | Li et al. (2012) [41] | |||
| ecosystem | Public green area per capita (Y5) | m2 | Wang et al. (2017) [42] | |
| Harmless treatment rate of municipal solid waste (Y6) | % | Peng et al. (2021) [43] | ||
| living conditions | Water penetration rate (Y7) | % | Zhu et al. (2010) [38] | |
| Gas penetration rate (Y8) | % | Zhu et al. (2015) [44] | ||
| Domestic waste treatment rate (Y9) | % | Peng et al. (2021) [43] |
| Type | Content | |
|---|---|---|
| 0.8 < C ≤1 | Superior coupling | Fully related and mostly based on positive promotion |
| 0.5 < C ≤ 0.8 | Benign coupling | Has entered a coupling process |
| 0.3 < C ≤ 0.5 | Moderate coupling | There is a trend of positive correlation, the interaction between the two is getting closer |
| 0 ≤ C ≤ 0.3 | Low coupling | The degree of association is not high, the overall chaos is disordered |
| Type | Content | |
|---|---|---|
| 0.7 < D ≤ 1 | Superior balanced development(Ⅰ) | Enter the stage of coordinated development |
| 0.5 < D ≤ 0.7 | Barely balanced development(Ⅱ) | Basic coordination, the overall coordination is optimized |
| 0.3 < D ≤ 0.5 | Slightly unbalanced development(Ⅲ) | overall coordination is poor |
| 0 < D ≤ 0.3 | Seriously unbalanced development(Ⅳ) | Interaction is chaotic |
| Year | Moran’s I | E(I) | Z |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2005 | 0.2515 | −0.1667 | 2.9363 |
| 2009 | 0.2061 | −0.1667 | 2.0524 |
| 2014 | 0.2090 | −0.1667 | 2.7159 |
| 2018 | 0.2701 | −0.1667 | 3.3641 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, W.; Peng, B.; Wei, G.; Wan, A. Is There Coupling Effect between Financial Support and Improvement of Human Settlement? A Case Study of the Middle and Lower Regions of the Yangtze River, China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8131. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13158131
Yan W, Peng B, Wei G, Wan A. Is There Coupling Effect between Financial Support and Improvement of Human Settlement? A Case Study of the Middle and Lower Regions of the Yangtze River, China. Sustainability. 2021; 13(15):8131. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13158131
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Weimin, Benhong Peng, Guo Wei, and Anxia Wan. 2021. "Is There Coupling Effect between Financial Support and Improvement of Human Settlement? A Case Study of the Middle and Lower Regions of the Yangtze River, China" Sustainability 13, no. 15: 8131. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13158131
APA StyleYan, W., Peng, B., Wei, G., & Wan, A. (2021). Is There Coupling Effect between Financial Support and Improvement of Human Settlement? A Case Study of the Middle and Lower Regions of the Yangtze River, China. Sustainability, 13(15), 8131. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13158131







