Abstract
The increase in customer complaints on the reliability of 3PL services among online sellers has become prominent in the industry, as confirmed by 3PL service providers in Malaysia. The increase in customer complaints increases the tendency to switch to other 3PL service providers. As Asian markets lead the growth of e-commerce, covering approximately 50% of the global e-commerce market, whether the customer will continue to shop online or not is no longer the issue. Although having the proper logistics provider to support online sellers’ business is crucial, most studies have focused on the online shopper’s perspective and employ the service quality theory. Observably, the satisfaction and reuse intention of the 3PL from the online retailer’s perspective is largely neglected. This study identified the factors influencing the satisfaction and reuse intention of 3PL services among online sellers in Malaysia by employing and expanding the stimulus–organism–response (SOR) theory. A purposive sampling method was employed, and the data were gathered via an online survey among online sellers. Additionally, smart partial least squares (SmartPLS) was applied to test the hypotheses. The results indicated that reliability had a positive effect on satisfaction, and satisfaction had a positive relationship with the reuse intention of certain 3PL services. Moreover, satisfaction mediated the relationship between reliability and reuse intention, whereas price fairness strengthened the positive relationship between satisfaction and reuse intention. The findings enhance studies that employed the SOR theory, particularly relating to online sellers’ behaviour on 3PL services. The findings also benefit online sellers and 3PL service providers to create attractive marketing strategies for business sustainability.
1. Introduction
Global courier, express, and parcel (CEP) delivery services are currently experiencing strong growth partly because of the developing e-commerce sector and increasing consumer demand for online shopping. Multiple logistic providers have attempted to provide first-class services to enhance customer satisfaction [1] and the service reuse intention. Online sellers rely heavily on logistics capability to deliver products to various customer locations, which is considered as a backbone for the tremendous growing e-commerce [1,2]. Hence, the increase in e-commerce activities should be aligned with the capability of logistic providers.
In 2019, worldwide retail e-commerce sales reached USD 3.53 trillion and are anticipated to reach USD 6.54 trillion in 2022 [3] (Global Retail E-Commerce Sales 2014–2024, 2020). Moreover, the International Post Corporation predicted a surge in Asia–Pacific regional sales of up to two-thirds of the global e-commerce by 2021 [4]. Along with government intervention, Malaysia’s industry could achieve more than 20 per cent growth, equivalent to more than RM 170 billion in 2020. Thus, the reliability of the service providers is one crucial factor to be considered by e-commerce retailers to ensure the goods are delivered at the right time, in good condition, and at competitive prices.
The reliability of 3PL services is a never-ending issue despite the vast volume of parcel delivery services. For instance, Pos Malaysia Bhd. is one of the biggest third-party parcel delivery services admitted to receiving numerous complaints on delivery services [5]. Additionally, Dalsey Hillblom Lynn (DHL) Malaysia’s managing director and customer service director welcomed customers’ comments and suggestions by providing an email address for direct complaints to the management. Hence, the delivery service is a critical issue in Malaysia. Significantly, increasing customer complaints increases customers’ tendency to switch to another 3PL service provider.
Sustaining high service quality to minimise customer complaints is fundamental in service industries, specifically for the third-party logistics service industry [6] in order to promote loyalty among online sellers. As the Asian market leads e-commerce growth, covering around 50% of the global e-commerce market, whether the customer will continue to shop online or not is no longer the issue [7]. Nonetheless, having the right logistics provider to support the online business is crucial for the online seller. Furthermore, the emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the e-commerce trajectory, highlighting the importance of selecting the right logistics provider to ensure online business sustainability during this challenging period. Hence, investigating and identifying the factors influencing online sellers’ reuse intention for 3PL services is critical.
Although various studies investigated logistic services providers, most focused on the service quality theory, [8] satisfaction by employing the service quality theory, and logistics service quality [9,10]. Besides, the studies also highlighted the intention to use parcel services [11], omni-channel retailing [12], online logistic service value [13], and customer satisfaction on the logistics service quality and capabilities [9]. Studies were also conducted on selecting the third-party logistics related to reverse logistics [14], based on service performance [15] and green logistics [16]. Consequently, studies on the reuse intention of 3PL services among online sellers remain limited, particularly regarding the SOR model. Hence, this study aimed to identify factors influencing the reuse intention of certain 3PL services among online sellers in Malaysia by employing a quantitative study using the SOR model by Mehrabian and Russell [17]. Customer satisfaction has become a popular subject, particularly in today’s dynamic and highly competitive business [18].
The study enhanced the predictive power by testing satisfaction as a mediator between reliability and flexibility with the reuse intention. Although customer satisfaction is usually used as a mediator in business studies, many tested customer satisfaction as a mediator between reliability and flexibility toward reuse intention in the logistics context. The study also contributes to the current literature by introducing the moderation effect of price fairness on the relationship between satisfaction and reuse intention. In Malaysia, most online sellers advertise products on social media such as Facebook and Instagram or Whatsapp, displaying the product prices and transportation costs separately. Moreover, the online sellers require customers to pay the delivery cost upon customers’ enquiry. Price fairness is commonly associated with buyers, whereby customers will pay for the products and the logistics charges as a sum of the total price, influencing the potential buyers’ decision. Even if the online seller does not bear the logistics cost, the sellers will decide which logistics provider will deliver the products to the respective customers. Thus, the study analysed price fairness from the online sellers’ perspective. Notably, online sellers are also customers of the logistics providers. Thus, expanding the online business also increases the importance of the logistics industry [2], which is considered a backbone to online businesses [1]. The findings will benefit many parties, specifically online sellers and logistics providers to craft better marketing strategies for business sustainability. Significantly, both parties rely on each other to survive in the dynamic and competitive business field.
Thus, the study contributes by providing an advanced understanding of the online retailer’s perspective on selecting the third-party logistics service providers by using the SOR model, which has received little attention from logistics scholars. The study also contributes by introducing the new SOR model, of which there is no similar model to the author’s knowledge. The flexibility of the SOR allows researchers to develop their model, provided it fits with the stimulus–organism–response concept. Third, the study also introduces satisfaction as the mediator for the relationship between reliability and flexibility towards the reuse intention. Although satisfaction was commonly used as a mediator in other studies, the limited literature has confirmed the mediation effect of satisfaction between reliability and flexibility towards the reuse intention, specifically concerning online retailers. Lastly, the study includes price fairness as a moderator for the relationship between satisfaction and reuse intention.
2. Literature Review and Hypotheses Development
2.1. SOR Theory
The SOR model by Mehrabian and Russell [17] was employed as the study theory, explaining the inter-related factors between variables in the model. Originally, the SOR model was developed to explain the effect of environmental stimuli on emotions and future behaviour. In the consumer behavioural context, the theory describes that individual emotions are enhanced once a certain stimulus is brought to light, leading to a certain behaviour [17].
The SOR theory has been modified according to the various context of studies [19,20]. Moreover, the theory has been widely applied to explore how the environmental stimuli influence customers’ evaluations based on experience to form a new response in a particular context. The flexibility of the theory allows researchers to develop a new model based on the SOR approach of expounding the new model of consumer behaviour. Meanwhile, studies on tourism [21], voluntourism [22], technology adoption [23], and others confirmed the capability of SOR in predicting future behaviour. Nonetheless, few studies highlighted logistics based on the SOR theory, whereby scholars adjusted environmental stimuli based on the research setting. In this study, environmental stimuli were represented by the reliability and flexibility of the logistics services, which are crucial factors as they are influenced by various factors such as location, firm size, business environment, and others.
“Organism” refers to the internal state affected by environmental stimuli [17]. According to Baghozzi [24], “organism” refers to individual internal states of perception, affect, and feelings, which influence individual’s future behaviour. The literature has also confirmed the importance of the internal state in influencing future behaviour, such as dissatisfaction (internal state) towards discontinued usage [23]. Similarly, the study conceptualised satisfaction as the internal state influenced by the environmental stimuli of reliability and flexibility of the third-party logistics. Besides, the SOR model also proposed that the organism indirectly affects the relationship between stimuli and response [25,26].
A response is affected by an organism. For online retailers, satisfaction influences the response to continue using or shifting to other providers with numerous logistics providers offering similar services; hence, the probability of shifting to other providers is high. As the study had a sequential effect on the capability of the 3PL and online sellers’ emotions and responses, the SOR theory was thus suitable to be applied. Additionally, the reliability of the logistic provider represents the stimulus factor, while satisfaction as an organism and the reuse intention represents the organism factor in the study.
2.2. Reliability
Reliability is the provider’s capability to deliver customers the promised services [27], a dimension of the service quality theory by Parasuraman et al. [28]. Nevertheless, Zeithaml et al. [29] argued that not all the theory dimensions are suitable for other studies. Therefore, this study chose reliability as a single factor to act as stimuli towards the organism. In a service marketing environment, reliability is a fundamental element to be evaluated to ensure customer satisfaction with the service. No reliability makes customers unhappy, switching to other providers at any chance. Moreover, providing reliable services is the quickest way to satisfy customers [18].
In logistic services, reliability is vital to ensure that the required services are trusted and dependable. Once customer expectations are met (particularly reliability), the complaints will diminish, increasing their satisfaction. A longer delivery period is sometimes acceptable, especially with the minimum charge posed by providers. Nonetheless, the incapability of 3PL to deliver the goods as promised could produce complaints and dissatisfied customers. For example, Nonthapot and Nasoontorn [30] and Othman et al. [27] found that reliability positively affects satisfaction. Therefore, the study proposed the following:
Hypothesis 1 (H1).
Reliability has a positive effect on online sellers’ satisfaction.
2.3. Satisfaction
The organism factor concerns the internal emotional state of individuals reflected by the environmental stimuli [17]. In the study, satisfaction represents an organism and acts as a comparison between the expected and actual outcomes of the services received by customers. Besides, satisfaction commonly refers to the perception of the overall internal judgement of the performance, mostly on products, services, or retailers [31]. The study specifically focused on customer satisfaction based on online sellers’ satisfaction with the service provided by 3PL to deliver the products to customers.
Higher satisfaction of the 3PL services leads to online sellers’ reuse intention. Generally, online sellers are satisfied if the goods are delivered in good condition on time, and thus no complaints will be raised by their customers. In marketing studies, satisfaction is commonly positively related to reuse behaviour [32,33]. Moreover, past literature argued that higher satisfaction forms a higher tendency of reuse intention that is also part of gaining loyalty. Meanwhile, past studies in logistics revealed that satisfaction leads to loyalty [12], and Alalwan [34] discovered that satisfaction positively relates to the reuse intention. Thus, the study proposed:
Hypothesis 2 (H2).
Satisfaction has a positive effect on the reuse intention.
2.4. Flexibility
Logistics flexibility is the logistic providers’ capability to entertain customer demands in delivery, support, and service [35]. The study highlights logistics flexibility in terms of the ability of the 3PL providers to arrange the delivery process for pick-up and delivery of online sellers’ products to the designated destinations. Notably, the 3PL providers tend to be more customer-driven to secure the business due to competition [36]. Customers also start to seek variety and flexibility of services before concluding a transaction or future interaction. Additionally, the number of transactions, retailers’ experience, high competition among 3PL providers, and the increasing number of online sellers significantly enhance service flexibility.
Flexibility is also closely related to company size. For instance, large logistics providers have large assets and workforces to offer more flexible services than a small company with limited assets. Chavez et al. [37] and Yu et al. [38] found that flexibility positively correlates with customer satisfaction. Flexibility also has a positive relationship with the reuse intention of 3PL services [39]. Based on the findings, the study proposed:
Hypothesis 3 (H3).
Flexibility has a positive effect on customer satisfaction.
Hypothesis 4 (H4).
Flexibility has a positive relationship with the reuse intention of 3PL service providers.
2.5. Reuse Intention
Reuse intention is another way to measure consumer behaviour in marketing studies. The major difference between reuse intention and the intention to use is respondent characteristics. Besides, the reuse intention focuses on the respondents that already gained experience, whereas the intention to use relates to potential users. Because of the significant number of logistics providers, studying the factors influencing reuse intention is critical because maintaining current customers is easier than gaining new customers in business. Hence, one way to measure how successful the services is by analysing the reuse behaviour [40].
Most studies have been focused on customer satisfaction from the buyer’s perspective (individuals buying the products and receiving delivered goods). Nevertheless, the buyers are not involved in deciding which logistics providers they prefer—the decision falls on online sellers.
2.6. Price Fairness (Moderator)
Price fairness refers to the customer’s emotional evaluation and whether the price differences between current and other providers are reasonable [41]. Most studies showed a strong relationship between satisfaction and reuse intention. Nevertheless, Lin et al. [42] stated that the logistics service quality did not significantly affect the reuse intention. Numerous studies have introduced the moderating factor to understand better the relationship between satisfaction and reuse intention [43]. Moreover, price always significantly affects the reuse or repurchase intention. Besides the service quality, price is also a significant issue when online sellers select logistics services [9]. Therefore, excellent service that lacks price fairness negatively influences the reuse intention.
Although customers pay the transportation charges, the logistics providers are selected by online sellers, thus affecting the total price of the products. The logistics providers charge services according to weight, size, distance, and difficulties in delivering the products. Hence, all logistics providers have different capabilities about staffing, technology, and assets to handle the delivery; thus, the price differs among the logistics providers. Therefore, this study proposed price fairness as a moderator in the relationship between satisfaction and reuse intention:
Hypothesis 5 (H5).
The positive relationship between satisfaction and reuse intention is stronger when the price fairness is high.
2.7. Satisfaction (Mediator)
Introducing the mediating variable is vital to enhance the explanatory power of the research model. The mediating variable is highly used in business social research as a way for the study to contribute to the body of knowledge. Mehrabian and Russell [17] stated that the organism was designed as a mediator between stimuli and response. Consequently, the study introduced satisfaction as a mediator for the relationship between reliability and flexibility towards the reuse intention in logistics service providers. Hence, the study proposed:
Hypothesis 6 (H6).
Satisfaction mediates the relationship between reliability and reuse intention.
Hypothesis 7 (H7).
Satisfaction mediates the relationship between flexibility and reuse intention.
Figure 1 illustrates the research model.
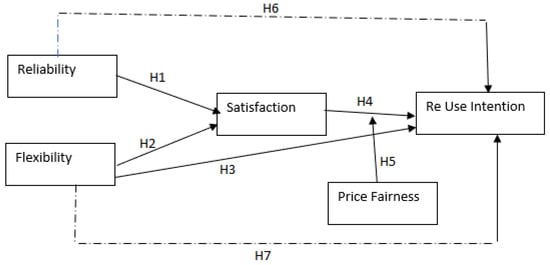
Figure 1.
Proposed research framework.
3. Methodology
The study items were adopted from established articles specific to the study area. For example, reliability measures were adopted from Le et al. [44], the measurement for customer satisfaction was based on Huma et al. [9], flexibility referred to Sorkun et al. [45], the reuse intention was from Venkatesh et al. [46], and price fairness was taken from Konuk [41]. All constructs were measured by using a five-point Likert scale, except for the reuse intention. The reuse intention was measured using a seven-point Likert scale. Moreover, the different scales were used to measure the study variables to overcome common method variance (CMV) as per MacKenzie and Podsakoff [47].
Sampling Method
The study focused on online sellers who advertise products via Facebook, Instagram, and other social media channels without a website; thus, the study unit was at the individual level. Because of the targeted respondents being online sellers, the questionnaire link was provided via the channels from early January 2020 until the end of March 2020. The respondents were also encouraged to share the link with colleagues involved in online selling activities. The study applied the purposive sampling method as the population was unknown with specific criteria for the valid respondents. Additionally, using convenience sampling suffices as the nature of the study highlights the integrity of the theoretical effects [48].
This study ensured respondent validity by using filter questions. Firstly, the study confirmed that the respondents are online sellers without a website to promote products. Next, all the logistics costs were paid by the customers. Besides being voluntary, the system automatically stops those that do not fulfil the study criteria. Furthermore, the respondents had to declare the logistics companies they use to deliver their products. Initially, the system gathered 311 respondents, but only 217 were valid respondents, with 75 respondents being invalid because of having a website and the remaining for answering “no” to the second filter question. Online sellers sometimes promote free delivery in certain occasions. Out of the 217 data received, 12 were discarded because of poor data quality, such as answering in a straight line and incompletely. Additionally, all data were gathered in Microsoft Excel before further analysis.
The study employed structural equation modelling with Smart PLS [49]; hence, the power of analysis was applied to determine the minimum sample size of the study determined by model complexity. Based on the power of 0.8, referring to Gefen et al. [50] for the medium effect size and using the four predictors of the study, the minimum sample was 85. Hence, the sample size of 205 respondents was sufficient to test the research model.
Out of the 205 respondents, 70.7% were female, most respondents (53.2%) were 18–24 years old, 61.5% were single, 48.3% had a degree as the minimum qualification, and 43.9% had less than two years of experience in online selling. Meanwhile, 58% of the respondents sell between four to six products, 63% deliver the products twice a week, and 38% sell healthcare products.
4. Data Analysis
The study aimed for predictive purposes; hence, smart partial least squares (PLS) was a better-suited software for application. According to Hair et al. [51], the smart PLS is for studies with predictive purposes.
4.1. Common Method Bias
Common method bias could be a critical issue in the study as independent and dependant variables are answered by the same person simultaneously [52]. Thus, a procedural method with a different anchor scale was used to measure independent and dependent variables, and the statistical method [47] with full collinearity analysis [53] was applied to remedy the issue. The CMV could be severe if the variance-inflated factor (VIF) value was higher than 3.3 [53]. Table 1 illustrates the results of full collinearity testing, showing that the VIF value was lower than the threshold value of 3.3, indicating that CMV was not an issue in the study.

Table 1.
Full collinearity testing.
4.2. Measurement Model
As proposed by Hair et al. [51], the analysis fulfilled the two-step approach, comprising a measurement model and a structural model. For the measurement model, the convergent validity and discriminant validity must be established before continuing to the structural model. Convergent validity is a test to ensure that the items used to measure the construct can explain the construct. Additionally, convergent validity is confirmed if the loading and average variance extracted (AVE) is ≥0.5 and the composite reliability is ≥0.7. Table 2 shows the results of convergent validity. As all the values for loading, AVE, and CR were higher than the minimum value set by Hair et al. [51], the convergent validity was established in this study.

Table 2.
The measurement model and convergent validity.
The discriminant validity testing ensures that items that measure a single construct will not load highly in other constructs. For example, Franke and Sarstedt [54] stated that a hetrotrait–monotrait (HTMT) ratio should establish discriminant validity. The authors proposed that given that the HTMT values were lower than 0.85, the discriminant validity was confirmed. Table 3 shows the results of the discriminant validity of the study.

Table 3.
Discriminant validity (HTMT ratio).
4.3. Structural Model
Once the measurement model was established, the study proceeded to the structural model to test the hypothesis. Based on Ngah et al. [55], the study confirmed that the data was not multivariate normal because of the Mardia’s multivariate skewness (β = 38.424, p < 0.01) and the Mardia’s multivariate kurtosis (β = 105.971, p < 0.01). The multicollinearity issue could be addressed before confirming the hypothesis testing [51]. Table 4 indicates that the VIF was lower than ≤3.3 [56], verifying that the multicollinearity issue was not a problem for the study.

Table 4.
Hypothesis testing: direct effect.
Following Hair et al. [51], the study referred to the beta value (the direction of the beta value must be aligned with the hypothesis direction), t-values (≥1.645), p-values (≤0.05), and the confidence interval gained from employing a bootstrapping procedure (no zero value in between the lower level (LL) and the upper level (UL)) with 5000 resampling techniques to prove that the hypothesis is supported. Table 4 summarises the hypotheses criteria developed in the study, particularly for the direct effect, whereas Table 5 shows the mediating and moderating effects. For the direct hypothesis, only one hypothesis was unsupported from the four tested hypotheses.

Table 5.
Hypothesis testing: moderator and mediation analysis.
Notably, with (β = 0.358, p < 0.01), the R2 was 0.435, indicating that reliability and flexibility explained 43.5% of the variance in satisfaction. Consequently, the reliability of the service provided by the logistics companies had a positive effect on customer satisfaction, thus supporting H1. The flexibility of the service also positively affected customer satisfaction (β = 0.366, p < 0.01), hence supporting H2. Meanwhile, flexibility (β = 0.036, p = 0.396) had no significant effect on the reuse intention of the particular 3PL services; hence, H3 was unsupported. For the last direct hypothesis, satisfaction (β = 0.328, p < 0.01) had no positive effect on the reuse intention, hence supporting H4. The R2 for reuse intention was 0.489, indicating that the flexibility, satisfaction, and the moderation effect of price fairness explained 48.9% of the variance on the reuse intention of 3PL services among the online sellers. Table 4 and Figure 2 illustrate the results of the direct effect of the study.
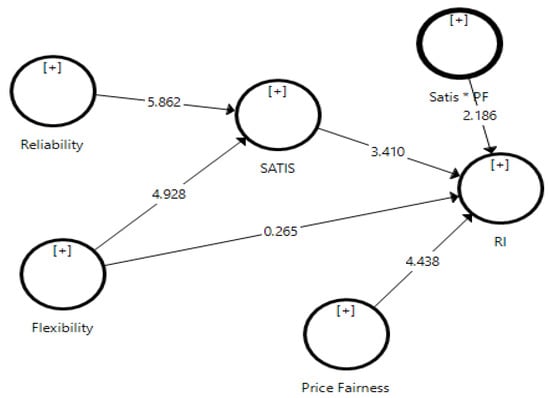
Figure 2.
Results of the direct effect and the moderating effect.
For the moderating analysis, the study discovered that (β = 0.196, p < 0.05), showing that price fairness strengthened the positive relationship between satisfaction and reuse intention of the 3PL services among the online sellers; thus, H5 was supported. Table 5 illustrates the moderation and mediation analysis results, whereas Dawson’s plot in Figure 3 provides a clearer view of the moderation effect.
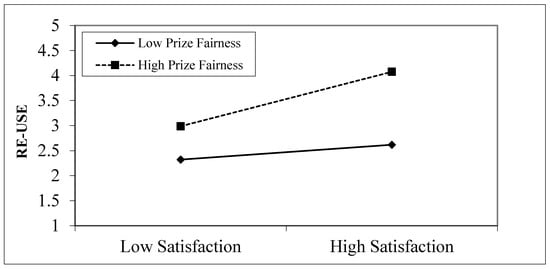
Figure 3.
Moderating effect.
The study followed the guidelines by Preacher and Hayes [57] to test the mediation analysis by bootstrapping the indirect effect. The results showed that (β = 0.117, t = 2.186: LL = 0.014, UL 0.295, p < 0.01) for the relationship between reliability → satisfaction → reuse intention, confirming that satisfaction had a mediating effect on the relationship between reliability and reuse intention; thus, H6 was supported. Interestingly, satisfaction also mediated the relationship between flexibility and reuse intention (β = 0.120, t = 2.238: LL = 0.026, UL 0.048, p < 0.05), hence H7 was supported. Therefore, all moderation and mediation effects were supported.
4.4. PLS Predict
Instead of using the blindfolding procedure for predictive relevance, Shmueli et al. [58] claimed an issue in the analysis. Thus, PLS predict was introduced to overcome weaknesses in the blindfolding procedure. By applying the PLS predict procedure, predictive relevance will be based on the error created by PLS compared to the linear regression (LM). If the score of the PLS root mean square error (RMSE) minus LM RMSE is (PLS-LM) negative, the PLS modelling has a lower error. If the score of all the items were negative, the model has high predictive power.
If the majority score is low, the model has moderate predictive power, and if the minority items were negative, the model has low predictive power. Meanwhile, if all values were positive, the predictive power is not confirmed. Table 6 demonstrates the results of the PLS predict. The two items used in the study found the reuse intention (RI1 and RI3) positive, indicating low predictive power. For customer satisfaction, all items were negative, suggesting strong predictive power.

Table 6.
PLS predict.
5. Discussions and Findings
The study discovered that reliability positively affected customer satisfaction, in line with [27,30], whereby reliability had a positive relationship with satisfaction in the service quality of the Nakhon Phanom Municipality-Thakhek (Lao People’s Democratic Republic) ferry in Thailand and the self-service technology in Malaysia. Hence, the reliability of logistics services is vital for customer satisfaction. Consequently, to enhance customer satisfaction, 3PL providers must fulfil the promises to deliver products. The issue is not about the delivery speed but the ability to deliver the products on time as promised when the transaction is established.
Furthermore, flexibility positively affected customer satisfaction in line with Chavez et al. [37] and Yu et al. [38], who revealed that logistics flexibility positively influences customer satisfaction. The findings showed that the flexibility of 3PL services is a crucial factor that online sellers must consider. Thus, 3PL service providers should not be too rigid in providing services. In this highly competitive business, online sellers can choose which 3PL service providers to deliver the products to the customers’ destination. Hence, 3PL service providers offering more flexible services have an enormous chance to satisfy online sellers. Besides online sellers visiting the centres, some 3PL service providers offer door-to-door services. The approach involves online sellers calling the centres and the 3PL collecting the goods at the online sellers’ location.
Unfortunately, flexibility does not affect the reuse intention of 3PL services among online sellers, contrary to de Grahl et al.’s [39] study but in line with Tontini et al. [59], who found that flexibility did not significantly affect the reuse intention of the 3PL services from specific 3PL service providers. The discovery proves that flexibility only positively affects satisfaction, not the reuse intention. Therefore, online sellers have many options, causing them not to reuse the same 3PL provider even if the services are flexible. Meanwhile, other factors to be considered before selecting 3PL service providers are geographical coverage, experience, and other factors that other studies should further investigate.
The study also revealed that satisfaction positively affects the online sellers’ reuse intention of particular 3PL services, confirming [12,34]. The results indicated that once the online sellers are satisfied with the current 3PL service providers, they form a high intention to continue using the services in the future. Hence, the 3PL providers intending to garner loyalty among online sellers should ensure customer satisfaction is fulfilled. Thus, 3PL service providers should strengthen efforts in reducing complaints and increasing customer satisfaction. Moreover, customer satisfaction starts once customers begin communicating online or during the first step of coming to the business centre. Customer satisfaction is also influenced by how they were entertained in the beginning, which could enhance the reuse intention. For example, the efforts undertaken by DHL managers to provide a special link for customer complaints could reduce the problem since customer service managers might be unhappy if their boss directly attends to customer complaints.
Interestingly, the study also discovered that price fairness strengthened the relationship between satisfaction and reuse intention of 3PL services. The findings suggested that even if online sellers are satisfied with the current logistics providers, the intention to reuse their services will be stronger if 3PL providers provide a fair price. Although the customers pay delivery costs, because of the delivery cost also including in the total price, the delivery cost plays a significant role in online sellers’ decisions. Furthermore, if the online sellers are happy with the particular 3PL service but the price is not competitive, they would shift to other logistics providers. Currently, most 3PL service providers in Malaysia offer similar services with similar capabilities.
Satisfaction mediates the relationship between reliability and reuse intention and the relationship between flexibility and reuse intention. Hence, satisfaction is vital in influencing the reuse intention of 3PL services among the online sellers in Malaysia. The findings also proved that 3PL providers should ensure customer satisfaction to gain loyalty. Generally, service providers must satisfy customers to reduce complaints. Nonetheless, the function of customer services and tracking systems is undeniable, whereby customers are assured of the goods’ safety, provided they could track or are entertained by the customer service department at any time.
5.1. Theoretical Implications
The results produce notable theoretical contributions for the reuse intention of logistics providers among online sellers. First, the study applied the SOR theory in explaining the reuse intention of the logistics providers, which is limited in the logistics context. Most studies focused on the service quality or logistics service quality theory to predict the satisfaction and the reuse intention of 3PL among online sellers. Instead of analysing buyers as respondents, the study presented online sellers’ perspectives because choosing the 3PL is the power to decide, thus extending the literature on the online sellers’ behaviour to select the 3PL.
Although price fairness is mostly used to predict buyers’ decisions, the study used price fairness as a moderating factor between satisfaction and reuse intention for the online sellers. The findings offer new insight into how price fairness strengthens the relationship between satisfaction and reuse intention of 3PL among online sellers. Lastly, the study also strengthens the role of satisfaction as a mediating factor to predict the reuse intention. Despite satisfaction being commonly used as a mediating factor in marketing studies, most studies focused on satisfaction as a mediator for the relationship between reliability and flexibility toward the reuse intention of the 3PL services, hence enriching studies on online sellers’ behaviour and 3PL reuse intentions.
5.2. Managerial Implications
The study presented notable practical contributions for 3PL managers to convince online sellers to remain loyal. Understanding the factors influencing the reuse intention among online sellers enables the managers of 3PL companies to scheme better and more meaningful marketing strategies and attract and retain current online sellers. Increasing service flexibility and reliability enhances customer satisfaction and creates a better chance for online sellers to reuse their services. Additionally, increasing business flexibility and reliability produces good results for all parties (3PL, online sellers, and online shoppers). Thus, managers (particularly those dealing directly with customers) should train or develop their business operations to be more flexible and reliable during work. Overpromising or lacking consideration should be avoided to reduce customer complaints and promote customer loyalty, leading to business sustainability.
5.3. Limitation and Future Research Recommendations
Despite the theoretical and practical implications, the study has several limitations. First, the study was limited to online sellers and 3PL providers in Malaysia. Hence, the research should be replicated in other settings to ensure model consistency. In the future, the findings should be compared between Malaysia and other Association of South-East Asian Nations (ASEAN) countries with similar criteria. Besides, other factors should be considered to further enhance the model’s predictive power to explain the reuse intention variance. Lastly, instead of using the SOR theory, other theories such as technology continuance theory [60] could be applied in the study area.
6. Conclusions
The e-commerce industry is increasing rapidly in Western countries and developing countries such as Malaysia. Online sellers have created a multiplier effect on the economy, with undeniable contributions. Online sellers in Malaysia have various options of 3PL to select from. Hence, understanding the factors influencing online sellers’ reuse intention of 3PL is crucial. The literature review suggested that online sellers’ reuse intention of 3PL providers is underexplored. Hence, the study attempted to disclose the factors influencing the reuse intention of 3PL providers among the online sellers in Malaysia by adopting the SOR model. Interestingly, only one of the seven hypotheses tested was supported.
The results proved that reliability and flexibility positively affect satisfaction, and satisfaction positively affects online sellers’ reuse intention of particular 3PL service providers in Malaysia. Contrarily, flexibility was found insignificant towards the reuse intention. Hence, introducing a moderator and mediator deepens the knowledge on factors influencing online sellers’ satisfaction and reuse intention. Furthermore, the study enhances the literature by introducing price fairness as a moderator between customer satisfaction and reuse intention. Although marketing studies claimed that satisfied customers would reuse the services, Seiders et al. [61] mentioned that only 30–40% of them repurchased. Therefore, the study discovered that price fairness has a moderating effect between customer satisfaction and reuse intention. The findings also confirmed that even if theoretically satisfied customers positively affect the reuse intention, the relationship could be strengthened by introducing related factors towards the reuse intention. Besides, satisfaction is not the only variable that enhances the reuse intention among satisfied customers.
Although the study highlighted the online seller’s perspective on 3PL service, the findings are not limited to online sellers and are applicable in other study areas. Service providers should be aware of customer satisfaction and be more realistic in setting the service price. Although higher prices could increase profit, customers look at price fairness in this highly competitive business. Furthermore, instead of looking for immediate income for the short term, businesses should focus on the long-term perspective. Consequently, top management should seriously consider the price fairness factor if it intends to be treasured by customers and regarded by competitors.
The study was conducted in Malaysia, but the findings could be useful for 3PL providers in developing countries with similar characteristics to Malaysia. Hence, countries such as ASEAN countries could use the findings as a guideline to modify their marketing strategy accordingly to ensure customers are satisfied and willing to continue using their services in the future.
Author Contributions
All the authors contributed to the conceptualisation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, and writing and editing of the original draft. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Because of the observational nature of the study, and in the absence of any involvement of therapeutic medication, no formal approval of the institutional review board of the local ethics committee was required. Nonetheless, all subjects were informed about the study and participation was fully on a voluntary basis. Participants were ensured of the confidentiality and anonymity of the information associated with the surveys. The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The dataset used in this research are available upon request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available because of restrictions, i.e., privacy or ethical.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cichosz, M.; Wallenburg, C.M.; Knemeyer, A.M. Digital transformation at logistics service providers: Barriers, success factors and leading practices. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2020, 31, 209–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvin, M.; Asimiran, S.B.; Ayub, A.F.B.M. Impact of introducing e-commerce on small and medium enterprises—A case on logistics provider. Soc. Bus. Rev. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistica. Retail E-Commerce Sales Worldwide from 2014 to 2024 (in Billion U.S. Dollars). 2020. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/379046/worldwide-retail-e-commerce-sales/ (accessed on 31 January 2021).
- Businesswire.com. E-Commerce Sales in Asia Pacific to Nearly Double by 2025, Reaching USD 2 Trillion. 2021. Available online: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20210524005631/en/E-Commerce-Sales-in-Asia-Pacific-to-Nearly-Double-by-2025-Reaching-USD-2-Trillion (accessed on 24 May 2021).
- Kamal, S.M. Amid Complaints, Pos Malaysia Says Some Issues with “Intermittent System Accessibility” but Tracking Service Fine. Available online: https://www.malaymail.com/news/malaysia/2019/11/07/amid-complaints-pos-malaysia-says-some-issues-with-intermittent-system-acce/1807778 (accessed on 20 January 2021).
- Gidener, N.G.; Deveci, D.A. An Analysis of Service Failures and Recovery Strategies in the Third Party Logistics Service Industry. Trans. Marit. Sci. 2020, 9, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, V.R. As E-Commerce Start to Mature in Asian Market, Retailers Must Rise to a New Challenges. The end of the Beginning of E-Commerce; Asia Pacific Food Industry: Singapore, 2021; pp. 56–57. Available online: https://apfoodonline.com/ebook/AprMay21/html5/index.html?locale=ENG&pn=67&utm_source=APFI+-+FOREIGN&utm_campaign=795274afe2-EMAIL_CAMPAIGN_2021_04_14_07_17_COPY_01&utm_medium=email&utm_term=0_36038dc2f8-795274afe2-10025527 (accessed on 25 May 2021).
- Vu, T.P.; Grant, D.B.; Menachof, D.A. Exploring logistics service quality in Hai Phong, Vietnam. Asian J. Shipp. Logist. 2020, 36, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, D.W.; Moori, R.G.; Filho, V.A.V. Logistic service quality as a mediator between logistics capabilities and customer satisfaction. Rev. Gestão 2018, 25, 358–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huma, S.; Ahmed, W.; Ikram, M.; Khawaja, M.I. The effect of logistics service quality on customer loyalty: Case of logistics service industry. South. Asian J. Bus. Stud. 2019, 9, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yuen, K.F.; Wong, Y.D.; Teo, C.-C. Consumer participation in last-mile logistics service: An investigation on cognitions and affects. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2019, 49, 217–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murfield, M.; Boone, C.A.; Rutner, P.; Thomas, R. Investigating logistics service quality in omni-channel retailing. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2017, 47, 263–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Xie, G. Determinants of customer perceived online shopping logistics service quality value: An empirical study from China. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2018, 22, 614–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Sarkis, J. Integrating and extending data and decision tools for sustainable third-party reverse logistics provider selection. Comput. Oper. Res. 2019, 110, 188–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asian, S.; Pool, J.K.; Nazarpour, A.; Tabaeeian, R.A. On the importance of service performance and customer satisfaction in third-party logistics selection. Benchmarking Int. J. 2019, 26, 1550–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jakšič, M.; Budler, M. Environmental-sustainability Aspect in the Outsourcing of Business-logistics Services. In Challenges on the Path toward Sustainability in Europe; Emerald: Somerville, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 147–169. [Google Scholar]
- Mehrabian, A.; Russell, J.A. An Approach to Environmental Psychology; MIT Press: Cambridge, UK, 1974; pp. 62–65. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, F.T.; Syed, Z.; Imam, A.; Raza, A. The impact of airline service quality on passengers’ behavioral intentions using passenger satisfaction as a mediator. J. Air Transp. Manag. 2020, 85, 101815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jibril, A.B.; Kwarteng, M.A.; Pilik, M.; Botha, E.; Osakwe, C.N. Towards understanding the initial adoption of online retail stores in a low internet penetration context: An exploratory work in Ghana. Sustainability 2020, 12, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, L.; Guo, F.; Yu, F.; Liu, S. The Effects of Online Shopping Context Cues on Consumers’ Purchase Intention for Cross-Border E-Commerce Sustainability. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hung, K.-P.; Peng, N.; Chen, A. Incorporating on-site activity involvement and sense of belonging into the Mehrabian-Russell model—The experiential value of cultural tourism destinations. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2019, 30, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abd Rahman, U.H.; Hafaz Ngah, A.; Gabarre, S. Factors that Influencing Behavioural Towards Voluntourism. Int. J. E-Navig. Maritime Econ. 2019, 12, 32–41. [Google Scholar]
- Luqman, A.; Masood, A.; Weng, Q.; Ali, A.; Rasheed, M.I. Linking Excessive SNS Use, Technological Friction, Strain, and Discontinuance: The Moderating Role of Guilt. Inf. Syst. Manag. 2020, 37, 94–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghozzi, R.P. Principles of Marketing Management; Science Research Associates, Inc.: Chicago, IL, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y. Key success factors for the launch of government social media platform: Identifying the formation mechanism of continuance intention. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 55, 750–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngah, A.H.; Kim, H.D.; Hanafiah, R.M.; Salleh, N.H.M.; Jeevan, N.S.J.; Asri, N.M. Willingness to pay for Halal transportation cost: The Stimulus-organism-response model. Int. J. E-Navig. Maritime Eco. 2019, 12, 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- Othman, A.K.; Hamzah, M.I.; Abu Hassan, L.F. Modeling the contingent role of technological optimism on customer satisfaction with self-service technologies. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2020, 33, 559–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasuraman, A.; Zeithml, V.A.; Berry, L.L. SERVQUAL: A Multi-Item Scale for Measuring Customer Perceptions of Service Quality; Report No. 86-108; Marketing Science Institute: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Zeithaml, V.A.; Parasuraman, A.; Malhorta, A. Service quality delivery through web sites: A critical review of extant knowledge. J. Acade. Mark. Sci. 2002, 30, 362–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nonthapot, S.; Nasoontorn, A. The effect of the service quality on passengers’ satisfaction. Manag. Sci. Lett. 2020, 10, 3717–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, R.L. Satisfaction: A Behavioral Perspective on the Consumer; M.E. Sharpe: Armonk, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Han, H.; Lho, L.; Raposo, A.; Radic, A.; Ngah, A. Halal Food Performance and Its Influence on Patron Retention Process at Tourism Destination. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngah, A.; Rahimi, A.; Gabarre, S.; Araya-Castillo, L.; Ariza-Montes, A.; Han, H. Fostering Voluntourism Satisfaction and Future Behaviour in Island Destinations. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alalwan, A. Mobile food ordering apps: An empirical study of the factors affecting customer e-satisfaction and continued intention to reuse. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 50, 28–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Vonderembse, M.A.; Lim, J.-S. Value chain flexibility: A dichotomy of competence and capability. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2002, 40, 561–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, S.; Chen, C.-W.; Kuo, Y.-T. Flexibility, collaboration and relationship quality in the logistics service industry. Asia Pac. J. Mark. Logist. 2018, 30, 555–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, R.; Yu, W.; Jacobs, M.; Feng, M. Data-driven supply chains, manufacturing capability and customer satisfaction. Prod. Plan. Control. 2017, 28, 906–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, K.; Cadeaux, J.; Song, H. Flexibility and quality in logistics and relationships. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2017, 62, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, I.E.; De Grahl, A. The Flexibility of Logistics Service Providers and its Impact on Customer Loyalty—An Empirical Study. In Success Factors in Logistics Outsourcing; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 7–51. [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra, N.; Sahadev, S.; Purani, K. Psychological contract violation and customer intention to reuse online retailers: Exploring mediating and moderating mechanisms. J. Bus. Res. 2017, 75, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Konuk, F.A. The influence of perceived food quality, price fairness, perceived value and satisfaction on customers’ revisit and word-of-mouth intentions towards organic food restaurants. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2019, 50, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Luo, J.; Cai, S.; Ma, S.; Rong, K. Exploring the service quality in the e-commerce context: A triadic view. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2016, 116, 388–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homburg, C.; Koschate, N.; Hoyer, W.D. Institut für Marktorientierte Unternehmensführung Do Satisfied Customers Really Pay More? A Study of the Relationship between Customer Satisfaction and Willingness to Pay. J. Mark. 2005, 69, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, D.N.; Nguyen, H.T.; Truong, P.H. Port logistics service quality and customer satisfaction: Empirical evidence from Vietnam. Asian J. Shipp. Logist. 2020, 36, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorkun, M.F.; Hüseyinoğlu, I.Ö.Y.; Börühan, G. Omni-channel capability and customer satisfaction: Mediating roles of flexibility and operational logistics service quality. Int. J. Retail. Distrib. Manag. 2020, 48, 629–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Brown, S.; Hoehle, H. Understanding technology adoption in the household context: A comparison of seven. Euro. Conf. Info. Syst. 2012, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- MacKenzie, S.B.; Podsakoff, P.M. Common Method Bias in Marketing: Causes, Mechanisms, and Procedural Remedies. J. Retail. 2012, 88, 542–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngah, A.H.; Gabarre, S.; Eneizan, B.; Asri, N. Mediated and moderated model of the willingness to pay for halal transportation. J. Islam. Mark. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.; Hollingsworth, C.L.; Randolph, A.B.; Chong, A.Y.L. An updated and expanded assessment of PLS-SEM in information systems research. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2017, 117, 442–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling: Rigorous Applications, Better Results and Higher Acceptance. Long Range Plan. 2013, 46, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Risher, J.; Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M. When to use and how to report the results of PLS-SEM. Eur. Bus. Rev. 2019, 31, 2–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngah, A.H.; Thurasamy, R.; Aziz, N.A.; Ali, H.; Khan, M.I. Modelling the adoption of halal warehousing services among halal pharmaceutical and cosmetic manufacturers. J. Sustain. Sci. Manag. 2019, 14, 103–116. [Google Scholar]
- Kock, N. Common method bias in PLS-SEM: A full collinearity assessment approach. Int. J. e-Collab. 2015, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franke, G.; Sarstedt, M. Heuristics versus statistics in discriminant validity testing: A comparison of four procedures. Internet Res. 2019, 29, 430–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngah, A.H.; Ramayah, T.; Ali, M.H.; Khan, M.I. Halal transportation adoption among pharmaceuticals and comestics manufacturers. J. Islam. Mark. 2019, 11, 1619–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamantopoulos, A.; Siguaw, J.A. Formative Versus Reflective Indicators in Organizational Measure Development: A Comparison and Empirical Illustration. Br. J. Manag. 2006, 17, 263–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preacher, K.J.; Hayes, A.F. Asymptotic and resampling strategies for assessing and comparing indirect effects in multiple mediator models. Behav. Res. Methods 2008, 40, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmueli, G.; Sarstedt, M.; Hair, J.F.; Cheah, J.-H.; Ting, H.; Vaithilingam, S.; Ringle, C.M. Predictive model assessment in PLS-SEM: Guidelines for using PLSpredict. Eur. J. Mark. 2019, 53, 2322–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tontini, G.; Söilen, K.S.; Zanchett, R. Nonlinear antecedents of customer satisfaction and loyalty in third-party logistics services (3PL). Asia Pac. J. Mark. Logist. 2017, 29, 1116–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Palvia, P.; Chen, J.-L. Information technology adoption behavior life cycle: Toward a Technology Continuance Theory (TCT). Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2009, 29, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiders, K.; Voss, G.B.; Grewal, D.; Godfrey, A.L. Do Satisfied Customers Buy More? Examining Moderating Influences in a Retailing Context. J. Mark. 2005, 69, 26–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).