Towards Sustainability in Higher-Education Institutions: Analysis of Contributing Factors and Appropriate Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
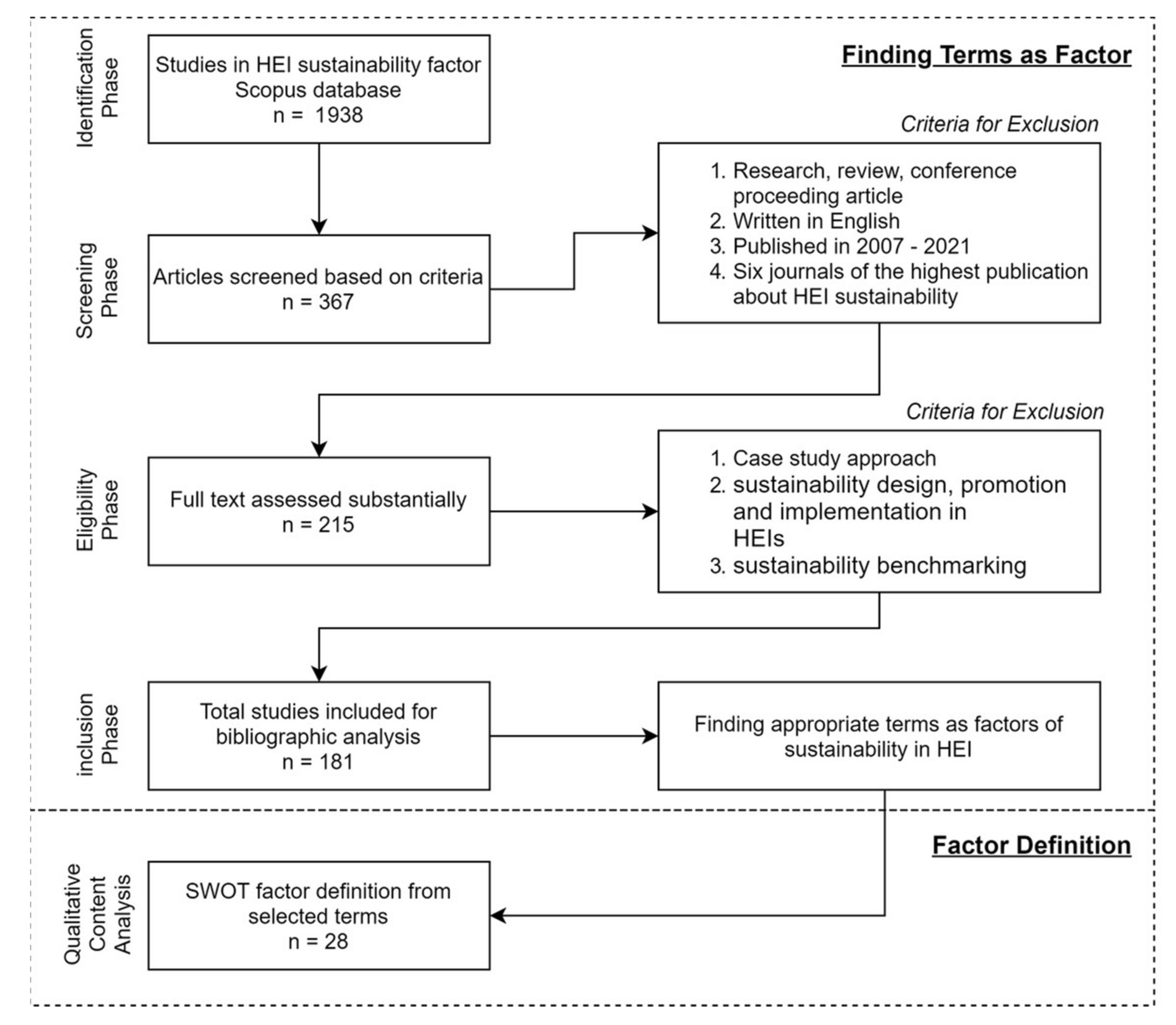
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Systematic Review
2.2. Qualitative Content Analysis
2.3. UNDIP Profile Data Collection
2.4. SWOT–QSPM Analysis
3. Result
3.1. Sustainability Factors in HEI
3.2. Strategies Enhancing Sustainability Implementation at UNDIP
4. Discussion
4.1. Fostering External Collaboration in Research, Community-Development, and Education Programs
4.2. Implementing Plan–Do–Check–Act Tool for Continuous Improvement in Teaching and Education Ecosystems
4.3. Promoting Institutional Systems to External Stakeholders
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Díaz-Iso, A.; Eizaguirre, A.; García-Olalla, A. Extracurricular activities in higher education and the promotion of reflective learning for sustainability. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngang, T.K.; Hashim, N.H.; Yunus, H.M. Novice Teacher Perceptions of the Soft Skills Needed in Today’s Workplace. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 177, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Butt, L.; More, E.; Avery, G.C. The myth of the “green student”: Student involvement in Australian university sustainability programmes. Stud. High. Educ. 2014, 39, 786–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, F.; Yan, J. The Potential of Distributed Energy Resources in Building Sustainable Campus: The Case of Sichuan University. Energy Procedia 2018, 145, 582–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burford, G.; Hoover, E.; Velasco, I.; Janoušková, S.; Jimenez, A.; Piggot, G.; Podger, D.; Harder, M.K. Bringing the “Missing Pillar” into sustainable development goals: Towards intersubjective values-based indicators. Sustainability 2013, 5, 3035–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales de Aguiar, T.R.; Paterson, A.S. Sustainability on campus: Knowledge creation through social and environmental reporting. Stud. High. Educ. 2018, 43, 1882–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubakar, I.R.; Aina, Y.A.; Alshuwaikhat, H.M. Sustainable development at Saudi Arabian universities: An overview of institutional frameworks. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sima, M.; Grigorescu, I.; Bălteanu, D. An overview of campus greening initiatives at universities in Romania. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2019, 20, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fissi, S.; Romolini, A.; Gori, E.; Contri, M. The path toward a sustainable green university: The case of the University of Florence. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo-Iacono-Ferreira, V.G.; Capuz-Rizo, S.F.; Torregrosa-López, J.I. Key Performance Indicators to optimize the environmental performance of Higher Education Institutions with environmental management system—A case study of Universitat Politècnica de València. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 178, 846–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moqbel, S.; Abu-Zurayk, R.; Bozeya, A.; Alsisan, R.; Al Bawab, A. Assessment of sustainable recycling at The University of Jordan. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2020, 21, 1111–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okanović, A.; Ješić, J.; Ðaković, V.; Vukadinović, S.; Panić, A.A. Increasing university competitiveness through assessment of green content in curriculum and eco-labeling in higher education. Sustainability 2021, 13, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, H.; Sun, M.; Huisingh, D.; Hansson, L.; Wang, R. Moving towards an ecologically sound society? Starting from green universities and environmental higher education. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 61, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Suárez, M.; Guadalajara, N.; Osca, J.M. A comparative analysis between global university rankings and environmental sustainability of universities. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atici, K.B.; Yasayacak, G.; Yildiz, Y.; Ulucan, A. Green University and academic performance: An empirical study on UI GreenMetric and World University Rankings. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 291, 125289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourrinx, E.; Budihardjo, M.A. Implementation of UI GreenMetric at Diponegoro University in order to Environmental Sustainability Efforts. E3S Web Conf. 2019, 125, 02007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambariyanto, A.; Utama, Y.J.; Budihardjo, M.A.; Purwanto, P. Undip Initiative for Sustainability (UNITY): A University Sustainability Program. E3S Web Conf. 2018, 73, 9–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapitulčinová, D.; AtKisson, A.; Perdue, J.; Will, M. Towards integrated sustainability in higher education–Mapping the use of the Accelerator toolset in all dimensions of university practice. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 172, 4367–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piwowar-Sulej, K.; Krzywonos, M.; Kwil, I. Environmental entrepreneurship–Bibliometric and content analysis of the subject literature based on H-Core. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 295, 126227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalieri, A.; Reis, J.; Amorim, M. Circular economy and internet of things: Mapping science of case studies in manufacturing industry. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Int. J. Surg. 2021, 88, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiró, P.S.; Raufflet, E. Sustainability in higher education: A systematic review with focus on management education. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 106, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad-Segura, E.; González-Zamar, M.-D.; Infante-Moro, J.C.; García, G.R. Sustainable management of digital transformation in higher education: Global research trends. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, A. Urban sustainability assessment: An overview and bibliometric analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Tang, M.; Luo, L.; Li, C.; Chiclana, F.; Zeng, X.J. A bibliometric analysis and visualization of medical big data research. Sustainability 2018, 10, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lis, A.; Tomanek, M. Sport management: Thematic mapping of the research field. J. Phys. Educ. Sport 2020, 20, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Lu, Q.; Bai, J.; Deng, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Global publications on stigma between 1998–2018: A bibliometric analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 274, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corallo, A.; Latino, M.E.; Menegoli, M.; De Devitiis, B.; Viscecchia, R. Human factor in food label design to support consumer healthcare and safety: A systematic literature review. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezazadeh, S.; Jahani, A.; Makhdoum, M.; Meigooni, H.G. Evaluation of the Strategic Factors of the Management of Protected Areas Using SWOT Analysis—Case Study: Bashgol Protected Area-Qazvin Province. Open J. Ecol. 2017, 07, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, E.; Vahdani, F.A.; Ahmadi, S.H.; Behrouz, R. Developing and ranking strategies for machinery companies via QSPM and SWOT matrix: A case study in Toolid Atash machinery company. Nat. Soc. Sci. 2013, 2, 452–461. [Google Scholar]
- Xin-gang, Z.; Yi-sheng, Y.; Tian-tian, F.; Yu-heng, Y. International cooperation on renewable energy electricity in China - A critical analysis. Renew. Energy 2013, 55, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahabi, R.S.; Basiri, M.H.; Kahag, M.R.; Zonouzi, S.A. An ANP-SWOT approach for interdependency analysis and prioritizing the Iran’s steel scrap industry strategies. Resour. Policy 2014, 42, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.; Xue, D.Q. Sustainable development of cultural industry in Shaanxi Province of Northwest China: A SWOT and AHP analysis. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viegas, C.V.; Bond, A.J.; Vaz, C.R.; Borchardt, M.; Pereira, G.M.; Selig, P.M.; Varvakis, G. Critical attributes of Sustainability in Higher Education: A categorisation from literature review. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 126, 260–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, F.U.; Sáez-Navarrete, C.; Lioi, S.R.; Marzuca, V.I. Adaptable model for assessing sustainability in higher education. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 107, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beynaghi, A.; Trencher, G.; Moztarzadeh, F.; Mozafari, M.; Maknoon, R.; Leal Filho, W. Future sustainability scenarios for universities: Moving beyond the United Nations Decade of Education for Sustainable Development. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 3464–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Casarejos, N.; Sáez-Pérez, L.A. Internships for higher education students to promote the local sustainability of rural places. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, T.B.; Caeiro, S.; Van Hoof, B.; Lozano, R.; Huisingh, D.; Ceulemans, K. Experiences from the implementation of sustainable development in higher education institutions: Environmental Management for Sustainable Universities. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 106, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, L.M.; Wang, D. Integrating sustainability learning outcomes into a university curriculum: A case study of institutional dynamics. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2018, 19, 699–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varouchas, E.; Sicilia, M.; Sánchez-Alonso, S. Academics’ perceptions on quality in higher education shaping key performance indicators. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Qudah, N.F.; Yang, Y.; Anjum, M.A. Transformational training programs and quality orientation of employees: Does employees’ loyalty matter? Sustainability 2018, 10, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abelha, M.; Fernandes, S.; Mesquita, D.; Seabra, F.; Ferreira-Oliveira, A.T. Graduate employability and competence development in higher education-A systematic literature review using PRISMA. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, Z.; Van der Merwe, D. Innovative management for organizational sustainability in higher education. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2016, 17, 208–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrechts, W.; Verhulst, E.; Rymenams, S. Professional development of sustainability competences in higher education: The role of empowerment. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2017, 18, 697–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusinko, C.A. Integrating sustainability in higher education: A generic matrix. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2010, 11, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, R.; Lukman, R.; Lozano, F.J.; Huisingh, D.; Lambrechts, W. Declarations for sustainability in higher education: Becoming better leaders, through addressing the university system. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 48, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleixo, A.M.; Leal, S.; Azeiteiro, U.M. Conceptualization of sustainable higher education institutions, roles, barriers, and challenges for sustainability: An exploratory study in Portugal. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 1664–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, W.L.; Eustachio, J.H.P.P.; Caldana, A.C.F.; Will, M.; Salvia, A.L.; Rampasso, I.S.; Anholon, R.; Platje, J.; Kovaleva, M. Sustainability leadership in higher education institutions: An overview of challenges. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zen, I.S. Exploring the living learning laboratory: An approach to strengthen campus sustainability initiatives by using sustainability science approach. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2017, 18, 939–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, R.; Ceulemans, K.; Alonso-Almeida, M.; Huisingh, D.; Lozano, F.J.; Waas, T.; Lambrechts, W.; Lukman, R.; Hugé, J. A review of commitment and implementation of sustainable development in higher education: Results from a worldwide survey. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 108, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugé, J.; Mac-Lean, C.; Vargas, L. Maturation of sustainability in engineering faculties—From emerging issue to strategy? J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 4277–4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-H.; Schaltegger, S. Organizational transformation and higher sustainability management education: The case of the MBA sustainability management. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2014, 15, 450–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan Ahmad, W.N.K.; Rezaei, J.; Sadaghiani, S.; Tavasszy, L.A. Evaluation of the external forces affecting the sustainability of oil and gas supply chain using Best Worst Method. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 153, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putri, N.T.; Amrina, E.; Nurnaeni, S. Students’ Perceptions of the Implementation of Sustainable Campus Development Based on Landscape Concepts at Andalas University. Procedia Manuf. 2020, 43, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-M.; Hsieh, M.-Y. An interdisciplinary research on students’ employability in technology education to advance higher education enrollment sustainability. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrone, P.; Orsini, F.; Asdrubali, F.; Guattari, C. Environmental performance of universities: Proposal for implementing campus urban morphology as an evaluation parameter in Green Metric. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 42, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas-Ch, W.; Palacios-Pacheco, X.; Luján-Mora, S. Application of a smart city model to a traditional university campus with a big data architecture: A sustainable smart campus. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda Filho, N.P.; Beuter, B.P. Transculturality as a drive for the SDGs achievement. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2019, 20, 822–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldureanu, G.; Ionescu, A.M.; Bercu, A.-M.; Bedrule-Grigoruţă, M.V.; Boldureanu, D. Entrepreneurship education through successful entrepreneurial models in higher education institutions. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boo, B.; Cha, J. ICT in Context of Student-Driven Project-Based Active Learning; ICT: Mumbai, India, 2011; ISBN 9785901642351. [Google Scholar]
- Terziev, V.; Lyubcheva, M.; Georgiev, M. Domestic and International Challenges in Higher Education. 2021. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3840258 (accessed on 27 February 2021).
- Carlson, S. Colleges Get Greener in Operations, but Teaching Sustainability Declines. Chron. High. Educ. 2008, 55, A24. [Google Scholar]
- Mulà, I.; Tilbury, D.; Ryan, A.; Mader, M.; Dlouhá, J.; Mader, C.; Benayas, J.; Dlouhý, J.; Alba, D. Catalysing Change in Higher Education for Sustainable Development: A review of professional development initiatives for university educators. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2017, 18, 798–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caeiro, S.; Azeiteiro, U.M.; Filho, W.L.; Jabbour, C. Sustainability Assessment Tools in Higher Education Institutions: Mapping Trends and Good Practices Around the World; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 1–417. [Google Scholar]
- Tight, M. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses of higher education research. Eur. J. High. Educ. 2019, 9, 133–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukman, R.; Krajnc, D.; Glavic, P. Fostering collaboration between universities regarding regional sustainability initiatives—The University of Maribor. J. Clean. Prod. 2009, 17, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz Pareja, E.M.; Cámara Estrella, Á.M.; Muñoz Galiano, I.M.; Ortega-Tudela, J.M. Group work: Prospective teachers’ acquisition of transversal competences. Educ. Stud. 2018, 44, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Tudela, J.M.; Cámara-Estrella, Á.M.; Diaz-Pareja, E.M. Aprendizaje-Servicio como estrategia favorecedora del desarrollo de la competencia mediática en futuros docentes. Cult. Educ. 2015, 27, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero-Ferrero, I.; Fernández-Izquierdo, M.Á.; Muñoz-Torres, M.J.; Bellés-Colomer, L. Stakeholder engagement in sustainability reporting in higher education: An analysis of key internal stakeholders’ expectations. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2018, 19, 313–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.T.; Elezi, F.; Lindemann, U. Towards Recursive Plan-Do-Check-Act Cycles for Continuous Improvement. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Engineering Managemen, Selangor, Malaysia, 9–12 December 2014; pp. 1486–1490. [Google Scholar]
- Asif, M.; Searcy, C.; Zutshi, A.; Fisscher, O.A. An integrated management systems approach to corporate social responsibility. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 56, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosseck, G.; Tîru, L.G.; Bran, R.A. Education for sustainable development: Evolution and perspectives: A bibliometric review of research, 1992–2018. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, D.R.E.; Alcock, I. Commitment to environmental sustainability in the UK student population. Stud. High. Educ. 2013, 38, 1457–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Dimensions | Terms as Factors (Link Strength and Occurrence Frequency) | Factor Definition | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Teaching and Learning | Internship (90, 9) | Student, academic-staff, and lecturer mobility and internship | [37,38] |
| University education, university curricula, and curriculum design (419, 19) | Inclusivity of sustainable development goals in curriculum design | [39,40] | |
| Interactive features, technology education (268, 13) | Interactive teaching techniques | [41] | |
| Competence development, competency and transformational training, transformational training program (786, 44) | Transformational training program and competence development | [42,43] | |
| Participatory approach, lifelong learning, higher learning (395, 22) | Dynamic learning environment | [44] | |
| Quality orientation, management education (401, 22) | Sustainable development education for the educators | [45] | |
| Departments, academic programs (428, 21) | Stand-alone sustainability course(s) or academic program(s) | [46] | |
| Student perspective, academic performance, student satisfaction (754, 28) | Student satisfaction related to academic productivity and performance | [15] | |
| Transdisciplinary learning (40, 5) | Transdisciplinary teaching consortium and learning process | [35] | |
| Research | Research productivity, plagiarism, publication, research activity and performance (3270, 62) | Encouragement of sustainable development research | [47] |
| Financial sustainability indicator, funding (1282, 36) | Funding availability and financial autonomy | [48] | |
| Researcher, collaboration, international collaboration (1954, 70) | HEI collaboration in research activities | [36] | |
| Campus Operation | Waste-management strategy, strategic agility, university policy (987, 23) | HEI policy and strategy in sustainability | [49] |
| Sustainability effort, waste management, waste minimization, recycling, sustainability activity (1151, 58) | Sustainable-development-related nonacademic activities of each academician (students, lecturers, and academic staff) | [50] | |
| Organizational sustainability, organizational culture, institutionalization (319, 16) | Inclusivity of sustainable development goals in the institutional framework | [51] | |
| Job satisfaction, academic staff, institutional change (2107, 28) | Involvement of internal stakeholders (lecturers, academic staff, course directors) at a different level to institutional change | [22] | |
| Heterogeneity, international students, environmental worldview, internationalization (852, 50) | International attraction to HEI academic system | [48] | |
| Outreach | Community engagement, social engagement, stakeholder engagement (735, 30) | External stakeholders (municipalities, communities, NPOs, industry, government, NGOs, academia) engagement | [37] |
| Loyalty (705, 22) | Institutional commitment to achieve sustainable development goals | [52,53] | |
| Academic leaders, university leaders, sustainability leadership, and leadership (970, 42) | Leadership pattern and its effect on sustainability | [36] | |
| Environmental legitimacy, communication (738, 35) | Environmental legitimacy and communication system between internal and external stakeholders | [54] | |
| Water, transportation, energy consumption, energy efficiency, infrastructure, and green university (1217, 60) | Morphological characteristics including landscape setting and green infrastructure | [15,55] | |
| Employability, student employability, graduate employability, and labor market (536, 29) | Student employability and market needs | [43,56] | |
| Administration | Sustainability assessment, environmental performance, EMS practices, sustainability reporting (1030, 65) | Continuous improvement, assessment, reporting, and promotion | [36] |
| Data analysis, web, website, quality management (984, 43) | Website and extensive data management | [57,58] | |
| Sustainability plan, campus sustainability plan, guidelines (940, 42) | Clear guidance for implementing sustainability and green practices | [59] | |
| Reputation, corporate reputation, competitiveness, and competitive advantage (855, 33) | HEI reputation and competition to achieve sustainability | [48] | |
| Sustainability governance, political skill (165, 12) | The political stability of the government | [54] | |
| Digital innovation, distance education, online learning (241, 16) | Fast-growing of distance and e-learning education system | [60] |
| No | Code | Factors | Normalized Weight | Rank | Weighted Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | S1 | Encouragement of sustainable-development research | 0.072 | 4 | 0.287 |
| 2 | S2 | HEI policy and strategy in sustainability | 0.072 | 4 | 0.287 |
| 3 | S3 | Inclusivity of Sustainable Development Goals in the institutional framework | 0.072 | 4 | 0.287 |
| 4 | S4 | Continuous improvement, assessment, reporting, and promotion | 0.067 | 3 | 0.201 |
| 5 | S5 | Institutional commitment to Sustainable Development Goals | 0.104 | 4 | 0.417 |
| 6 | S6 | Sustainable-development-related nonacademic activities of each academician (students, lecturers, and academic staff) | 0.046 | 3 | 0.139 |
| 7 | S7 | Morphological characteristics including landscape setting and green infrastructure | 0.021 | 3 | 0.063 |
| 8 | S8 | Interactive teaching techniques | 0.046 | 4 | 0.185 |
| 9 | W1 | Inclusivity of sustainable development goals in curriculum design | 0.060 | 1 | 0.060 |
| 10 | W2 | Involvement of internal stakeholders (lecturers, academic staff, course directors) at a different level to institutional change | 0.095 | 2 | 0.190 |
| 11 | W3 | Lack of appreciation and motivation to pro-environmental behavior changes | 0.067 | 2 | 0.134 |
| 12 | W4 | Sustainable-development education for educators | 0.044 | 1 | 0.044 |
| 13 | W5 | Stand-alone sustainability course(s) or academic program(s) | 0.053 | 1 | 0.053 |
| 14 | W6 | Leadership pattern and its effect on sustainability | 0.058 | 2 | 0.116 |
| 15 | W7 | Website and big-data management | 0.063 | 1 | 0.063 |
| 16 | W8 | Student, academic-staff, and lecturer mobility and internship | 0.060 | 2 | 0.120 |
| IFE | 1 | 2.646 | |||
| No | Code | Factors | Normalized Weight | Rank | Weighted Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | O1 | HEI collaboration in research activities | 0.104 | 4 | 0.417 |
| 2 | O2 | External stakeholders (municipalities, communities, NPOs, industry, government, NGOs, academia) engagement | 0.080 | 3 | 0.241 |
| 3 | O3 | Transdisciplinary teaching consortium and learning process | 0.068 | 4 | 0.274 |
| 4 | O4 | Transformational training program and competence development | 0.048 | 3 | 0.143 |
| 5 | O5 | Clear guidance for implementing sustainability and green practices | 0.101 | 4 | 0.405 |
| 6 | O6 | Dynamic learning environment | 0.060 | 3 | 0.179 |
| 7 | O7 | International attraction to HEI academic system | 0.039 | 3 | 0.116 |
| 8 | T1 | Environmental legitimacy and communication system between internal and external stakeholders | 0.089 | 2 | 0.179 |
| 9 | T2 | Student satisfaction related to academic productivity and performance | 0.086 | 2 | 0.173 |
| 10 | T3 | HEI reputation and competition to achieve sustainability | 0.074 | 1 | 0.074 |
| 11 | T4 | Funding availability and financial autonomy | 0.098 | 2 | 0.196 |
| 12 | T5 | Political stability of government | 0.039 | 1 | 0.039 |
| 13 | T6 | Student employability and market needs | 0.048 | 1 | 0.048 |
| 14 | T7 | Fast-growing distance and e-learning education system | 0.065 | 1 | 0.065 |
| EFE | 1 | 2.548 | |||
| Conservative strategies (WO) 1. Conducting seminars, workshops, and training for trainer programs, which are lectures by professionals inside and outside HEIs related to sustainability implementation in higher education 2. Creating fundamental sustainability through open and closed courses or programs that are taught by a multi- and transdisciplinary educator (cross-teaching) 3. Establishing gamification (award and punishment) systems in the sustainability implementation of internal stakeholders | Aggressive Strategies (SO) 1. Fostering external collaboration in research, community development, and education programs 2. Simultaneously promoting academic and nonacademic HEI systems to external stakeholders 3. Implementing the Plan–Do–Check–Act tool for continuous improvement in teaching and education ecosystems |
| Defensive Strategies (WT) 1. Improving nominal budgets of sustainability-research and community-development programs 2. Implementing and improving accountability and good-governance programs 3. Downsizing organizational systems for effective resource management | Competitive Strategies (ST) 1. Adding more physical and nonphysical infrastructure related to sustainability programs 2. Intensifying academic-quality assurance systems 3. Strengthening cooperative systems between HEI and commercializing research output |
| Sustainability Factors | Normalized Weight | First Strategy | Second Strategy | Third Strategy | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AS | TAS 1 | AS | TAS 2 | AS | TAS 3 | ||
| S1 | 0.072 | 3 | 0.215 | 4 | 0.287 | 4 | 0.287 |
| S2 | 0.072 | 3 | 0.215 | 2 | 0.144 | 4 | 0.287 |
| S3 | 0.072 | 4 | 0.287 | 2 | 0.144 | 2 | 0.144 |
| S4 | 0.067 | 2 | 0.134 | 2 | 0.134 | 4 | 0.269 |
| S5 | 0.104 | 4 | 0.417 | 2 | 0.208 | 4 | 0.417 |
| S6 | 0.046 | 4 | 0.185 | 3 | 0.139 | 2 | 0.093 |
| S7 | 0.021 | 1 | 0.021 | 2 | 0.042 | 2 | 0.042 |
| S8 | 0.046 | 2 | 0.093 | 3 | 0.139 | 3 | 0.139 |
| W1 | 0.060 | 2 | 0.120 | 2 | 0.120 | 4 | 0.241 |
| W2 | 0.095 | 3 | 0.285 | 1 | 0.095 | 4 | 0.380 |
| W3 | 0.067 | 3 | 0.201 | 2 | 0.134 | 2 | 0.134 |
| W4 | 0.044 | 3 | 0.132 | 2 | 0.088 | 2 | 0.088 |
| W5 | 0.053 | 3 | 0.160 | 2 | 0.106 | 2 | 0.106 |
| W6 | 0.058 | 2 | 0.116 | 1 | 0.058 | 2 | 0.116 |
| W7 | 0.063 | 1 | 0.063 | 2 | 0.125 | 2 | 0.125 |
| W8 | 0.060 | 2 | 0.120 | 2 | 0.120 | 2 | 0.120 |
| O1 | 0.104 | 4 | 0.417 | 2 | 0.208 | 3 | 0.313 |
| O2 | 0.080 | 2 | 0.161 | 3 | 0.241 | 1 | 0.080 |
| O3 | 0.068 | 4 | 0.274 | 2 | 0.137 | 3 | 0.205 |
| O4 | 0.048 | 3 | 0.143 | 2 | 0.095 | 1 | 0.048 |
| O5 | 0.101 | 3 | 0.304 | 2 | 0.202 | 3 | 0.304 |
| O6 | 0.060 | 2 | 0.119 | 3 | 0.179 | 3 | 0.179 |
| O7 | 0.039 | 3 | 0.116 | 3 | 0.116 | 2 | 0.077 |
| T1 | 0.089 | 1 | 0.089 | 2 | 0.179 | 1 | 0.089 |
| T2 | 0.086 | 2 | 0.173 | 3 | 0.259 | 2 | 0.173 |
| T3 | 0.074 | 3 | 0.223 | 2 | 0.149 | 2 | 0.149 |
| T4 | 0.098 | 1 | 0.098 | 1 | 0.098 | 1 | 0.098 |
| T5 | 0.039 | 1 | 0.039 | 1 | 0.039 | 1 | 0.039 |
| T6 | 0.048 | 1 | 0.048 | 2 | 0.095 | 1 | 0.048 |
| T7 | 0.065 | 2 | 0.131 | 3 | 0.196 | 3 | 0.196 |
| TAS for Each Strategy | 5.097 | 4.277 | 4.983 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Budihardjo, M.A.; Ramadan, B.S.; Putri, S.A.; Wahyuningrum, I.F.S.; Muhammad, F.I. Towards Sustainability in Higher-Education Institutions: Analysis of Contributing Factors and Appropriate Strategies. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6562. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13126562
Budihardjo MA, Ramadan BS, Putri SA, Wahyuningrum IFS, Muhammad FI. Towards Sustainability in Higher-Education Institutions: Analysis of Contributing Factors and Appropriate Strategies. Sustainability. 2021; 13(12):6562. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13126562
Chicago/Turabian StyleBudihardjo, Mochamad Arief, Bimastyaji Surya Ramadan, Soraya Annisa Putri, Indah Fajarini Sri Wahyuningrum, and Fadel Iqbal Muhammad. 2021. "Towards Sustainability in Higher-Education Institutions: Analysis of Contributing Factors and Appropriate Strategies" Sustainability 13, no. 12: 6562. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13126562
APA StyleBudihardjo, M. A., Ramadan, B. S., Putri, S. A., Wahyuningrum, I. F. S., & Muhammad, F. I. (2021). Towards Sustainability in Higher-Education Institutions: Analysis of Contributing Factors and Appropriate Strategies. Sustainability, 13(12), 6562. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13126562







