A Methodology for Assessing Groundwater Pollution Hazard by Nitrates from Agricultural Sources: Application to the Gallocanta Groundwater Basin (Spain)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
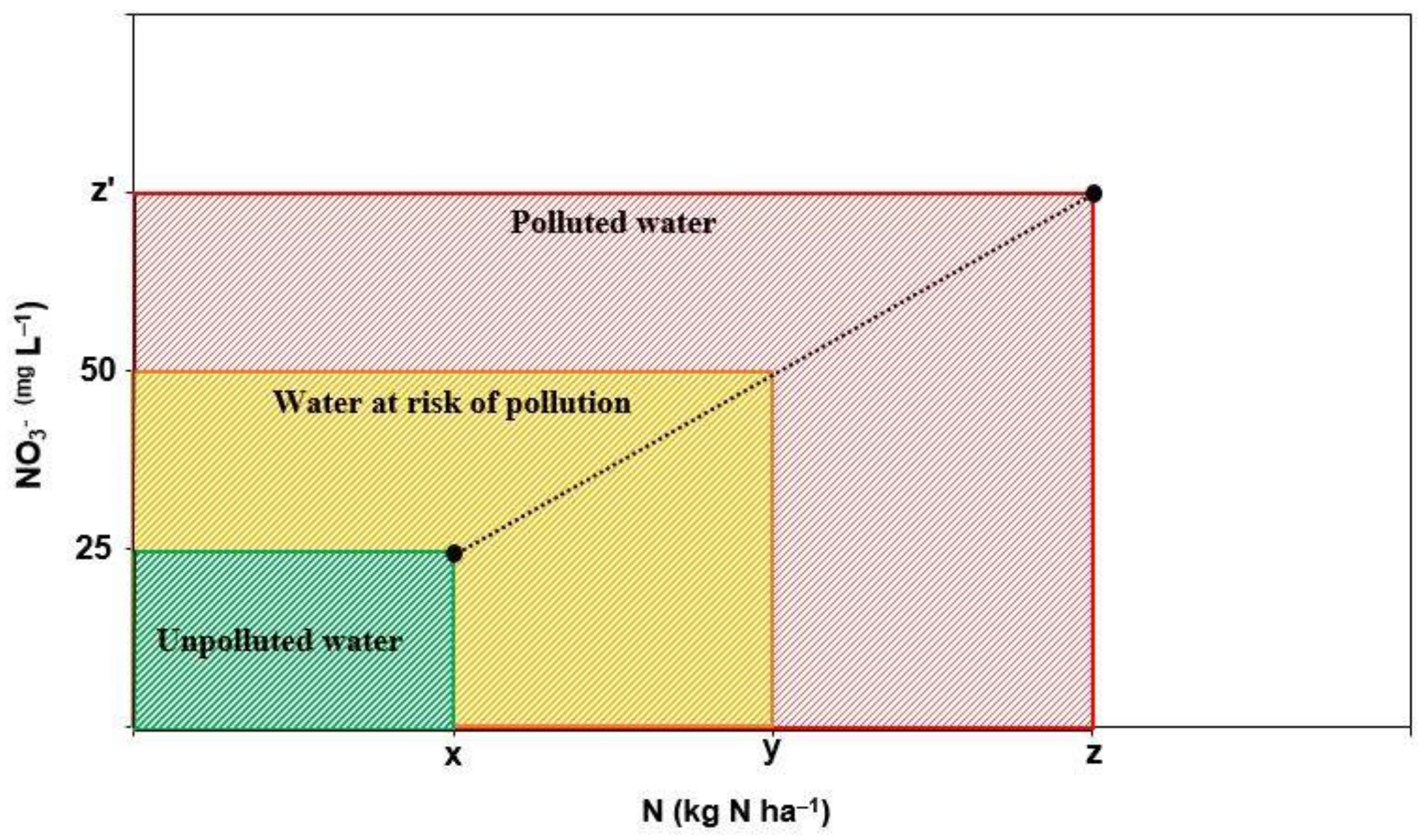
2.1. Nitrogen Input Hazard Index
- >
- Low, when NR calculated is lower than the NR estimated to reach 25 mg L–1.
- >
- Medium, when NR calculated is lower than the NR estimated to reach 50 mg L–1.
- >
- High, when NR calculated is higher than the NR estimated to reach 50 mg L–1.
2.2. Application of the NIHI to the Gallocanta Groundwater
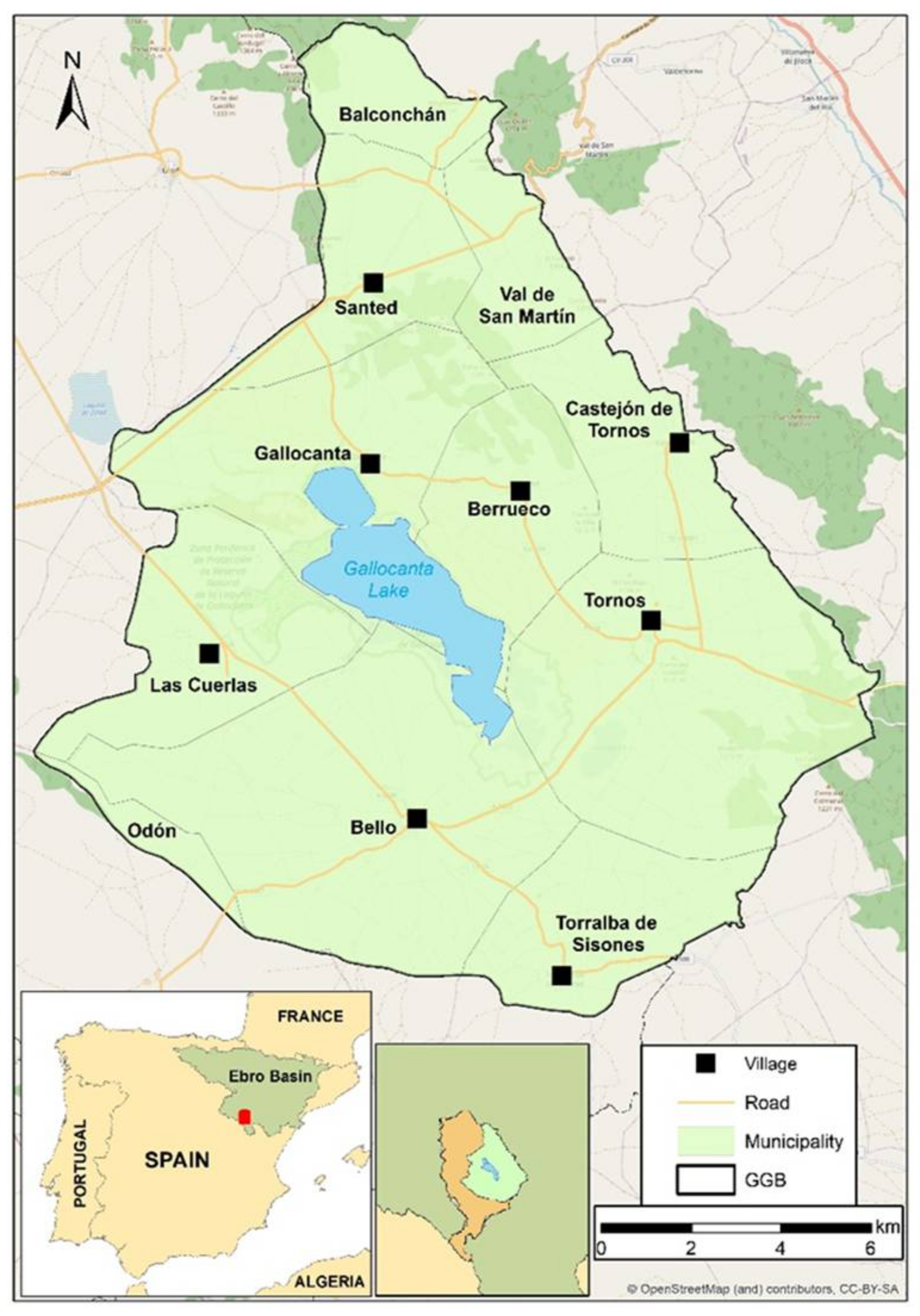
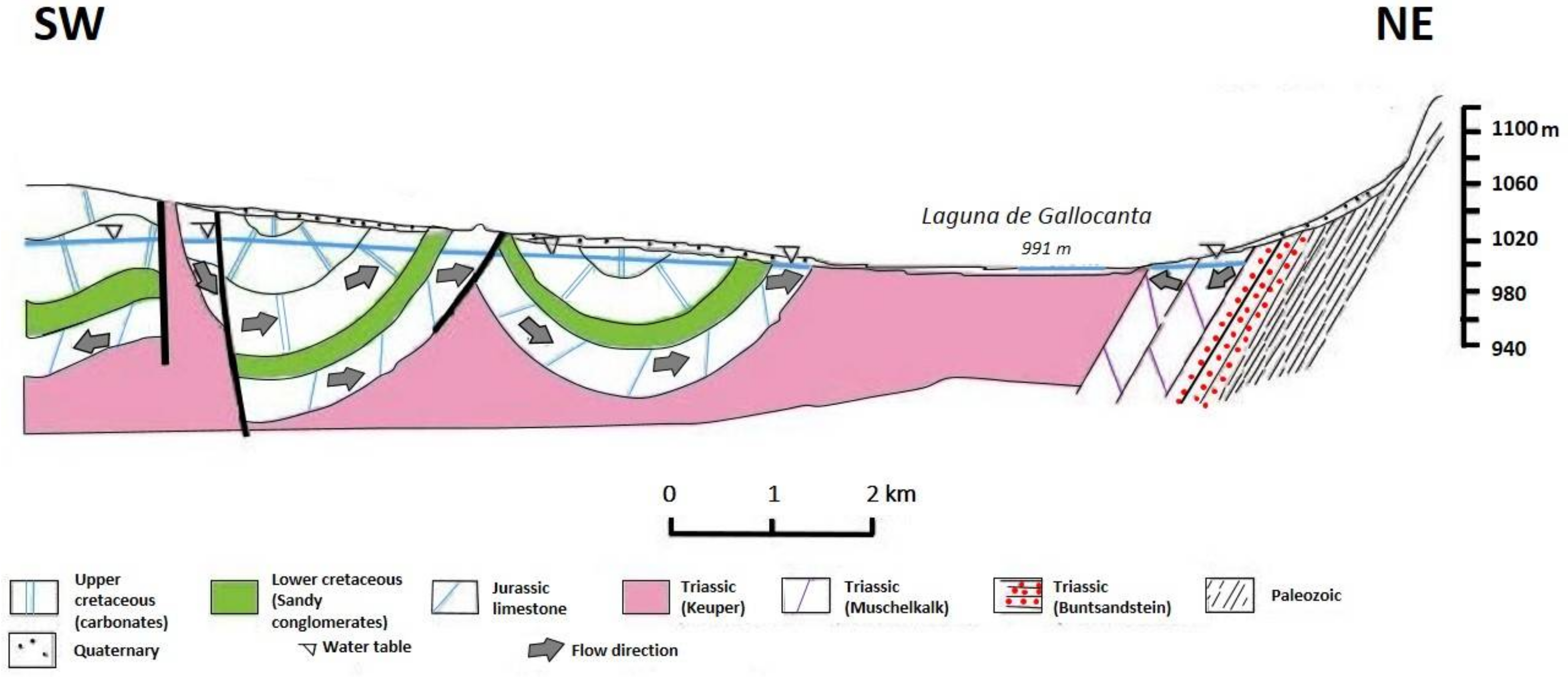
2.2.1. Study Area Description
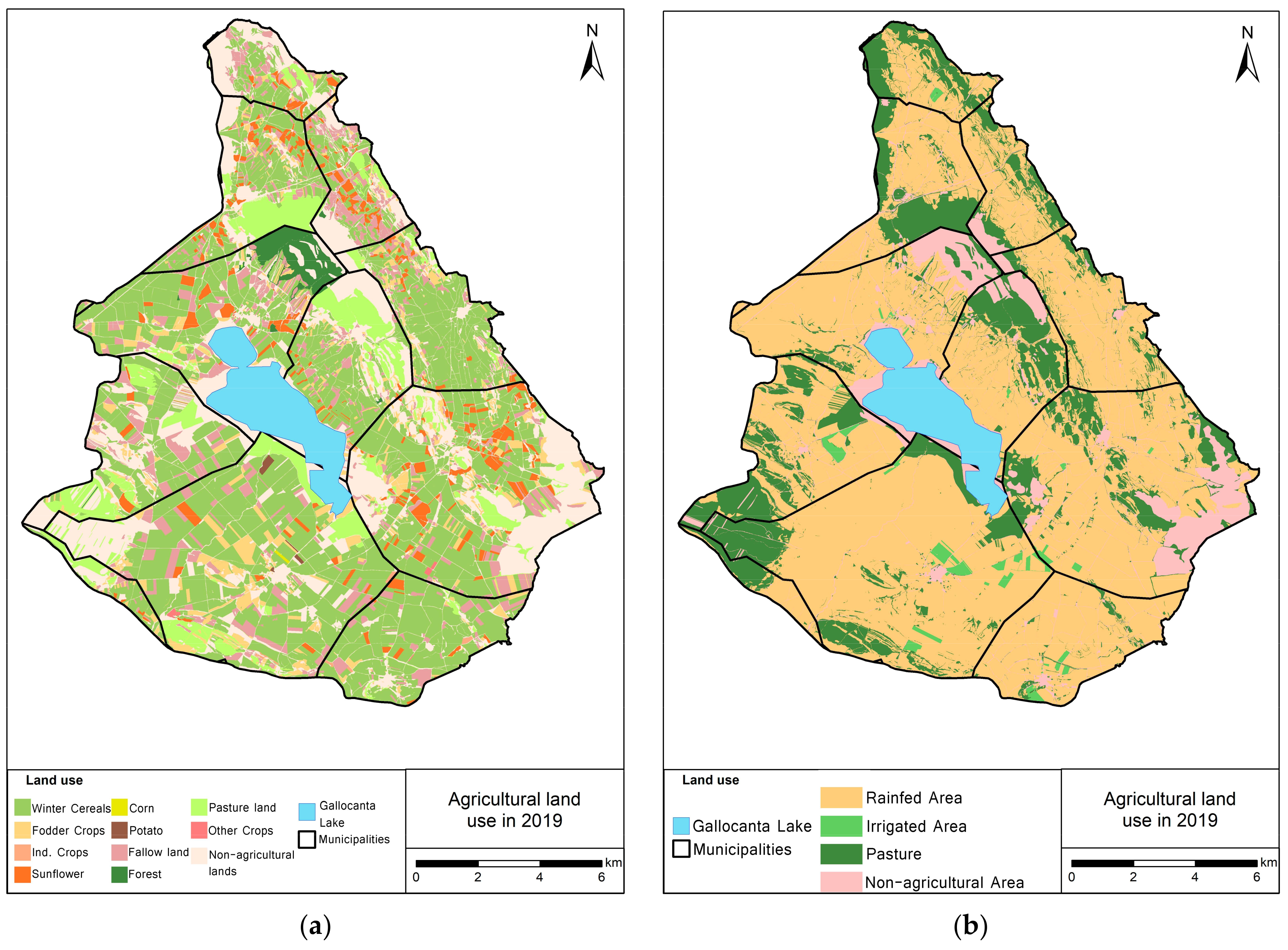
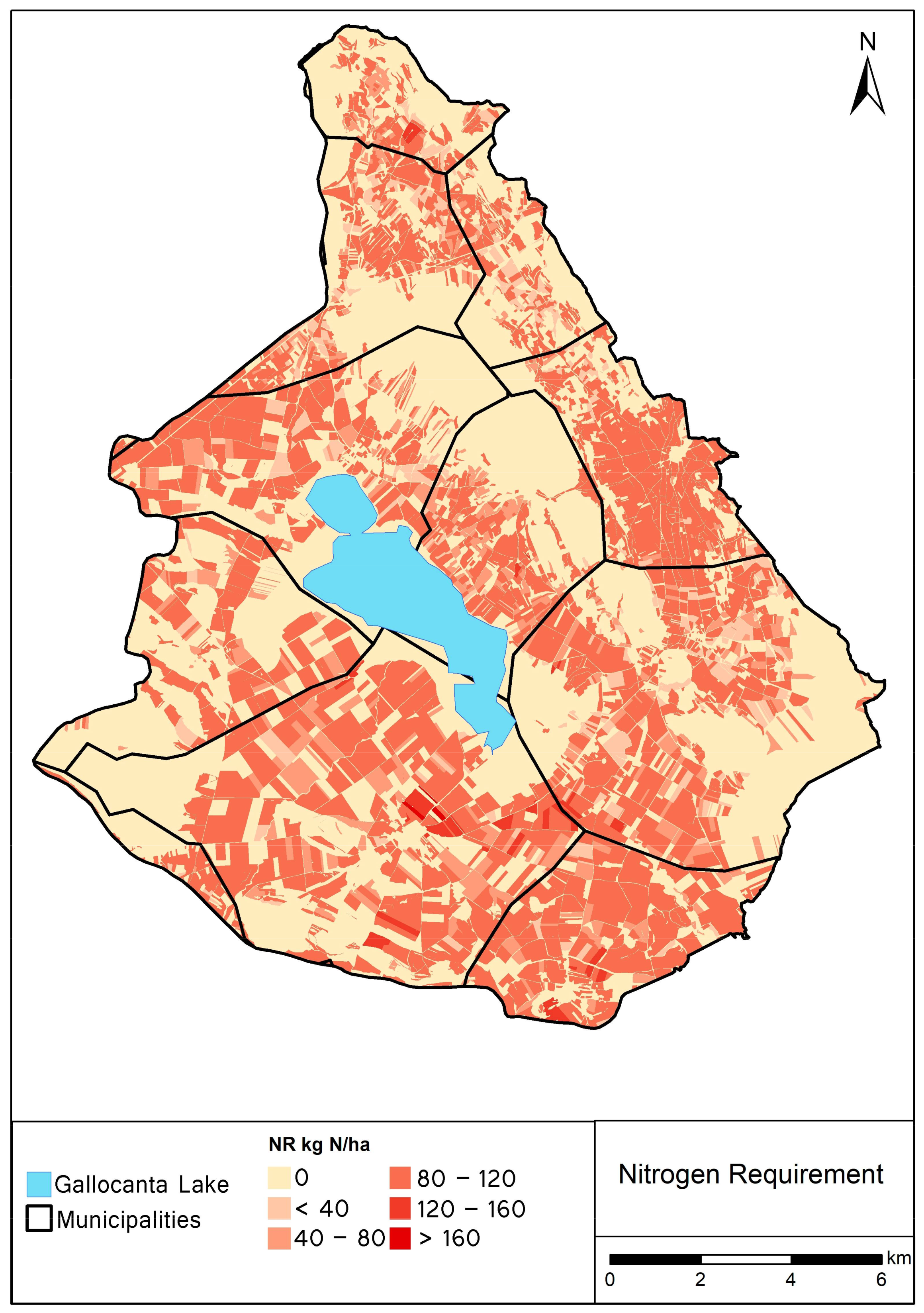
2.2.2. NIHI Application
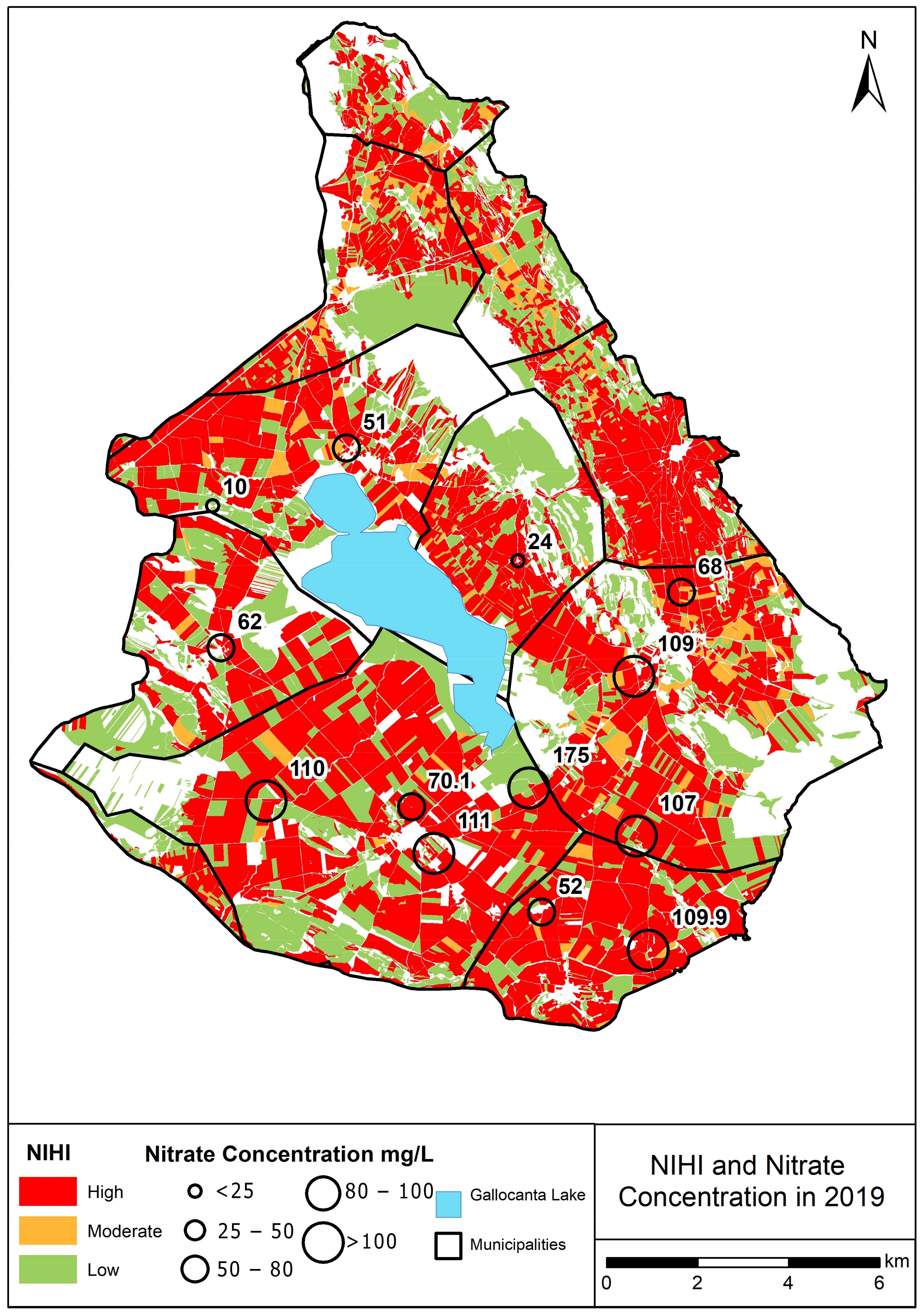
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Efectiveness of the NIHI
4.2. Patterns in the Gallocanta Groundwater Body
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Capri, E.; Civita, M.; Corniello, A.; Cusimano, G.; De Maio, M.; Ducci, D.; Fait, G.; Fiorucci, A.; Hauser, S.; Pisciotta, A.; et al. Assessment of nitrate contamination risk: The Italian experience. J. Geochem. Explor. 2009, 102, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, M.A.; Howard, C.M.; Erisman, J.W.; Billen, G.; Bleeker, A.; Grennfelt, P.; Van Grinsven, H.; Grizzetti, B. The European Nitrogen Assessment: Sources, Effects and Policy Perspectives; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, R.; Wang, Y.; Ye, R. The evaluation and prediction of agriculture-related nitrate contamination in groundwater in Chengdu Plain, southwestern China. Hydrogeol. J. 2019, 27, 785–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y. Health Risk Assessment of Nitrate Contamination in Groundwater: A Case Study of an Agricultural Area in Northeast China. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 3025–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Rauf, M.; Mukhtar, Z.; Saeed, N.A. Excessive use of nitrogenous fertilizers: An unawareness causing serious threats to environment and human health. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 26983–26987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, M.A.D.; Soegaard, H.; Hinsby, K. Temporal trends in N & P concentrations and loads in relation to anthropogenic effects and discharge in Odense River 1964–2002. Hydrol. Res. 2008, 39, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billen, G.; Garnier, J.; Lassaletta, L. The nitrogen cascade from agricultural soils to the sea: Modelling nitrogen transfers at regional watershed and global scales. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchán, D.; Auqué, L.F.; Acero, P.; Gimeno, M.J.; Causapé, J. Environment Geochemical processes controlling water salinization in an irrigated basin in Spain : Identification of natural and anthropogenic in fluence. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 502, 330–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viers, J.H.; Liptzin, D.; Rosenstock, T.S.; Jensen, V.B.; Hollander, A.D.; McNally, A.; King, A.M.; Kourakos, G.; Lopez, E.M.; De La Mora, N.; et al. Nitrogen Sources and Loading to Groundwater. Technical Report 2. In Addressing Nitrate in California’s Drinking Water with a Focus on Tulare Lake Basin and Salinas Valley Groundwater. Report for the State Water Resources Control Board Report to the Legislature; Center for Watershed Sciences, Ed.; University of California: Davis, CA, USA, 2012; pp. 53–131. [Google Scholar]
- Novotny, V. Diffuse pollution from agriculture—A worldwide outlook. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 39, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrington, G.; Winder, L.; Parkinson, R.; Redman, M. Agricultural Pollution: Problems and Practical Solutions; Spon Press: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Dorgham, M. Effects of Eutrophication. In Eutrophication Causes, Consequences and Control; Ansari, A.A., Gill, S.S., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 2, pp. 29–44. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, M.H. Too much of a good thing? Nitrate from nitrogen fertilizers and cancer. Rev. Environ. Health 2009, 24, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canada Water Act. Canada Justice Law Website. Available online: https://laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/eng/acts/c-11/index.html (accessed on 13 November 2020).
- USGS. United States Geological Survey. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/mission-areas/water-resources/science/national-water-quality-assessment-nawqa-1991-2012?qt-science_center_objects=0#qt-science_center_objects (accessed on 13 November 2020).
- Europan Economic Council. Council Directive 2000/60/EC; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- European Economic Community (EEC). Council Directive 91/676/EEC; European Economic Community: Brussels, Belgium, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- European Union. Council Directive 2006/118/EC; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Malagó, A.; Bouraoui, F.; Pastori, M.; Gelati, E. Modelling nitrate reduction strategies from diffuse sources in the Po River Basin. Water 2019, 11, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arauzo, M.; Martínez-Bastida, J.J. Environmental factors affecting diffuse nitrate pollution in the major aquifers of central Spain: Groundwater vulnerability vs. groundwater pollution. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 8271–8286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana-Macías, J.M.; Merchán, D.; Causapé, J. Evolution and assessment of a nitrate vulnerable zone over 20 years: Gallocanta groundwater body (Spain). Hydrogeol. J. 2020, 28, 2207–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Girolamo, A.M.; Spanò, M.; D’Ambrosio, E.; Ricci, G.F.; Gentile, F. Developing a nitrogen load apportionment tool: Theory and application. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 226, 105806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNDRO. Natural Disasters and Vulnerability Analysis. Report of Experts Group Meeting of 9–12 July 1979; UNDRO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- UN/ISDR (United Nations/International Strategy for Disaster Reduction). Living with Risk: A Global Review of Disaster Reduction Initiatives; United Nations: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004.
- UN/ISDR (United Nations/International Strategy for Disaster Reduction). Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction; United Nations: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- Birkmann, J. Risk. In Encyclopedia of Natural Hazards. Encyclopedia of Earth Sciences Series; Bobrowsky, P.T., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadim, F. Hazard. In Encyclopedia of Natural Hazards. Encyclopedia of Earth Sciences Series; Bobrowsky, P.T., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civita, M.V.; De Maio, M. Assessing Groundwater contamination risk using ArcInfo via GRID function. In Proceedings of the ESRI Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 8–11 July 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, S.; Hirata, R.; Gomes, D.; D’Elia, M.; Paris, M. Groundwater Quality Protection; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- De Ketelaere, D.; Hötzl, H.; Neukum, C.; Civita, M.; Sappa, G. Hazard Analysis and Mapping. In Vulnerability and Risk Mapping for the Protection of Carbonate (Karst) Aquifers (COST Action 620); Zwahlen, F., Ed.; Directorate-General XII Science, Research and Development, European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2004; pp. 86–105. [Google Scholar]
- Padovani, L.; Trevisan, M. I nitrati di origine agricola nelle acque sotterranee. Quad di Tech di Prote Ambien 75. Pitagora Editrice 2002, 15, 103. [Google Scholar]
- Passarella, G.; Vurro, M.; D’Agostino, V.; Giuliano, G.; Barcelona, M.J. A probabilistic methodology to assess the risk of groundwater quality degradation. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2002, 79, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diodato, N.; Esposito, L.; Bellocchi, G.; Vernacchia, L.; Fiorillo, F.; Guadagno, F.M. Assessment of the Spatial Uncertainty of Nitrates in the Aquifers of the Campania Plain (Italy). Am. J. Clim. Chang. 2013, 2, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shaffer, M.J.; Delgado, J.A. Essentials of a national nitrate leaching index assessment tool. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2002, 57, 327–335. [Google Scholar]
- Birkle, D.; French, C.; Letey, J.; Wu, L.; Wood, Y. Nitrate leaching hazard index developed for irrigated agriculture. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2005, 60, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- O’Geen, A.T.; Hopmans, J.; Harter, T. California Department of Food and Agriculture. Available online: https://www.cdfa.ca.gov/is/docs/14-0452-OGeen.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2020).
- Orellana-Macías, J.M.; Perles Roselló, M.J. A comparative analysis of methods for mapping groundwater pollution hazard: Application to the Gallocanta Hydrogeologic Unit. Boletín Asoc. Geógrafos Españoles 2020. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corniello, A.; Ducci, D.; Ruggieri, G. Areal identification of groundwater nitrate contamination sources in periurban areas. J. Soils Sediments 2007, 7, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.; Anderson, R.; Tatham, R.; Black, W. Análisis Multivariante; Prentice Hall Iberia: Madrid, Spain, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- San Román, J. Establecimiento de las Normas de Explotación de la Unidad Hidrogeológica “Gallocanta” y Delimitación de los Perímetros de Protección de la Laguna; Confederación Hidrográfica del Ebro: Zaragoza, Spain, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Gracia, F.J.; Gutiérrez, F.; Gutiérrez, M. Evolución geomorfológica del polje de Gallocanta (Cordillera Ibérica). Rev. Soc. Geol. España 1999, 12, 351–368. [Google Scholar]
- MAPA. Balance del Nitrógeno en la Agricultura Española: Año 2016; Ministerio de Agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación: Madrid, Spain, 2018.
- Jiménez-Madrid, A.; Martínez, C.; Luque, J.A.; Rubio-Campos, J.C.; Carrasco, F. Estrategias de protección del agua subterránea destinada al consumo humano en la cuenca del Guadalquivir. Bol. Geol. Min. 2013, 124, 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- CHE (Confederación Hidrográfica del Ebro). Available online: https://www.chebro.es/ (accessed on 20 October 2020).
- Ducci, D. An easy-To-use method for assessing nitrate contamination susceptibility in groundwater. Geofluids 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UCANR. University of California Agriculture and Natural Resources. Available online: http://ciwr.ucanr.edu/files/168490.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2020).
- Arauzo, M.; Valladolid, M. Drainage and N-leaching in alluvial soils under agricultural land uses: Implications for the implementation of the EU Nitrates Directive. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 179, 94–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macgregor, C.J.; Warren, C.R. Evaluating the Impacts of Nitrate Vulnerable Zones on the Environment and Farmers’ Practices: A Scottish Case Study. Scott. Geogr. J. 2015, 132, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzón, A.; Pérez, A.; Mayayo, M.J.; Soria, A.R.; Sánchez Goñi, M.F.; Roc, A.C. Holocene environmental changes in the Gallocanta lacustrine basin, Iberian Range, NE Spain. Holocene 2007, 17, 649–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ITGE (Instituto Tecnológico y Geológico de España). Plan Nacional de Investigación de Aguas Subterrráneas de la Cuenca del Ebro; Ministerio de Industria y Energía: Zaragoza, Spain, 1982.
- Valiente, N.; Carrey, R.; Otero, N.; Soler, A.; Sanz, D.; Muñoz-Martín, A.; Jirsa, F.; Wanek, W.; Gómez-Alday, J.J. A multi-isotopic approach to investigate the influence of land use on nitrate removal in a highly saline lake-aquifer system. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aschonitis, V.G.; Mastrocicco, M.; Colombani, N.; Salemi, E.; Castaldelli, G. Assessment of the intrinsic vulnerability of agricultural land to water and nitrogen losses: Case studies in Italy and Greece. IAHS-AISH Proc. Rep. 2014, 364, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busico, G.; Kazakis, N.; Colombani, N.; Khosravi, K.; Voudouris, K.; Mastrocicco, M. The importance of incorporating denitrification in the assessment of groundwater vulnerability. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menéndez-Serra, M.; Triadó-Margarit, X.; Castañeda, C.; Herrero, J.; Casamayor, E.O. Microbial composition, potential functional roles and genetic novelty in gypsum-rich and hypersaline soils of Monegros and Gallocanta (Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IGME. Proyecto para la Actualización de Datos de la Cuenca alta del Jiloca. Estudio Sobre las Explotaciones, Problemática del Uso del Acuífero y Ordenación del Mismo. Ministerio de Industria y Energía, Secretaría de la Energía y Recursos Minerals: Zaragoza, Spain, 1986. [Google Scholar]
| ID | NO3− [mg L–1] | NR | Vulnerability |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 127 | 90 | 75 |
| 2 | 65 | 16 | 73 |
| 3 | 52 | 85 | 37 |
| 4 | 26 | 0 | 79 |
| 5 | 53 | 98 | 66 |
| 6 | 6 | 0 | 66 |
| 7 | 114 | 98 | 37 |
| 8 | 110 | 98 | 37 |
| 9 | 154 | 0 | 79 |
| 10 | 57 | 98 | 66 |
| 11 | 113 | 78 | 66 |
| 12 | 112 | 97 | 66 |
| 13 | 76 | 127 | 79 |
| Cluster | n | NO3− [mg L–1] | Vulnerability | NR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8 | 82 | 66 | 86 |
| 2 | 3 | 62 | 73 | 0 |
| 3 | 2 | 112 | 37 | 98 |
| Group | Crop | NR (kg N ha–1) | Rainfed | Irrigated | Ha |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cereals | Wheat | 97 | X | X | 1664 |
| Barley | 98 | X | X | 6809 | |
| Oat | 74 | X | 46 | ||
| Rye | 69 | X | X | 967 | |
| Triticale | 79 | X | 418 | ||
| Corn | 263 | X | 5 | ||
| Legumes | Vetch | - * | X | 6 | |
| Bitter Vetch | - * | X | 11 | ||
| Tubers | Potato | 192 | X | 21 | |
| Industrial crops | Sunflower | 38 | X | X | 861 |
| Fodder crops | Alfalfa | - * | X | 924 | |
| Sainfoin | - * | X | 303 | ||
| Vegetables | Cucumber | 44 | X | 0.5 | |
| Tomato | 117 | X | 0.5 | ||
| Onion | 91 | X | 1 | ||
| Carrot | 136 | X | 0.2 | ||
| Other vegetables | 147 | X | 1 | ||
| Fruit trees | Almond | 58 | X | 10 |
| NO3– Concentration (mg L–1) | NR (kg N ha–1) | Hazard Level |
|---|---|---|
| <25 | <22 | Low |
| 25–50 | 22–45 | Moderate |
| >50 | >45 | High |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Orellana-Macías, J.M.; Perles Roselló, M.J.; Causapé, J. A Methodology for Assessing Groundwater Pollution Hazard by Nitrates from Agricultural Sources: Application to the Gallocanta Groundwater Basin (Spain). Sustainability 2021, 13, 6321. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13116321
Orellana-Macías JM, Perles Roselló MJ, Causapé J. A Methodology for Assessing Groundwater Pollution Hazard by Nitrates from Agricultural Sources: Application to the Gallocanta Groundwater Basin (Spain). Sustainability. 2021; 13(11):6321. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13116321
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrellana-Macías, José María, María Jesús Perles Roselló, and Jesús Causapé. 2021. "A Methodology for Assessing Groundwater Pollution Hazard by Nitrates from Agricultural Sources: Application to the Gallocanta Groundwater Basin (Spain)" Sustainability 13, no. 11: 6321. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13116321
APA StyleOrellana-Macías, J. M., Perles Roselló, M. J., & Causapé, J. (2021). A Methodology for Assessing Groundwater Pollution Hazard by Nitrates from Agricultural Sources: Application to the Gallocanta Groundwater Basin (Spain). Sustainability, 13(11), 6321. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13116321






