Ethical Leadership and Employee Green Behavior: A Multilevel Moderated Mediation Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
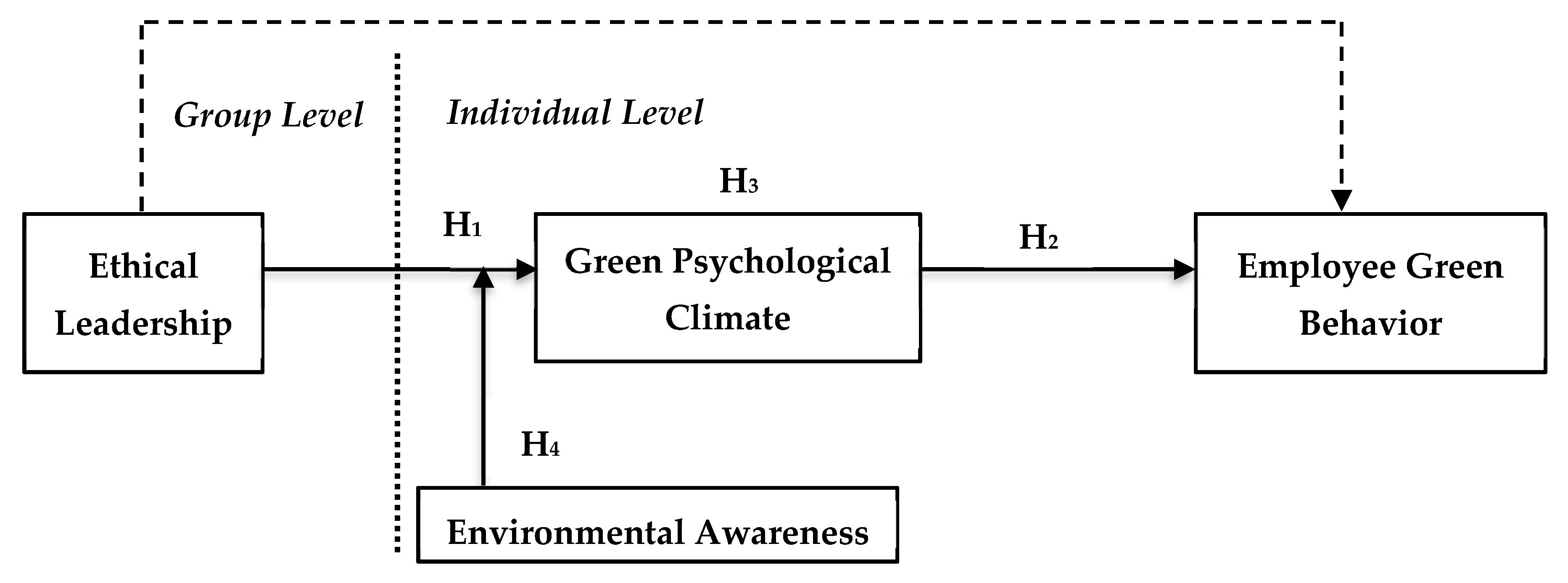
2. Hypotheses Development
2.1. Ethical Leadership and Green Psychological Climate
2.2. Green Psychological Climate and Employee Green Behavior
2.3. Mediation of Green Psychological Climate
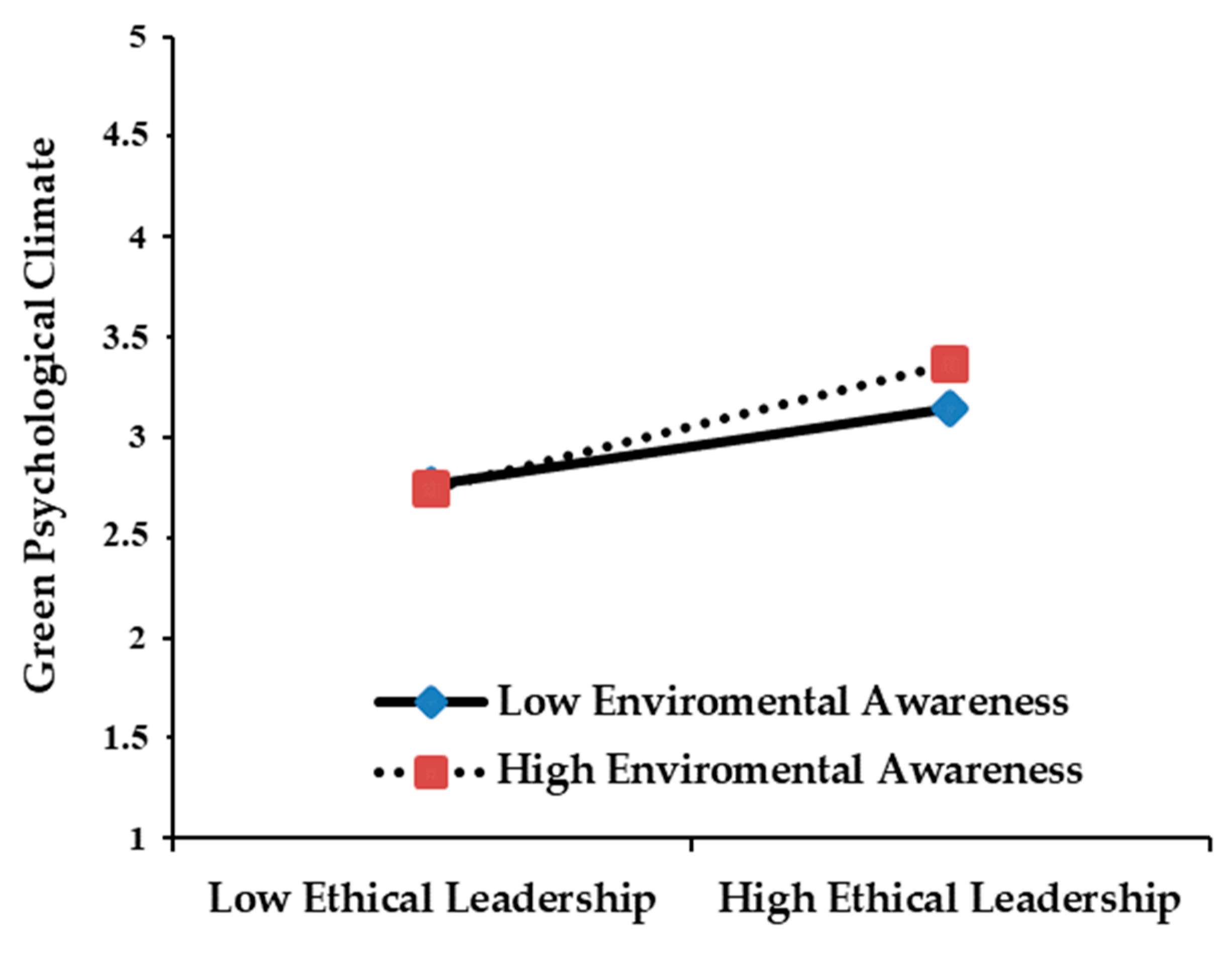
2.4. Moderation of Environmental Awareness
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Measures
3.2. Analytical Strategy
4. Data Analysis and Results
4.1. Descriptive Analysis
4.2. Hypotheses Testing
5. Discussions and Conclusions
5.1. Practical Implications
5.2. Limitations and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aguinis, H.; Glavas, A. What we know and don’t know about corporate social responsibility a review and research agenda. J. Manag. 2012, 38, 932–968. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.; Lee, S. Self-discipline or self-interest? The antecedents of hotel employees’ pro-environmental behaviours. J. Sustain. Tour. 2019, 27, 1457–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swim, J.K.; Clayton, S.; Howard, G.S. Human behavioral contributions to climate change: Psychological and contextual drivers. Am. Psychol. 2011, 66, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testa, F.; Corsini, F.; Gusmerotti, N.M.; Iraldo, F. Predictors of organizational citizenship behavior in relation to environmental and health & safety issues. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2018, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, P.; Hoffman, A.J. The Oxford Handbook of Business and the Natural Environment; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, J.L.; Barling, J. “Introduction”. In The Psychology of Green Organizations; Robertson, J.L., Barling, J., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Q.; Robertson, J.L. How and when does perceived CSR affect employees’ engagement in voluntary pro-environmental behavior? J. Bus. Ethics 2019, 155, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ones, D.S.; Dilchert, S. Environmental sustainability at work: A call to action. Ind. Organ. Psychol. 2012, 5, 444–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, T.A.; Zacher, H.; Parker, S.L.; Ashkanasy, N.M. Bridging the gap between green behavioral intentions and employee green behavior: The role of green psychological climate. J. Organ. Behav. 2017, 38, 996–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, J. The relationship between pro-environmental attitude and employee green behavior: The role of motivational states and green work climate perceptions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 7341–7352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, T.A.; Zacher, H.; Ashkanasy, N.M. Pro-environmental organizational culture and climate. In The Psychology of Green Organizations; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 322–348. [Google Scholar]
- Lamm, E.; Tosti-Kharas, J.; King, C.E. Empowering employee sustainability: Perceived organizational support toward the environment. J. Bus. Ethics 2015, 128, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramus, C.A.; Steger, U. The roles of supervisory support behaviors and environmental policy in employee “ecoinitiatives” at leading-edge European companies. Acad. Manag. J. 2000, 43, 605–626. [Google Scholar]
- Bissing-Olson, M.J.; Iyer, A.; Fielding, K.S.; Zacher, H. Relationships between daily affect and pro-environmental behavior at work: The moderating role of pro-environmental attitude. J. Organ. Behav. 2013, 34, 156–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, A.; Salehzadeh, R.; Panahi, R.; Abolghasemian, S. Multiple pathways linking environmental knowledge and awareness to employees’ green behavior. Corp. Gov. Int. J. Bus. Soc. 2018, 18, 81–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afsar, B.; Badir, Y. Workplace spirituality, perceived organizational support and innovative work behavior. J. Workplace Learn. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, B.B.; Afsar, B.; Hafeez, S.; Khan, I.; Tahir, M.; Afridi, M.A. Promoting employee’s proenvironmental behavior through green human resource management practices. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2019, 26, 424–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, C.; Clarke, N.; Cloke, P.; Malpass, A. The political ethics of consumerism. Consum. Policy Rev. 2005, 15, 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Afsar, B.; Badir, Y.; Kiani, U.S. Linking spiritual leadership and employee pro-environmental behavior: The influence of workplace spirituality, intrinsic motivation, and environmental passion. J. Environ. Psychol. 2016, 45, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.L.; Barling, J. Greening organizations through leaders’ influence on employees’ pro-environmental behaviors. J. Organ. Behav. 2013, 34, 176–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, C.; Ma, J.; Bartnik, R.; Haney, M.H.; Kang, M. Ethical leadership: An integrative review and future research agenda. Ethics Behav. 2018, 28, 104–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, A.; Walters, R.H. Social Learning Theory; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, M.E.; Treviño, L.K. Ethical leadership: A review and future directions. Leadersh. Q. 2006, 17, 595–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuenzi, M.; Mayer, D.M.; Greenbaum, R.L. Creating an ethical organizational environment: The relationship between ethical leadership, ethical organizational climate, and unethical behavior. Pers. Psychol. 2019, 73, 43–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, D.M.; Kuenzi, M.; Greenbaum, R.L. Examining the link between ethical leadership and employee misconduct: The mediating role of ethical climate. J. Bus. Ethics 2010, 95, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuenzi, M.; Schminke, M. Assembling fragments into a lens: A review, critique, and proposed research agenda for the organizational work climate literature. J. Manag. 2009, 35, 634–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, T.A.; Zacher, H.; Ashkanasy, N.M. On the Importance of Pro-Environmental Organizational Climate for Employee Green Behavior. Ind. Organ. Psychol. 2012, 5, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.-Z.; Kwan, H.K.; Yim, F.H.-K.; Chiu, R.K.; He, X. CEO ethical leadership and corporate social responsibility: A moderated mediation model. J. Bus. Ethics 2015, 130, 819–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, B.M. Leadership, Psychology, and Organizational Behavior; Harper & Row: New York, NY, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Grojean, M.W.; Resick, C.J.; Dickson, M.W.; Smith, D.B. Leaders, values, and organizational climate: Examining leadership strategies for establishing an organizational climate regarding ethics. J. Bus. Ethics 2004, 55, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walumbwa, F.O.; Lawler, J.J. Building effective organizations: Transformational leadership, collectivist orientation, work-related attitudes and withdrawal behaviours in three emerging economies. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2003, 14, 1083–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalshoven, K.; Den Hartog, D.N.; De Hoogh, A.H. Ethical leadership at work questionnaire (ELW): Development and validation of a multidimensional measure. Leadersh. Q. 2011, 22, 51–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, L.R.; Choi, C.C.; Ko, C.-H.E.; McNeil, P.K.; Minton, M.K.; Wright, M.A.; Kim, K.-I. Organizational and psychological climate: A review of theory and research. Eur. J. Work Organ. Psychol. 2008, 17, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eva, N.; Newman, A.; Miao, Q.; Wang, D.; Cooper, B. Antecedents of duty orientation and follower work behavior: The interactive effects of perceived organizational support and ethical leadership. J. Bus. Ethics 2020, 161, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedi, A.; Alpaslan, C.M.; Green, S. A meta-analytic review of ethical leadership outcomes and moderators. J. Bus. Ethics 2016, 139, 517–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavik, Y.L.; Tang, P.M.; Shao, R.; Lam, L.W. Ethical leadership and employee knowledge sharing: Exploring dual-mediation paths. Leadersh. Q. 2018, 29, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, R.M.; Weng, Q.; Hameed, Z.; Rasheed, M.I. Ethical leadership and work engagement: A moderated mediation model. Ethics Behav. 2020, 30, 63–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suifan, T.S.; Diab, H.; Alhyari, S.; Sweis, R.J. Does ethical leadership reduce turnover intention? The mediating effects of psychological empowerment and organizational identification. J. Hum. Behav. Soc. Environ. 2020, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, M.; Asif, M.; Hussain, A.; Jameel, A. Exploring the impact of ethical leadership on job satisfaction and organizational commitment in public sector organizations: The mediating role of psychological empowerment. Rev. Manag. Sci. 2019, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.; Mayer, D.M.; Chiang, F.F.; Crossley, C.; Karlesky, M.J.; Birtch, T.A. Leaders matter morally: The role of ethical leadership in shaping employee moral cognition and misconduct. J. Appl. Psychol. 2019, 104, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M.-Y.; Wang, L. The mediating effect of ethical climate on the relationship between paternalistic leadership and team identification: A team-level analysis in the Chinese context. J. Bus. Ethics 2015, 129, 639–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, S.D.; Dunford, B.B.; Alge, B.J.; Jackson, C.L. Corporate social responsibility, ethical leadership, and trust propensity: A multi-experience model of perceived ethical climate. J. Bus. Ethics 2016, 137, 649–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.-S.; Lin, C.-C. The effects of ethical leadership and ethical climate on employee ethical behavior in the international port context. J. Bus. Ethics 2014, 124, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Sung, S.Y.; Choi, J.N.; Kim, M.S. Top management ethical leadership and firm performance: Mediating role of ethical and procedural justice climate. J. Bus. Ethics 2015, 129, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ones, D.S.; Dilchert, S. Environmental sustainability at work—A call to action. Industrial and Organizational Psychology. Perspect. Sci. Pract. 2012, 5, 444–466. [Google Scholar]
- Littleford, C.; Ryley, T.J.; Firth, S.K. Context, control and the spillover of energy use behaviours between office and home settings. J. Environ. Psychol. 2014, 40, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, B.; Ehrhart, M.G.; Macey, W.H. Organizational climate and culture. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2013, 64, 361–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulki, J.P.; Jaramillo, J.F.; Locander, W.B. Critical role of leadership on ethical climate and salesperson behaviors. J. Bus. Ethics 2009, 86, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubert, M.J.; Carlson, D.S.; Kacmar, K.M.; Roberts, J.A.; Chonko, L.B. The virtuous influence of ethical leadership behavior: Evidence from the field. J. Bus. Ethics 2009, 90, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, C.P.; Baltes, B.B.; Young, S.A.; Huff, J.W.; Altmann, R.A.; Lacost, H.A.; Roberts, J.E. Relationships between psychological climate perceptions and work outcomes: A meta-analytic review. J. Organ. Behav. 2003, 24, 389–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, T.A.; Zacher, H.; Ashkanasy, N.M. Organisational sustainability policies and employee green behaviour: The mediating role of work climate perceptions. J. Environ. Psychol. 2014, 38, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zhang, D.; Lyu, C.; Zhang, H. Does Seeing “Mind Acts Upon Mind” Affect Green Psychological Climate and Green Product Development Performance? The Role of Matching Between Green Transformational Leadership and Individual Green Values. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.S.; Ali, M.; Usman, M.; Saleem, S.; Jianguo, D. Interrelationships between ethical leadership, green psychological climate, and organizational environmental citizenship behavior: The moderating role of gender. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, J.; Shen, J.; Deng, X. Effects of green HRM practices on employee workplace green behavior: The role of psychological green climate and employee green values. Hum. Resour. Manag. J. 2017, 56, 613–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhou, Q. Exploring the impact of responsible leadership on organizational citizenship behavior for the environment: A leadership identity perspective. Sustainability 2019, 11, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, T.T. CSR and customer value co-creation behavior: The moderation mechanisms of servant leadership and relationship marketing orientation. J. Bus. Ethics 2019, 155, 379–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatoki, O.J.S. Hotel Employees’ Pro-Environmental Behaviour: Effect of Leadership Behaviour, Institutional Support and Workplace Spirituality. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junsheng, H.; Masud, M.M.; Akhtar, R.; Rana, M.J.S. The Mediating Role of Employees’ Green Motivation between Exploratory Factors and Green Behaviour in the Malaysian Food Industry. Sustainability 2020, 12, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Wang, Q.; Yan, X.J.S. How Responsible Leadership Motivates Employees to Engage in Organizational Citizenship Behavior for the Environment: A Double-Mediation Model. Sustainability 2019, 11, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalshoven, K.; Den Hartog, D.N. Ethical leader behavior and leader effectiveness: The role of prototypicality and trust. Int. J. Leadersh. Stud. 2009, 5, 102–120. [Google Scholar]
- Madsen, H.; Ulhøi, J.P. Greening of human resources: Environmental awareness and training interests within the workforce. Ind. Manag. Data. Syst. 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar Jahanshahi, A.; Brem, A.; Gholami, H.J.S. Working in a Physically Dangerous Work Environment: Employee Vitality and Sustainable Behavior. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, E.S.; Hon, A.H.; Chan, W.; Okumus, F. What drives employees’ intentions to implement green practices in hotels? The role of knowledge, awareness, concern and ecological behaviour. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2014, 40, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zsóka, Á.; Szerényi, Z.M.; Széchy, A.; Kocsis, T. Greening due to environmental education? Environmental knowledge, attitudes, consumer behavior and everyday pro-environmental activities of Hungarian high school and university students? J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 48, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; MacKenzie, S.B.; Lee, J.-Y.; Podsakoff, N.P. Common method biases in behavioral research: A critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. J. Appl. Psychol. 2003, 88, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatersleben, B.; Murtagh, N.; Abrahamse, W. Values, identity and pro-environmental behaviour. Contemp. Soc. Sci. 2014, 9, 374–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, L.M.; Sarkis, J.; Zhu, Q. How transformational leadership and employee motivation combine to predict employee proenvironmental behaviors in China. J. Environ. Psychol. 2013, 35, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsboom, D.; Mellenbergh, G.J.; Van Heerden, J. The concept of validity. Psychol. Rev. 2004, 111, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamantopoulos, A. The C-OAR-SE procedure for scale development in marketing: A comment. Int. J. Mark. Res. 2005, 22, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, A.; Kayande, U. How fine is C-OAR-SE? A generalizability theory perspective on Rossiter’s procedure. Int. J. Mark. Res. 2005, 22, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coltman, T.; Devinney, T.M.; Midgley, D.F.; Venaik, S. Formative versus reflective measurement models: Two applications of formative measurement. J. Bus. Res. 2008, 61, 1250–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthén, L.; Muthén, B. The Comprehensive Modelling Program for Applied Researchers: User’s Guide; Muthén & Muthén: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2016; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Preacher, K.J.; Zhang, Z.; Zyphur, M.J. Alternative methods for assessing mediation in multilevel data: The advantages of multilevel SEM. Struct. Equ. Model. 2011, 18, 161–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, D. Functional relations among constructs in the same content domain at different levels of analysis: A typology of composition models. J. Appl. Psychol. 1998, 83, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farh, C.I.; Chen, Z. Beyond the individual victim: Multilevel consequences of abusive supervision in teams. J. Appl. Psychol. 2014, 9, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthén, B.O. Multilevel covariance structure analysis. Sociol. Methods Res. 1994, 22, 376–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, L.R. Aggregation bias in estimates of perceptual agreement. J. Appl. Psychol. 1982, 67, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, L.R.; Demaree, R.G.; Wolf, G. Rwg: An assessment of within-group interrater agreement. J. Appl. Psychol. 1993, 78, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.; Kim, Y.; Han, K.; Jackson, S.E.; Ployhart, R.E. Multilevel influences on voluntary workplace green behavior: Individual differences, leader behavior, and coworker advocacy. J. Manag. 2017, 43, 1335–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, F.; Qadeer, F.; Abbas, Z.; Hussain, I.; Saleem, M.; Hussain, A.; Aman, J.J.S. Corporate Social Responsibility and Employees’ Negative Behaviors under Abusive Supervision: A Multilevel Insight. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.K.; Biswas, S.R.; Jilani, A.K.; Muhammad, M.; Uddin, M.J.S. Corporate environmental strategy and voluntary environmental behavior—Mediating effect of psychological green climate. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirtas, O.; Akdogan, A.A. The effect of ethical leadership behavior on ethical climate, turnover intention, and affective commitment. J. Bus. Ethics 2015, 130, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, M.M.S.; Hills, P.; Hau, B.C.H. Engaging employees in sustainable development–a case study of environmental education and awareness training in Hong Kong. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2017, 26, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindarajulu, N.; Daily, B.F. Motivating employees for environmental improvement. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perron, G.M.; Côté, R.P.; Duffy, J.F. Improving environmental awareness training in business. J. Clean. Prod. 2006, 14, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzadi, G.; Qadeer, F.; John, A.; Jia, J.F. CSR and identification: The contingencies of employees’ personal traits and desire. Soc. Responsib. J. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, A.; Qadeer, F.; Shahzadi, G.; Jia, F. Getting paid to be good: How and when employees respond to corporate social responsibility? J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 215, 784–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salancik, G.R.; Pfeffer, J. A social information processing approach to job attitudes and task design. Adm. Sci. Q. 1978, 23, 224–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenberger, R.; Karagonlar, G.; Stinglhamber, F.; Neves, P.; Becker, T.E.; Gonzalez-Morales, M.G.; Steiger-Mueller, M.J. Leader–member exchange and affective organizational commitment: The contribution of supervisor’s organizational embodiment. J. Appl. Psychol. 2010, 95, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashforth, B.E.; Mael, F.J. Social identity theory and the organization. Acad. Manag. 1989, 14, 20–39. [Google Scholar]
| Items | Cronbach Alpha | AVE | MSV | CR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 (Individual) | |||||
| Green Psychological Climate | 5 | 0.93 | 0.50 | 0.29 | 0.91 |
| Employee Green Behavior | 12 | 0.86 | 0.59 | 0.43 | 0.72 |
| Environmental Awareness | 12 | 0.72 | 0.62 | 0.10 | 0.69 |
| Level 2 (Group) | |||||
| Ethical Leadership | 10 | 0.96 | 0.57 | 0.32 | 0.81 |
| Mean | SD | Skewness | Kurtosis | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 (Individual) | |||||||
| 1. Green Psychological Climate | 4.22 | 0.76 | −1.55 | 2.4 | 1 | ||
| 2. Employee Green Behavior | 4.09 | 0.52 | 1.32 | 1.35 | 0.64 * | 1 | |
| 3. Environmental Awareness | 4.52 | 0.39 | −0.86 | 0.74 | 0.34 ** | 0.35 * | 1 |
| Level 2 (Group) | |||||||
| 4. Ethical Leadership | 4.21 | 0.43 | −1.75 | 1.59 | 0.18 ** | 0.36 * | 0.28 * |
| Estimates | 95% CI | Remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|
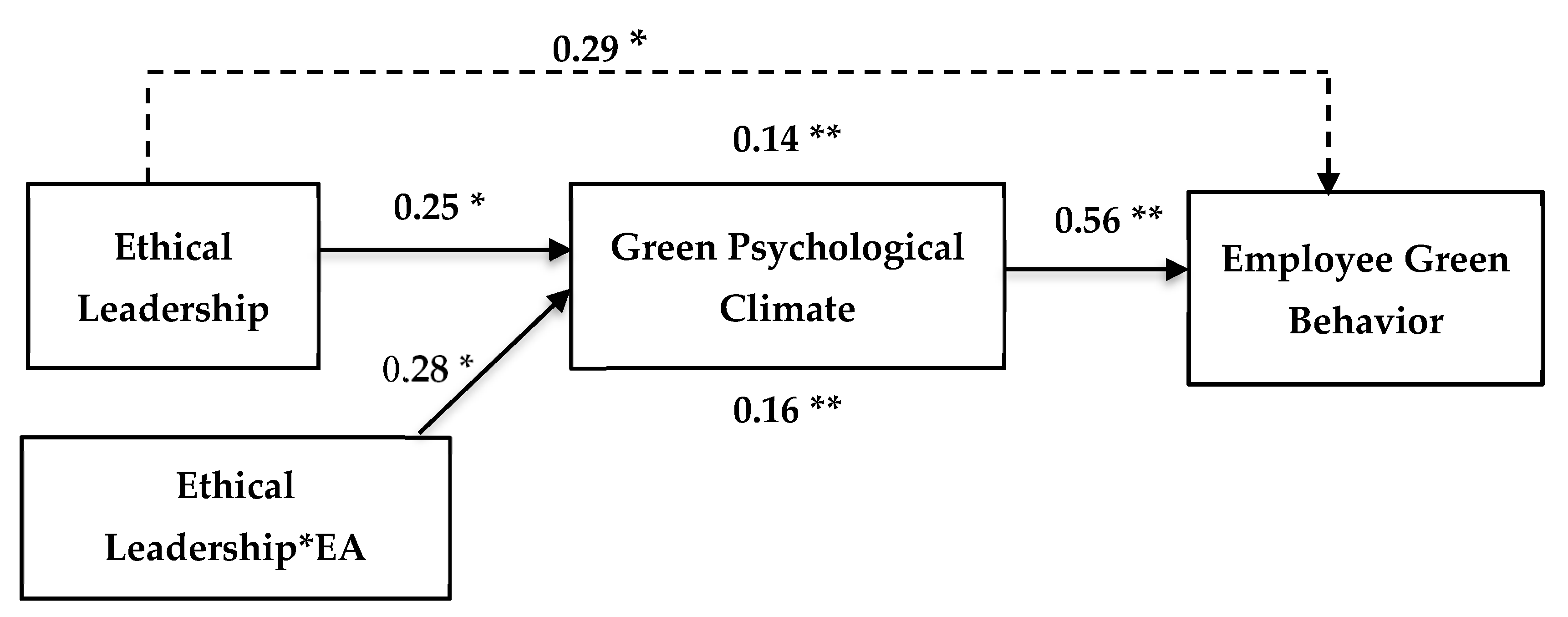
Ethical Leadership  GPC GPC | 0.25 * | (0.007, 0.484) | Supported (H1) |
GPC  EGB EGB | 0.56 * | (0.289, 0.837) | Supported (H2) |
Ethical Leadership*EA  GPC GPC | 0.28 * | (0.072, 0.301) | |
Ethical Leadership  EGB EGB | 0.29 * | (0.221, 0.400) | |
Ethical Leadership  GPC GPC  EGB EGB | 0.14 ** | (0.030, 0.146) | Supported (H3) |
Ethical Leadership*EA  GPC GPC  EGB EGB | 0.16 ** | (0.081, 0.172) | Supported (H4) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saleem, M.; Qadeer, F.; Mahmood, F.; Ariza-Montes, A.; Han, H. Ethical Leadership and Employee Green Behavior: A Multilevel Moderated Mediation Analysis. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3314. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12083314
Saleem M, Qadeer F, Mahmood F, Ariza-Montes A, Han H. Ethical Leadership and Employee Green Behavior: A Multilevel Moderated Mediation Analysis. Sustainability. 2020; 12(8):3314. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12083314
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaleem, Maria, Faisal Qadeer, Faisal Mahmood, Antonio Ariza-Montes, and Heesup Han. 2020. "Ethical Leadership and Employee Green Behavior: A Multilevel Moderated Mediation Analysis" Sustainability 12, no. 8: 3314. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12083314
APA StyleSaleem, M., Qadeer, F., Mahmood, F., Ariza-Montes, A., & Han, H. (2020). Ethical Leadership and Employee Green Behavior: A Multilevel Moderated Mediation Analysis. Sustainability, 12(8), 3314. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12083314







