Effects of Earthworm Cast Application on Water Evaporation and Storage in Loess Soil Column Experiments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Preparation
2.2. Earthworm Cast Source
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
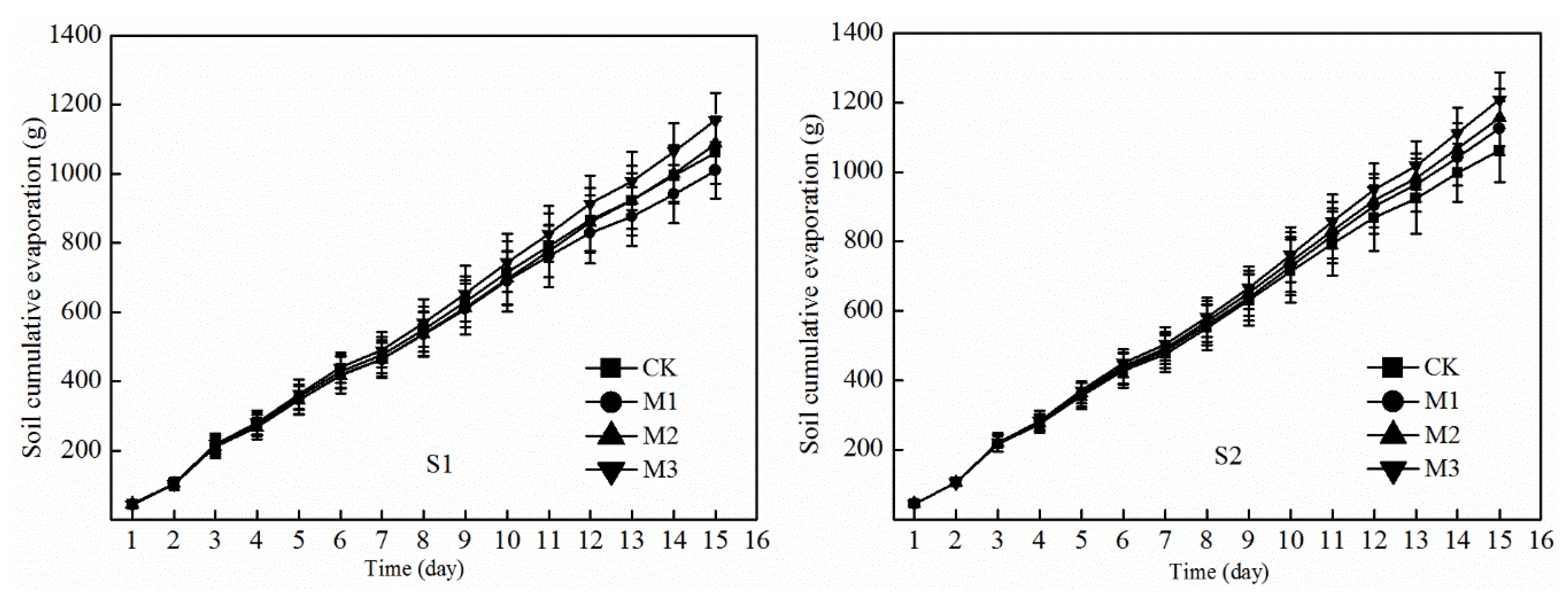
3.1. Soil Evaporation Characteristics
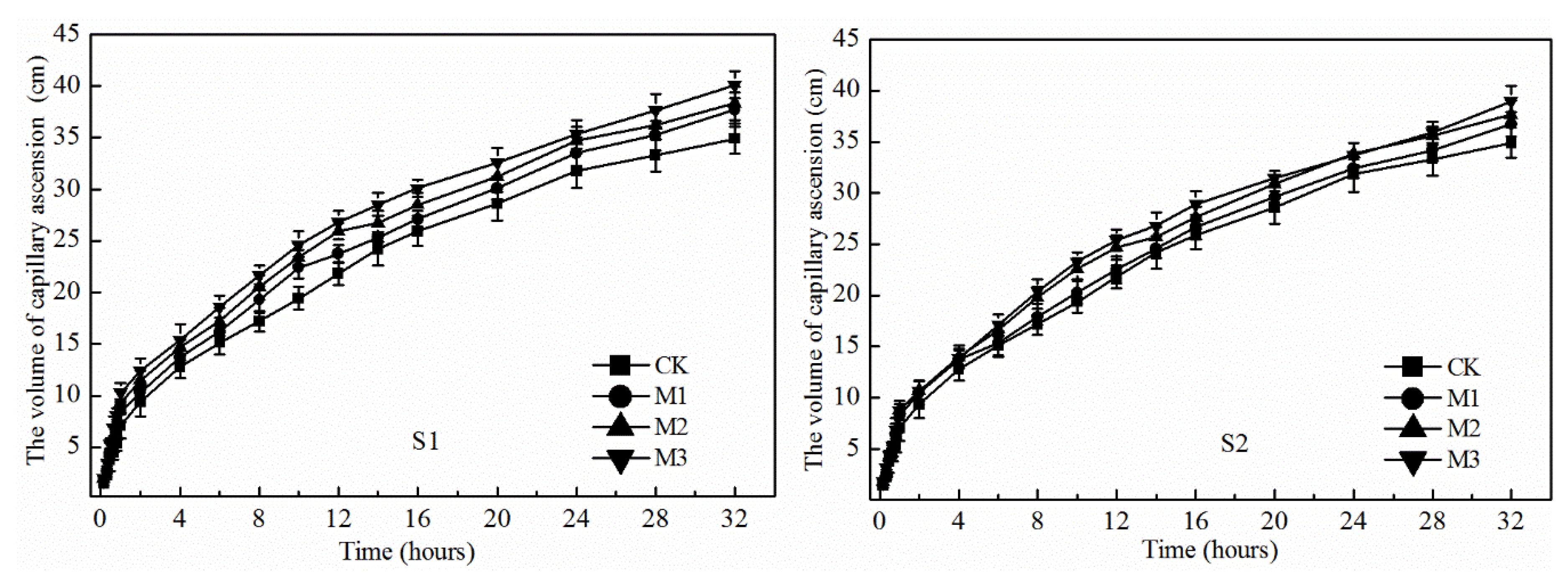
3.2. Capillary Water Upward Movement
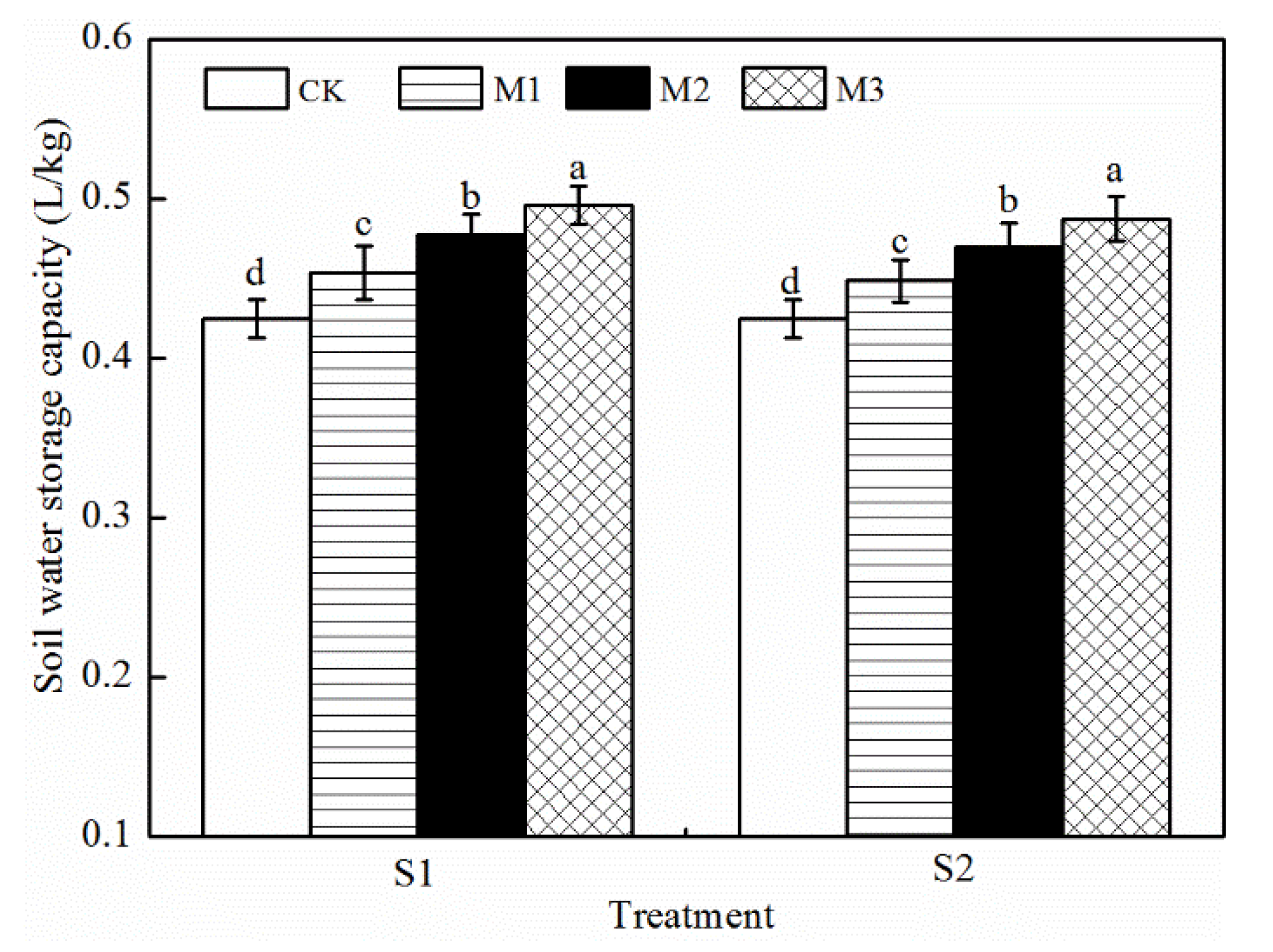
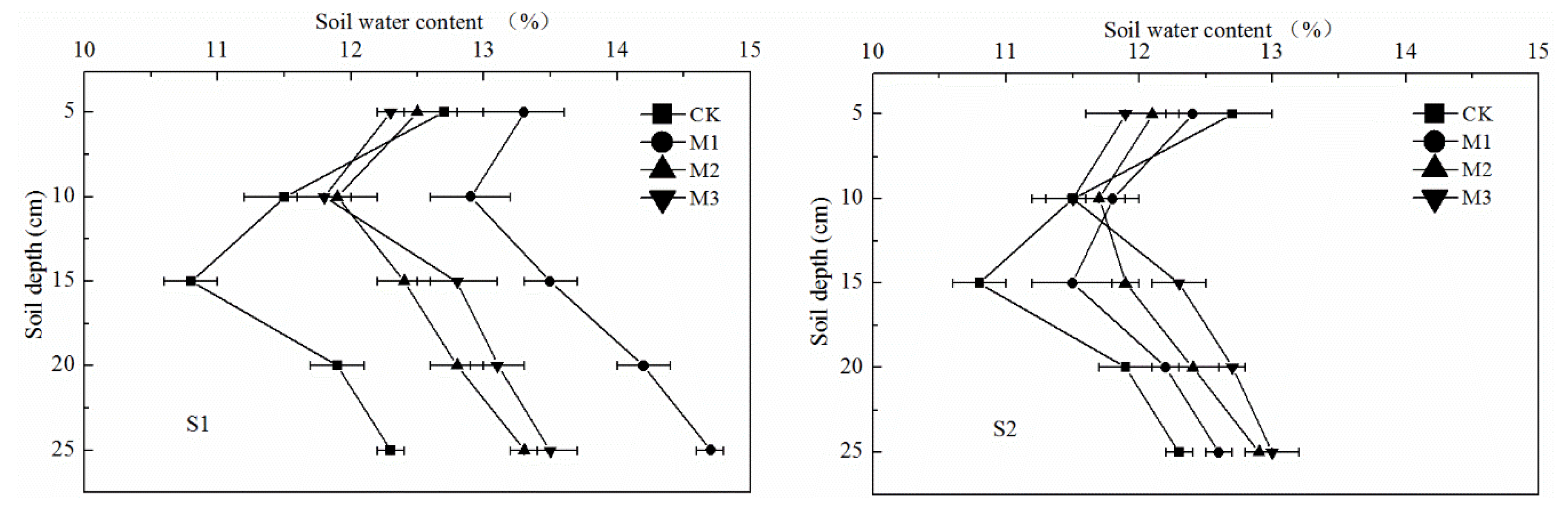
3.3. Soil Water Storage Capacity and Water Profile Distribution
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Earthworm Cast on Soil Evaporation
4.2. Effects of Earthworm Cast on Upward Capillary Water, Soil Water Storage Capacity and Water Profile Distribution
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, X.; Wan, L.; Fang, B.; Cao, W.B.; Wu, S.J.; Hu, F.S.; Feng, W.D. Soil moisture potential and water content in the unsaturated zone within the arid Ejina oasis in northwest China. Environ. Geol. 2004, 46, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durre, T.; Brye, K.R.; Wood, L.S.; Gbur, E.E. Soil moisture regime and mound position effects on soil profile properties in a native tallgrass prairie in northwest Arkansas, USA. Geoderma 2019, 352, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiemann, L.K.; Billings, S.A. Changes in variability of soil moisture alter microbial community C and N resource use. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1837–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Tan, K. Research on the spatial variability of soil moisture. In Computer and Computing Technologies in Agriculture II, Volume 1; Li, D., Zhao, C., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2009; Volume 293, pp. 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, P.K.; Singh, K.C.; Mondal, K.; Nath, R.; Ghosh, P.K.; Kumar, N.; Basu, P.S.; Singh, S.S. Effects of stubble length of rice in mitigating soil moisture stress and on yield of lentil (Lens culinaris medik) in rice-lentil relay crop. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 173, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Jiao, X.; Du, Q.; Song, X.; Li, J. Reducing the excessive evaporative demand improved photosynthesis capacity at low costs of irrigation via regulating water driving force and moderating plant water stress of two tomato cultivars. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 199, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, G.; Malhi, S.S.; Vera, C.L.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, Y. Particle-size effects on soil temperature, evaporation, water use efficiency and watermelon yield in fields mulched with gravel and sand in semi-arid loess plateau of northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wythers, K.R.; Lauenroth, W.K.; Paruelo, J.M. Bare-soil evaporation under semiarid field conditions. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1999, 63, 1341–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmas, C.; Marathianou, M.; Gerontidis, S.; Detsis, V.; Tsara, M.; Poesen, J. Parameters affecting water vapor adsorption by the soil under semi-arid climatic conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 48, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.J.; Sun, S.J.; Zhu, Z.C.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, X.D. Assessing the effects of plant density and plastic film mulch on maize evaporation and transpiration using dual crop coefficient approach. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Zhao, Y.G.; Shao, M.A. Characteristics and numeric simulation of soil evaporation in biological soil crusts. J. Arid. Environ. 2010, 74, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zribi, W.; Aragüés, R.; Medina, E.; Faci, J.M. Efficiency of inorganic and organic mulching materials for soil evaporation control. Soil Till. Res. 2015, 148, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxton, K.E.; Rawls, W.J. Soil water characteristic estimates by texture and organic matter for hydrologic solutions. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2006, 70, 1569–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiz, G.; Wander, F.M.; Pelster, D.E.; Ngetich, W.; Okalebo, J.R.; Rufino, M.C.; Butterbach-Bahl, K. Long-term assessment of soil and water conservation measures (Fanya-juu terraces) on soil organic matter in South Eastern Kenya. Geoderma 2016, 274, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Huang, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Zhang, W.H. Effect of different organic matter content on soil moisture dynamics. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 477–478, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.C.; Larson, W.E. Estimating soil water retention characteristics from particle size distribution, organic matter content, and bulk density. Water Resour. Res. 1979, 15, 1633–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouattara, K.; Ouattara, B.; Assa, A.; Sédogo, P.M. Long-term effect of ploughing, and organic matter input on soil moisture characteristics of a Ferric Lixisol in Burkina Faso. Soil Till. Res. 2006, 88, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuhamdeh, N.H.; Reeder, R.C. Soil thermal conductivity: Effects of density, moisture, salt concentration, and organic matter. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 1285–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekfeldt, J.D.S.; Kjaergaard, C.; Magid, J. Long-term effects of organic waste fertilizers on soil structure, tracer transport, and leaching of colloids. J. Environ. Qual. 2017, 46, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hati, K.M.; Swarup, A.; Mishra, B.; Manna, M.C.; Wanjari, R.H.; Mandal, K.G.; Misra, A.K. Impact of long-term application of fertilizer, manure and lime under intensive cropping on physical properties and organic carbon content of an alfisol. Geoderma 2008, 148, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.L.; Wu, T.Y.; Lim, P.N.; Shak, K.P.Y. The use of vermicompost in organic farming: Overview, effects on soil and economics. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 1143–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dexter, A.R.; Czyz, E.A.; Niedzwiecki, J.; Mackowiak, C. Water retention and hydraulic conductivity of a loam sand soil as influenced by crop rotation and fertilization. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2001, 46, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, T.; Tian, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Li, M.; Wang, S.X.; Wang, Z.H. Improving winter wheat grain yield and water use efficiency through fertilization and mulch in the loess plateau. Agron. J. 2015, 107, 2059–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, R.K.; Power, J.F. Use of crop residue and manure to conserve water and enhance nutrient availability and pearl millet yields in an arid tropical region. Soil Till. Res. 1997, 41, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hati, K.; Swarup, A.; Dwivedi, A.; Misra, A.K.; Bandyopadhyay, K.K. Changes in soil physical properties and organic carbon status at the topsoil horizon of a vertisol of central India after 28 years of continuous cropping, fertilization and manuring. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 119, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.C.; Wang, P.; Li, J.L.; Chen, Y.R.; Ying, X.Z.; Liu, S.Y. The effects of two organic manures on soil properties and crop yields on a temperate calcareous soil under a wheat-maize cropping system. Eur. J. Agron. 2009, 31, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, M.E.; Benito, E.; De Blas, E. Impact of wildfires on surface water repellency in soils of northwest Spain. Hydrol. Process. 2005, 19, 3649–3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A. Short and long-term effects of the endogeie earthworm Millsonia anomala (Omodeo) (Megaseoleeldae, Oligochaeta) of tropical savannas, on soil organic matter. Biol. Fert. Soils 1991, 11, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.J.; Liu, X.C.; Sun, L.H.; Song, C.Y. Earthworm as a potential protein resource. Ecol. Food Nutr. 1997, 36, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, B.N.K. Earthworms: Their Ecology and relationships with soils and land use: By K. E. Lee. Academic Press, Orlando, Florida. 1985. ISBN 0 12 44086005. Price: US $65·00/£55·00. Environ. Pollut. 1985, 42, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaoui, H.I.; Zibilske, L.M.; Ohno, T. Effects of earthworm casts and compost on soil microbial activity and plant nutrient availability. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomati, U.; Grappelli, A.; Galli, E. The hormone-like effect of earthworm casts on plant growth. Biol. Fert. Soils 1988, 5, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senesi, N.; Saiz-Jimenez, C.; Miano, T.M. Spectroscopic characterization of metal-humic acid-like complexes of earthworm-composted organic wastes. Sci. Total Environ. 1992, 117, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco, F.H.; Cegarra, J.; Trujillo, L.M.; Roig, A. Vermicomposting of coffee pulp using the earthworm Eisenia fetida: Effects on C and N contents and the availability of nutrients. Biol. Fert. Soils 1996, 22, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekrem, L.A.; Serdar, S.; Ilker, A. Effect of vermicompost application on soil aggregation and certain physical properties. Land. Degrd. Dev. 2016, 27, 983–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazão, J.; de Goedea, R.G.M.; Capowiez, Y.; Pulleman, M.M. Soil structure formation and organic matter distribution as affected by earthworm species interactions and crop residue placement. Geoderma 2019, 338, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wondafrash, T.T.; Sancho, I.M.; Miguel, V.G.; Serrano, R.E. Relationship between soil color and temperature in the surface horizon of Mediterranean soils. Soil Sci. 2005, 170, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larink, O.; Werner, D.; Langmaack, M.; Schrader, S. Regeneration of compacted soil aggregates by earthworm activity. Biol. Fert. Soils 2001, 33, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marashi, A.R.A.; Scullion, J. Earthworm casts form stable aggregates in physically degraded soils. Biol. Fert. Soils 2003, 37, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atiyeh, R.M.; Edwards, C.A.; Suler, S.; Metzger, J.D. Pig manure vermicompost as a component of a horticultural bedding plant medium: Effects on physico-chemical properties and plant growth. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 78, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeniyi, S.O.; Dexter, A.R. Effect of soil structure on soil water status. Soil Till. Res. 1984, 4, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Vomocil, J.A.; Childs, S.W. Pore size, particle size, aggregate size, and water retention. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1990, 54, 952–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Jia, Z.K.; Liang, L.Y.; Kang, S.Z. Effect of manure management on the temporal variations of dryland soil moisture and water use efficiency of maize. J. Agric. Sci. Techn-Iran. 2013, 15, 1293–1304. [Google Scholar]
- Degens, B.P. The contribution of carbohydrate c and earthworm activity to the water-stable aggregation of a sandy soil. Soil Res. 1997, 35, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, E.; Tuller, M.; Moldrup, P.; Resurreccion, A.C.; Meding, M.S.; Kawamoto, K.; Komatsuf, T.; Jongeg, L.W.D. Soil specific surface area and non-singularity of soil-water retention at low saturations. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2013, 77, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.X.; Wang, Z.H.; Li, S.Q.; Gao, Y.J.; Tian, X.H. Effect of plastic sheet mulch, wheat straw mulch, and maize growth on water loss by evaporation in dryland areas of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 116, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, M.I.; Shalaby, A.A.; AlâOmran, A.M. Water holding capacity and evaporation of calcareous soils as affected by four synthetic polymers. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1995, 26, 2205–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shurbaji, A.R.; Campbell, A.R. Study of evaporation and recharge in desert soil using environmental tracers, New Mexico, USA. Environ. Geol. 1997, 29, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, G.S.; Fraser, P.M. The effects of three earthworm species on soil macroporosity and hydraulic conductivity. Appl. Soil Ecol. 1998, 10, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, L.; Jimenez, J.; Torrese, A.; Amezquitae, E.; Decaens, T. Rainfall impact effects on ageing casts of a tropical anecic earthworm. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2010, 58, 1525–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norgrove, L.; Hauser, S. Production and nutrient content of earthworm casts in a tropical agrisilvicultural system. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 1651–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, S.; Norgrove, L.; Asawalam, D.; Schulz, S. Effect of land use change, cropping systems and soil type on earthworm cast production in West and Central Africa. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2012, 49, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A. Verms and Vermitechnology; APH Publishing Corporation: New Delhi, India, 2005; pp. 23–39. [Google Scholar]
- Albanell, E.; Plaxats, J.; Crbrero, T. Chemical changes during vermicomposting (Elsenia fetida) of sheep manure mixed with cotton industrial wastes. Biol. Fert. Soils 1988, 6, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducharne, A.; Laval, K. Influence of the realistic description of soil water-holding capacity on the global water cycle in a GCM. J. Clim. 2000, 13, 4393–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.C.; Shao, M.A.; Jia, Y.H. Characteristics of soil evaporation and temperature under aggregate mulches created by burrowing ants. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2017, 81, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivannan, S.; Balamurugan, M.; Parthasarathi, K.; Gunasekaran, G.; Ranganathan, L.S. Effect of vermicompost on soil fertility and crop productivity-beans (Phaseolus vulgaris). J. Environ. Biol. 2009, 30, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arancon, N.Q.; Edwards, C.A.; Bierman, P.; Metzger, J.D.; Lee, S.; Welch, C. Effects of vermicomposts on growth and marketable fruits of field-grown tomatoes, peppers and strawberries. Pedobiologia 2003, 47, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guggenberger, G.; Thomas, R.J.; Zech, W. Soil organic matter within earthworm casts of an anecic-endogeic tropical pasture community, Colombia. Appl. Soil Ecol. 1996, 3, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Micro Porosity/% | Effective Porosity/% | Total Porosity/% | Bulk Density/g cm−3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Earthworm cast (1 cm < diameter ≤ 3 cm) | 3.6 ± 0.8 | 57.4 ± 1.6 | 61.1 ± 2.3 | 0.73 ± 0.06 |
| Earthworm cast (3 cm < diameter < 5 cm) | 5.9 ± 1.1 | 51.1 ± 1.3 | 57.4 ± 1.7 | 0.65 ± 0.05 |
| Soil | 1.8 ± 0.7 | 48.2 ± 1.2 | 50.3 ± 1.9 | 1.34 ± 0.08 |
| Application Dose | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | 5% | 7.5% | 10% | ||
| Earthworm cast (1 cm < diameter ≤ 3 cm) | Initial soil water content (%) | 21.1 ± 1.2 | 22.4 ± 1.7 | 23.2 ± 1.4 | 24.6 ± 2.1 |
| Bulk density (g cm−3) | 1.34 ± 0.07 | 1.22 ± 0.05 | 1.19 ± 0.09 | 1.17 ± 0.06 | |
| Total porosity (%) | 50.3 ± 1.9 | 52.6 ± 1.7 | 53.5 ± 1.6 | 55.2 ± 2.4 | |
| Organic matter content (g kg−1) | 5.36 ± 0.32 | 6.12 ± 0.42 | 6.35 ± 0.47 | 6.88 ± 0.53 | |
| Earthworm cast (3 cm < diameter < 5 cm) | Initial soil water content (%) | 21.1 ± 1.2 | 21.9 ± 1.5 | 22.8 ± 1.7 | 24.1 ± 1.2 |
| Bulk density (g cm−3) | 1.34 ± 0.07 | 1.18 ± 0.03 | 1.15 ± 0.04 | 1.10 ± 0.04 | |
| Total porosity (%) | 50.3 ± 1.9 | 53.3 ± 1.1 | 54.1 ± 2.3 | 55.7 ± 2.7 | |
| Organic matter content (g kg−1) | 5.36 ± 0.32 | 6.08 ± 0.37 | 6.31 ± 0.41 | 6.83 ± 0.43 | |
| Parameters | SEAE | Soil Cumulative Evaporation | Deep Water Recharge | Soil Water-Holding Capacity | Soil Water Content | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size | p | 0.043 | 0.036 | 0.015 | 0.023 | 0.033 |
| F | 15.23 | 27.75 | 17.62 | 34.39 | 23.52 | |
| Dose | p | 0.028 | 0.045 | 0.023 | 0.017 | 0.031 |
| F | 7.86 | 11.25 | 21.34 | 43.57 | 29.33 | |
| Size × Dose | p | 0.037 | 0.043 | 0.067 | 0.083 | 0.029 |
| F | 7.15 | 10.34 | 2.15 | 1.73 | 7.42 | |
| Treatment | S1 | S2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K | n | R2 | RMSE | K | n | R2 | RMSE | |
| CK | 1.14624 | 0.50955 | 0.996 | 0.0038 | 1.14624 | 0.50955 | 0.996 | 0.0037 |
| M1 | 1.93526 | 0.4912 | 0.996 | 0.0039 | 1.47256 | 0.5036 | 0.998 | 0.0033 |
| M2 | 2.64726 | 0.47331 | 0.997 | 0.0036 | 2.26941 | 0.48022 | 0.996 | 0.0038 |
| M3 | 2.91617 | 0.44612 | 0.996 | 0.0038 | 2.46439 | 0.47865 | 0.996 | 0.0037 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Shao, M.; Wang, J.; Li, T. Effects of Earthworm Cast Application on Water Evaporation and Storage in Loess Soil Column Experiments. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3112. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12083112
Li Y, Shao M, Wang J, Li T. Effects of Earthworm Cast Application on Water Evaporation and Storage in Loess Soil Column Experiments. Sustainability. 2020; 12(8):3112. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12083112
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yanpei, Mingan Shao, Jiao Wang, and Tongchuan Li. 2020. "Effects of Earthworm Cast Application on Water Evaporation and Storage in Loess Soil Column Experiments" Sustainability 12, no. 8: 3112. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12083112
APA StyleLi, Y., Shao, M., Wang, J., & Li, T. (2020). Effects of Earthworm Cast Application on Water Evaporation and Storage in Loess Soil Column Experiments. Sustainability, 12(8), 3112. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12083112





