Spatio-Temporal Correlation Analysis of Air Quality in China: Evidence from Provincial Capitals Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. The Characteristics of AQI Time Distribution
2.2. The Characteristics of AQI Spatial Distribution
2.3. The Characteristics of AQI Spatio-Temporal Distribution
3. Research Design
3.1. Data Sources
3.2. Research Models
3.2.1. Time Autocorrelation Model
3.2.2. Spatial Autocorrelation Model
3.2.3. Panel Data Model
4. The Temporal Analysis of AQI
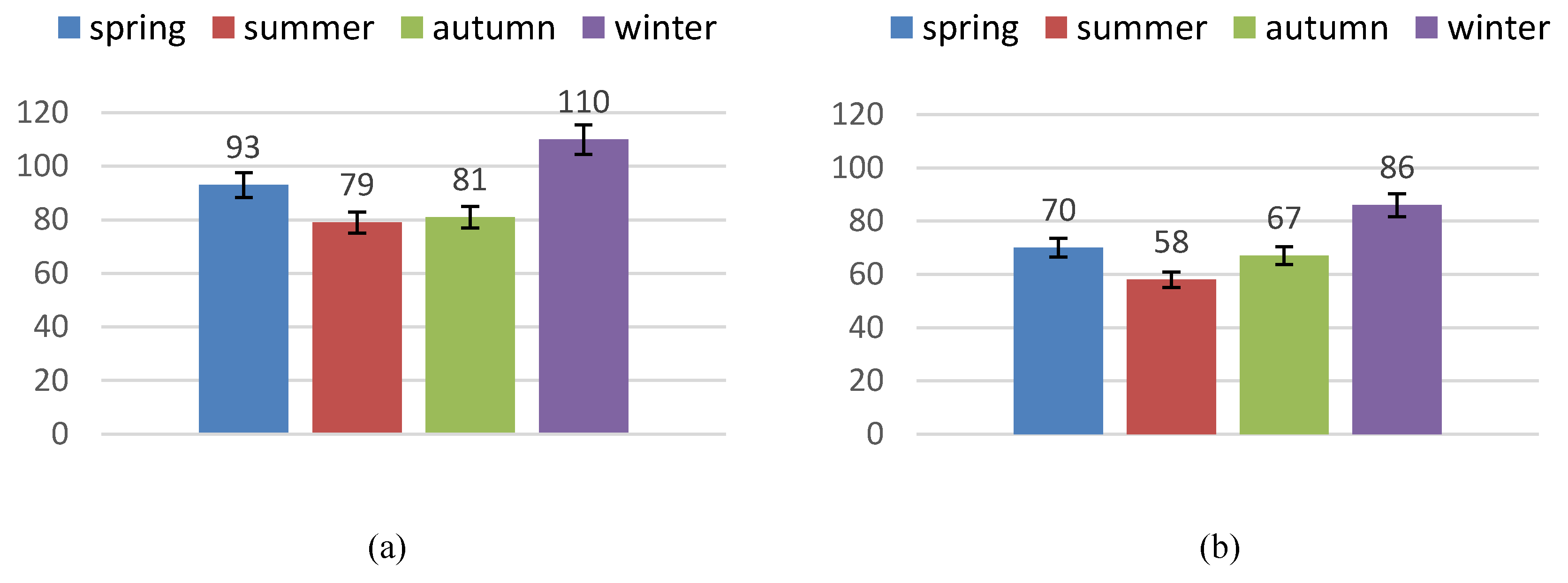
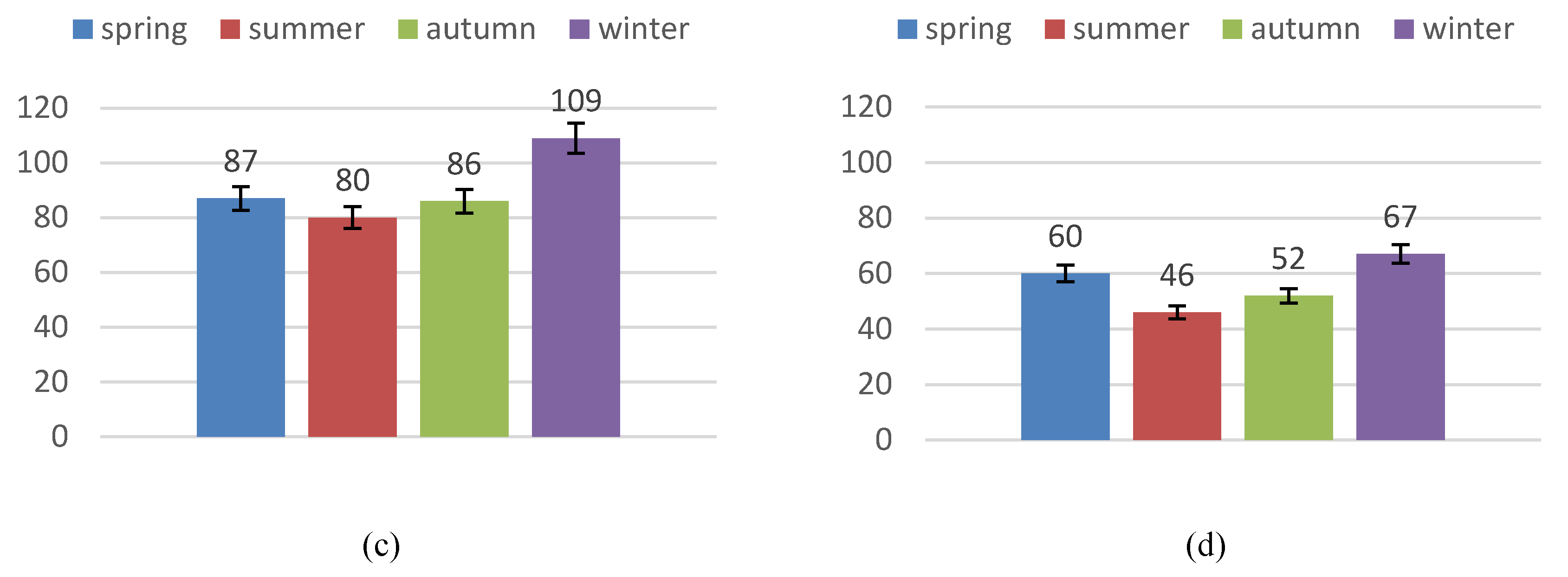
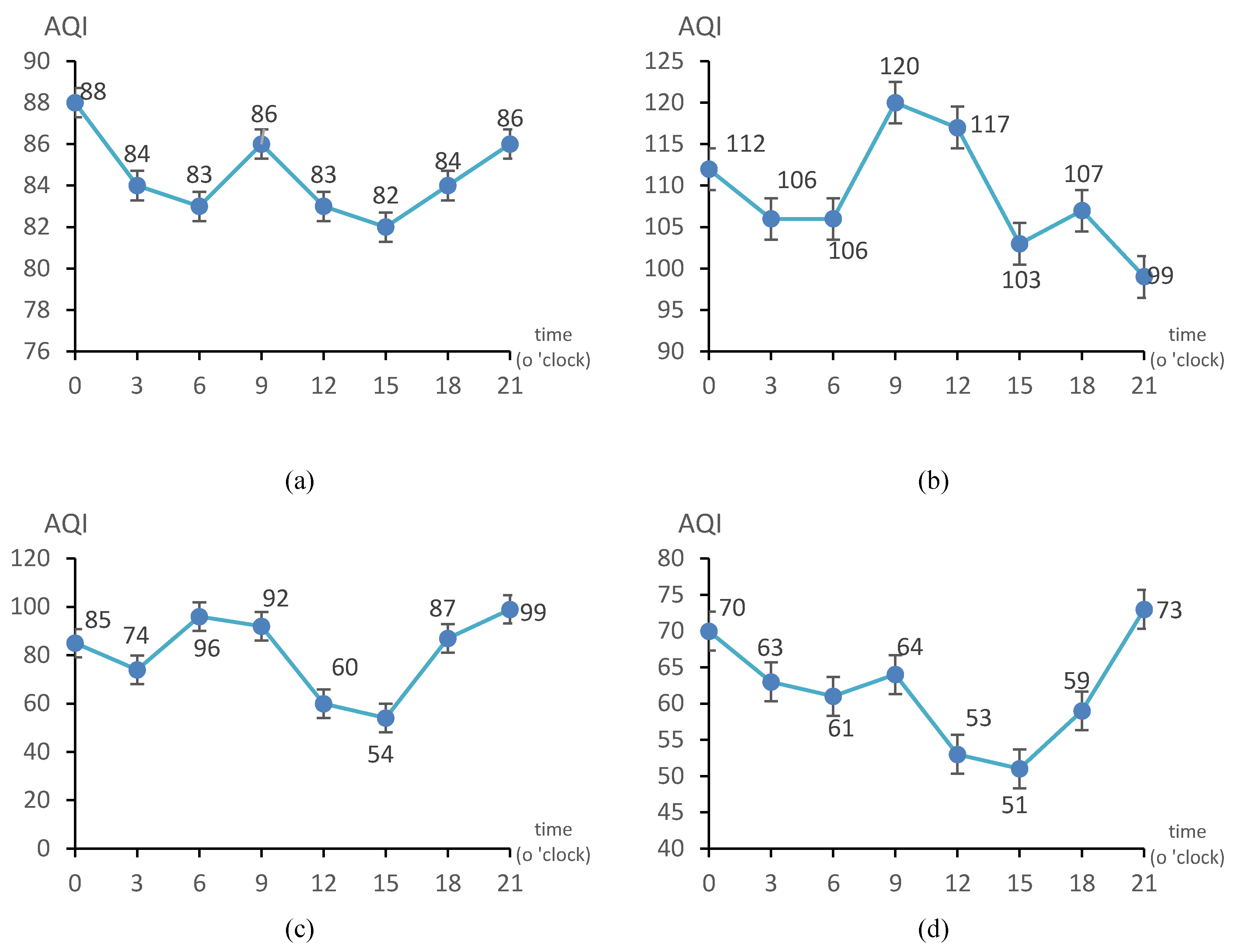
4.1. The Multiscale Temporal Characteristics of AQI’s Change
4.2. Time Autocorrelation Analysis of AQI
5. The Spatial Analysis of AQI
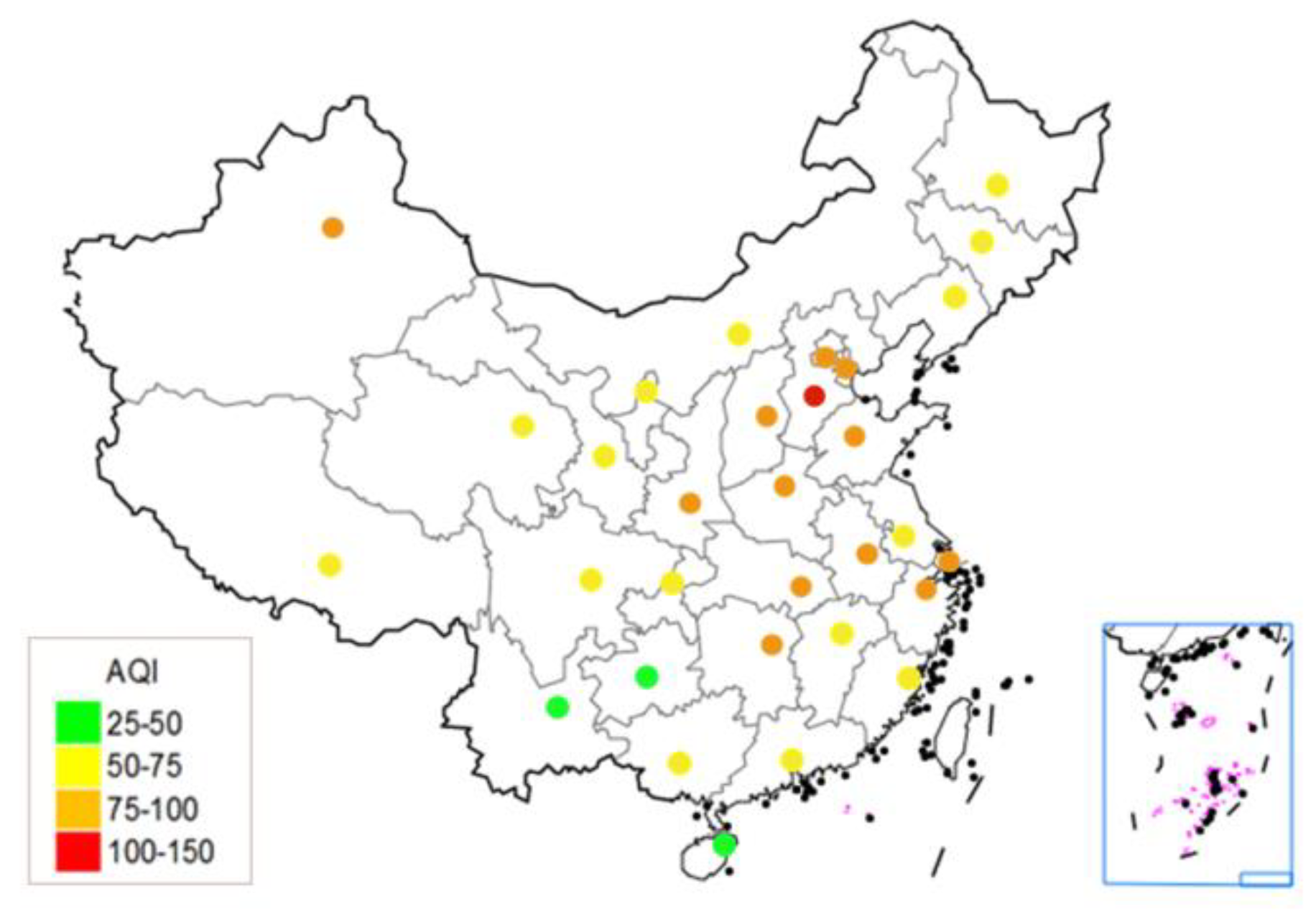
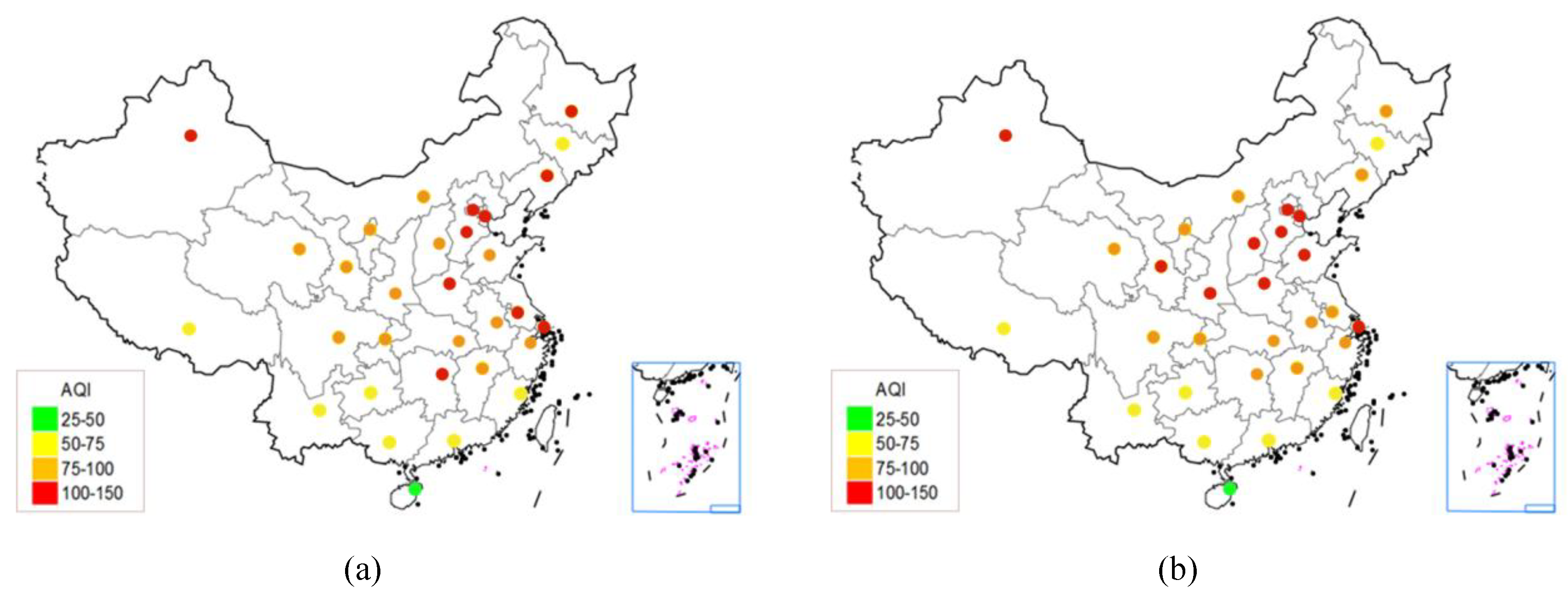
5.1. The Characteristics of Spatial Distribution of AQI
5.2. Spatial Correlation Analysis of AQI
6. Spatio-Temporal Analysis of AQI
6.1. The Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of AQI
6.2. Spatio-Temporal Correlation Analysis of AQI
7. Conclusions and Discussion
7.1. The Characteristics of Air Quality of Chinese Cities Can Be Analyzed on Multiple Time Scales
7.2. The Air Quality of Provincial Capitals in China is Better in the South than in the North, and Better in the Coastal Areas than the Inland Areas
7.3. The Air Quality of Chinese Cities Has Improved From 2015 to 2018.
7.4. The Relationship between the Correlation Coefficient of Chinese Urban Air Quality Has a Lag Period
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xie, R.; Zhao, G.; Zhu, B.Z. Examining the Factors Affecting Air Pollution Emission Growth in China. Environ. Model. Assess. 2018, 23, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.X.; Liu, H.M.; Salvo, A. Severe Air Pollution and Labor Productivity: Evidence from Industrial Towns in China. Am. Econ. J. Appl. Econ. 2019, 11, 173–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, L.; Wang, Z.Z.; Cui, L.L. Air pollution characteristics in China during 2015–2016: Spatiotemporal variations and key meteorological factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 902–915. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.T.; Liu, X.Y.; Wang, Z.B. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of urban air quality in China based on AQI index. J. Guangxi Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2019, 37, 187–196. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Tian, Y.Z.; Xu, W.X.; Wu, J.J.; Tian, L. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of air quality in China in recent 10 years. J. Eco-Environ. 2017, 26, 243–252. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Gu, X.; Ma, G. Spatial and temporal variations of air quality and six air pollutants in China during 2015–2017. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Qi, Q.; Liang, H.; Zhang, A.; Jiang, L.; Ye, Y.; Liu, C.; Huang, Y. Pattern of Spatial Distribution and Temporal Variation of Atmospheric Pollutants during 2013 in Shenzhen. China ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2017, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, D.S.; Kwan, M.P.; Zhang, W.Z. The driving factors of air quality index in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 197, 1342–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.L.; Jiang, Y.J.; Liu, Q.; Xu, D.X.; Zhao, S.D.; He, L.H.; Liu, H.J.; Xu, H. Temporal and spatial trends in air quality in Beijing. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 185, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.J.; Gong, S.L.; Yu, Y. Air pollution characteristics and their relation to meteorological conditions during 2014–2015 in major Chinese cities. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.T.; Wu, Y.Q. Analysis of the spatio-temporal pattern of national air quality based on Moran ‘I index. J. Nat. Disasters 2018, 27, 107–113. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.G.; Han, S.M.; Cui, D.Y. Discussion on the statistics of spatial autocorrelation analysis. Chin. J. Schistosomiasis Control 2008, 20, 315–318. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, C.; Liu, H.; Li, G.; Sun, D.; Miao, Z. Estimating the Impact of Urbanization on Air Quality in China Using Spatial Regression Models. Sustainability 2015, 7, 15570–15592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.R.; Zhu, L.B.; Zhou, K.S. Spatial autocorrelation analysis of air quality index (AQI) in eastern China based on residuals of time series models. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2017, 37, 2459–2467. [Google Scholar]
- Dadhich, A.P.; Goyal, R.; Dadhich, P.N. Assessment of spatio-temporal variations in air quality of Jaipur city, Rajasthan, India. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2018, 21, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.J.; Du, G.J. Spatial pattern and distribution of air pollution in Chinese cities: An empirical study based on 161 AQI and 6 sub-pollutants. Econ. Geogr. 2016, 36, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Yang, X.; Wang, M.; Long, Y.; Shen, H.; Nie, Y.; Chen, L.; Guo, H.; Jia, F.; Nelson, J.; et al. Climate Change, Air Quality and Urban Health: Evidence from Urban Air Quality Surveillance System in 161 Cities of China 2014. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2018, 6, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, J.; Fu, Y.P. Spatial econometric analysis of air quality in provinces in China. Sci. Technol. Bull. 2018, 34, 256–260. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Tian, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X. Understanding the Spatio-Temporal Patterns and Influential Factors on Air Quality Index: The Case of North China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wang, H.; Wei, Y. Endogenous or Exogenous? Examining Trans-Boundary Air Pollution by Using the Air Quality Index (AQI): A Case Study of 30 Provinces and Autonomous Regions in China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.F.; Zhang, M.J.; Wang, S.J. Analysis of the characteristics and influencing factors of China’s air pollution index. Environ. Sci. 2012, 33, 1936–1943. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, H.; Luo, K.; Wang, P. Spatial variation of air quality index and urban driving factors linkages: Evidence from Chinese cities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.P.; Yu, Y.; Yin, D.Y.; He, J.J.; Liu, N.; Qu, J.J.; Xiao, J.H. Annual and diurnal variations of gaseous and particulate pollutants in 31 provincial capital cities based on in situ air quality monitoring data from China National Environmental Monitoring Center. Environ. Int. 2016, 86, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhou, J.X.; Guo, Y. Spatiotemporal pattern of air quality index and its associated factors in 31 Chinese provincial capital cities. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2017, 10, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.P.; Wu, J.G.; Yu, D.Y. Characterizing spatiotemporal patterns of air pollution in China: A multiscale landscape approach. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 76, 344–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.L. Cluster analysis of air quality panel data of major cities in China. Mod. Bus. Ind. 2014, 07, 12–13. [Google Scholar]
- Boyce, M.S.; Pitt, J.; Northrup, J.M.; Morehouse, A.T.; Knopff, K.H.; Cristescu, B.; Stenhouse, G.B. Temporal autocorrelation functions for movement rates from global positioning system radiotelemetry data. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 2213–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, H.W.; Yang, J. Research on Influencing Factors of Air Pollution in China—Analysis Based on China’s Urban Dynamic Spatial Panel Model. J. Hohai Univ. 2017, 19, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Modarres, R.; Dehkordi, A.K. Daily air pollution time series analysis of Isfahan City. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 2, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, W.; Nakhlé, M.M.; Abboud, M. Time series analysis of air pollutants in Beirut. Lebanon. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 8203–8213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, O.; Lange, H. Trends of air pollution in the Fichtelgebirge Mountains Bavaria. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. 1999, 6, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiang, S. A note on fuzzy time series model selection with sample autocorrelation functions. Cybern. Syst. 2010, 93–107. [Google Scholar]
- Getis, A. Spatial Autocorrelation. Handbook of Applied Spatial Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 255–278. [Google Scholar]
- Tiefelsdorf, M. The saddlepoint approximation of Moran’s I’s and local Moran’s Ii’s reference distributions and their numerical evaluation. Geogr. Anal. 2002, 34, 187–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhorst, J.P. Spatial Panel Data Models. In Spatial Econometrics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 37–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.M.; Scherngell, T.; Reismann, M. Knowledge Spillovers and Total Factor Productivity: Evidence Using a Spatial Panel Data Model. Geogr. Anal. 2009, 41, 204–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhorst, J.P. Specification and Estimation of Spatial Panel Data Models. Int. Reg. Sci. Rev. 2003, 26, 244–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltagi, B.H.; Song, S.H.; Koh, W. Testing panel data regression models with spatial error correlation. J. Econ. 2003, 117, 123–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halaby, C.N. Panel Models in Sociological Research: Theory into Practice. Ann. Rev. Sociol. 2004, 30, 507–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, S.; Delgado, M.; Henderson, D.; Parmeter, C. Fixed vs Random: The Hausman Test Four Decades Later. Adv. Econ. 2012, 29, 479–513. [Google Scholar]
- Mutl, J.; Pfaffermayr, M. The Hausman test in a Cliff and Ord panel model. Econ. J. 2011, 14, 48–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; You, S.J.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, W.D.; Zheng, X.J.; Jia, J.; Ye, T.Z.; Zou, L.J. Modelling of AQI related to building space heating energy demand based on big data analytics. Appl. Energy 2017, 203, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ding, A.J.; Mao, H.T.; Nie, W.; Zhou, D.R.; Liu, L.X.; Huang, X.; Fu, C.B. Impact of synoptic weather patterns and inter-decadal climate variability on air quality in the North China Plain during 1980–2013. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 124, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Wang, Z.H.; Wang, C. Biospheric and anthropogenic contributors to atmospheric CO2 variability in a residential neighborhood of Phoenix, Arizona. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 3317–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, P.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Wei, F.; Zhang, J. A Review of Air Pollution and Control in Hebei Province, China. Open J. Air Pollut. 2013, 2, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Xu, J.; Jia, M.; Li, H.; Wang, S. Influence of Straw Burning on Urban Air Pollutant Concentrations in Northeast China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, J.; Yang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yu, C.; Li, X. The Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of Air Pollution in China from 2001–2014. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 15875–15887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Kobernus, M.; Liu, H. Public Perception Survey Study on Air Quality Issues in Wuhan, China. J. Environ. Prot. 2017, 8, 1194–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Tang, H.Z.; Zhao, H.M. Urban air quality evaluations under two versions of the national ambient air quality standards of China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2016, 7, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, E.; Zhang, T. Spatial and Temporal Patterns of Air Pollution in Chinese Cities. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, C.; Myint, S.W.; Wang, Z.H. Landscape determinants of spatio-temporal patterns of aerosol optical depth in the two most polluted metropolitans in the United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 1556–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
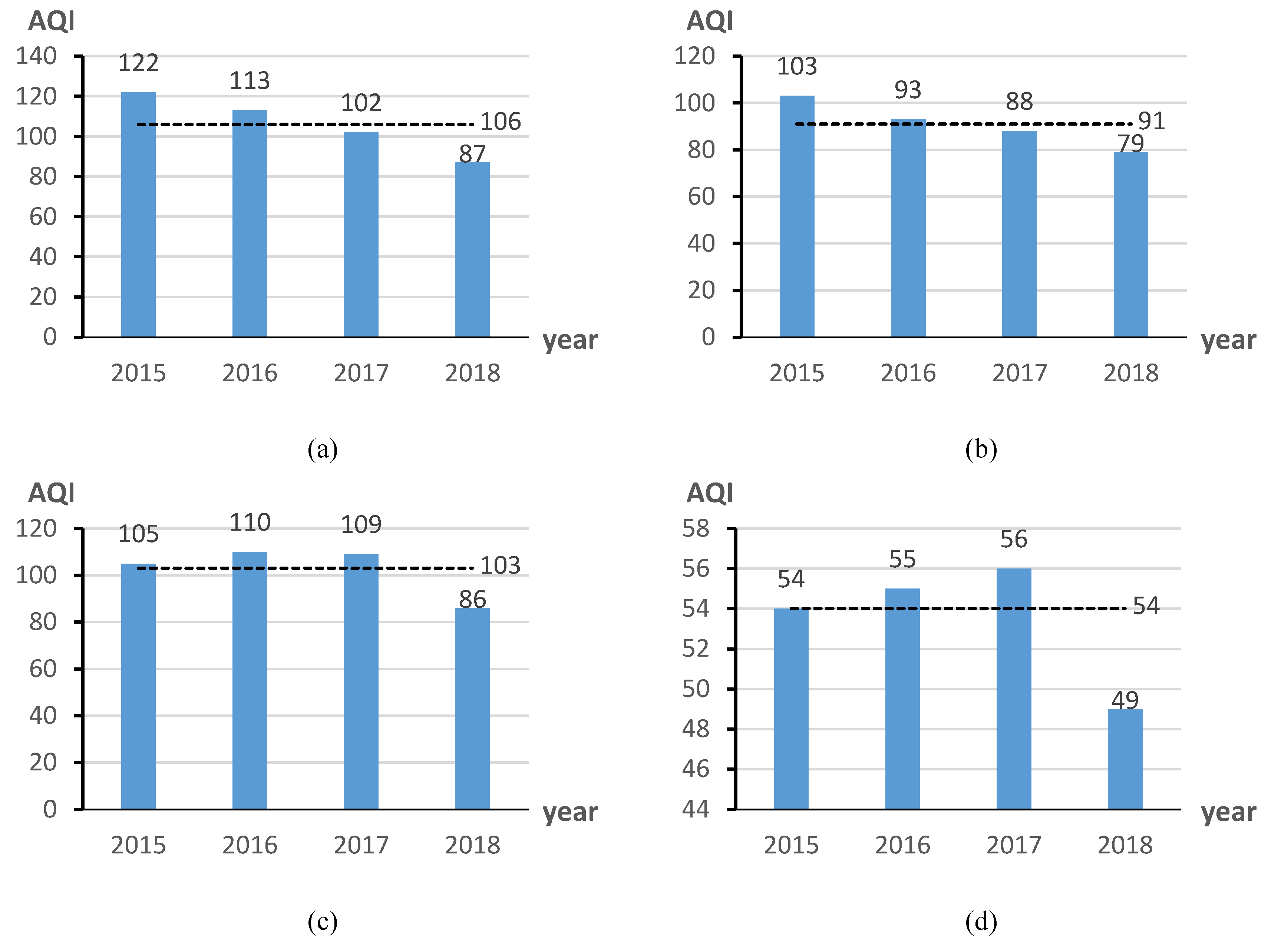

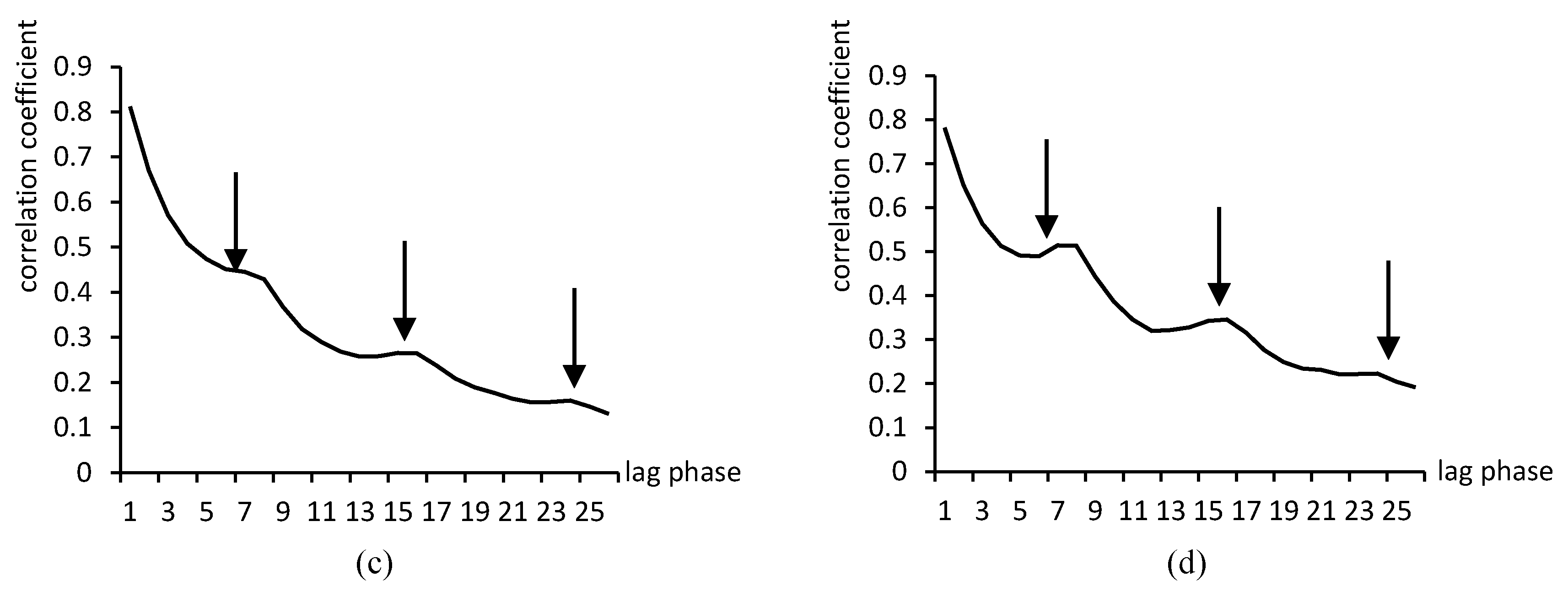
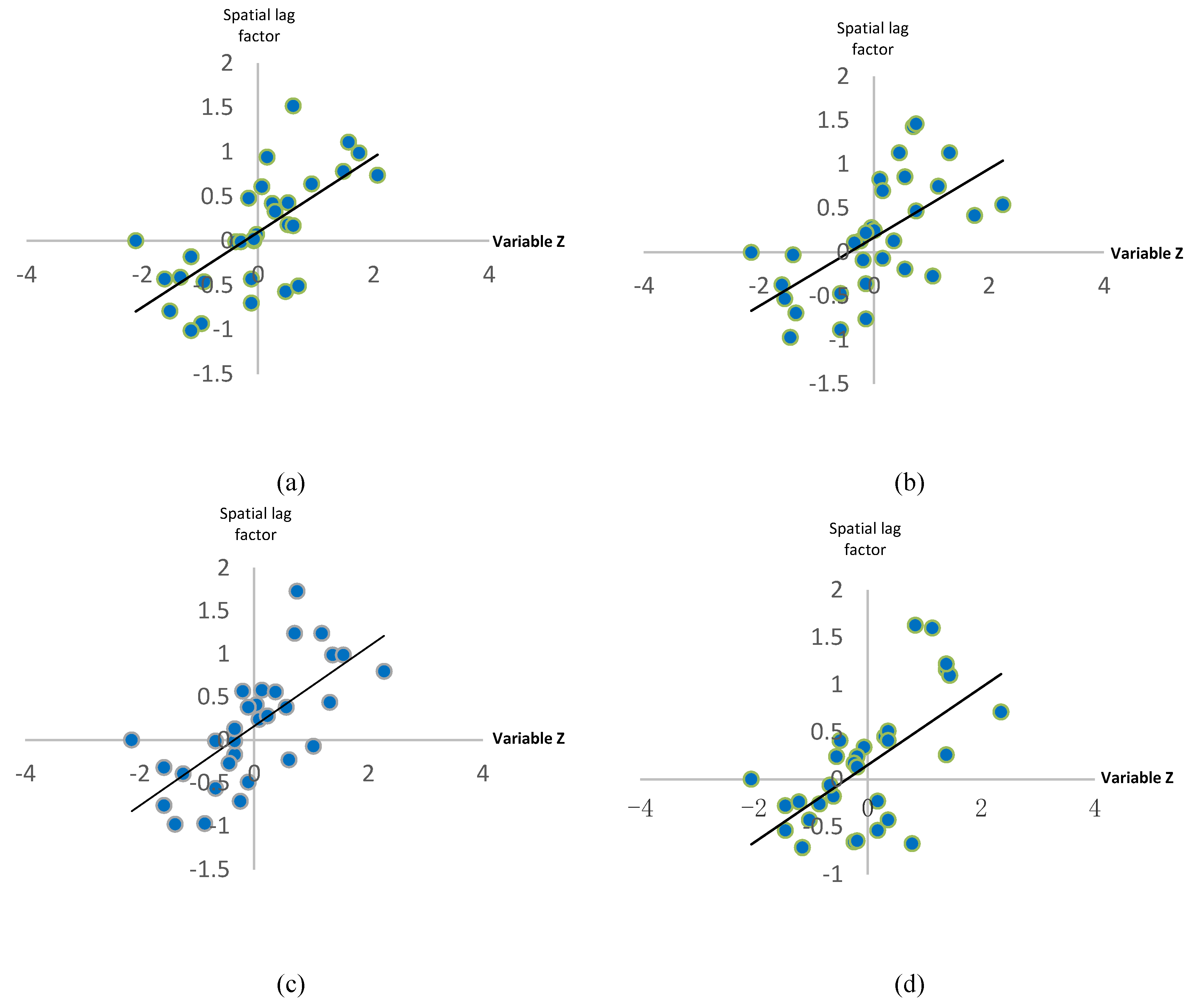
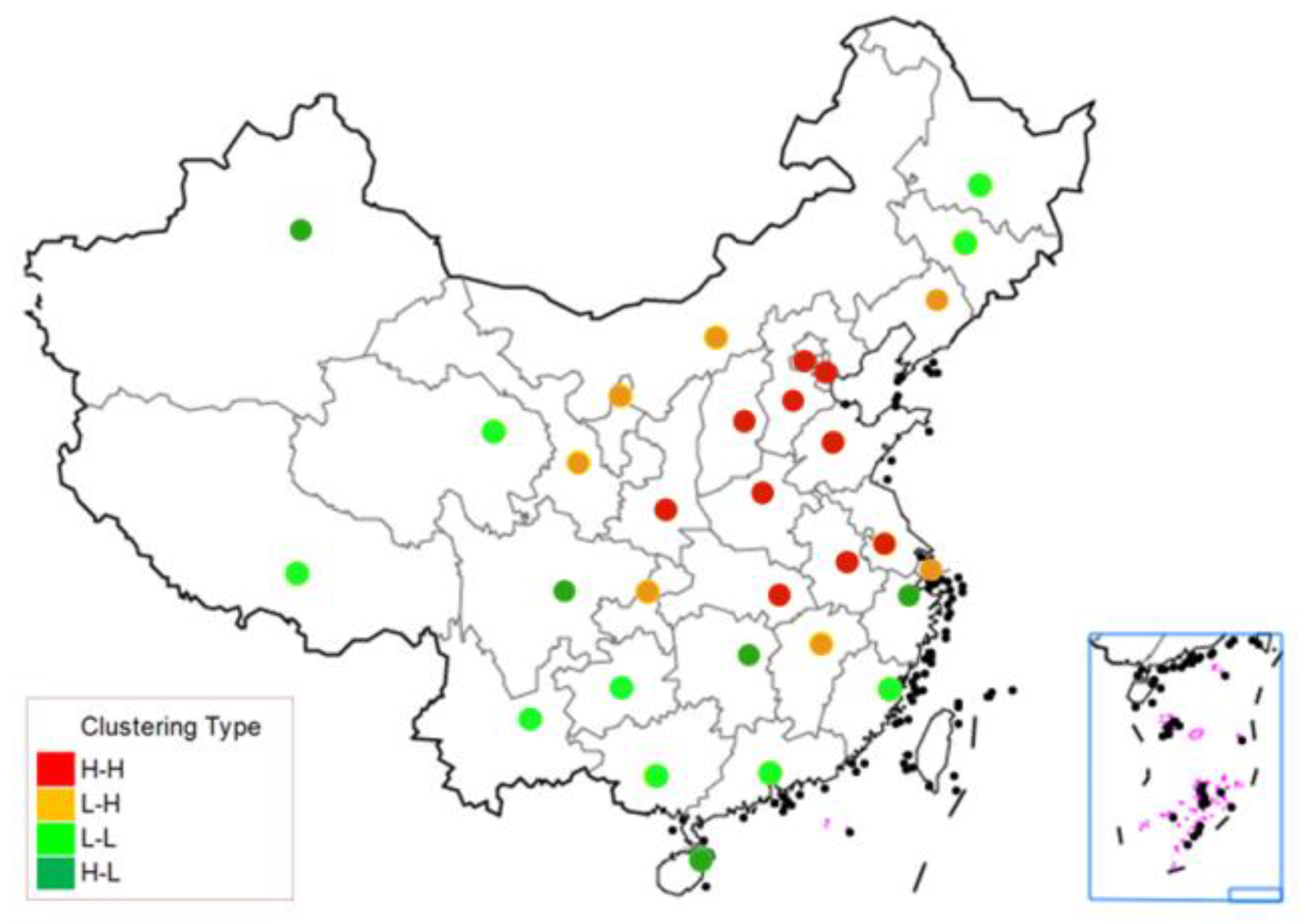

| Lag | BJ | HZ | CQ | SY | FZ | NN | GZ | HEB | TY | KM | YC | CC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| City | |||||||||||||
| 1 | 0.83 | 0.81 | 0.80 | 0.78 | 0.77 | 0.78 | 0.77 | 0.63 | 0.70 | 0.72 | 0.72 | 0.63 | |
| 2 | 0.69 | 0.67 | 0.67 | 0.61 | 0.65 | 0.65 | 0.64 | 0.43 | 0.55 | 0.54 | 0.54 | 0.42 | |
| 3 | 0.60 | 0.57 | 0.58 | 0.51 | 0.56 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.40 | 0.45 | 0.47 | 0.42 | 0.31 | |
| 4 | 0.53 | 0.51 | 0.53 | 0.47 | 0.49 | 0.51 | 0.51 | 0.34 | 0.34 | 0.44 | 0.34 | 0.29 | |
| 5 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 0.51 | 0.44 | 0.45 | 0.49 | 0.49 | 0.28 | 0.32 | 0.42 | 0.29 | 0.26 | |
| 6 | 0.43 | 0.45 | 0.51 | 0.44 | 0.43 | 0.49 | 0.49 | 0.25 | 0.26 | 0.43 | 0.26 | 0.27 | |
| 7 | 0.40 | 0.45 | 0.51 | 0.47 | 0.41 | 0.52 | 0.49 | 0.30 | 0.24 | 0.52 | 0.23 | 0.34 | |
| 8 | 0.38 | 0.43 | 0.49 | 0.46 | 0.39 | 0.51 | 0.50 | 0.31 | 0.25 | 0.58 | 0.22 | 0.35 | |
| 9 | 0.33 | 0.37 | 0.44 | 0.41 | 0.36 | 0.44 | 0.45 | 0.25 | 0.20 | 0.47 | 0.17 | 0.31 | |
| 10 | 0.28 | 0.32 | 0.38 | 0.35 | 0.31 | 0.39 | 0.40 | 0.19 | 0.21 | 0.35 | 0.14 | 0.21 | |
| 11 | 0.24 | 0.29 | 0.34 | 0.30 | 0.28 | 0.35 | 0.37 | 0.20 | 0.22 | 0.32 | 0.12 | 0.21 | |
| 12 | 0.22 | 0.27 | 0.32 | 0.28 | 0.26 | 0.32 | 0.35 | 0.17 | 0.20 | 0.31 | 0.12 | 0.22 | |
| 13 | 0.21 | 0.26 | 0.32 | 0.27 | 0.25 | 0.32 | 0.35 | 0.12 | 0.23 | 0.31 | 0.15 | 0.22 | |
| 14 | 0.19 | 0.26 | 0.33 | 0.28 | 0.27 | 0.33 | 0.36 | 0.13 | 0.24 | 0.32 | 0.17 | 0.23 | |
| 15 | 0.17 | 0.27 | 0.33 | 0.29 | 0.27 | 0.34 | 0.36 | 0.17 | 0.22 | 0.39 | 0.17 | 0.23 | |
| 16 | 0.16 | 0.27 | 0.31 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.35 | 0.38 | 0.20 | 0.24 | 0.44 | 0.16 | 0.27 | |
| 17 | 0.13 | 0.24 | 0.28 | 0.23 | 0.26 | 0.32 | 0.34 | 0.13 | 0.21 | 0.36 | 0.13 | 0.22 | |
| 18 | 0.11 | 0.21 | 0.23 | 0.20 | 0.24 | 0.28 | 0.29 | 0.11 | 0.22 | 0.27 | 0.11 | 0.19 | |
| 19 | 0.10 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.22 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.13 | 0.23 | 0.26 | 0.12 | 0.17 | |
| 20 | 0.08 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.20 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.13 | 0.21 | 0.27 | 0.13 | 0.16 | |
| 21 | 0.07 | 0.16 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.21 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.11 | 0.21 | 0.27 | 0.12 | 0.13 | |
| 22 | 0.07 | 0.16 | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.21 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.13 | 0.19 | 0.30 | 0.12 | 0.16 | |
| 23 | 0.06 | 0.16 | 0.19 | 0.20 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.37 | 0.12 | 0.19 | |
| 24 | 0.07 | 0.16 | 0.19 | 0.20 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.21 | 0.19 | 0.42 | 0.14 | 0.20 | |
| 25 | 0.05 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.20 | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.34 | 0.13 | 0.15 | |
| Year | Moran’s I |
|---|---|
| 2015 | 0.406 |
| 2016 | 0.458 |
| 2017 | 0.386 |
| 2018 | 0.384 |
| Method | Statistic | Prob. | Cross-Sections | Obs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Null: Unit root (assumes common unit root process) | ||||
| Levin, Lin & Chu t | −20.4271 | 0.0000 | 31 | 90,209 |
| Null: Unit root (assumes individual unit root process) | ||||
| Im, Pesaran and Shin W-stat | −49.4335 | 0.0000 | 31 | 90,209 |
| ADF-Fisher Chi-square | 2360.07 | 0.0000 | 31 | 90,209 |
| PP-Fisher Chi-square | 6139.39 | 0.0000 | 31 | 90,489 |
| Autocorrelation | Partial Correlation | AC | PAC | Q-Stat | Prob | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
  | 1 | 0.809 | 0.809 | 1910.8 | 0.000 | |
| 2 | 0.686 | 0.093 | 3286.8 | 0.000 | ||
| 3 | 0.599 | 0.060 | 4335.7 | 0.000 | ||
| 4 | 0.533 | 0.043 | 5166.2 | 0.000 | ||
| 5 | 0.481 | 0.036 | 5844.3 | 0.000 | ||
| 6 | 0.447 | 0.051 | 6429.5 | 0.000 | ||
| 7 | 0.421 | 0.041 | 6949.8 | 0.000 | ||
| 8 | 0.400 | 0.033 | 7419.2 | 0.000 | ||
| 9 | 0.363 | -0.028 | 7804.9 | 0.000 | ||
| 10 | 0.325 | -0.014 | 8114.7 | 0.000 | ||
| 11 | 0.311 | -0.011 | 8532.5 | 0.000 | ||
| Lag | LogL | LR | FPE | AIC | SC | HQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | −20,829.83 | NA | 250,447.4 | 18.10676 | 18.11175 | 18.10858 |
| 1 | −19,094.51 | 3466.109 | 55,612.60 | 16.60192 | 16.61689 | 16.60738 |
| 2 | −18,989.31 | 209.9356 | 50,929.95 | 16.51396 | 16.53891 | 16.52306 |
| 3 | −18,843.40 | 290.9283 | 45,019.99 | 16.39062 | 16.42555 | 16.40335 |
| 4 | −18,651.82 | 381.6724 | 38,246.79 | 16.22757 | 16.27248 | 16.24394 |
| 5 | −18,371.40 | 558.1535 | 30,078.22 | 15.98731 | 16.04220 | 16.00732 |
| 6 | −18,001.50 | 735.6164 | 21,884.26 | 15.66928 | 15.73415 | 15.69293 |
| 7 | −17,794.42 | 411.4690 | 18,343.02 | 15.49276 | 15.56761 | 15.52005 |
| 8 | −17,421.06 | 741.2064 | 13,305.87 | 15.17171 | 15.25655 | 15.20264 |
| Variable | Coefficient | Std. Error | t-Statistic | Prob. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 7.094672 | 0.187074 | 37.92441 | 0.0000 |
| AQI(-1) | 0.615542 | 0.003315 | 185.6643 | 0.0000 |
| AQI(-2) | 0.083921 | 0.003896 | 21.53917 | 0.0000 |
| AQI(-3) | 0.033636 | 0.003906 | 8.611525 | 0.0000 |
| AQI(-4) | 0.028408 | 0.003901 | 7.281393 | 0.0000 |
| AQI(-5) | 0.014703 | 0.003898 | 3.772412 | 0.0002 |
| AQI(-6) | 0.005298 | 0.003896 | 1.359862 | 0.1739 |
| AQI(-7) | 0.020360 | 0.003884 | 5.241592 | 0.0000 |
| AQI(-8) | 0.082582 | 0.003301 | 25.01919 | 0.0000 |
| Variable | Coefficient | Std. Error | t-Statistic | Prob. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 8.533101 | 0.198580 | 42.97050 | 0.0000 |
| AQI(-1) | 0.610168 | 0.003317 | 183.9326 | 0.0000 |
| AQI(-2) | 0.081511 | 0.003889 | 20.96025 | 0.0000 |
| AQI(-3) | 0.031613 | 0.003898 | 8.110045 | 0.0000 |
| AQI(-4) | 0.026505 | 0.003893 | 6.807735 | 0.0000 |
| AQI(-5) | 0.012783 | 0.003890 | 3.286554 | 0.0010 |
| AQI(-6) | 0.003301 | 0.003888 | 0.849068 | 0.3958 |
| AQI(-7) | 0.017961 | 0.003877 | 4.632740 | 0.0000 |
| AQI(-8) | 0.077332 | 0.003302 | 23.41681 | 0.0000 |
| Fixed Effects (Cross) | ||||
| BJ--C | 2.068339 | |||
| HK--C | −4.426904 | |||
| CQ--C | −2.484907 | |||
| FZ--C | −3.537358 | |||
| WLMQ--C | 3.239456 | |||
| CD--C | −0.132934 | |||
| NC--C | −1.155403 | |||
| JN--C | 4.455403 | |||
| SH--C | −1.341894 | |||
| LZ--C | 2.365996 | |||
| HF--C | 0.321737 | |||
| HHHT--C | 1.017041 | |||
| HEB--C | −2.088062 | |||
| NN--C | −1.338221 | |||
| TJ--C | 2.047075 | |||
| TY--C | 4.706302 | |||
| GZ--C | −2.110657 | |||
| LS--C | −3.515151 | |||
| KM--C | −1.849293 | |||
| HZ--C | −2.079130 | |||
| WH--C | 0.349940 | |||
| SY--C | −1.310719 | |||
| SJZ--C | 5.808012 | |||
| XA--C | 4.003164 | |||
| GY--C | −2.614649 | |||
| ZZ--C | 3.647143 | |||
| YC--C | 2.355495 | |||
| CC--C | −0.837571 | |||
| CS--C | −0.675244 | |||
| NJ--C | 0.166678 | |||
| XN--C | 0.557123 |
| Effects Test | Statistic | d.f. | Prob. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cross-section F | 15.003473 | (30,90233) | 0.0000 |
| Cross-section Chi-square | 449.179363 | 30 | 0.0000 |
| Test Summary | Chi-Sq. Statistic | Chi-Sq.d.f. | Prob. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cross-section random | 450.042246 | 8 | 0.0000 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Liu, T.; Zhao, X. Spatio-Temporal Correlation Analysis of Air Quality in China: Evidence from Provincial Capitals Data. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2486. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12062486
Liu Q, Li X, Liu T, Zhao X. Spatio-Temporal Correlation Analysis of Air Quality in China: Evidence from Provincial Capitals Data. Sustainability. 2020; 12(6):2486. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12062486
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Qingchen, Xinyi Li, Tao Liu, and Xiaojun Zhao. 2020. "Spatio-Temporal Correlation Analysis of Air Quality in China: Evidence from Provincial Capitals Data" Sustainability 12, no. 6: 2486. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12062486
APA StyleLiu, Q., Li, X., Liu, T., & Zhao, X. (2020). Spatio-Temporal Correlation Analysis of Air Quality in China: Evidence from Provincial Capitals Data. Sustainability, 12(6), 2486. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12062486




