Morphological Intervention in Promoting Higher-Order Reading Abilities among College-Level Second Language Learners
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Review of Literature
3. Method
3.1. Participants
3.2. Intervention
Undaunted, they continued in their spare time, late at night by candlelight, to pour out their pent-up emotion, writing of what they knew best, of women in conflict with their natural desires and social condition- in reality, less fiction than autobiography!
3.3. Data Collection Procedure
3.4. Measurement
3.4.1. Pre-test Control Variables
3.4.2. Post-test Outcome Variables
- Morpheme form knowledge
- Morpheme meaning knowledge
- Pseudoword inference
- Real word inference
- Text comprehension
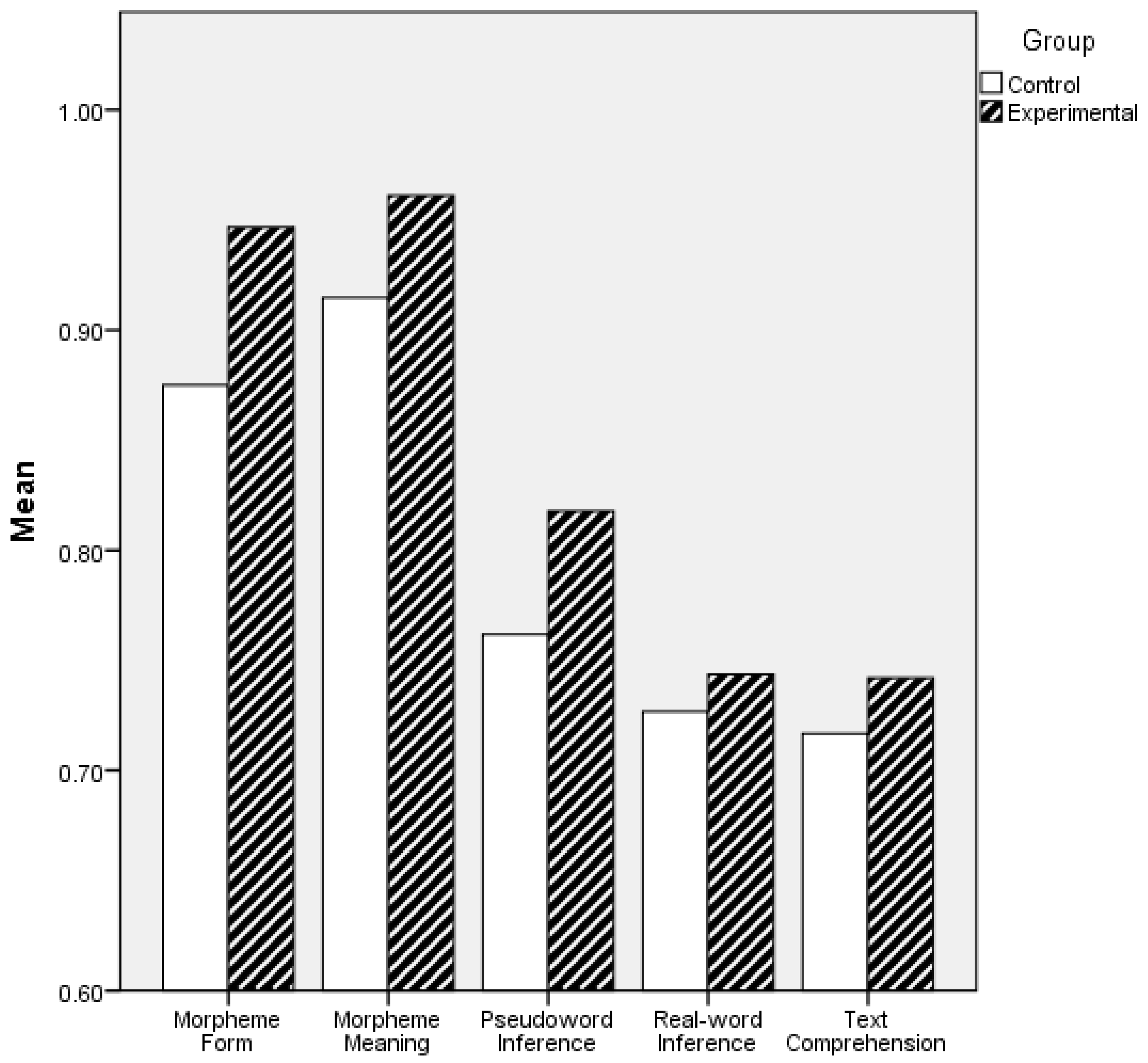
4. Results
4.1. Descriptive analyses of the pre-test and post-test results
4.2. MANOVA analyses of outcome variables
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions and Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paran, A.; Williams, E. Reading and literacy in developing countries. J. Res. Read. 2007, 30, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trudell, B. Local-language literacy and sustainable development in Africa. Int. J. Educ. Dev. 2009, 29, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassool, N. Literacy for Sustainable Development in the Age of Information; Multilingual Matters: Clevedon, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Koda, K. Insights into Second Language Reading: A Cross-Linguistic Approach; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Pasquarella, A.; Chen, X.; Lam, K.; Luo, Y.C.; Ramirez, G. Cross-language transfer of morphological awareness in Chinese–English bilinguals. J. Res. Read. 2011, 34, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.S. Morphological awareness in vocabulary acquisition among Chinese-speaking children: Testing partial mediation via lexical inference ability. Read. Res. Q. 2015, 50, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieffer, M.J.; Lesaux, N.K. Breaking down words to build meaning: Morphology, vocabulary, and reading comprehension in the urban classroom. Read. Teach. 2007, 61, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Packard, J.L. The Morphology of Chinese: A Linguistic and Cognitive Approach; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.S. Testing reciprocity between lexical knowledge and reading comprehension among Chinese children: A cross-lagged panel analysis. Eur. J. Psychol. Educ. 2020, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hao, M.; Geva, E.; Zhu, J.; Shu, H. The role of compound awareness in Chinese children’s vocabulary acquisition and character reading. Read. Writ. 2009, 22, 615–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.D.; McBride-Chang, C.; Wong, T.T.Y.; Shu, H.; Wong, A.M.Y. Morphological awareness in Chinese: Unique associations of homophone awareness and lexical compounding to word reading and vocabulary knowledge in Chinese children. Appl. Psycholinguist. 2013, 34, 755–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H. Morphological awareness in literacy acquisition of Chinese second graders: A path analysis. J. Psycholinguist. Res. 2016, 45, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlisle, J.F. Morphological Awareness and Early Reading Achievement; Feldman, L.B., Ed.; Morphological aspects of language processing; Erlbaum: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1995; pp. 189–209. [Google Scholar]
- McBride-Chang, C.; Shu, H.; Zhou, A.; Wat, C.P.; Wagner, R.K. Morphological awareness uniquely predicts young children’s Chinese character recognition. J. Educ. Psychol. 2003, 95, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saiegh-Haddad, E.; Geva, E. Morphological awareness, phonological awareness, and reading in English–Arabic bilingual children. Read. Writ. 2008, 21, 481–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xuan, W.W. Word knowledge in academic literacy skills among collegiate ESL learners. Appl. Linguist. Rev. 2019, 10, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Cheng, C.; Chen, S.W. Contribution of morphological awareness to Chinese-English biliteracy acquisition. J. Educ. Psychol. 2006, 98, 542–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, P.N.; Kirby, J.R. Effects of morphological instruction on vocabulary acquisition. Read. Writ. 2010, 23, 515–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, A.P. Effectiveness of word solving: Integrating morphological problem-solving within comprehension instruction for middle school students. Read. Writ. 2016, 29, 91–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, J.F.; Edwards, E.C.; Boland, E.M.; Olejnik, S.; Kame’enui, E.J. Vocabulary tricks: Effects of instruction in morphology and context on fifth-grade students’ ability to derive and infer word meanings. Am. Educ. Res. J. 2003, 40, 447–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlisle, J.F. Effects of instruction in morphological awareness on literacy achievement: An integrative review. Read. Res. Q. 2010, 45, 464–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W. Integrated skills of English, 3rd ed.; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lesaux, N.K.; Kieffer, M.J.; Faller, S.E.; Kelley, J.G. The effectiveness and ease of implementation of an academic vocabulary intervention for linguistically diverse students in urban middle schools. Read. Res. Q. 2010, 45, 196–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nation, I.S.P.; Beglar, D. A vocabulary size test. Lang. Teach. 2007, 31, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Ku, Y.M.; Anderson, R.C. Development of morphological awareness in Chinese and English. Read. Writ. 2003, 16, 399–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasao, Y. Diagnostic Tests of English Vocabulary Learning Proficiency: Guessing from Context and Knowledge of Word Parts. Ph.D. Thesis, Victoria University of Wellington, Wellington, New Zealand, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Nagy, W.E. Metalinguistic Awareness and the Vocabulary—Comprehension Connection; Wagner, R.K., Muse, A.E., Tannenbaum, K.R., Eds.; Vocabulary Acquisition: Implications for Reading Comprehension; Guilford: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 52–77. [Google Scholar]
- Kintsch, W. The role of knowledge in discourse comprehension: A construction-integration model. Psychol. Rev. 1988, 95, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagy, W.E.; Carlisle, J.F.; Goodwin, A.P. Morphological knowledge and literacy acquisition. J. Learn. Disabil. 2014, 47, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levesque, K.C.; Kieffer, M.J.; Deacon, S.H. Inferring meaning from meaningful parts: The contributions of morphological skills to the development of children’s reading comprehension. Read. Res. Q. 2019, 54, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H. Does morphology play an important role in L2 Chinese vocabulary acquisition? Foreign Lang. Ann. 2016, 49, 384–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, P.N.; Kirby, J.R.; Deacon, S.H. The effects of morphological instruction on literacy skills: A systematic review of the literature. Rev. Educ. Res. 2010, 80, 144–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Morphological instruction | |
|---|---|
| Steps | Examples |
| Identification of new words with morphologically complex structures. | Undaunted, autobiography |
| Segmentation of morphemic units in morphologically complex words. | un-daunt-ed, auto-bio-graphy |
| Learning morphemic meanings. | un-: not, opposite of, -ed: past tense, past participle, participial adjective auto-: self bio-: life -graph-: to write, written |
| Making associations based on similar word parts. | un-: unpleasant, unafraid, unfair, unconformable -ed: surprised, tested, talked auto-: autograph, automate, automobile bio-: biology, biography, biome, biosphere -graph-: photograph, geography, calligraphy, graphic, grapheme |
| Applying and using words in a sentence or context. | “My spirits were undaunted, and my commitment as firm as ever.” “Bill Clinton wrote about his experiences in his autobiography.” “Traditional tools are being replaced by automated machines.” “Fans are surging around the hotel to ask for autographs.” |
| Group | Measurement | Mean | Std. Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment (n = 31) | Pre-test Morphological knowledge (20) Vocabulary knowledge (60) | 18.40 41.52 | 1.63 5.40 |
| Post-test Morpheme form (40) Morpheme meaning (34) Pseudoword inference (20) | 37.87 32.68 16.35 | 3.43 1.30 1.85 | |
| Real word inference (20) | 14.87 | 2.53 | |
| Text comprehension (20) | 14.84 | 1.79 | |
| Control (n = 31) | Pre-test Morphological knowledge (20) Vocabulary knowledge (60) | 18.39 39.45 | 1.76 4.65 |
| Post-test Morpheme form (40) Morpheme meaning (34) Pseudoword inference (20) Real word inference (20) Text comprehension (20) | 35.00 31.03 15.10 14.48 14.29 | 6.35 2.55 2.93 2.53 2.30 |
| Variable | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N = 31 (treatment group above the diagonal)/N = 31 (control group below the diagonal) | |||||
| 1. Morpheme form | - | 0.44 * | 0.61 *** | 0.78 *** | 0.66 *** |
| 2. Morpheme meaning | 0.35 * | - | 0.45 * | 0.42 * | 0.34 * |
| 3. Pseudoword inference | 0.19 | 0.19 | - | 0.68 *** | 0.55 ** |
| 4. Real word inference | 0.54 ** | 0.44 * | 0.35 * | - | 0.59 ** |
| 5. Text comprehension | 0.52 ** | 0.44 * | 0.37 ** | 0.55 ** | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Zou, W. Morphological Intervention in Promoting Higher-Order Reading Abilities among College-Level Second Language Learners. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12041465
Zhang H, Zou W. Morphological Intervention in Promoting Higher-Order Reading Abilities among College-Level Second Language Learners. Sustainability. 2020; 12(4):1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12041465
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Haomin, and Weicheng Zou. 2020. "Morphological Intervention in Promoting Higher-Order Reading Abilities among College-Level Second Language Learners" Sustainability 12, no. 4: 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12041465
APA StyleZhang, H., & Zou, W. (2020). Morphological Intervention in Promoting Higher-Order Reading Abilities among College-Level Second Language Learners. Sustainability, 12(4), 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12041465





