Adsorption of Heavy Metals on Soil Collected from Lixisol of Typical Karst Areas in the Presence of CaCO3 and Soil Clay and Their Competition Behavior
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Materials
2.2. Analysis Method
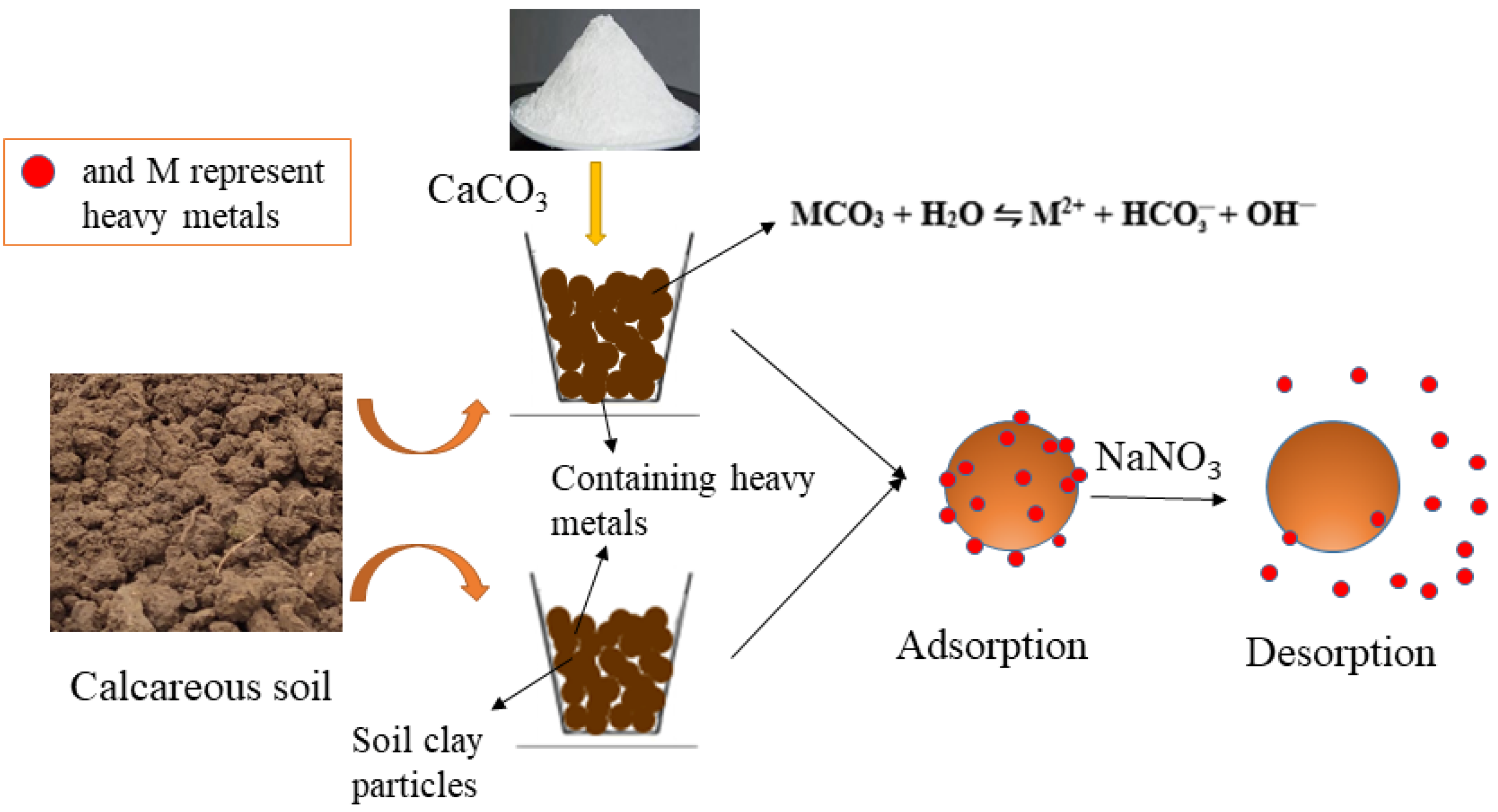
2.3. Effect of Different Calcium Carbonate Contents on Adsorption and Desorption
2.4. Particle Size Distribution of Soil
2.5. Adsorption Kinetic
2.6. Adsorption Isotherm
2.7. Estimation of Thermodynamic Parameters
2.8. Effect of Initial pH on Adsorption
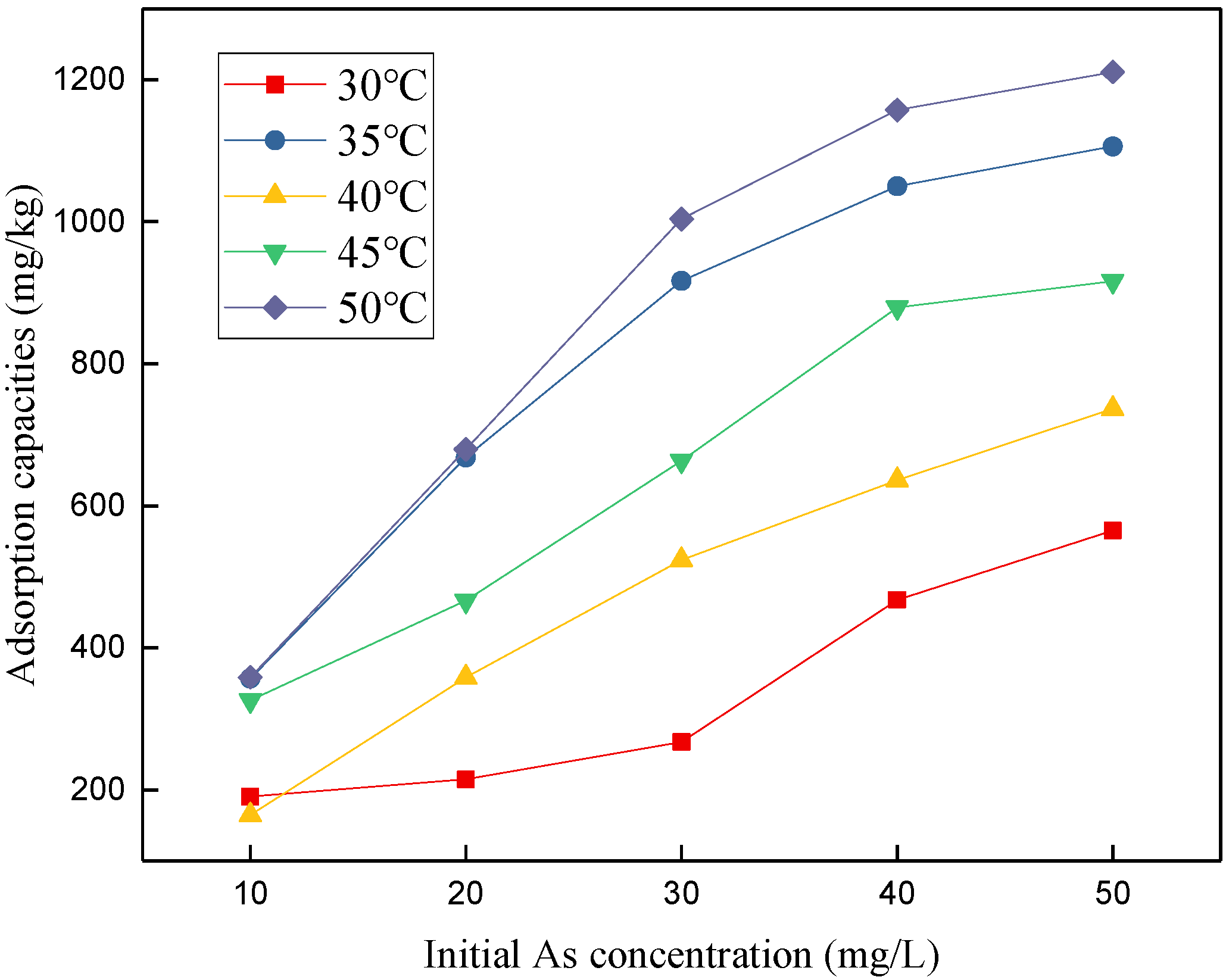
2.9. Effect of Temperature on Adsorption
2.10. Influence of Electrolyte on Adsorption
3. Results and Discussion
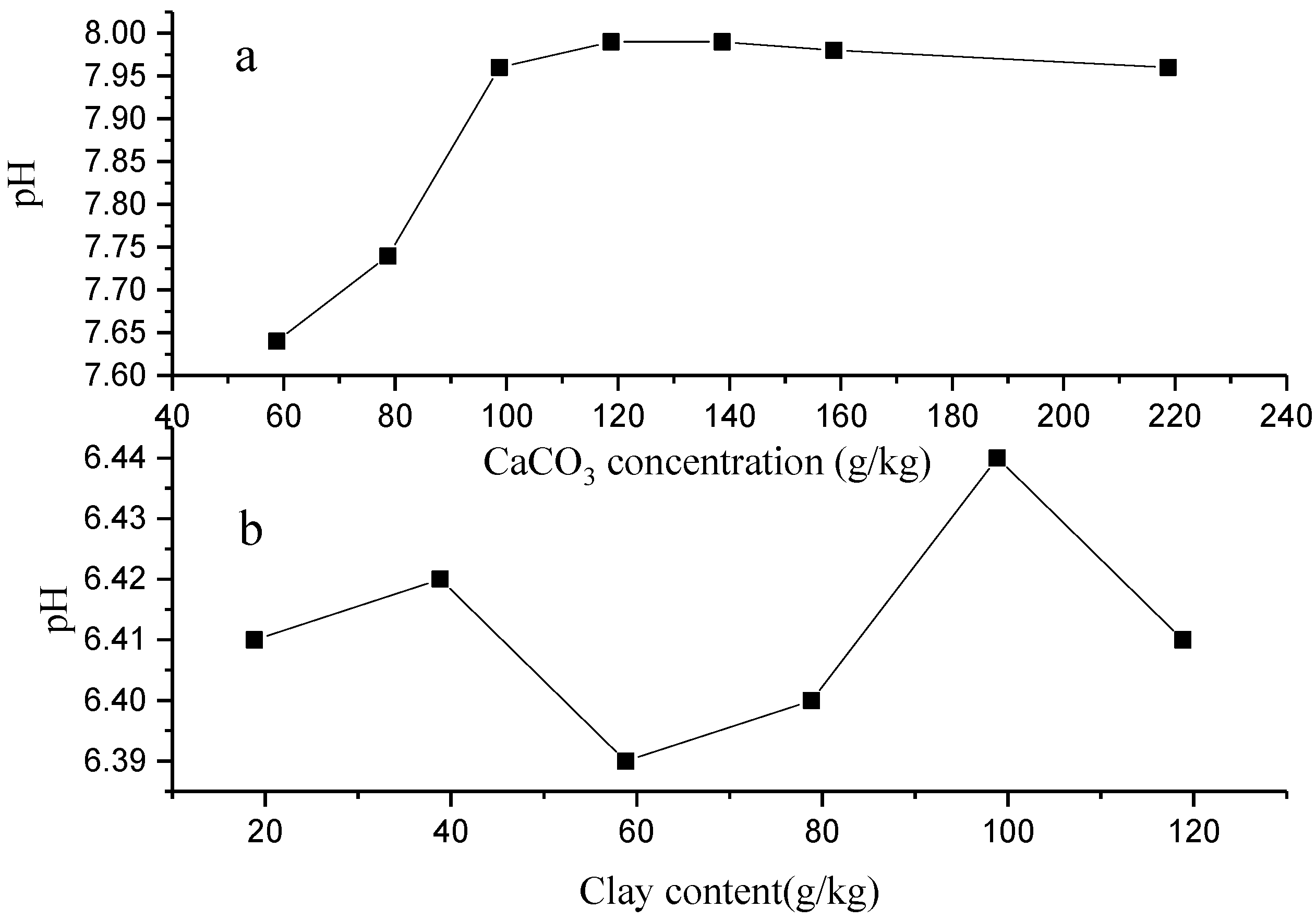
3.1. Physical and Chemical Indexes of Topsoil Sample Collected from Lixisol
3.2. Effect of Calcium Carbonate and Soil Clay on Adsorption and Desorption of Heavy Metals in Topsoil Sample Collected from Lixisol
3.3. Adsorption Kinetics of Heavy Metals Adsorbed on Topsoil Sample Collected from Lixisol
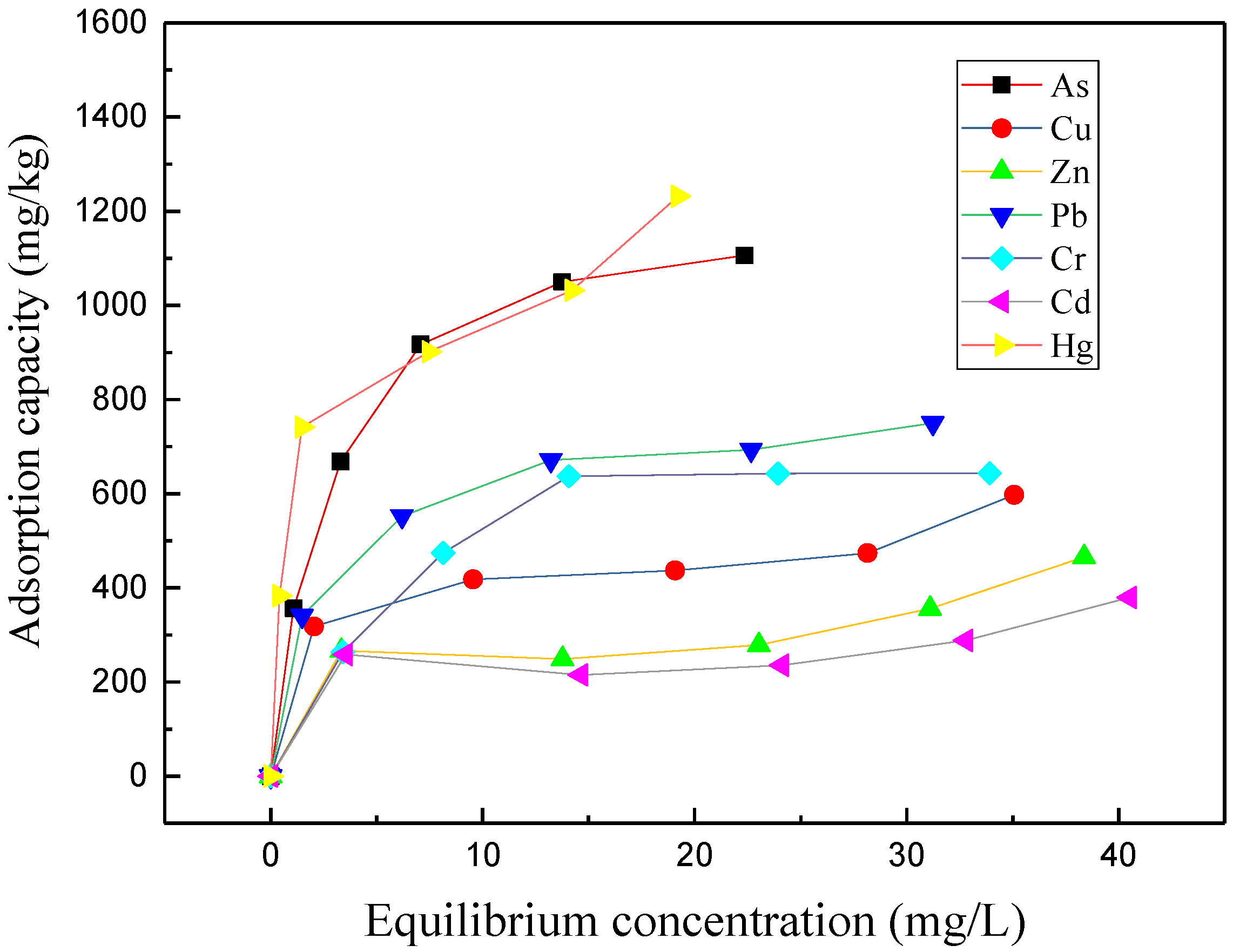
3.4. Adsorption Isotherms of Heavy Metals Adsorbed on Topsoil Sample Collected from Lixisol
3.5. Thermodynamic Study
3.6. Effect of pH and Electrolyte on Adsorption of Heavy Metals by Lime Soil
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, L.L.; Liao, F.F.; Zhang, A.M. Study of Cd resistance of pepper planted in yellow soil and calcareous soil. Guangdong Agric. Sci. 2018, 45, 79–86. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.G.; Liu, C.Q.; Pan, W.; Zhang, G.P.; Zhu, W.H. Heavy metal accumulation from zinc smelters in a carbonate rock region in Hezhang County, Guizhou Province, China. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2006, 174, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.B.; Wang, S.J.; Yang, O.; Zhang, Y.Z. Geochemistry of red residua underlying dolomites in karst terrains of Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau: II. The mobility of rare earth elements during weathering. Chem. Geol. 2004, 203, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, S.; Fujimori, H.; Hidaka, A.; Ioku, K. Effects of components on the rate of heat liberation of the hydration in the system of glass/gypsum/lime. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2006, 26, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Li, L.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Shen, J.Z.; Xia, M.; Wang, Y.H.; Fang, W.P.; Zhu, X.J. Zn, Ni, Mn, Cr, Pb and Cu in soil-tea ecosystem: The concentrations, spatial relationship and potential control. Chemosphere 2018, 204, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, X.B.; Xiang, W.H.; Fang, X. Heavy metal concentrations and pollution assessment of limestone forests in Huaxi district, Guiyang City. J. Ecol. 2009, 4, 527–535. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.Y.; Wen, X.F.; Pan, W.; Liu, H.Y.; Liu, Y.S.; Pan, Q.Z.; Wei, X.; Wu, S.S. Excessive degrees and migration characteristics of heavy metals in typical weathering profiles in karst areas. Earth Environ. 2019, 47, 50–56. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xian, X.; Homma, S.; Kuno, K. Relationship between concentration of heavy metals in soil and contents of that absorbed by mulberry plant. J. Sericult. Sci. Jpn. 2010, 57, 481–488. [Google Scholar]
- Yohey, H.; Hiroki, M.; Masaki, T.; Hajime, T.; Takeshi, S. Impacts of chemical amendment and plant growth on lead speciation and enzyme activities in a shooting range soil: An X-ray absorption fine structure investigation. J. Environ. Qual. 2009, 38, 1420–1427. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W. Buffer action and its influencing factors of different types of soil in changchun region. J. Jilin Agric. Univ. 2001, 23, 78–83. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Su, X.; Rizwan, M.S.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, H. Chemical immobilization of Pb, Cu, and Cd by phosphate materials and calcium carbonate in contaminated soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 16845–16856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaei, A.; Mosaddeghi, M.R.; Mahboubi, A.A. Impacts of test conditions, soil organic matter, clay and calcium carbonate contents on mean weight diameter and tensile strength of aggregates of some Hamedan soils. J. Sci. Technol. Agric. Nat. Res. 2008, 12, 123–134. [Google Scholar]
- Kužel, S.; Kolář, L.; Gergel, J.; Peterka, J.; Borová-Batt, J. Influence of the degree of soil organic matter lability on the calcium carbonate equilibrium of soil water. Soil Water Res. 2010, 5, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silveira, M.R.; Ivancko, I.N.; Valério, M.B.; Reznik, L.Y.; De Carvalho, L.J.; Rodrigues, A.D.C.; Da Silva, A.L.N. Effect of the addition of calcium carbonate on the barrier behavior of polyamide 11 used in offshore applications by electrochemical impedance analysis. Polym. Test. 2018, 69, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.F.; Liu, P.Y.; Feng, X.H.; Wang, Z.M.; Cheng, T.; Liang, Y.Z.; Lin, Z.; Shi, Z.Q. Kinetics of heavy metal adsorption and desorption in soil: Developing a unified model based on chemical speciation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2018, 224, 282–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Meng, Z.; Song, Y. Adsorption and Desorption Behaviors of Spirotetramat in Various Soils and Its Interaction Mechanism. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 12471–12478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.M.; Wu, X.L.; Wu, Q.S.; Huang, X.F.; Zhang, J.C.; Fang, H. Speciation and accumulation pattern of heavy metals from soil to rice at different growth stages in farmland of southwestern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, K.C.M.; Santos, M.D.S.F.D.; Santos, M.R.M.C. Effects of acid treatment on the clay palygorskite: XRD, surface area, morphological and chemical composition. Mater. Res. 2014, 17, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Li, X.P.; Cai, Y. Geochemical behavior and risk of heavy metals in different size lead-polluted soil particles. China Environ. Sci. 2017, 37, 4212–4221. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qin, S.; Wang, Z.Y.; Liu, M.J. Contents and its characters of heavy metals with tobacco-growing soils in Zhengan County of remote karst agricultural area. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2007, 21, 72–75. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Wen, Q.; Hu, L.; Gong, M. Effect of adsorbate concentration to adsorbent dosage ratio on the sorption of heavy metals on soils. J. Environ. Eng. 2018, 144, 04017094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhou, J.G.; Zhou, P.; Liu, X.L.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.S. Response of regional agricultural soil phosphorus status to net anthropogenic phosphorus input (NAPI) determined by soil pH value and organic matter content in subtropical China. Chemosphere 2018, 200, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pestana, M.N.; Gomes, A.A. The effect of soil on cork capacity. Front. Chem. 2014, 2, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Luo, L.; Zhang, S. Adsorption of tetrabromobisphenol A on soils: Contribution of soil components and influence of soil properties. Colloid. Surf. A 2013, 428, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.D. Influence of soil sample preparation on soil organic matter determination. Heilongjiang Environ. J. 2018, 42, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Elfaki, J.T.; Gafei, M.A.; Sulieman, M.M.; Ali, M.E. Assessment of calcimetric and titrimetric methods for calcium carbonate estimation of five soil types in central Sudan. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2016, 4, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Elfaki, J.T.; Sulieman, M.M.; Ali, M.E. Hydrometer method against Pipette method for estimating soil particle size distribution in some soil types selected from central Sudan. Int. J. Eng. Res. 2016, 2, 25–41. [Google Scholar]
- Guzmán, G.; Gómez, J.A.; Giráldez, J.V. Measurement of particle size distribution of soil and selected aggregate sizes using the hydrometer method and laser diffractometry. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference, Vienna, Austria, 2–7 May 2010; Available online: https://meetingorganizer.copernicus.org/EGU2010/EGU2010-4422-1.pdf (accessed on 27 August 2020).
- Kumar, K.V.; Sivanesan, S. Pseudo second order kinetics and pseudo isotherms for malachite green onto activated carbon: Comparison of linear and non-linear regression methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.Y.; Hou, Y.Z.; Lin, Y.L.; Deng, Y.G.; Hua, S.J.; Du, Y.F.; Chen, C.W.; Wu, C.H. Kinetics and model development of iohexol degradation during UV/H2O2 and UV/S2O2-8 oxidation. Chemosphere 2019, 229, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.I.; Chen, W.W.; Liao, L.; Xie, P.C. Comparative adsorption of emerging contaminants in water by functional designed magnetic poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)/chitosan hydrogels. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 671, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, J.A.; Bumiller, K.C.; Tynan, K.J.; Ebner, A.D. On the use of the dual process Langmuir model for binary gas mixture components that exhibit single process or linear isotherms. Adsorption 2019, 25, 1511–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dau, P.D.; Armentrout, P.B.; Michelini, M.C.; Gibson, J.K. Activation of carbon dioxide by a terminal uranium-nitrogen bond in the gas-phase: A demonstration of the principle of microscopic reversibility. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 7334–7340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Liu, F.; Ma, X.; Cui, P.; Guo, M. Effects of biodiesel blends on the kinetic and thermodynamic parameters of fossil diesel during thermal degradation. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 198, 111930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Dai, J.L.; Wang, R.Q. Progress in the Effect of Dissolved Organic Matter on Adsorption of Heavy Metals by Soil. Soil Bull. 2012, 258, 761–768. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Omekeh, A.V.; Friis, H.A.; Evje, S.; Fjelde, I. A model for low salinity flooding experiments: Dissolution and ion exchange. J. Porous Media 2015, 18, 189–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Q.; Zhang, S.R.; Wu, J. The relationship between soil pH and calcium carbonate content. Soil 2002, 34, 279–288. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Q.Y.; Zeng, M.; Liao, B.H. Elects of CaCO3 adkdition on upake of heavy metals and ansenie in paddy fields. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 1242–1248. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ren, L.L.; Wu, W.C.; Chen, X.B.; Liu, X.C.; Li, Y.B.; Song, Q.M. Different Effects of CaCO3 and Ca(OH)2 on Heavy Metals Remediation in Contaminated Farmland Soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 39, 22–27. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bogusz, A.; Oleszczuk, P.; Dobrowolski, R. Adsorption and desorption of heavy metals by the sewage sludge and biochar-amended soil. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 1663–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, H.R.; Lox, C.D.; Heine, W.; Christian, C.D. Intrauterine fetal sex determination by radioimmunoassay of amniotic fluid testosterone. Gynecol. Obst. Investig. 1974, 5, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lambert, B.; Henry, D. Nanoparticulate Affinity Capture for Label Independent Detection System. U.S. Patent US20100129911A1, 24 January 2012. Available online: https://www.freepatentsonline.com/8101405.pdf (accessed on 27 August 2020).
- Milewska-Duda, J.; Duda, J.T. New BET-like models for heterogeneous adsorption in microporous adsorbents. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2002, 196, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, S.; Da Silva, C.; Aires-Barros, M.R.; Dias-Cabral, A.C.M.; Azevedo, A.M. Thermodynamics of the adsorption of monoclonal antibodies in phenylboronate chromatography: Affinity versus multimodal interactions. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1569, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumediene, M.; Benassa, H.; George, B.; Molina, S.; Merlin, A. Characterization of two cellulosic waste materials (orange and almond peels) and their use for the removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions. Maderas Ciencia Tecnología 2015, 17, 39–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Verma, S.; Gautam, R.K.; Krishna, V. Copper adsorption onto synthesized nitrilotriacetic acid functionalized Fe3O4 nanoparticles: Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2161–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirekar, D.B.; Pramila, G.; Farooqui, M. Kinetics and isotherm studies on crystal violet dye adsorption onto black gram seed husk. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2015, 7, 427–434. [Google Scholar]
- Gramss, G.; Voigt, K.D.; Bublitz, F.; Bergmann, H. Increased solubility of (heavy) metals in soil during microbial transformations of sucrose and casein amendments. J. Basic Microb. 2003, 43, 483–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk, Z.; Siwek, B.; Zembala, M. Influence of transport mechanism on adsorption of interacting colloid particles. Colloid Surf. A 1993, 76, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.N.; Wang, J.; Xue, W.; Zhao, J.B.; Wang, J. Effect of the size of variable charge soil particles on cadmium accumulation and adsorption. J. Soil. Sediments 2017, 17, 2810–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.C.; Ye, H. Influence of redox potential on heavy metal behavior in soils: A review. Res. Environ. Sci. 2018, 31, 1669–1676. [Google Scholar]
- Wit, H.D. Process intensification and fuel cells using a Multi-Source Multi-Product approach. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2012, 51, 88–108. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, P.; Huang, Q.; Jiang, D.; Rong, X.; Liang, W. Microcalorimetric studies on the adsorption of DNA by soil colloidal particles. Colloid Surf. B 2006, 49, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
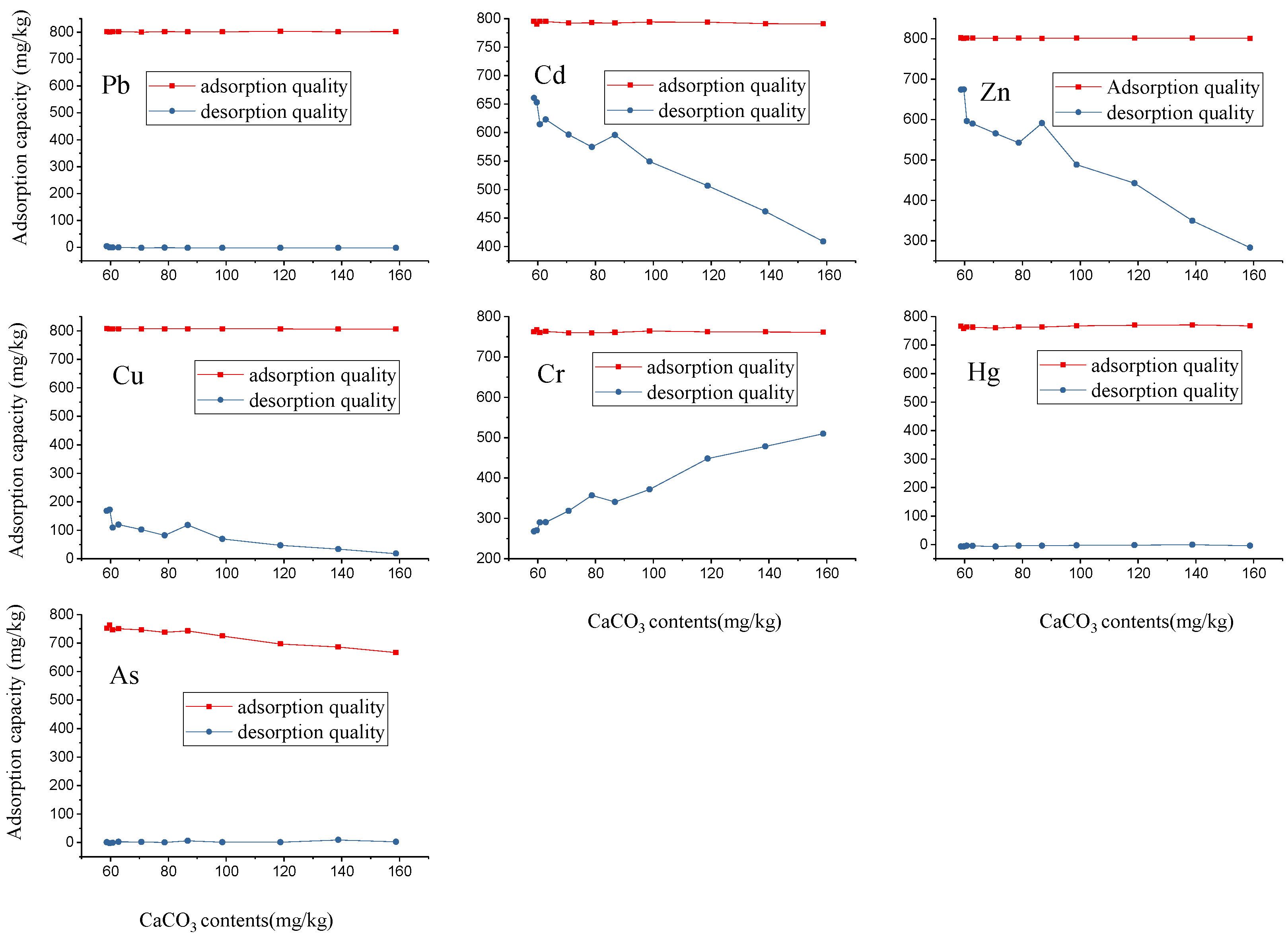




| CaCO3 Contents(g/kg) | Pb (mg/kg) | Cd (mg/kg) | Zn (mg/kg) | Cu (mg/kg) | Cr (mg/kg) | Hg (mg/kg) | As (mg/kg) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AQ | DQ | AQ | DQ | AQ | DQ | AQ | DQ | AQ | DQ | AQ | DQ | AQ | DQ | |
| 58.8 | 802 | 3.45 | 795 | 661 | 802 | 673 | 807 | 168 | 762 | 268 | 767 | −7.07 | 752 | 0.970 |
| 59.8 | 800 | −0.492 | 790 | 653 | 800 | 674 | 807 | 172 | 767 | 270 | 758 | −7.70 | 763 | −2.36 |
| 60.8 | 801 | −0.830 | 795 | 614 | 802 | 596 | 807 | 109 | 760 | 300 | 763 | −4.36 | 746 | −1.14 |
| 62.8 | 802 | −0.332 | 795 | 623 | 801 | 590 | 807 | 120 | 763 | 290 | 762 | −4.84 | 750 | 2.16 |
| 70.8 | 799 | −2.24 | 792 | 596 | 801 | 565 | 807 | 103 | 759 | 319 | 760 | −7.24 | 746 | 1.31 |
| 78.8 | 802 | −1.75 | 793 | 575 | 801 | 542 | 807 | 81.6 | 760 | 357 | 763 | −4.06 | 738 | 0.146 |
| 86.8 | 800 | −2.17 | 792 | 596 | 801 | 591 | 807 | 118 | 760 | 341 | 763 | −3.71 | 743 | 5.61 |
| 98.8 | 800 | −2.12 | 794 | 549 | 802 | 488 | 807 | 70.1 | 764 | 372 | 768 | −3.18 | 724 | 0.864 |
| 119 | 802 | −2.03 | 793 | 507 | 802 | 442 | 806 | 46.6 | 762 | 448 | 770 | −2.64 | 697 | 0.842 |
| 139 | 801 | −1.92 | 791 | 462 | 801 | 349 | 806 | 33.5 | 762 | 478 | 771 | −0.436 | 686 | 8.90 |
| 159 | 801 | −2.60 | 791 | 409 | 801 | 282 | 806 | 18.1 | 761 | 510 | 767 | −4.04 | 666 | 2.22 |
| Clay Particle (g/kg) | Pb (mg/kg) | Cd (mg/kg) | Zn (mg/kg) | Cu (mg/kg) | Cr (mg/kg) | Hg (mg/kg) | As (mg/kg) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AQ | DQ | AQ | DQ | AQ | DQ | AQ | DQ | AQ | DQ | AQ | DQ | AQ | DQ | |
| 354 | 400 | 304 | 292 | 413 | 352 | 391 | 404 | 408 | 168 | 448 | 394 | 66.9 | 365 | 286 |
| 355 | 400 | 309 | 281 | 407 | 346 | 388 | 403 | 411 | 145 | 436 | 391 | 63.7 | 357 | 272 |
| 356 | 402 | 310 | 280 | 403 | 337 | 379 | 401 | 407 | 171 | 443 | 389 | 65.6 | 368 | 288 |
| 358 | 400 | 315 | 280 | 401 | 341 | 376 | 401 | 404 | 173 | 434 | 389 | 62.9 | 365 | 273 |
| 366 | 400 | 328 | 257 | 391 | 315 | 367 | 395 | 410 | 167 | 431 | 391 | 87.7 | 358 | 279 |
| 374 | 399 | 337 | 240 | 385 | 288 | 355 | 378 | 407 | 188 | 441 | 393 | 98.7 | 364 | 284 |
| 382 | 400 | 315 | 277 | 404 | 335 | 381 | 397 | 411 | 190 | 437 | 395 | 81.2 | 360 | 277 |
| 394 | 401 | 319 | 280 | 405 | 341 | 382 | 402 | 412 | 200 | 434 | 389 | 67.3 | 367 | 283 |
| 414 | 417 | 293 | 236 | 378 | 353 | 344 | 425 | 375 | 212 | 439 | 400 | 77.5 | 353 | 274 |
| 434 | 434 | 301 | 252 | 388 | 361 | 360 | 420 | 394 | 228 | 443 | 412 | 82.8 | 355 | 283 |
| 454 | 431 | 306 | 289 | 412 | 372 | 389 | 431 | 408 | 231 | 439 | 415 | 84.4 | 343 | 282 |
| As | Cu | Zn | Pb | Cr | Cd | Hg | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first-order kinetic | Qe (mg/g) | 0.703 | 0.065 | 0.003 | 0.116 | 0.387 | 0.026 | 0.367 |
| k1 (10−3 min−1) | 0.925 | 0.056 | 38.200 | 3.100 | 1.572 | 40.225 | 0.697 | |
| R | 0.281 | 0.056 | −0.056 | −0.056 | 0.070 | −0.056 | 0.190 | |
| Pseudo-second-order kinetic | Qe(mg/g) | 0.787 | 0.056 | 0.020 | 0.075 | 0.465 | 0.018 | 0.480 |
| k2 (10−3 g mg−1min−1) | 0.343 | 4.025 | 1.181 | 4.399 | 0.171 | 3.808 | 0.101 | |
| R | 0.999 | 0.975 | 0.973 | 0.948 | 0.999 | 0.970 | 0.997 | |
| Particle diffusion model | k3 (mg g−1mim−0.5) | 0.007 | 0.005 | 0.000 (0.0004) | 0.045 | 0.004 | 0.009 | 0.007 |
| C | 0.603 | 0.065 | 0.000 (0.0001) | 0.115 | 0.334 | 0.026 | 0.281 | |
| R | 0.950 | 0.928 | 0.916 | 0.924 | 0.990 | 0.989 | 0.980 |
| Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm | KL | R2 | KF | 1/n | R2 |
| 757 | 0.161 | 0.817 | 166 | 2.370 | 0.920 |
| ΔH0 (kJ·mol−1) | ΔS0 (J·mol−1K−1) | ΔG0 (kJ/mol) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 303.150 K | 308.150 K | 313.150 K | 318.150 K | 323.150 K | |||
| As | 40.172 | 136.474 | −0.571 | −1.160 | −0.566 | −0.688 | −0.757 |
| Cu | −1.309 | −1.792 | −0.397 | −0.678 | −0.552 | −0.303 | −0.093 |
| Zn | −6.377 | 18.945 | −0.898 | −2.099 | 0.937 | 1.974 | −0.577 |
| Pb | −30.558 | −97.157 | −1.168 | −1.941 | −1.074 | −1.051 | −1.752 |
| Cr | 2.188 | 5.157 | −0.434 | −0.559 | −0.521 | −0.605 | −0.358 |
| Cd | 1.081 × 10−5 | 5.081 | −4.212 | −3.563 | −3.420 | −2.347 | −3.424 |
| Hg | 2.153 × 10−4 | 78.417 | −0.571 | −1.160 | −0.566 | −0.688 | −0.757 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, G.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, X.; Cui, M.; Zhang, J.; Huang, X. Adsorption of Heavy Metals on Soil Collected from Lixisol of Typical Karst Areas in the Presence of CaCO3 and Soil Clay and Their Competition Behavior. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7315. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187315
He G, Zhang Z, Wu X, Cui M, Zhang J, Huang X. Adsorption of Heavy Metals on Soil Collected from Lixisol of Typical Karst Areas in the Presence of CaCO3 and Soil Clay and Their Competition Behavior. Sustainability. 2020; 12(18):7315. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187315
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Guandi, Zhenming Zhang, Xianliang Wu, Mingyang Cui, Jiachun Zhang, and Xianfei Huang. 2020. "Adsorption of Heavy Metals on Soil Collected from Lixisol of Typical Karst Areas in the Presence of CaCO3 and Soil Clay and Their Competition Behavior" Sustainability 12, no. 18: 7315. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187315
APA StyleHe, G., Zhang, Z., Wu, X., Cui, M., Zhang, J., & Huang, X. (2020). Adsorption of Heavy Metals on Soil Collected from Lixisol of Typical Karst Areas in the Presence of CaCO3 and Soil Clay and Their Competition Behavior. Sustainability, 12(18), 7315. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12187315





