Mobile Access Hub Deployment for Urban Parcel Logistics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Problem Description and Modeling
3.1. Problem Description
- Mobile access hub candidate locations are known and can be reserved for a fixed price at the beginning of each day
- Unit zones are to be served by at most one mobile access hub at the time
- Mobile access hubs can be stored nearby their local hub if not deployed
- Mobile access hubs are big enough to hold the load of parcels of their assigned unit zone(s)
- Mobile access hubs are to be replenished by out-and-back rider trips
3.2. Sustainability Performance Indicators
3.2.1. Economic Assessment
3.2.2. Time Efficiency Assessment
3.2.3. Environmental Assessment
3.3. Operations Modeling
3.3.1. Pickup and Delivery Routes
3.3.2. Baseline Operations and Transit Time
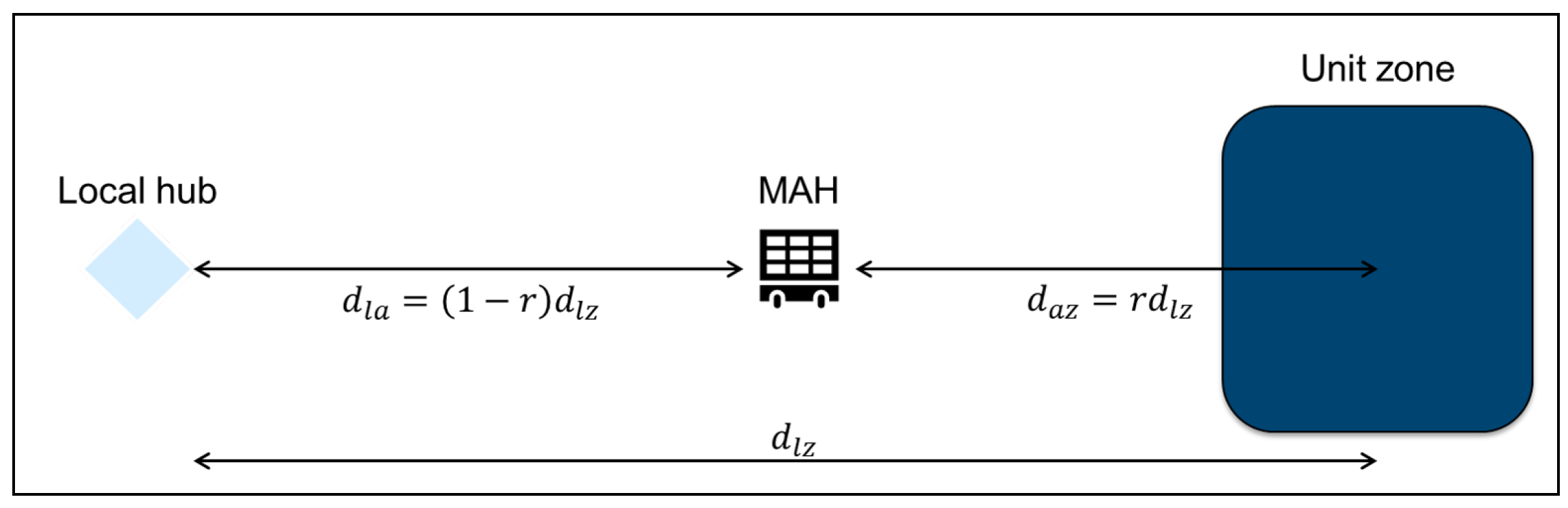
3.3.3. Mobile Access Hub Operations and Transit Time
3.4. Mobile Access Hub Deployment Optimization
4. Results
4.1. Assessing Economic Viability of a Mobile Access Hub
4.2. Assessing the Performance of Mobile Access Hub Deployments
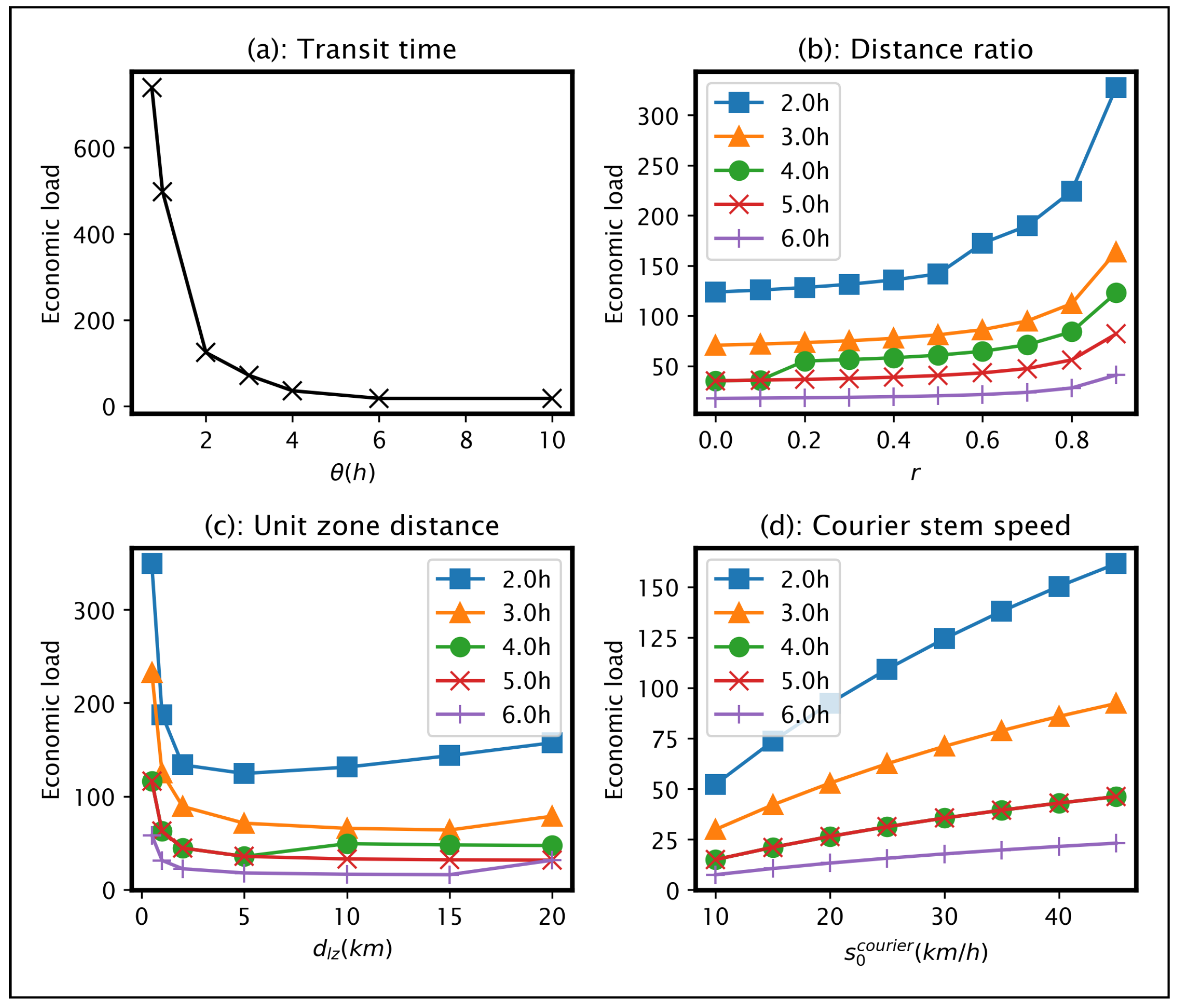
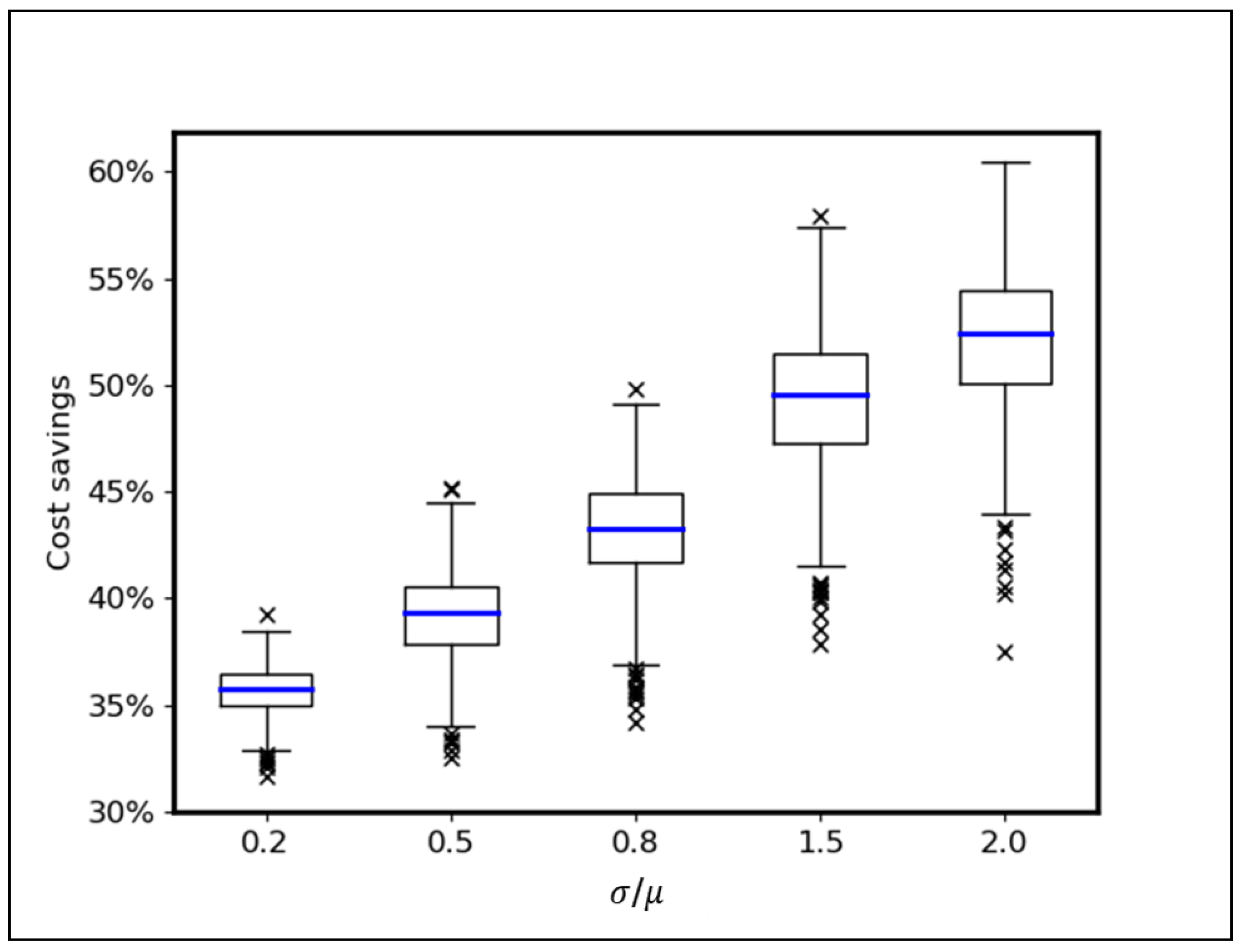
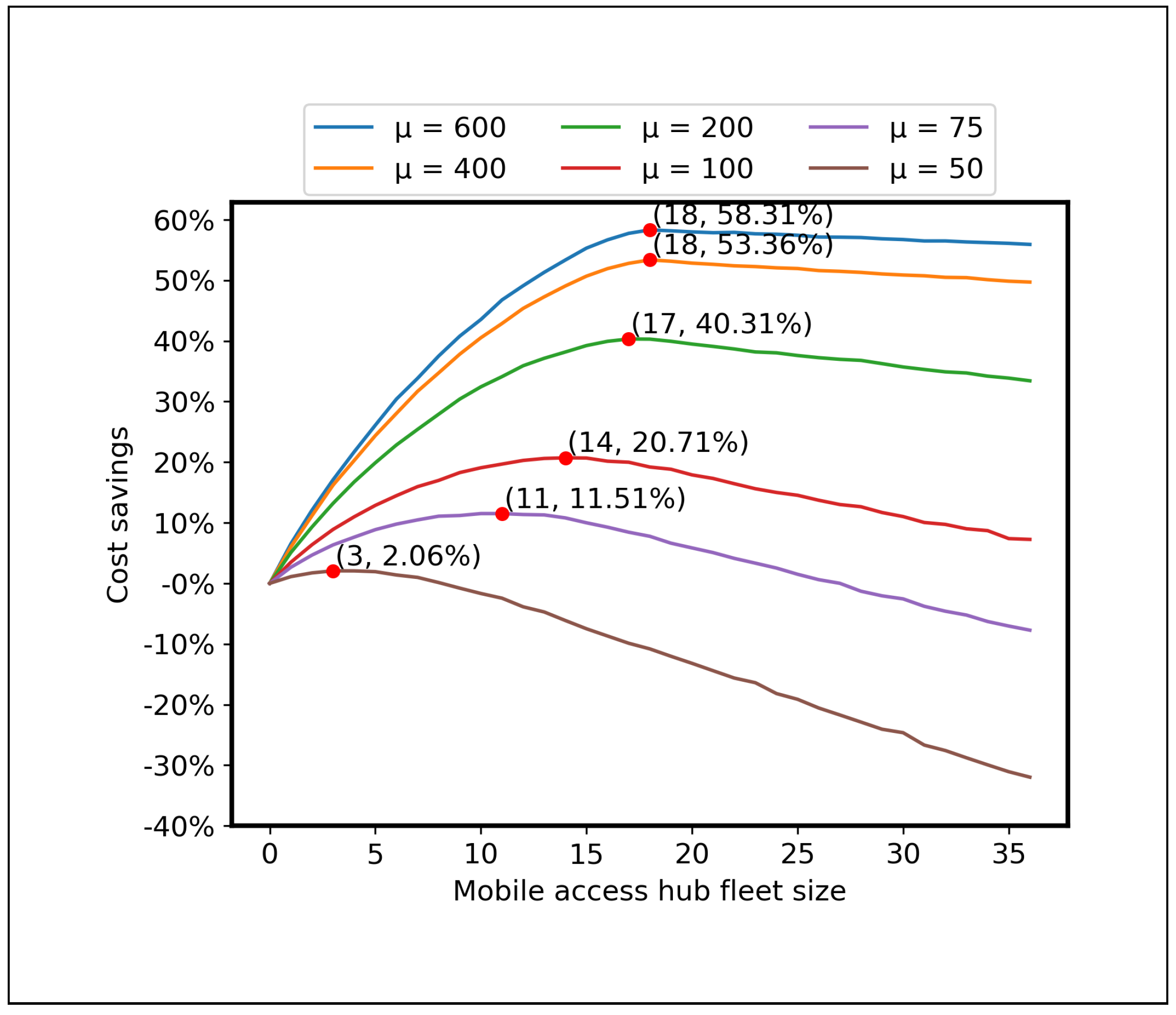
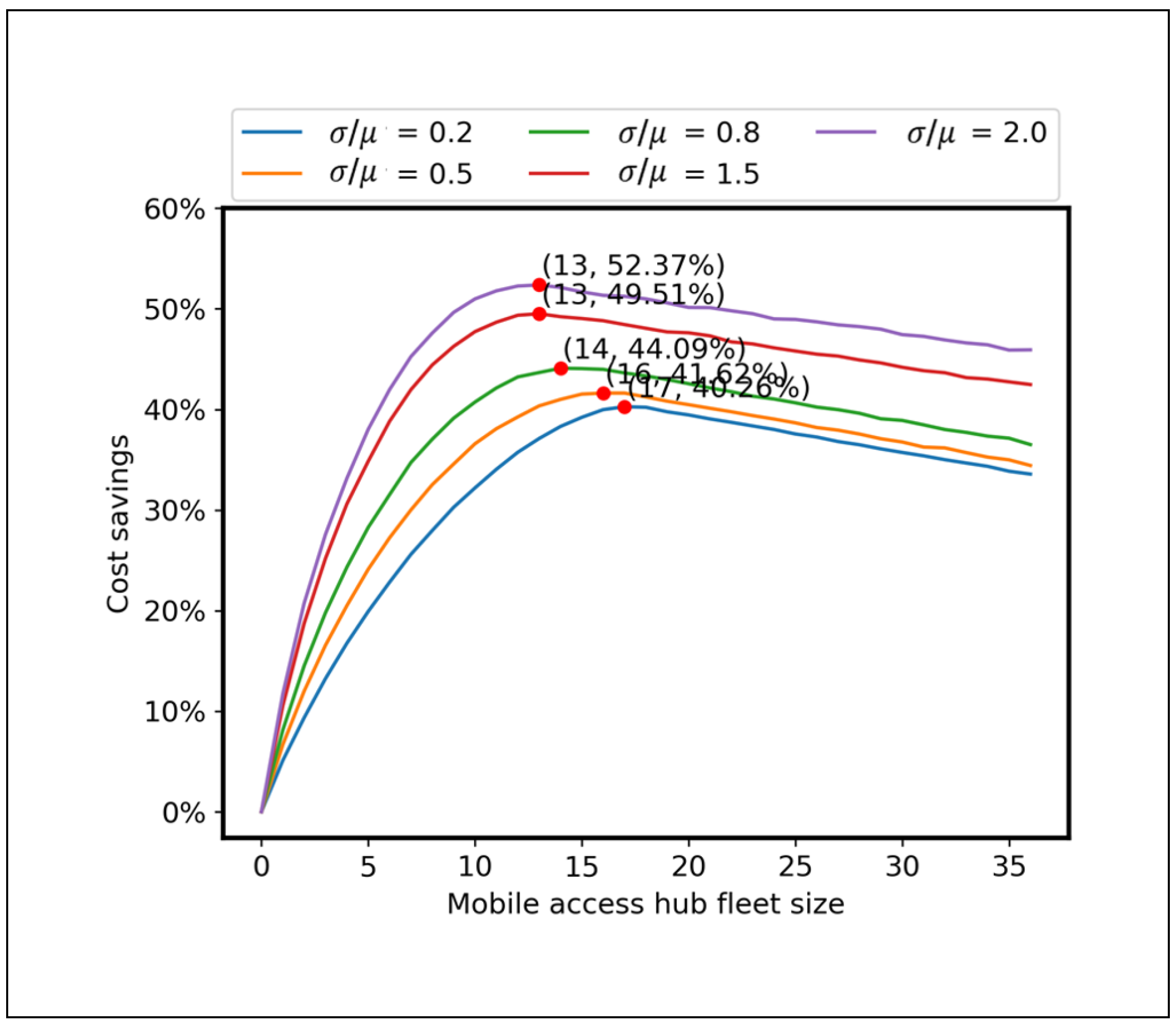
4.2.1. Impact of Demand Variability
4.2.2. Impact of Transit Time Constraints
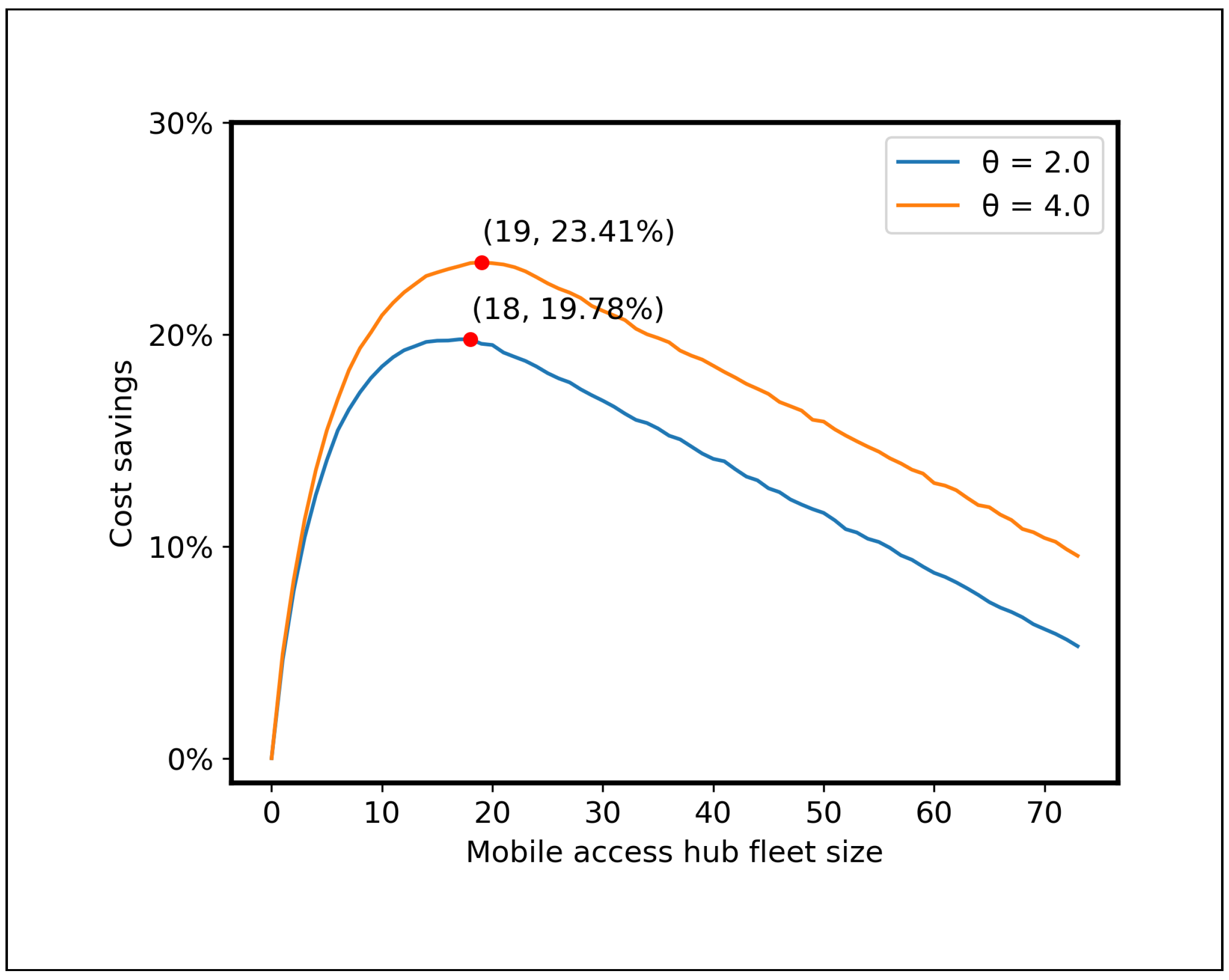
4.2.3. Impact of Mobile Access Hub Fleet Size
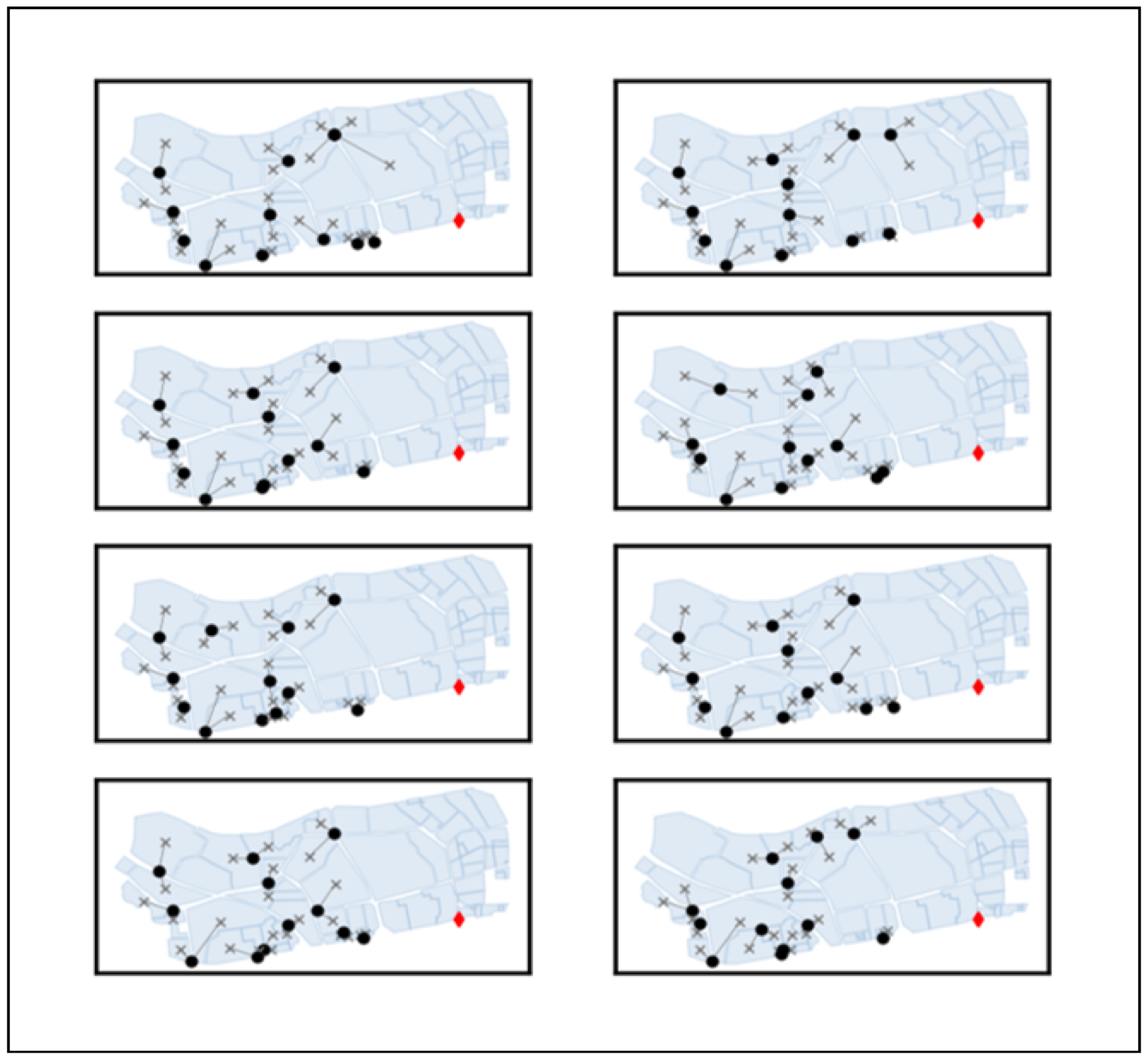
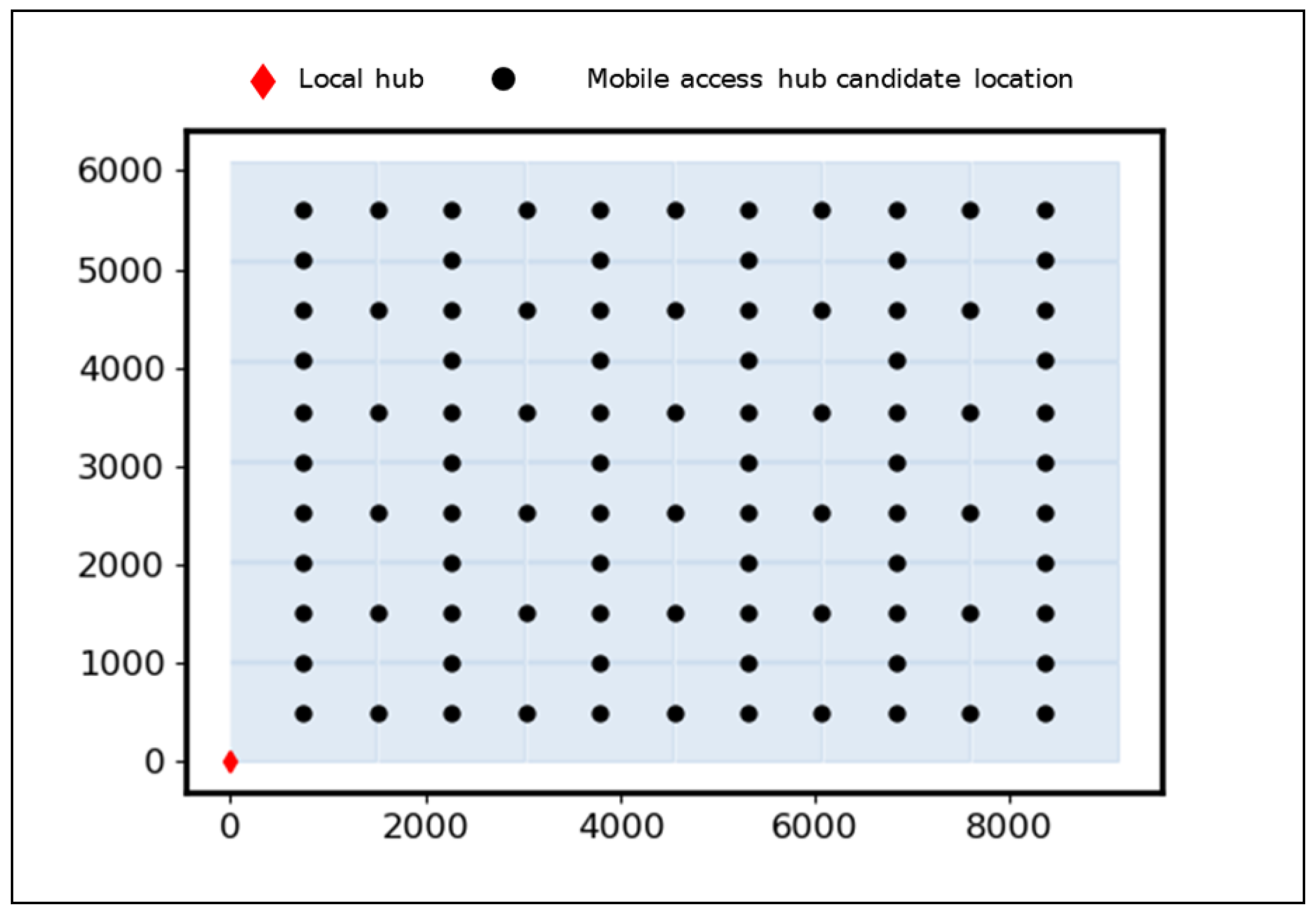
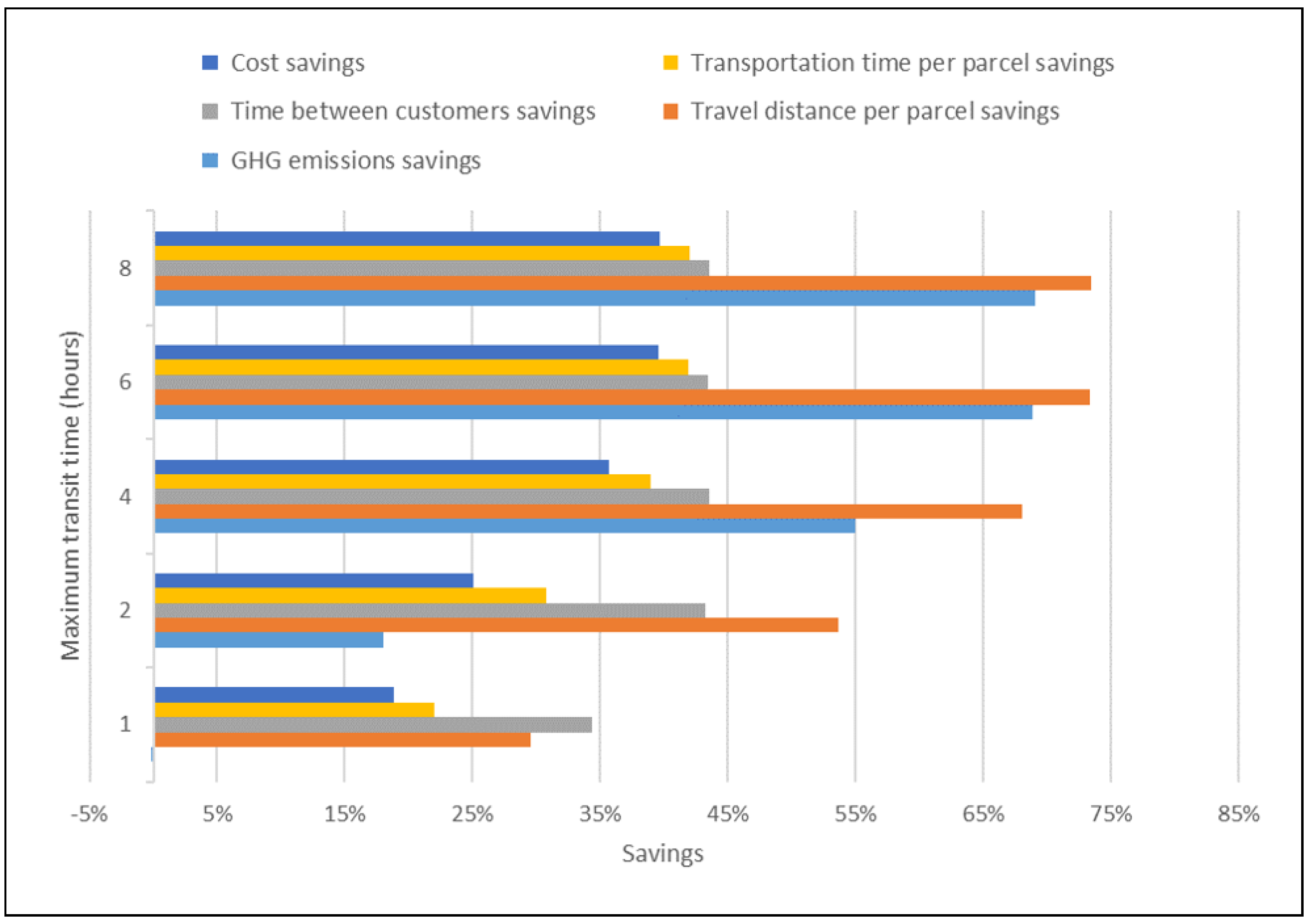
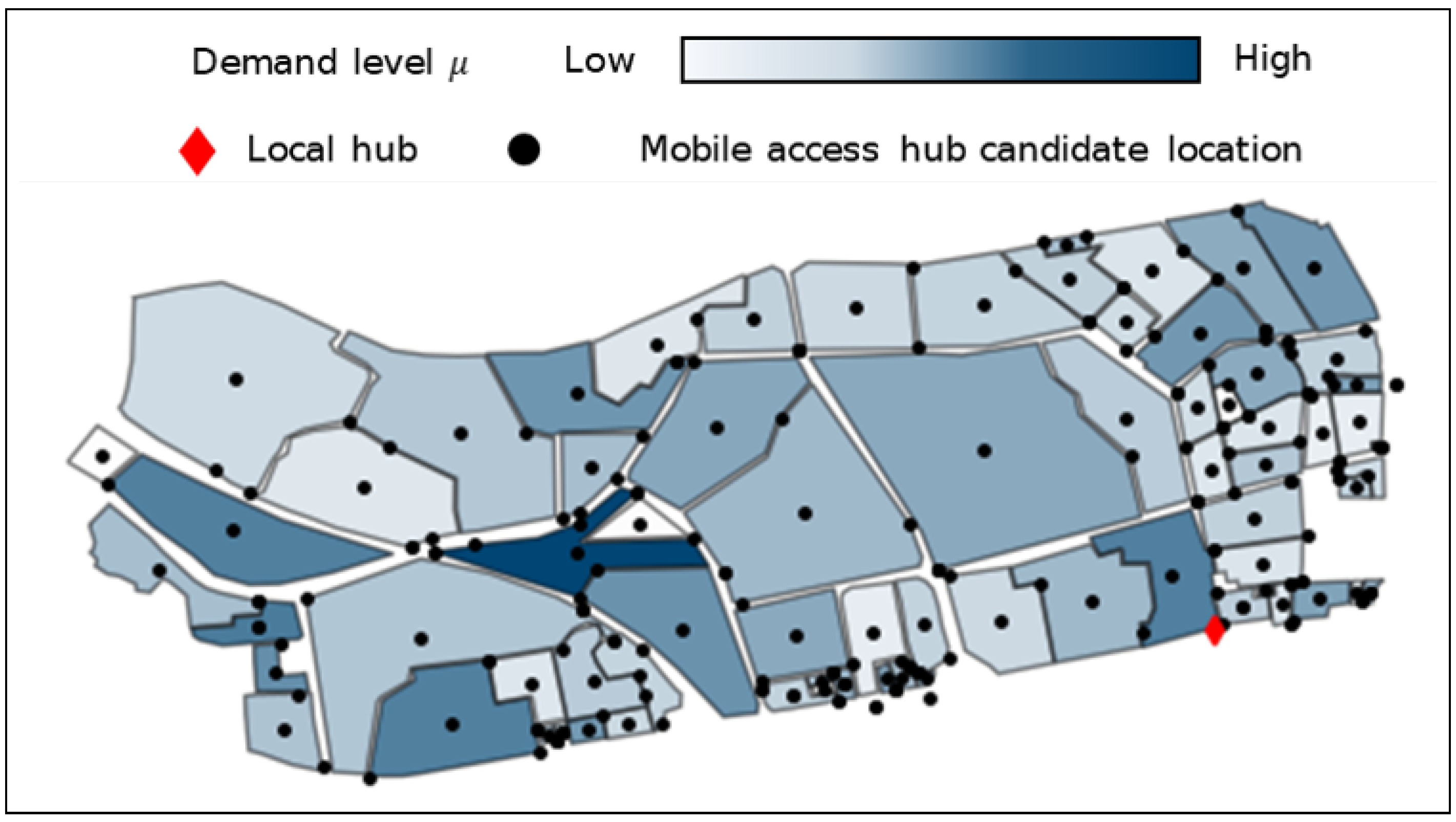
4.3. Illustrative Case
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
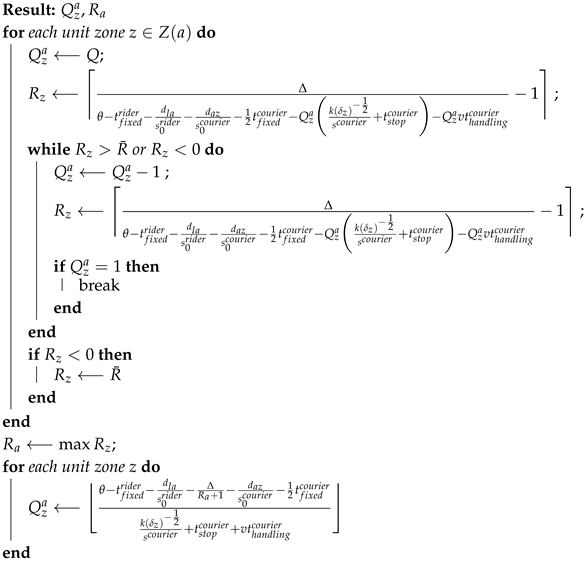
Appendix A. Mobile Access Hub Modeling
Appendix A.1. Transit Time Feasibility
Appendix A.2. Transit Time Constraint
| Algorithm A1: Setting replenishment frequency and route length for a mobile access hub serving multiple unit zones. |
 |
Appendix B. Mobile Access Hub Deployment Experiments
Appendix B.1. Default Parameters
| Parameter | Value | Description | Parameter | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| $0.1/km | Courier variable cost in tour | 15 stops | Courier capacity | ||
| $0.15/km | Courier variable cost in stem | 33 | Maximum replenishments per day | ||
| $10/h | Courier hourly rate | 7 km/h | Courier tour speed | ||
| $0.25/km | Mobile access hub variable transportation cost | 30 km/h | Courier stem speed | ||
| $0.20/km | Rider variable cost | 35 km/h | Rider speed | ||
| $10/h | Rider hourly rate | 40 | Standard deviation of load per day | ||
| $22/day | Mobile access hub depreciation | 0.5 min | Courier handling time per parcel | ||
| g/km [27] | Courier greenhouse gas emissions | 1 min | Courier setup time | ||
| g/km [39] | Rider greenhouse gas emission | 0.5 min | Courier stopping time | ||
| $25/day | Location reservation cost | 5 min | Rider setup time per trip | ||
| k | 1.15 [40] | Route length estimation constant | 2 min | Rider stopping time | |
| 200 | Average load per day |
Appendix B.2. Illustrative Case
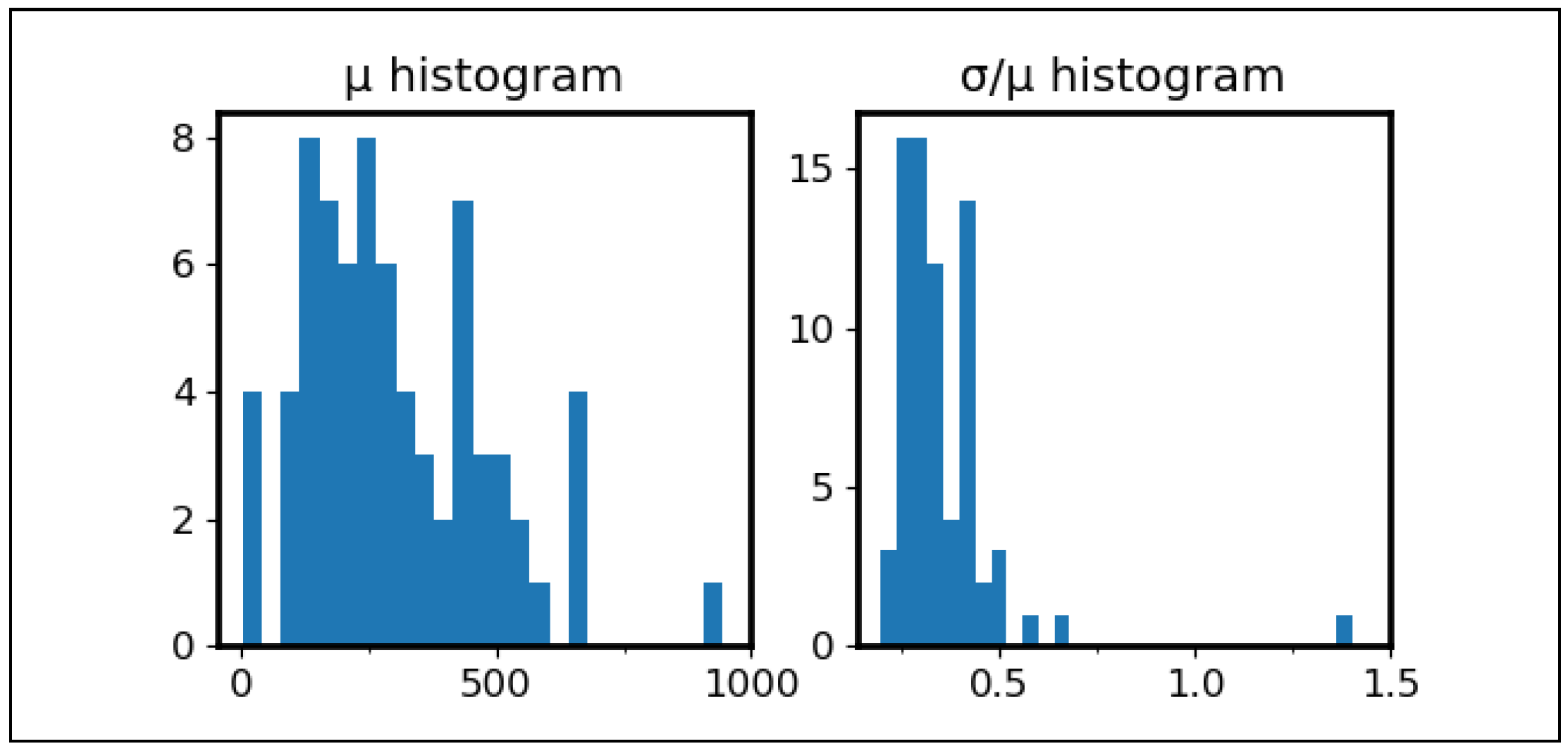
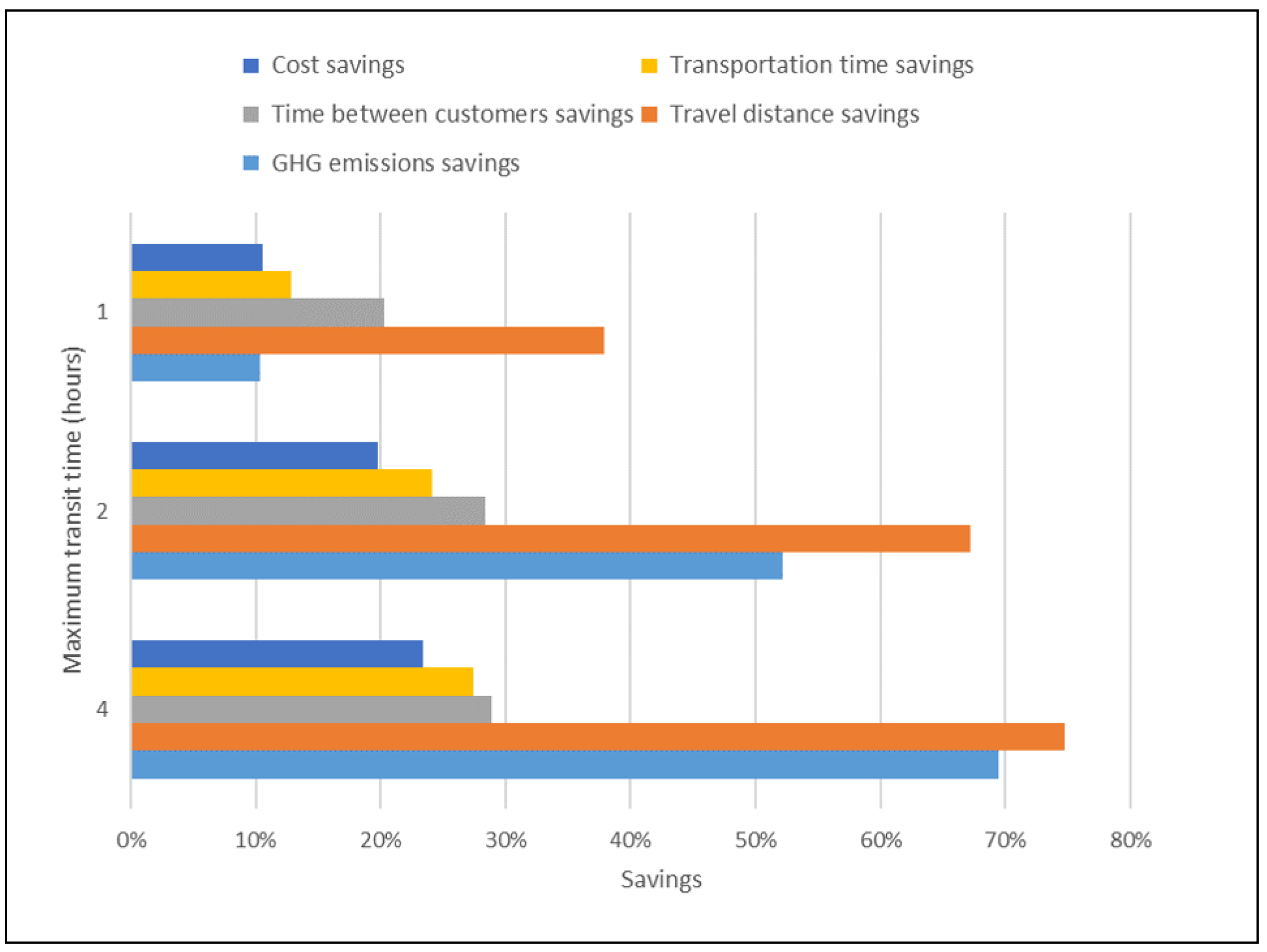
| Max transit time | 4:00 | 2:00 | 1:00 |
| Fleet size | 19 | 18 | 9 |
| UZ covered by a MAH | 38 | 36 | 18 |
| Mean max transit | 2:36 | 1:19 | 0:37 |
| Max transit | 3:53 | 1:54 | 0:56 |
| Total cost | $6283.28 | $6571.65 | $7327.93 |
| Cost per parcel | $0.28 | $0.30 | $0.37 |
| Cost savings | 23.41% | 19.78% | 10.55% |
| Transportation time per parcel | 1.4 min | 1.46 min | 1.68 min |
| Transportation time savings | 27.42% | 24.08% | 12.81% |
| Time between customers | 1.37 min | 1.38 min | 1.54 min |
| Time between customers savings | 28.90% | 28.31% | 20.28% |
| Travel distance per parcel | 90 m | 120 m | 220 m |
| Travel distance savings | 74.77% | 67.19% | 37.86% |
| GHG emissions | 515.17 kg | 537.48 kg | 775.82 kg |
| GHG per parcel | 22.96 g | 24.54 g | 39.17 g |
| GHG emissions savings | 69.49% | 52.15% | 10.31% |
References
- Goodman, R.W. Whatever you call it, just don’t think of last-mile logistics, last. Glob. Logist. Supply Chain. Strateg. 2005, 9, 46–51. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Roadmap to a Single European Transport Area-Towards a competitive and resource efficient transport system. White Pap. Commun. 2011, 144, 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. 2018 Revision of World Urbanization Prospects; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- eMarketer. Annual Retail e-Commerce Sales Growth Worldwide from 2014 to 2023; eMarketer: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Savelsbergh, M.; Van Woensel, T. 50th anniversary invited article—City logistics: Challenges and opportunities. Transp. Sci. 2016, 50, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holguín-Veras, J.; Leal, J.A.; Sanchez-Diaz, I.; Browne, M.; Wojtowicz, J. State of the art and practice of urban freight management Part II: Financial approaches, logistics, and demand management. Transp. Res. Part Policy Pract. 2020, 137, 383–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, M.; Bjerkan, H. Three Proactive Response strategies to COVID 19 business Challenges. MIT Sloan Manag. Rev. 2020; in print. [Google Scholar]
- Holguín-Veras, J.; Leal, J.A.; Sánchez-Diaz, I.; Browne, M.; Wojtowicz, J. State of the art and practice of urban freight management: Part I: Infrastructure, vehicle-related, and traffic operations. Transp. Res. Part Policy Pract. 2020, 137, 360–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranieri, L.; Digiesi, S.; Silvestri, B.; Roccotelli, M. A Review of Last Mile Logistics Innovations in an Externalities Cost Reduction Vision. Sustainability 2018, 10, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, C.M.; Albergaria De Mello Bandeira, R.; Vasconcelos Goes, G.; Schmitz Gonçalves, D.N.; D’Agosto, M.D.A. Sustainable vehicles-based alternatives in last mile distribution of urban freight transport: A systematic literature review. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
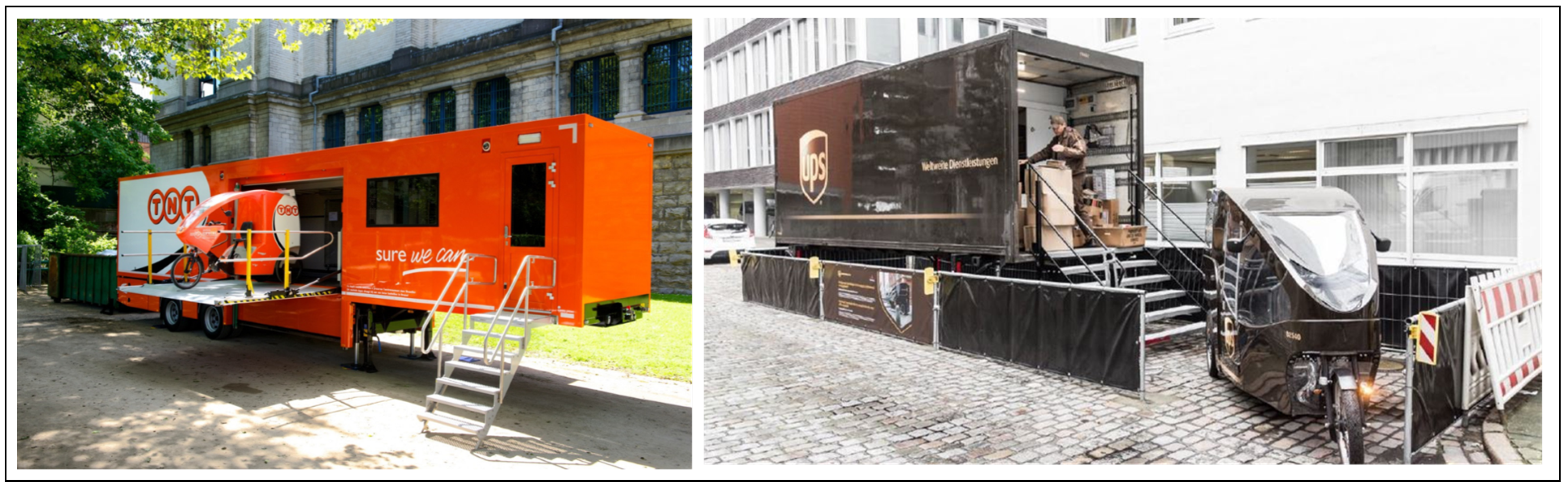
- Verlinde, S.; Macharis, C.; Milan, L.; Kin, B. Does a mobile depot make urban deliveries faster, more sustainable and more economically viable: Results of a pilot test in Brussels. Transp. Res. Procedia 2014, 4, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montreuil, B.; Buckley, S.; Faugère, L.; Khir, R.; Derhami, S. Parcel Logistics Hub Design: The Impact of Modularity and Hyperconnectivity. Prog. Mater. Handl. Res. 2018, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- TNT Express. TNT Express is Using a Mobile Depot in Brussels to Enable More Efficient Delivery. 2013. Available online: http://www.tnt.de/__C1257442002D0760.nsf/html/pressemitteilungen_tntexpresseroeffnetmobilesdepotinbruessel.html (accessed on 10 July 2020).
- UPS. Letzte Meile: Studie zu Micro-Hubs. 2018. Available online: https://logistik-heute.de/news/letzte-meile-studie-zu-micro-hubs-14471.html (accessed on 10 July 2020).
- Hu, W.; Dong, J.; Hwang, B.g.; Ren, R.; Chen, Z. A Scientometrics Review on City Logistics Literature: Research Trends, Advanced Theory and Practice. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quak, H.J.H.; de Koster, M.R.B.M. Delivering Goods in Urban Areas: How to Deal with Urban Policy Restrictions and the Environment. Transp. Sci. 2009, 43, 211–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, C.; Roca-Riu, M.; Furió, S.; Estrada, M. Designing new models for energy efficiency in urban freight transport for smart cities and its application to the Spanish case. Transp. Res. Procedia 2016, 12, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, J.; Nemoto, T.; Browne, M. Home delivery and the impacts on urban freight transport: A review. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2014, 125, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crainic, T.; Ricciardi, N.; Storchi, G. Advanced freight transportation systems for congested urban areas. Transp. Res. Part Emerg. Technol. 2004, 12, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjelloun, A.; Crainic, T. Trends, challenges, and perspectives in city logistics. Transp. Land Use Interact. Proc. TRANSLU 2008, 8, 269–284. [Google Scholar]
- Mancini, S. Multi-echelon distribution systems in city logistics. Eur. Transp. 2013, 54, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Guastaroba, G.; Speranza, M.; Vigo, D. Intermediate facilities in freight transportation planning: A survey. Transp. Sci. 2016, 50, 763–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjevic, M.; Winkenbach, M.; Merchán, D. Integrating collection-and-delivery points in the strategic design of urban last-mile e-commerce distribution networks. Transp. Res. Part Logist. Transp. Rev. 2019, 131, 37–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raicu, S.; Costescu, D.; Burciu, S. Distribution System with Flow Consolidation at the Boundary of Urban Congested Areas. Sustainability 2020, 12, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjevic, M.; Ndiaye, A.B. Development and Application of a Transferability Framework for Micro-consolidation Schemes in Urban Freight Transport. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2014, 125, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, J.; Browne, M.; Allen, J. Before-after assessment of a logistics trial with clean urban freight vehicles: A case study in London. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 39, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marujo, L.; Goes, G.; D’Agosto, M.; Ferreira, A.; Winkenbach, M.; Bandeira, R. Assessing the sustainability of mobile depots: The case of urban freight distribution in Rio de Janeiro. Transp. Res. Part Transp. Environ. 2018, 62, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stodick, K.; Deckert, C. Sustainable Parcel Delivery in Urban Areas with Micro De-pots. Mobil. Glob. World 2018 2019, 22, 233. [Google Scholar]
- Assmann, T.; Lang, S.; Müller, F.; Schenk, M. Impact Assessment Model for the Implementation of Cargo Bike Transshipment Points in Urban Districts. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, M.; Allen, J.; Leonardi, J. Evaluating the use of an urban consolidation centre and electric vehicles in central London. IATSS Res. 2011, 35, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvidsson, N.; Pazirandeh, A. An ex ante evaluation of mobile depots in cities: A sustainability perspective. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2017, 11, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, B.; Ramos, A.G.; de Sousa, J.P. A classification of two-tier distribution systems based on mobile depots. Transp. Res. Procedia 2020, 47, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, M.; Allen, J.; Nemoto, T.; Patier, D.; Visser, J. Reducing social and environmental impacts of urban freight transport: A review of some major cities. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 39, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daganzo, C.F.; Gayah, V.V.; Gonzales, E.J. The potential of parsimonious models for understanding large scale transportation systems and answering big picture questions. EURO J. Transp. Logist. 2012, 1, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.; Başdere, M.; Li, X.; Ouyang, Y.; Smilowitz, K. Advancements in continuous approximation models for logistics and transportation systems: 1996–2016. Transp. Res. Part Methodol. 2018, 107, 229–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daganzo, C.F. The length of tours in zones of different shapes. Transp. Res. Part Methodol. 1984, 18, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daganzo, C.F. Logistics Systems Analysis; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Faugère, L.; Klibi, W.; White, C., III; Montreuil, B. Dynamic Pooled Capacity Deployment for Urban Parcel Logistics. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.11270. [Google Scholar]
- United States Environment Protection Agency (EPA). The 2019 EPA Automotive Trends Report: Greenhouse Gas Emissions, Fuel Economy, and Technology Since 1975; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2020.
- Winkenbach, M.; Kleindorfer, P.R.; Spinler, S. Enabling Urban Logistics Services at La Poste through Multi-Echelon Location-Routing. Transp. Sci. 2016, 50, 520–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Assessment | Performance Indicator |
|---|---|
| Economic | Total cost |
| Cost per parcel | |
| Time efficiency | Transportation time per parcel |
| Average time between customers | |
| Environmental | Greenhouse gas emissions |
| Travel distance per parcel |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Faugère, L.; White, C., III; Montreuil, B. Mobile Access Hub Deployment for Urban Parcel Logistics. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7213. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12177213
Faugère L, White C III, Montreuil B. Mobile Access Hub Deployment for Urban Parcel Logistics. Sustainability. 2020; 12(17):7213. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12177213
Chicago/Turabian StyleFaugère, Louis, Chelsea White, III, and Benoit Montreuil. 2020. "Mobile Access Hub Deployment for Urban Parcel Logistics" Sustainability 12, no. 17: 7213. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12177213
APA StyleFaugère, L., White, C., III, & Montreuil, B. (2020). Mobile Access Hub Deployment for Urban Parcel Logistics. Sustainability, 12(17), 7213. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12177213





