Comparative Study of AI-Based Methods—Application of Analyzing Inflow and Infiltration in Sanitary Sewer Subcatchments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
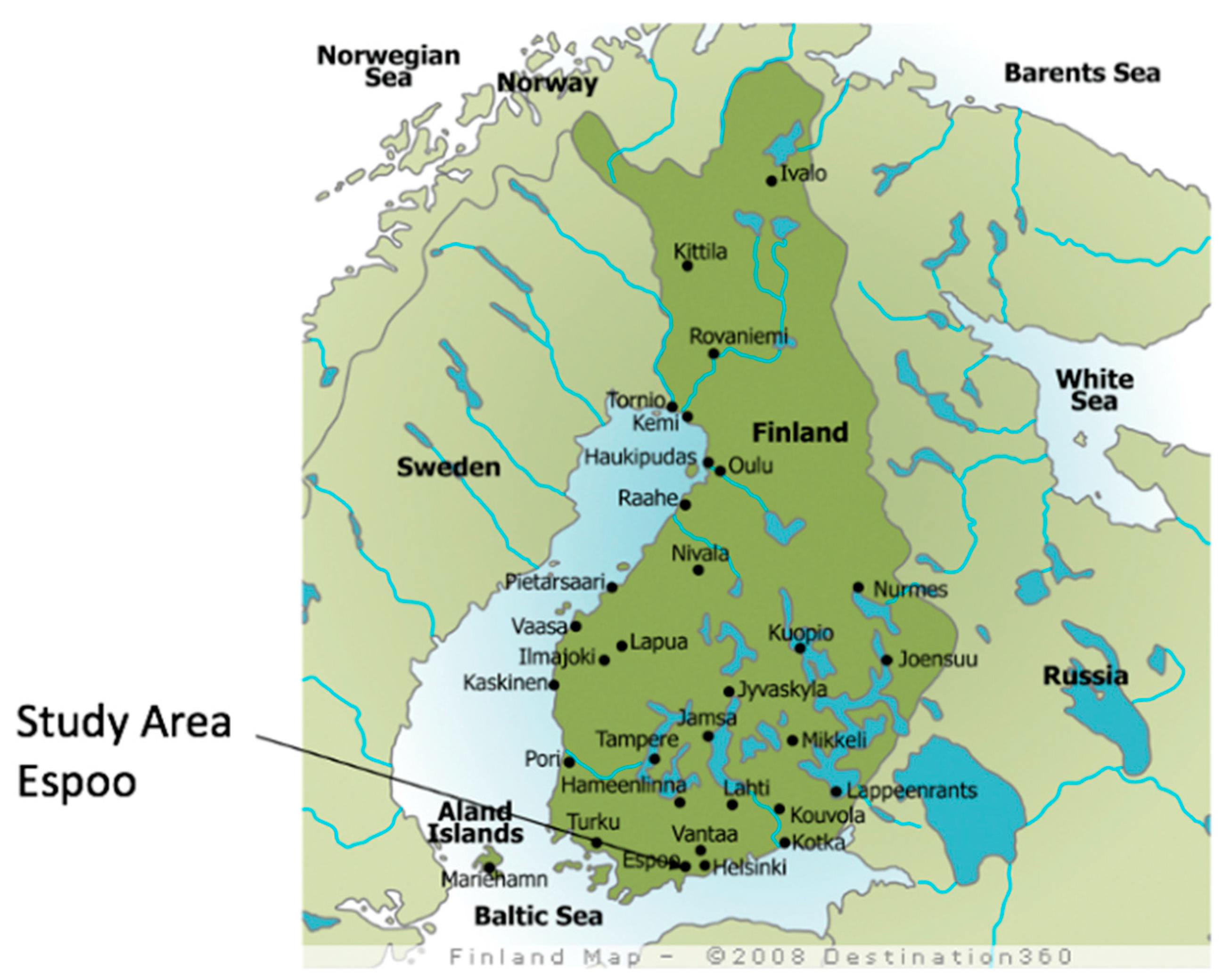
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection and Processing
2.3. Water Consumption in Study Areas
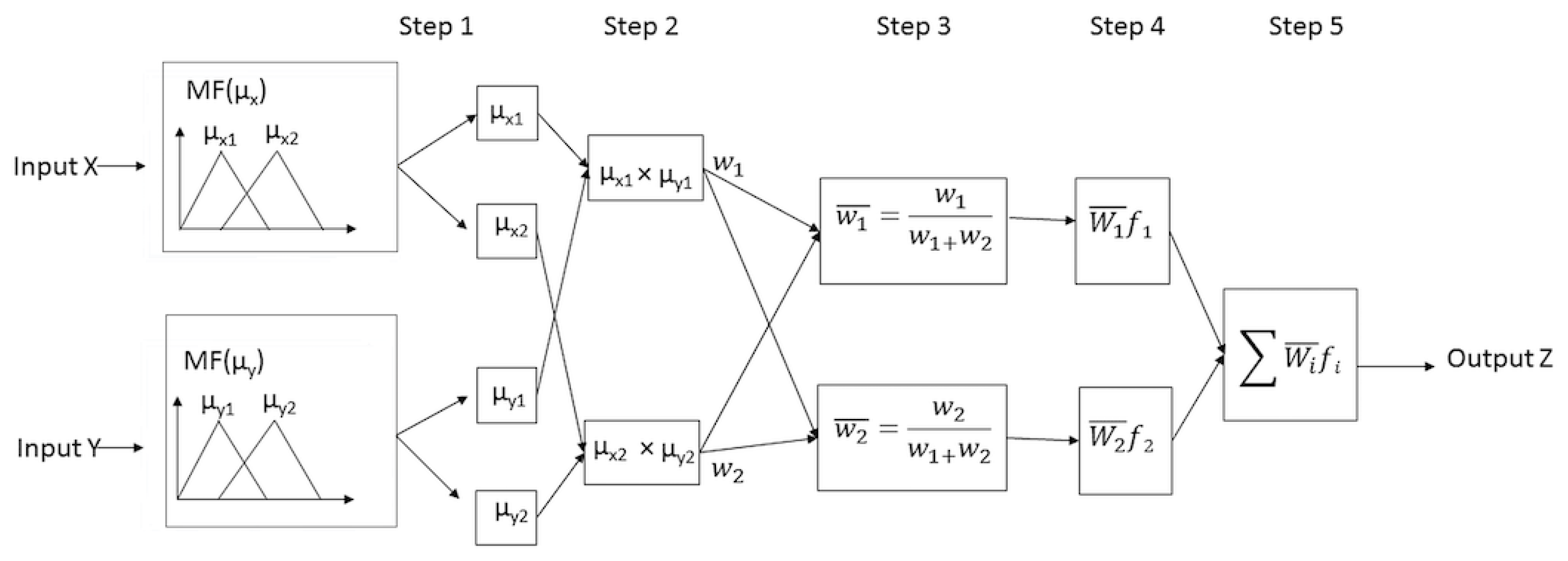
2.4. Adaptive Neurofuzzy Inference System (ANFIS)
then f1 = a1 µx1+b1 µy1+r1
then f2 = a2 µx2+b2 µy2+r2.
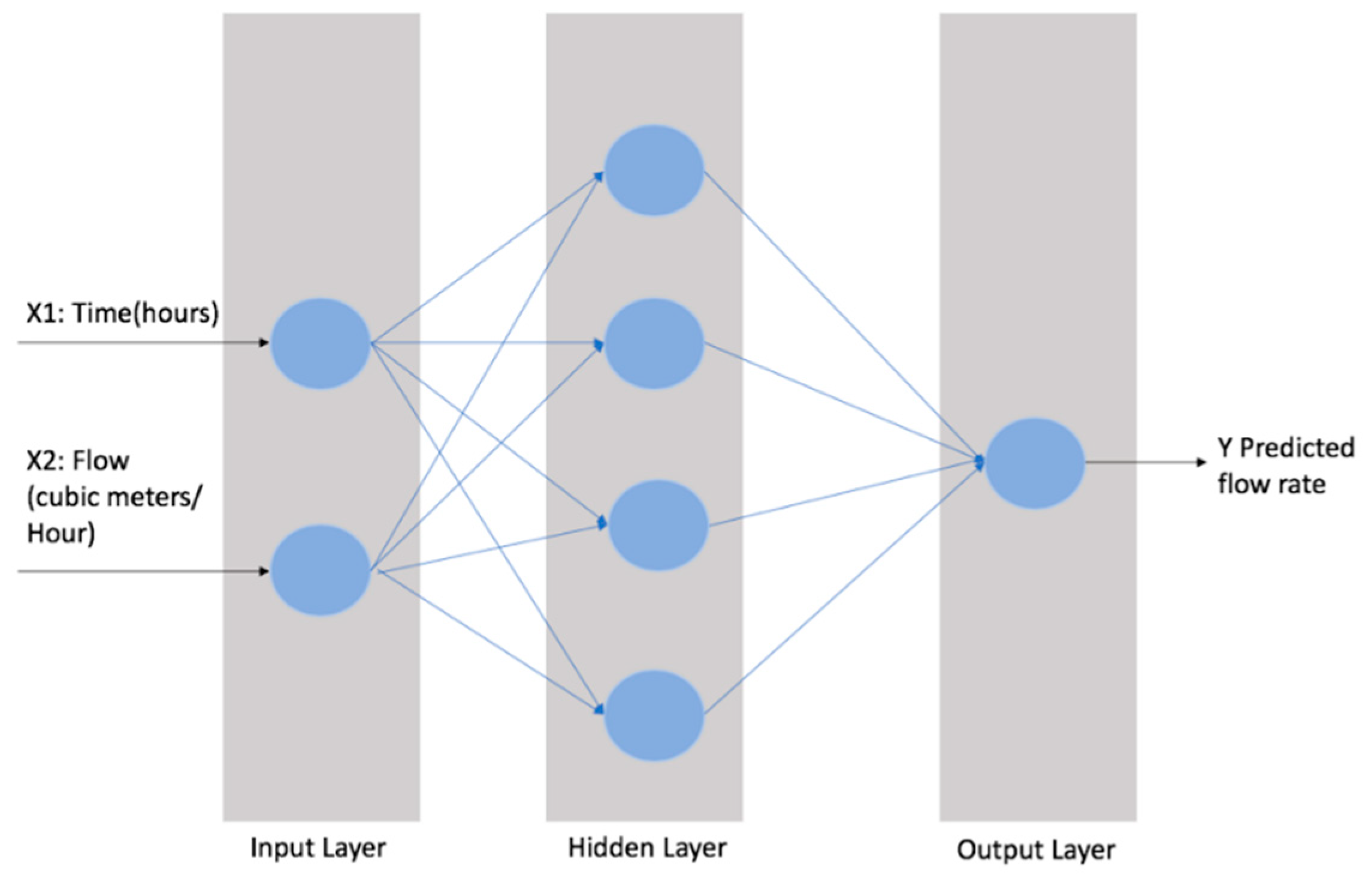
2.5. Multilayer Perceptron Neural Network
2.6. Model Evaluation
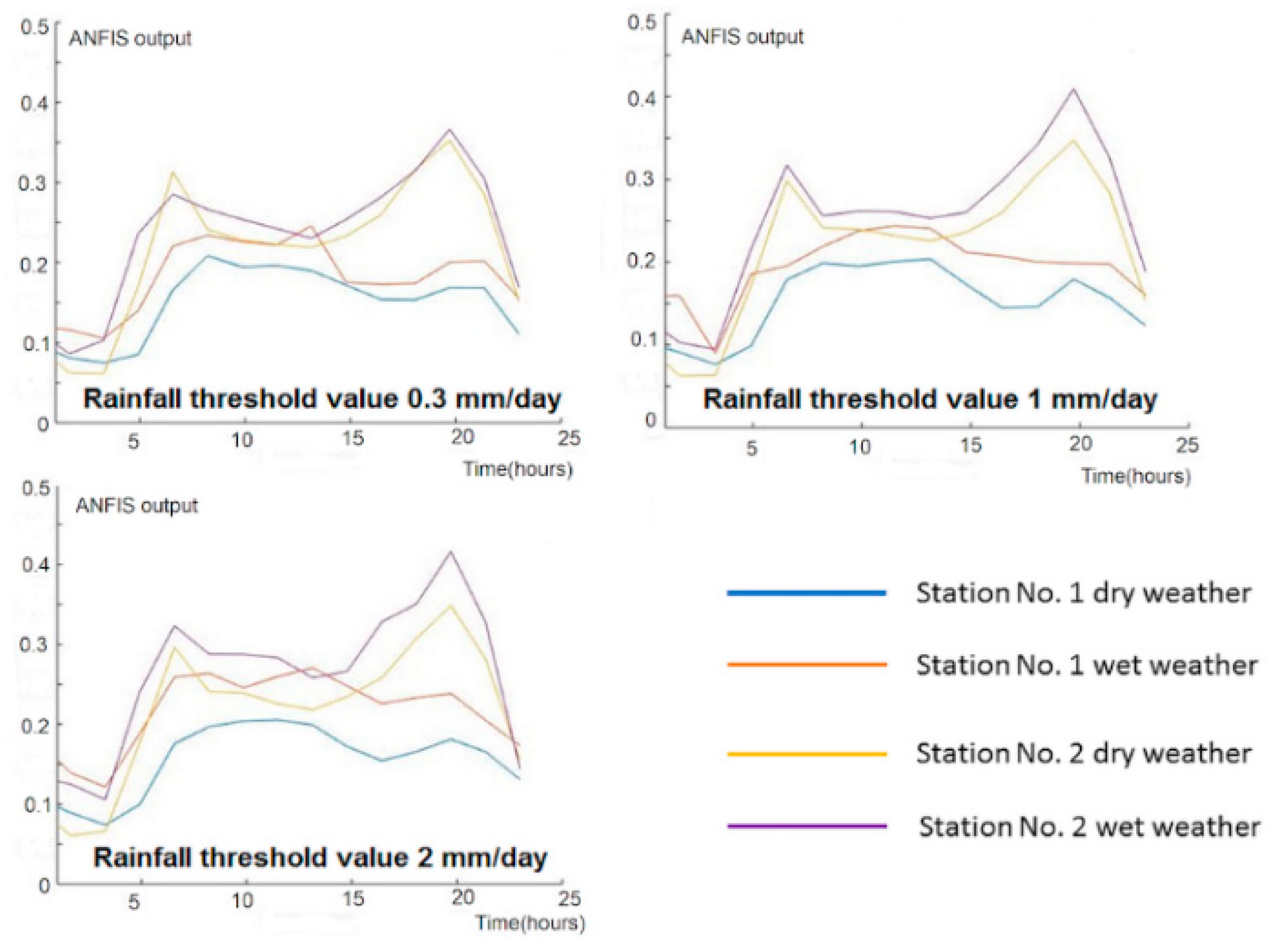
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tan, P.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, D.Z.; Zhang, T. Assessment and pathway determination for rainfall-derived inflow and infiltration in sanitary systems: A case study. Urban Water J. 2019, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. Flow data, Inflow/Infiltration Ratio, and Autoregressive Error Models. J. Environ. Eng. 2005, 131, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, X.; Zhu, D.Z.; Shi, H.; Yuan, Z. Quantifying rainfall-derived inflow and infiltration in sanitary sewer systems based on conductivity monitoring. J. Hydrol. 2018, 558, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, H.T.; Ngien, S.K.; Othman, N.; Ghani, A.A.; Abd, N. Preliminary inflow and infiltration study of sewerage systems from two residential areas in Kuantan, Pahang. ESTEEM Acad. J. 2017, 13, 98–106. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yao, Y.; Zhou, W.; You, L.; Zeng, S. Quantification of Inflow and Infiltration in Urban Sewer Systems Based on Triangle Method. Water Pollut. Treat. 2019, 7, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrin, T.; Sharma, A.K.; Muttil, N. Impact of short duration intense rainfall events on sanitary sewer network performance. Water 2017, 9, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bénédittis, J.D.; Bertrand-Krajewski, J.L. Infiltration in sewer systems: Comparison of measurement methods. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 52, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpf, C.; Krebs, P. Quantification of groundwater infiltration and surface water inflows in urban sewer networks based on a multiple model approach. Water Res. 2011, 45, 3129–3136. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Karpf, C.; Krebs, P. Modelling of groundwater infiltration into sewer systems. Urban Water J. 2013, 10, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittenberg, H.; Aksoy, H. Groundwater intrusion into leaky sewer systems. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 62, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, R.S.; Almeida, M.C.; Matos, J.S. Estimating flow data in urban drainage using partial least squares regression. Urban. Water J. 2016, 14, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staufer, P.; Scheidegger, A.; Rieckermann, J. Assessing the performance of sewer rehabilitation on the reduction of infiltration and inflow. Water Res. 2012, 46, 5185–5196. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shehab, T.; Moselhi, O. Automated detection and classification of infiltration in sewer pipes. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2005, 11, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, F.J.; Seco, A.; Ferrer, J.; Rodrigo, M.A. Use of neurofuzzy networks to improve wastewater flow-rate forecasting. Environ. Model. Softw. 2009, 24, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haimi, H.; Mulas, M.; Corona, F.; Vahala, R. Data-derived soft-sensors for biological wastewater treatment plants: An overview. Environ. Model. Softw. 2013, 47, 88–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imrie, C.E.; Durucan, S.; Korre, A. River flow prediction using artificial neural networks: Generalisation beyond the calibration range. J. Hydrol. 2000, 233, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathian, F.; Mehdizadeh, S.; Sales, A.K.; Safari, M.J.S. Hybrid models to improve the monthly river flow prediction: Integrating artificial intelligence and non-linear time series models. J. Hydrol. 2019, 575, 1200–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy Logic Toolbox, for Use with Matlab. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/help/pdf_doc/fuzzy/fuzzy.pdf (accessed on 6 June 2020).
- Alvisi, S.; Franchini, M. Fuzzy neural networks for water level and discharge forecasting with uncertainty. Environ. Model. Softw. 2011, 26, 523–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddasi, M.; Bazzazi, A.A.; Aalianvari, A. Prediction of ground water inflow rate using non-linear multiple regression and ANFIS models: A case study of Amirkabir tunnel in Iran. In Proceedings of the International Black Sea Mining&Tunnelling Symposium, Trabzon, Turkey, 2–4 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, M.; Abrahart, R.J.; Mount, N.; Chang, F.J. Including spatial distribution in a data-driven rainfall runoff model to improve reservoir inflow forecasting in Taiwan. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 28, 1055–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, S.; Deligianni, A.; Aslani, P.; Agathokleous, A. Risk-based asset management of water piping networks using neurofuzzy systems. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2009, 33, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaloop, M.; EI-Diasty, M.; Hu, J. Real-time prediction of water level change using adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2017, 8, 1320–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haykin, S. Neural Networks a Comprehensive Foundation, 2nd ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Zounemat-Kermani, M.; Stephan, D.; Barjenbruch, M.; Hinkelmann, R. Ensemble data mining modeling in corrosion of concrete sewer: A comparative study of network-based (MLPNN & RBFNN) and tree-based (RF, CHAID, & CART) models. Adv. Engin. Inform. 2020, 43, 101030. [Google Scholar]
- Hornik, K.; Stinchcombe, M.; White, H. Multilayer feedforward networks are universal approximators. Neural Netw. 1989, 2, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornik, K. Approximation capabilities of multilayer feedforward networks. Neural Netw. 1991, 4, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Heddam, S.; Nyarko, E.K.; Hadzima-Nyarko, M.; Piccolroaz, S.; Wu, S. Modeling daily water temperature for rivers: Comparison between adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference systems and artificial neural networks models. Environ. Sci. Pollution Res. 2019, 26, 402–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heddam, S.; Kisi, O.; Sebbar, A.; Houichi, L.; Djemili, L. Predicting water quality indicators from conventional and nonconventional water resources in Algeria country: Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference systems versus artificial neural networks. In The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Springer: Berlin/Hidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- FMI Finnish Meteorological Institute. Sadetta Ja Poutaa. Available online: http://ilmatieteenlaitos.fi/sade (accessed on 6 June 2020).
- Saltikoff, E.; Nevvonen, L. First experiences of the operational use of a dual-polarisation weather radar in Finland. Meteorol. Z. 2011, 20, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peura, M. Rack-a program for anomaly detection, product generation, and compositing. In Proceedings of the 7th European Conference on Radar in Meteorology and Hydrology (ERAD 2012), Toulouse, France, 25–29 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Leinonen, J.; Moisseev, D.; Leskinen, M.; Petersen, W.A.A. Climatology of disdrometer measurements of rainfall in Finland over five years with implications for global radar observations. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2014, 51, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control. 1965, 8, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.-S.R. ANFIS: Adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference system. IEEE Trans. Syst. Manag. Cybern. 1993, 23, 665–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, T.; Draxler, R.R. Root mean square error (RMSE) or mean absolute error (MAE)?–Arguments against avoiding RMSE in the literature. Geosci. Model Dev. 2014, 7, 1247–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normalization. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Normalization_(statistics) (accessed on 6 June 2020).

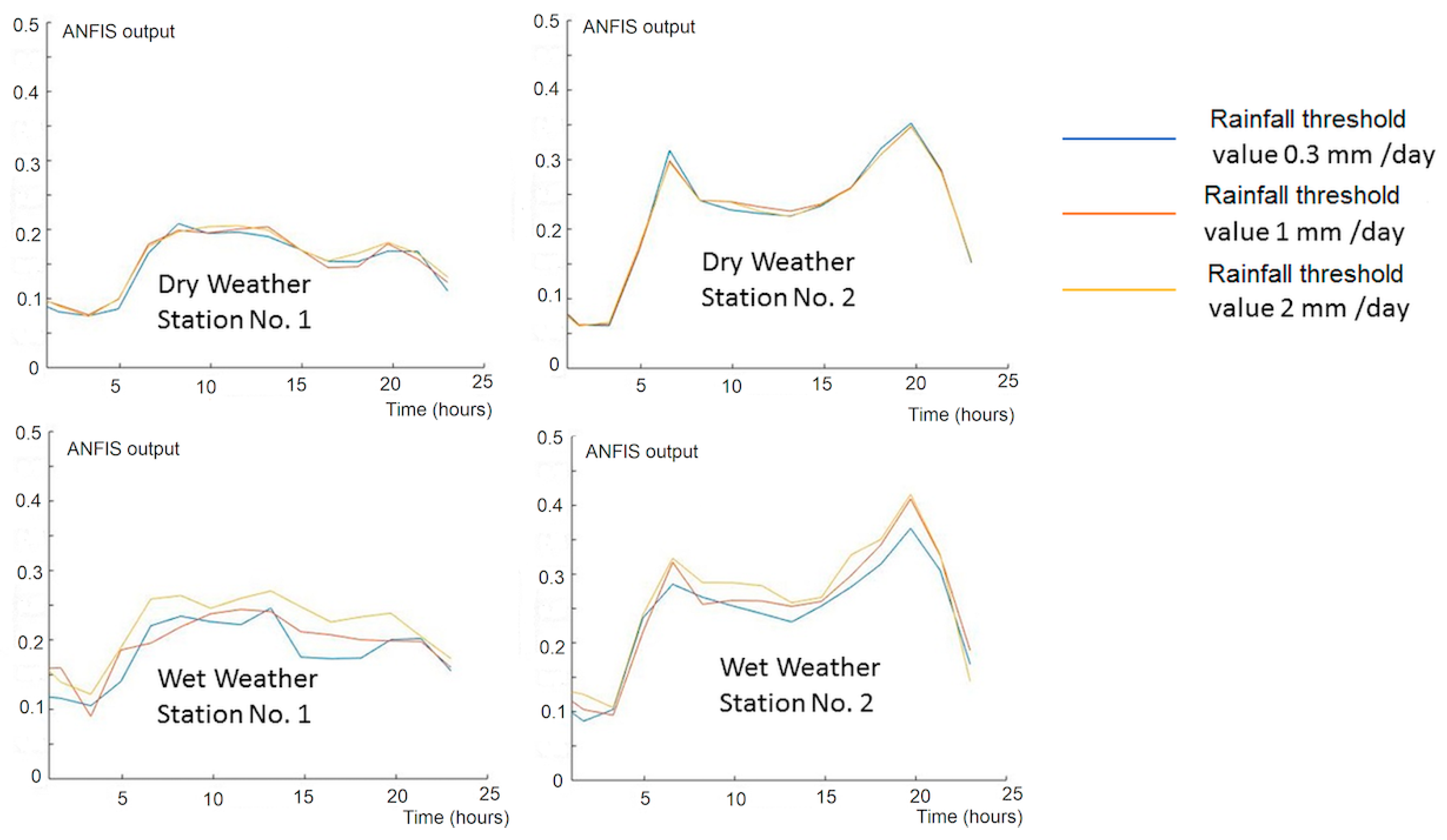
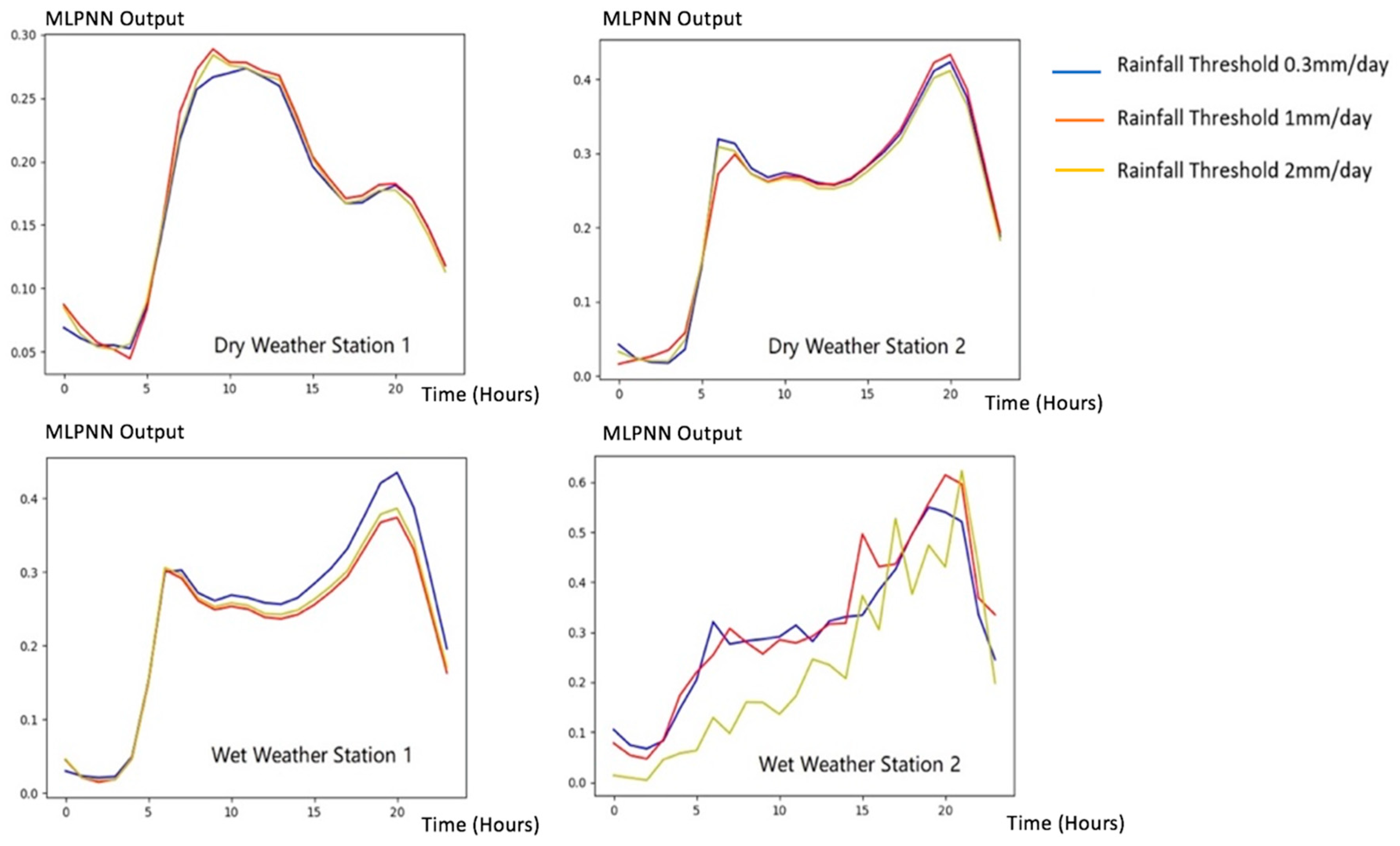
| Input Variables | Time (hours); Wastewater flow rate (cubic meters) |
| Output Variable | Predicted wastewater flow at the corresponding time in hours |
| Stations | Rainfall-Threshold Values | RMSE ANFIS | RMSE MLPNN |
|---|---|---|---|
| Station 1 | 0.3 | 0.0962 (dry weather), 0.1199 (wet weather) | 0.5328 (dry weather), 0.4272 (wet weather) |
| 1 | 0.106 (dry weather), 0.138 (wet weather) | 0.5247 (dry weather), 0.3334 (wet weather) | |
| 2 | 0.1035 (dry weather), 0.1492 (wet weather) | 0.5228 (dry weather), 0.2084 (wet weather) | |
| Station 2 | 0.3 | 0.076 (dry weather), 0.097 (wet weather) | 0.3932 (dry weather), 0.3566 (wet weather) |
| 1 | 0.0774 (dry weather), 0.1035 (wet weather) | 0.3932 (dry weather), 0.2495 (wet weather) | |
| 2 | 0.0775 (dry weather), 0.112 (wet weather) | 0.3938 (dry weather), 0.1072 (wet weather) |
| Stations | Rainfall-Threshold Values | R2 ANFIS | R2 MLPNN |
|---|---|---|---|
| Station 1 | 0.3 | 0.8661 (dry weather), 0.8351 (wet weather) | 0.6103 (dry weather), 0.6139 (wet weather) |
| 1 | 0.8622 (dry weather), 0.8034 (wet weather) | 0.5247 (dry weather), 0.4731 (wet weather) | |
| 2 | 0.8501 (dry weather), 0.6701 (wet weather) | 0.6092 (dry weather), 0.4565 (wet weather) | |
| Station 2 | 0.3 | 0.9146 (dry weather), 0.6218 (wet weather) | 0.7341 (dry weather), 0.5972 (wet weather) |
| 1 | 0.9443 (dry weather), 0.5881 (wet weather) | 0.7273 (dry weather), 0.4472 (wet weather) | |
| 2 | 0.6678 (dry weather), 0.8765 (wet weather) | 0.7256 (dry weather), 0.6381 (wet weather) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Laakso, T.; Wang, Z.; Pulkkinen, S.; Ahopelto, S.; Virrantaus, K.; Li, Y.; Cai, X.; Zhang, C.; Vahala, R.; et al. Comparative Study of AI-Based Methods—Application of Analyzing Inflow and Infiltration in Sanitary Sewer Subcatchments. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6254. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12156254
Zhang Z, Laakso T, Wang Z, Pulkkinen S, Ahopelto S, Virrantaus K, Li Y, Cai X, Zhang C, Vahala R, et al. Comparative Study of AI-Based Methods—Application of Analyzing Inflow and Infiltration in Sanitary Sewer Subcatchments. Sustainability. 2020; 12(15):6254. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12156254
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhe, Tuija Laakso, Zeyu Wang, Seppo Pulkkinen, Suvi Ahopelto, Kirsi Virrantaus, Yu Li, Ximing Cai, Chi Zhang, Riku Vahala, and et al. 2020. "Comparative Study of AI-Based Methods—Application of Analyzing Inflow and Infiltration in Sanitary Sewer Subcatchments" Sustainability 12, no. 15: 6254. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12156254
APA StyleZhang, Z., Laakso, T., Wang, Z., Pulkkinen, S., Ahopelto, S., Virrantaus, K., Li, Y., Cai, X., Zhang, C., Vahala, R., & Sheng, Z. (2020). Comparative Study of AI-Based Methods—Application of Analyzing Inflow and Infiltration in Sanitary Sewer Subcatchments. Sustainability, 12(15), 6254. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12156254







