The Ripple Effect and Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Intra-Urban Housing Prices at the Submarket Level in Shanghai, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Data and Methodology
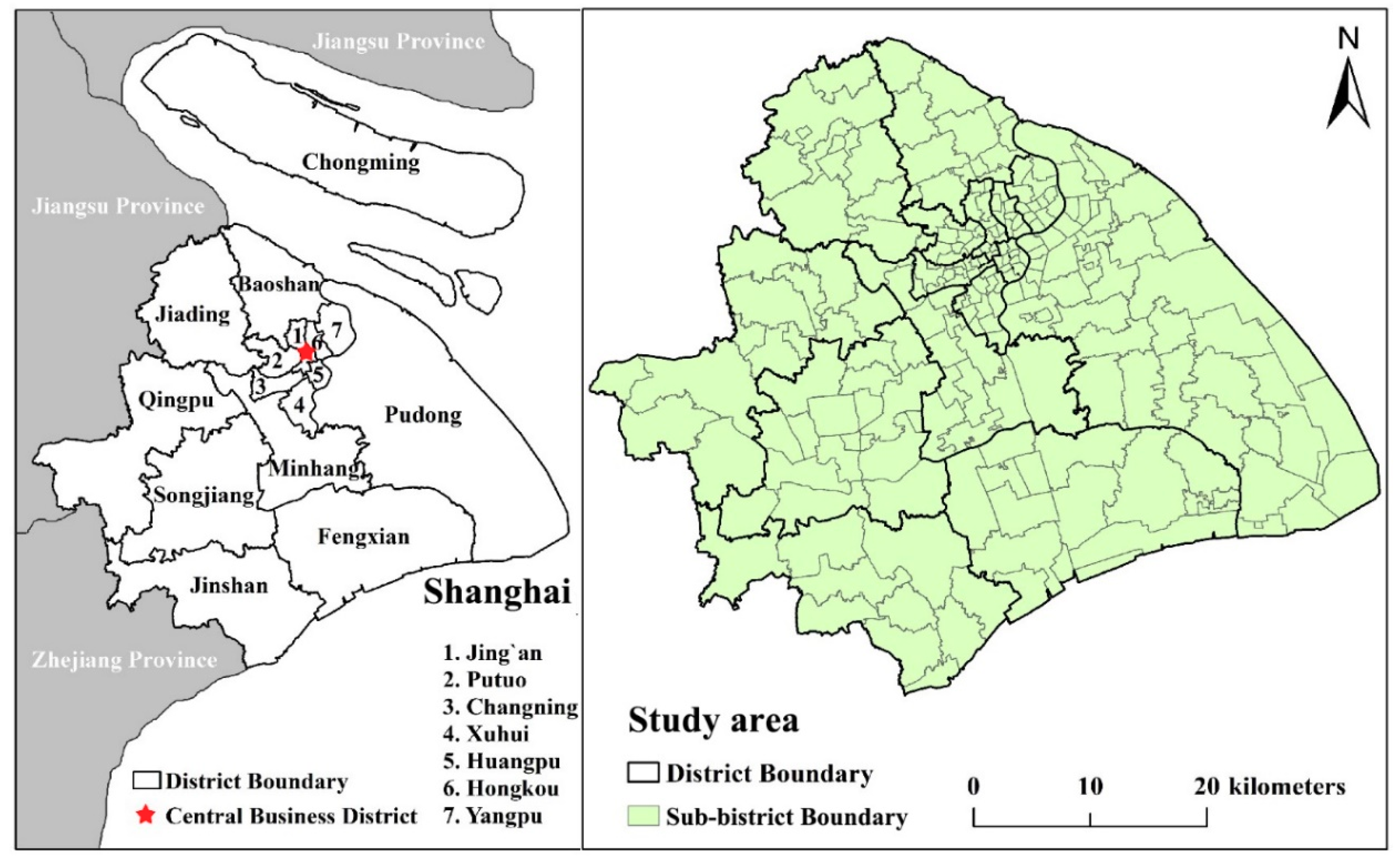
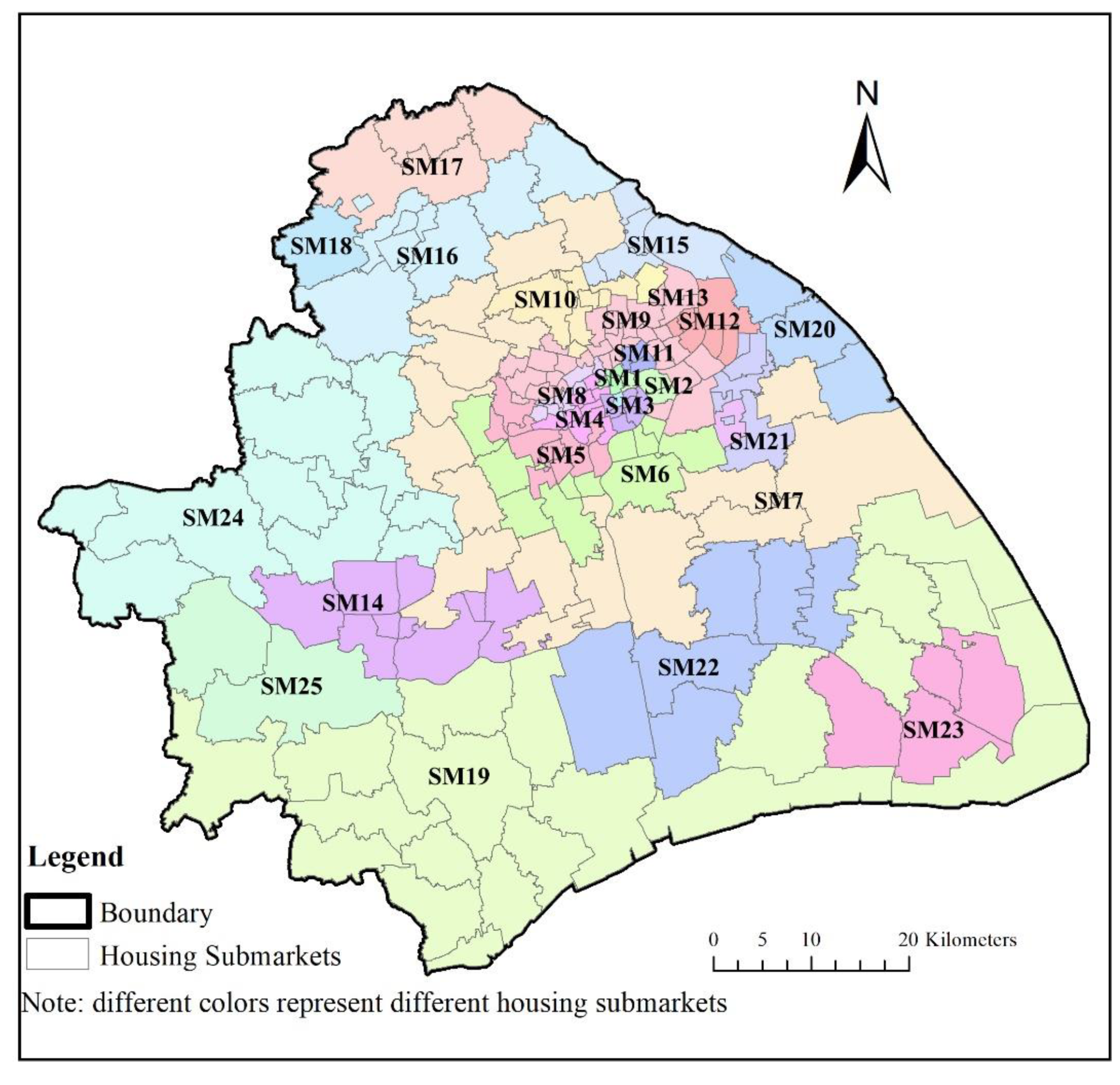
3.1. Study Area and Data Processing
3.2. Methodology
3.2.1. Grouping Analysis and Space–Time Analysis
3.2.2. The Convergence Test and Convergence Club Identification
4. Empirical Results
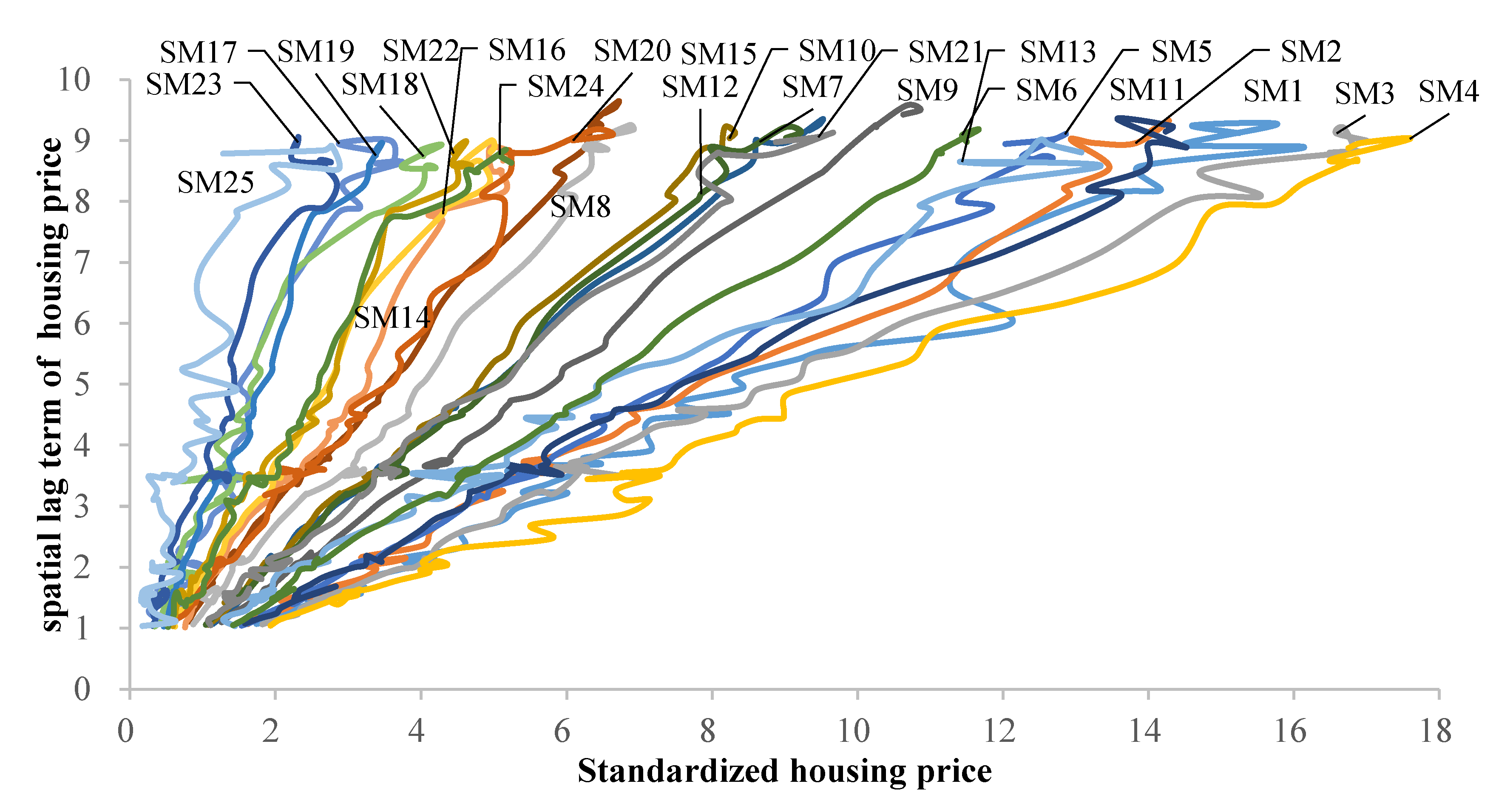
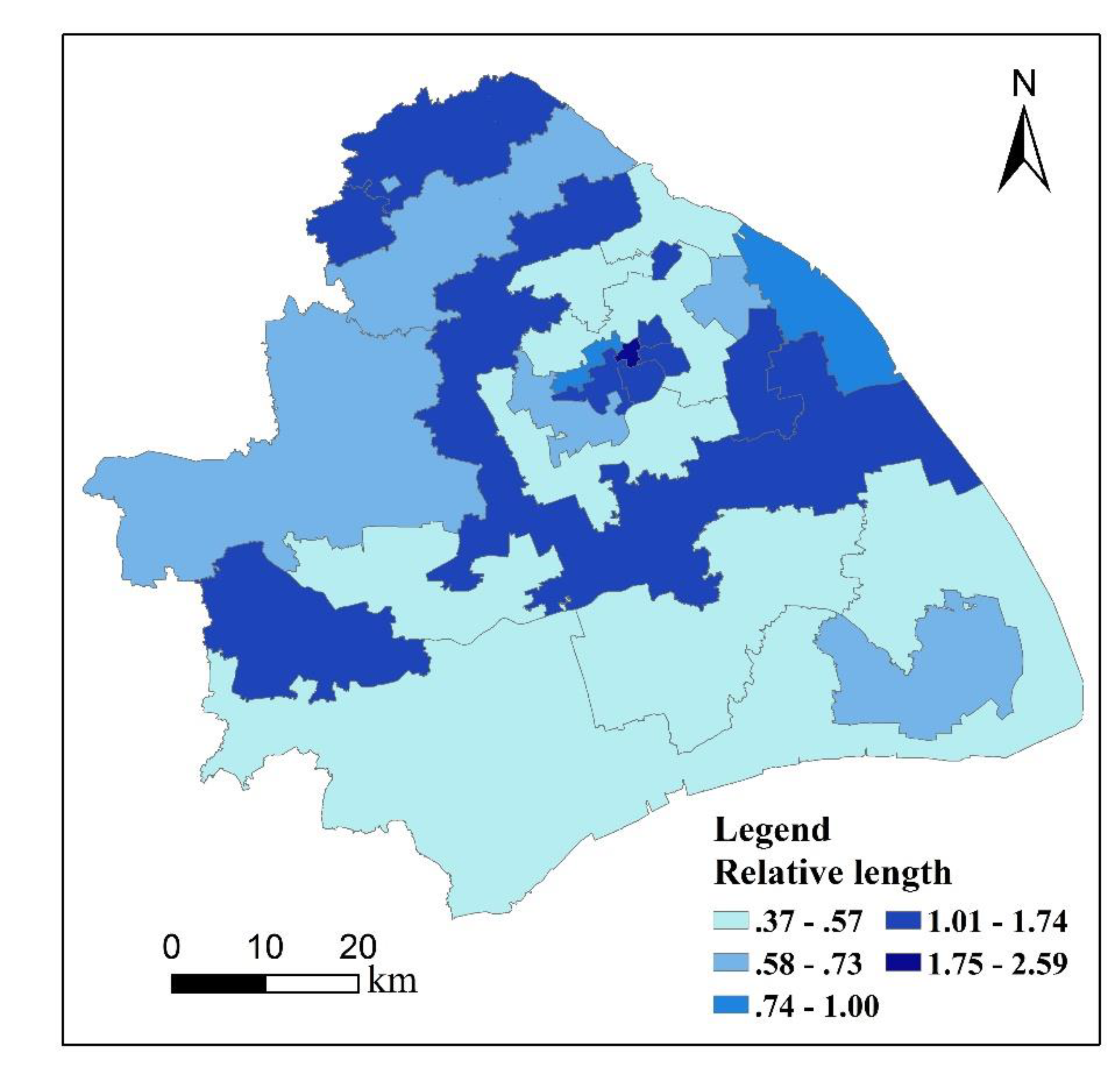
4.1. Spatiotemporal Distribution and Diffusion of Housing Prices across Submarkets in Shanghai
4.2. Convergence Club Formation among Different Submarkets in Shanghai
5. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations (UN). Sustainable Development Goals Report; UN: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- De Bruyne, K.; Van Hove, J. Explaining the spatial variation in housing prices: An economic geography approach. Appl. Econ. 2013, 45, 1673–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.-Z.; Ong, S.E.; Koh, H.C. Determinants of house price: A decision tree approach. Urban Stud. 2006, 43, 2301–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, S. Chapter 41 Hedonic analysis of housing markets. In Handbook of Regional and Urban Economics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1999; Volume 3, pp. 1595–1635. [Google Scholar]
- Glaeser, E.L.; Gyourko, J.; Saks, R.E. Why have housing prices gone up? Am. Econ. Rev. 2005, 95, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mankiw, N.G.; Weil, D.N. The baby boom, the baby bust, and the housing market. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 1989, 19, 235–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plantinga, A.J.; Détang-Dessendre, C.; Hunt, G.L.; Piguet, V. Housing prices and inter-urban migration. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2013, 43, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abelson, P. House and land prices in Sydney from 1931 to 1989. Urban Stud. 1997, 34, 1381–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banzhaf, H.S.; Farooque, O. Interjurisdictional housing prices and spatial amenities: Which measures of housing prices reflect local public goods? Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2013, 43, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schläpfer, F.; Waltert, F.; Segura, L.; Kienast, F. Valuation of landscape amenities: A hedonic pricing analysis of housing rents in urban, suburban and periurban Switzerland. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 141, 24–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, W. Location and Land Use; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Helbich, M.; Brunauer, W.; Vaz, E.; Nijkamp, P. Spatial heterogeneity in hedonic house price models: The case of Austria. Urban Stud. 2013, 41, 390–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hui, E.C.; Zhong, J.; Yu, K. Heterogeneity in spatial correlation and influential factors on property prices of submarkets categorized by urban dwelling spaces. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2014, 142, 04014047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X. Spatial and temporal dependence in house price prediction. J. Real Estate Financ. Econ. 2013, 47, 341–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Wu, J.; Wei, Y.D.; Wang, L. Policy change, amenity, and spatiotemporal dynamics of housing prices in Nanjing, China. Land Use Policy 2018, 75, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piketty, T.; Zucman, G. Capital is back: Wealth-income ratios in rich countries 1700–2010. Q. J. Econ. 2014, 129, 1255–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, J. Housing Affordability and Housing Policy in Urban China; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Goodman, A.C.; Thibodeau, T.G. Housing market segmentation. J. Hous. Econ. 1998, 7, 121–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, B.; Watkins, C. Defining spatial housing submarkets: Exploring the case for expert delineated boundaries. Urban Stud. 2017, 54, 1446–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watkins, C.A. The definition and identification of housing submarkets. Environ. Plan. A 2001, 33, 2235–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meen, G. Regional house prices and the ripple effect: A new Interpretation. Hous. Stud. 1999, 14, 733–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, S. Housing markets in China and policy implications: Comovement or ripple effect. China World Econ. 2014, 22, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hui, E.C.; Wen, H. The regional house prices in China: Ripple effect or differentiation. Habitat Int. 2017, 67, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, M.J.; Otero, J.; Panagiotidis, T. Property heterogeneity and convergence club formation among local house prices. J. Hous. Econ. 2019, 43, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.; De Vita, G. Pairwise convergence of district-level house prices in London. Urban Stud. 2012, 49, 721–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, M.J.; Otero, J.; Panagiotidis, T. A pair-wise analysis of intra-city price convergence within the Paris housing market. J. Real Estate Financ. Econ. 2017, 54, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bangura, M.; Lee, C.L. House price diffusion of housing submarkets in Greater Sydney. Hous. Stud. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzezicka, J.; Łaszek, J.; Olszewski, K.; Waszczuk, J. Analysis of the filtering process and the ripple effect on the primary and secondary housing market in Warsaw, Poland. Land Use Policy 2019, 88, 104098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Lee, G. Exploring spatiotemporal dynamics in a housing market using the spatial vector autoregressive Lasso: A case study of Seoul, Korea. Trans. GIS 2019, 24, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, A.; Castro, E.; Maiti, T.; Marques, J. Endogenous spatial regression and delineation of submarkets: A new framework with application to housing markets. J. Appl. Econom. 2016, 31, 32–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Miller, S.M. “Ripple effects” and forecasting home prices in Los Angeles, Las Vegas, and Phoenix. Ann. Reg. Sci. 2012, 48, 763–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cook, S.; Watson, D. A new perspective on the ripple effect in the UK housing market: Comovement, cyclical subsamples and alternative indices. Urban Stud. 2016, 53, 3048–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacDonald, R.; Taylor, M.P. Regional house prices in Britain: Long-run relationships and short-run dynamics. Scott. J. Polit. Econ. 1993, 40, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, L.S.; Ma, Y.; Haurin, D.R. Domino effects within a housing market: The transmission of house price changes across quality tiers. J. Real Estate Financ. Econ. 2008, 37, 299–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Young, M.; Hargreaves, B. The ripple effect of local house price movements in New Zealand. J. Prop. Res. 2009, 26, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Andre, C.; Gil-Alana, L. Comovement in Euro area housing prices: A fractional cointegration approach. Urban Stud. 2015, 52, 3123–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leung, C.K.Y.; Cheung, P.W.Y.; Tang, E.C.H. Financial crisis and the comovements of housing sub-markets: Do relationships change after a crisis? Int. Real Estate Rev. Asian Real Estate Soc. 2013, 16, 68–118. [Google Scholar]
- Meen, G. Spatial Housing Economics: A Survey; Sage Publications Sage UK: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, M.-C.; Tsai, I.-C. Ripple effect and contagious effect in the US regional housing markets. Ann. Reg. Sci. 2016, 56, 55–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holly, S.; Pesaran, M.H.; Yamagata, T. The spatial and temporal diffusion of house prices in the UK. J. Urban Econ. 2011, 69, 2–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geng, B.; Bao, H.; Liang, Y. A study of the effect of a high-speed rail station on spatial variations in housing price based on the hedonic model. Habitat Int. 2015, 49, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Boelhouwer, P.; De Haan, J. Interurban house price gradient: Effect of urban hierarchy distance on house prices. Urban Stud. 2015, 53, 3317–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saphores, J.-D.; Aguilar-Benitez, I. Smelly local polluters and residential property values: A hedonic analysis of four Orange County (California) cities. Estud. Econ. 2005, 20, 197–218. [Google Scholar]
- Drake, L. Testing for convergence between UK regional house prices. Reg. Stud. 1995, 29, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, M.J. How convergent are regional house prices in the United Kingdom? Some new evidence from panel data unit root testing. J. Econ. Soc. Res. 2007, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson, S. House price diffusion and inter-regional and cross-border house price dynamics. J. Prop. Res. 2004, 21, 301–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapp, J.M.; Dolde, W.; Tirtiroglu, D. Imperfect information and investor inferences from housing price dynamics. Real Estate Econ. 1995, 23, 239–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikarinen, E. The diffusion of housing price movements from center to surrounding areas. J. Hous. Res. 2004, 15, 3–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollakowski, H.O.; Ray, T.S. Housing price diffusion patterns at different aggregation levels: An examination of housing market efficiency. J. Hous. Res. 1997, 8, 107–124. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, B.; Füss, R.; Rottke, N.B. Spatial linkages in returns and volatilities among US regional housing markets. Real Estate Econ. 2013, 41, 29–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, C.; Hudson, J.; Morley, B. Differing house price linkages across UK regions: A multi-dimensional recursive ripple model. Urban Stud. 2018, 55, 1636–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, M.J.; Grimes, A. Is there long-run convergence among regional house prices in the UK? Urban Stud. 2008, 45, 1531–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balcilar, M.; Beyene, A.; Gupta, R.; Seleteng, M. ‘Ripple’ effects in South African house prices. Urban Stud. 2013, 50, 876–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- André, C.; Gupta, R.; Mwamba, J.W.M. Are housing price cycles asymmetric? Evidence from the US States and Metropolitan areas. Int. J. Strateg. Prop. Manag. 2019, 23, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cook, S.; Thomas, C. An alternative approach to examining the ripple effect in UK house prices. Appl. Econ. Lett. 2003, 10, 849–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apergis, N.; Payne, J.E. Convergence in U.S. house prices by state: Evidence from the club convergence and clustering procedure. Lett. Spat. Resour. Sci. 2012, 5, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Rous, J.J. House price convergence: Evidence from US state and metropolitan area panels. J. Hous. Econ. 2012, 21, 169–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagnoli, A.; Nagayasu, J. UK house price convergence clubs and spillovers. J. Hous. Econ. 2015, 30, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blanco, F.; Martín, V.; Vazquez, G. Regional house price convergence in Spain during the housing boom. Urban Stud. 2016, 53, 775–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomal, M. House price convergence on the primary and secondary markets: Evidence from Polish provincial capitals. Real Estate Manag. Valuat. 2019, 27, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Apergis, N.; Simo-Kengne, B.D.; Gupta, R. Convergence in provincial-level South African house prices: Evidence from the club convergence and clustering procedure. Rev. Urban Reg. Dev. Stud. 2015, 27, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, H.; Xie, W.-J.; Zhou, W.-X. Club convergence of house prices: Evidence from China’s ten key cities. Int. J. Mod. Phys. 2015, 29, 1550181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, R.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Dong, J. Heterogeneous convergence of regional house prices and the complexity in China. Zb. Rad. Ekon. Fak. Rijeci Čas. Ekon. Teor. Praksu 2015, 33, 325–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awaworyi Churchill, S.; Inekwe, J.; Ivanovski, K. House price convergence: Evidence from Australian cities. Econ. Lett. 2018, 170, 88–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montañés, A.; Olmos, L. Convergence in US house prices. Econ. Lett. 2013, 121, 152–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, Z.; Fan, G.-Z.; Horsewood, N. Price bubbles and policy interventions in the Chinese housing market. J. Hous. Built Environ. 2016, 32, 133–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W. City profile: Shanghai. Cities 1999, 16, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Lu, C.L.; Chen, M.C.; Chu, F.N. What forces drive the dynamic interaction between regional housing prices? Int. J. Strateg. Prop. Manag. 2017, 21, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, S. The convergence of regional house prices in the UK. Urban Stud. 2003, 40, 2285–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, M.J.; Otero, J.; Panagiotidis, T. Climbing the property ladder: An analysis of market integration in London property prices. Urban Stud. 2018, 55, 2660–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Wei, Y.D.; Wu, Y.; Tian, G. Analyzing housing prices in Shanghai with open data: Amenity, accessibility and urban structure. Cities 2019, 91, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z. Overreaction to policy changes in the housing market: Evidence from Shanghai. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2016, 58, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, H.; Wu, C. Empirical analysis of Chinese and South Korean housing policies and their effects on housing prices change: Taking Shanghai and Seoul as example. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Sustainable Development, New York, NY, USA, 23–24 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Yenneti, K.; Wei, Y.D.; Yuan, F.; Wu, J.; Gao, J. Polycentricity in the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration (YRDUA): More cohesion or more disparities? Sustainability 2019, 11, 3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Wei, Y.D.; Li, Q.; Yuan, F. Economic transition and changing location of manufacturing industry in China: A study of the Yangtze River Delta. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, J. Housing reform and the housing market in urban China. In Housing Affordability and Housing Policy in Urban China; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 15–43. [Google Scholar]
- Shih, Y.-N.; Li, H.-C.; Qin, B. Housing price bubbles and inter-provincial spillover: Evidence from China. Habitat Int. 2014, 43, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Wei, Y.D.; Xiao, W. Land marketization, fiscal decentralization, and the dynamics of urban land prices in transitional China. Land Use Policy 2019, 89, 104208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Sharma, R. Housing submarket classification: The role of spatial contiguity. Appl. Geogr. 2012, 32, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Rey, S. A framework for exploratory space-time analysis of economic data. Ann. Reg. Sci. 2013, 50, 315–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, H.; Leatham, D.J. The multi-market analysis of a housing price transmission model. Appl. Econ. 2013, 45, 3810–3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, P.C.; Sul, D. Transition modeling and econometric convergence tests. Econometrica 2007, 75, 1771–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phillips, P.C.; Sul, D. Economic transition and growth. J. Appl. Econom. 2009, 24, 1153–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, K. Econometric convergence test and club clustering using Stata. Stata J. 2017, 17, 882–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gao, J.; Yuan, F.; Wei, Y.D. Spatial Determinants of Urban Land Expansion in Globalizing Nanjing, China. Sustainability 2016, 8, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hodrick, R.J.; Prescott, E.C. Postwar US business cycles: An empirical investigation. J. Money Credit Bank. 1997, 29, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lean, H.H.; Smyth, R. Regional house prices and the ripple effect in Malaysia. Urban Stud. 2013, 50, 895–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-C.; Chien, M.-S. Empirical modelling of regional house prices and the ripple effect. Urban Stud. 2011, 48, 2029–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Wei, Y.D.; Wu, J. Amenity effects of urban facilities on housing prices in China: Accessibility, scarcity, and urban spaces. Cities 2020, 96, 102433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


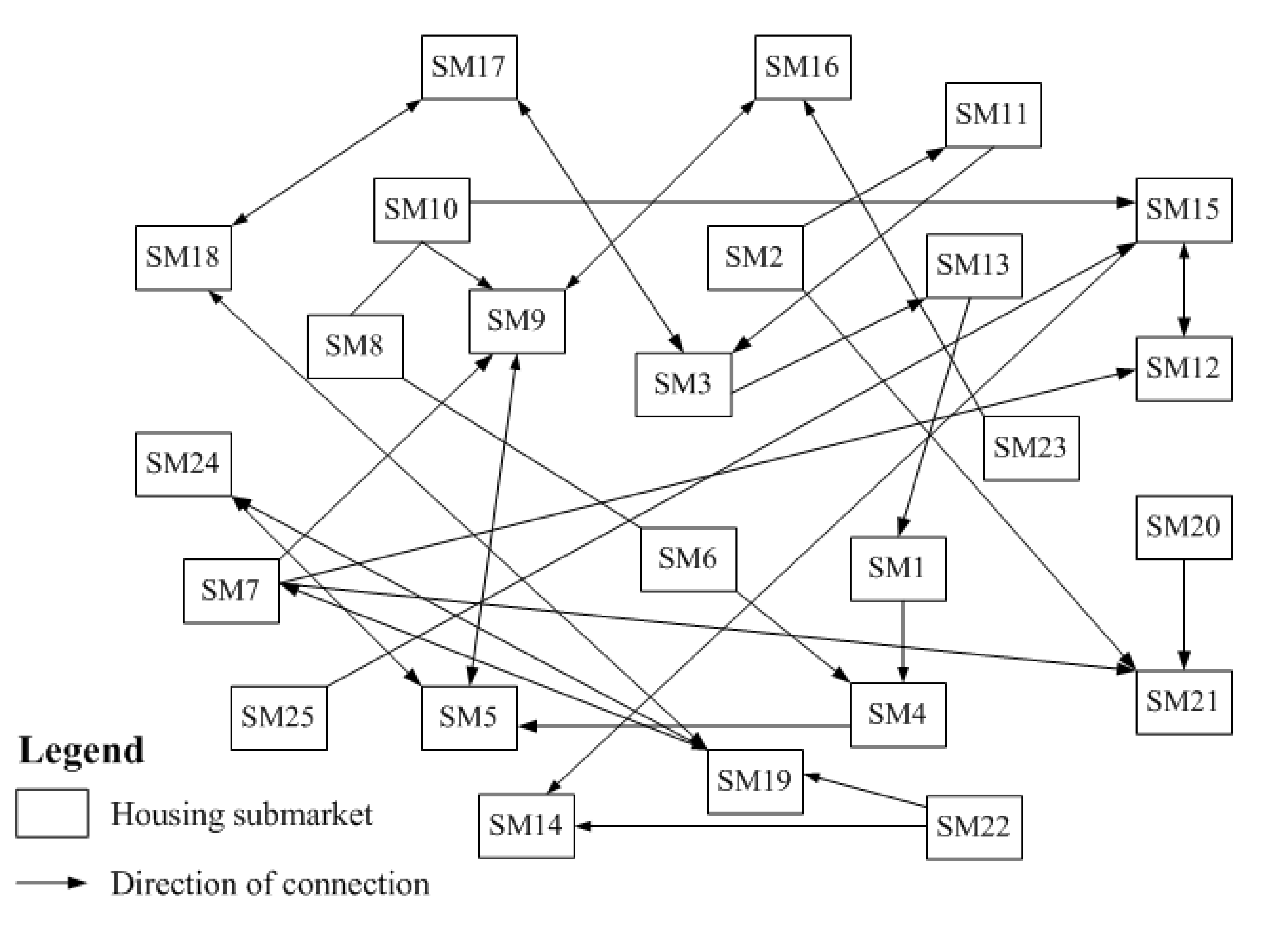
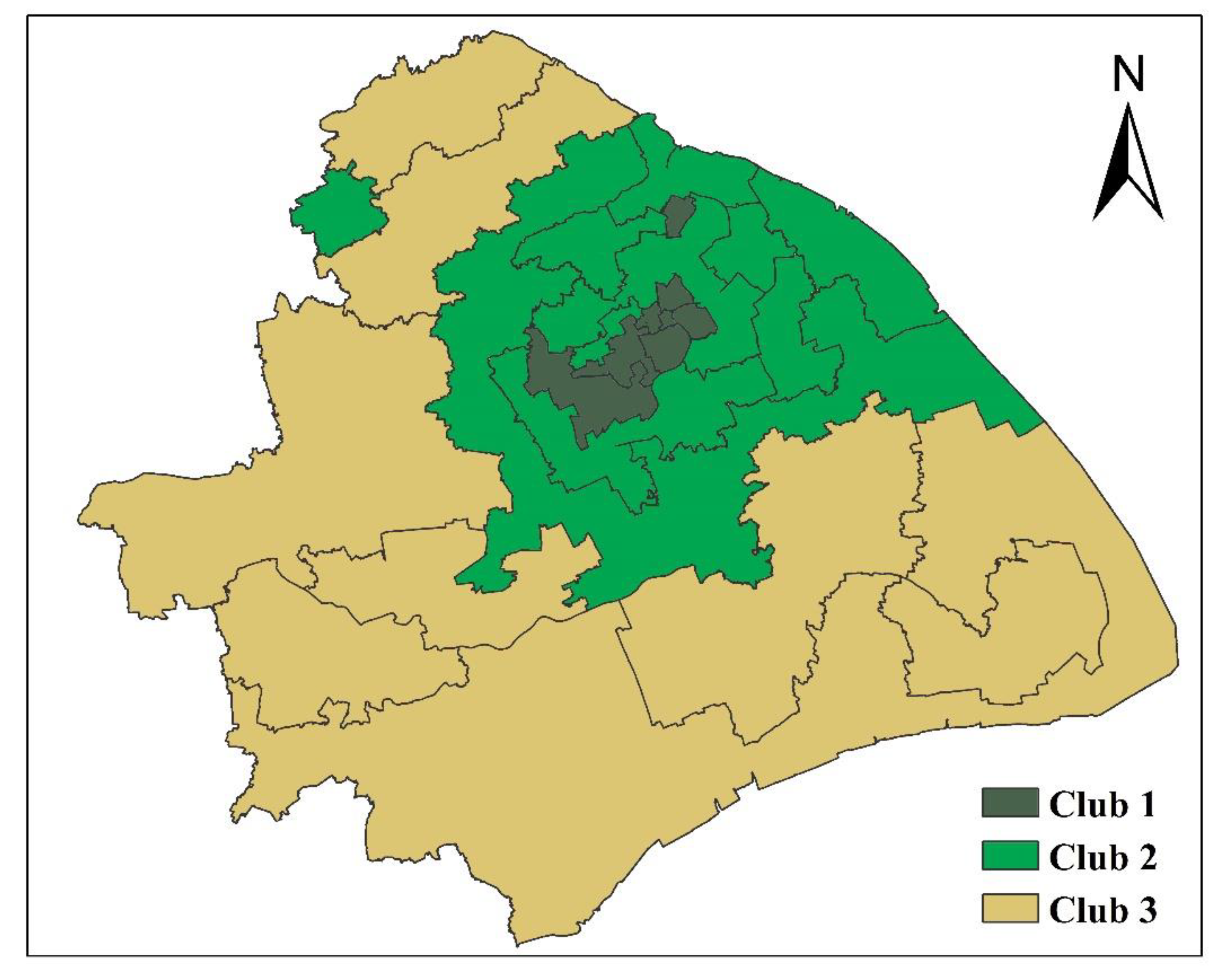
| Initial Classification | Tests of Club Merging | Final Classification | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Club | β coeff. | t-stat. | Club | β coeff. | t-stat. | Club | β coeff. | t-stat. |
| 1 | 0.508 | 8.603 | 1 + 2 | 0.275 | 19.021 | 1 | 0.275 | 19.021 |
| 2 | 0.080 | 3.683 | 2 + 3 | −0.014 | −2.594 | 2 | 0.091 | 1.649 |
| 3 | 0.010 | 0.198 | 3 + 4 | 0.091 | 1.649 | 3 | 0.224 | 3.464 |
| 4 | 0.008 | 0.058 | 4 + 5 | 0.064 | 1.825 | |||
| 5 | 0.026 | 0.717 | ||||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, J.; Xiong, X.; Cai, Y.; Yuan, F. The Ripple Effect and Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Intra-Urban Housing Prices at the Submarket Level in Shanghai, China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5073. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12125073
Hu J, Xiong X, Cai Y, Yuan F. The Ripple Effect and Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Intra-Urban Housing Prices at the Submarket Level in Shanghai, China. Sustainability. 2020; 12(12):5073. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12125073
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Jin, Xuelei Xiong, Yuanyuan Cai, and Feng Yuan. 2020. "The Ripple Effect and Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Intra-Urban Housing Prices at the Submarket Level in Shanghai, China" Sustainability 12, no. 12: 5073. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12125073
APA StyleHu, J., Xiong, X., Cai, Y., & Yuan, F. (2020). The Ripple Effect and Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Intra-Urban Housing Prices at the Submarket Level in Shanghai, China. Sustainability, 12(12), 5073. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12125073





