Abstract
Over the past century, the impacts of human activities on the natural environment have continued to increase. Historic evolution of the environment under anthropogenic influences is an important reference for sustainable social development. Based on the geochemical analyses of a short sediment core of 49 cm from Lake Balkhash, the largest lake in Central Asia, potential factors historically influencing geochemical variation were revealed, and influences of human activity on regional environmental change were reconstructed over the past 150 years. The results showed that the dominant factor inducing changes in potentially toxic elements (V, Cr, Co, Ni, Zn, Cu, Cd, and Pb) is the physical weathering of the terrestrial materials. The variation in Ca content was influenced by the formation of authigenic carbonate. Since 1930, potentially toxic elements (Cr, Co, Ni, Zn, Cu, Cd, and Pb) in the lake sediments have obviously been affected by human activities, but the impact of human activities has not exceeded that of natural terrestrial weathering. In particular, the enrichment factors (EFs) for Cd and Pb reached 1.5. The average ecological risks of Cd were higher than the criterion of 30, suggesting a moderate risk to the local ecosystem in recent years. Total risk indices indicated moderate potential ecological risk for the lake ecology. The results will provide support for the environmental protection and better management practices of the Lake Balkhash watershed.
1. Introduction
As element composition in lake sediments is generally derived from weathered rock, eroded soil, and anthropogenic inputs, it has been widely used to study environmental change for the reconstruction of human impacts [1,2,3,4]. Over the past century, the impacts of human activities on the natural environment have continued to increase [5,6]. With the promotion of modernization since the industrial revolution, element profiles in sediments have been affected not only by natural processes but also by human activities [7]. Hence, further study of the geochemistry of elements in lake sediments is needed to better understand the evolution of the physical geographical environment under the influence of human activities [8,9]. Meanwhile, the enrichment and contamination of potentially toxic elements in the natural environment have been receiving more and more attention due to the biological toxicity and environmental persistence of these elements [10].
As the largest inland lake in Central Asia, Lake Balkhash plays an important role in maintaining ecological equilibrium across the region. Unfortunately, Lake Balkhash is vulnerable to anthropogenic disturbances due to its shallowness, relatively fragile ecosystems, and proximity to metallurgical industries [4]. Ever since intensive agricultural development began following the settlement of the Russian population in the late 19th century [11], the chemical and physical characteristics of Lake Balkhash have undergone obvious changes; for example, there has been a considerable increase in the lake’s salt content since the second half of the 20th century [12], and pollutants containing potentially toxic elements and oil products have appeared [11]. In addition, a dramatic decrease in the lake’s water level following the filling of the Kapchagay Reservoir in the 1970s aroused worldwide concern that Lake Balkhash would face the same fate as the Aral Sea [13]. Scientific research is necessary for the protection and sustainable development of Lake Balkhash. Studies have been carried out on the changing lake dynamics [14,15,16], regional climate [17], and aquatic ecology [18,19]. However, the environmental responses of Lake Balkhash to the increasing human activity in the region are not yet well understood. Furthermore, previous studies on the sediments of Bosten Lake [20], Ebinur Lake [21], and Chaiowpu Lake [22] have indicated what influence human activities have had on other arid regions of China adjacent to Lake Balkhash with similar natural conditions; however, spatial differences in the response to global change still need to be explored.
This paper focused on the scientific hypothesis of whether the potentially toxic elements in the sediments of Lake Balkhash are enriched by human activities over time, and different from those in the adjacent area under the background of significant enhancement of human activities. With the geochemical composition of Lake Balkhash’s sediments, this study aims to identify element sources and to reconstruct the influences of human activities on regional environmental change. In turn, this will provide support for the environmental protection of Lake Balkhash and the application of better management practices to the watershed.
2. Regional Setting
The Ili–Balkhash Basin (IBB) covers 4.1 × 105 km2, and the Kazakh part of the basin contains one-fifth of that country’s total population [23] (Figure 1). The multiyear mean temperature and precipitation in the basin range from 3.1–9.2 °C and 124–633 mm, respectively [17]. In the north, the IBB is dominated by grassland, and the Saryesik–Atyrau desert lies to the south of the lake. Forest prevails southeast of the IBB, and the arable land is mainly distributed along rivers. The rapid economic development in this region benefited from the construction of the railroad and the rise of the nonferrous metal industry in the 1930s [11]. Irrigation land for agriculture expanded from an area of 3520 km2 in 1955 to 5596 km2 in 1984. Consequently, water shortages and pollutant emissions in conjunction with population growth and economic development had an adverse impact on the ecosystem of Lake Balkhash [11,24].
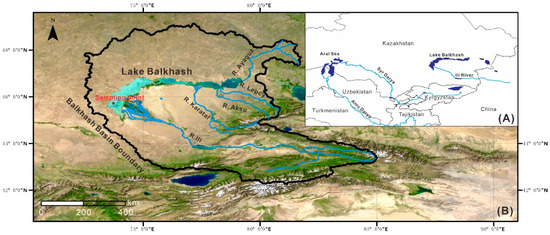
Figure 1.
Location of Lake Balkhash in Central Asia (A), and location of the sampling site in Lake Balkhash (B).
The surface are of Lake Balkhash (44°48′–48°49′ N, 73°30′–79°16′ E) is variable and generally ranges from 17,000 to 22,000 km2 [25]. Lake Balkhash is divided into two relatively independent parts. The western part is shallower with an average depth of 7–11 m and less mineralized due to the influence of the Ili River (supplying 78% of the total riverine runoff) that flows into it. An extensive delta is formed where the river flows into the lake, which naturally regulates ecological and water balance within the Ili–Lake Balkhash system [26]. Other rivers such as the Karatal, Aksu, Lepsy, and Ayaguz terminate in the eastern part of Lake Balkhash. Mineralization in the southwestern basin is 1.85 g L−1, whereas in the eastern basin it is 4.58 g L−1 [12]. Based on our analysis, water of Lake Balkhash belongs to the sulfate class with the sodium group [12]. The climate in the area of the lake is continental, with low annual precipitation (150 mm) but intense evaporation (1000 mm), and an annual mean temperature of 6 °C [27].
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sampling and Laboratory Analyses
A 49 cm long sediment core was extracted in 2017 from the sampling site (45°41′5.2′’ N, 73°45′5.5′’ E) in Lake Balkhash using a piston–percussion corer fitted with 60 mm internal diameter Perspex tubes (Figure 1). The sediment core was sliced in situ into thin horizontal sections at 1 cm intervals using a plastic cutter. Forty-nine (49) sediment samples were obtained and dried at –50 °C in a continuous vacuum freeze dryer for subsequent dating and geochemical analysis. The freeze-dried samples were homogenized and weighed, and then analyzed for 137Cs by direct gamma spectrometry using an Ortec HPGe GWL series well-type, coaxial low background intrinsic germanium detector (EG&G ORTEC, Oak Ridge, TN, USA) [28]. The sediment has been analyzed for both major and potentially toxic elements as this gives a better overall picture of the geochemistry of the lake sediment. The mathematical statistical analysis has been carried out including the major and potentially toxic elements as it gives a better picture of how the potentially toxic elements are associated with the terrigenous clastic source. Finally, the calculation of the enrichment coefficient of potentially toxic elements also requires major elements (in this case Al) that are rich and stable in the earth surface. For the analysis of elements, samples were milled with a mortar and pestle to a 200 mesh size and digested with HF-HNO3-HClO4 in a microwave digester (Berghof MWS-3, Berghof Group, Eningen, Germany) [29]. Inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES, Prodigy, Teledyne Leeman Labs, Hudson NH, USA) was used to measure the concentrations of Al (limit of detection, 20 mg kg−1), Ca (limit of detection, 5 mg kg−1), Fe (limit of detection, 5 mg kg−1), K (limit of detection, 80 mg kg−1), Mg (limit of detection, 2 mg kg−1), Mn (limit of detection, 0.5 mg kg−1), Na (limit of detection, 20 mg kg−1), P (limit of detection, 20 mg kg−1), Ti (limit of detection, 1 mg kg−1), and V (limit of detection, 2 mg kg−1), and inductively coupled plasma–mass spectroscopy (ICP–MS, 7700x, Agilent Technologies, Palo Alto, USA) to measure potentially toxic elements including Cr (limit of detection, 0.1 mg kg−1), Co (limit of detection, 0.01 mg kg−1), Ni (limit of detection, 0.05 mg kg−1), Cu (limit of detection, 0.02 mg kg−1), Zn (limit of detection, 0.2 mg kg−1), Cd (limit of detection, 0.01 mg kg−1), and Pb (limit of detection, 0.02 mg kg−1). The standard reference materials for stream sediments GBW07311 (GSD-11) [30] is used for monitoring the analysis. The relative error was determined to be less than 5%. The laboratory analyses for 137Cs and geochemical elements were conducted in the State Key Laboratory of Lake Science and Environment (SKLLSE), Nanjing, China. Carbonate content was determined according to the ASTM D4373-14 standard test method for rapid determination of carbonate content of soils [31] at the Xinjiang Institute of Ecology and Geography, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
3.2. Enrichment Factor
The enrichment factor was used to assess the degree of human activity and heavy metal contamination. In this study, enrichment factors were determined for all of the elements normalized against aluminum concentration, with values greater than one being considered anthropogenic [32,33,34,35]. Enrichment factors were calculated according to the following equation:
where M is the concentration of the element being normalized against aluminum concentration and BV is the background concentration based on the average concentration of the element in the bottom 5 cm section of the core.
3.3. Potential Ecological Risk Assessment
The potential ecological risk (PER) [36] was used to evaluate ecological risks caused by potentially toxic elements and was calculated using the following equations:
where RI is the sum of risk indices for potentially toxic elements; Er is the monomial potential ecological risk index; Tr is the toxic-response factor for a given potentially toxic element accounting for both the toxic and sensitivity requirements, with values for each element in the order of V = Zn = Cr = 2 < Cu = Co = Ni = Pb = 5 < Cd = 30 [37]; Cf is the pollution factor; Cn is the concentration of the potentially toxic element; and C0 is the background concentration of the potentially toxic element. The classification criteria for the potential ecological risk [36,38] are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Adjusted classification criteria of the potential ecological risk index.
4. Results
4.1. Chronology of the Sediment Profile
137Cs is an artificial isotope formed as one of the products of nuclear fission [39]. The peak in 137Cs radioactive intensity is closely related to nuclear weapons tests. 137Cs began to accumulate from a depth of 22 cm, which temporally coincides with the development of nuclear tests in 1954. The 137Cs activity profile peaked at 17 and 8 cm, corresponding to the maximum global atmospheric fallout of 137Cs in 1964 and the accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant in 1986, respectively. The sedimentation rate was determined to be 3.4 mm a−1, which is consistent with the results reported for the northern part of Lake Balkhash by Endo et al. [40]. Based on the sedimentation rate, the bottom of the core was dated as 1798.
4.2. Element Concentrations in the Lake Balkhash Sediment Core
The concentrations of total carbonate and various elements measured in the sediment core are shown in Table 2. The total carbonate concentration ranged from 317.22 to 445.99 g kg−1 with an average value of 360.62 g kg−1. The Al concentration ranged from 45.18 to 57.67 g kg−1, with an average value of 50.62 g kg−1. The concentration of K had a range of 15.30 to 19.96 g kg−1, with an average value of 17.28 g kg−1. The Fe concentration ranged from 24.51 to 33.85 g kg−1, and the Mn concentration from 0 to 28.73 mg kg−1. The Ti concentration ranged from 2.42 to 2.97 g kg−1, with an average value of 2.65 g kg−1. The concentration of Mg had a range of 16.53 to 19.39 g kg−1, with an average value of 18.31 g kg−1. The Na concentration ranged from 7.19 to 10.93 g kg−1, and the P concentration from 362.31 to 650.66 mg kg−1. The concentration of Ca ranged from 108.10 to 145.10 g kg−1. The concentration profiles of elements (Al, K, Fe, Ti, Ca, Mg, Na, P, and Mn) and potentially toxic elements (V, Cr, Co, Ni, Zn, Cu, Pb, and Cd) are shown in Figure 2. Aluminum concentrations were consistent below 30 cm and increased to a maximum value at about 27 cm, then decreased to the top of the core. Most potentially toxic elements, including V, Cr, Co, Ni, Zn, Cu, and Pb, exhibited similar distribution patterns to Al. Calcium concentrations showed an opposite trend to Al. The concentration of Cd was stable below 30 cm and then increased to the top of the core.

Table 2.
Summary statistics of total carbonate and element concentrations in Lake Balkhash sediment core.
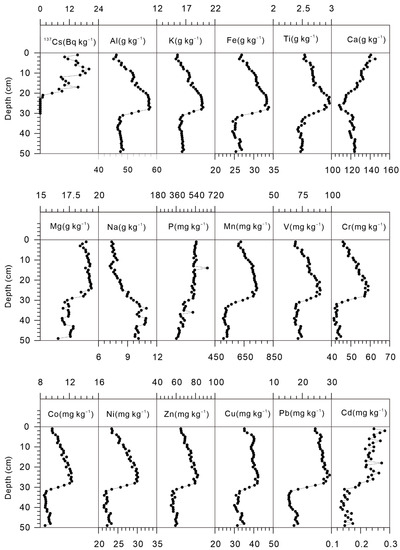
Figure 2.
Vertical distribution of 137Cs activity and geochemical elements in the Lake Balkhash sediment core.
5. Discussion
Differences in the sediment concentrations of various elements are the result of their different geochemical behaviors in surface environments and the simultaneous effect of multiple environmental agents [2]. Principal component analysis (PCA) [20,41,42,43] and hierarchical clustering analysis [44,45] were applied to identify influences possibly acting on elements in the sediment core. Using the PCA extraction method, trivial principal components were eliminated and two significant components were obtained, with a cumulative variance of 96.4%. The PCA score plot is shown in Figure 3.
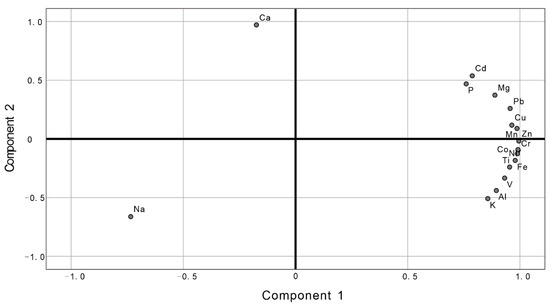
Figure 3.
Principal component analysis score plot of elements measured in the sediment core from Lake Balkhash.
The conservative elements Al, K, Ti, Fe, and Mn are the main products that resulted from the weathering of the alumino–silicate minerals, which represent natural materials eroded at the land surface within the drainage area [46]. High correlation distances were observed between Al and other elements, indicating a common source for these elements (Figure 4). The first component dominated the sediment sources, accounting for 79.9% of the total variance, with relatively high positive loadings for Al, K, Ti, Fe, Mn, V, Cr, Co, Zn, Cu, Pb, Cd, P, and Mg, which were mainly derived from terrigenous detrital minerals.
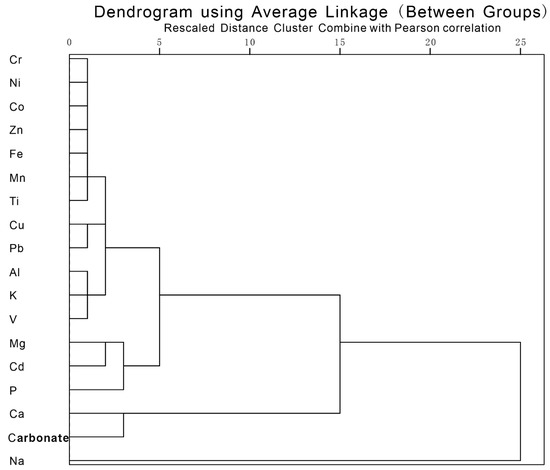
Figure 4.
Dendrogram showing relationships between elements in the Lake Balkhash sediment core.
The second component explained 16.5% of the total variance and was heavily loaded with Ca (positive). The score plot (Figure 3) shows Ca to be separated from Al, demonstrating different sources for these elements in the sediments. The carbonate content in the lake sediments was closely related to the Ca content (Figure 4). Lake Balkhash is located in Central Asia where the sharply continental climate is characterized by high evaporation, thus contributing to the formation of authigenic carbonate. Investigations on the hydrochemistry of Lake Balkhash have shown that Ca2+ concentrations in the lake are lower than in the Ili River, implying a possible mechanism of calcium removal through calcite or dolomite precipitation [47].
Sodium (Na) had negative loadings on the two abovementioned components. This is because Na is widely associated with silicate minerals and dissolved terrigenous Na enters the lake through surface runoff. Therefore, the changes in Na represent a combination of terrigenous detrital inputs and authigenic formation.
Based on the above analysis, the dominant factor influencing potentially toxic elements in the lake sediments is the physical weathering of terrestrial materials. However, there are usually both natural and anthropogenic sources of potentially toxic elements in lake sediments [48]. Discharges from the metallurgical industry and the combustion of fossil fuels are usually the main sources of Cu, Pb, and Cd [1]. Wastewaters from the Balkhash copper smelting industry and lead–zinc industrial complex as well as contaminants from the thermal power plant and the open-pit mine caused enrichment of potentially toxic elements in Lake Balkhash [18]. The enrichment factor (EF) of potentially toxic elements was calculated to identify anthropogenic influences on the environmental evolution of Lake Balkhash. Based on the EFs, two distinct stages divided by the year 1930 were apparent in the sediment core (Figure 5). During the first stage, the EFs of potentially toxic elements varied in a manner consistent with their concentrations, indicating that these elements are mainly controlled by the sedimentation rate, which correlated with local climate and geological background.
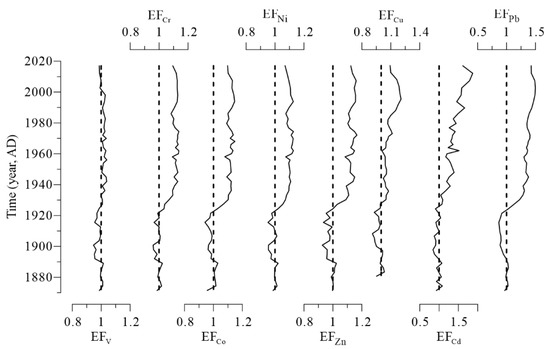
Figure 5.
Variation in the enrichment factors of potentially toxic elements in the Lake Balkhash sediment core.
The EFs of V were nearly constant since 1930 with a value of about 1.0, indicating that it was mainly derived from a natural source. However, the contents of Cr, Co, Ni, Zn, Cu, Cd, and Pb in the sediments have been affected by intensive anthropogenic inputs since 1930. In particular, the EFs of Cd and Pb reached a value of 1.5. Since 2000, improvements in waste-free production technologies have resulted in less industrial effluents discharging into the lake [49], which is reflected in the decreasing EFs of potentially toxic elements in more recent times. The EFs for Cr, Co, and Ni in the topmost sediment is close to 1.1, but the EFs for Pb and Cd were more than 1.4, reaching 1.4 and 1.6, respectively. Therefore, it can be concluded that Cr, Co, Ni, Zn, Cu, Cd, and Pb in sediments have obviously been affected by human activities, but the impact of human activities has not exceeded that of natural terrestrial weathering. Man-made potentially toxic elements enter the lake through rivers and atmospheric deposition [50,51]. Some parts of man-made potentially toxic elements affect the content of soluble potentially toxic elements in the lake water [52], and the others directly entered the sediment and influenced the geochemical composition [53]. There are relatively few studies on the water quality of Balkhash Lake [12,54,55,56], and the existing research results show that the contents of Zn, Cu, Cd, and Pb in the Lake Balkhash water were 5.99 μg L−1, 8.35 μg L−1, 0.99 μg L−1, 12.55 μg L−1, respectively [54]. Limited to the research data, the specific sources of potentially toxic elements and the interaction between lake sediments and lake water have not been specifically determined in this study.
The average Er values in the top 5 cm of the core for observed elements were ranked in increasing order as follows: V (1.9) < Cr (2.2) = Zn (2.2) < Ni (5.3) < Co (5.4)< Cu (5.6) < Pb (7.1) < Cd (49.0). The ecological risks for Cd were higher than the criterion of 30 (Table 1), suggesting that Cd in the surface sediment poses a moderate risk. Compared with other regions, this is still at a relatively low risk level. For example, the single risk indices of Cd in the sediments of Lake Dalinouer in Inner Mongolia, which is located in the underdeveloped area of China, is as high as 85.96, indicating that it has a high risk to lake ecology [57]. Compared with Cd in lake sediments in the developed eastern coastal areas of China, Cd pollution has reached a very serious level [58]. Cd has also been observed as posing serious potential ecological risks in lakes in some parts of India [59]. The RI values (RI = 78.7) throughout the core of Lake Balkhash fell within the range of 60–120, indicating a moderate potential ecological risk for the lake ecology.
Nevertheless, spatial differences resulting from localized human activities are noted between Lake Balkhash and other lakes in arid Central Asia, particularly in the adjacent Xinjiang Province of China. For example, the sediment cores from Bosten Lake recorded enrichment in Pb, Cd, and P beginning in the 1960s resulting from agricultural land expansion [20], and similar observations were noted for Ebinur Lake [7]. However, the enrichment of potentially toxic elements in the sediments of Lake Balkhash since the 1930s is closely related to the development of mining and smelting around the lake in Kazakhstan [60]. The results of these studies reflect differing impacts of human activities on lakes in arid Central Asia under different local socioeconomic backgrounds.
It cannot be denied that this paper also has some limitations which may determine the future research direction. The Lake Balkhash is huge with complex hydrological factors and varied human impact within the catchment area. The complex interaction of natural and anthropogenic factors indicated that the results of this paper can only represent the variation characteristics of elements in the sediments of the western part of Lake Balkhash. Mathematical statistics analysis can only reflect the overall influences of human activities on the changes of elements in lake sediments, and the determination of potential sources of potentially toxic elements needs to be combined with isotope tracing and other methods. However, the results will provide support for the environmental protection and better management practices of the Lake Balkhash watershed.
6. Conclusions
The study of geochemical elements in a 49 cm sediment core from Lake Balkhash revealed environmental changes induced by human activities over the past 150 years. The following conclusions can be drawn:
- (1)
- The dominant factor that has influenced most elements in the lake sediments, including potentially toxic elements (V, Cr, Co, Ni, Zn, Cu, Cd, and Pb), is the physical weathering of terrestrial materials. Calcium (Ca) levels have been influenced by the formation of authigenic carbonate.
- (2)
- Since 1930, potentially toxic elements (Cr, Co, Ni, Zn, Cu, Cd, and Pb) in the lake sediments have obviously been affected by human activities, but the impact of human activities has not exceeded that of natural terrestrial weathering.
- (3)
- The average ecological risks of Cd were higher than the criterion of 30, suggesting a moderate risk to the local ecosystem in recent years. The assessment of total risk indices indicated moderate potential ecological risk for the lake ecology.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.M.; data curation, K.H.; funding acquisition, L.M. and J.A.; investigation, G.I. and G.S.; methodology, L.L.; project administration, J.A.; visualization, W.L.; writing—original draft, K.H., L.M. and W.L.; writing—review & editing, L.M., J.A. and L.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is funded by the West Light Foundation of Chinese Academy of Sciences (2016−QNXZ−A−4), National Natural Science Foundation of China (U1603242; U1903115), Tianshan Youth Project of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region of China (2018Q008), and Shandong provincial water resources research project (SDSLKY201813).
Acknowledgments
We thank two anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments and suggestions that improved the manuscript, and Alim Samat, Yongxiao Ge, and Abdulla Saparov for their help in the field.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Loska, K.; Wiechuła, D. Application of principal component analysis for the estimation of source of heavy metal contamination in surface sediments from the Rybnik Reservoir. Chemosphere 2003, 51, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wan, G.; Zhang, D.D.; Chen, Z.; Xu, J.; Xiao, T.; Huang, R. The ‘Little Ice Age’ recorded by sediment chemistry in Lake Erhai, southwest China. Holocene 2005, 15, 925–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Hou, X.; Cheng, X.; Yao, S.; Xia, W.; Wang, S. Combining geochemical and statistical methods to distinguish anthropogenic source of metals in lacustrine sediment: A case study in Dongjiu Lake, Taihu Lake catchment, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2007, 52, 1467–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F. A multi-element sediment record of hydrological and environmental changes from Lake Erie since 1800. J. Paleolimnol. 2017, 58, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, T.R.; Trenberth, K.E. Modern Global Climate Change. Science 2003, 302, 1719–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meybeck, M. The global change of continental aquatic systems: Dominant impacts of human activities. Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 49, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wu, J.; Abuduwaili, J.; Liu, W. Geochemical Responses to Anthropogenic and Natural Influences in Ebinur Lake Sediments of Arid Northwest China. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhbarizadeh, R.; Moore, F.; Keshavarzi, B.; Moeinpour, A. Microplastics and potentially toxic elements in coastal sediments of Iran’s main oil terminal (Khark Island). Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 720–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, L.-C.; Chen, H.-W.; Chan, Y.-T.; Teah, H.Y.; Chen, T.-Y.; Chang, C.-F.; Liu, Y.-T.; Tzou, Y.-M.; Huang, C.-Y.; Chuang, Y.-H. Accumulation of heavy metals and trace elements in fluvial sediments received effluents from traditional and semiconductor industries. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ma, D.; Pan, J.; Nie, W.; Wu, K. Application of multivariate statistical approach to identify heavy metal sources in sediment and waters: A case study in Yangzhong, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2007, 54, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willén, E. The Lakes Handbook, Volume II. Lake Restoration and Rehabilitation. Freshw. Boil. 2007, 2, 213–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petr, T. Lake Balkhash, Kazakhstan. Int. J. Salt Lake Res. 1992, 1, 21–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Yuan, Y.; Yu, S. Tree-ring indicators of rainfall and streamflow for the Ili-Balkhash Basin, Central Asia since CE 1560. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclim. Palaeoecol. 2017, 482, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, A.; Deng, M.; Xie, L.; Wang, J.; Li, X. A study of the water balance of Lake Balkhash. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2011, 33, 1341–1352. [Google Scholar]
- Propastin, P. Patterns of Lake Balkhash water level changes and their climatic correlates during 1992–2010 period. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 2012, 17, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Yang, L.; Fang, H. Changes in the area of inland lakes in arid regions of central Asia during the past 30 years. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 178, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Xia, Z. Temperature and precipitation long-term trends and variations in the Ili-Balkhash Basin. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2013, 115, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupa, E.; Stuge, T.S.; Lopareva, T.Y.; Shaukharbaeva, D.S. Distribution of planktonic crustaceans in Lake Balkhash in relation to environmental factors. Inland Water Boil. 2008, 1, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barinova, S.; Krupa, E.; Kadyrova, U. Spatial dynamics of species richness of phytoplankton of Lake Balkhash in the gradient of abiotic factors. Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2017, 19, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Abuduwaili, J.; Ma, L. Geochemistry of major and trace elements and their environmental significances in core sediments from Bosten Lake, arid northwestern China. J. Limnol. 2019, 78, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Ma, L.; Wu, J.; Abuduwaili, J. Environmental variability and human activity over the past 140 years documented by sediments of Ebinur Lake in arid central Asia. J. Limnol. 2017, 76, 534–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wu, J.; Abuduwaili, J. Climate and environmental changes over the past 150 years inferred from the sediments of Chaiwopu Lake, central Tianshan Mountains, northwest China. Acta Diabetol. 2012, 102, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiman, I.; Niels, T.; Sebastian, S.; Sabir, N.; Ruslan, S. Vegetation, fauna, and biodiversity of the Ile Delta and southern Lake Balkhash-A review. J. Gt. Lakes Res. 2015, 41, 688–696. [Google Scholar]
- Panyushkina, I.; Meko, D.M.; Macklin, M.G.; Toonen, W.H.J.; Mukhamadiev, N.S.; Konovalov, V.G.; Ashikbaev, N.Z.; Sagitov, A.O. Runoff variations in Lake Balkhash Basin, Central Asia, 1779–2015, inferred from tree rings. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 51, 3161–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isbekov, K.B.; Tsoy, V.N.; Crétaux, J.-F.; Aladin, N.V.; Plotnikov, I.S.; Clos, G.; Berge-Nguyen, M.; Assylbekova, S.Z. Impacts of water level changes in the fauna, flora and physical properties over the Balkhash Lake watershed. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 2019, 24, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myrzakhmetov, A.; Dostay, Z.; Alimkulov, S.; Madibekov, A. Level regime of Balkhash Lake as the indicator of the state of the environmental ecosystems of the region. Int. J. Adv. Res. Sci. Eng. Tech. 2017, 4, 4554–4563. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.-D.; Wu, H.; Zhang, C.; Ran, M.; Sun, A. Bioclimatic change of the past 2500 years within the Balkhash Basin, eastern Kazakhstan, Central Asia. Quat. Int. 2013, 311, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Qiao, Q.; McGowan, S.; Zeng, L.; Stevenson, M.A.; Xu, L.; Huang, C.; Liang, J.; Cao, Y. Determination of geochronology and sedimentation rates of shallow lakes in the middle Yangtze reaches using 210Pb, 137Cs and spheroidal carbonaceous particles. Catena 2019, 174, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Abuduwaili, J.; Liu, W. Spatial Distribution and Health Risk Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Surface Soils of Bosten Lake Basin, Central Asia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2019, 16, 3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Yan, M.; Wang, C.; Li, L.; Shen, H. Geochemical standard reference samples GSD 9–12, GSS 1–8 AND GSR 1–6. Geostand. Newsl. 1989, 13, 83–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard test method for rapid determination of carbonate content of soils. In ASTM D4373-14; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014.
- Yadav, I.C.; Devi, N.L.; Singh, V.K.; Li, J.; Zhang, G. Spatial distribution, source analysis, and health risk assessment of heavy metals contamination in house dust and surface soil from four major cities of Nepal. Chemosphere 2018, 218, 1100–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, E.; Yan, T.; Birch, G.; Zhu, Y. Pollution and health risk of potentially toxic metals in urban road dust in Nanjing, a mega-city of China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2014, 476, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, A.M. Combining multivariate analysis and geochemical approaches for assessing heavy metal level in sediments from Sudanese harbors along the Red Sea coast. Microchem. J. 2008, 90, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S. Abundance of chemical elements in the continental crust: A new table. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1964, 28, 1273–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control.a sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Deng, H.; Wang, D.; Chen, Z.; Xu, S. Toxic heavy metal contamination and risk assessment of street dust in small towns of Shanghai suburban area, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 20, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempter, H.; Krachler, M.; Shotyk, W.; Zaccone, C. Major and trace elements in Sphagnum moss from four southern German bogs, and comparison with available moss monitoring data. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 78, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaarina, W.; Saunders, K.; Gell, P.; Skilbeck, C. Applications of Paleoenvironmental Techniques in Estuarine Studies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Endo, K.; Chiba, T.; Sugai, T.; Haraguchi, T.; Hideo, Y.; Nakayama, Y.; Yoshinaga, Y.; Miyata, K.; Ogi, S. Reconstruction of Lake Level and Paleoenvironmental Changes from a Core from Balkhash Lake, Kazakhstan. In Proceedings of Reconceptualizing Cultural and Environmental Change in Central Asia; An Historical Perspective on the Future: Kyoto, Japan, 2012; pp. 93–104. [Google Scholar]
- Grunsky, E.; Mueller, U.; Corrigan, D. A study of the lake sediment geochemistry of the Melville Peninsula using multivariate methods: Applications for predictive geological mapping. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 141, 15–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, P.K.; Guimarães, J.T.F.; Souza-Filho, P.W.M.; Powell, M.A.; da Silva, M.S.; Moraes, A.M.; Alves, R.; Leite, A.S.; Júnior, W.N.; Rodrigues, T.M.; et al. Statistical analysis of lake sediment geochemical data for understanding surface geological factors and processes: An example from Amazonian upland lakes, Brazil. Catena 2019, 175, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.-S.; Huang, J.-J.S.; Burr, G.; Kao, L.C.; Wei, K.-Y.; Liou, S.Y.H. High resolution record of heavy metals from estuary sediments of Nankan River (Taiwan) assessed by rigorous multivariate statistical analysis. Quat. Int. 2019, 527, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Chen, C.; Cantin, J.; Saunders, D.M.V.; Sun, J.; Tang, S.; Codling, G.; Hecker, M.; Wiseman, S.; Jones, P.; et al. Untargeted Screening and Distribution of Organo-Bromine Compounds in Sediments of Lake Michigan. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, M.A.; Overy, D.P.; Blais, J.M. A continental scale spatial investigation of lake sediment organic compositions using sedimentomics. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 719, 137746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing, H.; Wu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Yao, S. Historical trends of heavy metal contamination and their sources in lacustrine sediment from Xijiu Lake, Taihu Lake catchment, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 1671–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabata, Y.; Tsukatani, T.; Katayama, Y. A demineralization mechanism for Lake Balkhash. Int. J. Salt Lake Res. 1999, 8, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Shen, J.; Liu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, S. Variation characteristics of heavy metals and nutrients in the core sediments of Taihu Lake and their pollution history. Sci. China Ser. D: Earth Sci. 2006, 49, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakytzhanova, B.; Kopylov, I.; Dal, L.; Satekov, T. Geoecology of Kazakhstan: Zoning, environmental status and measures for environment protection. Eur. J. Nat. Hist. 2016, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Chien, C.-T.; Allen, B.; Dimova, N.T.; Yang, J.; Reuter, J.; Schladow, G.; Paytan, A. Evaluation of atmospheric dry deposition as a source of nutrients and trace metals to Lake Tahoe. Chem. Geol. 2019, 511, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-L.; Zhou, J.; Li, M.; Hu, Y.-M.; Liu, X.; Zhou, J. Study of the bioavailability of heavy metals from atmospheric deposition on the soil-pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 362, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzymski, P.; Klimaszyk, P.; Niedzielski, P.; Marszelewski, W.; Borowiak, D.; Nowiński, K.; Baikenzheyeva, A.; Kurmanbayev, R.; Aladin, N. Pollution with trace elements and rare-earth metals in the lower course of Syr Darya River and Small Aral Sea, Kazakhstan. Chemosphere 2019, 234, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Ding, M.; Xie, Z. Level, source identification, and risk analysis of heavy metal in surface sediments from river-lake ecosystems in the Poyang Lake, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 21902–21916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.J.; Mitrofanov, I.V.; Valentini, S.S.; Volkov, V.V.; Kurbskiy, A.V.; Zhimbey, E.N.; Eglinton, L.B.; Stegeman, J.J. Cytochrome P4501A expression, chemical contaminants and histopathology in roach, goby and sturgeon and chemical contaminants in sediments from the Caspian Sea, Lake Balkhash and the Ily River Delta, Kazakhstan. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2003, 46, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzhetimov, M.; Andasbayev, E.; Esengabylov, I.; Koyanbekova, S.; Tokpanov, E. Physical and chemical research of processes of salt formation in the water of Balkhash lake. CBU Int. Conf. Proc. 2013, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirgaliev, N. Polychlorinated biphenyls in the water of Lake Balkhash and the rivers flowing into it. J. Sect. 2019, 121, 121. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, D.; He, J.; Lü, C.; Ren, L.; Fan, Q.; Wang, J.; Xie, Z. Distribution characteristics and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals (Cu, Pb, Zn, Cd) in water and sediments from Lake Dalinouer, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 93, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Kong, L.; Liu, E.; Wang, L.; Zhu, J. Spatial distribution, ecological risk assessment and source identification for heavy metals in surface sediments from Dongping Lake, Shandong, East China. Catena 2015, 125, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, G.; Sutharsan, P.; Ramasamy, V.; Venkatachalapathy, R. Assessment of spatial distribution and potential ecological risk of the heavy metals in relation to granulometric contents of Veeranam lake sediments, India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 84, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-H.; Wang, Z.-H.; Yang, N.; Chen, Z.-L.; Han, S.-G. Geological characteristics of and metallogenic model for large-scale sayak copper ore field in Balkhash metallogenic belt, Central Asia. J. Geomech. 2010, 16, 189–202. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).