Ecological Stoichiometry Homeostasis of Six Microelements in Leymus chinensis Growing in Soda Saline-Alkali Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Testing Methods
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Microelement Contents and Ratios in Soda Saline-Alkali Soil and L. chinensis
3.2. Effects of Soil pH, Total Alkalinity and Na on Microelement Contents
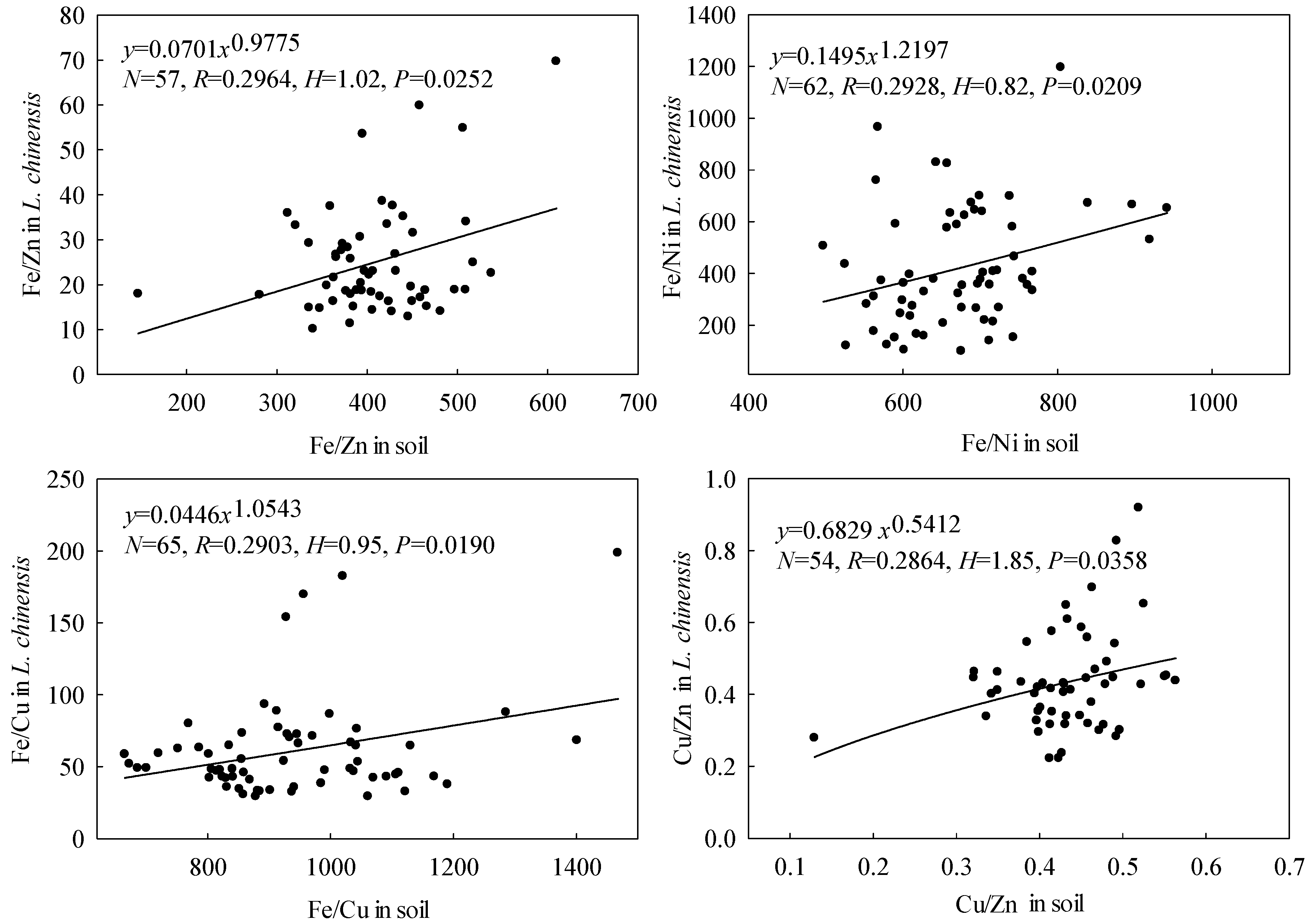
3.3. Microelement Homeostasis of L. chinensis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clemens, S. Metal ligands in micronutrient acquisition and homeostasis. Plant Cell Environ. 2019, 42, 2902–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mundus, S.; Lombi, E.; Holm, P.E.; Zhang, H.; Husted, S. Assessing the plant availability of manganese in soils using Diffusive Gradients in Thin films (DGT). Geoderma 2012, 183, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Ling, H.Q. FIT-binding proteins and their functions in the regulation of Fe homeostasis. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldelas, C.; Weiss, D.J. Zinc homeostasis and isotopic fractionation in plants: A review. Plant Soil 2016, 411, 17–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.P.; Wang, Y.F.; Hu, Z.Y.; Chen, Z.Z.; Fleckenstein, J.; Schnug, E. Status of iron, manganese, copper, and zinc of soils and plants and their requirement for ruminants in Inner Mongolia steppes of China. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2011, 34, 655–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.Y.; Zuo, Y.B.; Wang, B.R.; Li, J.M.; Ma, Y.B. Toxicity and accumulation of copper and nickel in maize plants cropped on calcareous and acidic field soils. Plant Soil 2010, 333, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowska, B.; Szulc, W.; Spychaj-Fabisiak, E.; Pior, N. Prediction of molybdenum availability to plants in differentiated soil conditions. Plant Soil Environ. 2017, 63, 491–497. [Google Scholar]
- McGrath, S.P.; Mico, C.; Curdy, R.; Zhao, F.J. Predicting molybdenum toxicity to higher plants: Influence of soil properties. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 3095–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.P.P.; Deng, W.; Yang, X.M.M. The background concentrations of 13 soil trace elements and their relationships to parent materials and vegetation in Xizang (Tibet), China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2002, 21, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pita-Barbosa, A.; Ricachenevsky, F.K.; Wilson, M.; Dottorini, T.; Salt, D.E. Transcriptional plasticity buffers genetic variation in zinc homeostasis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Zhao, X.; Yang, F.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, F. Effect of restoration interference techniques on vegetation and soil carbon discharge of saline-alkali grassland. Terr. Nat. Resour. Study 2014, 6, 55–58. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Guo, J.; Zhao, J. Dynamics of nutrient element iron in soil-plant ecosystem of the Songnen Plain Leymus chinensis grassland. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2004, 15, 2250–2254. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Guo, J.; Li, Y. Dynamic distribution of Mn element between soil and plant in Leymus chinensis grassland in Songnen Plains of China. J. Northeast For. Univ. 2008, 36, 36–38. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Guo, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, T. Dynamics of Zn between soil and plant in Northeast Leymus chinensis grassland. J. For. Res. 2006, 17, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Liang, Z. Review of zinc supply and plant zinc nutrition of soda-alkaline soils in Songnen Plain. Syst. Sci. Compr. Studies Agric. 2010, 26, 378–384. [Google Scholar]
- Han, W.X.; Fang, J.Y.; Reich, P.B.; Woodward, F.I.; Wang, Z.H. Biogeography and variability of eleven mineral elements in plant leaves across gradients of climate, soil and plant functional type in China. Ecol. Lett. 2011, 14, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterner, R.W.; Elser, J.J. Ecological Stoichiometry: The Biology of Elements from Molecules to the Biosphere; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Fu, D. Available evaluation of soil trace elements in the west area of Jilin Province. Soil 2002, 2, 86–93. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.; Ge, Y. Studies on the interrelative absorption of the main nutrient elements in Leymus chinensis community. Chin. Bull. Bot. 1995, 12, 136–141. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, Y.; Geng, Y. The element content characteristics of main species in Leymus Chinensis grassland in Inner Mongolia, China. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2015, 24, 1118–1124. [Google Scholar]
- Karimi, R.; Folt, C.L. Beyond macronutrients: Element variability and multielement stoichiometry in freshwater invertebrates. Ecol. Lett. 2006, 9, 1273–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Chen, Q.S.; Elser, J.J.; He, N.P.; Wu, H.H.; Zhang, G.M.; Wu, J.G.; Bai, Y.F.; Han, X.G. Linking stoichiometric homoeostasis with ecosystem structure, functioning and stability. Ecol. Lett. 2010, 13, 1390–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Elser, J.J.; He, N.; Wu, H.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, G.; Han, X. Stoichiometric homeostasis of vascular plants in the Inner Mongolia grassland. Oecologia 2011, 166, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, H.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. Ecological stoichiometry-based study of the influence of soil saline-alkali stress on nutrient homeostasis in L. chinensis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 165, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Guo, D.; Liang, S.; Wang, Y. Ecological stoichiometry homeostasis of Leymus chinensis in degraded grassland in western Jilin Province, NE China. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 90, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, S.; Ghadiri, H.; Chen, C.; Marschner, P. Salt-affected soils, reclamation, carbon dynamics, and biochar: A review. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güsewell, S. N: P ratios in terrestrial plants: Variation and functional significance. New Phytol. 2004, 164, 243–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Tang, J.; Li, Z.; Yang, W.; Duan, Y. The influence of soil physico-chemical properties and enzyme activities on soil quality of saline-alkali agroecosystems in western Jilin Province, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Liang, S.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Li, W.B.; Wang, Y.J. Machine learning for the prediction of L. chinensis carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus contents and understanding of mechanisms underlying grassland degradation. J. Environ. Manage. 2017, 192, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.K. Analytical Methods for Soil and Agro-Chemistry; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z. Agricultural Chemistry of Microelements; Chinese Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 1991; p. 19. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, B.; He, X. Nutrition of Plants; Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 1985; pp. 314–323. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, F.; Li, C. Essential micronutrients for plant growth—nickel. Soil 1996, 4, 176–179. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Z.; Wu, Y. Nutritional feature of trace elements in soil, forage and animal from Hexi semi-desert area. Acta Pratac. Sin. 1993, 2, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, B.; Liu, G.; Fan, B.; He, G.; Shi, L.; Li, J.; Ji, Z. Relationships between plant stoichiometry and biomass in an arid-hot valley, Southwest China. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2015, 39, 807–815. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X. Study on the Main Microelements between Soil, Grass and Livestock in Leymus chinensis Grassland of Songnen Plain. Ph.D. Thesis, Northeast Normal University, Changchun, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, Q. Micronutrient Fertilizer; Jiangsu Science and Technology Press: Nanjing, China, 1991; p. 104. [Google Scholar]
- Munns, R.; Tester, M. Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 651–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, D.M.; Oliveira, M.M.; Saibo, N.J.M. Regulation of Na+ and K+ homeostasis in plants: Towards improved salt stress tolerance in crop plants. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2017, 40, 326–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Ma, X.; Wan, P.; Liu, L. Plant salt-tolerance mechanism: A review. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 495, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munns, R. Comparative physiology of salt and water stress. Plant Cell Environ. 2002, 25, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, X.; Bressan, R.A.; Hasegawa, P.M.; Pardo, J.M. Ion homeostasis in NaCl stress environments. Plant Physiol. 1995, 109, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumberi, A.; Yamada, M.; Yamada, S.; Fujiyama, H. Salt tolerance of grain crops in relation to ionic balance and ability to absorb microelements. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2001, 47, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Persson, J.; Fink, P.; Goto, A.; Hood, J.M.; Jonas, J.; Kato, S. To be or not to be what you eat: Regulation of stoichiometric homeostasis among autotrophs and heterotrophs. Oikos 2010, 119, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, A.R.; Chalfun-Junior, A.; Aarts, M. Strategies to increase zinc deficiency tolerance and homeostasis in plants. Braz. J. Plant Physiol. 2012, 24, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Celma, J.; Chou, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Long, T.A.; Balk, J. Hemerythrin E3 ubiquitin ligases as negative regulators of iron homeostasis in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

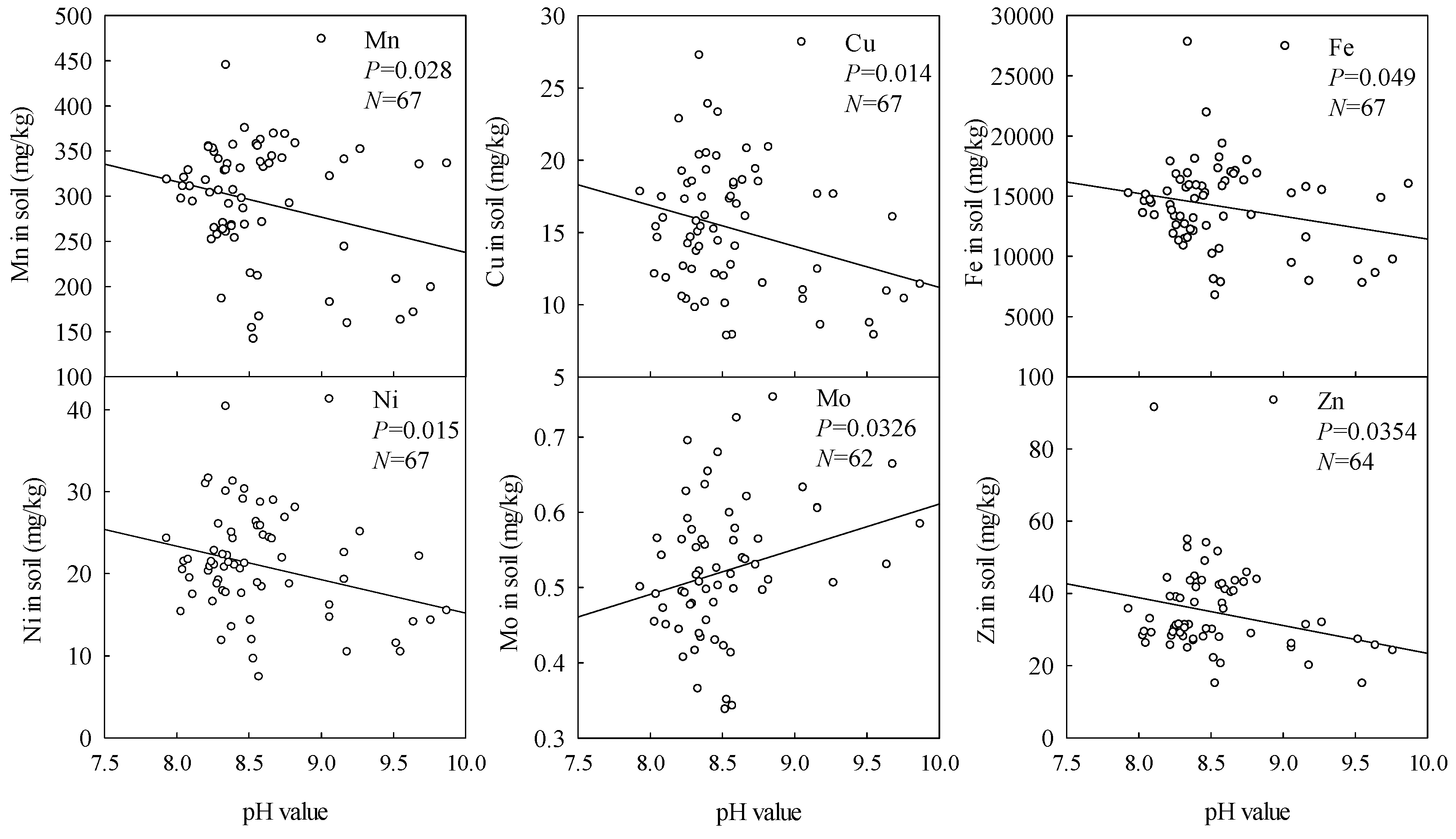
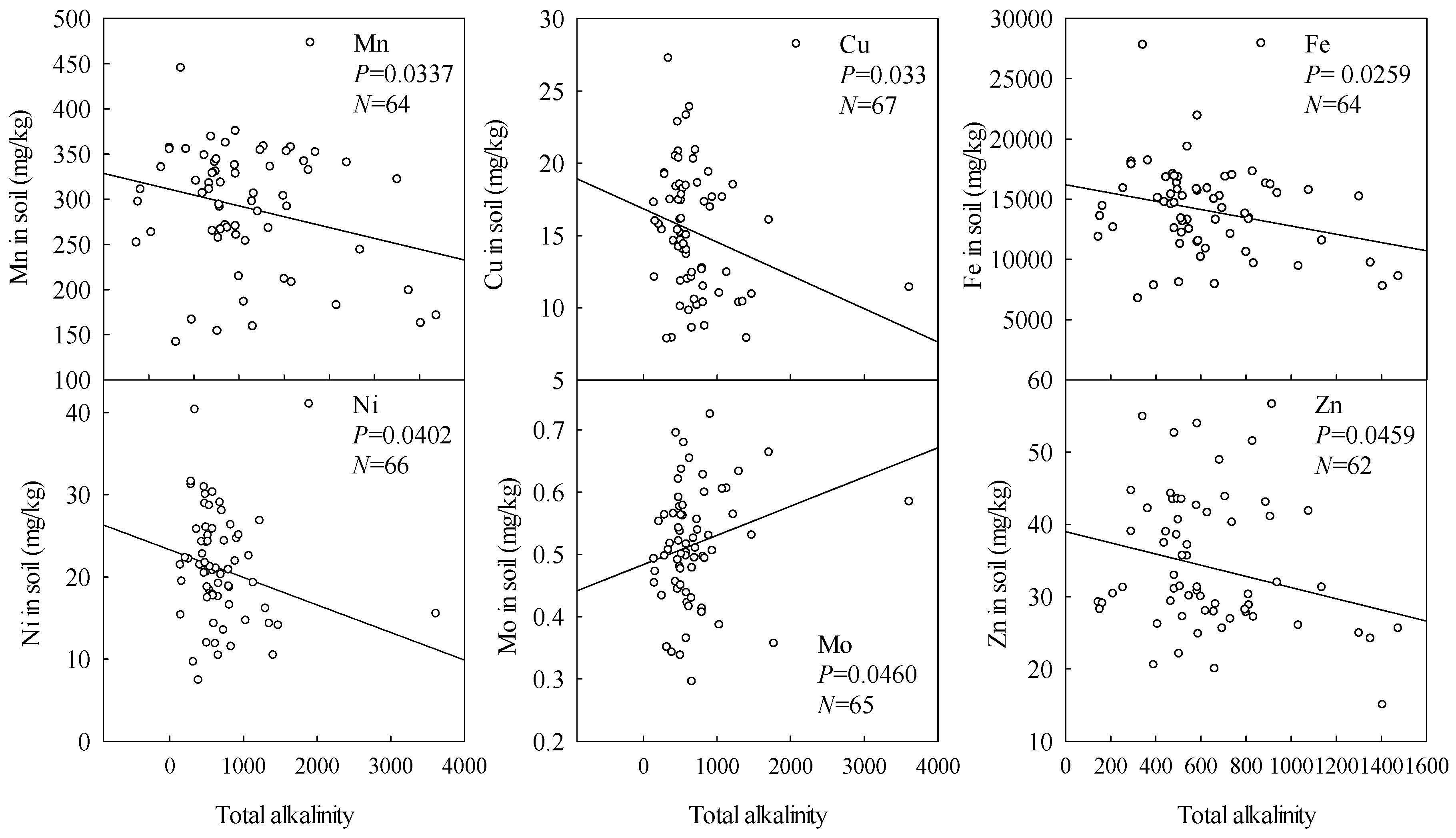
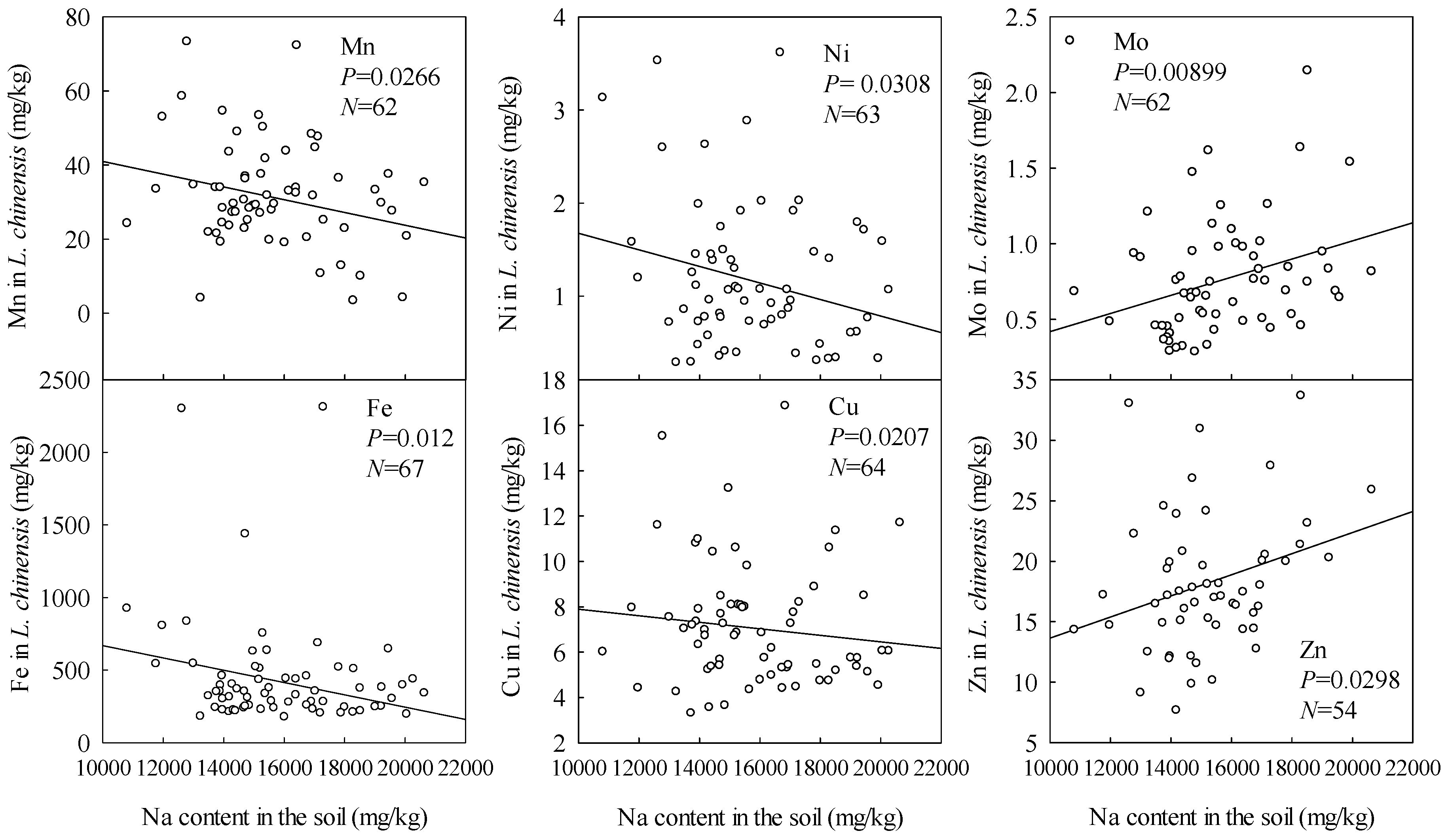
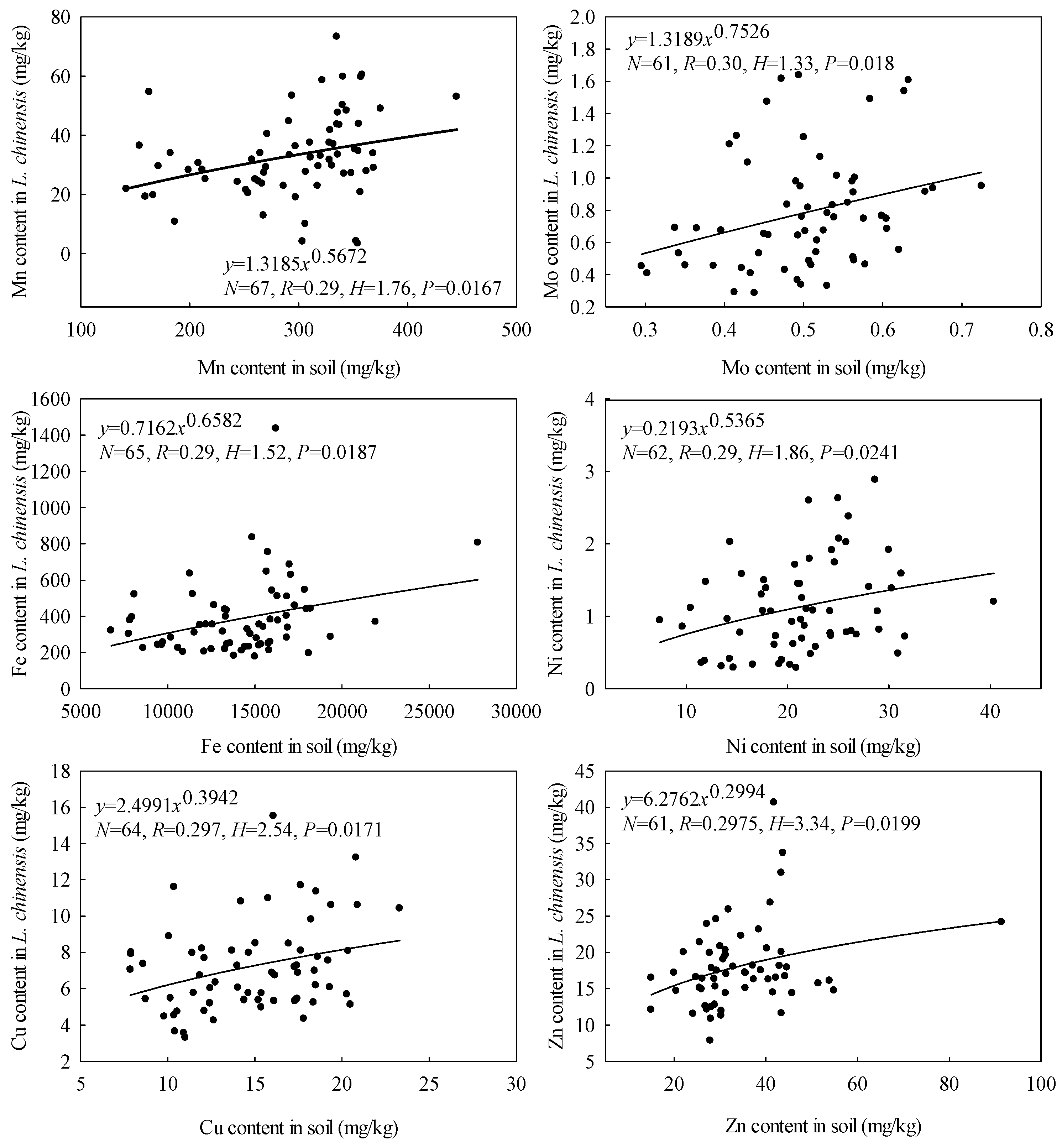
| Sampling Sites | Number of Quadrats | Central Location | Soil pH | Total Alkalinity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range | Mean | Range | Mean | |||
| Da’an City | 19 | 123°58′34″ E 45°38′21″ N | 8.26–9.87 | 8.82 | 446.52–3615.66 | 969.99 |
| Taonan City | 4 | 122°56′16″ E 45°14′28″ N | 8.39–8.78 | 8.54 | 439.20–830.52 | 645.42 |
| Changling County | 6 | 123°41′10″ E 44°32′08″ N | 8.20–8.56 | 8.34 | 256.20–468.48 | 336.72 |
| Tongyu County | 5 | 122°23′22″ E 45°02′39″ N | 8.34–8.58 | 8.48 | 484.80–684.12 | 571.21 |
| Zhenlai County | 8 | 123°10′19″ E 45°43′08″ N | 8.53–9.76 | 9.23 | 322.08–1475.76 | 934.84 |
| Qian’an County | 9 | 123°58′15″ E 44°58′27″ N | 8.22–8.56 | 8.34 | 622.20–812.52 | 712.89 |
| Qianguo County | 16 | 124°30′18″ E 44°55′44″ N | 7.93–8.47 | 8.21 | 146.40–589.26 | 426.39 |
| Microelements | Mean | Standard Deviation | Coefficient of Variation | Maximum | Minimum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil | Mn (mg/kg) | 293.61 | 65.45 | 0.22 | 445.08 | 141.76 |
| Fe (mg/kg) | 14,150.09 | 3546.30 | 0.25 | 27,797.17 | 6745.10 | |
| Ni (mg/kg) | 21.02 | 6.20 | 0.29 | 40.38 | 7.41 | |
| Cu (mg/kg) | 15.26 | 4.28 | 0.28 | 27.25 | 7.85 | |
| Zn (mg/kg) | 34.87 | 11.40 | 0.33 | 91.50 | 15.02 | |
| Mo (mg/kg) | 0.51 | 0.09 | 0.18 | 0.73 | 0.30 | |
| L. chinensis | Mn (mg/kg) | 32.90 | 14.24 | 0.43 | 73.26 | 3.37 |
| Fe (mg/kg) | 421.46 | 315.66 | 0.75 | 2301.99 | 176.87 | |
| Ni (mg/kg) | 1.30 | 0.96 | 0.74 | 6.11 | 0.29 | |
| Cu (mg/kg) | 7.06 | 2.47 | 0.35 | 15.52 | 3.30 | |
| Zn (mg/kg) | 17.78 | 6.17 | 0.35 | 40.64 | 7.68 | |
| Mo (mg/kg) | 0.77 | 0.39 | 0.51 | 2.14 | 0.29 | |
| Soil | Mn | Fe | Ni | Cu | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | 0.9212 * (0.0000) | ||||
| Ni | 0.8055 * (0.0000) | 0.8708 * (0.0000) | |||
| Cu | 0.6990 * (0.0000) | 0.8080 * (0.0000) | 0.9104 * (0.0000) | ||
| Zn | 0.5770 * (0.0000) | 0.6254 * (0.0000) | 0.6134 * (0.0000) | 0.6136 * (0.0000) | |
| Mo | 0.5274 * (0.0000) | 0.4542 * (0.0001) | 0.4359 * (0.0002) | 0.4176 * (0.0004) | 0.3111 (0.0104) |
| L. chinensis | Mn | Fe | Ni | Cu | Zn |
| Fe | 0.4155 * (0.0005) | ||||
| Ni | 0.3158 * (0.0092) | 0.4593 * (0.0001) | |||
| Cu | 0.4704 * (0.0001) | 0.4425 * (0.0002) | 0.4251 * (0.0003) | ||
| Zn | 0.3656 * (0.0023) | 0.4748 * (0.0000) | 0.3068 (0.0116) | 0.5051 * (0.0000) | |
| Mo | −0.1692 (0.1710) | 0.1075 (0.3863) | −0.1614 (0.1918) | −0.1308 (0.2914) | −0.1292 (0.2976) |
| Microelement Ratio | Mean | Standard Deviation | Coefficient of Variation | Maximum | Minimum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil | Fe/Mn | 48.22 | 4.21 | 0.09 | 62.62 | 37.78 |
| Mn/Ni | 14.45 | 2.69 | 0.19 | 22.46 | 9.85 | |
| Fe/Ni | 691.75 | 113.35 | 0.16 | 1057.09 | 496.98 | |
| Mn/Cu | 19.88 | 4.29 | 0.22 | 34.03 | 10.62 | |
| Fe/Cu | 948.94 | 167.37 | 0.18 | 1467.69 | 664.99 | |
| Cu/Ni | 0.74 | 0.10 | 0.13 | 1.14 | 0.52 | |
| Mn/Zn | 8.75 | 1.78 | 0.20 | 13.83 | 3.21 | |
| Fe/Zn | 418.65 | 73.82 | 0.18 | 609.61 | 146.33 | |
| Cu/Zn | 0.45 | 0.08 | 0.17 | 0.59 | 0.13 | |
| L. chinensis | Fe/Mn | 15.46 | 14.03 | 0.91 | 94.20 | 4.88 |
| Mn/Ni | 33.53 | 20.94 | 0.62 | 116.25 | 5.20 | |
| Fe/Ni | 410.69 | 227.78 | 0.55 | 1196.52 | 93.39 | |
| Mn/Cu | 4.89 | 2.26 | 0.46 | 11.99 | 0.71 | |
| Fe/Cu | 60.22 | 33.73 | 0.56 | 198.55 | 29.17 | |
| Cu/Ni | 7.49 | 4.23 | 0.57 | 22.98 | 1.30 | |
| Mn/Zn | 1.97 | 0.98 | 0.50 | 5.67 | 0.16 | |
| Fe/Zn | 24.07 | 12.90 | 0.54 | 69.65 | 9.85 | |
| Cu/Zn | 0.42 | 0.16 | 0.37 | 0.92 | 0.20 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Gong, H.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y. Ecological Stoichiometry Homeostasis of Six Microelements in Leymus chinensis Growing in Soda Saline-Alkali Soil. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4226. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12104226
Li Y, Gong H, Li S, Zhang Y. Ecological Stoichiometry Homeostasis of Six Microelements in Leymus chinensis Growing in Soda Saline-Alkali Soil. Sustainability. 2020; 12(10):4226. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12104226
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yuefen, Heyang Gong, Shujie Li, and Yushu Zhang. 2020. "Ecological Stoichiometry Homeostasis of Six Microelements in Leymus chinensis Growing in Soda Saline-Alkali Soil" Sustainability 12, no. 10: 4226. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12104226
APA StyleLi, Y., Gong, H., Li, S., & Zhang, Y. (2020). Ecological Stoichiometry Homeostasis of Six Microelements in Leymus chinensis Growing in Soda Saline-Alkali Soil. Sustainability, 12(10), 4226. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12104226





