Abstract
Because corporate sustainability enhances corporate governance principles, firms are increasing their efforts to provide transparency and public disclosure. These efforts inform the public about the relationship between corporate governance and sustainability. Well-informed shareholders know about this relationship, which is becoming more apparent over time. In this study, we empirically examined the possible bilateral relationships between institutional ownership and a firm’s capital structure. Methodologically, we used an instrumental variable approach and the two-step generalized method of moments. The implications of this study are two-fold. First, we found that a firm’s debt level was low if its institutional ownership level was high. Institutional monitoring may substitute for external debt monitoring, leading firms to employ low leverage. Second, we found that the level of institutional ownership was high if a firm’s debt level was high. This association suggests that institutional investors prefer high-leveraged firms because institutional owners decrease their monitoring costs through debt monitoring. In the long run, sustainable institutional ownership materially impacts the capital structures of firms.
1. Introduction
Decent corporate governance is important for both firms and society. Corporate leaders earn the public’s trust by fostering a sound corporate governance environment. Societies avoid threats and problems by implementing legislative processes. Recent corporate scandals have emphasized the importance of corporate responsibility to society and stakeholders. Thus, firms place pressure on themselves to find the best methods for enhancing their relationships with stakeholders, especially large institutional investors. The institutional ownership of corporations has grown substantially in the United States [1]. Institutional investors play increasingly important roles in corporate management because they are large shareholders and, thus, are strongly incentivized to monitor corporations. However, little research has been done into the relationship between institutional investors and their firm’s capital structure [2], even though management generally determines a firm’s debt policy.
Jensen and Meckling [3] constructed the agency theory of firms by hypothesizing that managers have incentives to maximize their own benefits rather than the shareholders’ wealth. Jensen [4] claims that the use of debt mitigates the agency problem because firms commit to making periodic interest and principal payments. However, Jensen and Meckling [3] raised awareness of risk shifts and asset substitution. High leverage motivates equity holders to engage in risky and negative net present value (NPV) projects. Furthermore, Myers [5] argues that high leverage leads a firm’s equity holders to underinvest in positive NPV projects because high leverage indicates that equity holders bear costs but realize only partial benefits. Huddart [6] points out that large shareholders (e.g., institutional investors) are strongly motivated to monitor corporate management because they benefit from active monitoring by increasing firm value. However, Bhide [7] and Coffee [8] argue that the costs associated with active monitoring may exceed its benefits. Brickley et al. [9] and Almazan et al. [10] suggest that pressure sensitivity is a decisive factor for active or passive monitoring in financial markets. They claim that institutions such as banks and insurance firms are sensitive to pressure on business ties and, thus, are prone to collusion with incumbent executives. Pressure-sensitive institutions tend to perform passive monitoring on investee firms. In contrast, mutual funds and similar institutions are less sensitive to pressure from business ties and, thus, actively monitor managerial behavior.
In a recent study, Garde Sánchez et al. [11] analyzed university institutions. They claim that the determinants of transparency in corporate social responsibility (CSR) are board size, committees, and the stakeholders’ degree of participation. They argue that the profile of the governance board and the frequency of board meetings do not contribute to information disclosure. As part of their incentive to monitor, institutional investors may be extremely interested in maintaining a firm’s long-term reputation and survival. In particular, they are likely to be motivated by CSR preferences. These preferences may prompt corporate investment decisions that affect not only a firm’s performance and sustainability, but also the wealth and rights of its various stakeholders. For example, El Ghoul et al. [12] show that firms with greater CSR engagement tend to have lower costs of equity. Wu and Lin [13] also find that CSR activities have positive effects on firms’ financial capabilities. Janney and Gove [14] suggest that firms can benefit from CSR because it helps to protect their reputations, even during major crises or scandals. Moreover, Freeman [15] argues that if firms seek opportunities to gain strategic competitive advantages, they must adapt to their stakeholders. For instance, Turban and Greening [16] find that CSR provides strategic advantages by helping firms attract and retain talented employees. Moreover, because CEO overconfidence is negatively associated with CSR activities [17], effective monitoring by institutional investors and their motivations are important in determining the directions and objectives of CSR. Ding et al. [18] claim that there is a bilateral relationship between executives and institutional investors in that executives who receive long-term incentives implement institutional CSR strategies, whereas dedicated institutional investors weaken executives’ hypocritical behaviors. Fich et al. [19] find that institutional monitoring varies depending on the shares of targeted firms in an institution’s portfolio. They claim that blockholders positively affect institutional monitoring, owing to increases in bid completion rates and higher premiums.
As firms recognize their impacts on the environment, they create a sense of sustainability and accountability. Because sustainability involves considering the future, sustainable operations are the core of CSR, as firms and societies observe the evidence of present and future changes. Specifically, large institutional investors, such as blockholders, appreciate firms’ efforts to create sustainable capital structures. The recent global financial crisis highlighted the importance of corporate governance mechanisms which benefit key stakeholders in the long run, as stakeholders experienced agency problems requiring a sustainable capital structure. Choi et al. [20] empirically show that the passive blockholder monitoring of Korea’s national pension fund (the Korea National Pension Service, or KNPS) enhances corporate earnings quality. In another study of Korea [21], however, even the KNPS, which is the largest institutional blockholder, did not appear to consider firms’ CSR initiatives to enhance its long-term performance. Overall, institutional investors should be more active in corporate governance, especially in emerging Asian economies, where long-term corporate governance is important and companies aim for profits.
The costs and benefits of monitoring by institutional investors and external debt holders, as well as its substitutability, lead to potential interrelationships between institutional ownership and firms’ capital structures. In particular, we predicted that a firm’s level of institutional ownership would be significantly negatively related to its level of debt because monitoring by institutional investors can be a substitute for external debt monitoring. In addition, we predicted that a firm’s level of debt would be positively related to its level of institutional ownership because debt monitoring reduces institutional investors’ own monitoring costs, leading them to prefer such firms.
In this study, we examined the bilateral relationship between institutional ownership and a firm’s capital structure. Specifically, we examined how a firm’s level of institutional ownership influenced its debt level and vice versa. We employed an instrumental variable approach and the two-step generalized method of moments (IV-GMM). This simultaneous examination was important because monitoring by institutional investors could have been a substitute for debt monitoring, but institutional investors may also have preferred firms with a certain debt level. Thus, identifying such relationships individually could have caused spurious results owing to the endogeneity problem. We found that a firm’s level of debt tended to be low when the level of institutional ownership was high. This result implies that institutional investors help to reduce agency costs in a firm by substituting for the external debt monitoring role. In addition, we found that the level of institutional ownership tended to be high when a firm’s level of debt was high. This relationship suggests that institutional investors prefer firms with high levels of debt, presumably because debt monitoring reduces their own monitoring costs. These findings contribute to the literature by identifying the influence of institutional investors on corporate debt policy and governance. Previous literature finds that institutional investors monitor managerial activities through negotiations and by presenting shareholders’ proposals at annual corporate meetings [22,23,24]. In addition, the findings of this study are in line with the notion that the most important reason for firms to direct some of their attention to sustainability is that it ultimately improves their ability to thrive and prosper. In particular, given the interrelationship between institutional monitoring and CSR, our findings extend the current understanding of corporate governance and sustainability, which is comprehensively summarized by Li [25]. Furthermore, our results have significant implications for markets. If a small number of entities with concentrated economic power are influential, markets are inefficient, government-related organizations are important economic players, and network-based behaviors are prevalent. Policies promoting the roles of institutional investors may enhance corporate governance environments and firms’ decisions in these markets.
2. Data and Methodology
We focused on the sample period from 1985 to 2008 using three sources of data. Data on the institutional ownership of each firm in each year were taken from the CDA/Spectrum database of 13F institutional investors (i.e., those with at least USD 100 million in equity assets under management). The corresponding security and firm accounting characteristics were constructed from the Center for Research in Security Prices and Compustat databases. We excluded highly regulated firms, such as corporations in the financial and utility sectors.
For each firm, we defined leverage as total debt divided by the sum of total debt and the market value of equity. In addition to considering institutional ownership, we included variables commonly used in the literature to explain a firm’s capital structure, pertinent to the trade-off between the costs of financial distress and the tax benefits of debt [26,27]. In particular, we used the market-to-book ratio (M/B) to measure a firm’s growth opportunities. We employed earnings before interest, taxes, and depreciation/total assets (EBITD) to represent a firm’s profitability. Then, we included research and development (R&D) expenditures/sales (a dummy variable that took a value of one if a firm did not have R&D expenditures (R&D D)), selling expenditures/sales (SE), and net property, plant, and equipment/total assets (PPE) to capture the nature of the assets employed by a firm, as these assets potentially influence the firm’s debt level. We controlled for R&D D because many firms did not disclose R&D expenditures. Thus, this variable could control for certain R&D effects that R&D levels alone could not measure. Additionally, firm size (log of sales) and the asset beta (equity/total assets × equity beta) were associated with firms’ debt levels because they were related to firms’ risk.
We used nine firm characteristics in addition to leverage to explain the level of institutional ownership. We employed these firm-specific characteristics to consider the heterogeneous preferences of institutional investors, which were different from those of individual investors. Specifically, we used beta, the standard deviation of returns, and firm-specific volatility as measures of risk. We employed firm size, age, and dividend yield to consider institutional investment constraints, and we used share price and share turnover to capture a firm’s liquidity. Finally, we added lagged returns to control for momentum. These characteristics are commonly used in the existing literature. See Bennett et al. [28] for further details.
Figure 1 shows that the institutional ownership of U.S. firms grew steadily throughout the sample period. Table 1 presents the mean, standard deviation, and 10th and 90th percentiles of institutional shareholdings and firm leverage. During the sample period, from 1985 to 2008, institutional investors held 39% of each of the firms’ shares on average. Firms employed debt financing of approximately 35%, on average, over the sample period. However, debt levels varied substantially, indicating that firms may have had heterogeneous levels of optimal debt that may have changed over time. Although we have not reported the results in the text for brevity, we examined the univariate association between a firm’s institutional ownership and leverage as a preliminary test for this study. We found a significant negative relationship between institutional ownership and a firm’s leverage, with a correlation coefficient of −0.101. A firm’s debt level tended to be low if institutional ownership was high. This result implies that monitoring by institutional investors may substitute for debt monitoring. However, this correlation should be interpreted with caution because it is crucial to identify the simultaneous bilateral associations between institutional ownership and a firm’s debt level. In addition, it is necessary to address the potential interconnections with the firm-specific characteristics discussed above.
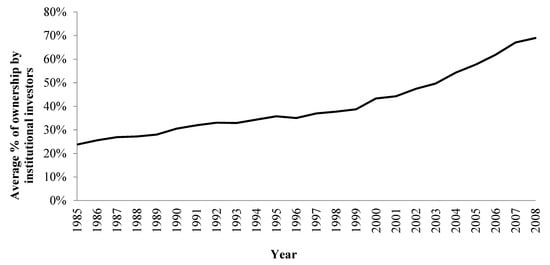
Figure 1.
Average percentage of ownership by institutional investors.

Table 1.
Summary statistics.
Specifically, we constructed a multivariate regression model captured by the following system of equations, where u and v are error terms:
The econometric methodology focused on simultaneously identifying two relationships: how the level of institutional ownership affected a firm’s leverage and how a firm’s leverage affected its level of institutional ownership. Specifically, we adopted an IV-GMM. First, we replaced the endogenous variables with instrumental variables in the system of equations. Then, we estimated the predicted values from the reduced-form regressions on the exogenous variables for these instrumental variables. We employed a Tobit regression model to obtain the predicted values, as the levels of institutional ownership and leverage were restricted to values between zero and one. Second, we used the two-step generalized method of moments for the system of equations to address the inefficiency related to the cross-correlation of the error terms. Using industry and year dummy variables also helped to alleviate the potential correlation between the explanatory variables and a firm’s individual and year effects in the error terms.
3. Empirical Results
Table 2 reports the estimation results for the system of equations. A firm’s level of institutional ownership was negatively related to its level of debt. This result implies that institutional investors play a monitoring role, and that this monitoring can substitute for alternative monitoring by external debt holders. This substitution of institutional monitoring for debt monitoring helps to decrease the costs related to debt problems, such as risk shifting and underinvestment. This finding is aligned with that of Bathala et al. [29] but is more robust. The latter study also investigated the effect of institutional ownership on a firm’s debt level and found a negative association. However, in contrast to their study, we relied on extensive institutional ownership data and considered the simultaneous association between a firm’s institutional ownership and its capital structure. Furthermore, we found that a firm’s debt level was positively related to its institutional ownership level. This regression indicates that institutional investors prefer firms with high levels of debt because intensive debt monitoring reduces an investor’s monitoring costs. In addition, this positive association differs from the negative association described above, which emphasizes the importance of examining both directions of the relationship between institutional ownership and capital structure. However, this result should be interpreted with a degree of caution. For example, based on trade-off theory, a firm’s debt level may convey information about its value. Overall, we found evidence supporting the substitutability of institutional investor monitoring and external debt monitoring of management, given their relative costs and benefits.

Table 2.
Associations between institutional ownership and leverage.
4. Conclusions
Because corporate sustainability improves corporate governance principles, firms are more seriously considering transparency and public disclosure. Their efforts to enhance transparency provide the public with information on the relationship between corporate governance and sustainability. Insider shareholders know about this relationship slightly earlier, but this relationship becomes conspicuous over time. This study examined the two-way associations between a firm’s institutional ownership and its capital structure using an instrumental variable approach and the two-step generalized method of moments. We found that a firm’s debt level tended to be low if institutional ownership was high, supporting the hypothesis that firms use low leverage because monitoring by institutional investors substitutes for monitoring by external debt holders. Furthermore, institutional ownership tended to be high if a firm’s debt level was high. This result implies that, on a corporate sustainability basis, institutional investors prefer high-leverage firms because the intensive monitoring of debt reduces institutions’ own monitoring costs.
We note that this study faces a number of limitations. First, there are many types of institutional owners, and their interests in sustainability are quite different [30]. Short-term institutional traders, such as hedge funds, may prioritize arbitraging out mispriced stocks over very short time spans. In contrast, long-term institutional investors are more likely to leverage their ownership to influence a firm’s management in a sustainable manner [31]. It may be necessary to differentiate between these two types of investors. Second, as this study was an empirical study, we are liable for the types of data used herein. Extending the sample period in another study with a broader focus and testing the robustness of this study’s empirical implications are imperative going forward. Third, this empirical estimation was not immune to the endogeneity problem, and the potential endogeneity problem between institutional ownership and capital structure may be addressed using the recent remedy developed by Li [32]. Finally, this study could obtain better results by considering the channels of institutional monitoring which affect corporate debt policy. One important channel may be alternative corporate governance mechanisms, such as the impacts of market competition, CEO characteristics, and CEO compensation. For example, Giroud and Muller [33] and Coles et al. [34] document the effects of product market competition on corporate governance mechanisms. Li [25,35] shows that mutual fund monitoring is interrelated with CEO characteristics and finds that this monitoring mitigates the agency problem. In addition, Core and Guay [36] and Li et al. [37] show that a CEO compensation structure that is aligned with firm value helps to mitigate the agency problem. Hence, these governance mechanisms interacting with institutional monitoring should be further investigated to clarify the exact channels affecting the corporate debt policy, which is also associated with the agency problem. These limitations are left for future studies to address.
Author Contributions
C.Y.C. designed and conducted the research and analyzed the data. C.Y.C., P.M.S.C., and Y.J.A. wrote the paper. J.H.C. and Y.J.A. revised the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the research grant program at Ewha Womans University in South Korea.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chung, C.Y.; Wang, K. Do institutional investors monitor management? Evidence from the relationship between institutional ownership and capital structure. N. Am. J. Econ. Financ. 2014, 30, 203–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaganti, R.; Damanpour, F. Institutional ownership, capital structure, and firm performance. Strateg. Manag. J. 1991, 12, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.C.; Meckling, W.H. Theory of the firm: Managerial behavior, agency cost, and ownership structure. J. Financ. Econ. 1976, 3, 305–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.C. Agency cost of free cash flow, corporate finance, and takeovers. Am. Econ. Rev. 1986, 76, 323–329. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, S.C. Determinants of corporate borrowing. J. Financ. Econ. 1977, 5, 147–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huddart, S. The effect of a large shareholder on corporate value. Manag. Sci. 1993, 39, 1407–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhide, A. Efficient markets, deficient governance: US securities regulations protect investors and enhance market liquidity. But do they alienate managers and shareholders? Harvard Bus. Rev. 1994, 72, 128–140. [Google Scholar]
- Coffee, J.C. Liquidity versus control: The institutional investor as corporate monitor. Columbia Law Rev. 1991, 91, 1277–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brickley, J.A.; Lease, R.C.; Smith, C.W. Ownership structure and voting on antitakeover amendments. J. Financ. Econ. 1988, 20, 267–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almazan, A.; Hartzell, J.C.; Starks, L.T. Active institutional shareholders and costs of monitoring: Evidence from executive compensation. Financ. Manag. 2005, 34, 5–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garde Sánchez, R.; Flórez-Parra, J.M.; López-Pérez, M.V.; López-Hernández, A.M. Corporate governance and disclosure of information on corporate social responsibility: An analysis of the top 200 universities in the Shanghai Ranking. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ghoul, S.; Guedhami, O.; Kwok, C.C.; Mishra, D.R. Does corporate social responsibility affect the cost of capital? J. Bank. Financ. 2011, 35, 2388–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.I.; Lin, H.F. The correlation of CSR and consumer behavior: A study of convenience store. Int. J. Mark. Stud. 2014, 6, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janney, J.J.; Gove, S. Reputation and corporate social responsibility aberrations, trends, and hypocrisy: Reactions to firm choices in the stock option backdating scandal. J. Manag. Stud. 2011, 48, 1562–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, R.E. Strategic Management: A Stakeholder Approach; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Turban, D.B.; Greening, D.W. Corporate social performance and organizational attractiveness to prospective employees. Acad. Manag. J. 1997, 40, 658–672. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.-H.; Byun, J.; Choi, P.M.S. Managerial overconfidence, corporate social responsibility, and financial constraints. Sustainability 2020, 12, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, L. Executive incentives matter for corporate social responsibility under earnings pressure and institutional investors supervision. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fich, E.M.; Harford, J.; Tran, A.L. Motivated monitors: The importance of institutional investors’ portfolio weights. J. Financ. Econ. 2015, 118, 21–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Choi, P.M.S.; Choi, J.H.; Chung, C.Y. Does sustainable corporate governance enhance accounting practice? Evidence from the Korean market. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Choi, P.M.S.; Choi, J.H.; Chung, C.Y. Corporate governance and corporate social responsibility: Evidence from the role of the largest institutional blockholders in the Korean market. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carleton, W.T.; Nelson, J.M.; Weisbach, M.S. The influence of institutions on corporate governance through private negotiations: Evidence from TIAA-CREF. J. Financ. 1998, 53, 1335–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillan, S.L.; Starks, L.T. Corporate governance proposals and shareholder activism: The role of institutional investors. J. Financ. Econ. 2000, 57, 275–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.P. Shareholder activism by institutional investors: Evidence from CalPERS. J. Financ. 1996, 51, 227–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.F. A survey of corporate social responsibility and corporate governance. In Research Handbook of Finance and Sustainability; Boubaker, S., Cumming, D., Nguyen, D.K., Eds.; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kayhan, A.; Titman, S. Firms’ histories and their capital structures. J. Financ. Econ. 2007, 83, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modigliani, F.; Miller, M. Corporation income taxes and the cost of capital: A correction. Am. Econ. Rev. 1963, 53, 433–443. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, J.A.; Sias, R.W.; Starks, L.T. Greener pastures and the impact of dynamic institutional preferences. Rev. Financ. Stud. 2003, 16, 1203–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathala, C.T.; Moon, K.P.; Rao, R.P. Managerial ownership, debt policy, and the impact of institutional holdings: An agency perspective. Financ. Manag. 1994, 23, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.F.; Patel, S.; Ramani, S. The role of mutual funds in corporate social responsibility. J. Bus. Ethics 2020. forthcoming. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Harford, J.; Li, K. Monitoring: Which institutions matter? J. Financ. Econ. 2007, 86, 279–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F. Endogeneity in CEO power: A survey and experiment. Invest. Anal.J. 2016, 45, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giroud, X.; Mueller, H. Corporate governance, product market competition, and equity prices. J. Financ. 2011, 66, 563–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coles, J.L.; Li, Z.; Wang, A.Y. Industry tournament incentives. Rev. Financ. Stud. 2018, 31, 1418–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.F. Mutual monitoring and corporate governance. J. Bank. Financ. 2014, 45, 255–269. [Google Scholar]
- Core, J.; Guay, W. The use of equity grants to manage optimal equity incentive levels. J. Account. Econ. 1999, 28, 151–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Lin, S.; Sun, S.; Tucker, A. Risk-adjusted inside debt. Glob. Financ. J. 2018, 35, 12–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).